#How Does Net Metering Work With Solar?
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Solar Energy Consultants in the USA: A Comprehensive Guide

As the demand for renewable energy continues to rise, solar energy has emerged as one of the most viable and sustainable sources of power. Solar energy consultants play a crucial role in helping businesses and homeowners transition to solar energy solutions. In the USA, these professionals provide expertise in system design, financial analysis, regulatory compliance, and installation processes. This article explores the importance of solar energy consultants, their roles, and how to choose the right consultant for your needs.
The Role of Solar Energy Consultants
Solar energy consultants in USA are industry experts who guide clients through the entire process of adopting solar energy. Their responsibilities include:
Assessing Energy Needs: Consultants evaluate a client’s current energy consumption and identify the best solar solutions to meet their needs.
Site Evaluation: They conduct a thorough analysis of the location, considering factors like roof space, shading, and sun exposure.
System Design and Recommendations: Based on the evaluation, consultants propose the most efficient and cost-effective solar panel systems.
Financial Analysis and Incentives: They help clients understand the cost savings, return on investment, and available tax credits or incentives.
Regulatory Compliance: Consultants ensure that the installation complies with local, state, and federal regulations.
Installation Support: While they may not install the system themselves, they work closely with certified solar installers to ensure proper setup.
Post-Installation Monitoring: Some consultants offer ongoing support to monitor energy production and optimize system performance.
Why Hire a Solar Energy Consultant?
Many individuals and businesses consider hiring a Solar energy consultants in USA because:
Expert Guidance: Navigating the solar industry can be complex, and consultants provide expert knowledge to simplify the process.
Cost Savings: Consultants help maximize financial benefits by identifying rebates, incentives, and the best financing options.
Time Efficiency: They handle paperwork, permits, and utility company negotiations, saving clients time and effort.
Optimal System Design: A well-designed solar system ensures maximum efficiency and long-term savings.
How to Choose the Right Solar Energy Consultant
When selecting a solar energy consultant, consider the following factors:
1. Experience and Credentials
Look for consultants with a proven track record in the solar industry. Certifications from organizations like the North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners (NABCEP) indicate expertise.
2. Customer Reviews and Testimonials
Check online reviews and testimonials from past clients to gauge the consultant’s reliability and service quality.
3. Knowledge of Incentives and Policies
A knowledgeable consultant should be well-versed in federal, state, and local incentives, such as the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and net metering policies.
4. Transparent Pricing
Ensure the consultant provides clear pricing and does not have hidden fees.
5. Comprehensive Services
Some consultants only offer assessments, while others provide end-to-end services, including post-installation monitoring. Choose one that fits your needs.
Top Solar Energy Consulting Firms in the USA
Several consulting firms in the USA specialize in solar energy solutions. Some of the top names include:
1. Sunrun
Sunrun offers solar consulting and installation services nationwide, helping homeowners switch to solar with flexible financing options.
2. Solar Energy World
This company provides expert consultation and high-quality solar panel installations with a focus on sustainability.
3. Momentum Solar
Momentum Solar is known for its personalized approach, offering in-depth consultations to design the best solar solutions.
4. Palmetto Solar
Palmetto Solar specializes in helping customers navigate solar incentives and optimize their energy savings.
5. Tesla Energy
Tesla Energy offers solar panel and solar roof installations, along with battery storage solutions.
Future Trends in Solar Energy Consulting
The solar industry continues to evolve, and solar energy consultants must stay updated with the latest trends. Some key trends include:
Advancements in Solar Technology: Innovations such as bifacial panels, solar shingles, and battery storage solutions are reshaping the industry.
Increased Adoption of AI and Data Analytics: AI-powered tools are improving energy predictions and system optimization.
Community Solar Projects: More consultants are focusing on community solar initiatives, allowing multiple households to share solar energy benefits.
Government Policy Changes: As federal and state policies evolve, consultants must remain informed about new incentives and regulations.
Conclusion
Solar energy consultants in the USA play a vital role in helping individuals and businesses transition to clean and sustainable energy. By providing expert advice, financial analysis, and regulatory support, they ensure a smooth and cost-effective solar adoption process. Whether you are a homeowner looking to reduce energy bills or a business aiming for sustainability, hiring a solar energy consultant can be a valuable investment in a greener future.
0 notes
Text
Electric Bill with Solar Panels: How to Save Money on Energy Costs
As more homeowners switch to renewable energy, understanding the impact of solar power on electricity costs is essential. One of the key benefits is reducing your electric bill with solar panels. But how much can you really save? Let’s explore how a electric bill with solar panels is calculated, the factors influencing savings, and what to expect after installation.
How Does an Electric Bill with Solar Panels Work?

A electric bill with solar panels depends on energy consumption, solar production, and utility policies. Solar panels generate electricity during the day, reducing the amount of power drawn from the grid. Excess energy can be sent back to the grid for credits, lowering overall costs.
Factors Affecting Your Electric Bill with Solar Panels
Energy Consumption: The more electricity you use, the more significant the savings from a electric bill with solar panels.
Solar System Size: A larger system produces more energy, potentially eliminating your electric bill with solar panels.
Net Metering Policies: Some utilities offer credits for surplus power, reducing a electric bill with solar panels further.
Time-of-Use Rates: Using stored solar power during peak hours lowers costs on a electric bill with solar panels.
Battery Storage: Storing excess energy helps maximize savings on a electric bill with solar panels.
How Much Can You Save on Your Electric Bill with Solar Panels?
On average, homeowners see a 50-90% reduction in their electric bill with solar panels. Factors like location, system size, and local electricity rates determine overall savings. With tax incentives and rebates, the investment in solar panels can pay off within a few years.
Steps to Reduce Your Electric Bill with Solar Panels
Optimize Energy Usage: Running appliances during sunlight hours maximizes benefits on your electric bill with solar panels.
Invest in Energy-Efficient Appliances: Lower energy use further decreases your electric bill with solar panels.
Monitor Energy Production: Solar monitoring systems help track efficiency and savings on your electric bill with solar panels.
Consider Battery Storage: Storing solar energy for nighttime use further minimizes your electric bill with solar panels.
Conclusion
A electric bill with solar panels offers significant cost savings and energy independence. With the right setup, you can dramatically cut down expenses while contributing to a greener future. If you’re considering making the switch, now is the best time to start reducing your electric bill with solar panels and enjoying long-term financial benefits.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Solar Panels 101: Your Guide to Renewable Energy Savings

Tired of high electricity bills? Want to help the planet? Solar panels could be the answer. More folks are switching to solar, and it's easy to understand why. But before you jump in, understand the basics. This guide will get you started.
Understanding Solar Panel Basics
Solar panels, also called photovoltaics (PV), convert sunlight into electricity. It's like magic, but it's science! But how does it work? Let's break down the magic.
How Solar Panels Work: The Science of Photovoltaics
The photovoltaic effect is key. Sunlight is made of tiny particles called photons. These photons hit the solar panel. Solar panels contain silicon, a semiconductor material. When photons strike the silicon, they knock electrons loose. These electrons flow through an electrical circuit, creating electricity.
[Diagram or Illustration of the Photovoltaic Effect]
Types of Solar Panels: Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin-Film
There are different solar panels. Monocrystalline panels are made from a single crystal of silicon. Polycrystalline panels are made from many silicon fragments. Thin-film panels use different materials applied to a surface.
Monocrystalline panels are generally the most efficient. They also tend to be the most expensive. Polycrystalline panels are less efficient but cheaper. Thin-film panels are the least efficient but also the most flexible. They can be a good choice for curved surfaces. Monocrystalline looks sleek and black. Polycrystalline has a blue, speckled appearance. Thin-film panels can vary in color and transparency.
Key Components of a Solar System: Beyond the Panels
Solar panels are not the only component. Inverters are also key. They convert the DC electricity from the panels to AC electricity, which powers your home. Racking systems mount the panels on your roof or the ground. Batteries store excess energy for later use, like at night.
Assessing Your Energy Needs and Solar Potential
How much energy do you use? Is your home a good spot for solar? Let's figure it out.
Calculating Your Energy Consumption: Understanding Your Bills
Your utility bill shows how much energy you use each month. Look for the "kWh" (kilowatt-hours) used. Add up your monthly usage for a year. Divide by 12 to get your average monthly consumption. Divide that by 30 (days) to find your average daily consumption.
Evaluating Your Roof: Orientation, Angle, and Shading
South-facing roofs are best. They get the most sunlight throughout the day. The tilt angle of your roof matters too. An angle equal to your latitude is often ideal. Shade from trees or buildings will hurt solar panel production.
Solar Potential Maps and Online Tools
Online tools can help you estimate solar potential. Google's Project Sunroof is one option. These tools use satellite data to assess your roof's sunlight exposure. They can estimate how much energy you could generate with solar panels.
Navigating Solar Panel Costs and Incentives
Solar panels can cost a lot. But incentives can lower the cost. Let's explore the money side.
Initial Investment: Panel Costs, Installation, and Permitting
A typical solar panel system can cost $15,000 to $25,000. Costs vary depending on panel quality, system size, and installation complexity. Roof complexity and accessibility can affect install costs. You'll also need permits, which add to the overall price.
Federal Tax Credits and State Incentives: Maximizing Your Savings
The federal solar tax credit (ITC) can save you money. It can cover 30% of the system's cost. Many states also offer rebates and incentives. Check your state's energy website for details.
Understanding Net Metering: Getting Credit for Excess Energy
Net metering allows you to get credit for excess energy. When your solar panels generate more electricity than you need, it gets sent back to the grid. Your utility company will credit your bill for this excess power.
Choosing the Right Solar Panels and Installer
Choosing the right Solar Panels and installer matters. Here's how to make smart choices.
Panel Efficiency and Warranty: What to Look For
Panel efficiency indicates how much sunlight a panel turns into electricity. Look for panels with high efficiency ratings. A strong warranty protects your investment. Pay attention to both product and performance warranties. Performance warranties guarantee a certain level of output over time.
Researching Solar Installers: Licensing, Reviews, and Experience
Check that your installer is licensed and insured. Read online reviews on sites like Yelp and Google. Ask for references from past customers. Experience matters. Look for installers with a proven track record.
Getting Multiple Quotes: Comparing Offers and Financing Options
Get quotes from at least three installers. Compare their prices, equipment, and warranties. Explore different financing options. Loans, leases, and power purchase agreements (PPAs) are common.
Maintaining Your Solar Panel System
Solar panels don't need much maintenance. But some upkeep helps. Let's learn how to keep them running well.
Cleaning and Inspections: Keeping Your Panels Performing Optimally
Clean your solar panels a couple times a year. Dust and dirt can reduce their output. You can clean them yourself with a hose and soft brush. Or hire a professional cleaning service. Visually inspect your panels regularly. Look for any damage or debris.
Monitoring System Performance: Identifying Potential Issues
Most solar systems have monitoring apps or websites. Use these to track your system's performance. If you notice a sudden drop in power production, it could indicate a problem.
Conclusion
Solar panels can save you money and help the environment. It's important to plan carefully and do your research. Take the next step toward solar energy. Consider contacting a local installer for a free quote.
0 notes
Text
What Are PV Plan Sets? A Beginner’s Guide
Introduction
As the demand for solar energy continues to grow, so does the need for proper documentation and approvals to ensure safe and efficient installations. One of the most crucial components of a solar project is a PV plan set. Whether you're a homeowner considering solar power or a contractor working on an installation, understanding PV plan sets is essential. In this guide, we’ll explain what PV plan sets are, their purpose, and their importance in solar installations.
What Is a PV Plan Set?
A PV (photovoltaic) plan set is a detailed set of documents required for the design, approval, and installation of a solar power system. It includes technical drawings, calculations, and specifications that outline how the solar system will be installed on a property. These documents are essential for obtaining permits from local authorities and ensuring the system complies with building codes and safety regulations.
Components of a PV Plan Set
A complete PV plan set typically includes the following elements:
Cover Page – Contains project details such as the property address, system size, and installer information.
Site Plan – Shows the layout of the solar panels on the property, including their placement on the roof or ground.
Electrical Diagram – Provides a schematic representation of the electrical components, wiring, and connections.
Structural Analysis – Ensures that the roof or mounting structure can support the solar panels safely.
Line Diagrams – Illustrates how the solar system integrates with the main electrical panel and utility grid.
Compliance Documents – Includes information on fire safety, NEC (National Electrical Code) compliance, and manufacturer specifications.
Purpose of a PV Plan Set
A PV plan set serves multiple important purposes in the solar installation process:
1. Permit Approval
Before installing a solar energy system, you must obtain a permit from the local building department. A well-prepared PV plan set ensures that your application is approved quickly, reducing project delays.
2. Safety and Compliance
PV plan sets help ensure that the system adheres to national and local electrical and building codes. Compliance with standards such as NEC and UL certification prevents electrical hazards and structural failures.
3. Efficient Installation
A clear and precise PV plan set helps installers understand how to set up the system correctly, minimizing errors and ensuring optimal performance.
4. Grid Connection Approval
If your solar system is designed for net metering or grid-tied operation, the utility company will require a PV plan set to approve the connection.
Importance of PV Plan Sets in Solar Installations
Streamlining the Permitting Process
A complete and accurate PV plan set helps expedite the approval process, allowing projects to move forward without unnecessary revisions or resubmissions.
Avoiding Costly Mistakes
Errors in design or non-compliance with regulations can lead to rejected permits or required modifications. A well-structured PV plan set prevents these setbacks, saving time and money.
Ensuring Long-Term Performance
Proper planning and documentation contribute to a more reliable and efficient solar energy system, maximizing energy production and return on investment.
Conclusion
PV plan sets are an essential part of any solar installation, ensuring regulatory compliance, safety, and efficiency. Whether you’re a solar professional or a property owner looking to go solar, understanding the role and importance of PV plan sets can help streamline the process and lead to a successful installation. Investing in a high-quality PV plan set is a crucial step toward harnessing clean and sustainable energy for years to come.
If you’re planning a solar project, make sure to work with experienced professionals who can provide a comprehensive PV plan set tailored to your needs!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Solar System for Home in India Government Subsidy
The Indian government is taking strides towards renewable energy with its revolutionary PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana. This scheme, launched in February 2024, empowers homeowners to install rooftop solar systems with attractive financial benefits. By providing subsidies and free electricity, the program addresses both rising energy costs and the environmental need for sustainable solutions. Here's everything you need to know about the scheme, its benefits, eligibility, and how to apply.

What is PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana?
The PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana is a plan by the government to help millions of people use solar power at home. With this program, you can set up solar panels on your roof to make your own electricity. Not only does this cut your electricity bills, but you even get free energy each month!
Also, if you make extra electricity, you can sell it to the power company to earn some money. This plan helps protect the Earth by using clean energy, and it is also good for your wallet.
Benefits of PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana
Here are the amazing PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana benefits that make this program exciting for families.
Free Energy – You can get free power every month for your home.
Savings – Spend less money on electricity by using the power from the sun.
Better for Nature – Solar energy is clean and helps keep Earth safe for the future.
Earn Money – If your solar panels make more energy than you need, you can sell it to make extra income.
Create Jobs – The program also helps create jobs for people who work in solar panel installation and maintenance.
Who Can Join the PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana?
Before you start your PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana registration, make sure you meet these simple rules:
You must live in India.
You should own your home or have permission to install solar panels.
You must have an electricity connection.
You should not already get help for solar panels under another program.
This program is meant to help families, especially those with smaller incomes.
How to Sign Up for PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana
Joining this program is easy! Just follow these steps to get started:
Go Online – Visit the official website pmsuryaghar.gov.in.
Sign Up – Fill out your details like your state, your electricity company, and your contact info.
Approval – Wait for the power company to check if your house is a good fit for solar panels.
Pick a Vendor – Choose an approved installer to set up your solar panels.
Set Up – Once everything is installed, apply for the net meter to track your energy use and savings.
After everything is ready, you can start enjoying your solar-powered home!
Tips to Make the Most of Solar Energy
Here are some easy tips to help you enjoy solar energy even more:
Find the Best Spot – Make sure your roof is clear and gets lots of sunlight.
Keep It Clean – Clean your solar panels often so they work well.
Save Power – Use appliances that save energy to reduce your usage even more.
Check Your Energy – Track how much energy you make and use with the net meter.
Why Solar Power is Important
Solar energy is not just good for savings—it’s also good for the planet. By using solar power, we use less fuel that pollutes the air. This helps India move closer to clean, sustainable energy.
The PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana makes it super easy for families to start using solar power. It’s a win for you, your budget, and our Earth!
Start Now!
Think about a future where your home runs on sunlight, and your energy bills are super low. Don’t wait! Start your PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana registration today and enjoy these benefits for years to come.
Switching to solar power helps your family and makes a big difference for India’s future. It’s time to be a part of this bright change!
#solar panel installation#commercial solar panels installation#aesthetic#animals#residential solar panels installation
0 notes
Text
What is Net Metering, and How Does It Work?
The innovative idea of net metering enables people and companies with solar panel installations to optimize their energy savings. Fundamentally, net metering allows solar energy users to credit the grid with surplus electricity produced by their installations. They are compensated for this excess energy with credits that can be used to future electricity costs.
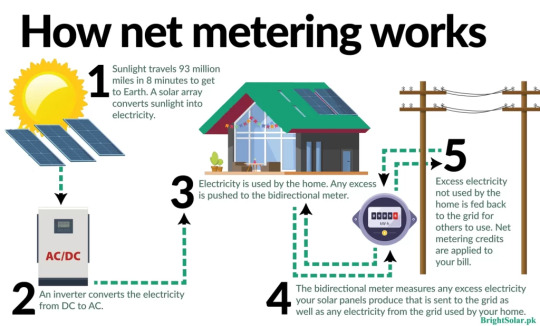
Benefits of Net Metering
Cost Savings: The ability of net metering to lower electricity prices is one of its biggest benefits. Only the "net" amount of electricity used—which is determined by subtracting the energy supplied back into the grid—is paid for by users. Energy Efficiency: Sustainable behaviors and effective energy consumption are promoted by net metering. You may lessen your reliance on fossil fuels and your carbon footprint by using solar electricity. Grid Support: Especially during periods of high demand, excess energy injected into the grid aids in stabilising the energy network.
Net Metering in India
As part of its renewable energy objectives, the Indian government has put rules in place to encourage net metering. Regarding the installation and advantages of net metering, each state has its own rules and regulations. For instance, Maharashtra makes solar installations more feasible by providing alluring incentives for both business and residential solar users.
Why Consider Net Metering?
Net metering is a win-win solution for those investing in renewable energy. It reduces electricity costs, provides energy independence, and contributes to a greener planet. With state and central government support, adopting net metering has never been more accessible.
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Roof Solar Solutions for Your Energy Needs

What is Roof Solar?
Roof solar refers to solar panels installed on the roofs of residential, commercial, or industrial buildings. These systems capture sunlight and convert it into usable electricity, providing a clean and renewable energy source.
Benefits of Roof Solar Systems
Cost Savings
Environmental Impact
Energy Independence
Property Value
How Does a Roof Solar System Work?
Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
Inverter: Converts DC electricity into alternating current (AC) for household or industrial use.
Battery Storage (Optional): Stores excess energy for use during nighttime or cloudy days.
Net Metering: Allows you to sell surplus electricity back to the grid, reducing overall costs.
Choosing the Best Roof Solar System
Type of Panels:
Monocrystalline: High efficiency and sleek appearance.
Polycrystalline: Cost-effective and durable.
Thin Film: Lightweight and flexible for unique roof designs
System Size:
Assess your energy consumption to determine the required capacity.
Consult with professionals to optimize system performance.
Installation Company:
Choose certified and experienced installers.
Verify warranties and after-sales services.
Steps to Install Roof Solar Panels
Site Assessment:
Analyze roof condition, angle, and sunlight exposure.
System Design:
Tailor the solar system to your energy needs and roof specifications.
Permits and Approvals:
Obtain necessary permissions from local authorities.
Installation:
Secure the panels, connect inverters, and integrate with your electrical system.
Testing and Monitoring:
Ensure proper functioning and monitor performance regularly.
Maintenance Tips for Roof Solar Systems
Regular Cleaning: Remove dust and debris to maintain efficiency.
Periodic Inspections: Check for loose wires or damaged panels.
Monitor Performance: Use apps or monitoring systems to track energy output.
Professional Servicing: Schedule annual maintenance with certified technicians.
Cost of Roof Solar Systems
The cost of installing a roof solar system varies based on factors such as:
Type and number of panels.
Installation complexity.
Battery storage options.
Government incentives.
Why Choose Roof Solar for Your Energy Needs?
Investing in roof solar is a long-term commitment to savings and sustainability. With advancements in solar technology and increasing affordability, now is the best time to switch to clean energy.
FAQs About Roof Solar Systems
How long do solar panels last? Most panels come with a 25-year warranty but can last up to 30-35 years with proper maintenance.
Can I install roof solar on a flat roof? Yes, panels can be angled appropriately on flat roofs for optimal sunlight exposure.
What if my roof is shaded? Consider microinverters or trimming surrounding trees to maximize sunlight.
Conclusion
Roof solar systems are an excellent way to reduce energy costs, promote sustainability, and gain energy independence. Whether you’re a homeowner or a business owner, switching to solar is a step toward a greener future.
0 notes
Text
What is an On-Grid Solar System? A Complete Overview
As the world shifts toward renewable energy sources, solar power has become a popular choice for both residential and commercial use. Among the different types of solar systems, the On-Grid Solar System stands out due to its efficiency and ability to integrate with the public electricity grid. In this article, we will explore what an on-grid solar system is, how it works, its benefits, and other essential details to help you understand this innovative energy solution.
What is an On-Grid Solar System?
An On-Grid Solar System, also known as a Grid-Tied Solar System, is a type of solar power system that is connected to the public electricity grid. Unlike off-grid systems, which are standalone and do not require an external power source, an on-grid system generates electricity and sends any excess power back to the grid. It relies on the grid to provide power during times when the solar system is not generating enough energy, such as at night or on cloudy days.
The system typically consists of the following components:
Solar Panels: These convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
Inverter: This device converts the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is used in homes and businesses.
Grid Connection: The system is connected to the utility grid, allowing it to send excess energy back to the grid or draw power when needed.
Metering System: A net meter records the energy produced by the solar panels and the energy consumed from the grid, often enabling net metering (explained below).
How Does an On-Grid Solar System Work?
Solar Energy Generation: During the day, solar panels absorb sunlight and convert it into DC electricity.
Inverter Conversion: The DC electricity is then sent to an inverter, which converts it into AC electricity for household or business use.
Energy Consumption: The AC electricity powers appliances, lights, and devices in your home or business.
Excess Energy: If the solar system generates more electricity than you need, the excess power is sent back to the grid. This can be credited to your account, depending on your utility provider's net metering policy.
Grid Support: At night or during cloudy periods when the solar system isn’t producing enough energy, the system automatically draws power from the grid to meet your electricity needs.
Benefits of an On-Grid Solar System
Cost Savings: One of the biggest advantages of an on-grid solar system is the potential for reduced electricity bills. By generating your own solar power and feeding excess energy back to the grid, you can earn credits or offset your energy consumption, lowering your overall electricity costs.
Environmentally Friendly: On-grid solar systems help reduce your carbon footprint by relying on clean, renewable energy from the sun. By using solar power, you reduce your reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to a cleaner environment.
No Battery Storage Required: Unlike off-grid systems that require expensive battery storage, on-grid systems don't need batteries. The electricity grid itself serves as a virtual storage system, making on-grid systems more affordable and simpler to install.
Easy Integration with the Grid: On-grid solar systems seamlessly integrate with the existing electricity grid, allowing you to use the grid as a backup power source when solar energy production is low.
Net Metering: Many regions offer net metering, which allows you to earn credits for the surplus energy you send to the grid. These credits can offset the cost of electricity you draw from the grid during times when your solar system isn't producing enough power.
Scalability: On-grid solar systems can be expanded as needed. If you require more energy in the future, additional solar panels can be added to the system to increase capacity.
Key Considerations for Installing an On-Grid Solar System
Location: On-grid solar systems are ideal for areas with reliable access to the electricity grid. The system relies on grid power when solar generation is insufficient, so being connected to a stable grid is essential.
Utility Provider Policies: Net metering policies and rates vary by region and utility provider. It's important to understand the net metering agreement with your local utility before installing an on-grid system.
Electricity Demand: The size of your on-grid system should be matched to your electricity consumption needs. A professional solar installer can assess your energy usage and recommend an appropriate system size.
Grid Stability: On-grid solar systems depend on the grid's reliability. In the event of a power outage, your solar system will shut down for safety reasons, as it cannot feed electricity into a grid that is not functioning.
Conclusion
An On-Grid Solar System is a highly efficient and cost-effective way to generate renewable energy while staying connected to the public electricity grid. With the ability to reduce energy bills, provide environmental benefits, and offer easy scalability, on-grid solar systems are a great choice for homeowners and businesses looking to transition to cleaner energy. By understanding how it works and its advantages, you can make an informed decision about whether an on-grid solar system is the right choice for your energy needs.
If you are considering an on-grid solar system, it is essential to consult with a professional solar installer to ensure the system is properly designed and integrated with your energy requirements and local grid regulations.
0 notes
Text
Solar Power System for Homes: A Sustainable Energy Solution

In today's world, where climate change and environmental concerns are becoming increasingly prominent, finding alternative energy sources is essential. Among the most popular and effective solutions is solar power. Solar power systems for homes are a sustainable, cost-effective, and eco-friendly way to meet a household's energy needs. This article will explore the benefits, components, installation process, and costs associated with solar power systems for residential use.
What is a Solar Power System?
A solar power system is a setup that converts sunlight into electricity through solar panels. These panels are made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells, which capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. The system consists of several key components: solar panels, an inverter, batteries (optional), and a monitoring system. The energy produced can be used to power everything from lights and appliances to heating and air conditioning in your home.
How Does a Solar Power System Work?
Solar Panels: Solar panels are the most prominent component of a solar power system. When sunlight hits the panels, the photovoltaic cells inside generate a flow of electricity.
Inverter: Solar panels produce direct current (DC) electricity. However, most household appliances use alternating current (AC). The inverter converts the DC electricity into AC electricity, making it usable for everyday purposes.
Batteries (optional): Some homeowners choose to install batteries to store excess energy generated by the solar panels. This allows them to use solar power even when the sun isn't shining, like during nighttime or cloudy days.
Monitoring System: A monitoring system tracks the performance of the solar power system, helping homeowners see how much energy is being produced, consumed, and stored.
Grid Connection: In many cases, homes with solar systems are connected to the electrical grid. If the solar panels produce more energy than the household needs, the excess power is fed back into the grid. Some regions offer net metering, where homeowners get credit for the excess energy they supply.
Benefits of Solar Power Systems for Homes
Cost Savings: One of the biggest advantages of solar power is the potential for long-term cost savings. Once the system is installed, the electricity generated is essentially free. While the initial investment can be significant, tax incentives and rebates can reduce the upfront cost. Over time, homeowners can see a substantial reduction in their electricity bills.
Environmentally Friendly: Solar energy is a clean, renewable resource. By choosing solar power, homeowners reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, decrease their carbon footprint, and contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. This is an essential step in combating climate change and preserving the environment.
Energy Independence: With a solar power system, homeowners can reduce or eliminate their dependence on the electrical grid. This can be particularly beneficial in areas where electricity prices are high or where power outages are frequent. Solar power systems give homeowners control over their energy production.
Increased Property Value: Homes with solar power systems tend to have higher property values. Buyers are often attracted to homes with solar panels due to the potential for lower energy costs and sustainability.
Government Incentives: Many governments offer incentives to encourage the adoption of solar energy. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, grants, and net metering programs. These financial incentives can significantly offset the installation cost.
Components of a Solar Power System
Solar Panels: The heart of the system, solar panels are made up of photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into electricity. They come in various types, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film, each offering different efficiencies and costs.
Inverter: The inverter is crucial for converting DC electricity from the panels into AC electricity that can be used in your home. There are two main types of inverters: string inverters and microinverters. String inverters are typically used in large systems, while microinverters are ideal for homes with shading issues or roofs with multiple orientations.
Batteries: Batteries are not always necessary, but they can be helpful for storing excess solar energy. This stored energy can be used when sunlight is not available, such as at night or on cloudy days. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used for solar power storage.
Mounting and Racking System: The panels need to be securely mounted on your roof or ground area. The mounting system ensures the panels are at the right angle for maximum sun exposure.
Charge Controller (optional): In systems with batteries, a charge controller ensures the batteries are charged correctly and prevents overcharging.
Monitoring System: A solar monitoring system tracks your system’s performance and energy production. It can be accessed via an app or web portal and allows homeowners to optimize energy usage and ensure the system is functioning efficiently.
Steps to Install a Solar Power System
Assess Your Home's Energy Needs: Before installing a solar power system, evaluate your household's energy consumption. This helps determine how many solar panels you need and the system's size.
Get a Professional Assessment: A solar installer can assess your roof's condition, the amount of sunlight it receives, and other factors that influence energy generation. They will provide a proposal with system size, costs, and expected savings.
Obtain Permits and Approvals: Most regions require permits for solar installations. Your installer will handle the necessary paperwork, including permissions from local authorities and utility companies.
Installation: The installer will mount the solar panels, set up the inverter, and connect the system to the grid (if applicable). This process typically takes a few days to complete.
Inspection and Activation: After installation, a final inspection by a licensed professional ensures the system is working correctly. Once approved, the system is activated, and you can start producing your own electricity.
Costs of Solar Power Systems
The cost of installing a solar power system can vary depending on several factors, such as the size of the system, the type of panels, and the complexity of installation. On average, the cost can range from $10,000 to $30,000 before incentives. However, government incentives can reduce the overall cost by up to 30%.
Despite the initial cost, the return on investment (ROI) for solar power is impressive. Homeowners can expect to see a reduction in their electricity bills, and many systems pay for themselves in 5 to 10 years. After that, the energy generated is essentially free.
Conclusion A solar power system for your home offers numerous benefits, including lower electricity bills, environmental sustainability, and energy independence. While the initial cost may seem high, the long-term savings and potential government incentives make it a smart investment for homeowners looking to reduce their carbon footprint and embrace renewable energy. As technology advances and installation costs continue to decrease, solar power will become an increasingly accessible and popular option for homeowners worldwide.
More info - +1(818) 650 1464 or [email protected]
1 note
·
View note
Text
Net Metering Rates For Solar Buyback
Solar buyback rates, also known as net metering rates, refer to the price per
kilowatt-hour (kWh) that utility companies pay homeowners for the excess electricity generated by their solar panels. These rates vary widely based on the utility provider and the chosen plan.
Why Are Solar Buy Back Rates Important?
Solar buyback rates are crucial because they directly impact the return on investment (ROI) for your solar energy system. Higher buyback rates mean more savings on your electricity bill and a shorter payback period for your solar installation.
Best Solar Buy Back Rates in Texas
1. Green Mountain Energy
Buy Back Rate: Up to 11.1 cents per kWh
Green Mountain Energy offers one of the highest solar buyback rates in Texas. Their Solar Buy Back program credits customers for the excess solar energy they produce at he same rate they pay for electricity. This means significant savings and quicker ROI for solar panel owners.
Related Source: Green Mountain Energy Solar Buy Bac
How Does Green Mountain Energy Work?
Green Mountain Energy is a company dedicated to providing clean, renewable energy options to consumers. Their primary goal is to reduce the environmental impact of energy consumption by offering alternatives to traditional fossil fuel-based energy. Here’s a detailed look at how Green Mountain Energy works and examples of their offerings.
1. Energy Sourcing
Renewable Energy Sources: Green Mountain Energy sources electricity from renewable energy resources such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power. These sources generate electricity with minimal environmental impact compared to fossil fuels.
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): The company enters into agreements with renewable energy producers to purchase large amounts of clean energy. This helps support the growth and sustainability of renewable energy projects.
2. Energy Plans
Green Mountain Energy offers a variety of energy plans tailored to different consumer
needs, all focused on providing 100% renewable energy.
For more information on solar panels, visit our website at: https://solarbuyback.com/
0 notes
Text
Solar Panel Investment: Why It’s a Smart Move for a Sustainable Future
Installing solar power on your property is regarded as more than just a fashionable “green” gesture; it is an investment in the out-with-the-old-and-in-with-the-new principle, which means that it brings about savings, energy independence (by minimizing their carbon footprints), and environmental conservation. Have you ever considered solar panel investment? Then, this article will walk you through its pros, technology, and why it’s a good idea to switch over to solar energy now.

What is Solar Panel Investment?
Solar panel investment, to put it in a nutshell, is the process of installing a solar panel system on your property to get solar energy from the sun and convert it to electricity. You can achieve this by either producing the energy from new energy sources or cutting down on your reliance on traditional energy sources, thus working toward cleaner energy. Similarly, you can promote a healthier environment by reducing your resource consumption in favor of green technology.
The present-day solar technology has made many systems more energy-effective, more robust, and cheaper than in previous models. The trend in solar power investments has been on the increase, making your space look even more comfortable and productive whether you are a homeowner or an owner of a business.
Why Should You Consider Solar Power Investment?
Financial Savings: One of the principal merits of solar panel production is the prospect of considerable electricity bill economies. After your solar panels are mounted, they produce free electricity for you for 25 or more years. Gradually this can represent several thousand of rupees saved.
Government Incentives: Most governments give out subsidies, tax rebates, and other incentives to people who set up solar energy systems. These programs decrease the initial costs, thereby making the transition to clean energy more attractive.
Increased Property Value: Properties with solar panels installed have a higher resale value for both homes and businesses. At purchase, buyers would be willing to pay a premium on such properties which are already equipped with a renascent energy supply.
Environmentally Friendly: The switch to solar energy as a power source is an effective way to reduce your carbon footprint. You can be part of a sustainable future by producing clean energy and ending the era of fossil fuels.
Energy Independence: Investing in solar power will make you less dependent on grid electricity that is often unstable with prices and causes the outage. This is a vital step for businesses that rely on a stable supply of energy.
How Does Solar Panel Investment Work?
Here’s a simple breakdown of how your solar panel system works:
Solar Panels Capture EnergySolar panels absorb sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
Inverter Converts EnergyAn inverter changes the DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which is used to power your home or business.
Net Metering Balances Energy UseIf your system produces more energy than you need, the excess is sent back to the grid, and you receive credits. During cloudy days or at night, you can draw power from the grid.
Savings BeginBy offsetting your electricity use with solar power, your energy bills shrink dramatically.
The Role of Solar Technology in Maximizing ROI
Modern solar technology has revolutionized the efficiency and affordability of solar panel systems. Today’s panels can generate more power with less sunlight, making solar investments viable even in areas with moderate sunlight.
Innovations like smart inverters, energy storage systems, and monitoring apps ensure that you get the most out of your investment. These advancements also help identify performance issues, enabling quick fixes and consistent energy production.
Steps to Get Started with Solar Panel Investment
Assess Your Energy NeedsUnderstand your current electricity consumption to determine the size of the solar panel system you’ll need.
Choose a Reliable Solar ProviderWork with a reputable company to design and install solar systems tailored to your property and requirements.
Explore Financing OptionsIf upfront costs seem daunting, look into financing options like loans, leases, or power purchase agreements (PPAs).
Check for IncentivesResearch local government incentives, subsidies, or tax benefits that can significantly reduce installation costs.
Install Solar Systems and Start SavingOnce installed, your solar panel system begins working immediately, reducing your reliance on grid power and slashing your energy bills.
Benefits of Switching to Solar Energy
Switching to solar energy isn’t just about saving money; it’s also about creating a sustainable future. Here are a few key benefits:
Long-Term SavingsThe ROI from solar panel investment often surpasses other traditional investments.
Clean Energy ProductionSolar power generates electricity without emitting harmful greenhouse gases, making it a clean and sustainable energy source.
Job CreationThe growing solar industry has created millions of jobs worldwide, contributing to economic growth while promoting renewable energy.
Grid StabilityAs more people adopt solar systems, the strain on traditional power grids decreases, reducing the risk of blackouts and power shortages.
Wrapping Up
Investing in solar panels is not just an environmentally conscious choice—it’s a smart financial decision. With lower costs, government incentives, and advanced solar technology, there has never been a better time to make the switch.
Whether you’re looking to reduce energy bills, increase property value, or make a positive impact on the environment, solar panel investment delivers on all fronts.
So, why wait? Take the first step toward energy independence today. Contact a trusted solar provider, explore your options, and join the growing community of people who are reaping the benefits of switching to solar energy.
#solar technology#Solar Panel Investment#switching to solar energy#solar panels for home#solar energy#solar panel installation#solar panel system#rooftop solar panels
0 notes
Text
Understanding On-Grid Solar Systems: A Complete Guide

India, with its abundant sunlight, is witnessing a transformative shift toward renewable energy sources. Among these, solar energy has emerged as a frontrunner, with increasing adoption driven by environmental awareness and cost savings. For households and businesses alike, on-grid solar systems present a powerful solution to meet energy needs efficiently. This guide explores everything you need to know about on-grid solar systems, from how they work to the benefits they offer.
Solar Energy in India
India has achieved significant milestones in harnessing solar power, thanks to ambitious government initiatives like the PM Surya Ghar Yojana. The country's solar power capacity has reached over 70 GW (as of 2024), with rooftop solar systems playing a vital role. With abundant sunshine for most of the year, investing in solar energy is both a sustainable and economical choice for Indian consumers.
What is On-Grid Solar?
An on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tied system, is connected directly to the local electricity grid. Unlike off-grid systems, it does not rely on battery storage. This type of solar plant is ideal for urban households, businesses, and industrial units that aim to reduce electricity costs while contributing to a greener environment.
How Does It Work? The Complete Flow
Solar Panels Capture Sunlight: Photovoltaic (PV) panels absorb sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
Inverter Converts Electricity: The DC power is sent to an inverter, which converts it into alternating current (AC) for household use.
Grid Connection: Any excess power generated is fed back into the local grid, and you receive credit for this through net metering.
Electricity Usage: When your solar system produces less power than required, you can draw electricity from the grid, ensuring an uninterrupted supply.
This seamless flow ensures maximum efficiency and consistent power availability.
Components of an On-Grid Solar System
Solar Panels: The heart of the system, capturing sunlight to generate power.
Inverter: Converts DC to AC power for practical use.
Net Meter: Tracks energy sent to and drawn from the grid.
Mounting Structures: Supports and secures the panels in optimal positions.
Cables and Wiring: Ensures efficient power transmission.
Benefits of On-Grid Solar Systems
Cost Savings: Reduces electricity bills significantly by offsetting grid consumption.
Minimal Maintenance: No need for batteries, lowering maintenance costs.
Environmental Impact: Reduces carbon footprint by promoting clean energy.
Government Incentives: Benefit from subsidies and tax rebates.
Scalability: Easily expandable to meet increasing energy demands.
Installation Process
Site Assessment: A solar panels installation company evaluates your rooftop or ground space for feasibility.
System Design: The system is customized to match your energy requirements and site conditions.
Procurement and Installation: Solar EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction) teams ensure proper setup.
Testing and Commissioning: The system is tested for efficiency and connected to the grid.
Net Metering Setup: Enables credit for surplus energy fed back to the grid.
Subsidy on On-Grid Solar
The Indian government offers attractive subsidies for rooftop solar installations to encourage adoption. Here’s a snapshot of the subsidy benefits:

Subsidy amounts vary by state and capacity, making on-grid solar systems a lucrative investment for homeowners and businesses.
Conclusion
With its potential for energy savings and environmental benefits, an on-grid solar power plant is a smart choice for anyone looking to optimize their electricity usage. From substantial savings on utility bills to government-backed incentives, the advantages of switching to solar are undeniable. Collaborate with a trusted solar panels installation company or solar EPC provider to start your journey toward a sustainable and cost-effective energy solution.
#solar#solar panels#solarcompany#solarenergy#solarforhome#ongridsolar#investment#solar epc company#rooftop solar#energysavings#pm surya ghar muft bijli yojana#solar power#residential solar
0 notes
Text
Everything You Need to Know About On-Grid Solar Inverters
The demand for renewable energy solutions has grown significantly, and a key component in grid-connected solar systems is the on-grid inverter. This device ensures that solar energy is efficiently utilized and shared with the electricity grid. Let’s explore what on-grid inverters are, how they function, and their benefits.

What Is an On-Grid Solar Inverter?
An on-grid solar inverter is a device that converts the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which powers appliances and integrates with the electricity grid. Unlike off-grid systems, these inverters are connected directly to the grid, allowing surplus solar energy to be exported and grid power to be used when solar energy is insufficient.
How Does an On-Grid Inverter Work?
Here’s a simple explanation of its operation:
Solar Energy Conversion: Solar panels produce DC electricity, which the inverter converts into AC.
Energy Distribution: The AC electricity powers your appliances, and excess energy is sent to the grid.
Grid Backup: If solar energy is unavailable or insufficient, the grid supplies electricity seamlessly.
This integration makes on-grid inverters a practical choice for areas with reliable grid infrastructure.
Advantages of On-Grid Inverters
1. Cost Savings Through Net Metering Many utility companies provide net metering, allowing you to offset electricity bills by exporting surplus energy to the grid.
2. Seamless Grid Integration On-grid inverters are designed to synchronize with the grid, ensuring smooth energy flow without disruptions.
3. High Efficiency Modern on-grid inverters offer impressive efficiency, minimizing energy losses during conversion.
4. Scalable Solutions Whether for a small home setup or a large commercial project, on-grid inverters can easily scale to meet varying energy demands.
5. Environmental Benefits Using solar power reduces dependence on fossil fuels and lowers carbon emissions, promoting sustainability.
Choosing the Right On-Grid Inverter
When selecting an on-grid inverter, consider these key aspects:
Capacity: Ensure the inverter aligns with the size of your solar system.
Efficiency Ratings: Higher efficiency means less energy is wasted during conversion.
Brand Reputation: Opt for reliable brands like Solplanet, Sofar, and INVT for quality and durability.
Advanced Features: Features like remote monitoring and performance tracking can add convenience.
Warranty and Support: A solid warranty ensures long-term reliability.
Applications of On-Grid Solar Inverters
Residential Systems: Perfect for homeowners aiming to reduce electricity bills.
Commercial Installations: Helps businesses cut operational energy costs.
Utility-Scale Solar Projects: Supports large-scale solar energy production.
Conclusion
Switching to solar energy with an on-grid inverter is a smart and sustainable choice for homes and businesses. These inverters allow you to save on energy costs, contribute to a greener environment, and make efficient use of available resources. With continuous advancements in technology, on-grid solar inverters are becoming more user-friendly and efficient.
Take the first step toward energy independence—explore on-grid solar inverters today and unlock the potential of renewable energy for your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can an on-grid inverter work during a power outage? No, on-grid inverters depend on the electricity grid for synchronization and will not function without grid power unless paired with a battery backup.
Q2: Are on-grid inverters suitable for areas with limited sunlight? Yes, though their performance is influenced by sunlight availability. Areas with intermittent sunlight may need additional energy management strategies.
Q3: How long can an on-grid inverter last? With proper care, an on-grid inverter typically lasts 10-15 years, depending on its quality and usage conditions.
0 notes
Text
Save On Energy Costs With Net Metering Today!
In today's world, rising energy costs are a significant concern for households and businesses alike. As utility bills continue to increase, many people are seeking effective solutions to manage their energy expenses. One innovative and cost-effective approach is through net metering. This system allows solar panel users to receive credits for the excess energy they generate and feed back into the grid. If you're considering adopting solar power, understanding net metering is essential for maximizing your savings.
What is Net Metering?
Net metering is a billing arrangement that allows solar energy system owners to receive credits for surplus electricity generated by their solar panels. When your solar panels produce more energy than you use, the excess energy is sent back to the grid, and you earn credits. These credits can offset the cost of electricity you consume from the grid when your solar system isn't producing enough energy, such as at night or during cloudy days.
This concept provides a seamless way for homeowners and businesses to benefit from renewable energy without the need for battery storage systems. Instead of relying on batteries to store excess energy, net metering enables users to simply send their surplus electricity to the grid and draw power from it when needed.
How Does Net Metering Work?
Understanding how net metering works can help you appreciate its financial benefits. When your solar panels generate electricity, the energy is used to power your home or business first. If you produce more electricity than you consume, the excess is sent to the utility grid. Your utility company then records the amount of surplus energy you contribute, often using a special bi-directional meter.
At the end of each billing cycle, your utility company calculates your net energy consumption. If you've generated more energy than you've used, you receive credits that can be applied to your future bills. This arrangement ensures that solar users are fairly compensated for their contributions to the grid.
Benefits of Net Metering Solar
Cost Savings: The primary advantage of net metering solar is the significant reduction in electricity bills. The credits earned from excess energy production can lead to substantial savings, especially during peak consumption periods. As utility rates rise, having a net metering system can protect you from skyrocketing costs.
Return on Investment: Investing in a solar energy system becomes more financially attractive with solar net metering. The combination of savings on energy bills and potential government incentives can lead to a quicker return on your investment. Many states offer tax credits, rebates, or grants that further enhance the financial viability of solar installations.
Environmental Impact: By using solar energy and contributing to the grid, you’re helping reduce reliance on fossil fuels, leading to a cleaner environment. This not only benefits your local community but also plays a role in combating climate change on a global scale. Utilizing net metering empowers individuals and businesses to make a positive impact on the planet.
Energy Independence: With net metering, you gain greater control over your energy consumption. By generating your own electricity, you reduce your dependence on traditional energy sources and contribute to a more sustainable energy future. This independence can be especially beneficial during power outages or natural disasters when the grid may be unreliable.
Understanding Net Metering vs. Gross Metering
It's important to understand the differences between net metering vs gross metering. While net metering allows users to receive credits for surplus energy, gross metering requires all generated electricity to be fed into the grid. In gross metering, users receive a fixed price per unit of energy supplied, without the ability to offset their consumption. This can result in lower overall savings compared to net metering.
Under a gross metering system, the financial benefits of solar energy can be limited, as users cannot directly reduce their electricity bills. This can make the initial investment in solar panels less appealing. In contrast, net metering creates a more equitable system that rewards solar users for their contributions and helps them save on energy costs.
How to Apply for Net Metering
If you’re interested in leveraging net metering, you’ll need to complete a net metering application with your local utility provider. The application process varies by location, so be sure to check the requirements specific to your area. Typically, you’ll need to provide details about your solar panel system, such as the type, size, and installation date.
Before applying, it’s essential to ensure that your solar system meets the eligibility criteria set by your utility company. This may include specific inverter types, system size limitations, and other technical requirements. Additionally, you may need to have your solar system inspected by a certified professional to ensure it meets safety and performance standards.
Overcoming Common Misconceptions
Despite the many benefits of net metering, there are still misconceptions that may deter potential solar users. One common concern is that net metering only benefits wealthy homeowners. However, many states are working to ensure that solar energy is accessible to all income levels. Programs designed for low-income households can help make solar energy more affordable, allowing everyone to benefit from net metering.
Another misconception is that solar panel systems are too complicated to install. In reality, many solar providers offer comprehensive installation services, making the process simple and hassle-free. By partnering with a reputable solar company, you can receive guidance throughout the entire installation and application process, ensuring a smooth transition to solar energy.
Conclusion
Incorporating net metering into your solar energy strategy can lead to significant cost savings and a more sustainable energy solution. With the growing awareness of the benefits of solar energy, now is the perfect time to take action.
If you're ready to start saving on energy costs with net metering, contact us at SolarSense today! Our team can guide you through the process of installing solar panels and applying for net metering, ensuring you maximize your savings and contribute to a greener future. Together, we can make a positive impact on your wallet and the environment.
#net metering#net metering solar#solar net metering#net metering upsc#net metering vs gross metering#net metering application
0 notes
Text
Best Solar Panel in Delhi NCR
In an era where climate change and energy sustainability are at the forefront of global concerns, solar energy emerges as a beacon of hope. Harnessing the power of the sun stands as one of the most promising solutions to our growing energy needs and environmental challenges. If you are looking for solar panel in Delhi NCR you can contact Sakshine Solar Pvt ltd which is franchise of Waaree energies.This blog post explores the many facets of solar energy: its benefits, technology, and the future.
The Basics of Solar Energy
Solar energy is derived by capturing radiant light and heat from the sun. This renewable resource is abundant and, with the right technology, can be converted into electricity or thermal energy to power homes, businesses, and even transportation.
How Solar Energy Works
At the heart of solar power are photovoltaic (PV) cells, which convert sunlight directly into electricity. These cells are typically made from silicon and are organized into panels, which can be installed on rooftops, open spaces, or solar farms. Another key technology is solar thermal systems, which use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight and generate heat, which can then be used to produce electricity through steam turbines or heat engines.
The Advantages of Solar Energy
Renewable and Abundant: The sun provides an inexhaustible supply of energy. Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy will be available as long as the sun shines.
Environmentally Friendly: Solar power generation does not produce greenhouse gases or air pollutants. Reducing our reliance on fossil fuels helps in mitigating climate change and reduces the overall carbon footprint.
Reduces Electricity Bills: By generating your own electricity, you can significantly lower your utility bills. Moreover, in many regions, surplus energy can be sent back to the grid in exchange for credits, a process known as net metering.
Low Maintenance Costs: Once installed, solar panels require minimal maintenance. They are durable, with most manufacturers offering warranties of 20-25 years.
Job Creation: The growth of the solar industry has led to the creation of numerous jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
Current Challenges
While solar energy has numerous benefits, it also faces several challenges:
Initial Costs: The upfront investment for purchasing and installing solar panel cost in Delhi NCR can be high, although costs have been decreasing and various financing options are now available.
Intermittency: Solar power generation depends on sunlight, which means it is not constant and can be affected by weather conditions and day-night cycles. Energy storage solutions, such as batteries, are being developed to address this issue.
Space Requirements: Large-scale solar installations require significant space, which can be a limitation in densely populated areas.
Energy Conversion Efficiency: Though improving, the efficiency of photovoltaic cells is still a major area of research. Higher efficiency panels can produce more electricity from the same amount of sunlight, making solar power more viable.
Innovations and Future Trends
The solar energy sector is evolving rapidly, with innovations that promise to overcome current challenges and enhance efficiency:
Perovskite Solar Cells: These are a new class of materials that offer higher efficiency at a lower cost compared to traditional silicon-based cells.
Solar Skin Design: Innovative designs that blend solar panels with the aesthetics of buildings, allowing for more integrated and visually appealing solar installations.
Energy Storage Solutions: Advances in battery technology, such as Tesla’s Powerwall, are making it possible to store excess energy for use during cloudy days or at night.
Floating Solar Farms: These installations on bodies of water can save land space and also reduce water evaporation, offering dual benefits.
Artificial Intelligence and IoT: The integration of AI and Internet of Things (IoT) for smart monitoring and management of solar installations can optimize performance and maintenance.
Conclusion
The potential of solar energy is immense. As technology continues to advance and costs decline, solar power is set to become a cornerstone of our renewable energy portfolio. Adopting solar energy not only supports a sustainable future but also paves the way for technological innovations and economic growth. By embracing this clean, abundant, and renewable source of power, we can make significant strides toward a greener and more sustainable world.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Advantages of Installing an On-Grid Solar System for Your Home
As the world transitions towards sustainable energy solutions, solar power has emerged as one of the most reliable and eco-friendly energy sources. For homeowners, installing an on-grid solar system offers a host of benefits ranging from significant cost savings to a reduced environmental footprint. An on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tied system, is designed to work in harmony with the local electricity grid, providing a seamless energy solution. In this article, we’ll explore the key advantages of installing an on-grid solar system in your home, including cost savings, energy efficiency, and environmental impact.
1. Cost Savings Through Reduced Electricity Bills
One of the most compelling reasons to install an on-grid solar system is the potential for substantial cost savings. Solar energy is free, and by harnessing the power of the sun, homeowners can significantly reduce their reliance on grid electricity. Here’s how:
Lower Monthly Bills: Once the system is installed, you will generate your own electricity, reducing the amount of energy you need to purchase from the grid. On average, a solar-powered home can reduce its electricity bill by 50-70%, depending on the size of the system and your energy consumption.
Net Metering: Many regions offer net metering, which allows homeowners with solar systems to sell excess power back to the grid. If your system generates more electricity than you need, the excess is fed back into the grid, and you earn credits or payments. This helps to offset costs during months when your energy consumption is higher than average (such as in the winter or during cloudy days).
Energy Independence: By generating your own electricity, you become less reliant on fluctuating energy prices. This gives you greater financial stability, particularly with the rising costs of traditional energy sources.
2. Energy Efficiency and Reliability
On-grid solar systems are designed for maximum energy efficiency. They convert the energy from sunlight into usable electricity for your home and seamlessly integrate with your local power grid. Here are some ways on-grid solar systems enhance energy efficiency:
Real-Time Energy Use Management: An on-grid system continuously monitors your energy production and consumption. If your solar panels are producing more energy than you need, the surplus is sent to the grid, where it can be used by others. Conversely, if your solar output is lower than your consumption (for example, at night or on cloudy days), the system automatically draws power from the grid to meet your needs.
Smart Inverter Technology: On-grid solar systems often feature smart inverters, which optimize the conversion of DC power generated by the solar panels into AC power that can be used in your home. These inverters also provide real-time data on energy production and help manage power flow efficiently.
Grid Synchronization: Since on-grid systems are connected to the local power grid, they ensure that your home always has access to electricity, even when your solar production is insufficient. This means you don’t need to worry about power outages during times when your system isn’t generating electricity.
3. Environmental Impact: Going Green with Solar Power
Installing an on-grid solar system also plays a significant role in reducing your carbon footprint and contributing to a cleaner environment. Here are the environmental benefits:
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: By using solar energy instead of fossil fuels, you help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, including carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and nitrogen oxides (NOx), which contribute to air pollution and climate change. Solar power is a clean, renewable source of energy that does not release harmful pollutants into the atmosphere.
Renewable Energy Source: Unlike coal or natural gas, solar energy is inexhaustible. As long as the sun shines, solar energy will be available to generate power. By investing in solar, you are helping reduce the global reliance on finite fossil fuels, which are responsible for environmental degradation and pollution.
Sustainable Home Practices: By transitioning to a solar-powered home, you are embracing sustainable living practices. Solar energy is not only environmentally friendly but also a proactive step towards achieving energy sustainability in the long term. Using solar energy supports broader global efforts to transition to a green economy.
4. Increase in Property Value
Homes with solar systems installed are often seen as more attractive and valuable on the market. Many buyers are becoming more conscious of sustainability and energy efficiency, and the presence of a solar system can be a major selling point. Here’s how an on-grid solar system can affect your property:
Higher Market Value: Studies have shown that homes with solar panels sell at a premium. In some regions, homes with solar systems can see an increase in value by as much as 4-6%. This is because buyers are increasingly looking for energy-efficient homes that offer long-term savings and environmental benefits.
Faster Sale: Homes equipped with solar systems often sell faster than those without, as they offer lower ongoing utility costs, which is appealing to potential buyers. The demand for homes with energy-efficient features continues to rise, making solar an attractive investment for homeowners looking to increase their property value.
5. Low Maintenance and Long Lifespan
On-grid solar systems are low maintenance and highly durable. After installation, the only maintenance typically required is occasional cleaning of the solar panels to remove dirt, leaves, or debris. Here’s why they are a long-term investment:
Durable Components: Solar panels are designed to last for 25-30 years or more, with many manufacturers offering warranties of up to 25 years. The inverters and other system components are also built to last, with warranties typically covering 10-12 years.
Low Maintenance: Solar systems are relatively low maintenance compared to other home improvement projects. With few moving parts and robust design, the solar panels require little upkeep beyond basic cleaning and periodic inspections.
6. Government Incentives and Subsidies
In many countries, governments offer financial incentives to encourage homeowners to install solar energy systems. These incentives can reduce the initial installation cost of the solar system and make it more affordable. Some of the common incentives include:
Tax Credits: Many governments offer tax credits for solar installations, reducing the overall cost of the system.
Rebates and Subsidies: Some regions offer direct rebates or subsidies to homeowners who install solar energy systems, further lowering the upfront cost.
Feed-in Tariffs: In certain regions, homeowners can benefit from feed-in tariffs, which pay them for the solar energy they feed back into the grid.
These incentives make solar installation more financially viable, accelerating the return on investment.
Conclusion: Why an On-Grid Solar System is a Smart Investment
Installing an on-grid solar system offers numerous benefits that go beyond just lowering your electricity bill. From reducing your carbon footprint to increasing your property value, the advantages of switching to solar power are clear. With lower installation costs due to government incentives, enhanced energy efficiency, and long-term savings, an on-grid solar system is a smart, sustainable investment for homeowners looking to embrace renewable energy.
By tapping into the power of the sun, you can enjoy a steady stream of clean, renewable energy while helping to protect the planet. So, if you're considering an energy upgrade for your home, an on-grid solar system is an excellent choice that benefits both your wallet and the environment.
0 notes