#I do acknowledge that most of this manga was written in the early 2000s but come on Punk Hazard was literally not that long ago
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Maybe it's just me and I just don't understand the arc. Or maybe this arc will get some grand conclusion I'm really starting to doubt. But like I'm sick and tired of Tashigi being used as Zoro's misogyny proxy. Like the "a woman swordsman could never beat a man" belief and trauma made sense for both Kuina and Tashigi and was a very valid fear way back in the East Blue when they were still fighting relatively normal people and had no scope of how big the world is
but at this point where there are literally 20 feet tall dudes and people can blow up a whole city with just Haki the only reason Tashigi is still weak is because she is being written that way. Which is really hard to understand because it seems now more than ever One Piece has been getting more and more strong female characters so I don't know why every time Tashigi is on screen with Zoro we have to rehash this. It's even worse cause all she does in the scene is prove Zoro right by getting in a fight that she can't handle and needing saving. It's such a confusing message and honestly doesn't really apply or come up anywhere but with Tashigi and Zoro (outside of that one time where Zoro yells at enel for blasting Robin because she's a woman which was weird because Robin's been in a lot of fights before but seemed there just so enel could point out just how ruthless it is.)
Hell with the exception of the G5 all being in love with her. She is treated like a regular character and not just "the woman"
It honestly feels like both Tashigi and Smoker got lost in the narrative and Oda just doesn't know where to put their arcs. It feels like she was being written to help Zoro overcome whatever mental block Kuina's death instilled in him about facing female opponents with his sword. But she is just sooooo far behind him it renders the point moot and strengthens his convictions (it's weird that he will literally crush a woman's face rather than use his sword and is the only reason I won't say he doesn't fight women he does he just seems to have a mental block about cutting them down especially if they fight with anything blade like) but also we've only ever seen him face female character he knows can't challenge him it would have been interesting to see what he'd do in a fight against someone like big mom, tsuru or smoothie doubt that will happen though. But here's to hoping for Tashigi to have an actual arc.
#I'm just tired of this woman in fantasy situations still needing to be physically weaker than men#not to actually explore misogny but just because#like one dude tried to argue that Maki is inherently weaker than toji because she's a woman#like what? we are talking about a world where a dude literally has infinity at his disposable biology doesn't matter#stop infecting it with your misogny#or maybe she has this huge final role Oda is the god of bringing back random characters and leveling them up after all#like we are talking about a world where there's a dude literally made of fire I do not want to hear about the biological reality#this isn't reality#youre female characters arent strong because they aren't written to be strong and that's a you problem#I like tashigi 95% of the time she's a great character. But can women just be “weak” without it being because they are women?#can we just do that#been having so much fun in the mishanks/cross guild section of the fandom#I genuinely forgot how much the portrayal of women in one piece irritated me and was a big reason I stopped keeping up in the first place#here's my rant I guess#op#one piece#ranting#mini rant#roronoa zoro#tashigi#feminism#one piece women#I do like that it's a least alot better now with inclusion of more female characters#I do acknowledge that most of this manga was written in the early 2000s but come on Punk Hazard was literally not that long ago#one piece thoughts#women
57 notes
·
View notes
Note
@goryachiychai
The questions you asked are very much valid and everything you did say is observable in the manga. I actually do think that Kishi did not intentionally wrote his female characters in sexist nor misogynistic roles because it shows how much he cared for his female characters by actually taking the time to write them in a way that women or girls would relate them. Women in Japan liked to be in love and they were oftentimes shy due to their culture.
People sometimes forget to consider that yes, there will be instances that women are written or represented that one can call it sexist or misogynistic because people forget that Kishi comes and lives in a country where their views in women haven’t change much and they still follow norms that would make the 21st century woke person hyperventilate and scream, “misogynist! misogynist! sexist fucker!”
The women in the manga while there are those who stray from usual conventional roles, they reflect japanese society at that time. Women mostly wish to fall in love (shoujo), start a family, become mothers, and (this is what I always hate about these fucking feminist) but asian culture takes so much pride in motherhood, they do not see it as weak nor pitiful, they find a mother’s love to her children and family to be the most enduring, beautiful, sacrificial and powerful love. Mothers are not downgraded in Japan nor Asia in general. They are highly praised and respected. And this disparity of beliefs is why we have so much debates about women representation in manga written in the early 2000’s. I’m not saying that (wherever you come from) that your culture don’t value mothers and I’m sure there’s a lot of Asians out there who would have the opposite opinion but there’s a clear distinction on how much importance are given in such roles and not to mention, the influence of modern feminism has change the outlooks of many in wanting to be a mother or wife and I won’t necessarily find that a bad thing but it’s downright comical, ludicrous even, to perpetuate that women are weak simply because they are wives or mothers because you sound like a certain system and species of humanity that cause women to revolt in the first place, want a hint? It’s called MEN AND PATRIARCHY.
Anyway, I don’t think it’s bad to acknowledge that there have been some sexism in Naruto albeit, not entirely since we do see that Kishi does put women in high positions and make them powerful and at the same time, not make them lose their femininity, which just means that women can attain those roles it’s just rare or not common for them because in the first place, society doesn’t expect them to take on those roles in the first place. So, I don’t think that at that time Kishi even knows that he was being sexist or misogynistic because what he draw was simply the things he observed in his surroundings and culture and what he thought was “normal” and he probably didn’t see anything wrong. Now we can see that in Boruto, more of the women are in high positions, they work and at the same time manage the family, and have vital roles in the village and in the story.
All in all, there is a disparity in how men and women are represented in the manga and it’s not wrong for us to acknowledge those nor does it make the manga and the female characters any less interesting or powerful, if your read any classical book or any piece of media written between the 90’s to the early 2000’s you’re not gonna find a woman that isn’t in some way or another, not in a sexist role. Being understanding of these authors and how they are a product of their environment and culture does not make us tolerant, I’m not saying that it’s okay and we should give it a pass but to simply be understandable of it especially when writing an analysis and criticism about a story or manga because a piece of media is heavily influenced by the reality of that time when it’s written.
P.s, I also do agree on the argument that the manga is mainly geared to boys and likely that’s also one of the factors why the manga heavily emphasized the men. When making a product you really have to consider your target audience.
Sometimes I don't understand these people


How is a woman supporting a man, sexist? What is wrong with being supportive? That's not called sexism that's traditionalism, these people force their own views on others and it's infuriating sometimes.
Didn't Naruto say he likes Hinata?
Didn't Sasuke thank Sakura ?
Wasn't Shikamaru greatful when Temari came to his aid, didn't you see the fondness in his face
Most of the complaints there are untrue.
Wtf do they want Mikoto to do? Play ninja while her sons are infants. They want her to be a bad mother. What just to chase a career of death.
And no Sakura isn't a bad mom, she prioritizes Sarada over her work. We see her spend more time with Sadara and being a good mom.
I don't understand it,do they want a man in a woman's body? Sakura Hinata Kushina and Mikoto chose family over work because they are good women. They are selfless and love their families. And that Hinata is basically a pacifist.
Heck Tsunade who I reckon as the best of them all is still devoted to her love and family (Dan and Nawaki). After all she became Hokage for them if I remember correctly.
Btw is Mikoto even a Jonin?! I remember Sasuke saying fucking toddler Itachi is better than her in shuriken jutsu.
Kaguya is the origins behind chakra but it's Zetsu that causes all the problems. It was he who planned her resurrection and it was he who brainwashed the Uchiha.
Most of the story men were villains so when a woman is finally the villain it's suddenly sexist?
I don't get the sexism in here tbh
"Sexism" is another one of those annoying buzzwords that people just love to carelessly throw around and grossly misuse in this fandom, right up there with "misogyny", "homophobic" and "fangirl". Everything that person said is complete and utter unadulterated nonsense, everything. I was actually left dumbfounded by the sheer level of absurdity emanating from what I just read. I thought I had read it all in the Naruto fandom but fucking hell, there are literally no bounds to the amount of drivel people can spew in this fandom.

So apparently, every single female character was defined by her relationships to men, and most of them were also boy-crazy. I'm not gonna bother listing a plethora of female characters proving this statement to be idiotic, but it also shows how much of the female cast's characters this person is ignoring by claiming how all of them are defined by their relationships to men.
People love to say how someone like Sakura was "obsessed with Sasuke", despite the fact that by their logic, Naruto was even more obsessed with Sasuke. But then they'll try and counter by highlighting his other relationships with Jiraiya, Iruka etc. As if Sakura didn't have her own other relationships with Tsunade, Ino, Hinata etc. They think someone like Ino is "boy-crazy", as if she didn't have very prominent and platonic relationships with Shikamaru, Choji, Asuma and her father. The relationships she had with them were far more prominent and important than her romantic relationships, but this person will of course ignore all of that and insinuate that Ino was boy-crazy, as if the romantic relationships were all her character amounted to.

Apparently, Shikamaru not being shown to marry Temari during his Infinite Tsukuyomi dream is evidence that he actively dislikes her. God only knows how they reached that conclusion.
Sai ultimately didn't find Ino ugly, as evidenced by Shikamaru Hiden's conclusion.
The amount of times Naruto has praised and held Hinata in high regard... The blood promise during the Chuunin Exams, the "Proud Failure" speech, him reassuring her during the skirmish with the White Zetsus, the hand holding scene, the entirety of The Last...
Sasuke called Sakura annoying at the very beginning, but she became one of his most precious comrades, as he himself stated.
This person literally picks and chooses where the story just ends for certain characters because they just ignore all of the later developments for these characters and their relationships.

Another stupid generalisation, acting as if all men who showed some measure of interest in women were just like Jiraiya or Ebisu.

Not every scene depicting Naruto's crush on Sakura showed goofy immaturity and innocence, and his growing feelings for Hinata certainly didn't demonstrate that.
Lee's crush on Sakura wasn't dropped entirely, they were brought up again during his Infinite Tsukuyomi dream.
So because Obito retained his feelings for Rin into adulthood, it means he was still the same childish boy? So by this person's logic, you can only truly grow up once you've moved on from the romantic feelings you had as a child? That's the same ridiculous argument I hear about Sakura - she developed in so many different ways as a person, but because she held on to her feelings for Sasuke, all of her development doesn't matter and her character regressed according to these people. It's pathetic.

"Women were almost always healers and support", despite the fact that 57% of all the Medic-Nins shown in the series were male, yeah I did my research on that one.
"Women make up less than 1/3 of ninjas even at Genin level", no. The ratio is definitely in favour of the male characters, but it's not that large. But that's to be expected, it's a battle shounen catered to young boys, so of course there will be more male characters. The vast majority of battle shounens have noticeably more male characters - Bleach, One Piece, Dragon Ball, My Hero Academia, Demon Slayer and Jujutsu Kaisen just to name a few.
"Girls are almost all desperate to become wives and earn the attention of boys who don't even like them!", more blanket statements, more gross generalisations based on the early chapters of one or two characters, and more misinformation regarding boys who apparently didn't like them.

Who the hell ever said or even remotely implied that Fugaku "married into the main family"?
To answer your question about Mikoto though, she was indeed a Jonin, but Itachi being better than her at something ninja related as a toddler isn't surprising, he was a literal prodigy.

Minato was the Hokage because he earned that title due to his unprecedented skills and accomplishments during the Third Shinobi War. Just because Kushina was "borderline royalty" and from a prestigious clan doesn't mean that she had more of a right to be the Hokage. Was she more competent as a leader than Minato was? Did she have the same level of respect in the village that Minato did? Was she more capable of defending the village than Minato was? No. If she had done what Minato had done during the War, and she wasn't Kurama's Jinchuuriki, then perhaps Hiruzen would have chosen her as his successor instead. There was no sexism in the choice of Hokage for fuck's sake.
How the hell can this person exaggerate Kushina's status by claiming that she was "borderline royalty", while simultaneously severely downplaying Minato's prestige by ignoring everything he had done to earn the Hokage title, and not see the glaring double standard? They're complaining about how Kushina's credentials were apparently ignored, while they themselves were ignoring Minato's.

Wow, the reach here is insane. This person really just wants to feel victimised from non existent sexism. The vast majority of the "sins" committed in the series were done by men, but we'll just ignore that I guess, like they chose to ignore so many other things proving their claims to be preposterous.

Kishi has no idea the sexism is there because it's not fucking there. However, nowhere did he claim that the women have "epic girl power", and at least with regards to Sakura, he openly acknowledged the errors that he made when writing her as the heroine. I won't dignify this person's further bullshit about the men apparently hating their wives, their loveless marriages, men being forced to marry women they don't like and Kishi apparently blaming women for this. It's just a bunch of baseless bullshit, like everything else they said.
93 notes
·
View notes
Text
FEATURE: Japanese Myths And How They're Depicted In Horror Anime

No matter the time or place, the folklore and myths of the past always persist. The same can also be said for anime, especially when it comes to horror. Certain franchises, such as Shigeru Mizuki’s classic GeGeGe no Kitaro, have solidified the omnipresent status of traditional Japanese folk monsters in popular culture. Other series, such as Osamu Tezuka’s Dororo interpret traditional folklore in relation to historical periods and changing attitudes toward religion. More recently, series from the 2010s and 2000s, such as Bakemonogatari and Ghost Stories, interpret the classics with modern sensibilities. When it comes to stories with a penchant for horror, it would be far more surprising if they didn’t allude to a shared supernatural mythology — the ubiquity is the point.

Neko-Musume on her smartphone
The best horror always tries to do something new. While creatures like yōkai (a wide umbrella of supernatural entities) are well-known among English-speaking fans today thanks to series like Yokai Watch, these re-imaginings always tend to play fast and loose with fidelity. Wouldn’t it be boring if every vampire movie started and ended with Dracula? In a 2016 interview with The Comics Journal, veteran manga translator Zack Davisson emphasizes this important tendency to re-contextualize old folklore:
“It’s a tricky question, as it is impossible to say what is ‘actual folklore.’ Vampires bursting into flame is considered ‘authentic,’ but that actually comes from the films, not folkloric sources. Folklore evolves and [Shigeru] Mizuki is an important part of that evolution. If you trace them back, most yokai we know come from Toriyama Sekien, who also just made things up. In fact, I would say that making up yokai is part of the grand tradition of yokai! If you are a writer/artist working with yokai and not making up at least a few of your own, you are missing the point!”

The original spirit gun
So that’s all to say — there really is no such thing as a definitive, one-to-one story based on centuries of tradition. Yōkai, as endearing as they are, are also just one part of the equation. Long-running anime such as Folktales from Japan and fantasy series Inuyasha-continuation Yashahime: Princess Half-Demon either re-tell or draw inspiration from that folklore. But that’s beyond the scope of this piece. Whether it be adaptations of urban legends about school bathrooms or vengeful spirits, I hope this round-up helps any casual or long-time anime fan appreciate how these series reimagine supernatural traditions.
Fantastic Folklore: GeGeGe no Kitaro & Mononoke
The late Shigeru Mizuki’s most influential character, Kitaro, hardly needs any introduction. In his book Yokai Attack! The Japanese Monster Survival Guide, translator Matt Alt describes yōkai as “the attempts of the fertile human imagination to impose meaning and rationality on a chaotic, unpredictable, often difficult-to-explain world.” Many yōkai are quite strange and sometimes even comedic. Scholar-artists, such as the previously mentioned Toriyama Sekien, are largely credited with inspiring their uncanny visual representations, making them the perfect subject matter for an accessible series.

The tanuki plot world domination
The titular Kitaro himself is a half-human, half-yōkai one-eyed boy who travels between the human and spirit world to resolve monster-of-the-day conflicts with his friends. Although Mizuki’s Kitaro as we know it began serialization in 1960, Mizuki originally received permission to re-imagine the character from Masami Itō, who first created Kitaro in the 1930s in pre-war Japan. The most recent 2018 anime series re-establishes Kitaro in a modern setting, yet still adapts many of the most iconic stories. Characters such as Neko-Musume, based on volatile cat spirits called bakeneko, are updated with new designs while Kitaro mostly remains the same. Mizuki’s older creations, such as the jubokko (vampire tree) yōkai, are still featured alongside a new re-imagining of the “wall monster” nurikabe — inspired by the discovery of an Edo manuscript in 2007. The appeal of Kitaro isn’t so much the meticulous adherence to yōkai mythos, but rather Mizuki’s continual improvisation of the folklore-informed monster-making tradition.

The Medicine Seller
Beyond Kitaro, other series, such as 2006’s Mononoke, dedicate entire storylines to a wider category of ayakashi (sea-bound yōkai) and funayūrei (boat spirits) written by none other than Chiaki J. Konaka. Later episodes feature bakeneko and nue (chimera monsters), but with a twist. The term mononoke itself refers to a variety of yōkai specifically referring to vengeful spirits possessing people or things. When it comes to series taking a more “fantastical” approach to folklore, both Mononoke and Kitaro thankfully never dissolve into simple rogue galleries of monsters — their (mostly) human protagonists largely remain the heart of their chilling saga.
Horror-Historical: Osamu Tezuka’s Dororo

Lord Kagemitsu Daigo makes a pact with the demons (Source: Amazon)
In Anime and Its Roots in Early Japanese Monster Art scholar Zília Papp comments Mizuki’s “Kitaro characters became synonymous with yōkai in the postwar period, continuing to the present time” compared to his peers like Tezuka. But if Kitaro made yōkai big in comedic manga, then Tezuka’s short-lived Dororo manga drove this interest toward the historical context of the Sengoku Period, or the “warring states” era of feudal Japan.
Rather than depicting spirits as purely whimsical mischief-makers, Dororo’s inciting event is a feudal lord of the fictional Daigo clan forging a pact with 48 demons, who persist to hunt his son long after the pact is forged. In his feature The History Behind Osamu Tezuka’s Dororo, Marco Oliveros comments that by depicting yōkai during this period, Dororo draws inspiration from actual shifts in changing Buddhist attitudes toward these entities:
“One of the foremost examples of this change to yokai is the tengu. Wrathful and demonic, the avian creature tricked and assaulted Buddhist clerics and civilians alike, becoming characterized as the sworn enemy of Buddhism. The apparent hostility of these yokai to Buddhism makes their dark deals with Dororo's Daigo an unsurprising turn of events for the Sengoku Jidai era.”

The Amanojaku is captured and sealed inside a Buddhist temple (Source: Amazon)
Matt Alt’s 2016 translation of Japandemonium Illustrated: The Yokai Encyclopedias of Toriyama Sekien describes the tengu (mask-wearing entities usually depicted as half-man half-bird) as “deeply associated with the religion of Shugendō,” which originated during the Heian period; however they were depicted very differently in major Buddhist sects of the same era. Unlike solely “fantastical” stories of the supernatural without much acknowledgment to historical context, Dororo is interested in this context regarding capricious attitudes of spirits of people alike. Impressive malevolent entities such as kyūbi (nine-tailed foxes) also fight against Dororo’s protagonist, Hyakkimaru, typical of supernatural jidaigeki (period drama) horror stories set in feudal Japan.
However, Dororo also features lesser entities such as amanojaku (tiny, goblin-like demons). According to the influential illustrated encyclopedia Wakan Sansai Zue compiled by Sekien-predecessor Terajima Ryōan, amanojaku and tengu were described as paired descendants of the evil goddess Amanozako (literally "tengu god"). According to scholar Haruko Wakabayashi in The Seven Tengu Scrolls: Evil and the Rhetoric of Legitimacy in Medieval Japanese Buddhism, tengu were symbolically invoked in inter-personal and religious feuds amongst Buddhist sects during the Heian period. The amanojaku depicted in Dororo is minor. But with a (simplified) understanding of its affiliation with tengu’s pre-Heian origins and its subsequent disavowal by influential Buddhist sects, Dororo's amanojaku cameo is an undeniable nod toward its theme of “old ways” impacted by a "new" institutionalized status quo.

Hyakkimaru battles the nine-tailed fox spirit in its spectral form (Source: Amazon)
While the nine-tailed fox spirit is flashy, Dororo’s amanojaku ends up pathetically sealed inside a Buddhist temple. Ironically, the amanojaku trapping scene pans from the top of a Buddhist statue, ending with the cartoonish amanojaku crushed underneath to visually imply its irrelevancy. Dororo is a story about the cultural and religious tensions brewing during this violent episode in history — making Hyakkimaru’s journey one that doesn’t simply depict supernatural folkloric tradition in stasis, but as something always under complicated socio-political stakes.
Modern Ghoul School: Ghost Stories & Bakemonogatari
What do you do if you can’t solve your evil spirit problems with a sword? For the most part, classics like Kitaro and Dororo take place in the past, or at least worlds very unlike our own. A traveling demon slayer never has to deal with student council or smartphones.
In a previous article, From Bakeneko to Bakemonogatari, I discussed all the possible lineages of the catgirl character archetype. In that piece, I claimed one of the more accurate representations of the bakeneko today was Bakemonogatari’s Tsubasa Hanekawa’s cat spirit-possessed alter-ego. It’s not simply because she is a supernatural catgirl, but rather her portrayal was obviously informed by the wider context of pre-existing bakeneko mythos. Is it possible for a “modern-day” series to tackle yesterday’s folktales while still preserving the uncanniness of the past?
The spirits possessing Bakemonogatari’s cast, referred to as “oddities,” all nearly function like vengeful mononoke spirits. For example, Bakemonogatari’s first arc, Hitagi Crab, features a crab “oddity” haunting classmate Hitagi Senjougahara. The existence of heikekani (face-shaped crabs allegedly the spirits of drowned Heike warriors from the Sengoku Period), might be a parallel, considering the arc’s theme of unresolved conflict. Another arc, Suruga Monkey, features an “oddity” taking the form of a beastly paw growing on classmate Kanbaru Suruga’s arm. Senjougahara and Suruga's crab/monkey relationship can be read as alluding to the well-known Buddhist tale “The Monkey and the Crab.” According to The National Gallery of Art on its 2019 The Life of Animals in Japanese Art exhibit, the monkey and crab are usually depicted as friends, then compete until they either make amends or resolve their conflict. Often the subject of artistic interpretation, it’s no surprise this tale found its way into anime as a metaphor for teen drama.

The kids scan a talisman and e-mail it to exorcise internet demons. Yes, this really happens.
In comparison, the 2000 series Ghost Stories is best known to English-speaking audiences for being an edgy comedy. However, its original source material, a book series titled Gakkō no Kaidan (School Ghost Stories), is more akin to a heavily researched Goose Bumps. Written by folklore scholar Toru Tsunametsu, the series showcases various urban myths and monsters, most famously “Hanako” a ghost girl who haunts school bathrooms. A 2014 NPR piece describes the most popular version of Hanako being a schoolgirl in WWII “using the bathroom when a bomb fell on top of the building.” Although Hanako gained enough popularity from the books to warrant her own spin-off anime series in 1994, she only makes a handful of cameos in the 2000 series. Entities like the previously mentioned amanojaku also appear, alongside shinigami (death gods) depicted in many other anime.
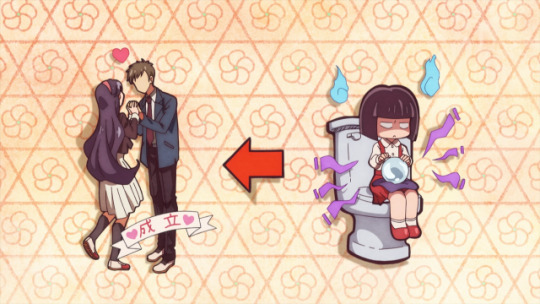
How to channel your ghost powers for success (Source: Funimation)
Hanako, because of her relatively modern backstory, is just as ubiquitous. Versions of Hanako appear in an episode of the 2018 Kitaro and most recently in the 2020 series Toilet Bound Hanako-kun. Tsunametsu currently edits the Folklore Society of Japan’s official academic journal, no doubt a testament to his priceless contributions to folklore representation in anime.
Who You Gonna Call?
There’s no way to tell the same ghost story twice. With such a layered history, contemporary anime have a nearly endless well of folkloric material to pull from. Recent series like the hit Demon Slayer: Kimetsu no Yaiba and Toilet Bound Hanako-kun prove that fans will never get enough of the supernatural, just as long as things stay fresh.

Hanako politely warns the ghost-hunting kids
Long live artistic liberty and specters trying to watch you pee.

Blake P. is a weekly columnist for Crunchyroll Features. His twitter is @_dispossessed. His bylines include Fanbyte, VRV, Unwinnable, and more. He'd like a tiny yōkai cat.
Do you love writing? Do you love anime? If you have an idea for a features story, pitch it to Crunchyroll Features!
By: Blake Planty
25 notes
·
View notes