#Ibd Nutrition Therapy
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Easy-to-Follow Ulcerative Colitis Diet Plans: Recipes and Tips for a Healthy Gut
Unveils the intricacies of Proper dietary Plan For Ulcerative Colitis
Starting the process of making an easy-to-follow and a proper diet plan for Ulcerative Colitis is like carving health; each recipe is like a brushstroke that helps grow a healthy gut.
This blog unveils the intricacies of dietary recommendations for Ulcerative Colitis, offering a palette of recipes and tips that form a symphony of nourishment.
Picture this as a culinary canvas, where each dish harmonizes with the needs of individuals seeking a healthy gut amidst the challenges of Ulcerative Colitis.
Navigating the Culinary Maze: The Essence of Ulcerative Colitis Diet Plans
Navigating the culinary maze of Ulcerative Colitis diet plans involves recognizing the burstiness of dietary recommendations for this condition. Each individual's journey is unique, and the culinary landscape must be as diverse as the people it caters to.
Envision dietary recommendations for Ulcerative Colitis as a compass, guiding individuals through the maze of food choices towards a destination of gut health.
Consider this as a journey of discovery, where easy-to-follow Ulcerative Colitis diet plans are not rigid prescriptions but adaptable roadmaps. The burstiness is in the recognition that crafting a healthy gut involves flexibility, customization, and an understanding that there is no one-size-fits-all approach.
It's not about restrictions but about cultivating a culinary landscape that fosters wellness, with dietary recommendations for Ulcerative Colitis evolving as the compass points towards nourishment and digestive harmony.
Diet Plans for Ulcerative Colitis: Nutrient-Rich Recipes from Harvesting Healing
The foundation of Ulcerative Colitis diet regimens is nutrient-dense recipes that promote healing. Consider this segment to be a verdant garden, wherein every component has been meticulously selected to support the digestive system rather than pose a challenge.
The epitome of success lies in the understanding that straightforward recipes for Ulcerative Colitis involve embracing the abundance of sustenance that nature provides, as opposed to simply avoiding certain foods.
Consider nutrient-rich recipes as the seeds of healing, planted in the soil of a well-balanced Ulcerative Colitis diet plan. The burst of variety involves incorporating a spectrum of colorful fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, each contributing to the flourishing garden of gut health. It's the acknowledgment that healing is not only about avoiding triggers but about actively cultivating a nutritional haven that promotes overall well-being.
Culinary Alchemy: Transformative Cooking Tips for Ulcerative Colitis Diet Plans
The culinary alchemy of transformative cooking tips is an essential element in the crafting of Ulcerative Colitis diet plans. Picture this as a chef's masterclass, where the burstiness lies in the transformative power of culinary techniques that make dishes not only delicious but also gut-friendly.
The burst of creativity here involves reimagining cooking methods, ingredient combinations, and meal structures to enhance digestibility without compromising flavor.
Consider this as the art of culinary adaptation, where easy-to-follow Ulcerative Colitis diet plans become a canvas for transformative cooking tips. The burstiness is in discovering alternative seasoning options, experimenting with gentle cooking methods, and finding innovative ways to add depth and richness to dishes.
It is recognition that the objective of culinary alchemy is not to impose constraints, but rather to broaden the range of potentialities in order to craft gastronomic pleasures that cater to the distinct requirements of those who are managing Ulcerative Colitis.
A Conscious Approach to Ulcerative Colitis Diet Plans Based on Mindful Eating
A guiding philosophy known as mindful eating is increasingly being incorporated into Ulcerative Colitis diet regimens. Consider this an instance of introspection in which people engage in a mindful experience of their physical selves, relishing every bite while being cognizant of its impact on their overall state of health.
Consider mindful eating as a therapeutic practice, fostering a deep appreciation for the flavors, textures, and nutritional value of each meal. The burst of mindfulness involves being attuned to the body's signals, recognizing hunger and satiety cues, and cultivating a positive and stress-free environment during meals.
It's the acknowledgment that easy-to-follow Ulcerative Colitis diet plans are not just about what is on the plate but about the entire experience of nourishing the body and the mind.
Navigating Challenges: Adapting Ulcerative Colitis Diet Plans to Individual Needs
Navigating the challenges of Ulcerative Colitis involves recognizing adjusting diet plans based on the uniqueness of individual experiences. This section unfolds like a personalized journey, exploring how easy-to-follow diet plans for Ulcerative Colitis can be adapted to meet the unique needs of each person.
Consider this as the evolution of Ulcerative Colitis diet plans, with dietary recommendations being fluid and responsive to individual responses. The burst of adaptability involves ongoing communication with healthcare professionals, staying attuned to the body's signals, and being open to adjusting the culinary compass as needed.
It's the acknowledgment that the journey towards a healthy gut is not a linear path but a dynamic process that evolves with each individual's unique challenges and triumphs.
Conclusion
Ultimately, creating simple Ulcerative Colitis meal plans involves a deep understanding of each person's unique path to improving their gut health. From navigating the culinary maze to harvesting healing through nutrient-rich recipes and embracing transformative cooking tips, the essence lies in fostering a positive relationship with food.
As individuals embark on this gastronomic journey, may the compass of Ulcerative Colitis diet plans guide them towards a landscape of nourishment, mindfulness, and digestive harmony.

0 notes
Text
Understanding the Long-Term Effects of Ulcerative Colitis
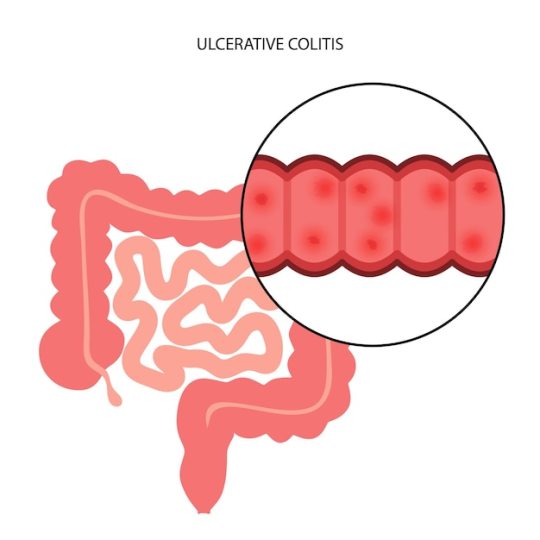
A chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that affects the colon (large intestine) and the rectum is called ulcerative colitis (UC). Many individuals get treatment to deal with their side effects, this medical condition can have lasting effects that affects many pieces of a person's life. The long term effects of the condition will be discussed in this article, with possible risk and the management techniques.
Effects of Chronic Inflammation
Inflammation over time in the colon causes long-term damage, which is one of the main concerns related to ulcerative colitis.
Risk of Colorectal Cancer: People who experienced UC for longer than 8 to 10 years are more likely to develop colorectal cancer due to ongoing inflammation of the colon.
Tissue Scarring: Prolonged inflammation can result in colon tissue scarring, which can lead to problems like strictures (colon constriction) and restrictive symptoms.
Severe Flare-ups: As UC progresses, a person's colon may enlarge rapidly and more frequently. This can result in challenges including toxic megacolon, a potentially fatal illness.
Effects on the Digestive Systems
Ulcerative colitis can cause major, long lasting changes to the digestive system.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Iron, calcium, and a lack of vitamin D can result from impaired nutrient caused by steady irritation and recurrent diarrhea.
Dehydration: UC patients frequently struggle with dehydration, especially during flare-ups, which can be set on by tireless diarrhea.
Changes in Bowel Function: Many UC patients could require a medical surgery to remove all or a part of their colon, which will modify their capacity to pass stool. The body's ability to control the digestion of water and supplements might be affected by this.
Systemic Health Improvement
Ulcerative colitis doesn't just affect the colon; it can also affect different regions of the body.
Joint pain (Joint Irritation): A great deal of people with UC experience joint inflammation, which brings side effects like joint inflammation.
Skin Conditions: UC can lead to skin issues like difficult red bumps known as erythema nodosum and ulcerative skin lesions called pyoderma gangrenosum.
Inflammation of the eye, like in uveitis and episcleritis, is more common in patients with ulcerative colitis.
Impact on the Brain and Heart
A constant sickness, for example, UC can negatively affect one's mental health.
Stress and Tension: Dealing with a condition with painful and unpleasant side effects that is unstable brings higher pressure and nervousness.
Depression: There is a higher possibility of creating depression because of the chronic nature of ulcerative colitis (UC) as well as expected limitations on everyday activity and interaction with others.
Body Image Issues: Certain people may have issues with their body image because of weight loss, actual look of their condition, or medical surgery, (for example, a colectomy or the requirement for a stoma).
Perspectives Affecting Quality of Life
An individual's personal satisfaction can be affected by UC in various areas of day to day existence.
Physical Restrictions: Exhaustion, continuous bowel movements, and pain during eruptions can cause limitations on actual work and create some issues for social or professional commitments.
Dietary Limitations: To control their side effects, many people with UC should stick to diets that reject explicit things that could cause eruptions.
Surgical Results: A colonoscopy, or the expulsion of the colon, might be important for specific UC patients at some point. This procedure can change a patient's bowel designs and require long lasting modifications.
Extended-Term Care and Therapy
Ulcerative colitis cannot be cured, long-term care can greatly enhance results.
Medication: Immunosuppressants, biologics, and anti-inflammatory meds are habitually used to reduce inflammation and treat side effects for an extended timeframe.
Continuous Monitoring: To follow the course of the condition and identify any possible issues, like colorectal disease, from the beginning, patients should have routine colonoscopies and other diagnostic testing.
Way of life Changes: Reducing pressure, eating a balanced diet, practising habitually, and stopping smoking are great ways of working on the side effects of ulcerative colitis (UC) and reducing its eruptions.
Don't forget to read our next article on''Ulcerative Colitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Key Factors."
There is something else to ulcerative colitis besides eruptions and side effect the board; it is a persistent sickness. Dr Nisarg patel best gastroenterologist in sids hospital surat, will give you the best advice and cure for your IBD issue. Patients and medical care experts can make better designs for decreasing complexities, upgrading personal satisfaction, and deflecting risks by having a better understanding of the disease's drawn out effects. Living with ulcerative colitis can be figured out how to consider a satisfying existence with the right care, checking, and lifestyle changes.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
From Burps to Bloating: Decoding Your Child’s Digestive Symptoms
Understanding and managing children’s digestive health is a vital yet often overlooked aspect of pediatrics. As parents and caregivers, it’s natural to worry about the meaning behind common digestive issues like burping, bloating, or abdominal discomfort. This blog explores the underlying causes of these symptoms, when to seek medical help, and how conferences like the 15th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference can be instrumental in improving digestive care for children.

Why Pediatric Digestive Health Matters
Digestive health in children is a delicate balance influenced by diet, growth, and overall health. Common symptoms like gas, bloating, and abdominal pain can sometimes signal minor issues, but in other cases, they may indicate serious conditions such as:
Food intolerances or allergies
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Constipation or Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Understanding these symptoms and their implications is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Breaking Down the Symptoms
Burping: Often caused by swallowing air during meals or carbonated drinks, but persistent burping could point to GERD or indigestion.
Bloating: A common symptom due to gas buildup, but chronic bloating might suggest food intolerances, such as lactose or gluten intolerance.
Abdominal Pain: Can range from mild discomfort to severe cramping, potentially linked to conditions like IBS or appendicitis.
How Conferences Advance Knowledge in Pediatric Digestive Health
The 15th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference is a platform for discussing cutting-edge research, clinical insights, and emerging therapies in pediatric gastroenterology. Experts from across the globe share knowledge and collaborate to address challenges in managing digestive health issues in children.
Key sessions related to pediatric digestive health include:
Nutritional management in childhood digestive disorders
Advances in diagnosing pediatric IBD
Novel therapies for GERD in children
The gut microbiome and its impact on early-life health

Submit Your Abstract: Make a Difference
Do you have innovative research or clinical insights on pediatric digestive health? Share your expertise at the 15th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference. Abstract submissions are open, offering you the opportunity to contribute to this essential discussion.
Submit your abstract here: https://gastroenterology.utilitarianconferences.com/submit-abstract
Register Today: Join the Global Dialogue
Be a part of this transformative event. Register now to network with leading experts, participate in engaging sessions, and expand your understanding of pediatric digestive health.
Register here: https://gastroenterology.utilitarianconferences.com/registration
Explore More
Discover the full conference agenda, featured speakers, and event updates. Visit the home page: https://gastroenterology.utilitarianconferences.com/
Pediatric gastroenterology, digestive symptoms in children, IBD in children, GERD management, childhood nutrition, gut microbiome research, #ChildHealthMatters, #PediatricGI, #DigestiveHealth2025, #GastroenterologyConference, #GutHealthKids, #IBDResearch, #GERDSolutions, #HealthyDigestion
Empowering Better Digestive Health for Children
From burps to bloating, decoding your child’s digestive symptoms can lead to better health outcomes. Join the 15th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference to stay ahead in pediatric digestive care and connect with professionals dedicated to improving children’s health.
Let’s work together to advance pediatric gastroenterology and ensure every child receives the care they deserve!
0 notes
Text
Inflammatory bowel disease treatment
Kalyani Hospital, located in Gurgaon, Haryana, offers comprehensive treatment options for individuals suffering from Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Their multidisciplinary team of experienced gastroenterologists collaborates to provide personalized care aimed at reducing inflammation, managing symptoms, and enhancing patients' overall gastrointestinal health.
Understanding Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD):
IBD encompasses chronic inflammatory conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, primarily Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, fatigue, and weight loss. Effective management is crucial to improve quality of life and prevent complications.
Treatment Approaches at Kalyani Hospital:
Kalyani Hospital employs a range of treatment strategies tailored to the severity and specific needs of each patient:
Medication Therapy: Utilizing anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and biologic therapies to control inflammation and modulate the immune response.
Dietary Modifications: Implementing personalized nutrition plans to alleviate symptoms and promote digestive health.
Lifestyle Changes: Encouraging stress management techniques and regular exercise to support overall well-being.
Surgical Interventions: In cases where medical management is insufficient, surgical options are considered to remove damaged portions of the gastrointestinal tract.
The hospital emphasizes patient education and support throughout the treatment process, ensuring individuals are well-informed and actively involved in their care.
Expert Care Team:
Kalyani Hospital's gastroenterology department is staffed by skilled professionals dedicated to providing high-quality care. Their expertise ensures that patients receive the most effective and up-to-date treatments available.
Contact Information:
For more details or to schedule a consultation, you can reach Kalyani Hospital at:
Phone: +91-124-4666999
Email: [email protected]
Address: Opp. Govt Girls College, Anamika Enclave, MG Road, Near Sec-14, Gurgaon, Haryana – 122001
For additional information, visit their official website:
Kalyani Hospital
If you or a loved one is dealing with IBD, Kalyani Hospital's comprehensive and compassionate approach may provide the relief and support needed to manage this condition effectively.

0 notes
Text
15th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference

Submit Your Abstract on Gastroenterology: Shape the Future of Digestive Health
Are you a researcher, clinician, or healthcare professional specializing in gastroenterology? This is your opportunity to contribute to the evolving field of digestive health by sharing your groundbreaking work. Utilitarian Conferences is proud to host the 15th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference, a platform for exchanging knowledge, fostering collaboration, and sparking innovation in gastroenterology. Submit your abstract today at https://gastroenterology.utilitarianconferences.com/submit-abstra.
Why Submit Your Abstract?
The field of gastroenterology is dynamic, addressing critical challenges such as digestive diseases, liver disorders, and gut microbiota. By presenting your research, you can:
Showcase Your Expertise: Gain recognition for your work and receive valuable feedback from leading experts in the field.
Build Collaborative Networks: Connect with peers, mentors, and industry leaders to expand your professional network.
Advance Patient Care: Share insights and innovations that have the potential to improve diagnostic tools, treatment modalities, and overall patient outcomes.
Enhance Your Career: Publishing and presenting your research at a prestigious conference can open doors to career advancement opportunities, including collaborations, funding, and academic growth.
Topics of Interest
We welcome abstracts covering a wide range of topics, including but not limited to:
Advances in endoscopic techniques
Hepatology and liver transplantation
Gastrointestinal oncology
Gut microbiome research
Inflammatory bowel diseases
Pediatric gastroenterology
Nutrition and digestive health
Emerging therapies and technologies
Artificial intelligence and digital tools in gastroenterology
Public health and preventive strategies for digestive diseases
If your research addresses an area that can shape the future of gastroenterology, we want to hear from you.
Submission Guidelines
Submitting your abstract is simple and efficient. Follow these steps:
Visit https://gastroenterology.utilitarianconferences.com/submit-abstra.
Prepare your abstract, ensuring it includes the title, background, methods, results, and conclusion.
Adhere to the word limit and formatting guidelines provided on the submission page.
Submit your abstract before the deadline to ensure consideration.
Make sure your abstract reflects the novelty, relevance, and potential impact of your work. Submissions will be reviewed by an expert panel, ensuring a high standard of quality and scientific rigor.
Key Dates
Abstract Submission Deadline: [Insert Date Here]
Notification of Acceptance: [Insert Date Here]
Conference Dates: [Insert Date Here]
Join the Global Conversation
Gastroenterology is at the forefront of medical science, addressing complex health challenges with innovative solutions. By submitting your abstract, you join a global conversation that drives progress and improves lives. Whether you’re presenting pioneering research or novel case studies, your voice is vital.
Participation in the conference not only enhances your professional visibility but also provides access to cutting-edge knowledge and a platform to discuss ideas that can transform the landscape of digestive health. You’ll have the chance to engage in thought-provoking discussions, attend workshops, and network with experts from around the globe.
Conclusion
The 15th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference is more than just an event—it’s a milestone in the journey of innovation and collaboration in digestive health. By submitting your abstract, you can help shape the future of gastroenterology, address critical health challenges, and create meaningful change in the field. Don’t wait—take this opportunity to make your mark in the global medical community.
For more details and to submit your abstract, visit https://gastroenterology.utilitarianconferences.com/submit-abstra. Let’s innovate together! visit the website here: https://gastroenterology.utilitarianconferences.com/
0 notes
Text
Best Clinic For Gut Health in Chennai
In the bustling city of Chennai, where modern lifestyles often take a toll on health, The ARC Gut Clinic stands as a sanctuary for those seeking comprehensive and expert care for gut-related concerns. Recognized as the best clinic for gut health in Chennai, The ARC Gut Clinic offers a holistic approach to diagnosing, treating, and managing digestive disorders. With its state-of-the-art facilities, a team of renowned specialists, and a patient-centric philosophy, the clinic has become a trusted name for individuals striving to achieve optimal gut health.
Why Gut Health Matters
Gut health plays a pivotal role in overall well-being, impacting everything from digestion and immunity to mental health. An imbalance in the gut can lead to a myriad of issues such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), acid reflux, food intolerances, and even chronic conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The ARC Gut Clinic understands the intricate connection between the gut and the rest of the body, providing solutions that address not only the symptoms but also the root causes of these conditions.
Comprehensive Services at The ARC Gut Clinic
The ARC Gut Clinic is renowned for its wide range of services, catering to various digestive health needs. Some of the key services include:
Advanced Diagnostics: Utilizing cutting-edge technologies such as endoscopy, colonoscopy, and non-invasive breath tests to identify issues with precision.
Personalized Treatment Plans: Tailored strategies based on thorough assessments and individual health profiles.
Nutritional Guidance: Expert dietitians design customized meal plans to support digestive health and promote healing.
Probiotic and Microbiome Therapy: Restoring gut flora balance through scientifically backed probiotic interventions.
Minimally Invasive Procedures: Ensuring patient comfort while achieving accurate diagnoses and effective treatments.
A Team of Experts
The clinic’s success is attributed to its team of highly skilled gastroenterologists, nutritionists, and allied health professionals. These specialists bring a wealth of experience and are dedicated to providing compassionate and effective care. From routine consultations to complex procedures, the team ensures that every patient’s journey toward gut health is seamless and reassuring.
State-of-the-Art Facilities
The ARC Gut Clinic is equipped with the latest medical technology to offer world-class care. Its advanced diagnostic tools and therapeutic equipment set a benchmark in gastroenterological services. Patients benefit from a modern, hygienic, and comfortable environment that prioritizes their safety and well-being.
Holistic and Preventive Care
Understanding that gut health is influenced by lifestyle, diet, and stress, the clinic emphasizes preventive measures. Regular screenings, lifestyle coaching, and stress management programs are integral to their approach. Patients are educated about maintaining a healthy gut through proper nutrition, adequate hydration, and mindful living.
Focused on Patient Education
Empowering patients is a cornerstone of The ARC Gut Clinic’s philosophy. Through detailed consultations and informational resources, patients gain a clear understanding of their conditions and the steps needed for recovery. This transparency fosters trust and collaboration between patients and their care providers.
Testimonials from Satisfied Patients
The clinic’s impact is best illustrated through the words of its patients:
"After years of struggling with acid reflux, The ARC Gut Clinic provided me with a diagnosis and treatment plan that truly worked. Their personalized care made all the difference." – Kavitha R.
"The diet plan and probiotic therapy recommended by the clinic transformed my gut health. I feel healthier and more energetic than ever." – Sanjay T.
"The team’s professionalism and compassion are unparalleled. I finally feel understood and cared for." – Anjali M.
Convenient Location and Accessibility
Situated in a prime area of Chennai, The ARC Gut Clinic is easily accessible to residents across the city. The clinic’s thoughtful design ensures a pleasant experience for patients, with ample parking and a welcoming ambiance.
Commitment to Excellence
The ARC Gut Clinic’s dedication to excellence extends beyond clinical care. By staying abreast of the latest advancements in gastroenterology and continuously refining their services, the clinic ensures that patients receive the best possible outcomes. This commitment to innovation and quality has solidified its reputation as the premier destination for gut health in Chennai.
Conclusion
The ARC Gut Clinic stands as a beacon of hope for individuals grappling with digestive health challenges. Its patient-focused approach, advanced facilities, and commitment to excellence make it the ideal choice for anyone seeking expert gut health care. Whether addressing chronic conditions, offering preventive guidance, or educating patients on lifestyle adjustments, the clinic remains dedicated to enhancing the quality of life for its patients. By choosing The ARC Gut Clinic, you’re not just addressing a health issue—you’re investing in a healthier, more vibrant future. For more details visit https://thearcgut.clinic/
0 notes
Text
Reasons Your Cat Is Always Hungry
Cats normally eat small amounts of food throughout the day. However, some cats are never satisfied with the quantity of food you give them, they polish off their share and then they demand more. If your cat is always hungry, it can signify a problem. The condition is called polyphagia and it should be checked out by a veterinarian.
10 reasons your cat is always hungry
Boredom
Insufficient Food
Worms
Rapid Growth
Diabetes
Hyperthyroidism
Nutritional Deficiency
Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI)
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Side Effect of Medications
Learning about the 10 reasons your cat is always hungry:

1. Boredom
Cats, like humans, can eat out of boredom. When a cat has little to engage with, they might turn to food as a form of entertainment or comfort. This behaviour is more common in indoor cats who lack stimulation from their environment.
A cat that eats out of boredom might be constantly begging for food or searching for snacks, even after a full meal. To address this, ensure your cat has plenty of toys, scratching posts, and interactive activities to keep them mentally and physically stimulated.
2. Insufficient Food
Sometimes, your cat’s constant hunger is simply because they aren’t getting enough food. Cats have specific dietary needs, and if their meals are too small or lack essential nutrients, they may feel hungry all the time.
Ensure that your cat’s diet includes the right balance of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. It’s also important to feed them high-quality cat food designed to meet their nutritional requirements.
3. Worms
Parasites like worms can be a significant cause of increased hunger in cats. Intestinal worms, particularly tapeworms, feed off the nutrients in your cat’s diet, leaving them malnourished and hungry, no matter how much they eat.
If your cat has a voracious appetite along with symptoms like weight loss, vomiting, or a dull coat, it could be a sign of a parasitic infection. Regular deworming treatments and vet check-ups are essential to keep your cat healthy and free from parasites.
4. Rapid Growth
Kittens and young cats are in a phase of rapid growth, which requires more energy and nutrients. During this time, it’s normal for them to be hungrier as their bodies are developing.
However, even in adult cats, growth spurts or increased activity levels can lead to a temporary increase in hunger. It’s crucial to provide the right amount and quality of food to support their growth without overfeeding, which can lead to obesity.
5. Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus is a condition that affects the body’s ability to produce or respond to insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels. In cats, diabetes mellitus can cause increased hunger because their bodies can’t properly use the glucose from their food, leading them to eat more in an attempt to gain energy.
If your cat is always hungry, drinks more water than usual, and is losing weight despite eating more, it’s essential to consult a veterinarian for testing and appropriate management.
6. Hyperthyroidism

Hyperthyroidism is a common condition in older cats where the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. This hormone controls metabolism, and when in excess, it can cause rapid weight loss, increased thirst, and constant hunger.
If your cat has become ravenous but continues to lose weight, hyperthyroidism might be the cause. Treatment typically involves medication, dietary changes, or in some cases, surgery or radioactive iodine therapy.
7. Nutritional Deficiency
If your cat’s diet is lacking in essential nutrients, they may feel hungry even after eating. Nutritional deficiencies can arise from feeding low-quality food or an unbalanced diet that doesn’t meet their specific needs.
For instance, a lack of certain amino acids or vitamins might trigger persistent hunger as your cat tries to compensate. Ensuring that your cat’s food is complete and balanced, with the right mix of nutrients, is key to preventing this issue.
8. Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI)
EPI is a condition where the pancreas doesn’t produce enough enzymes to properly digest food. This leads to malabsorption, meaning your cat can eat a lot but still feel hungry because their body isn’t getting the nutrients it needs.
Symptoms of EPI in cats include weight loss, increased appetite, and greasy stools. If you suspect EPI, a vet can diagnose the condition with tests and recommend enzyme supplements to help your cat properly digest their food.
9. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Inflammatory Bowel Disease is a chronic condition that causes inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, leading to symptoms like vomiting, diarrhoea, and weight loss. Cats with IBD often feel hungry because their bodies aren’t absorbing nutrients properly.
The inflammation interferes with digestion, making it difficult for them to get the energy they need from their food. Managing IBD typically involves dietary changes, medications, and regular vet care to control symptoms and improve nutrient absorption.
10. Side Effect of Medications
Certain medications, such as steroids, can increase your cat’s appetite as a side effect. Steroids are often prescribed for conditions like allergies or inflammation, but they can make your cat feel hungrier than usual. Other medications, like anticonvulsants or treatments for chronic conditions, may also stimulate appetite. If your cat’s hunger suddenly increases after starting a new medication, consult your veterinarian. They may adjust the dosage or suggest alternative treatments.
How to Reduce Your Cat’s Appetite?
The ways to reduce your cat’s appetite if they are hungry all the time depends on the reason for their sudden increase in appetite.
If it is a heavy worm load, your veterinarian will recommend the right dose of dewormers for your cat.

If it’s hyperthyroidism or any other metabolic disorder, they will receive medication along with prescription food which will boost satiety.
In case they are hungry all the time because they are bored you will have to spend more quality time with your pet.
Steer clear of cheap dry cat food and invest in grain-free or veterinarian recommended cat food to keep your cat’s nutritional needs and hunger satisfied. This will also address the needs of cats (kittens) with sudden growth spurts.
Since, there can be at least 10 reasons why your cat is always hungry, you must visit the vet to find out the root cause. Formulate a feeding plan with your veterinarian that suits your cat’s age, nutritional needs and weight.
All in all, to manage the increased hunger, you can feed smaller, more frequent meals or offer low-calorie treats to satisfy your cat without risking weight gain. It’s important to monitor your cat’s weight and overall health while they are on medications that can affect their appetite to ensure they remain healthy.
0 notes
Text
Common Gastrointestinal Conditions and Their Treatments: Insights from a Gastroenterologist in Greater Noida

Gastrointestinal (GI) disorders are among the most common health issues affecting individuals today. Whether it’s a mild case of acid reflux or a more serious condition like Crohn's disease, these disorders can significantly impact your quality of life. A Gastroenterologist in Greater Noida is specially trained to diagnose, treat, and manage these conditions. This blog will provide an overview of common gastrointestinal conditions, their symptoms, and the available treatment options.
1. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a chronic condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation.
Symptoms:
Persistent heartburn
Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
Difficulty swallowing
Chest pain, especially when lying down
Treatment Options:
Lifestyle Changes: Eating smaller meals, avoiding spicy and fatty foods, not lying down after eating, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Medications: Antacids, H2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors to reduce stomach acid production.
Surgery: In severe cases, surgery such as fundoplication may be recommended to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter.
GERD is one of the most common conditions seen by a Gastroenterologist in Greater Noida, and early treatment can help prevent complications such as esophageal stricture or Barrett's esophagus.
2. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by a group of symptoms that occur together, including repeated pain in the abdomen and changes in bowel movements.
Symptoms:
Abdominal pain or cramping
Bloating and gas
Diarrhea, constipation, or alternating between both
Mucus in stool
Treatment Options:
Dietary Changes: Following a low FODMAP diet, increasing fiber intake, and avoiding trigger foods.
Medications: Antispasmodics, laxatives, or anti-diarrheal medications, depending on the dominant symptom.
Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness, cognitive behavioral therapy, and relaxation exercises.
IBS is a chronic condition that can significantly affect a person’s life. Consulting with a Gastroenterologist in Greater Noida can help tailor a treatment plan that addresses the unique symptoms of each patient.
3. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a term primarily used to describe two conditions: Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Both involve chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms:
Persistent diarrhea
Abdominal pain and cramping
Blood in the stool
Unintended weight loss
Fatigue
Treatment Options:
Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immune system suppressors, and biologics to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms.
Nutrition and Diet: Special diets and nutritional supplements to manage symptoms and prevent malnutrition.
Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove damaged portions of the digestive tract or to treat complications such as fistulas or strictures.
IBD requires long-term management and regular follow-ups with a Gastroenterologist in Greater Noida to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as necessary.
4. Celiac Disease
Celiac Disease is an autoimmune disorder where the ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine. It can cause a wide range of symptoms and often goes undiagnosed.
Symptoms:
Chronic diarrhea or constipation
Abdominal pain and bloating
Fatigue
Anemia
Skin rashes (dermatitis herpetiformis)
Treatment Options:
Strict Gluten-Free Diet: The only effective treatment for celiac disease is a lifelong gluten-free diet, which involves avoiding all foods containing wheat, barley, and rye.
Nutritional Supplements: To address deficiencies in vitamins and minerals caused by malabsorption.
Regular Monitoring: Ongoing follow-ups with a gastroenterologist to monitor health and ensure adherence to the diet.
A Gastroenterologist in Greater Noida can help diagnose celiac disease through blood tests and biopsies, and guide patients in managing their condition through diet and lifestyle changes.
5. Liver Diseases

Liver diseases encompass a variety of conditions that affect the liver's ability to function properly, including hepatitis, fatty liver disease, and cirrhosis.
Symptoms:
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Abdominal pain and swelling
Chronic fatigue
Nausea or vomiting
Dark urine and pale stool
Treatment Options:
Medications: Antiviral drugs for hepatitis, medications to manage symptoms, and slow the progression of liver disease.
Lifestyle Changes: Reducing alcohol consumption, managing weight, and eating a balanced diet to support liver health.
Surgery: In severe cases, a liver transplant may be necessary.
Early diagnosis and intervention are critical in managing liver diseases. Regular check-ups with a Gastroenterologist in Greater Noida can help detect liver conditions early and provide effective treatment options.
6. Peptic Ulcer Disease
Peptic Ulcer Disease refers to open sores that develop on the inner lining of the stomach and the upper portion of the small intestine.
Symptoms:
Burning stomach pain
Bloating
Nausea or vomiting
Weight loss without trying
Blood in vomit or stool (indicating a bleeding ulcer)
Treatment Options:
Medications: Proton pump inhibitors, antibiotics (if caused by H. pylori bacteria), and antacids.
Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), quitting smoking, and reducing alcohol consumption.
Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be required if the ulcer does not heal with medication or if there are complications like bleeding.
A Gastroenterologist in Greater Noida can provide a comprehensive treatment plan for peptic ulcer disease, helping to heal the ulcer and prevent its recurrence.
FAQs
What are the most common gastrointestinal conditions?
Some of the most common gastrointestinal conditions include GERD, IBS, IBD, celiac disease, liver diseases, and peptic ulcer disease.
When should I see a gastroenterologist?
You should see a gastroenterologist if you experience persistent digestive symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, blood in the stool, or unexplained weight loss.
How are gastrointestinal conditions diagnosed?
Gastrointestinal conditions are diagnosed through a combination of patient history, physical exams, and diagnostic tests such as blood tests, endoscopy, colonoscopy, and imaging studies.
What lifestyle changes can help manage gastrointestinal conditions?
Lifestyle changes that can help manage gastrointestinal conditions include eating a balanced diet, avoiding trigger foods, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Can gastrointestinal conditions be cured?
Some gastrointestinal conditions, such as peptic ulcers and certain infections, can be cured with appropriate treatment. Others, like IBS or IBD, require long-term management.
Conclusion
Gastrointestinal conditions can significantly impact your quality of life, but with the right diagnosis and treatment, they can be managed effectively. Whether you're dealing with GERD, IBS, IBD, or any other digestive disorder, a Gastroenterologist in Greater Noida can provide the specialized care you need. Understanding the symptoms and treatment options for these common conditions is the first step toward better digestive health. Regular consultations with a gastroenterologist can help you maintain a healthy digestive system and prevent complications from untreated GI disorders.
0 notes
Text
Effective Gastrointestinal Disorder Treatment with HealZen

Struggling with Gastrointestinal Disorders? Find Relief with HealZen!

HealZen offers specialized gastrointestinal disorder treatment that addresses the root cause of your digestive issues. With over 350+ patients finding relief, our approach is proven to work.

Why Choose HealZen for Gastrointestinal Disorder Treatment?
Uncover the Root Cause: We identify and address the underlying issues causing your digestive problems.
Medical Nutrition Therapy (MNT): Our evidence-based MNT plans promote optimal cellular function and gut health.
Prevention of Gastrointestinal Disorders: Early detection and targeted interventions prevent occasional issues from becoming chronic conditions.
Personalized Care: Tailored nutrition plans designed to meet your unique health needs.
Experience Faster Relief: Noticeable improvement in digestive health within 72 hours to a week.

Our Services Include:
IBD (Irritable Bowel Disease) Management
IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) Relief
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) Treatment
Chronic Constipation Solutions
Indigestion and Bloating Remedies
Contact Us Today! Start your journey to a healthier gut and overall well-being. Book an appointment with HealZen now and take control of your health.

Visit Us - https://www.healzengroup.com/
Address - 201/202, Ek Onkar Paradise, Pan Card Club Rd, Near Beverly Hills Apartment, Baner, Pune, Maharashtra- 411 045
Email - [email protected]
Call Us - +91 8208309931
HealZen – Your Partner in Gut Health and Wellness. Experience the power of targeted nutrition and personalized care today!
#healzen#healzen group#gastrointestinal#gastrointestinal disorders#gastrointestinal diseases#gastrointestinal disorders treatment#prevention of gastrointestinal disorders#medical nutrition therapy gastrointestinal disorder
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding the Dynamics of the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Market: Drivers, Barriers, and Future Outlook
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) refers to a group of chronic inflammatory conditions that affect the gastrointestinal tract. The two main types of IBD are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Here's an overview of each:
Crohn's Disease:
- Location: Can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from the mouth to the anus, often involving segments of the bowel with healthy tissue in between.
- Inflammation Type: Inflammation can extend through the entire thickness of the bowel wall (transmural).
- Symptoms: Abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody), weight loss, fatigue, and sometimes extraintestinal manifestations such as joint pain or skin rashes.
- Complications: Fistulas (abnormal connections between bowel and other organs), strictures (narrowing of the bowel), and abscesses.
- Treatment: Medications to reduce inflammation (e.g., corticosteroids, immunomodulators, biologics), nutritional therapy, and in severe cases, surgery to remove diseased bowel segments.
Ulcerative Colitis:
- Location: Limited to the colon (large intestine) and rectum, typically starting in the rectum and extending proximally in a continuous manner.
- Inflammation Type: Inflammation primarily affects the innermost lining of the colon (mucosa).
- Symptoms: Bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramps, urgency to defecate, weight loss, fatigue, and complications such as toxic megacolon or colorectal cancer (in long-standing disease).
- Complications: Severe disease may require hospitalization, intravenous steroids, immunosuppressive therapy, or surgery (colectomy) in cases of medically refractory disease or dysplasia/cancer.
- Treatment: Similar to Crohn's disease, management involves medications (including aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, biologics) and sometimes surgery for severe cases.
Common Features of IBD:
- Chronic Inflammation: Both conditions involve chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, which can lead to tissue damage and complications over time.
- Periods of Remission and Flare-ups: Patients may experience periods of remission with few or no symptoms followed by flare-ups of active disease.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms, endoscopic findings (e.g., colonoscopy), histology (biopsy results showing characteristic inflammation), and imaging studies (e.g., MRI or CT scans).
- Risk Factors: Genetics, environmental factors (such as diet and smoking), and dysregulation of the immune system play roles in the development and progression of IBD.
- Quality of Life Impact: IBD can significantly impact quality of life due to its chronic nature, symptoms, and potential complications. Management often involves multidisciplinary care, including gastroenterologists, dietitians, and psychologists.
Emerging Treatments and Research:
- Biological Therapies: Advances in biologic medications targeting specific molecules involved in the inflammatory process have revolutionized IBD treatment, improving outcomes and reducing the need for surgery.
- Microbiome Research: Studying the gut microbiome's role in IBD pathogenesis and treatment response is an active area of research, with potential implications for personalized medicine approaches.
- Precision Medicine: Tailoring treatments based on individual patient characteristics, biomarkers, and disease behavior to optimize therapeutic outcomes.
- Nutritional Therapies: Investigating the role of diet, prebiotics, probiotics, and exclusive enteral nutrition in managing symptoms and inducing remission.
In summary, IBD represents a complex group of chronic inflammatory conditions with distinct clinical features, management strategies, and ongoing research efforts aimed at improving diagnosis, treatment options, and quality of life for affected individuals.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Market Drivers
The market for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) treatments is influenced by several key drivers that shape the development, accessibility, and adoption of therapies. Here are the primary market drivers for IBD:
Increasing Prevalence and Incidence:
The prevalence of IBD, including both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, has been steadily increasing globally. This rise in prevalence drives demand for effective treatments and healthcare services to manage the disease burden.
Advancements in Treatment Options:
Biologics: The advent of biologic therapies, such as anti-TNF agents (e.g., infliximab, adalimumab), integrin inhibitors (e.g., vedolizumab), and interleukin inhibitors (e.g., ustekinumab), has transformed the treatment landscape for IBD. These targeted therapies offer improved efficacy, reduced side effects compared to traditional therapies, and the potential for inducing and maintaining remission.
Small Molecule Inhibitors: Emerging small molecule inhibitors targeting specific pathways in the inflammatory cascade (e.g., Janus kinase inhibitors) provide additional therapeutic options, particularly for patients who do not respond to or cannot tolerate biologics.
Pipeline of Innovative Therapies:
Ongoing research and development efforts focus on novel therapies, including next-generation biologics with enhanced pharmacokinetic profiles, oral formulations of biologics, and targeted therapies aimed at modulating the immune response more selectively.
Personalized Medicine Approaches:
Increasing emphasis on personalized medicine in IBD treatment involves biomarker-driven strategies to predict treatment response and tailor therapies based on individual patient characteristics (e.g., genetic markers, disease phenotype).
Precision medicine approaches aim to optimize therapeutic outcomes, reduce adverse effects, and improve patient adherence to treatment regimens.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Market Barriers
The market for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) treatments faces several barriers that impact the development, accessibility, and adoption of therapies. These barriers include:
1. Complex Pathophysiology and Heterogeneity: Inflammatory Bowel Disease encompasses diverse conditions such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, each with varying disease presentations and responses to treatment. The complexity and variability make it challenging to develop universal treatment approaches that are effective for all patients.
2. Limited Understanding of Disease Mechanisms: Despite significant advancements, the exact causes and mechanisms triggering IBD are not fully understood. This limits the development of targeted therapies and precision medicine approaches tailored to individual patient profiles.
3. High Cost of Treatment: The expenses associated with IBD management, including medications (such as biologics and immunosuppressants), diagnostic procedures (like endoscopies and imaging), and potential hospitalizations, can be substantial. This financial burden may strain healthcare systems and pose challenges for patients, especially those without adequate insurance coverage.
4. Safety and Side Effects of Therapies: Many of the medications used to treat IBD, such as corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and biologics, carry risks of adverse effects. These can include increased susceptibility to infections, infusion reactions, and long-term complications such as malignancies. Balancing the benefits of treatment with these risks requires careful consideration and monitoring.
5. Access to Specialized Care and Therapies: Effective management of IBD often requires access to specialized healthcare providers, including gastroenterologists, nutritionists, and sometimes surgeons. Disparities in healthcare access, particularly in rural or underserved areas, can hinder timely diagnosis and optimal management.
6. Regulatory Challenges and Market Competition: The process of obtaining regulatory approvals for new therapies can be lengthy and costly. Strict regulatory requirements for demonstrating safety, efficacy, and manufacturing consistency pose hurdles for drug developers. Additionally, competition within the market for established therapies can limit market penetration and innovation.
7. Patient Adherence and Compliance: Treatment regimens for IBD can be complex, involving multiple medications, dietary modifications, and regular monitoring. Poor patient adherence to prescribed therapies may compromise treatment efficacy and disease management outcomes.
8. Emerging Therapies and Research Gaps: While there have been advancements in biologic therapies and targeted treatments for IBD, there remains a need for novel therapeutic approaches. Research gaps in understanding disease progression, biomarkers for personalized medicine, and mechanisms of treatment resistance require further investigation to address unmet medical needs effectively.
Addressing these barriers requires collaborative efforts among healthcare providers, pharmaceutical companies, regulatory bodies, patient advocacy groups, and policymakers. Strategies to improve disease understanding, reduce treatment costs, enhance access to care, and advance therapeutic innovation are essential for optimizing outcomes and quality of life for individuals living with Inflammatory Bowel Disease.
Future Inflammatory Bowel Disease Market Analysis
The Inflammatory Bowel Disease market is poised for significant growth in the coming years, driven by ongoing research, technological advancements, and evolving treatment paradigms. Key trends and developments shaping the future of the market include:
Looking ahead, the market for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is expected to undergo significant changes driven by advancements in treatment approaches, evolving healthcare policies, and shifts in patient management strategies. Here’s an analysis of the future trends and dynamics likely to shape the IBD market:
Growth Drivers:
1. Advancements in Biologic Therapies:
- Next-Generation Biologics: Continued innovation in biologic medications targeting specific inflammatory pathways (e.g., TNF-alpha inhibitors, integrin inhibitors, interleukin inhibitors) is expected. These therapies aim to improve efficacy, reduce side effects, and provide more convenient administration options (e.g., subcutaneous formulations).
- Biosimilars: Increased availability and adoption of biosimilar versions of biologic drugs could enhance competition, lower treatment costs, and expand patient access to effective therapies.
2. Precision Medicine and Personalized Treatment Approaches:
- Biomarker Development: Advances in identifying biomarkers associated with disease activity, treatment response, and prognosis may enable personalized medicine approaches. Tailoring treatments based on individual patient profiles could optimize therapeutic outcomes and minimize adverse effects.
- Genomic Research: Growing understanding of the genetic basis of IBD through genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and genetic sequencing may lead to the development of targeted therapies aimed at specific disease subtypes or genetic mutations.
3. Emerging Therapeutic Modalities:
- Microbiome-based Therapies: Research into the gut microbiome’s role in IBD pathogenesis is yielding insights into novel therapeutic strategies, such as fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) and microbiome-modulating agents. These approaches aim to restore microbial balance and alleviate symptoms.
- Cellular Therapies: Investigational therapies involving stem cell transplantation or engineered immune cells (e.g., CAR-T cells) may offer potential curative treatments or disease-modifying effects in refractory cases of IBD.
4. Digital Health Solutions:
- Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring: Increasing adoption of telehealth platforms and digital tools for remote patient monitoring and management of IBD could improve access to specialized care, enhance patient engagement, and optimize treatment adherence.
- Digital Biomarkers: Integration of digital biomarkers, such as smartphone apps and wearable devices, for real-time monitoring of symptoms, medication adherence, and disease activity may support personalized treatment decision-making and clinical trial endpoints.
5. Patient-Centered Care and Supportive Services:
- Integrated Care Models: Implementation of multidisciplinary care teams, including gastroenterologists, dietitians, psychologists, and social workers, to provide comprehensive support for patients managing chronic symptoms and psychosocial aspects of IBD.
- Patient Education and Empowerment: Enhanced patient education initiatives and self-management programs aimed at improving disease awareness, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to treatment plans.
Challenges and Considerations:
1. Cost and Affordability:
- The high cost of biologic therapies and emerging treatments for IBD poses challenges for healthcare systems, insurers, and patients. Efforts to address pricing transparency, cost-effectiveness assessments, and reimbursement strategies will be critical.
2. Regulatory and Market Access Hurdles:
- Regulatory requirements for demonstrating safety, efficacy, and manufacturing consistency for new therapies remain stringent. Navigating these regulatory pathways and securing timely approvals can impact market entry and adoption rates.
3. Disease Complexity and Treatment Response Variability:
- The heterogeneous nature of IBD, with variability in disease presentation, progression, and response to therapies, underscores the need for personalized treatment approaches and ongoing research into predictive biomarkers.
4. Healthcare Disparities and Access to Specialized Care:
- Disparities in healthcare access, particularly in rural or underserved areas, may limit timely diagnosis, access to advanced therapies, and participation in clinical trials. Addressing these disparities through telemedicine, community outreach, and healthcare policy initiatives is essential.
Future Outlook:
The future IBD market is poised for growth driven by innovation in biologic therapies, precision medicine approaches, and digital health solutions aimed at enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life. Collaboration among stakeholders, including healthcare providers, pharmaceutical companies, regulators, and patient advocacy groups, will be crucial in overcoming challenges and realizing the potential of emerging therapies for individuals living with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Continued investment in research, clinical trials, and patient-centered care models will shape the landscape of IBD management in the coming years.
Evolving Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treatment Outlook
The treatment landscape for Inflammatory Bowel Disease is evolving rapidly, with a shift towards targeted therapies and personalized approaches. Key developments shaping the evolving treatment outlook include:
The landscape of treatment options for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) continues to evolve, driven by advancements in understanding the disease mechanisms, development of novel therapeutic approaches, and efforts to improve patient outcomes. Here are some of the evolving treatment options for IBD:
Biologic Therapies:
1. Next-Generation Biologics:
- Anti-TNF Therapies: TNF-alpha inhibitors (e.g., infliximab, adalimumab) have been pivotal in managing moderate to severe IBD. Next-generation TNF inhibitors with improved pharmacokinetic profiles and reduced immunogenicity are under development.
- Integrin Inhibitors: Vedolizumab targets α4β7 integrin, which plays a role in leukocyte trafficking to the gut. It offers a gut-selective mechanism of action and has shown efficacy in both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
- IL-12/IL-23 Inhibitors: Ustekinumab targets IL-12 and IL-23 cytokines and is approved for moderate to severe Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Newer agents targeting IL-23 alone (e.g., risankizumab) are also being investigated.
2. Biosimilars:
- Increasing availability of biosimilar versions of biologic therapies, such as infliximab and adalimumab biosimilars, aims to enhance competition, reduce treatment costs, and improve access for patients.
Small Molecule Therapies:
1. JAK Inhibitors:
- Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors (e.g., tofacitinib) target intracellular signaling pathways involved in inflammation. They offer an oral alternative for patients who may prefer non-biologic therapies or have failed biologic treatment.
2. S1P Receptor Modulators:
- Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor modulators (e.g., ozanimod) regulate lymphocyte trafficking and have shown efficacy in clinical trials for ulcerative colitis, providing a new oral treatment option.
Cellular Therapies:
1. Stem Cell Therapy:
- Investigational therapies involving hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) aim to reset the immune system and induce disease remission in severe and refractory cases of IBD. Research is ongoing to optimize safety and efficacy.
Novel Approaches and Therapeutic Strategies:
1. Microbiome-Based Therapies:
- Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) and microbiome-targeted therapies aim to restore microbial balance in the gut and modulate immune responses. Clinical trials are exploring their efficacy and safety in IBD management.
2. Topical and Local Therapies:
- Local delivery systems, such as rectal foams, enemas, and controlled-release formulations, provide targeted therapy for distal colonic involvement in ulcerative colitis, minimizing systemic side effects.
3. Nutritional Therapy:
- Exclusive enteral nutrition (EEN) and specific carbohydrate diets (SCD) are dietary approaches that can induce remission and improve symptoms in some patients with IBD, particularly in pediatric populations.
Future Directions:
- Precision Medicine: Advances in biomarker research may enable personalized treatment strategies tailored to individual patient characteristics, disease subtypes, and treatment responses.
- Gene Therapy: Investigational gene editing technologies (e.g., CRISPR-Cas9) hold promise for correcting genetic mutations associated with IBD, potentially offering curative treatments in the future.
- Digital Health and Telemedicine: Integration of digital health solutions for remote monitoring of disease activity, medication adherence, and patient-reported outcomes aims to optimize patient management and healthcare delivery.
- Regenerative Medicine: Research into tissue engineering and organoids may lead to bioengineered tissues for repairing damaged intestinal mucosa and restoring functional gut architecture in IBD.
In summary, the evolving landscape of IBD treatment options reflects a shift towards personalized medicine, innovation in biotechnology, and a commitment to improving patient outcomes through targeted therapies and multidisciplinary care. Ongoing research, clinical trials, and collaborative efforts among healthcare providers, researchers, and pharmaceutical companies are essential in advancing the field and addressing unmet medical needs in IBD management.
Role of Companies in the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Market
In the Inflammatory Bowel Disease market, companies such as Takeda Pharmaceutical, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Hoffmann-La Roche, Genentech, AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead Sciences, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, and others play a pivotal role in driving innovation, research, development, and the provision of treatments and therapies for individuals.
Get a more detailed overview, at: Inflammatory Bowel Disease Market Outlook and Forecast
0 notes
Text
Understanding Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a term used to describe two chronic conditions that cause inflammation of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract: Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. These conditions can significantly impact the quality of life for those affected, causing a range of symptoms and complications. In this blog, we'll delve into what IBD is, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and ways to manage and possibly prevent it.
What is Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
IBD is a group of disorders characterized by chronic inflammation of the GI tract. The two primary types are:
Crohn's Disease: This can affect any part of the GI tract, from the mouth to the anus, but most commonly affects the end of the small intestine (ileum) and the beginning of the colon. The inflammation can penetrate deep into the layers of the bowel, causing complications such as strictures, fistulas, and abscesses.
Ulcerative Colitis: This condition is limited to the colon (large intestine) and rectum. The inflammation is typically continuous and affects only the innermost lining of the colon, starting from the rectum and extending proximally.
Call for Online Speaker /Poster Participate at the CME/CPD accredited 14th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference from December 17-19, 2024, in Dubai, UAE & Virtual. WhatsApp us: https://wa.me/442033222718?text= Virtually Registration Here: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/virtual-registration/

Symptoms of IBD
The symptoms of IBD can vary depending on the location and severity of the inflammation. Common symptoms include:
Abdominal pain and cramping
Persistent diarrhea, which may be bloody
Weight loss
Fatigue
Urgent need to defecate
Fever
Reduced appetite
Causes of IBD
The exact cause of IBD is unknown, but it is believed to result from a combination of factors:
Genetic Predisposition: A family history of IBD increases the risk.
Immune System Dysfunction: An abnormal immune response to normal gut flora.
Environmental Factors: Diet, smoking, and stress can influence the onset and progression of the disease.
Gut Microbiome: Imbalance in the gut bacteria may play a role in the development of IBD.
Diagnosing IBD
Diagnosing IBD involves a combination of methods:
Medical History and Physical Exam: Initial assessment by a healthcare provider.
Endoscopic Procedures: Colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy to visualize the inflammation and take biopsies.
Imaging Studies: CT scans, MRI, and intestinal ultrasound to assess the extent and severity of inflammation.
Laboratory Tests: Blood tests to check for anemia and inflammation markers, and stool tests to rule out infections.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for IBD, several treatments can help manage symptoms and induce remission:
Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs (aminosalicylates), corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and biologic therapies (TNF inhibitors, integrin inhibitors).
Surgery: In severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to remove damaged portions of the GI tract.
Lifestyle Modifications: Diet changes, stress management, and regular exercise can help manage symptoms.
Living with IBD
Managing IBD is an ongoing process that involves:
Diet and Nutrition: Tailored diets can help manage symptoms. This may include low-residue diets, specific carbohydrate diets, or personalized nutrition plans based on individual tolerance.
Regular Medical Care: Routine check-ups with a gastroenterologist to monitor disease activity and adjust treatment plans.
Support Systems: Psychological support, counseling, and support groups can help cope with the emotional aspects of living with a chronic illness.
Education and Advocacy: Staying informed about the disease and advocating for oneself in healthcare settings can empower patients and improve their quality of life.
Preventing IBD
While it may not be possible to prevent IBD entirely due to its complex etiology, certain measures may reduce the risk:
Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Avoiding Smoking: Smoking cessation can lower the risk of Crohn's disease and improve overall health.
Stress Management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, and regular physical activity can help manage stress levels.
Judicious Use of Antibiotics: Minimizing unnecessary use of antibiotics to avoid disrupting the gut microbiome.
Breastfeeding: Some studies suggest breastfeeding may reduce the risk of developing IBD in children.
Call for Online Speaker /Poster Participate at the CME/CPD accredited 14th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference from December 17-19, 2024, in Dubai, UAE & Virtual. WhatsApp us: https://wa.me/442033222718?text= Virtually Registration Here: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/virtual-registration/
How to avoid Bowel Disease ?
While doctors can't guarantee prevention of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) due to its complex and not fully understood causes, they do offer recommendations that may reduce the risk or delay the onset, especially for those with a higher genetic predisposition. Here are some strategies often recommended by healthcare professionals:
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet
Balanced Nutrition: Emphasize a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. This promotes overall gut health.
Fiber Intake: Incorporate sufficient fiber, as it supports a healthy digestive system. However, those with sensitivities should adjust their fiber intake accordingly.
Reduce Processed Foods: Limit intake of processed foods high in refined sugars, fats, and additives, which can negatively impact gut health.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Include foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish and flaxseeds, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
Probiotics and Prebiotics: Consume foods rich in probiotics (yogurt, kefir) and prebiotics (bananas, onions) to support a healthy gut microbiome.
2. Avoid Smoking
Smoking Cessation: Quit smoking, as it is a known risk factor for Crohn's disease and can worsen symptoms in existing cases. Doctors can provide resources and support for quitting.
3. Manage Stress
Stress Reduction Techniques: Engage in activities that reduce stress, such as yoga, meditation, and regular physical exercise. Chronic stress can exacerbate gut issues and potentially trigger IBD.
4. Use Antibiotics Judiciously
Antibiotic Stewardship: Avoid unnecessary use of antibiotics, as they can disrupt the gut microbiome, potentially increasing the risk of IBD. Use antibiotics only when prescribed and necessary.
5. Promote a Healthy Gut Microbiome
Microbial Exposure: Allow for some natural exposure to diverse environments, especially in childhood, to help build a balanced immune system. This aligns with the "hygiene hypothesis," which suggests that too much cleanliness may hinder immune development.
6. Breastfeeding
Infant Nutrition: If possible, breastfeeding may provide protective benefits against the development of IBD due to its positive effects on the infant's immune system and gut microbiome.
7. Regular Medical Check-Ups
Family History Awareness: Those with a family history of IBD should have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor for early signs and symptoms. Early intervention can be crucial in managing the disease effectively.
Screening: Regular screenings and monitoring for symptoms can help in early detection and treatment, potentially reducing the severity and complications.
8. Stay Informed About Research
Continuous Learning: Keep up-to-date with the latest research and advances in IBD prevention and management. This can provide new insights into potential preventive measures and treatments.
9. Vaccinations
Prevent Infections: Stay up-to-date with vaccinations to prevent infections that might trigger or exacerbate IBD symptoms.
10. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Exercise: Regular physical activity supports overall health and helps manage stress.
Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight, as obesity can contribute to various health issues, including gastrointestinal problems.
Call for Online Speaker /Poster Participate at the CME/CPD accredited 14th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference from December 17-19, 2024, in Dubai, UAE & Virtual. WhatsApp us: https://wa.me/442033222718?text= Virtually Registration Here: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/virtual-registration/

Conclusion
Inflammatory Bowel Disease is a challenging condition that requires a comprehensive and personalized approach to management. By understanding the disease, its causes, and treatment options, those affected can better navigate their health journey. Through lifestyle changes, medical care, and support, individuals with IBD can lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by the disease. If you suspect you have IBD or are experiencing symptoms, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
0 notes
Text
Unraveling the Intricate Dance: Exploring the Interaction Between the Gut Microbiome and Probiotics

Introduction: In the bustling ecosystem of the human gut, trillions of microorganisms engage in a complex and dynamic dance that profoundly influences our health and well-being. At the forefront of this intricate interplay are probiotics—beneficial bacteria with the potential to modulate the composition and function of the gut microbiome. In this blog, we delve into the fascinating interaction between the gut microbiome and probiotics, uncovering the mechanisms, benefits, and implications for human health. The Gut Microbiome: A Dynamic Ecosystem: The gut microbiome, comprising a diverse array of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms, forms a complex ecosystem within the gastrointestinal tract. This microbial community plays a pivotal role in various physiological processes, including digestion, nutrient metabolism, immune function, and even neurological signaling. A delicate balance of microbial diversity and composition is essential for maintaining gut health and overall well-being. Probiotics: Guardians of Gut Health: Probiotics, often referred to as "friendly" or "beneficial" bacteria, are living microorganisms that confer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. Found in certain foods, supplements, and fermented products, probiotics have garnered attention for their potential to modulate the gut microbiome and promote health. Common probiotic strains include Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Saccharomyces, each with its unique properties and mechanisms of action. Join us for an unforgettable workshop experience. Attend the workshop with Probulin Probiotics' Dr. Jason Mitchell. We are pleased to invite you to the free workshop on May 21, 2024, at Grand Hyatt Dubai Riyadh Street, United Arab Emirates. Workshop Title: The Evolution in Probiotic Therapy For workshop details, visit here: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/the-evolution-in-probiotic-therapy/ Benefits to Attendees: 1. These opportunities can lead to valuable connections and potential business partnerships. 2. Opportunities for Networking 3. Novel Ways of Thinking 4. Developing New Prowess 5. Free access to professional consultation on key issues 6. Hear new ideas that might help you Workshop Audience: Gut Health Specialists, GPs, Internal Medicine, Gastroenterologists, Nutrition and Wellness Professionals, Probiotics Health Professionals, Digestive Diseases Medical Professionals, GI doctors, etc. The Dance of Interaction: The interaction between probiotics and the gut microbiome is a dynamic and multifaceted dance, orchestrated by a myriad of molecular signals and metabolic pathways. Probiotics exert their influence through various mechanisms, including competitive exclusion of pathogenic bacteria, production of antimicrobial compounds, modulation of immune responses, and enhancement of gut barrier function. These interactions can help restore microbial balance, alleviate gastrointestinal symptoms, and support overall gut health. Benefits for Health and Well-being: The symbiotic relationship between probiotics and the gut microbiome yields a host of benefits for human health and well-being. Clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of probiotics in managing various gastrointestinal conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Additionally, probiotics may confer benefits beyond the gut, including immune modulation, allergy prevention, and even mood regulation. Conclusion: The interaction between the gut microbiome and probiotics represents a captivating nexus of science and health, with profound implications for human well-being. Through their intricate dance within the gastrointestinal tract, probiotics wield the power to modulate microbial balance, support gut health, and promote overall wellness. By unraveling the mysteries of this dynamic interplay and harnessing its therapeutic potential, we can embark on a journey towards a healthier, more vibrant future.
0 notes
Text
Exploring Advances in Esophageal and Gastric Diseases at the 15th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference
Esophageal and gastric diseases represent significant challenges in gastroenterology, ranging from common conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) to life-threatening malignancies such as esophageal and gastric cancers. The 15th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference is an unparalleled opportunity to delve into the latest advancements in this field, fostering collaboration and innovation among healthcare professionals, researchers, and industry experts.

Why Esophageal and Gastric Diseases Matter: The esophagus and stomach play crucial roles in digestion, yet they are vulnerable to a spectrum of diseases. These include:
· Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): A prevalent condition causing significant discomfort and potential complications like Barrett's esophagus. GERD affects millions worldwide, with symptoms that can disrupt daily life and lead to long-term health consequences if untreated.
· Esophageal Cancer: Often diagnosed in advanced stages, esophageal cancer demands innovative diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Research into early detection methods, such as biomarkers and imaging technologies, is essential to improving survival rates.
· Gastric Cancer: A leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, requiring urgent advancements in prevention, screening, and treatment. Helicobacter pylori infection remains a significant risk factor, highlighting the need for effective eradication strategies.
· Functional Disorders: Conditions like achalasia and dyspepsia impact quality of life and pose diagnostic challenges. Understanding their pathophysiology is key to developing effective, targeted treatments.
At this conference, attendees will explore the latest breakthroughs in understanding, diagnosing, and treating these diseases, contributing to better patient outcomes globally. The event serves as a forum for sharing groundbreaking research, clinical insights, and technological innovations.
Submit Your Abstract and Share Your Research: We invite researchers, clinicians, and academicians to submit abstracts on esophageal and gastric diseases. Whether you are investigating the role of the microbiome, developing innovative therapies, or exploring precision medicine approaches, your contributions are invaluable.
Submit your abstract here: https://gastroenterology.utilitarianconferences.com/submit-abstract
Key Topics for Abstracts Include:
· Advances in GERD Management
· Barrett's Esophagus: Pathophysiology and Treatment
· Early Detection and Screening for Esophageal and Gastric Cancers
· Role of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Diseases
· Novel Therapeutics for Functional Esophageal and Gastric Disorders
· Endoscopic Innovations in Diagnosis and Treatment
· Nutritional Interventions in Esophageal and Gastric Disease Management
Join Us as a Speaker, Poster Presenter, or Delegate: This conference provides a platform for professionals to:
· Present cutting-edge research.
· Share clinical insights and innovative practices.
· Network with global leaders in gastroenterology.
Whether you are an established expert or an emerging voice in the field, your participation will contribute to shaping the future of gastroenterology. Register today to secure your participation: https://gastroenterology.utilitarianconferences.com/registration
What to Expect at the Conference: The 15th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference offers:
· Interactive Sessions: Engage in thought-provoking discussions on the latest findings, including hands-on workshops and case-based learning.
· Networking Opportunities: Build connections with peers, industry leaders, and potential collaborators from across the globe. Discuss research trends, challenges, and future directions in esophageal and gastric health.
· Comprehensive Coverage: Explore a wide array of topics, from basic research to clinical applications, including innovations in molecular biology, pharmacology, and minimally invasive surgical techniques.
· Exhibitor Showcase: Discover the latest tools, devices, and solutions designed to improve diagnostics and patient care in gastroenterology.
The Global Burden of Esophageal and Gastric Diseases Esophageal and gastric diseases represent a significant burden on healthcare systems worldwide. According to recent studies, the prevalence of GERD continues to rise, particularly in Western countries, while gastric cancer remains a major health concern in Asia and other parts of the world. Addressing these diseases requires a multi-disciplinary approach, combining the expertise of gastroenterologists, oncologists, dietitians, and researchers
Esophageal diseases, gastric diseases, GERD, Barrett's esophagus, gastric cancer, esophageal cancer, endoscopic therapies, gastroenterology conference, #GastroenterologyConference2024, #EsophagealDiseases, #GastricHealth, #GERDResearch, #EndoscopyInnovations, #AbstractSubmission, #MedicalConferences2024
Conclusion The 15th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference is your chance to be at the forefront of advancements in esophageal and gastric diseases. By participating, you contribute to a global effort to improve diagnostics, treatments, and patient care. This conference is not just an event; it’s a movement towards innovation and collaboration in gastroenterology.
Submit your abstract, register to attend, and join us in shaping the future of gastroenterology. For more details, visit the Home Page: https://gastroenterology.utilitarianconferences.com/. Together, we can make a lasting impact on the lives of patients worldwide.
0 notes
Text
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treatment
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Treatment at Kalyani Hospital
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a group of chronic conditions, primarily Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, that cause inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Managing IBD requires a comprehensive approach involving medical expertise, lifestyle adjustments, and, in some cases, surgical intervention. At Kalyani Hospital, we offer state-of-the-art treatment tailored to the needs of each patient.
Understanding IBD
IBD can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. Symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue are common. Left untreated, IBD may lead to complications like intestinal strictures, fistulas, and an increased risk of colorectal cancer.
Our Approach to IBD Treatment
Kalyani Hospital combines cutting-edge technology with compassionate care to manage and treat IBD effectively. Our multidisciplinary team includes gastroenterologists, dietitians, surgeons, and mental health professionals who work collaboratively to provide holistic care.
Diagnostic Services
Endoscopy and Colonoscopy: Visualize and assess inflammation or damage in the gastrointestinal tract.
Imaging Studies: Advanced imaging such as MRI and CT scans for detailed evaluation.
Laboratory Tests: Comprehensive blood and stool tests to identify markers of inflammation and infection.
Medical Treatment
Medication Management:
Anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., aminosalicylates and corticosteroids).
Immunosuppressive agents to reduce immune system overactivity.
Biologic therapies targeting specific inflammatory pathways.
Nutritional Support:
Tailored diets to reduce symptoms and improve nutrient absorption.
Nutritional supplements, when necessary.
Surgical Options
For patients who do not respond to medication or develop complications, surgical intervention may be required. Common procedures include:
Strictureplasty: Widening narrowed areas of the intestine.
Resection: Removing diseased portions of the intestine.
Colectomy: Removal of the colon, often with ileostomy or ileoanal pouch creation.
Patient-Centric Care
At Kalyani Hospital, we prioritize patient education and support. We provide resources to help patients understand their condition, manage symptoms, and live fulfilling lives. Our team conducts regular follow-ups to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Why Choose Kalyani Hospital?
Expert Team: Highly qualified and experienced specialists in IBD management.
Advanced Facilities: Modern diagnostic and therapeutic technologies.
Comprehensive Care: Integrated services including nutrition, counseling, and rehabilitation.
Personalized Plans: Tailored treatment approaches for each patient’s unique needs.
Contact Us
If you or a loved one is dealing with IBD, Kalyani Hospital is here to help. Contact us at [phone number] or visit our website at [website link] to schedule an appointment. Together, we can manage IBD effectively and improve your quality of life.

0 notes
Text
Best Gastroenterology Hospital in Hyderabad | Madhapur - Sravani Hospitals..
Sravani Hospitals the Best Gastroenterology Hospital in Hyderabad, Madhapur: Pioneering Gastroenterology Care
Are you in search of the Best Gastroenterology Hospital in Hyderabad, Madhapur? Look no further than Sravani Hospitals, where excellence in gastroenterology care meets compassionate patient-centered service. With a team of renowned gastroenterologists and state-of-the-art facilities, Sravani Hospitals stands out as the premier choice for individuals in need of top-notch gastrointestinal treatment.
Why Choose Sravani Hospitals for Gastroenterology Care?
Expert Gastroenterologists: At Sravani Hospitals the Best Gastroenterology Hospital in Hyderabad, Madhapur, we boast a team of experienced and highly skilled gastroenterologists who are leaders in their field. Our specialists are adept at diagnosing and treating a wide range of gastrointestinal disorders, from common conditions like acid reflux and irritable bowel syndrome to complex diseases such as liver cirrhosis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Comprehensive Gastroenterology Services: We offer a comprehensive range of gastroenterology services, including consultation, diagnostic testing, medical management, endoscopic procedures, and surgical interventions. Our goal is to provide personalized care tailored to each patient's specific condition and needs, with a focus on improving digestive health and overall well-being.
State-of-the-Art Facilities: Our hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art gastroenterology facilities, including advanced endoscopy suites, diagnostic imaging technology, and specialized surgical theaters. We utilize the latest techniques and innovations in gastroenterology care to deliver the highest standard of treatment to our patients.
Patient-Centered Approach: At Sravani Hospitals, we prioritize the comfort, safety, and satisfaction of our patients above all else. From the moment patients enter our doors, they are greeted with warmth, empathy, and respect. Our dedicated staff ensure that patients receive personalized attention, clear communication, and support throughout their gastroenterology treatment journey.
Key Gastroenterology Services Offered
Endoscopic Procedures: We specialize in a wide range of advanced endoscopic procedures, including gastroscopy, colonoscopy, endoscopic ultrasound (EUS), ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography), and capsule endoscopy, for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Liver Care: Our hepatologists provide expert care for patients with liver diseases such as hepatitis, fatty liver disease, liver cirrhosis, and liver cancer, offering diagnosis, medical management, and liver transplant evaluation when necessary.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Management: We offer comprehensive care for patients with inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, including diagnosis, medical therapy, nutritional support, and surgical consultation for refractory cases.
Digestive Health Screening: We provide preventive care and screening services for digestive health conditions, including colorectal cancer screening, H. pylori testing, and surveillance endoscopies for patients at high risk of gastrointestinal malignancies.
Admissions and Appointments
Patients seeking gastroenterology care at Sravani Hospitals can schedule appointments through our website, phone, or by visiting our hospital in person. Our staff are available to assist with appointment scheduling, insurance verification, and any inquiries patients may have about our services.
Conclusion
Sravani Hospitals is the leading destination for Best Gastroenterology Hospital in Hyderabad, Madhapur. With our expert gastroenterologists, comprehensive services, state-of-the-art facilities, and patient-centered approach, we are committed to delivering exceptional care and helping patients achieve optimal digestive health. Visit Sravani Hospitals today and experience the difference in gastroenterology excellence.
#Best Gastroenterology Hospital in Hyderabad#Best Gastroenterology Hospital in Madhapur#Sravani Hospitals..
0 notes
Text
The Hidden Meaning of Constant Diarrhea

Constant diarrhea is a symptom that should not be overlooked because it may suggest a more serious underlying disease. While occasional bouts of diarrhea are usually innocuous and can be linked to something you ate or a mild infection, chronic diarrhea that persists for a lengthy period of time necessitates medical treatment.
Constant diarrhea can be caused by gastrointestinal diseases such as bacterial or viral gastroenteritis, food intolerances including lactose or gluten intolerance, and chronic conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It is critical to correctly diagnose and treat the underlying illness in order to avoid consequences such as dehydration and nutritional deficiencies.
If you have continuous diarrhea, you should visit a healthcare professional who can provide an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment options. They may perform a full evaluation, which includes a medical history review, a physical examination, and diagnostic procedures such as stool analysis, blood testing, or imaging studies.
Chronic diarrhea is treated based on the underlying reason. Rest, drinks, and over-the-counter symptom-relieving medications may be sufficient for gastrointestinal infections. However, if the diarrhea continues or is caused by an underlying illness, specific therapy may be required. This could include dietary adjustments to address food intolerances, anti-inflammatory drugs for illnesses such as IBS or IBD, or other targeted therapy.
0 notes