#LIDAR technology
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Archaeologists believe that around 417 cities, towns, and villages made up the unified civilization.
Remains of architectural forms and patterns, ceramics, sculptural art, architectural patterns, and unifying causeway constructions.
The magnitude of the labor int he construction of massive platforms, palaces, dams, causeways, and pyramids dating to the Middle and Late Preclassic periods, suggests a power to organize thousands of workers.
#history#archeology#archeologicalsite#discovery#ancient#ancient maya#ancient city#ancient civilizations#guatemala#rainforest#lidar technology#radar
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Theories about Legion's "mini headlamps" (N7 special)
A very happy N7 Day to all of you Mass Effect fans!
Although I still haven't finished Mass Effect 3 (I just haven't been able to pick it up again after the Rannoch arc), I nevertheless wanted to do something special for this occasion, and I thought to myself that I might as well devote a quick study to a subject that's been on my mind for quite a long time: the purpose of Legion's three additional "mini headlamps".
You see, aside from the big, obvious flashlight in the middle, Legion also possesses three smaller lights at the side of their head. Ever since discovering these, I've been wondering what exactly those are for. I've observed that they glow red when Legion is under "stress" (an effect which is unfortunately not present in the Legendary Edition) - or rather, in situations that require a lot of processing power - but as far as their practical function goes, I could only guess. However, going through the ME3 dialogues again, I noticed a small detail which could potentially explain what exactly those small lights are - and in addition, give us a little insight into how Geth perceive the world visually.
Disclaimer: Before going into this, I should mention that I have no technical education in robotics, laser scanning, or any related areas of engineering. I based my conclusions solely on what information I could find on the internet, as well as my own reasoning and observations.
[Potential spoilers for ME3]
LADAR/LiDAR scanning and three-dimensional perception
To start off, what basically led me on this track was this comment by Tali in ME3:
Their AI lets them use extremely detailed ladar pings. Xen's countermeasure overwhelmed them with garbage data.
First off, we need to clarify what exactly ladar is. LADAR, more commonly known as LiDAR, stands for "Light amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation detection and ranging" - or, in case of LiDAR, "Light detection and ranging/Light imaging, detection and ranging. It's a method for measuring the distance, speed, and surface structure of objects by the means of laser scanning, usually with beams in the infrared spectrum (there are different wavelengths of light in use, however). Essentially, LiDAR is based on the same principle as the echolocation of bats, the only difference being the use of light instead of sound. Every LiDAR system consists of three integral components: a transmitter, a receiver, and a timer. The transmitter will send out a laser beam, which will be reflected by the object it hits; afterwards, the reflection will be registered by the receiver. Because the speed of light is a known constant, the distance of the object can be deduced by the timer, which will determine the delay between the light impulse being send out and the reflection being captured, also known as "time of flight".
However, because each laser beam only represents the coordinates of a single point, multiple laser beams are necessary to create a detailed 3D map of the environment. Some LiDAR lasers, like those used in automated vehicles, pinwheel to collect data in a 360° radius, generating a 3D image of all objects in the vicinity, including cars, pedestrians, and other obstacles. This results in multiple "points" forming a "point cloud" together, digitally depicting the surroundings on a 3D level. Because each laser emits hundreds of impulses per second, this technology enables you to take highly precise measurements in a very short period of time. LiDAR technology is not only utilized in autonomous driving, but also all kinds of other areas too, like archaeology, topographical mapping, and monitoring of vegetation growth.
Now, with this in mind, my theory is that Legion's small headlamps are the transmitter and receiver components of the LiDAR system - more specifically, I think the transmitters are located on the right, while the singular light on the left is the receiver. However, since we know that normal scanning LiDAR requires multiple laser beams for a detailed 3D image, the question is why Legion would only have two of them implemented. Personally, my suspicion is that the Geth might be using a flash LiDAR: Flash LiDAR is a different type of LiDar emitting a single wide, diverging beam, similar in shape to the beam of a flashlight. By projecting the reflected light onto a sensor array, a flash LiDAR can create a complete 3D environment without the use of multiple impulses. In addition to being very compact, flash LiDAR sensors have no moveable parts, making them extremely resistant to any kind of vibration - an undeniable advantage in all situations that require quick movement, such as combat.
Analysis of atmospheric composition with LiDAR
Still, that doesn't explain why Legion would have an additional transmitter on the right side of their head. We do know, however, that the laser scans with LiDAR are precise enough to not only measure the exact distance between objects, but also analyze the density of particles in the air: Because the molecules in the air cause the light from the laser beam to backscatter, LiDAR is also utilized in monitoring air quality and detecting fine dust, being able to determine traces of atmospheric gases such as ozone, nitrous gases, carbon dioxide, and methane. Depending on the wavelength of light used, the LiDAR system might be more or less precise in measuring molecular backscattering. For that reason, LiDAR systems using multiple wavelengths of light are most efficient in determining the exact size distribution of particles in the air.
With this in mind, let's take a look at Legion's opening line in ME2 upon entering the Heretic station:
Alert. This facility has little air or gravity. Geth require neither.
Going by what I explained above, the reason why Legion was able to tell there is no oxygen in the atmosphere isn't because they have some built-in chemical sensors to analyze the air's components - it's because they can literally "see" the particles in the air.
Thus, I think the second transmitter on the right side of Legion's head might use a different kind of wavelength specifically intended for the detection of atmospheric particles, perhaps in the UV-spectrum (the general rule is that the shorter the wavelength, the higher the resolution of the 3D image is, and since UV has a shorter wavelength than infrared, I imagine it might be used for this purpose). Meanwhile, the big flashlight in the middle might be a photoreceptor, being able to detect "normal" light visible to humans. In addition, the Geth are probably able to see UV-light (since the Quarians are able to see it, it would be logical to assume the Geth are as well), and maybe even infrared and other wavelengths. To summarize the function of all of Legion's headlights, I imagine it works roughly like this:
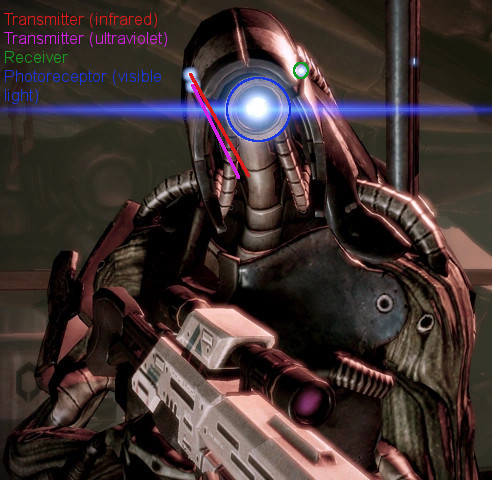

The two lights on the right side of Legion's head (marked with a red and magenta line) might be LiDAR transmitters, using infrared and UV-light, respectively; the single small light on the left (circled with green) might be the LiDAR sensor/receiver, while the big light in the middle (circled with blue) might be a photoreceptor (Source)
The effect of Xen's countermeasure (and potential means to bypass it)
It might be difficult to imagine from a human point of view, but judging from the information that the Geth use LiDAR as their main method of depth perception, Tali describing Xen's invention as a "flash bang grenade" actually makes a lot of sense: If you're normally able to observe your surroundings down to a molecular level, it would probably feel very disorienting if you're suddenly not, not to mention being unable to tell whether an object is far away or close by (which would be absolutely devastating if you suddenly come under attack).
Still, that doesn't mean there are no potential alternatives: Radar, which has been in use longer than LiDAR, is another method to determine the range, angle, and velocity of objects. Due to radar using long-waved micro- and radio waves, the measurements are generally a lot less precise than those with LiDAR; despite this, radar still has its use during inclement weather, when LiDAR systems are very prone to disturbances by dust, mist, and rainfall. Furthermore, LiDAR can only provide measurements up to 200 meters, while radar is more efficient at greater distances. In fact, most modern autonomous driving vehicles work both with LiDAR and radar, in addition to a conventional camera (the only vehicles that don't use LiDAR are those from Tesla, which have a reputation of being unsafe). So, it's only reasonable to assume that the Geth don't rely on LiDAR alone, but use various technologies in combination with it to compensate for each one's weaknesses.
Interestingly, a type of 4D radar is currently in development, intended to be used in autonomous driving. It provides 3D images with a similar resolution as LiDAR, at a potentially much cheaper cost. Still, whether LiDAR or 4D radar is the better choice for autonomous driving is still a heatedly debated question, and only time will tell which of both systems comes out on top. Nevertheless, assuming Xen's "flash bang grenade" only targets the Geth's LiDAR sensors, I wonder if they could've potentially found a way to adapt and bypass it, given enough time.
Anyway, that's the material for a different kind of analysis - for now, I hope you enjoyed this little deep dive into the science behind the Geth. Thank you all for reading and have a nice N7 Day! :-)
#mass effect#mass effect legion#geth#mass effect lore#lore theories#lidar technology#my contribution to N7 Day
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Archaeologists using laser-sensing technology have detected what may be an ancient Mayan city cloaked by jungle in southern Mexico, authorities said Wednesday.
The lost city, dubbed Valeriana by researchers after the name of a nearby lagoon, may have been as densely settled as the better-known pre-Hispanic metropolis of Calakmul, in the south part of the Yucatan peninsula.
What the study, published this week in the journal Antiquity, suggest is that much of the seemingly empty, jungle-clad space between known Maya sites may once have been very heavily populated.
"Previous research has shown that a large part of the present-day state of Campeche is a landscape that was transformed by its ancient inhabitants," said Adriana Velázquez Morlet of Mexico's National Institute of Anthropology and History, a co-author of the report. "Now, this study shows that a little-known region was a urbanized landscape."
Mexico's National Institute said about 6,479 structures have been detected in LiDAR images covering an area of about 47 square miles (122 square kilometers). The technique maps landscapes using thousands of lasers pulses sent from a plane, which can detect variations in topography that ware not evident to the naked eye."
continue reading
#archaeology#mexico#mayans#history#lidar#lidar technology#research#science#discovery#humanity#culture#society#anthropology#aerial survey#jungle#technology#lasers#laser-sensor technology#past#city
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Has anyone else read about the Mayan city that was recently discovered using LIDAR. I first saw it in WIRED & ABC News (the Australian one, though I think the American one will probably also have an article on it).
Anyway here is the link to the original paper, because mainstream media can be pretty bad at interpreting scientific papers. They actually did a good job this time, but you should be in the practice of finding the source journals & bypassing pay walls if you encounter one but can't afford to pay up ("I wanted to read these articles" isn't an excuse landlords accept) rather than just trusting non-science media to not screw up on science reporting.
#mayan ruins#maya#lidar#lidar technology#archaeology#mexico#campeche#valeriana#antiquity journal#it's annoying typing in the url letter by letter on my phone because the source article is on my desktop
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
LiDAR vs. Photogrammetry: Best Survey Tech for Projects

Introduction: For land surveying purposes, selecting between LiDAR and photogrammetry can frequently be a difficult choice for many people in a variety of businesses. Selecting the incorrect aerial survey technique can lead to project failure, expensive delays, and erroneous data. Since each approach has unique benefits and drawbacks, it can be difficult to decide which technology is most appropriate for a given use case. Acquiring accurate data about the surface of the planet from an overhead viewpoint is essential for aerial surveying, a crucial procedure in domains such as environmental science, forestry, urban planning, and mapping. This field is dominated by two key technologies: photogrammetry and light detection and ranging, or LiDAR. Every technique has distinct advantages and disadvantages that make some applications better suited for it than others.
Understanding LiDAR and Photogrammetry Light Detection and Ranging technology is known as LiDAR. It is a technique for remote sensing that measures varying distances to Earth using light in the form of a pulsed laser. These light pulses produce exact, three-dimensional information on the Earth's structure and surface properties when paired with other data captured by the aerial system.
Photogrammetry is the art and science of using photographic images, patterns of electromagnetic radiant imaging, and other phenomena to measure, record, and interpret accurate information about physical things and the surrounding environment.
1. The challenge lies in balancing accuracy and resolution LiDAR: Generates 3D models of the target region with high resolution and great accuracy. It can map ground characteristics accurately, with vertical accuracy as low as 5 cm and horizontal accuracy of roughly 10 cm. It is especially good at piercing foliage.
Photogrammetry: Photogrammetry offers a little less accuracy and resolution than LiDAR. The survey's ambient conditions and camera quality have a substantial impact on accuracy. The typical range for vertical accuracy is 15–30 cm, and the range for horizontal accuracy is 20–40 cm.
2. Issues revolving around cost-effectiveness and the availability of suitable equipment
LiDAR: Typically more costly because of the advanced gear and technology needed. Compared to photogrammetry, a LiDAR system may require a much larger initial setup.
Photogrammetry: More economical, particularly for simpler or smaller-scale tasks. It can be carried out with less expensive equipment and standard cameras installed on drones or airplanes.
3. Challenges related to time optimization
LiDAR: LiDAR is highly effective at quickly covering large areas, particularly in regions with dense vegetation, as it can penetrate canopy cover and deliver accurate ground data.
Photogrammetry: Surveying time varies based on the project's size and the level of detail needed in the images. It can be slower than LiDAR, especially in areas with complex topographies or dense vegetation. Read our blog for more details: https://www.gsourcedata.com/blog/lidar-vs-photogrammetry
#gsourcetechnologies#architecturedesign#engineeringdesign#lidarservices#photogrammetry#photogrammetryservices#engineeringservices#lidar technology#land survey
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
LiDAR Data: A Guide to Annotation and AI Integration
This article covers an introduction to LiDAR technology, the essentials of LiDAR data annotation, an overview of LiDAR data collection to its applications in AI models. Read to know how Cogito Tech can help with LiDAR data annotation.
0 notes
Text
#architecture#laser scanning#3d laser scanning#Lidar technology#cultural heritage#building information modeling
0 notes
Text
In the rapidly evolving fields of geospatial analysis, autonomous systems, and urban planning, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology has emerged as a groundbreaking tool. Known for its precision and efficiency, LiDAR is transforming the way we create 3D maps and models. For our UK audience, understanding the role of LiDAR in these advancements can unlock opportunities in industries such as construction, transportation, and environmental management. Let’s explore how this technology works and why it is indispensable in modern mapping and modeling.
0 notes
Text
Why Atom Aviation is the Leading LiDAR Survey Company in India

In today’s fast-paced world, the demand for precise and reliable data is growing across various industries. One of the most advanced technologies transforming survey work is LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging). When it comes to LiDAR survey services in India, Atom Aviation stands out as a top choice.
What is LiDAR Surveying?
LiDAR is a cutting-edge technology that uses laser light to measure distances and create high-precision, 3D representations of landscapes, structures, and other objects. The accuracy of LiDAR makes it a crucial tool in industries such as construction, agriculture, forestry, and urban planning.
Why Choose Atom Aviation for LiDAR Surveying?
Atom Aviation, a renowned LiDAR survey company in India, has established a solid reputation for offering top-notch surveying services. Here are a few reasons why Atom Aviation is the preferred choice for businesses seeking reliable LiDAR surveys:
1. Expertise and Experience
Atom Aviation has years of experience in delivering precise and comprehensive LiDAR data. Their team of skilled professionals is well-versed in using advanced drone technology, ensuring that surveys are completed efficiently and accurately. Whether it’s large-scale topographic mapping or detailed infrastructure analysis, Atom Aviation is equipped to handle it all.
2. State-of-the-Art Technology
As a leader in the field, Atom Aviation leverages the latest drone-based LiDAR systems that capture data quickly and accurately. These high-tech systems can cover vast areas and provide detailed topographic information, which is essential for making well-informed decisions in a wide range of industries.
3. Cost-Effective Solutions
Atom Aviation not only offers high-quality LiDAR surveys but also ensures that their services are budget-friendly. By using drones for LiDAR surveys, they reduce the need for costly manual data collection methods, ultimately saving businesses time and money.
4. Quick Turnaround Time
One of the major benefits of using drone-based LiDAR is the speed at which data can be collected and processed. Atom Aviation guarantees a fast turnaround time without compromising on the quality of the results. This makes it an excellent option for businesses that need survey results promptly.
5. Wide Range of Applications
Whether you’re in the construction industry, need forest mapping, or are working on a land development project, Atom Aviation provides LiDAR surveying solutions tailored to your specific needs. The versatility of their services ensures that businesses across various sectors can benefit from accurate, actionable data.
Industries Benefiting from LiDAR Surveying
Construction: LiDAR data helps with precise mapping and 3D modeling, aiding in construction planning and project management.
Agriculture: LiDAR surveys can assist in crop monitoring, soil health analysis, and irrigation planning.
Forestry: LiDAR can create detailed maps of forests, identifying tree heights, density, and canopy coverage.
Urban Planning: Cities can utilize LiDAR data for infrastructure mapping, flood risk assessments, and urban development projects.
Why LiDAR Surveys are Essential
Traditional surveying methods often require manual labor and long hours, making them less efficient and more prone to errors. LiDAR technology, however, provides highly accurate and reliable data while reducing the time and cost involved. By choosing a LiDAR survey company in India like Atom Aviation, businesses can enjoy faster, more precise results that are essential for the success of any project.
Conclusion
In a world where precision and efficiency are crucial, Atom Aviation remains one of the most trusted names in LiDAR surveying in India. Their innovative approach, advanced technology, and commitment to delivering high-quality results make them the go-to company for businesses seeking reliable LiDAR survey solutions.
If you are looking to take your project to the next level, don’t hesitate to contact Atom Aviation today and explore how their LiDAR surveying services can help you achieve accurate, actionable insights.
#LiDAR Surveying#LiDAR Mapping#Geospatial Solutions#Accurate Mapping#LiDAR Technology#Surveying Services India#LiDAR Data Acquisition#3D Mapping India#LiDAR Survey Company#Top LiDAR Companies India#Precision Mapping#LiDAR for Surveying#Geospatial Data Services#Mapping Solutions India#LiDAR Experts
1 note
·
View note
Text
In the rainforests of Guatemala were more than 900 habitations including at least 4 large cities and thousands of yards of raised causeways connecting them.
650 square miles across northern Guatemala’s Mirador-Calakmul Karst Basin (MCKB) revealed 30 of the famous ball courts of the Ancient Mesoamerican team sport, 195 cement reservoirs which literally drained nearby lakes dry, and 110 miles of elevated walkways connecting 417 villages.
Found in a (LiDAR) survey, which uses lasers to give centimeter-accuracy of the terrain features below a forest canopy, effectively allowing archaeologists to do what used to take decades of expensive excavations with a few fly overs in a plane.
4 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
LiDAR data import into Google Earth. Hidden historic ruins discovery!
0 notes
Text
Restoring the Past with Future Tech: Scan to BIM for Historic Structures

Historic buildings are pieces of our shared history. They hold stories, art, and craftsmanship that deserve to be preserved for future generations. But restoring them can be a real challenge. It is generally beyond repairing defective parts, it is about retaining the original beauty as well as the integrity of the building. That is where Scan to BIM comes in. This clever technology defines identifying existing structures using a fusion of laser scanning and 3D modeling to recreate them accurately and safely.
Here’s a closer look at how Scan to BIM is making historic restoration easier and better.
What is Scan to BIM?
Think of Scan to BIM as a high-tech way to "copy and paste" a building into the digital world. Advanced tools like laser scanners and LiDAR technology scan every angle of the structural surface recording all signified details-from cracks on the wall to strokes of intricate carvings. This scan creates a 3D digital model, called a Building Information Model (BIM).
For example, observing the building's design and condition in almost physical proximity without actually touching it is exactly what it means for a lot of historical buildings. It's almost like viewing the building in a virtual way, with which you can study, analyze, and restore.
Why Use Scan to BIM for Historic Structures?
Restoring Historic Buildings isn't like repairing modern ones-these old buildings were made from materials that have become rare today, techniques very few people have mastered, and in some cases, quite fragile because they were built over an intricate set of details. Scan to BIM solves this problem in many ways:
Capturing Details: Laser scanning picks up even the tiniest features in designs, assuring nothing is lost in the restore.
Accuracy Matters: The digital models are precise, so restoration work stays true to the original design.
Protecting Fragile Structures: Everything here is scanned in digital form, which means no disturbance of the building. This prevents accidental damage.
Keeping a Record: The 3D model also acts as a digital archive, preserving the building’s current condition for future use.
How Does Scan to BIM Work?
Here’s a quick breakdown of the process:
Scanning the Building: The first step is to scan the building using tools like LiDAR technology or laser scanners. These devices measure everything down to the tiniest detail, creating what’s called a point cloud (essentially a massive map of all surfaces that make up the building).
Processing the Data: The scan data is processed to create a clear, accurate digital 3D model.
Building the Model: This data is then used to make a full 3D BIM model, which includes not just the structure but also elements like plumbing, wiring, and ventilation if necessary.
Planning Restoration Work: Ultimately, that's a model that architects and engineers would use to find problems, plan repairs, and test ideas even before touching the building.
What Makes Scan to BIM So Useful?
Here’s why this method is changing the game for historic restoration:
Precision: Everything is accounted for, so nothing will potentially be overlooked.
Time-Saving: Traditional restoration takes a lot of manual measuring and guesswork. Scan to BIM speeds things up by providing accurate data right from the start.
Cost-Effective: By making fewer mistakes and planning faster, one can keep the costs of restoration under control.
Preservation First: By working with digital models, experts can protect the original structure from unnecessary wear and tear.
Where is Scan to BIM Used?
This technology is being used in all kinds of restoration projects, including:
Historic Monuments: Iconic landmarks are being digitally preserved and restored, ensuring their longevity.
Heritage Buildings: Centuries-old places like castles, libraries, and churches are being brought back to life.
Ancient Artwork: Detailed carvings, sculptures, and other decorative features can be captured and restored with precision.
Old Infrastructure Updates: Buildings can be modernized to meet today’s safety standards while keeping their original charm.
How Laser Scanning and LiDAR Technology Make a Difference
At the heart of Scan to BIM is the tech - laser scanning and LiDAR. These tools send out tiny light pulses that measure distances and shapes, creating a highly detailed digital copy of a structure. Such technology comes in handy while restoration of delicate and complicated structures requires a lot of care.
Examples of Successful Historic Restorations
Here are some ways Scan to BIM has been used to bring historic buildings back to life:
Cathedrals and Churches: Intricate stained glass windows and delicate arches are restored with stunning accuracy.
Forts and Palaces: Massive, centuries-old buildings are scanned and modeled to uncover damage and plan precise repairs.
Libraries and Museums: Fragile bookshelves and exhibits are preserved digitally, reducing the risk of harm during restoration.
Why Work with Experts?
Restoring historic buildings takes skill, the right tools, and experience. That is why working with experts like SmartCADD is a smart choice. They handle everything, from scanning the structure to delivering the final 3D model and have the expertise needed to make your project successful.
Preserving the Past with SmartCADD
SmartCADD is a company that specializes in Scan to BIM services meant especially for the restoration of historic buildings. We have helped restore countless buildings with unmatched precision and care. Whether it’s capturing the finest details or solving complex structural problems, our team has the knowledge and tools to get it done right.
Final Thoughts
Restoring historic buildings doesn’t have to be complicated. Thanks to Scan to BIM, it’s easier than ever to bring these treasures back to life. From capturing every detail to planning the restoration, this technology makes the process faster, safer, and more accurate. If you’re working on a historic building or just want to learn more, reach out to SmartCADD. They’re here to help you keep the past alive for future generations.
#Scan to BIM#Laser Scanning#LiDAR Technology#3D BIM Modeling#Restoring Historic Structures#Building Information Model
0 notes
Text
#lidar#lidar technology#lidar ld06 module#innovation#iot#technology#raspberry pi#time of flight technology#tof#Autonomous Vehicles#robotics#drone mapping#industrial automation#360 degree scanning#iot applications#projects#agriculture drone#agriculture products
0 notes
Text

How Does LiDAR Technology Work In Drones?
LiDAR is one of the coolest tech advancements out there, especially when mounted on drones. But how exactly does it work? Let’s break it down!
What Is LiDAR?
LiDAR stands for "Light Detection and Ranging." It uses lasers to measure distances. Picture a drone shooting rapid laser pulses at the ground and then measuring how long it takes for the light to bounce back. By doing this, it creates super detailed 3D maps of the area below.
How Drones Use LiDAR
When drones are equipped with LiDAR, they’re like flying 3D scanners. As the drone flies over a landscape, the LiDAR system sends out thousands of laser pulses per second. These pulses hit objects (like trees, buildings, or the ground) and bounce back to the drone. The drone records how long it takes for each pulse to return. This timing tells the drone how far away the object is.
The result? A highly accurate 3D map. This tech is awesome for things like surveying land, forestry, and construction sites. It can even “see” through tree canopies to map the ground below!
Why Use LiDAR On Drones?
LiDAR is faster and more accurate than traditional methods like photogrammetry. It’s perfect for large areas where detail matters. Plus, drones can fly low and slow, gathering data from tough-to-reach places. Whether you're mapping a forest, a city, or a construction zone, LiDAR-equipped drones get the job done faster and better.
Best LiDAR For Your Drone
Looking for the best LiDAR for your Matrice 300 RTK or Matrice 350 RTK? Check out the DJI ZENMUSE L2 – LIDAR from Mavdrones. It’s top-notch for precision mapping and surveying, offering unbeatable accuracy and range. You'll love how it levels up your drone’s capabilities!
0 notes