#MDA20009 Week7
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Week 7: Social Media and Public Health: A Platform for Dialogue or One-Way Messaging?
Social media has revolutionized the way public health campaigns communicate with the public. Social media refers to online social networking sites and is a broad example of Web 2.0, such as Twitter, YouTube, TikTok, Facebook, Snapchat, Reddit, Instagram, WhatsApp, and blogs. It is a new and ever-changing field. Access to the internet, social media platforms and mobile communications are all tools that can be leveraged to make health information available and accessible. (Kanchan & Gaidhane, 2023). But are these campaigns truly leveraging the interactive potential of these platforms, or are they simply using them as digital megaphones?

The One-Way Messaging Approach
Many public health campaigns still rely on traditional, one-way communication styles. These campaigns are typically centered around disseminating important messages, such as promoting COVID-19 vaccinations or raising awareness about mental health. For example:
The CDC’s Instagram posts during the pandemic often delivered visually appealing infographics and key health tips but rarely engaged directly with audience comments.
Similarly, campaigns like #EatHealthy often feature polished content that informs but doesn’t always invite interaction.
This approach ensures consistent messaging and allows organizations to maintain control over the narrative. However, it risks missing the mark in fostering trust or addressing specific concerns of the target audience, particularly in diverse or skeptical communities.
The Interactive Potential of Social Media
Conversely, campaigns that embrace social media as a platform for dialogue often see greater engagement and impact. Interactive features like polls, live Q&A sessions, and user-generated content can transform a campaign into a two-way conversation. Examples include:
The #ThisIsOurShot campaign, where doctors and nurses answered vaccine-related questions through live streams and short TikTok videos. This approach directly addressed misinformation and empowered users to engage with trusted professionals.
Mental health awareness campaigns like #BellLetsTalk use platforms like Twitter to encourage people to share their stories, creating a sense of community while driving the campaign's message.
These methods invite users to participate, ask questions, and share their perspectives, making them feel heard and valued.

Challenges to Fostering Dialogue
Despite the potential for interaction, creating two-way communication isn’t without its challenges. For one, public health organizations may struggle with the volume of responses and questions, especially during crises like the COVID-19 pandemic. Since the onset of COVID-19, incidents of racism and xenophobia have been occurring globally, especially toward people of East Asian appearance and descent. In response, this article investigates how an online Asian community has utilized social media to engage in cathartic expressions, mutual care, and discursive activism amid the rise of anti-Asian racism and xenophobia during COVID-19 (Abidin & Zeng, 2020). In the era of COVID-19, SAT has developed into a congregational Facebook hub for the Asian diaspora. SAT's 1000+ daily posts from its members have quickly shifted to reflecting on what it means to be "Asian" during the pandemic, from promoting "quarantine trends" (such as homemade dalgona coffees that require the effort of whipped coffee and milk but are Instagram worthy to simulate the café experience; and recommendations of Korean dramas in every genre to soothe the soul) to making fun of Asian mothers' pseudo-scientific anti-COVID remedies.
Additionally, misinformation and trolling can disrupt meaningful conversations.
To mitigate these issues, organizations can use strategies such as:
Employing community managers to monitor and respond to comments.
Partnering with influencers who align with the campaign's goals and can engage directly with their followers.
Providing clear guidelines for respectful dialogue to maintain a positive online environment.
The Sweet Spot: Balancing Information and Engagement
The most effective public health campaigns strike a balance between delivering essential information and fostering meaningful interaction. For example, the World Health Organization (WHO) frequently uses Instagram Stories to post health tips while also utilizing the "Ask Me Anything" feature to respond to followers' queries in real time. This dual approach ensures that their messages are both informative and engaging.

In conclusion, while many public health campaigns on social media remain rooted in one-way communication, the potential for meaningful dialogue is immense. By leveraging the interactive features of these platforms and actively engaging with their audience, public health organizations can not only amplify their messages but also build trust, address concerns, and foster lasting behavioural change.
References
Abidin, C., & Zeng, J. (2020). Feeling Asian Together: Coping With #COVIDRacism on Subtle Asian Traits. Social Media + Society, 6(3), 205630512094822. https://doi.org/10.1177/2056305120948223
Kanchan, S., & Gaidhane, A. (2023). Social Media Role and Its Impact on Public Health: a Narrative Review. Cureus, 15(1), e33737. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.33737
Kwai, I. (2018, December 11). How “Subtle Asian Traits” Became a Global Hit. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2018/12/11/world/australia/subtle-asian-traits-facebook-group.html
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Influencers Shaping Public Health Misinformation: "Dr. Tiktok" and Mukbang Culture
MDA20009 Digital Communities │ Week 7: Public Health Campaigns
Are you like me and every other human on this planet? Always on the phone, doomscrolling through Tiktok, Instagram reels and Youtube.

Undeniably, it has now gone out of bounds as social media can be a great source of entertainment, but they've also let the floodgates open for a lot of misinformation generally with reference to health and wellness. Once you spend long enough on such platforms, towards the end, you will begin to observe the visible rise of self-proclaimed "experts" giving out advice on every health issue, from mental to skincare, which is starting to raise eyebrows.
On the other hand, influencers involved in Mukbang culture are distorting the message about eating habits and body image. Their unethical health narratives, though not clearly disseminated, confuse the followers and damage public health campaigns well-designed to give accurate, science-backed messages.
The Rise of Self-Proclaimed Health Experts
TikTok's short video format encourages users to share quick tips, life hacks, and advice, earning it the nickname "the therapist's couch of Gen Z" (Weikle, 2024). Although it owes a great deal to destigmatizing mental health and making it easier to talk about issues, there have also been concerns about misinformation. Indeed, the unqualified pretender plays out their authority over complex issues, such as mental health, nutrition, or skincare.
Self-diagnosis and providing mental health advice has been an emerging trend as of late. The "Dr. TikToks" profess to know all the symptoms of illnesses like depression, anxiety, or ADHD and can influence viewers into self-diagnosing rather than visiting a professional. Research by the University of British Columbia found that of the 100 most popular TikTok videos about ADHD, over half contained misleading information, most of which relied on personal experiences rather than being clinical experts (Weikle, 2024).

Another disturbing thing is that some influencers take up roles as skincare experts by providing tips on easy access to perfect skin through their 'magic' ingredients. One infamous example is the TikTok influencer/physician's assistant (TikTok handle: devthepa) who promoted beef tallow, a rendered fat from beef, as a skincare miracle. According to her, beef tallow could give your skin a glowy look, like DUH, of course, fat is oil, so of course, it gives that "glowy effect" when, in reality, it's just oily. Dermatologists quickly debunked these claims. Despite concerning warnings, the video still went viral, and many people, particularly younger followers, began to follow this advice without understanding how useless it is.

Misinformation tends to be left unchecked. That underlines the utility of unverified advice. TikTok encourages conversations that can help destigmatize mental illness yet lends themselves to those throaty mouths and parroting personal anecdotes mixed with professional credentials as influencers.
Mukbang Culture: The Illusion of Eating Without Consequences

A comparison between 2 famous Mukbangers: Eat with Boki and Nikocado Avocado
Mukbang has invaded the world, coming from South Korea, where influencers devoured high volumes of food while engaging viewers. The practice has gained much prominence on sites like YouTube and TikTok. Mukbangers mainly eat a lot of calories while looking like they ate nothing at all through some strenuous workouts to attain and maintain their healthy-looking figures. This world creation misleads the average person into believing there are no health risks associated with overeating, especially when the influencers do not mention calorie deprivation or editing tricks (Amrane, 2020).
Encouragement towards excessiveness has been opposed to measures taken on public health with regard to balanced eating. Mukbang content may provide some retreat for viewers, or even a little companionship, but it then normalizes excessive consumption and food choice itself for being excessively unhealthy for audiences. For younger groups, this distortion can ruin their standards toward the reality of nutrition as well as create misinterpretations in eating patterns. Mukbang culture, according to Amrane (2020), relies on and impacts instant gratification sacrifices for long-term health, forming an unhealthy aspect over food.
The social consequences are huge. Public health efforts, such as anti-obesity campaigns, speak about moderation and mindful eating, while mukbangs endorse a lifestyle of excess, which is contrary. Beyond the individual consequences, this trend reveals a more universal ethical dilemma: waste normality and overconsumption in a world where there is still hunger.
The Dangers of Medical and Health Misinformation
Self-proclaimed medical experts and mukbang influencers on social media are more interested in entertainment and sponsorships than in the well-being of their audience, advertising useless supplements, self-medication and the wrong lifestyle. This shifts reliance from true healthcare providers to fake ones, thus allowing fake health information to spread quickly and widely without fact checking. The main characteristic of social media, which is lack of regulation, assists the spread of these fabrications to millions and complicates efforts in promoting public health.
Combating Misinformation: Key Strategies
So, how do we combat this growing wave of misinformation?
Platform Accountability: social media platforms take greater responsibility for what is shared online. While Instagram and TikTok have made important strides in tackling some harmful content, there is much further to go with respect to health-related advice from credible sources. Such platforms should focus their attention on verified health professionals and improve tools for flagging or reporting misleading advice.
Adapt Public Health Campaigns: Partner up with relevant influencers to relay accurate, engaging, and evidence-based health information.
Promote Media Literacy: Educate the public to tell the difference between real health advice from personal stories or unverifiable claims.
Conclusion
In an age of social media where viewpoints on health and wellness are created, this has become an important point for all awareness and updates. The healer "Dr TikTok" and, of course, Mukbang culture gives importance to the phrase mentioned above in such a way that it shows the power and pitfalls of digital platforms in the public health sphere.
Merely holding internet platforms accountable in dealing with misinformation, changing public health campaigns to bring them into the digital contemporary space, and building media literacy are steps to a country where more citizens benefit from being well-informed and health conscious. Public health campaigns must reform in the Internet age, ensuring that the right information reaches audiences before the wrong messages go viral.

List of References:
Amrane, S. (2020, November 16). Mukbangs and a culture of gluttony. Traversing Tradition. https://traversingtradition.com/2020/11/16/mukbangs-and-a-culture-of-gluttony/
Weikle, B. (2024, June 22). TikTok has been called the therapist’s couch of Gen Z. But not all the #mentalhealth info checks out. CBC. https://www.cbc.ca/radio/spark/mental-health-tiktok-1.7242717
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
'Social Media: The Unexpected Hero of the Pandemic?'
Social media? That cesspool of doomscrolling, misinformation, and endless arguments? But Hero of the pandemic? No way! Erdem, however argues the pandemic have enable social media to influence modern schooling of public health, essentially saving lives (Erdem 2021). Public health, as defined by Winslow, involves the science and practice of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting community health through organized efforts and informed choices made by various stakeholders (Winslow n.d.). These stakeholders include public and private entities, communities, individuals, and organizations. In contrast. Social media, on the other hand according to Gregersen, encompasses online platforms for mass communication, enabling users to connect and share content such as messages, ideas, and information(Gregersen 2024). In the modern era, public health and social media have increasingly intertwined. This interconnectedness prompts an important question: How effective is social media in disseminating information about COVID-19?

While pre-existing concerns about misinformation and echo chambers were amplified, the crisis also revealed the unprecedented power of these platforms for disease surveillance, information dissemination, community engagement, and health promotion. Social media became a virtual battleground where accurate information and dangerous falsehoods clashed, influencing public perception and behavior in ways never seen before.
Disease Surveillance and Public Health Monitoring
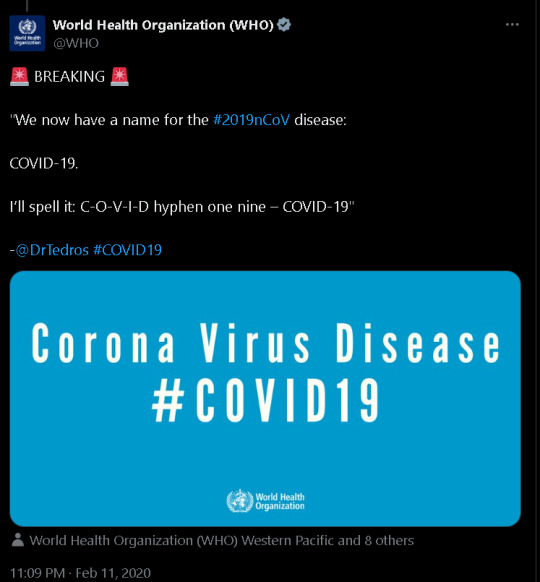
-First Alarm of Covid Emergence From Twitter (X)
The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the critical role of information in public health crises, with social media emerging as a dominant force. Platforms like Twitter and Facebook became primary sources for real-time updates, enabling organizations like the WHO and CDC to communicate directly with the public (Moorhead et al. as cited in Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023). This allowed for rapid dissemination of vital information about symptoms, prevention, and evolving public health recommendations, proving crucial in a dynamic situation with frequently changing guidelines (Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023).

-Snapshot of Facebook lives, providing updates in times of lockdown (Facebook-5.3 Million)
Furthermore, social media facilitated public health advocacy and policy shaping. Health professionals and advocacy groups utilized these platforms to engage with the public and decision-makers, promoting evidence-based policies like mask mandates and vaccination strategies (Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023). By amplifying diverse voices and marginalized perspectives, social media fostered a more inclusive and equitable public health response, ensuring a broader range of perspectives informed policy discussions and interventions.
Information Dissemination
However, this same speed and accessibility that made social media a valuable tool for public health communication also fueled the spread of misinformation, conspiracy theories, and unverified claims (Pool, Fatehi & Akhlaghpour 2021). The "infodemic" that accompanied the pandemic, as termed by the WHO (2020), hindered public health efforts, fueled distrust in authorities, and even led to harmful behaviors such as the rejection of vaccines or the promotion of unproven remedies (Pool, Fatehi & Akhlaghpour 2021). This effectively eluded the needs for effective strategies to combat misinformation and promote critical media literacy in the digital age.
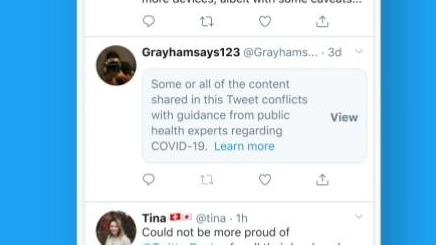
-Infodemic sources/Misinformation were censored and surveilled on Twitter (X)
Despite these challenges, social media also emerged as a powerful tool for combating misinformation. Experts and fact-checkers utilized these platforms to debunk false claims, provide evidence-based information, and promote adherence to public health guidelines (Sharma et al as cited in Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023). Social media also facilitated the rapid dissemination of research findings, clinical trial data, and treatment protocols, accelerating the global exchange of knowledge and helping healthcare professionals stay updated on the latest developments in COVID-19 management (Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023). This accelerated pace of information sharing proved crucial in a dynamic pandemic situation where scientific understanding and best practices were constantly evolving.
Community Engagement
youtube
-Solidarity among Malaysian Healthcare workers ticked up via social media, in times of Movement Control Order (MCO)
Beyond its role in information dissemination, social media played a crucial role in fostering a sense of community and providing support during a time of unprecedented isolation and anxiety. Online communities and forums became spaces for individuals to connect, share their experiences, and offer encouragement (Naslund et al. as cited in Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023). This virtual support network helped mitigate the mental health impacts of lockdowns and social distancing measures, reminding people that they were not alone in their struggles. Social media platforms also became hubs for organizing mutual aid initiatives, coordinating donation drives, and providing support to frontline healthcare workers, showcasing the potential of these platforms to galvanize collective action and foster resilience in the face of adversity (Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023).
Health promotion

-Facebook groups 'Caremongering' bring communities to our screens during MCO
Social media platforms also offer a opportunity to engage with individuals and communities in promoting healthy behaviors and facilitating positive change (Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023). Targeted campaigns and interventions can be delivered through social media, reaching specific demographics with tailored messages about disease prevention, healthy lifestyles, and mental well-being (Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023). Studies have shown the effectiveness of social media interventions in addressing issues such as risky drinking ,cannabis use among young adults and most importantly during Covid isolation (Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023).
Concluding, the COVID-19 pandemic served as a powerful demonstration of both the potential and the challenges of social media in public health. While the spread of misinformation and ethical concerns remain significant challenges, the pandemic also highlighted the unprecedented ability of these platforms to disseminate vital information, foster community support, empower individuals and communities to take action, and shape public health policies. As we move forward, it is crucial to learn from the experiences of the pandemic and harness the power of social media responsibly and ethically to build a more informed, connected, and resilient global community.

References
Erdem, B 2021, ‘The Role of Social Media in the Times of the Covid-19 Pandemic’, European Journal of Social Sciences, vol. 4, no. 2, p. 110.
Gregersen, E 2024, ‘Social Media’, Encyclopædia Britannica, viewed <https://www.britannica.com/topic/social-media>.
Kanchan, S & Gaidhane, A 2023, ‘Social Media Role and Its Impact on Public Health: a Narrative Review’, Cureus, vol. 15, no. 1, p. e33737, viewed <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9925030/>.
Pool, J, Fatehi, F & Akhlaghpour, S 2021, ‘Infodemic, Misinformation and Disinformation in Pandemics: Scientific Landscape and the Road Ahead for Public Health Informatics Research’, Studies in Health Technology and Informatics, vol. 281, pp. 764–768, viewed 31 August 2021, <https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34042681/>.
Winslow, C n.d., Public Health 101 Series Instructor name Title Organization, viewed <https://www.cdc.gov/training-publichealth101/media/pdfs/introduction-to-public-health.pdf>.
youtube
#MDA20009#Week7#SocialMedia#Covid19#Tumblr#StaySafe#Youtube#Malaysia#Current Events#Movement Control Order#Digital Communities
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Influence of the 'Aesthetic Template' on Body Modification Trends: How Social Media Shapes Our Faces
In recent years, “cosmetic surgery” products have witnessed an exponential increase in demand as aesthetics have become an important aspect of daily life. The rise in population focusing on aesthetic features has generated promising prospects for the growth of the cosmetic procedure market.
The trend among women towards aesthetic procedures, such as breast augmentation, eyelid surgery, liposuction, tummy tuck, and other surgeries to enhance appearance, is on the rise, leading to high demand. Additionally, preferences are shifting towards procedures inspired by social media influencers.

Standard Face: Idol-Inspired Facial Surgery
First, we can understand the "Standard Face" often refers to an idealized appearance that features symmetrical, well-defined facial traits, such as high cheekbones, full lips, and smooth skin. This look has been popularized by social media influencers, especially on platforms like Instagram and TikTok.
Celebrities, especially in the entertainment industry, have a significant influence on their fans. They are often viewed as ideal beauty models, leading fans to feel pressured to attain a similar appearance. Their images and videos on social media are frequently edited and curated to showcase a perfect look, creating a challenging standard to achieve.

A 33-year-old musician named Toby Sheldon spent $100,000 (over 2 billion VND) over five years on cosmetic surgery to resemble Justin Bieber. Sheldon underwent Botox injections, hair transplants, and "smile" surgery, among other procedures, to look like Bieber.

Twin brothers Matt and Mike Schlepp spent £15,000 to have their noses, chins, and cheekbones altered to look like movie star Brad Pitt. Their transformation process over two months was documented in an MTV reality show.
Analyze behavior
The Algorithm Factor: How Social Media Rewards the Aesthetic Template
The reason for celebrity look alike surgery is not just about their love for their idols.Many individuals frequently compare themselves to idols or attractive individuals on social media. This can create feelings of inadequacy, leading to dissatisfaction with oneself.The constant presence of meticulously edited images can lead others to believe that these characteristics are the new standard of "beauty," causing them to feel that their natural appearance is not good enough.Not only that, many people change their faces to look like their idols so they can take advantage of it as a basis for personal gain.
Many young Chinese people are willing to undergo plastic surgery to look like celebrities, hoping to quickly become famous so they can sell products online and enter showbiz.

Hà Thừa Hy (born 1993) gained fame on the Chinese reality show Super Girl for resembling Phạm Băng Băng. Since age 15, she has spent 8 million NDT (over 27 billion VND) on cosmetic surgery to achieve this look. Emulating Phạm Băng Băng's style, she often gets mistaken for her and earns significant income through event appearances and live streaming, reportedly making up to $500,000 a month at her peak.
The Real-World Impact: Facial surgery
Cosmetic procedures aimed at achieving a celebrity-like appearance often include various techniques. A nose job can help create a straight or curved nose, depending on the desired style. Jaw contouring is performed to create sharper jawline features, enhancing overall facial structure. Additionally, Botox or filler injections are used to plump the lips and enhance the cheekbones, giving a more defined look. Finally, eye surgeries, such as double eyelid surgery or brow lifting, can further refine the appearance, helping individuals achieve their ideal aesthetic.Individuals undergoing surgery must have a strong mental attitude.
They may not only go through a single procedure but could also face hundreds of different minor and major surgeries.
The Health Dilemma: surgical risks, post operative health
HEALTH: After cosmetic surgery, patients face potential infections if the surgical site is not cared for properly, and some may develop scarring, which can be raised or uneven. There’s also a risk of adverse reactions to anesthesia, and many experience pain and discomfort in the operated area, with soreness or swelling lasting from a few days to several weeks. Proper post-operative care is essential to minimize these risks.
Psychological Challenges: Many patients experience dissatisfaction with the results if their expectations are not met. This can lead to feelings of depression or anxiety, particularly due to the pressure to maintain their new appearance. Additionally, individuals may struggle to accept their new image, which can significantly impact their self-confidence. It is essential for patients to seek support and guidance during this adjustment period to foster a positive self-image.
Embracing Individuality: Rethinking Beauty Standards
The influence of social media on body modification trends cannot be overstated. The 'Aesthetic Template' propagated by influencers and celebrities sets a high bar for beauty standards, leading many individuals to pursue cosmetic procedures in an attempt to conform. While these surgeries can enhance physical appearance, they come with significant risks and psychological challenges. As society continues to evolve in its perception of beauty, it is crucial to foster a more inclusive understanding of aesthetics that values individuality over conformity to idealized standards. Encouraging open discussions about the implications of cosmetic surgery and promoting mental health support can help mitigate the negative effects associated with the pursuit of an idealized appearance.
References
staff, H. R. (2013, October 21). Justin Bieber fan spends $100,000 on surgery to resemble the singer. NBC News. https://www.nbcnews.com/entertainment/justin-bieber-fan-spends-100-000-surgery-resemble-singer-8C11431266
Tiga. (2024, April 19). Twins invest £15,000 to transform into Brad Pitt lookalikes. DailyWrap. https://dailywrap.uk/twins-invest-ps15-000-to-transform-into-brad-pitt-lookalikes,7018630501684865a
1 note
·
View note
Text
Beyond Tradition: Exploring Body Modification in East Asian Cultures
Body modification practices in East Asia, encompassing traditional methods such as tattooing and modern cosmetic surgery, reveal a rich tapestry of cultural, social, and economic influences. Understanding these practices through a process model helps elucidate the complex interplay of historical traditions, technological advancements, and societal norms. By applying the production of culture framework, we can unravel the complexities involved in creating, distributing, and consuming these forms of body modifications in East Asia.

The Production of Culture Framework
As discussed by Griswold (2013) and Peterson & Anand (2004), the production of culture framework focuses on the processes involved in creating, distributing, and consuming cultural forms. This approach emphasizes examining what people do rather than what they say, situating body modifications as cultural products shaped by social processes. It is particularly illuminating when examining body modifications in East Asia, where historical traditions intersect with contemporary influences.
Figure 1. Process-based framework for the analysis of body modification
Production: The Creation of Body Modifications
Historical Practices Traditional body modification practices in East Asia were deeply ingrained in cultural and social contexts. Practices such as tattooing, tooth blackening, and skull shaping served multiple purposes beyond mere decoration(Cheng 2013). These practices were personal expressions and communal rituals that reinforced social bonds and cultural identity.
Modern Practices In the 20th century, East Asia witnessed a significant shift towards cosmetic surgeries to enhance natural beauty. Procedures like double-eyelid surgery and augmentation rhinoplasty gained popularity, particularly in countries like South Korea and Japan. These surgeries often focus on subtle alterations perceived as enhancing natural features, reflecting evolving aesthetic preferences influenced by technological advancements (Holliday & Elfving-Hwang 2012).

Distribution: The Spread and Accessibility of Body Modifications
Traditional Methods Traditional body modification methods were traditionally localized and passed down through generations within specific cultural groups. These practices were closely tied to cultural rituals and societal roles, often performed by specialized practitioners within the community. They played a crucial role in maintaining cultural identity and social cohesion.
Modern Distribution The globalization of cosmetic surgery has dramatically transformed the accessibility and prevalence of body modifications in East Asia. Countries like South Korea have emerged as global leaders in cosmetic procedures, attracting a diverse clientele from around the world. This globalization is fueled by advancements in medical technology and amplified through media channels and social platforms, which disseminate beauty standards and trends internationally (Holliday & Elfving-Hwang 2012).

Consumption: The Adoption and Interpretation of Body Modifications
Cultural Significance Body modifications in East Asia are deeply embedded in cultural norms and societal expectations. For example, the preference for fair skin has historical roots and is associated with beauty and social status. This has led to widespread use of skin-whitening products and cosmetic procedures that reflect broader cultural ideals shaped by traditional aesthetics and contemporary media influences (Ashikari 2005).

Societal Pressure Modern body modification practices in East Asia are significantly influenced by societal pressures, including the competitive job market and social media influence. In South Korea, for instance, cosmetic surgery is often viewed as a means to enhance professional and personal success, creating a cultural environment where such procedures are normalized and even expected (Holliday & Elfving-Hwang 2012).

Body modification in East Asia presents a nuanced blend of tradition and innovation, shaped by historical legacies, technological advancements, and societal pressures. The application of a process model helps elucidate how these practices evolve over time, influenced by cultural values and global trends. As East Asia continues to navigate modernity and cultural identity, the meanings and manifestations of body modification will undoubtedly continue to evolve.

As these practices transcend borders, propelled by technological advancements and global connectivity, they embody a dynamic fusion of tradition and innovation. They remind us that the quest for beauty and identity is not merely skin-deep but a reflection of societies evolving amidst the currents of history and modernity
Reference list
Ashikari, M 2005, ‘Cultivating Japanese Whiteness’, Journal of Material Culture, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 73–91.
Brown, JK 1963, ‘A Cross-Cultural Study of Female Initiation Rites’, American Anthropologist, vol. 65, no. 4, pp. 837–853.
Griswold, W 2013, ‘Cultures and Societies in a Changing World’, SAGE Knowledge, 4th edn, Thousand Oaks, California, viewed <https://sk.sagepub.com/books/cultures-and-societies-in-a-changing-world-4e>.
Holliday, R & Elfving-Hwang, J 2012, ‘Gender, Globalization and Aesthetic Surgery in South Korea’, Body & Society, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 58–81.
Jones, M 2019, ‘Skintight: An Anatomy of Cosmetic Surgery’, Academia.edu, viewed 1 December 2019, <https://www.academia.edu/222157/Skintight_An_Anatomy_of_Cosmetic_Surgery>.
Sanders, CR 1982, ‘Structural and Interactional Features of Popular Culture Production: An Introduction to the Production of Culture Perspective’, The Journal of Popular Culture, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 66–74.
Spillman, L 2005, ‘Book Review: Cultures and Societies in a Changing World’, Teaching Sociology, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 111–112.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Usefulness of Social Media in Spreading Information on COVID-19
Public health refers to the study and practise of averting illness, extending life, and fostering well-being via planned initiatives and well-informed decisions made by public and private entities, communities, individual citizens, and organisations (Winslow, cited in Chin 2023). On the other hand, social media can be defined as an online venue for mass media communications where users may communicate and share messages, ideas, information, and other stuff (Britannica 2023). It can be said that both public health and social media complement each other in this day and age. That being said, is social media useful in spreading information on COVID-19?

At the height of the pandemic, social media platforms like Twitter/X, Facebook, and Instagram emerged as hubs for rapid and real-time updates and information on COVID-19. These sites gave users a place to share COVID-related information instantly. At the time, people were able to share and find information more rapidly because of social media's widespread use, and the same can be said when it comes to emerging infectious diseases (EIDs) like COVID-19 (Kothari, Walker & Burns 2022). In addition to tracking the spread of EIDs, social media was able to assist with the dissemination of preventative information and alerts (Houston et al., cited in Kothari, Walker & Burns 2022). Numerous studies have shown that social media not only helps spread information quickly and raise awareness, but that it also becomes more popular during these moments of distress when people are more likely to look for information (Taleb et al. 2021).

Besides that, social media allows for the authorities to connect with the people in regard to COVID-19. According to Gough et al. (cited in Reveilhac 2022), politicians and medical professionals, among others, are using social media more and more to share health information with the public. As an example, social media was utilised by the World Health Organisation (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to inform the public about health-related developments, as per Taleb et al. (2021). During the COVID-19 pandemic, this tendency reached heights previously unheard of, in an attempt to increase the public’s confidence in scientific knowledge relating to COVID-19 (van Dijck & Alinejad, cited in Reveilhac 2022). Simultaneously, people became more dependent on social media to get news and information on COVID-19 (Nielsen et al., cited in Reveilhac 2022). As a result, social media platforms were crucial in facilitating communication between political authorities and the public (Rauchfleisch, Vogler & Eisenegger, cited in Reveilhac 2022).

Furthermore, social media is beneficial in amplifying COVID-19 information. Chou et al. and Thackeray et al. (cited in Syn 2021) state that the use of social media in health communication has grown in importance. Not only that, but social media is an effective tool for spreading health information and promoting healthcare, according to both social media users and medical professionals (Thackeray et al.; Jha et al., cited in Syn 2021). Moreover, as mentioned by Reveilhac (2022), social media is crucial in this aspect because they enable people to get pass conventional forms of 'gatekeepers' like newspapers and political parties in order to encourage others to take pre-emptive action and ensure that related policies are followed by the general public.

In conclusion, there is no denying that social media was crucial in the dissemination of knowledge and information on COVID-19. The emergence and growth of social media platforms like Facebook, WhatsApp, and Twitter/X in recent times, which happened to coincide with a number of health crises, including the H1N1 virus in 2009, and the Ebola virus in 2013 have demonstrated how effective they are to distribute vital medical information to large audiences during public emergencies, such as EIDs (Taleb et al. 2021). In a separate study by Chang, Pham & Ferrara (2023), it was suggested that celebrities’ usage of social media and its potential for dissemination through various fan interaction channels can be crucial in the public’s responses to public health emergencies such as COVID-19. For example, entertainment artists who are globally recognised possess considerable broadcasting power due to their highly targeted audiences, which span national and ethnic boundaries, political ideologies, and personal convictions (Chang, Pham & Ferrara 2023). Needless to say, social media platforms were essential during the turbulent period of the pandemic and will continue to be in health crises by offering real-time updates to engagement between the authorities and the masses, boosting public health messaging, and encouraging worldwide awareness.

2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Influence of Social Media on Vaccine Discourse and Public Health
The relationship between social media and public health, particularly regarding vaccines, has evolved into a critical and multifaceted issue. In recent years, the digital age has reshaped the landscape of vaccine discourse, presenting both opportunities and challenges. This essay delves into the profound impact of social media on vaccine hesitancy, the role of celebrities and influencers in shaping vaccine opinions, the challenges of combating vaccine misinformation, and how young people's attitudes toward vaccines are influenced in this digital era.

The Impact of Social Media on Vaccine Hesitancy
The advent of social media has revolutionized the way information is disseminated and consumed. While it has democratized communication and enabled the rapid spread of knowledge, it has also become a breeding ground for misinformation and vaccine hesitancy. Vaccine-related discussions on social media platforms range from scientifically accurate information to unfounded fears and false narratives. This duality in content poses a central concern for public health worldwide. Social media offers a platform for open dialogue, where individuals can share personal vaccine experiences and access resources from reputable health organizations. However, this openness also amplifies the voices of vaccine opponents, enabling them to spread fear, uncertainty, and doubt regarding vaccines. The phenomenon of vaccine hesitancy, where individuals delay or refuse vaccinations despite their availability, is, in part, fueled by the information and sentiments encountered on social media. It creates an environment where misconceptions and skepticism can thrive.
The Role of Celebrities and Influencers in Shaping Vaccine Opinions
In the digital age, public figures and social media influencers have acquired unprecedented reach and influence. Their engagement in discussions about vaccines, either endorsing or opposing them, has substantial consequences. For instance, celebrity Jessica Biel's lobbying against a pro-vaccine bill garnered international attention. This case highlights the influential power of celebrities and their capacity to sway their followers' opinions on vaccines. Social media influencers, who often focus on health and wellness topics, can also play a pivotal role in vaccine discourse. They may unknowingly amplify vaccine misinformation, or, in some cases, deliberately spread false claims to promote their personal beliefs or agendas. These influencers can inadvertently contribute to vaccine hesitancy, particularly among their devoted followers.
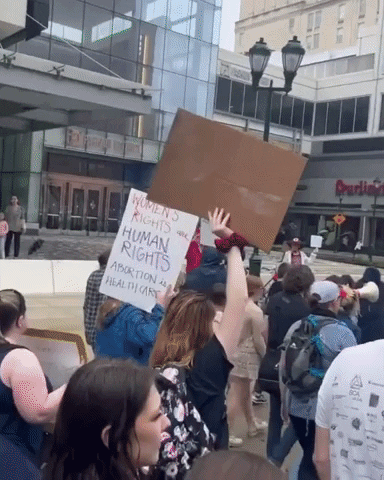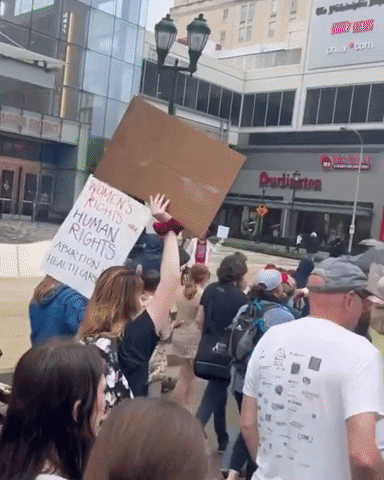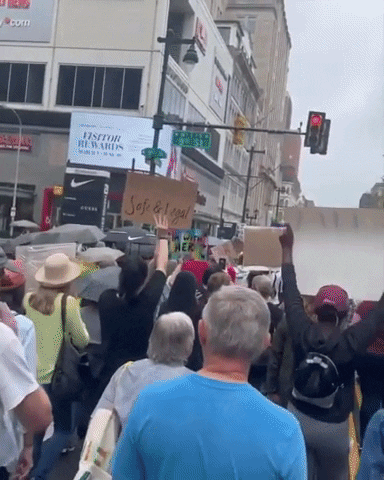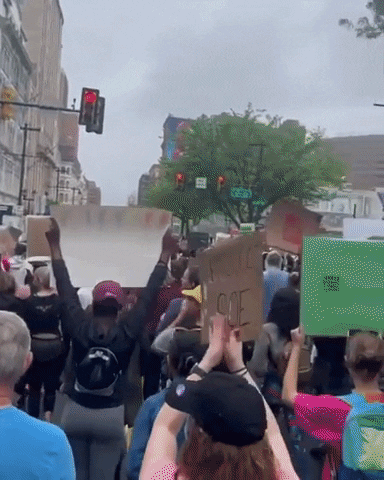
Challenges in Combating Vaccine Misinformation on Social Media
The spread of vaccine-related misinformation and disinformation on social media platforms poses distinct challenges to public health professionals. Misinformation typically results from individuals inadvertently drawing conclusions based on incorrect or incomplete facts. In contrast, disinformation involves the deliberate dissemination of falsehoods with the aim of advancing specific agendas. Combating these two types of false information necessitates diverse strategies and approaches.

Misinformation can often be addressed with factual information and patient education. Correcting false claims with credible sources and evidence can help individuals understand the safety and importance of vaccines. However, disinformation is more insidious and requires a multifaceted strategy. The deliberate spread of falsehoods necessitates a comprehensive approach that involves fact-checking, reporting harmful content, and educating the public about the tactics used to deceive.

The Digital Generation's Battle with Vaccine Hesitancy
Young people, who frequently rely on social media for information, find themselves in a unique position regarding vaccine hesitancy. They are growing up in a world where the internet is ubiquitous, and social media often plays a significant role in their lives. A study conducted in 2021 revealed that vaccine-hesitant students spent more time on social media, indicating a correlation between their online activities and vaccine hesitancy. The traditional education system has struggled to equip young people with the necessary digital literacy skills to critically assess information encountered on these platforms. While science education now includes the study of vaccines, the curriculum often falls short in addressing the rampant vaccine misinformation present online. Additionally, some English school curricula even lack the term "vaccine" or related concepts, potentially contributing to the digital generation's vulnerability to misinformation.
Digital literacy, defined as "the ability to use information and communication technologies to find, evaluate, create, and communicate information," is essential for young people to distinguish between scientific information and falsehoods online. The key word in this definition is "evaluate." Teaching students to apply a scientific approach when researching information and discerning between credible and unreliable sources is a valuable skill for the digital age. It not only aids in academic pursuits but also empowers young individuals to make informed decisions about their health and the world around them.
vaccines, social media, and the spread of misinformation. (2023, October 3). Executive and Continuing Professional Education. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/ecpe/vaccines-social-media-spread-misinformation/,viewed on 27 October 2023
Jimenez, D., & Jimenez, D. (2021, June 4). Covid-19 vaccines: the role of social media in disinformation. Pharmaceutical Technology. https://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/features/covid-19-vaccine-disinformation-social-media/,viewed on 27 October 2023
Young people and vaccine hesitancy - what role does social media play? (2021, November 15). British Science Association. https://www.britishscienceassociation.org/blog/young-people-and-vaccine-hesitancy-what-role-does-social-media-play,viewed on 27 October 2023
Mohamed, N. A., Solehan, H. M., Rani, M. D. M., Ithnin, M., & Arujanan, M. (2023). Understanding COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in Malaysia: Public perception, knowledge, and acceptance. PLOS ONE, 18(4), e0284973. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0284973,viewed on 27 October 2023
Vaccinate Your Family. (2023, September 13). Personal stories - Vaccinate your family. https://vaccinateyourfamily.org/why-vaccinate/personal-stories/,viewed on 27 October 2023
Redirect notice. (n.d.). https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Ftwitter.com%2FJKJAVMY%2Fstatus%2F1394096886932545536&psig=AOvVaw1VayABchu3MtLCsl0GTLFn&ust=1698473416244000&source=images&cd=vfe&opi=89978449&ved=0CBMQjhxqFwoTCLDOvNfIlYIDFQAAAAAdAAAAABAE viewed on 27 October 2023
Giphy. (n.d.). GIPHY - Be animated. GIPHY. https://giphy.com/,viewed on 27 Oct 2023
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Effects of Social Media on Body Image, Aesthetic Labour, and Digital Citizenship
Social Media Beauty Standards and Aesthetic Templates
Social media is dominated by standardised beauty trends, which are referred to as aesthetic templates (Duffy, 2017). These include particular photo filters, body modifications, and makeup looks, which contribute to the rise of unrealistic body ideals.
A popular beauty standard on Instagram is the idea of "Instagram Face," which is defined by full lips, sculpted cheekbones, and poreless, smooth skin (Carrotte et al., 2017). This template promotes excessive photo editing and cosmetic enhancements, which feeds into self-doubt and social comparison.
Appearance is a type of social currency in the visual culture that social media promotes. Influencers curate extremely polished images to keep followers interested, which can lead to negative self-perceptions and a distorted self-image, especially in younger audiences (Bishop, 2021).

Are Public Health Campaigns Beneficial or Dangerous?
Although social media is an effective tool for raising public awareness of health issues, it can also reinforce negative standards of beauty.
Some initiatives, like Movember, successfully advance men's health by enticing people to take part in awareness-raising events. Nonetheless, extreme dieting, impractical fitness objectives, and unachievable body ideals are encouraged by some fitness and wellness trends, and these behaviours have been connected to eating disorders and body dysmorphia (Daniels, 2016).
The emergence of thinspiration and fitspiration content shows how social media can perpetuate unhealthy ideals of beauty. Although platforms have made an effort to control these trends, users are still exposed to harmful content through algorithm-driven content recommendations (Duffy & Meisner, 2022).
The Cost of Internet Stardom: Aesthetic Labour & Microcelebrity
According to Senft (2012), the microcelebrity phenomenon is when people position themselves as influencers in an effort to attract followers and achieve financial success. However, aesthetic labor—the ongoing effort to preserve a skilfully constructed image—is necessary to maintain this status.
This work can be seen in a number of influencer categories:
To keep up a perfect online persona, beauty influencers use cosmetic enhancements, makeup, and filters.
Influencers in the fitness industry frequently portray an idealised view of health and body image that may not be true to their actual situation.
Influencers in the fashion industry advocate carefully chosen looks that demand hefty sums of money.
According to Dean (2005), the persistent pressure to appear flawless has detrimental effects on mental health, including low self-esteem, anxiety, and depression.

The pornification of online content
The growing sexualisation of self-presentation on digital platforms is referred to as pornification (Drenten et al., 2019). The way that men and women portray themselves online is one area where this trend is especially noticeable.
While men are urged to emphasise muscularity and dominance, women are frequently subjected to aesthetic pressures that centre on hyper-feminine beauty standards, such as exaggerated curves. Social media algorithms reinforce the emphasis on physical attractiveness by giving more visibility to highly sexualised or visually appealing content (Marshall, 2010).
This raises moral questions about the normalisation of unattainable beauty standards and self-objectification, especially for younger audiences who are more susceptible to influence.
Mental Health and the Crisis of Body Image
Increased body dissatisfaction has been closely associated with social media, with studies pointing to important risks including:
A rise in social comparison-related body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) (Dorfman et al., 2018).
Elevated anxiety and depression, particularly among regular image-based platform users (Duffy, 2017).
Younger people seeking to meet the ideal of beauty on social media are increasingly undergoing cosmetic surgery.
A few platforms have tried to implement policies to mitigate these impacts. For instance, Instagram has tried eliminating likes, and TikTok has prohibited specific weight-loss campaigns. The promotion of carefully chosen beauty content by engagement-driven algorithms, however, limits these efforts.

Ways to Make the Digital Environment Healthier
There are various actions that people and platforms can take to lessen the detrimental effects of social media on mental health and body image:
Recognise unattainable beauty standards by realising that the majority of photos on social media are heavily Photoshopped.
Instruct users in media literacy so they can evaluate influencer endorsements and beauty trends critically.
Encourage self-acceptance and a variety of body types by supporting body-positive influencers.
Control influencer content to guarantee ethical marketing and promotion strategies.
By highlighting the fact that beauty is varied and not solely determined by social media trends, you can promote self-acceptance.
References:
Bishop, S. (2021). Influencer management tools: Algorithmic cultures, brand safety, and bias. Social Media + Society, 7(1). https://doi.org/10.1177/20563051211003066
Carrotte, E. R., Prichard, I., & Lim, M. S. C. (2017). ‘Fitspiration’ on social media: A content analysis of gendered images. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 19(3).
Daniels, E. A. (2016). Sexiness on social media: The social costs of using a sexy profile photo. Sexualization, Media, & Society, 2(4), 1–10.
Dean, D. (2005). Recruiting a self: Women performers and aesthetic labour. Work, Employment & Society, 19(4), 761–774.
Dorfman, R. G., Vaca, E. E., Mahmood, E., Fine, N. A., & Schierle, C. (2018). Plastic surgery-related hashtag utilization on Instagram: Implications for education and marketing. Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 38(3), 332–338.
Drenten, J., Gurrieri, L., & Tyler, M. (2019). Sexualized labour in digital culture: Instagram influencers, porn chic, and the monetization of attention. Gender, Work and Organization, 1–26.
Duffy, B. E. (2017). (Not) getting paid to do what you love: Gender, social media, and aspirational work. Yale University Press.
Duffy, B. E., & Meisner, C. (2022). Platform governance at the margins: Social media creators’ experiences with algorithmic (in)visibility. Media, Culture & Society. https://doi.org/10.1177/01634437221111923
Marshall, D. (2010). The promotion and presentation of the self: Celebrity as a marker of presentational media. Celebrity Studies, 1(1), 35-48.
Senft, T. M. (2012). Microcelebrity and the branded self. In Hartley, J., Burgess, J., & Bruns, A. (Eds.), A Companion to New Media Dynamics. Blackwell, UK.
#DigitalCitizenship#BodyImage#SocialMediaActivism#InfluencerCulture#AestheticLabor#digital_community#mda20009#week7
0 notes
Text
Digital Citizenship, Algorithmic Bias & The Body Modification Crisis
🧠 How Social Media Shapes Our Perception of Beauty Does social media make us change how we look? Platforms like Instagram and TikTok prioritize visually appealing content, reinforcing unrealistic beauty standards. As a result, digital citizens feel increasing pressure to conform to "aesthetic templates"—leading to rising cosmetic surgeries, digital body modification, and self-esteem issues.
But who decides what beauty is? Algorithms.
This post explores how algorithmic bias shapes body modification trends, suppresses diverse beauty, and impacts digital citizens' autonomy over their identities.
Algorithmic Beauty Norms: Who Gets Seen & Who Doesn’t?
💡 Algorithms define beauty. Content with Eurocentric features, clear skin, and specific body shapes is promoted (Duffy & Meisner, 2022). Other appearances? Shadowbanned.
🔍 Case Study: TikTok’s Algorithmic Suppression of “Unattractive” Content
Internal reports from TikTok revealed moderators were told to suppress content from creators with “ugly facial looks” and “abnormal body shape” (Ghaffary, 2021). This discriminatory moderation policy shaped visibility for millions, showing how beauty standards are not just cultural—they’re coded into social media itself. 🔹 Aesthetic Labour: The Price of Visibility
Influencers engage in aesthetic labor by altering appearances to gain visibility (Marwick, 2013). More attractive = higher engagement = better algorithmic ranking (Becker, 2017). 💡 Result: Those who don’t fit these beauty norms are less visible, less marketable, and less likely to succeed in the creator economy.

The Rise of Cosmetic Surgery & Body Modification on Social Media
Why are influencers getting more surgery? The rise of digital beauty standards makes real-world features seem "flawed."
Filters & FaceTune: The “Instagram Face” Phenomenon
Studies show Snapchat Dysmorphia is driving cosmetic surgeries (Dorfman et al., 2018). Filters reinforce idealized facial features, making unfiltered faces appear "worse" by comparison. 2019 Plastic Surgery Statistics: 72% of surgeons reported clients wanting procedures to look like their filtered selfies (ASPS, 2019). 📌 Case Study: Brazil's Boom in Cosmetic Surgeries (2022)
Brazil became the world leader in cosmetic procedures, with 1.5 million surgeries per year, driven by influencer culture & algorithm-driven beauty norms (Adams, 2022). TikTok trends like #BBLTransformation & #GlowUpChallenge fueled unrealistic expectations. 💡 The problem?
It’s not just influencers modifying their bodies—it’s everyday users who feel forced to "catch up." Plastic surgery advertising on TikTok & Instagram normalizes body modification.
🚨 Algorithmic Discrimination & Marginalized Identities
🔹 Who gets suppressed?
Black creators reported lower visibility & engagement on TikTok compared to white influencers (Ghaffary, 2021). LGBTQ+ content is disproportionately shadowbanned, affecting queer influencers' ability to monetize their platforms (Duffy & Meisner, 2022). Tattooed & pierced influencers struggle for visibility, as platforms associate them with “non-mainstream” aesthetics. 📌 Case Study: Instagram’s 2021 "Racial Bias" Controversy
Black creators noticed their content was being removed while similar white-led posts remained. Instagram responded by pledging to fix racial bias in AI moderation (Frenkel, 2021). 💡 Bottom line: If beauty standards are coded into social media, marginalized identities will always struggle for visibility.

How Can We Disrupt Algorithmic Beauty Pressures?
Algorithmic Transparency
Platforms must disclose how they rank beauty content (Duffy & Meisner, 2022). 💡 Promote Inclusive Beauty Standards
TikTok & Instagram should support body-positive content, not suppress it. 💡 Educate Digital Citizens
We need better digital literacy programs to teach users how social media skews beauty standards. 💡 Support Marinalized Creators ✔️ Follow body-positive influencers. ✔️ Engage with creators outside of mainstream beauty standards. ✔️ Push platforms to audit their algorithms for bias.

💬 What Do You Think?
🔥 Is social media shaping how people view beauty? 🔥 Should platforms be responsible for algorithmic bias in beauty standards?
Comment below & reblog to continue the discussion!
📚 References
Adams, J. (2022). Bodies of Change: A Comparative Analysis of Media Representations of Body Modification Practices. Sociological Perspectives, 52(1), 103–129. https://doi.org/10.1525/sop.2009.52.1.103
American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). (2019). Plastic Surgery Statistics Report. https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2019/plastic-surgery-statistics-full-report-2019.pdf
Duffy, B. E., & Meisner, C. (2022). Platform Governance at the Margins: Social Media Creators’ Experiences with Algorithmic (in)visibility. Media, Culture & Society. https://doi.org/10.1177/01634437221111923
Frenkel, S. (2021). Instagram's Racial Bias Problem. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/04/21/technology/instagram-racial-bias.html
Ghaffary, S. (2021). How TikTok’s hate speech detection tool set off a debate about racial bias. Vox. https://www.vox.com/recode/2021/7/7/22566017/tiktok-black-creators-racial-bias
0 notes
Text
Week 7: Digital Citizenship and Health Education: Body Modification on Visual Social Media
Social media platforms have developed into effective instruments for community building and self-expression in the digital age. But they also have a big impact on how people view beauty standards and body image. With an emphasis on aesthetic templates, aesthetic labor, the idea of pornification, and the body image issue, this blog examines the relationship between digital citizenship, health education, and body modification on visual social media.
The influence of Aesthetic Templates
Users can access premade layouts that prioritize visual appeal using aesthetic templates on social media sites like Instagram and Pinterest. People's perceptions of their own and other people's bodies are influenced by these templates, which frequently feature idealized body types and beauty standards. However, the pursuit of unattainable beauty standards and body dissatisfaction can both be worsened by the use of aesthetic templates. These templates function as a collection of defined norms or patterns that people feel compelled to follow in order to get recognition and popularity. The desire to remain faithful to these models could lead to a similarity in body alteration practices, which could undermine the uniqueness and individuality that inspired the movement.

Aesthetic Labor in the digital age
The effort people make to control their appearance in order to satisfy social media's aspirations for beauty is known as "aesthetic labor." This idea goes beyond one's outer look to encompass the maintenance of one's online identity. A greater emphasis on physical beauty and severe psychological stress are two consequences of aesthetic labor, according to studies (Mann & Rawat 2023). Anxiety and despair are two detrimental mental health effects that might arise from the strain to live up to these ideals. According to Dean (2025), certain industries, like the entertainment sector, hire people based on their physical characteristics, which leads to prejudice against those who don't meet the standards, which can cause stress and burnout. Programs for health education must address these problems by encouraging resilience against social influences and self-acceptance.


The concept of Pornification
On social media, pornification—the popularization of pornographic aesthetics—has grown in popularity. “The normalization of pornographic representation in popular culture can be seen as directly linked to the normalization of pornography and to the sex industry more broadly” (Tyler & Quek 2016, p. 03). Particularly for young individuals, the normalization of such information can have a significant impact on self-esteem and body image. Exposure to pornographic material has been shown to cause unrealistic expectations regarding sexual conduct and body image (Merino et al. 2024). Critics caution that pornification blurs the lines between objectification and empowerment, affecting how society views sex and relationships, even as some claim that sexual expression has become more open and liberating. Parents and educators must collaborate to provide children the skills they need to evaluate these influences critically and fend them off.


The Body Image Crisis
The term "body image crisis" describes the widespread discontent with one's physical appearance, which is frequently made worse by social media. Both men and women are impacted by this crisis, which exacerbates eating disorders, anxiety, and low self-esteem. Perceptions of natural beauty are further distorted by filters, photo retouching, and celebrity endorsements. Even if movements for body positivity have arisen to question these principles, social norms are still very much in place. According to a research by Rodgers et al. (2023), social media's widespread influence has made body image issues a global mental health concern. The situation emphasizes how crucial it is to incorporate media literacy and body positivity into health education programs. We can lessen the negative impact of social media on body image by encouraging a more diverse and inclusive representation of bodies.

In conclusion, there are opportunities as well as obstacles at the connection of body alteration, health education, and digital citizenship on visual social media. We can enable people to use social media in a healthy and constructive manner by addressing the impact of aesthetic templates, aesthetic labor, pornification, and the body image issue. We can create a more welcoming and encouraging online community by promoting positive digital citizenship and thorough health education.

References
Dean, D 2005, ‘Recruiting a self: Women performers and aesthetic labour’, Work, Employment and Society, vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 761–774, viewed 27 February 2025, <https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/epdf/10.1177/0950017005058061>
Mann, S & Rawat, SR 2023, ‘You Got to Look Right! Mapping the Aesthetics of Labor by Exploring the Research Landscape using Bibliometrics’, The Open Psychology Journal, vol. 16, no. 1, viewed 27 February 2025, <https://openpsychologyjournal.com/VOLUME/16/ELOCATOR/e18743501260121/FULLTEXT/>
Merino, M, Tornero-Aguilera, JF, Rubio-Zarapuz, A, Villanueva-Tobaldo, CV, Martín-Rodríguez, A & Clemente-Suárez, VJ 2024, ‘Body perceptions and psychological well-being: A review of the impact of social media and physical measurements on self-esteem and mental health with a focus on body image satisfaction and its relationship with cultural and gender factors’, Healthcare, vol. 12, no. 14, viewed 28 February 2025, <https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9032/12/14/1396>
Rodgers, RF, Laveway, K, Campos, P & de Carvalho, PHB 2023, ‘Body image as a global mental health concern’, Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health, vol. 10, no. 9, viewed 28 February 2025, <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9970735/>
Tyler, M & Quek, K 2016, ‘Conceptualizing Pornographication: A Lack of Clarity and Problems for Feminist Analysis’, Sexualization, Media, & Society, pp. 1–14, viewed 28 February 2025, <https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/2374623816643281>
#digital communities#mda20009#week7#body modification#aesthetic template#pornification#body image#body posititivity
0 notes
Text
Microcelebrity & The Body Mod Boom: A Social Media Obsession
Recently, the rise of social media has brought a new type of celebrity to our attention, which is referred to as microcelebrities or influencers (Chae, 2018). Social media has birthed a new kind of fame, where niche influencers cultivate dedicated followings, turning their bodies into canvases for self-expression, status, and viral aesthetics. From extreme surgeries to DIY procedures, the pursuit of the "perfect" or "unique" look is no longer just about beauty—it's about branding.
Welcome to my blog, where I dive deep into the aesthetics, ethics, and consequences of the microcelebrity-driven body mod movement.
What is “microcelebrity”?
Celebrity is often defined as “individuals who have achieved a significant level of fame that makes them well known in society” (Mark Young & Pinsky, 2006). Traditionally, celebrity endorsers are movie stars, singers, models, and athletes (Hsu & McDonald, 2002). In recent years, the increased popularity of social media has created a new type of celebrity called microcelebrity (Chae, 2018).
The term "microcelebrity" was first introduced by Theresa Senft in 2008. It refers to individuals who gain fame through self-presentation and interaction on digital platforms, often targeting niche audiences. Unlike traditional celebrities, microcelebrities actively cultivate their online personas and engage directly with their followers, creating a sense of intimacy and accessibility.
Examples of Microcelebrities:

Bretman Rock: Known for his makeup tutorials and humorous personality, he has built a strong following on platforms like Instagram and TikTok.
Instagram:

Zach King: Famous for his "magic" video edits on platforms like Vine and TikTok, he has captivated a niche audience with his creativity.
TikTok:
The activities of microcelebrities, particularly beauty influencers, on digital platforms have been instrumental in shaping contemporary perceptions of beauty standards, often prompting individuals to engage in body modification procedures to align with these ideals.
What is body modification?
According to Stirn et al. (2011), body modification (BM) comprises procedures to achieve permanent alterations of the human body. It includes all voluntary body projects such as tattoos, piercings (Martin & Cairns, 2015), weight loss/gain, cosmetic surgery (Karupiah, 2013), and also gender reassignment (Aguayo-Romero et al., 2015).
There are four different motivations for bodies to be modified (Lane, 2017). However, the suitable motivation for today's blog, which is also the most documented motivation, is the capacity to take control over one's body to shape a more genuine representation of the self or identity, as highlighted by Atkinson (2003), is often paired with the experience of aesthetic satisfaction, as noted by Thomas et al. (2015).
Microcelebrities often present their body modifications as a means of achieving a more authentic self, inspiring their followers to pursue similar changes in their quest for personal identity and satisfaction. And here are a specific example.


Instagram:
Kim Kardashian and Kylie Jenner frequently showcase their appearances on social media, which reflect the results of various cosmetic procedures, including Botox, fillers, and breast surgeries (Isaac & Shilliday, 2025). The Brazilian butt lift, rumored to be favored by Kim and Kylie Jenner, has become the most popular Kardashian-inspired cosmetic surgery, helping people worldwide achieve shapely backsides, as seen in their social media photos (Cosmedical, 2025). This has raised a powerful impact to the public, which created the “Kardashian Effect”. The 'Kardashian Effect' has normalized cosmetic enhancements such as Botox and fillers, reshaping societal attitudes toward aesthetic procedures (Cosmedical, 2025). The U.K. cosmetic surgery group Transform also states that inquiries from patients mentioning Kardashian family members as inspiration have risen by 73 percent (Olya , 2015).
The culture of microcelebrities promoting body modification trends raises significant ethical concerns and societal consequences:
Normalization of Unrealistic Standards: Microcelebrities often present heavily curated and surgically enhanced appearances as attainable ideals. This can perpetuate unrealistic beauty standards, leading to body dissatisfaction among their followers
Informed Consent and Transparency: Ethical concerns arise when influencers fail to disclose the extent of their cosmetic procedures, misleading audiences into believing such transformations are natural or easily achievable (Abdoli et al., 2024)
Exploitation of Vulnerability: The promotion of body modifications can exploit individuals' insecurities, particularly among younger audiences, who may feel pressured to conform to these ideals
In summary, while microcelebrity culture has shaped beauty norms and empowered self-expression, it also raises concerns over unrealistic standards, mental health impacts, and cultural homogenization. Promoting inclusivity, body positivity, and informed choices is crucial to creating a healthier narrative around beauty and identity.
References
Abdoli, M., Scotto Rosato, M., Desousa, A., & Cotrufo, P. (2024). Cultural Differences in Body Image: A Systematic Review. Social Sciences, 13(6), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci13060305
Aguayo-Romero, R. A., Reisen, C. A., Zea, M. C., Bianchi, F. T., & Poppen, P. J. (2015). Gender Affirmation and Body Modification Among Transgender Persons in Bogotá, Colombia. International Journal of Transgenderism, 16(2), 103–115. https://doi.org/10.1080/15532739.2015.1075930
Atkinson, M. (2003). Tattooed : the sociogenesis of a body art. University Of Toronto Press.
Chae, J. (2018). Explaining Females’ Envy Toward Social Media Influencers. Media Psychology, 21(2), 246–262. https://doi.org/10.1080/15213269.2017.1328312
Cosmedical. (2025). Celebrity Influence on Cosmetic Surgery Trends | Cosmedical Rejuvenation Clinic. Cosmedical Rejuvenation Clinic. https://cosmedical.ca/blog/the-kardashian-effect-on-the-cosmetic-and-plastic-surgery-industry.html?form=MG0AV3
Hsu, C., & McDonald, D. (2002). An examination on multiple celebrity endorsers in advertising. Journal of Product & Brand Management, 11(1), 19–29. https://doi.org/10.1108/10610420210419522
Isaac, P. J., & Shilliday, B. (2025, January 30). Kylie Jenner Is No Stranger to Plastic Surgery: Her Transformation in Before and After Photos. Life & Style; Life & Style. https://www.lifeandstylemag.com/posts/did-kylie-jenner-get-plastic-surgery-see-transformation/?form=MG0AV3&form=MG0AV3
Karupiah, P. (2013). Modification of the body: a comparative analysis of views of youths in Penang, Malaysia and Seoul, South Korea. Journal of Youth Studies, 16(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/13676261.2012.693588
Lane, D. C. (2017). Understanding body modification: A process-based framework. Sociology Compass, 11(7), e12495. https://doi.org/10.1111/soc4.12495
Mark Young, S., & Pinsky, D. (2006). Narcissism and celebrity. Journal of Research in Personality, 40(5), 463–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2006.05.005
Martin, C., & Cairns, S. (2015). Why Would You Get THAT Done?! Stigma Experiences of Women with Piercings and Tattoos Attending Postsecondary Schools Pourquoi voudriez-vous vous faire CELA ? ! Expériences de stigmatisation de femmes au niveau postsecondaire qui ont des perçages et tatouages. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=e1d1f761b39ef2b7bce540e1a1ff5dff95d70931
Olya , G. (2015, November 24). The “Dash Effect”: Kardashian-Inspired Plastic Surgery Procedures on the Rise, Say Experts. PEOPLE.com. https://people.com/health/the-dash-effect-kardashian-inspired-plastic-surgery-procedures-on-the-rise-say-experts/
Stirn, A., Oddo, S., Peregrinova, L., Philipp, S., & Hinz, A. (2011). Motivations for body piercings and tattoos — The role of sexual abuse and the frequency of body modifications. Psychiatry Research, 190(2-3), 359–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2011.06.001
Thomas, J. N., Crosby, L., & Milford, J. (2015). Gender Differences among Self-Reported Genital Piercing Stories. Deviant Behavior, 36(6), 441–462. https://doi.org/10.1080/01639625.2014.944062
Usher, B. (2018). Rethinking microcelebrity: key points in practice, performance and purpose. Celebrity Studies; Informa UK Limited. https://www.academia.edu/119789942/Rethinking_microcelebrity_key_points_in_practice_performance_and_purpose?form=MG0AV3&form=MG0AV3
0 notes
Text
Aesthetic Pressure on Social Media: When Beauty Becomes a Duty
🎭 Aesthetic Labor - Unpaid Work on the Web
In the past, only celebrities or service industry workers needed to care about aesthetic labor, but now, anyone who uses social media is unwittingly participating in it. To have a "standard" photo, we not only have to edit it but also pose, choose clothes, and even invest in our appearance to be prioritized by the algorithm.
But not everyone has the same opportunities. Research by Duffy & Meisner (2022) shows that algorithms tend to prioritize content that fits popular beauty standards, while "algorithmically invisible" those who do not meet the standards. This causes many people to edit photos or even change their bodies to "fit in", creating a cycle of aesthetic pressure.

🧠 When Beauty Becomes a Psychological Burden
It doesn't stop at appearance. Constantly comparing yourself to edited images can lead to Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD), an obsession with an 'imagined' defect in appearance that causes severe distress and affects life (Veale et al., 1996)
Research by Rajanala et al. (2018) shows that the overuse of filtered selfies can exacerbate BDD and increase self-esteem in adolescents, especially those who already have signs of body dysmorphia. This creates a vicious cycle: users edit their photos to feel more confident, but the more they do so, the less they accept their true appearance.
It is not just ordinary users, even influencers are affected. According to Carah & Dobson (2016), many young women are not only monitored for their appearance, but also self-monitored. They edit photos and change the way they pose and present themselves to achieve the "hotness standard" set by the algorithm. This turns beauty from a personal choice into a digital obligation.
Not only is the algorithm involved, Instagram also promotes the commercialization of appearance through cosmetic surgery. A study by Dorfman et al. (2017) found that 67.1% of posts related to cosmetic surgery on Instagram were self-promotional rather than educational. This has led many to view cosmetic surgery as a trend, a way to “upgrade yourself” rather than a serious health decision.

🔄 Breaking the Aesthetic Standards Loop
So what can we do?
📌 Be aware of the algorithm: What you see on your feed is not an objective reflection of reality but a product of an interactive optimization system.
📢 Support diverse body and beauty content: Like and share posts that bring new perspectives so that algorithms can recognize their value.
🌍 Create a healthier online space: Platforms should be more transparent about how content is displayed and have policies to support vulnerable groups to avoid algorithmic invisibility.
Social media is not at fault, but if we let it determine our value, then perhaps it’s time to ask: Am I beautifying myself, or just following an algorithm?
References
Carah, N., & Dobson, A. (2016). Algorithmic hotness: Young women’s “promotion” and “reconnaissance” work via social media body images. Social Media + Society, 2(4), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/2056305116672885
Dorfman, R. G., Vaca, E. E., Mahmood, E., Fine, N. A., & Schierle, C. F. (2017). Plastic Surgery-Related Hashtag Utilization on Instagram: Implications for Education and Marketing. Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 38(3), 332–338. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjx120
Duffy, B. E., & Meisner, C. (2022). Platform Governance at the margins: Social Media Creators’ Experiences with Algorithmic (in)visibility. Media, Culture & Society, 45(2), 016344372211119. https://doi.org/10.1177/01634437221111923
Rajanala, S., Maymone, M. B. C., & Vashi, N. A. (2018). Selfies—Living in the Era of Filtered Photographs. JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery, 20(6), 443. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamafacial.2018.0486
Veale, D., Boocock, A., Gournay, K., Dryden, W., Shah, F., Willson, R., & Walburn, J. (1996). Body Dysmorphic Disorder. British Journal of Psychiatry, 169(2), 196–201. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.169.2.196
0 notes
Text
Influencers as Health Heroes! (Week 7)
aka The Role of Influencers in Public Health Messaging
QOTD: : How Social Media Influencers Can Drive Awareness and Change

He's Perry, Perry the Platypus!!!!
Perry's here to influence you to leave a like to my posts from now onwards including the previous ones hehe thank you!
If you know the show Phineas and Ferb, you will know about their iconic pet platypus that is an undercover agent. (watch it if you haven't, it's one of my childhood cartoon series and its funny)
Welcome back to another session of me yapping and this time it will be about social media influencers who plays an pivotal role in shaping public opinion, behavior and awareness.
These influencers are highly effective tools for public health campaigns. Their ability to reach diverse and expansive audiences, coupled with their personal connections to followers, offers a unique opportunity to spread health information and encourage behavioral changes.

Reaching Large and Diverse Audiences
So without stating the obvious reason, it is easier for these social media influencers to reach a large and diverse audiences. Social media platforms like Instagram, YouTube, TikTok and Twitter have millions of active users, making them ideal spaces for health communication. These influencers often have many followings that span various demographics including hard-to-reach groups like younger individuals or marginalized communities. For instance, a study on health influencers on Instagram showed that health-related content shared by influencers could reach and engage audiences more effectively than traditional communication channels due to trust and relatability (Yang & Saffer, 2018) which leads to my next point.
Building Trust and Credibility

omg Tzuyu is so cute here, if she asked me to sleep early, I would listen with no hesitation <3
Influencers often build relationships with their followers by sharing personal stories, experiences and their own opinions, fostering a sense of authenticity and trust. This trust is critical in public health messaging as people are more likely to heed advice from sources they perceive as credible and relatable. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, influencers were instrumental in promoting mask-wearing and vaccination among hesitant groups (Basch et al., 2021). Their ability to humanize health recommendations by embedding them into their narratives makes them particularly effective.
Encouraging Behavioral Changes

Besides just spreading awareness, influencers can also drive actionable change. Their influence can lead to increased adoption of healthy behaviors, such as exercising, eating nutritiously or participating in vaccination campaigns. For example, campaigns led by fitness influencers often report significant increases in physical activity levels among their followers (Lozada & Zolfaghari, 2020). Influencers who partnered with health organizations for vaccination drives observed improved vaccine uptake in communities previously hesitant to engage. This just shows the great power that influencers have towards their audiences. Wish I have such great power

everything has its obstacles that needs to be overcome!
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite their potential, leveraging influencers for public health comes with challenges such as misinformation spread by unqualified influencers can counteract public health efforts. Therefore, partnerships with influencers should involve proper vetting and collaboration with reputable health authorities while also ensuring transparency, such as disclosing paid partnerships, is essential to maintain credibility (Abidin, 2020).
Let's move on from the negative and look forward to the next part!

Outcomes and Impact
When properly managed, influencer-led campaigns have demonstrated tangible benefits. For example, the "This Close" campaign by Rotary International to end polio employed influencers to target millennials and successfully raised millions in donations and awareness (Rotary International, 2019). Campaigns addressing mental health, like the #HereForYou initiative, saw significant increases in mental health resource usage and conversation rates (Smith et al., 2022).

You're now at the part you have been waiting for before reaching the end of the post, yippee!!

Personally, I think it is very easy to be influenced by anything you see in social media, not just by these known influencers, but even through the engagement of the audience to the content cause even I would be all ears and even take actions relating to my health if say Taylor Swift were to spread awareness in social media about public health.
Before I finally stop yapping, Social media influencers hold immense power to drive awareness and encourage behavioral change in public health. By leveraging their reach, relatability and credibility, health organizations can effectively engage broader audiences especially those traditionally resistant to conventional messaging. In order to maximize impact, collaborations with influencers must be strategic, ethical and rooted in evidence-based practices so that the public would trust more.
reference list:
Abidin, C. (2020). Mediated authenticity: How influencers reshape public health communication. Social Media + Society, 6(3), 205630512093463.
Basch, C. H., Hillyer, G. C., & Jaime, C. (2021). COVID-19 on TikTok: Harnessing an emerging social media platform to convey important public health messages. International Journal of Adolescent Medicine and Health, 33(1), 29–32. <https://doi.org/10.1515/ijamh-2020-0111>.
Lozada, J., & Zolfaghari, H. (2020). The role of social media influencers in promoting health and wellness: A systematic review. Journal of Health Communication, 25(4), 350–362. <https://doi.org/10.1080/10810730.2020.1740500>.
Rotary International. (2019). This Close campaign raises awareness about polio eradication. <https://www.rotary.org>.
Smith, J., Brown, R., & Taylor, A. (2022). Impact of influencer-driven campaigns on mental health awareness: A longitudinal study. Health Communication Research, 38(2), 128–140. <https://doi.org/10.1080/10410236.2022.12345>.
Yang, Q., & Saffer, A. J. (2018). Health-related content on Instagram: The influence of credibility and relevance on engagement. Journal of Social Media Studies, 9(3), 415–432. <https://doi.org/10.1080/12345678.2018.09876>.
0 notes
Text
Lessons from the COVID-19 Response: What Public Health Campaigns Can Learn
Data-Driven Decision Making: Evaluating Impact Finally, the pandemic highlighted the necessity of data-driven decision-making in public health campaigns. As various strategies were implemented globally, it became clear that evaluating their effectiveness was essential for future planning. The use of data analytics allowed health officials to assess which messages resonated most with different demographics and adjust campaigns accordingly. Thus, it is imperative to understand which communication channels were most effective in reaching specific populations enabled more efficient resource allocation. According to Nerindo, Jamari and Wok (2021), different communication channels were preferred by specific demographics, such as younger adults relying on social media while older individuals favored television and online newspapers. This understanding enabled more targeted resource allocation and improved the effectiveness of public health campaigns. Public health agencies should continue to invest in data collection and analysis tools to inform their strategies, ensuring that campaigns are responsive to emerging trends and community needs. Conclusion: Moving Forward with Lessons Learned The COVID-19 response has provided invaluable insights for future public health campaigns. By focusing on tailored messaging, community engagement, combating misinformation, and leveraging data-driven decision-making, public health officials can enhance their effectiveness in addressing not only pandemics but also other pressing health issues.As we move forward into a post-pandemic world, it is crucial that we apply these lessons learned to build resilient public health systems capable of responding swiftly and effectively to future challenges. By fostering trust, understanding community needs, and prioritizing accurate information, we can create a healthier future for all. Reference List Foundation, C 2020, ‘CDC Foundation Launches Crush Covid-19 Campaign to Meet Urgent Needs Caused by Pandemic’, CDC Foundation: Together Our Impact Is Greater, CDC Foundation: Together Our Impact Is Greater, viewed 31 November 2024, <https://www.cdcfoundation.org/pr/2020/crush-covid-campaign>. Hunt, I de V, Dunn, T, Mahoney, M, Chen, M, Nava, V & Linos, E 2022, ‘A Social Media‒Based Public Health Campaign Encouraging COVID-19 Vaccination across the United States’, American Journal of Public Health, vol. 112, no. 9, pp. e1–e4, viewed 1 December 2024, <https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9382165/>. Nerindo, A, Jamari, J & Wok, S 2021, ‘The Effectiveness of COVID-19 Public Health Campaigns by the Ministry of Health Malaysia: an Exploratory Study in a University Campus’, Forum Komunikasi (FK), vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 1–25, viewed 1 December 2024, <https://ir.uitm.edu.my/id/eprint/49485/>. Papendick, K 2024, ‘How to Effectively Use Social Media for Public Health’, Social News Desk - Social Media Management, viewed 1 December 2024, <https://www.socialnewsdesk.com/blog/how-to-effectively-use-social-media-for-public-health/>.
0 notes
Text
An apple a day keeps the doctor away!
(What is the future of public health campaigns in a digital age?)
How I feel when I have a slight cough and a dry throat:

Health is wealth
Public health campaigns help spread awareness about diseases and health hazards, which can encourage people to seek medical attention for themselves or others (Team CSG 2024). Public health campaigns are essential in shaping community health outcomes by providing crucial information about prevention and treatment options. By leveraging various media channels, these campaigns effectively reach diverse populations, ensuring that important messages resonate well with different demographics.
Beep.. Entering the digital age.. beep
Over the past two decade, the use of digital media and digital technologies for health campaigns and promotion has grown at an unprecedented rate (Koh et al. 2021, p.171). Digital technologies revolutionize the way public health organisations reach and teach audiences as modern campaigns are increasingly using digital strategies to maximize their influence on health behaviours (Krawiec et al. 2021). Digital health campaigns also make it easier for people to consult with health professionals without having to go to a physical clinic or healthcare facility. The rise of telemedicine and digital communication tools has provided a more convenient and accessible alternative to in-person visits.
Digital platforms have enabled for public health campaigns to reach global audiences, which helps expand access and reduce cost. Social media platforms such as YouTube and Facebook helps target specific audiences. People who do not have easy access to any healthcare can benefit from these platforms and gain vital information about their health. Through informational posts and targeted ads, health organisations can deliver important health messages to individuals in remote areas, where conventional healthcare outreach methods might be limited or less effective. Aside from that, digital health campaigns also reduce cost as traditional public health campaigns such as in-person events often require lots of financial investment. Digital health campaigns can reach millions of people without requiring additional spending on manpower in the process, making it a highly cost-effective strategy as the costs of developing digital tools are much lower compared to traditional public health campaigns (Koh et al. 2021, p. 173). This just goes to show that digital health campaigns are the new frontier for public health issues.
WHO said WHAT?!
The digital age of rapid access to information has given rise to what is known as an ‘infodemic’. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes ‘infodemic’ as the overwhelming influx of information during an epidemic or disease outbreak, which includes both accurate and inaccurate content circulating across digital and physical environments (Khan 2023). Although the digital age has significantly improved access to vital health information, it has also led to challenges in managing the accuracy of health information.

For example, false information about the Covid-19 pandemic was widely circulated among the public and some would even be promoted by the media or prominent individuals which later allowed conspiracy theories to emerge as well (Zhang et al. 2023). The misinformation and conspiracy theory created false narratives, often fuelled by a mix of fear, mistrust and sensationalism, and contributed to the widespread confusion and resistance to public health measures. Vaccine fear is a predominant public health issue and a similar pattern of misconceptions emerged in response to the introduction of the Covid-19 vaccine and the concerns related to the Covid-19 vaccine reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) included fears about its impact on fertility in women, its potential to alter the human genome and beliefs in a global conspiracy aimed at reducing the world’s population (Caceres et al. 2022).
Take that!
There are several ways to combat misinformation in digital health campaigns. The government and health organizations should educate the public by teaching individuals how to critically examine and evaluate the information they encounter online. They can do so by providing resources on how to recognize misinformation and identify credible source. Besides that, health organizations can also collaborate with trusted celebrities and influencers as they can use their voices and platforms to counter misinformation with clear, scientifically backed messages. Therefore, health organizations should take advantage of this and partner up with trusted voices to avoid the spread of misinformation. Additionally, health professionals could also engage in direct communication with the public and respond to their questions and concerns about any health issues. They should also act quickly and tackle any common misconceptions through digital health campaigns so that the misinformation won’t spread far and wide.
Thoughts

In conclusion, the future of public health campaigns in the digital age holds immense promise, driven by the rapid glorious evolution of digital technologies and the growing reliance on online platforms for information. Digital health campaigns provide opportunities to reach a wider audience and promote health literacy to the public. Although the rise of digital health campaigns can bring about misinformation, I believe that health organizations can mitigate the risks effectively and harness the full potential of digital tools to improve public health.
(784 words)
References
Caceres, M.M.F, Sosa, J.P, Lawrence, J.A, Sestacovschi, C, Tidd-Johnson, A, Ul Rasool, M.H, Gadamidi, V.K, Ozair, S, Pandav, K, Cuevas-Lou, C, Parrish, M, Rodriguez, I & Fernandes, J.P 2022, The Impact of Misinformation on the Covid-19 pandemic, pp.262-277, National Library of Medicine, viewed 28th November 2024,
< https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9114791/ >
Khan, M 2023, How Infodemiology Shapes Public Health in the Digital Age, News Medical, viewed 28th November 2024,
< https://www.news-medical.net/health/How-Infodemiology-Shapes-Public-Health-in-the-Digital-Age.aspx >
Koh, A, Swanepoel, D.W, Ling, A, Ho, B.L, Tan, S.Y & Lim, J 2021, Digital health promotion: promise and peril, Health Promotion International, Volume 36, Issue Supplement 1, pp.170-180, ResearchGate
Krawiec, RJ, McInerney, J, McGuire, K & Malik, N 2021, The future of public health campaigns, Deloitte Insights, viewed 28th November 2024,
< https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/public-sector/successful-digital-public-health-campaigns.html >
Team CSG 2024, The Importance of Healthcare Awareness Campaigns 2024, CSG, viewed 28th November 2024,
<https://wearecsg.com/blog/importance-healthcare-awareness-campaigns/ >
Zhang, J, Pan, Y, Lin, H, Sun, Z, Wu, P & Tu, J 2023, Infodemic: Challenges and solutions in topic discovery and data process, Archives of Public Health, viewed 28th November 2024
0 notes
Text
Public Health in the Digital Era: Envisioning the Future of Online Campaigns
The Shift to Digital Public Health Campaigns
To begin, the shift to digital public health campaigns marks a significant evolution from traditional methods such as TV, radio, and posters to modern digital platforms including social media, mobile apps, and websites. This transition has been driven by the increasing prevalence of social media and online forums, which serve as powerful tools for health promotion, enabling campaigns to reach broader audiences more effectively. Digital technologies enhance the ability to influence perceptions and behaviors, making public health messaging more impactful than ever before (Krawiec, R., McGuire, K., Mclnerney, J., & Malik, N. 2021). As these digital strategies continue to evolve, they present both opportunities and challenges in effectively engaging communities and promoting health (Canada, P. H. A. of. 2024).

Personalization and Targeted Outreach
Digital public health campaigns have evolved significantly from traditional methods like TV, radio, and posters to modern digital platforms, including social media, mobile apps, and websites. This shift reflects the growing prevalence of social media and online forums as essential tools for health promotion, allowing campaigns to reach specific demographics more effectively through algorithm-driven targeting. By utilizing user data, these platforms can tailor messages to individual needs and preferences, enhancing engagement and impact. As a result, digital strategies are becoming increasingly vital in promoting health awareness and influencing public behavior in today's interconnected world.

The Role of Influencers and Advocates
Not to forget, influencers and advocates also play a crucial role in modern public health campaigns by leveraging trusted personalities to effectively spread health messages. Partnerships with influencers can enhance credibility and reach, as these individuals often have established relationships with their audiences. Additionally, encouraging user-generated content allows audiences to share their personal experiences, further amplifying the campaign's reach and impact. By harnessing the power of social media and the voices of influential figures, public health initiatives can foster a sense of community and engagement, ultimately driving greater awareness and action around important health issues.

Combatting Challenges in the Digital Space
Combatting challenges in the digital space is essential for effective public health campaigns, particularly in addressing misinformation, ensuring digital equity, and maintaining privacy. The spread of health-related myths can undermine public trust, making it crucial to provide accurate and accessible information to counteract these false narratives. Additionally, ensuring that campaigns reach underserved populations is vital, as many individuals lack internet access, which can exacerbate health disparities. Efforts to bridge the digital divide, such as investing in internet infrastructure and promoting digital literacy, are necessary to extend connectivity to remote areas and marginalized communities (Kloza, B. 2023). Furthermore, safeguarding user privacy is paramount to maintaining trust; public health organizations must implement robust measures to protect health data shared online, thereby fostering a safe environment for individuals seeking information and support. By addressing these challenges, public health initiatives can enhance their effectiveness and reach a broader audience.

Lessons from Recent Campaign
Recent public health campaigns offer valuable lessons through both successful initiatives and notable failures. For example, campaigns focused on vaccine awareness during COVID-19 and anti-smoking drives provide insights into effective strategies for engaging the public and promoting health behaviors. These successful campaigns often utilized targeted messaging, partnerships with trusted influencers, and digital platforms to reach diverse audiences. However, they also faced challenges, including backlash and misinformation controversies that highlighted areas for improvement. Learning from these experiences, public health organizations can refine their approaches by developing robust strategies for managing negative responses and proactively addressing misinformation. By analyzing both successes and shortcomings, future campaigns can be better equipped to navigate the complexities of public health communication in an increasingly digital landscape.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are paramount in the development of public health campaigns, particularly in balancing marketing strategies with a sense of responsibility. It is essential to avoid overly commercialized approaches that may undermine the seriousness of health messages and exploit vulnerable populations. Additionally, inclusivity is crucial; campaigns must reflect the diversity of the communities they serve and respect cultural sensitivities to ensure that all individuals feel represented and understood. By prioritizing ethical practices, public health initiatives can foster trust and credibility, ultimately enhancing their effectiveness in promoting health and well-being across varied demographics.

Call to Action Plan
To conclude, stakeholders including governments, tech companies, healthcare professionals, and the public are encouraged to collaborate in creating impactful, inclusive, and forward-thinking digital health campaigns. By working together, they can address the evolving challenges and opportunities in public health communication, ensuring that campaigns are effective and resonate with diverse audiences. This collaborative approach will not only enhance the effectiveness of health initiatives but also provide a comprehensive view of how public health campaigns are evolving in the digital age and what the future may hold.
Krawiec, R., McGuire, K., Mclnerney, J., & Malik, N. (2021, August 18). The future of public health campaigns. Deloitte Insights. https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/public-sector/successful-digital-public-health-campaigns.html
Canada, P. H. A. of. (2024, February 14). Defining the role of digital public health in the evolving digital health landscape: policy and practice implications in Canada, HPCDP: Vol 44(2), February 2024. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/reports-publications/health-promotion-chronic-disease-prevention-canada-research-policy-practice/vol-44-no-2-2024/defining-role-digital-public-digital-health-landscape-policy-practice-implications-canada.html
Kloza, B. (2023, February 3). Solutions to the Digital Divide: Moving Toward a More Equitable Future - Connecting the Unconnected. Connecting the Unconnected. https://ctu.ieee.org/blog/2023/02/03/solutions-to-the-digital-divide-moving-toward-a-more-equitable-future/
1 note
·
View note