#Hepatic Steatosis Symptoms
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Liver Regeneration तुमचं यकृत तुमच्या एकंदर आरोग्यासाठी अत्यंत महत्त्वाचं आहे. तुम्हाला हे लक्षणे दिसत असतील, तर यकृत तपासणी करणे योग्य ठरू शकते.
Know more: https://www.nsnpl2health.com/hepadetox/
0 notes
Text
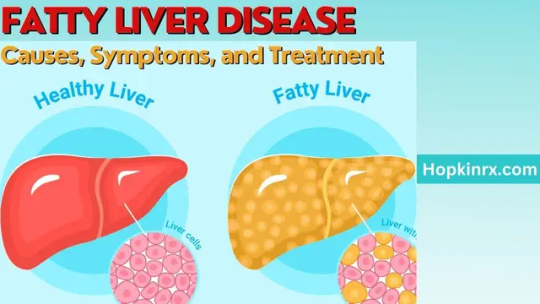
Fatty Liver Disease: Important Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Fatty Liver Disease: Important Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentIntroductionWhat is Fatty Liver Disease?Causes of Fatty Liver Disease Poor Dietary Habits Sedentary Lifestyle Obesity Alcohol ConsumptionSymptoms of Fatty Liver Disease Fatigue Abdominal Discomfort Jaundice SwellingDiagnosing Fatty Liver Disease Blood Tests Imaging Studies Liver BiopsyTreatment and Management Lifestyle Changes Balanced…
View On WordPress
#Alcoholic fatty liver#Fatty liver causes#Fatty liver complications#Fatty liver diagnosis#Fatty liver management#Fatty liver prevention#Fatty liver risks#Fatty liver symptoms#Fatty liver treatment#Hepatic steatosis#Liver and alcohol#Liver biopsy#Liver care#Liver cirrhosis#Liver damage#Liver disease progression#Liver exercise benefits#Liver function#Liver Health#Liver health tips#Liver inflammation#Liver steatosis#Liver-friendly diet#Non-alcoholic fatty liver#Obesity and fatty liver
0 notes
Text
Fatty Liver Specialist in Chennai
When it comes to managing liver health, finding a reputable fatty liver specialist in Chennai is crucial. Fatty liver disease, often a silent condition, can lead to serious complications if left undiagnosed or untreated. This comprehensive blog post will help you understand fatty liver disease, the role of a specialist, and introduce you to some of the best liver doctors in Chennai for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, occurs when excess fat builds up in the liver. It is categorized into:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) – Not linked to alcohol intake, often related to obesity, diabetes, or high cholesterol.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD) – Caused by excessive alcohol consumption.
While early stages may not show symptoms, fatty liver disease can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, or even liver cancer if not treated by an experienced liver specialist in Chennai.
Why You Need a Fatty Liver Specialist in Chennai
A fatty liver treatment doctor (hepatologist or gastroenterologist) specializes in liver health and offers:
Accurate diagnosis using advanced imaging and lab tests
Individualized treatment plans including diet, medications, and lifestyle advice
Ongoing monitoring to prevent disease progression
Management of related complications like cirrhosis, liver failure, or cancer
Consulting a fatty liver specialist in Chennai ensures expert care for a potentially reversible but dangerous condition.
Top Fatty Liver Specialists in Chennai
Here’s a curated list of leading liver specialists in Chennai known for their excellence in treating fatty liver disease and other liver conditions.
1. Dr. Aswin Krishna – Apollo Hospitals
Qualifications: MBBS, MD (Gen. Medicine), DM (Hepatology)
Experience: 6+ years
Specialties: NAFLD, NASH, cirrhosis
Dr. Aswin Krishna is a rising expert in hepatology and a renowned fatty liver specialist in Chennai. He uses cutting-edge diagnostic tools and customizes treatment plans for both alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver patients. His dedication to early intervention and patient-centric care sets him apart.
2. Dr. I. Shubha Vivekan – VS Hospitals
Qualifications: MD, DM
Experience: 13+ years
Specialties: NASH, liver cirrhosis, lifestyle counseling
Dr. Shubha Vivekan is known for her empathetic approach and in-depth experience in managing fatty liver and related complications. She emphasizes preventive care and lifestyle modification, making her a trusted fatty liver doctor in Chennai.
3. Prof. Dr. Mohammed Ali – VS Hospitals
Qualifications: MD, DM, FCIP
Experience: 27+ years
Specialties: Liver transplant, cirrhosis, fatty liver
Dr. Ali heads the Department of Gastroenterology and is a top liver transplant specialist in Chennai. His vast experience and holistic treatment methods make him ideal for patients with advanced or complex liver conditions.
4. Dr. Radhika Venugopal – CTS Hospitals
Qualifications: MBBS, MD, DM (Hepatology)
Experience: 24+ years
Specialties: Pediatric and adult hepatology
Dr. Radhika is one of the few liver specialists in Chennai catering to both children and adults. Her meticulous diagnostic techniques and gentle approach make her highly sought-after.
5. Prof. Mohamed Rela – Rela MS Hospital
Qualifications: MS, FRCS, DSc
Experience: 28+ years
Specialties: Liver transplant, cirrhosis, fatty liver
Internationally acclaimed liver transplant surgeon, Prof. Rela is often regarded as the best liver doctor in Chennai. His hospital offers state-of-the-art liver treatment and advanced surgical options.
6. Dr. Magnus Jayaraj Mansard – Magnus Liver Transplants and Gastro Clinic
Qualifications: MBBS, MS, DNB, MRCS (UK)
Experience: 25+ years
Specialties: Surgical gastroenterology, fatty liver treatment
Dr. Magnus offers comprehensive care from early diagnosis to liver transplant. His vast experience in both surgical and non-surgical treatment makes him a trusted name for liver patients in Chennai.
7. Dr. Elankumaran Krishnan – Apollo Hospital
Qualifications: MBBS, MS, MCh, PDF (Liver Transplantation)
Experience: 18+ years
Specialties: Cirrhosis, liver transplantation
A well-known fatty liver doctor in Chennai, Dr. Elankumaran is known for treating complex liver cases, especially those nearing liver failure or requiring surgery.
8. Dr. S. Arulprakash – MGM Healthcare
Qualifications: MBBS, DM, DNB, MD
Experience: 23+ years
Specialties: Pediatric and adult gastroenterology
Dr. Arulprakash has a dual specialization in pediatric and adult gastroenterology, making him ideal for families looking for multi-age liver care in Chennai. He offers strong emphasis on early-stage management and nutritional therapy.

9. Dr. Joy Varghese – Gleneagles Health City
Qualifications: MBBS, MD, DM
Experience: 28+ years
Specialties: Liver transplant, fatty liver, hepatology
Dr. Joy is a senior liver transplant expert and a reputed fatty liver specialist in Chennai, particularly for patients with progressive disease stages like NASH and cirrhosis.
10. Dr. B S Ramakrishna – SIMS Hospital
Qualifications: MBBS, MD, DM
Experience: 46+ years
Specialties: Fatty liver, cirrhosis, chronic liver disease
With over four decades of experience, Dr. Ramakrishna is a veteran in the field of liver care. His legacy in hepatology and patient trust is unmatched.
Signs You May Need a Fatty Liver Treatment Doctor
Fatty liver is often silent, but these symptoms should prompt immediate evaluation:
Persistent fatigue
Right upper abdomen discomfort
Jaundice (yellow skin/eyes)
Swelling in legs or abdomen
Sudden unexplained weight loss
Nausea, poor appetite
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver Disease
A fatty liver specialist in Chennai uses multiple diagnostic tools:
Blood Tests: ALT, AST, lipid profile, glucose
Imaging: Ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, FibroScan
Liver Biopsy: To confirm NASH or fibrosis
These methods help assess the extent of liver damage, allowing for an accurate and timely treatment plan.
Stages of Fatty Liver and Associated Risks
Simple Fatty Liver (NAFL): Fat buildup, no inflammation
NASH: Inflammation and liver cell injury
Fibrosis: Early scarring
Cirrhosis: Permanent scarring, potential liver failure
Liver Cancer: Advanced stage due to chronic inflammation
Risk factors include obesity, diabetes, sedentary lifestyle, high cholesterol, and family history of liver disease.
Treatment and Prevention
A fatty liver specialist in Chennai provides:
Personalized lifestyle interventions: diet, exercise, alcohol cessation
Medications (if needed) to reduce liver inflammation
Weight management programs
Routine follow-ups to monitor liver function
Conclusion
Choosing the right fatty liver specialist in Chennai is essential for early detection, effective treatment, and long-term liver health. With experienced doctors, advanced diagnostics, and patient-focused care, Chennai offers some of the best liver treatment options in India. If you experience symptoms or fall under a risk category, don’t delay — book a consultation with a liver specialist and take proactive steps toward healing and better health. For more details visit https://draswinkrishna.com/best-gastroenterologist-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text
India’s Silent Epidemic: Fatty Liver in Young Adults

Introduction
In recent years, a quiet but dangerous health issue has been growing in India—fatty liver disease in young adults. Once thought to affect only older people or those who drink alcohol heavily, fatty liver is now being found in teenagers and people in their 20s and 30s. Shockingly, many of them don’t even realize they have it.
This blog aims to explain what fatty liver is, why it’s becoming common among young Indians, its causes, symptoms, prevention, and how to manage it naturally.
What Is Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver, also known as Hepatic Steatosis, is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. There are two main types:
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD) – caused by heavy drinking.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) – occurs in people who drink little or no alcohol.
In India, NAFLD is increasing rapidly, especially among young adults. It often begins silently, without any symptoms, and slowly damages the liver over time.
Why Is It a Silent Epidemic?
Fatty liver is called a silent disease because most people don’t notice any signs in the early stages. It is often discovered during tests for other conditions or routine health check-ups.
The word “epidemic” may sound extreme, but the numbers support it. According to recent studies:
Over 30% of urban Indian adults under 40 may have fatty liver.
Young people are developing the disease as early as their late teens.
Many of them have normal weight, which proves that it's not just about being overweight.
Causes of Fatty Liver in Young Indians
Unhealthy Diet High intake of fast food, sugary drinks, processed snacks, and fried items increases fat accumulation in the liver.
Sedentary Lifestyle Long hours in front of screens and lack of physical activity are major contributors.
Obesity and Belly Fat Excess fat around the abdomen, even in normal-weight individuals, can lead to NAFLD.
Type 2 Diabetes and Insulin Resistance These conditions are on the rise among young Indians and are closely linked with fatty liver.
Genetics A family history of liver disease or obesity can increase the risk.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Young women with PCOS often develop insulin resistance and fatty liver as a result.
Signs and Symptoms
Most people with fatty liver have no obvious symptoms. But as the condition progresses, some may experience:
Constant tiredness
Mild pain in the upper right abdomen
Unexplained weight gain
Bloating or discomfort
Elevated liver enzymes in blood tests
If left untreated, fatty liver can lead to liver inflammation (NASH), fibrosis (scarring), and even liver cirrhosis or cancer in severe cases.
Diagnosis
Doctors may use the following methods to diagnose fatty liver:
Blood Tests – to check liver enzymes (ALT, AST).
Ultrasound or FibroScan – to detect fat accumulation.
MRI or CT scan – in advanced cases.
Liver Biopsy – rarely used unless needed to confirm severe damage.
Prevention: Simple Lifestyle Changes
Fatty liver is largely preventable and reversible in early stages. Here are some tips for young adults:
Eat a Balanced Diet Include whole grains, fresh fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins. Avoid junk food and reduce sugar intake.
Exercise Regularly Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise daily—walking, jogging, dancing, yoga, or sports.
Limit Sugar and Refined Carbs Cut down on sweets, soft drinks, white bread, and bakery items.
Avoid Alcohol Even social or occasional drinking can worsen fatty liver, especially in those already at risk.
Maintain Healthy Weight Keep your BMI in check, and don’t ignore belly fat even if you’re slim.
Sleep Well Poor sleep affects hormone balance and increases fat storage in the body and liver.
Manage Stress Chronic stress increases cortisol, which can lead to fat gain and liver problems.
Natural Remedies and Supportive Measures
While lifestyle change is the key, some natural ingredients may help support liver health:
Amla (Indian Gooseberry) – rich in antioxidants and vitamin C.
Turmeric – contains curcumin which helps reduce liver inflammation.
Milk Thistle – a western herb known to protect liver cells.
Green Tea – has catechins that support fat burning and liver health.
Always consult your doctor before using herbal supplements, especially if you're on medications.
When to See a Doctor
Don’t wait for symptoms. If you:
Have a family history of diabetes or liver disease
Are overweight or have PCOS
Drink alcohol regularly
Feel tired all the time without reason
…it’s a good idea to get a basic liver check-up. Early diagnosis can help reverse the damage before it becomes serious.
The Bigger Picture
Fatty liver disease in India’s youth is not just a health issue—it’s a wake-up call. Our modern lifestyles, food habits, and stress levels are putting a silent strain on one of the most vital organs in our body.
Schools, colleges, and workplaces should spread awareness. Families should encourage home-cooked meals, outdoor activities, and regular health checks.
Conclusion
Fatty liver is no longer just an old person’s disease. It is India’s Silent Epidemic: Fatty Liver in Young Adults. The good news is that it can be prevented and even reversed if caught early. By making small but consistent changes to our daily habits, young Indians can protect their liver and ensure a healthier future.
Don’t ignore the signs. Take action today and beat India’s Silent Epidemic: Fatty Liver in Young Adults before it’s too late.
0 notes
Text
Best Ayurvedic Medicine for Fatty Liver – A Complete Guide to Natural Healing
Fatty liver is a growing health concern in today’s world, especially among people with unhealthy eating habits, lack of exercise, stress, and sedentary lifestyles. It occurs when excess fat builds up in liver cells, and if left untreated, it can lead to inflammation, liver scarring (fibrosis), or even liver failure in extreme cases.
The good news is, Ayurveda—the ancient Indian system of natural healing—offers safe and effective ways to manage and reverse fatty liver. In this blog, we will discuss the best Ayurvedic medicine for fatty liver, explore its benefits, and also learn about natural ways to improve liver health.
What Is Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition where too much fat accumulates in the liver. There are two main types:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Not related to alcohol use.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): Caused by heavy alcohol consumption.
In Ayurveda, fatty liver is considered the result of an imbalance in Pitta dosha and the accumulation of Ama (toxins) in the liver. This slows down digestion, weakens liver function, and leads to fat buildup.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver
Pain or discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen
Constant tiredness or weakness
Loss of appetite
Weight gain around the belly
Bloating and indigestion
Dark urine or yellowish skin/eyes (in serious cases)
If you experience these symptoms, it’s time to consider natural healing. And choosing the best Ayurvedic medicine for fatty liver can be a great first step.
Why Choose Ayurveda for Fatty Liver Treatment?
Ayurveda treats the root cause, not just the symptoms. It aims to detoxify the liver, balance the doshas, and improve digestion. Ayurvedic remedies are made from herbs that are time-tested, safe, and without harmful side effects.
Unlike chemical-based medicines that can strain your liver more, the best Ayurvedic medicine for fatty liver helps repair and regenerate liver cells naturally.
Best Ayurvedic Medicine for Fatty Liver
Here are some of the most trusted and effective Ayurvedic medicines and herbs used to treat fatty liver:
1. Kayashree Liver Detox Capsules
One of the top choices for liver care, Kayashree Liver Detox is considered the best Ayurvedic medicine for fatty liver. It is made with a powerful blend of herbs like:
Kalmegh (Andrographis paniculata): Known for its liver-protective and anti-inflammatory properties.
Punarnava: Reduces swelling and supports liver detox.
Bhumiamla: Strengthens liver function and fights liver infections.
Kutki: A bitter herb that improves digestion and balances Pitta dosha.
Benefits:
Detoxifies the liver naturally
Reduces fat accumulation in the liver
Improves appetite and digestion
Restores enzyme balance
Safe for long-term use
2. Liv 52 by Himalaya
A well-known Ayurvedic formulation that supports liver health and improves metabolism. It helps regenerate liver cells and is especially useful in early stages of fatty liver.
Key Ingredients: Capers, Arjuna, Kasni, and Mandur Bhasma
3. Patanjali Liv D38 Tablets
Made from herbs like Bhringraj, Giloy, and Katuki, this tablet promotes liver regeneration, reduces toxins, and enhances bile production.
4. Herbal Powders (Churna)
Triphala Churna: Helps cleanse the digestive system and supports liver detox.
Avipattikar Churna: Balances stomach acids and helps in reducing liver-related acidity.
5. Individual Herbs
Kutki (Picrorhiza kurroa): One of the best liver tonics in Ayurveda.
Bhringraj: Known for its detoxifying effects.
Guduchi (Giloy): Strengthens the immune system and purifies blood.
Using a combination of these herbs under expert guidance can be very effective.
How the Best Ayurvedic Medicine for Fatty Liver Works
The action of Ayurvedic liver medicine is holistic. Here’s how it works:
Detoxifies liver cells by removing Ama (toxins)
Balances Pitta dosha
Improves bile flow for better digestion
Regenerates damaged liver tissues
Improves metabolism and reduces fat in the liver
With consistent use, patients notice better digestion, higher energy, reduced bloating, and improvement in overall liver function.
Ayurvedic Diet and Lifestyle Tips for Fatty Liver
To support the effect of the best Ayurvedic medicine for fatty liver, it is important to follow a healthy Ayurvedic lifestyle:
Foods to Eat:
Warm water with lemon in the morning
Moong dal, bottle gourd, bitter gourd, and leafy greens
Fresh fruits like papaya, pomegranate, and apple
Turmeric milk (haldi doodh)
Buttermilk with roasted cumin
Foods to Avoid:
Oily, spicy, and fried food
White sugar and refined flour (maida)
Processed or canned foods
Alcohol and carbonated drinks
Lifestyle Tips:
Do 30 minutes of yoga or walking daily
Practice stress-relief techniques like meditation or pranayama
Sleep early and wake up before sunrise
Avoid afternoon naps, especially after heavy meals
Expert Advice – What Doctors Say About Ayurvedic Liver Detox
Many Ayurvedic doctors recommend combining herbal remedies with lifestyle correction for best results. According to experts, consistency is key.
Drinking lukewarm water, avoiding late-night meals, and including bitter vegetables can help improve liver function. Along with this, the best Ayurvedic medicine for fatty liver like Kayashree Liver Detox can be taken daily for 2–3 months for visible benefits.
Final Thoughts
Fatty liver may seem like a silent issue, but ignoring it can lead to serious health risks. Thankfully, you don’t need to rely only on synthetic drugs. With the power of Ayurveda, you can heal your liver gently and effectively.
Choosing the best Ayurvedic medicine for fatty liver is the first step towards long-term wellness. Whether you go for Kayashree Liver Detox or other trusted herbal combinations, always consult with an Ayurvedic practitioner before starting any treatment.
Start your liver-healing journey today—naturally, safely, and powerfully with Ayurveda.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can fatty liver be cured with Ayurvedic medicine? Yes, with the right Ayurvedic treatment and lifestyle changes, fatty liver can be reversed in most cases.
Q2: How long should I take Ayurvedic medicine for fatty liver? Usually, a course of 2 to 3 months is recommended, but it can vary based on the severity.
Q3: Is it safe to use Ayurvedic liver detox capsules daily? Yes, most Ayurvedic capsules made from pure herbs like Kalmegh, Punarnava, and Kutki are safe for long-term use.
Q4: Does Ayurvedic medicine have any side effects? Generally, Ayurvedic medicines are safe. But always check for ingredient allergies and consult a qualified practitioner before use.
0 notes
Text
🌿 Fatty Liver: The Hidden Disease We’re All Ignoring
You won’t see it coming. You might not even feel it. But hepatic steatosis is here — and it’s more common than you think.
💡 Learn how lifestyle, genes, and even the food we eat are silently overwhelming our livers.
🔥 Full breakdown on symptoms, causes, and treatments (2025 update!) here: 👉 https://revisiontown.com/hepatic-steatosis-fatty-liver-disease-causes-symptoms-diagnosis-treatment-in-2025/

#FattyLiver#TumblrHealth#MedicalFacts#SilentIllness#BodyPositivity#HepaticSteatosis#WellnessTips#RevisionTown#healtheducation#healthawareness#chronicillness#raredisease#healthtips#world health organization#tumblrscience#healthcare#health and wellness#wellness
0 notes
Text
How alcohol affects your liver
The liver is one of the most vital organs in the human body, responsible for detoxifying harmful substances, metabolizing nutrients, and supporting overall health. Among the many substances the liver processes, alcohol poses a unique challenge. While moderate alcohol consumption may not cause noticeable harm, excessive or prolonged drinking can lead to significant liver damage, often going unnoticed until serious complications arise.
Understanding how alcohol affects your liver is essential for anyone who consumes alcohol even occasionally. From fatty liver to cirrhosis, the damage can be progressive and, in some cases, irreversible. This article explores how alcohol interacts with the liver, the stages of liver damage, symptoms to watch out for, and how to prevent alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD).

How Alcohol Is Processed by the Liver
When you consume alcohol, your liver gets to work breaking it down. Alcohol is metabolized into a toxic substance called acetaldehyde, which is then converted into a less harmful compound and eventually eliminated from the body. However, this process is taxing on the liver. Drinking more alcohol than the liver can efficiently process leads to a buildup of toxins, inflammation, and cellular damage.
The efficiency of this process varies from person to person, depending on factors such as:
Quantity and frequency of alcohol consumption
Gender and age
Body weight and metabolism
Overall liver health
Genetic predispositions
Early Signs: Fatty Liver (Steatosis)
One of the first stages of alcohol-related liver damage is alcoholic fatty liver, also known as steatosis. This condition occurs when fat begins to accumulate in the liver cells due to excessive alcohol consumption.
Symptoms:
Often asymptomatic
Mild discomfort or pain in the upper right abdomen
Fatigue and general weakness
Elevated liver enzymes on blood tests
Fatty liver is generally reversible if caught early and drinking is stopped. However, if ignored, it can progress to more serious conditions.
Stage Two: Alcoholic Hepatitis
Alcoholic hepatitis is an inflammatory condition that results from ongoing alcohol damage. This condition can range from mild to severe and may develop suddenly after binge drinking or gradually over time.
Common Symptoms:
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Abdominal pain and tenderness
Nausea and vomiting
Loss of appetite
Fever and fatigue
Severe alcoholic hepatitis can be life-threatening and may require hospitalization. If untreated, it can lead to permanent liver damage or failure.
Stage Three: Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
With continued alcohol abuse, the liver tries to repair itself, forming scar tissue in the process. This condition is known as fibrosis. Over time, extensive scarring leads to cirrhosis, a condition in which healthy liver tissue is permanently replaced by scar tissue.
Effects of Cirrhosis:
Poor liver function
Increased risk of liver cancer
Blood clotting issues
Internal bleeding (particularly in the esophagus)
Swelling in the abdomen and legs due to fluid buildup
Brain fog or confusion (hepatic encephalopathy)
Cirrhosis is largely irreversible, though further progression can be slowed or stopped if alcohol consumption ceases entirely and appropriate medical care is received.
Final Stage: Liver Failure
Liver failure is the most severe consequence of long-term alcohol abuse. At this stage, the liver can no longer carry out its essential functions, and without a liver transplant, survival is unlikely.
Symptoms of Liver Failure:
Severe jaundice
Swelling in the abdomen (ascites)
Confusion or coma
Bleeding disorders
Extreme fatigue and weakness
This stage requires immediate medical intervention. Unfortunately, liver failure due to alcohol is a leading cause of liver transplants worldwide.
Complications of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
Alcohol-related liver disease can cause a range of complications, including:
Increased infection risk: A damaged liver can’t fight infections as effectively.
Bleeding problems: Impaired liver function affects blood clotting.
Liver cancer: Chronic liver inflammation and cirrhosis significantly raise the risk of liver cancer.
Malnutrition: Alcohol impairs the liver’s ability to absorb and process nutrients.
How Much Alcohol is Too Much?
The threshold for liver damage differs by individual, but general guidelines suggest:
Men: No more than two standard drinks per day
Women: No more than one standard drink per day
Alcohol-free days: Recommended weekly to allow the liver to recover
Even these "moderate" levels can be harmful over time, especially if combined with other risk factors like obesity, viral hepatitis, or genetic conditions.
Reducing the Risk of Liver Damage
Protecting your liver starts with making mindful lifestyle choices. Here are some steps to reduce your risk:
1. Limit or Avoid Alcohol
The most effective way to prevent ARLD is to stop or significantly reduce alcohol intake.
2. Adopt a Liver-Friendly Diet
Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Avoid processed foods high in sugar and fat.
3. Stay Hydrated
Water helps flush toxins from your system and supports healthy liver function.
4. Get Regular Medical Checkups
Routine liver function tests can help detect problems early, even before symptoms appear.
5. Exercise Regularly
Maintaining a healthy weight lowers your risk of fatty liver disease.
Treatment for Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
If you've been diagnosed with ARLD, treatment depends on the stage and severity. Options include:
Abstinence from alcohol: The cornerstone of treatment
Medications: Corticosteroids or other drugs to reduce inflammation
Nutritional support: Supplements and a healthy diet to support recovery
Liver transplant: In cases of advanced cirrhosis or liver failure
Early intervention offers the best chance of reversing or halting the disease's progression.
Conclusion
The liver is incredibly resilient, but it has its limits. Excessive alcohol intake can overwhelm its ability to repair and regenerate, resulting in progressive and often silent damage. Understanding how alcohol affects your liver empowers you to make better choices, detect early warning signs, and seek treatment before irreversible harm occurs.
Whether you enjoy an occasional drink or consume alcohol more regularly, being informed about its impact on liver health is essential. By moderating intake, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and prioritizing liver care, you can prevent alcohol-related liver disease and protect one of your body’s most essential organs for years to come. Read Also : https://drmagnusjayaraj.com/gut-and-brain-connection/
0 notes
Text
Fatty liver disease, or hepatic steatosis, is a growing concern, especially with modern lifestyle habits and dietary patterns. It occurs when excess fat builds up in the liver cells, affecting the organ’s ability to function properly. Although often silent in the early stages, untreated fatty liver can lead to serious health complications, including liver inflammation, scarring (fibrosis), and even cirrhosis.
#Causes of Fatty Liver Disease#Fatty Liver Disease#fatty liver treatment#gastroenterologist for liver care#liver disease symptoms#Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease#best gastroenterologist in faridabad#best gastroenterologist near me
0 notes
Text
Fatty Liver vs. Liver Cirrhosis: What’s the Difference?
The liver plays a crucial role in digestion, detoxification, and metabolism. However, conditions like Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Cirrhosis can severely impact its function. Many people confuse these two liver conditions, but they are distinct in their causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches. If you are experiencing liver-related issues and searching for the best fatty liver doctors in Morbi, this guide will help you understand the key differences and why early diagnosis is essential.
What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty Liver Disease, also known as Hepatic Steatosis, occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver cells. This condition is common among people with obesity, diabetes, or those who consume excessive alcohol. It is classified into two types:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Fat buildup in the liver without excessive alcohol consumption.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): Caused by heavy alcohol consumption, leading to liver damage over time.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
Most people with a fatty liver do not experience noticeable symptoms. However, some may experience:
Fatigue and weakness
Mild abdominal discomfort
Unexplained weight loss
Elevated liver enzymes in blood tests
Seeking expert consultation from the best liver specialists in Morbi can help detect fatty liver in its early stages and prevent complications.
What is Liver Cirrhosis?
Liver Cirrhosis is a late-stage condition where healthy liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue, permanently affecting liver function. It is often the result of untreated Fatty Liver Disease, chronic hepatitis infections, or excessive alcohol consumption. Cirrhosis is irreversible, making early intervention crucial.
Symptoms of Liver Cirrhosis
Unlike Fatty Liver Disease, Cirrhosis has more severe symptoms, including:
Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
Swelling in the legs and abdomen
Frequent infections and easy bruising
Mental confusion due to toxin buildup
Severe fatigue and loss of appetite
If you or a loved one is experiencing any of these symptoms, consult the best liver treatment hospital near you for timely medical intervention.
Key Differences Between Fatty Liver and Liver Cirrhosis Feature Fatty Liver Disease Liver CirrhosisCause Fat accumulation in liver Long-term liver damage leading to scarring Reversibility Yes, with lifestyle changes No, but progression can be slowed Symptoms Often asymptomatic, mild fatigue, discomfort Severe symptoms like jaundice, swelling, mental confusion Treatment Lifestyle modifications, medication if needed Advanced medical treatment, liver transplant in severe cases Risk Factors Obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, poor diet Alcohol abuse, hepatitis infections, untreated liver diseases
Treatment Options for Fatty Liver and Cirrhosis
Fatty Liver Treatment in Morbi
If diagnosed early, Fatty Liver Disease can be reversed with lifestyle changes such as:
Healthy Diet: Reduce sugar, processed foods, and trans fats. Increase intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Regular Exercise: Helps burn excess fat stored in the liver. Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy BMI reduces liver fat accumulation. Limiting Alcohol Consumption: Essential for both NAFLD and AFLD patients. Medication: In some cases, doctors prescribe medications to control cholesterol, diabetes, or liver inflammation.
If you are looking for Fatty Liver Treatment Doctors in Morbi, Aayush Hospitals provides expert diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
Liver Cirrhosis Treatment in Morbi
Since Cirrhosis is irreversible, the goal of treatment is to slow down its progression and manage symptoms. Treatment options include:
Medications to Reduce Symptoms: Diuretics for fluid retention, antibiotics for infections, and medications to reduce ammonia levels in the blood. Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding alcohol, eating a liver-friendly diet, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Regular Monitoring: Frequent check-ups with the best fatty liver doctors in Morbi to assess liver function. Liver Transplant (Severe Cases): In advanced stages, a liver transplant may be necessary.
Why Choose Aayush Hospitals for Liver Treatment in Morbi?
At Aayush Hospitals, Morbi, we specialize in advanced liver care with state-of-the-art diagnostic tools and experienced specialists. Here’s why we are recognized as the best liver treatment hospital near you:
✔ Expert Team of Liver Specialists ✔ Advanced Diagnosis & Treatment Plans ✔ Personalized Patient Care ✔ Affordable & Comprehensive Liver Treatment
Both Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Cirrhosis require proper diagnosis and treatment to prevent severe health complications. If you are searching for the best liver specialists in Morbi, Aayush Hospitals is your trusted healthcare partner. Early detection can save lives—schedule your consultation today!
0 notes
Text
Alcoholic Liver Disease CAUSES AND IMPACT Causes, Incidence, Risk Factors, Impact Alcohol use has been linked with liver disease mortality and increased social and economic costs (NCBI, 2014; Bruha et al., 2009). Most recent statistics say that disorders in alcohol consumption afflict millions of people worldwide. The incidence has been increasing along with increasing alcohol consumption. Alcohol liver disease takes the form of acute alcoholic hepatitis and chronic liver disease, such as steatosis, steatohepatitis, fibrosis and cirrhosis. Seriousness and prognosis depend on the amount consumed, the pattern of drinking and the length of time of consumption, the presence of liver inflammation, diet and nutritional and genetic disposition. While steatosis is virtually benign, morbidity and mortality are both high in liver cirrhosis. Survival rate for advanced cirrhosis is 1 to 2 years and 50% mortality risk for those with severe acute alcoholic hepatitis have as much as 50% mortality (NCBI, 2014). Long-term intake of more than 30 grams of absolute alcohol a day raises the risk of alcoholic liver disease or ALD. Liver disease is almost sure to develop from long-term consumption of more than 80 grams of absolute alcohol a day (Bruha et al.). Alcohol liver disease or ALD or Alcohol-related disease or ARLD is damage to the liver by alcohol mis-use (NCBI, 2014). The symptoms do not manifest until the liver has been seriously damaged. I is the most complex organ in the body second only to the brain. It filters toxins from the blood, helps digest food, regulates blood sugar and cholesterol levels, and helps fight infection and disease. It is very resilient and can regenerate itself. But every alcohol consumption destroys some liver cells. While it can produce new cells to replace those that die, prolonged alcohol use for a number of years reduces its capabilities and soon damages it (NCBI). The three stages of ARLD or ALD are alcoholic fatty liver disease, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis (NCBI, Bruha et al. 2009). Fatty liver disease can result from heavy drinking for even a few days. It is reversible and liver health can be restored if drinking is stopped for two weeks. Alcoholic infectious hepatitis results from continued alcohol over-consumption, which inflames the liver. Liver health can be restored if drinking is stopped permanently. Otherwise, it is a life-threatening illness. And cirrhosis is the last stage in which the liver is substantially scarred. It is generally irreversible but immediate cessation can reduce further damage and largely increase life expectancy. Otherwise, life expectancy is limited to at least 5 years at 50%. Complications are likely and life-threatening, including internal bleeding, increased toxins in the brain or encephalopathy, fluid accumulation in the abdomen or ascites linked to kidney failure, and liver cancer (NBCI, Bruha et al.). Signs and Symptoms ALD or ARLD produces conditions and associated symptoms (NHS, 2013). The symptoms do not appear until the liver has been seriously damaged. Early symptoms are malaise, weight loss, loss of appetite, jaundice or yellowing of the eyes and skin, swelling of the ankles and the abdomen, drowsiness or confusion, vomiting of blood or blood in the stools, and diarrhea. Advanced symptoms develop when the liver becomes more severely damaged. These include jaundice, edema or swelling of the extremities because of fluid build-up, ascites or build up of abdominal fluid, strong skin itch, hair loss, clubbed fingers, blotchy red palms, considerable weight loss, muscle wasting, weakness, confusion and memory disruption, insomnia, personality changes because of toxin build-up in the brain, vomiting of blood, black stools because of internal bleeding, frequent bruises and bleeding and increases sensitivity to alcohol and drugs. The last is the result of the failure of the liver to process alcohol and drugs (NHS). Physical examination often reveals an enlarged and smooth but seldom tender liver (NHS, 2013). The signs of chronic liver disease, such as spider angiomas, ascites or asterixix, are likely absent. Symptoms may be non-specific and mild. These include loss of appetite and weight loss, painful or distended stomach, nausea or vomiting. Physical manifestations can include enlarged liver or hepatomegaly, jaundice, ascites, spider angiomas, fever and encephalopathy. Alcoholic cirrhosis may present itself in the form of decompensation even when fatty liver or alcoholic hepatitis did not precede it. It may also be diagnosed along with acute alcoholic hepatitis. The symptoms and signs of alcoholic cirrhosis are not distinguishable from its causes. The person may have jaundice, pruritus, abnormal laboratory findings, or complications of portal hypertension, such as variceal bleeding, ascites, or hepatic encephalopathy. Symptoms are often absent until the advanced stage (NHS). Treatment and Effects Abstinence is the ultimate goal of treatment as it improves ALD in all its stages (EASL, 2012). Disulfiram used to be the only effective medication for alcoholism until the discovery of its ill effects of possible hepatotoxicity. More recent medications have been developed without this risk and to complement psychosocial treatments. These are naltrexone and acamprosate. Both drugs were approved for the treatment of alcoholism although they have not been tested on cirrhosis (EASL). A large trial found that the intramuscular application of naltrexone in alcoholism has been effective (EASL, 2012). However, it has not been tested on ALD and has therefore not been recommended for those with this illness. Acamprosate, the other approved drug, is a modulator. A meta-analysis of 24 randomized controlled trials provided evidence of its effectiveness as an alcoholism treatment. The use of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid has been approved for use as medicine in European countries, like Italy and Austria, for alcoholism. But the risk of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid abuse requires additional research. However, these two drugs are still recommended for alcohol dependency without advance ALD in combination with counseling for alcohol reduction consumption and the prevention of relapse (EASL). With abstinence as goal, alcohol withdrawal syndrome is almost certain to occur (EASL, 2012). Benzodiazepines are recognized as the "gold standard" therapy for withdrawal. They are effective in reducing both withdrawal symptoms and risks of seizures and/or delirium tremens. Short and intermediate-acting benzodiazepines are safer for older patients and those with some hepatic problems (EASL). Nursing Care Strategies for the First 24 Hours Upon Admission A positive assessment of patients with unhealthy alcohol use satisfies the standard criteria for admission (Makdissi & Stewart, 2013). The patient is first assessed as to whether he has an alcohol use disorder or not. Those without are subjected to a brief intervention strategy, consisting of a minimum feedback on his alcohol use and condition, advice on how to reduce use, an explanation on why consumption should be limited, a non-confrontation inquiry on his interest in reducing consumption and a determined plan to reduce drinking. Outpatient referral shall be integrated into the brief intervention strategy (Makdissi & Stewart). If the patient must be hospitalized and had priori severe withdrawal or unstable medical disease, the management should be prevention for acute alcohol withdrawal (Makdissi & Stewart, 2013). He will be given fixed dose benzodiazepines at 50mg every 6 hours for the first 24 hours upon admission. This will be followed by 25 mg every 6 hours for the next 48 hours. He will The patient will be monitored for over-sedation or insufficient dosage. Benzodiazepine will be administered in case of active withdrawal but in decreased use and shorter duration of treatment. Shorter-acting benzodiazepines will be given to prevent recurrence of symptoms. First treatment of severe withdrawal will consist of intravenous benzodiazepines of 2-4 mg or 5-10 mg of diazepam. In case, additional dose is needed, which is seldom, the patient will be subjected to intensive monitoring and treatment with barbiturates or propofol. Phenobarbital is, however, most frequently used in this situation at 30mg, which is equivalent to 2 mg lorazepam, 25 mg chlodiazepoxide or 10 mg diazepam (Makdissi & Stewart). An alternative to benzodiazepines is pentoxifylline, as some suggest, as first-line treatment in a patient with severe alcoholic liver disease (Frazier, 2011). This is in combination with enteral nutrition as a suitable preference to corticosteroids in a patient with alcoholic severe hepatitis. Pentoxifylline or PTX was demonstrated to improve the condition of a patient with alcoholic hepatitis through the down regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines. At the same time, it possesses antibiotic effects that respond to disease severity. Furthermore, it asserts antifibriotic effects by enhancing both profibrogenic cytokine and procollagen effects. And lastly, it reduces mortality by reducing the incidence of hepatorenal syndrome by improving renal microcirculation and hemodynamic mechanism (Frazier). If the patient is a chronic heavy drinker, he is likely to suffer from other disorders related to drinking (Makdissi & Stewart, 2013). A chronic heavy drinker consumes at least 50-60 grams of alcohol daily. These disorders include pneumonia, wound infections, bleeding, myocardial dysfunction and increased stress responses. These disorders will be addressed with detoxification and abstinence before applying further procedures. These succeeding procedures will likely be parenteral thiamine, electrolyte replacement, and rigid monitoring and treatmemtnf for post-operative withdrawal. Benzodizepines will be used to prevent acute withdrawal. Morphine will be used to reduce post-operative pneumonia by correcting endocrine and immune imbalances produced by chronic heavy drinking and peri-operative abstinence (Makdissi & Stewart). BIBLIOGRAPHY Bruha, R., et al. (2009). Alcoholic liver disease. Vol. 110 # 3m Prague Medical Report: PubMed Central. Retrieved on April 6, 2014 from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19655694 EASL (2012). EASL clinical practical guidelines: management of alcoholic liver disease. Vol. 51 # 1, Journal of Hepatology: European Association for the Study of the liver. Retrieved on April 6, 2014 from http://www.easl.eu/assets/application/files/5e1b5512fb2cabb_file.pdf Frazier, T.H. (2011). Treatment of alcoholic liver disease. Vol. 4 # 1, Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology: PubMed Central. Retrieved on April 6, 2014 from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3036962/ Makdissi, R. And Steward, S.H. (2013). Care for hospitalized patients with unhealthy alcohol use: a narrative review. Makdissi and steward Addiction Science and Clinical Practice. Retrieved on April 6, 2014 from http://www.ascpjournal.org/content/pdf/1940-0640-8-11.pdf NCBI (2014). Alcoholic-related liver disease. National Center for Biotechnology: US National Library of Medicine. Retrieved on April 6, 2014 from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.go/pubmedhealth/PMH0047841 NHS (2013). Alcohol-related liver disease: symptoms. National Health Services: NHS England. Retrieved on April 6, 2014 from http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/liver_disease_(alcoholic)/Pages/symptoms.aspx Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Can a Fatty Liver Cause Other Health Issues? Managing Health

Fatty liver is a very common health condition where excess fat build-up in the liver cells usually stems from poor diet, unhealthy lifestyle patterns, and excessive alcohol intake. Usually, such a type of condition doesn’t show instance signs & symptoms but it can result in a life-threatening health condition that is left untreated immediately. Fatty liver have the potency to result in multiple other health complications such as diabetes and liver cirrhosis, if treatment and care are not given early on.
In addition, early identification and tailored treatment are extremely crucial when it comes to preventing further health complications. If you or your family member is experiencing symptoms of Fatty liver disease, seek immediate medical attention and fatty liver treatment in Siliguri to receive tailored treatment and care.
Understanding Fatty Liver and Its Causes
The liver is one of the most vital and largest organs inside our body and it plays a crucial role in aiding the body digest food removing poisons and storing energy. Fatty liver disease also known as steatotic liver and hepatic steatosis is a health condition where excess fat accumulates in the liver. People with this condition often suffer from mild tiredness or pain in the upper side of the abdomen but such type of diseases become extremely hard to spot early on.
This condition is commonly associated with other metabolic disorders like high blood pressure and insulin resistance. Seeking the best fatty liver treatment in Siliguri can aid in managing these complications and challenges more effectively by delivering personalized solutions to prevent further issues and complications.
How Fatty Liver Affects Overall Health?
Fatty Liver diseases can bring significant challenges and impact overall health if immediate medical attention and care are not provided. Some of the health complications associated with fatty liver are;
Liver Damage:
Fatty Liver can lead to inflammation and scarring in the liver. Over time, this could develop into cirrhosis, where the liver becomes extremely damaged and loses its capability to function accurately. Such complications can lead to various symptoms, such as weakness, fatigue, and jaundice.
Type 2 Diabetes:
Fatty liver plays a crucial role in insulin resistance which can result in type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is a chronic health condition where the body fails to use insulin in a proper manner which can lead to other health complications such as higher blood sugar levels. When the liver becomes extremely overloaded with accumulated fats, it loses its capability to regulate blood sugar levels more effectively and efficiently. This is a key factor in the development of diabetes for a large number of individuals.
Seeking the best fatty liver treatment in Siliguri can aid in addressing this condition by focusing on the root cause and enhancing liver function, this can, in turn, aid in better control of blood sugar levels.
Kidney Problems:
A fatty liver also places extra stress on other organs, particularly the kidneys. As the liver fails to function properly due to accumulated fats, it can lead to kidney damage which further gives rise to severe health complications such as kidney failure and kidney diseases if immediate medical attention is not provided.
Cardiovascular Disease:
Study shows that there is a strong relationship between heart disease and fatty liver. The buildup of fat in the liver can significantly contribute to health conditions such as high cholesterol and high blood pressure, both of which are the major risk factors for heart disease. Individuals suffering from a fatty liver are more vulnerable to developing atherosclerosis, a health condition where plaque gradually builds up in the arterial vessels.
If you are experiencing these mentioned symptoms, seeking immediate best fatty liver treatment in Siliguri from a reliable and seasoned professional can be extremely beneficial to mitigate the symptoms early on.
Managing Fatty Liver for Better Health
While fatty liver can result in various health complications it can be managed effectively with a tailored treatment approach and comprehensive care. The very first step to manage this issue is lifestyle modification, including;
Adopting a Healthy Diet:
An individual must focus on a balanced diet that is rich in lean proteins, vegetables, and leafy greens. Also, it is crucial for an individual to reduce the consumption of refined carbs, and sugars along with processed foods to enhance the function and health of the liver.
Regular exercise:
Indulging in regular physical activity plays a significant role when it comes to reducing liver fat and improves the overall health and well-being of an individual. Striving for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week can promote better liver health.
Avoid Alcohol and Toxins:
Alcohol is the main cause of fatty liver disease so it is crucial for an individual to avoid it at any cost to prevent liver damage. If you are searching for specialized treatment and care, seeking the best fatty liver treatment in Siliguri can be the most beneficial and effective option.
Conclusion
To conclude, managing fatty liver disease is extremely crucial in order to prevent further health complications such as cardiovascular diseases cirrhosis, and diabetes. Timely interventions along with lifestyle modification are key to mitigating the risks and challenges linked with this condition.
For an individual living in Siliguri, seeking the best fatty liver treatment in Siliguri can make a huge positive difference when it comes to managing your health and preventing further complications.
#Fatty Liver treatment in Siliguri#Best Fatty Liver Treatment in Siliguri#Fatty liver disease Siliguri#Liver specialist Siliguri#Best liver doctor Siliguri#Liver treatment Siliguri
0 notes
Text
Fatty Liver Disease Awareness: Risk Factors and Health Implications

Fatty liver disease, medically known as hepatic steatosis, occurs when excess fat accumulates in liver cells. This condition often presents no early symptoms, making awareness crucial for prevention and early intervention. Understanding the risk factors and potential health implications of fatty liver disease is essential for maintaining liver health and overall well-being.
Key Takeaways
Types of Fatty Liver Disease: Includes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic liver disease (ALD).
Risk Factors: Obesity, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and excessive alcohol consumption.
Symptoms: Often asymptomatic but can include fatigue and abdominal discomfort.
Complications: Can progress to cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer if untreated.
Management: Lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and weight management are key.
What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease is a condition characterized by the buildup of fat in liver cells. While a small amount of fat in the liver is normal, excessive accumulation can lead to inflammation and liver damage. There are two primary types:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Occurs in individuals who consume little to no alcohol. It's often associated with metabolic conditions like obesity and diabetes.
Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD): Results from excessive alcohol consumption, leading to fat accumulation and liver inflammation.
Causes and Risk Factors of Fatty Liver Disease
Lifestyle Factors
Poor Diet: High intake of processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can contribute to fat buildup in the liver.
Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise can lead to weight gain and increased fat deposition in the liver.
Health Conditions
Obesity: Excess body weight is a significant risk factor for developing fatty liver disease.
Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin resistance associated with diabetes can promote fat accumulation in the liver.
High Cholesterol and Triglycerides: Elevated levels can lead to fat buildup in the liver.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Family History: Genetics can play a role in susceptibility to fatty liver disease.
Medications: Certain drugs, like corticosteroids and some cancer treatments, can increase liver fat.
Alcohol Consumption
Excessive Drinking: Heavy alcohol use is a direct cause of alcoholic liver disease.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
Early Stage Symptoms
Fatigue: Persistent tiredness without a clear cause.
Abdominal Discomfort: Mild pain or fullness in the upper right abdomen.
Advanced Stage Symptoms
Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Swelling: Fluid accumulation in the abdomen (ascites) and legs.
Weight Loss: Unintended and unexplained loss of weight.
It's important to note that many individuals with fatty liver disease may not experience noticeable symptoms, especially in the early stages.
Health Implications of Fatty Liver Disease
Potential Complications
Liver Fibrosis: Scarring of liver tissue due to ongoing inflammation.
Cirrhosis: Severe scarring that impairs liver function and can lead to liver failure.
Liver Cancer: Increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
Impact on Overall Health
Cardiovascular Diseases: Higher risk of heart disease and stroke.
Metabolic Syndrome: Cluster of conditions increasing the risk of diabetes and heart disease.
Diagnosing Fatty Liver Disease
Medical History and Physical Exam
Assessment: Review of lifestyle, medical history, and physical examination to detect signs of liver disease.
Diagnostic Tests
Blood Tests: Check liver enzymes to identify liver inflammation or damage.
Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI to visualize fat in the liver.
Liver Biopsy: A sample of liver tissue may be taken to assess the extent of fat accumulation and inflammation.
Treatment and Management Strategies
Lifestyle Changes
Balanced Diet: Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Weight Management
Gradual Weight Loss: Losing 7-10% of body weight can significantly reduce liver fat.
Medication Options
Managing Underlying Conditions: Medications to control diabetes, cholesterol, and triglycerides.
Monitoring and Regular Checkups
Routine Follow-ups: Regular monitoring of liver function and overall health.
Prevention Tips for Fatty Liver Disease
Healthy Eating Habits
Nutrient-Rich Diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods.
Limit Sugars and Fats: Reduce intake of added sugars and saturated fats.
Physical Activity
Consistent Exercise: Incorporate both aerobic exercises and strength training.
Alcohol Moderation
Limit Intake: Adhere to recommended guidelines for alcohol consumption.
Routine Health Screenings
Regular Checkups: Early detection through routine medical examinations.
Conclusion
Raising awareness about fatty liver disease is vital to preventing severe liver damage and other related health complications. By understanding the risk factors, recognizing early symptoms, and adopting healthier lifestyle choices, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their liver health. Regular medical checkups and proper monitoring are essential for those at higher risk. With the right knowledge and preventive measures, fatty liver disease can often be managed and even reversed.
FAQs About Fatty Liver Disease
1. What is the main cause of fatty liver disease?Fatty liver disease is primarily caused by poor dietary habits, obesity, excessive alcohol use, and metabolic conditions like diabetes. It can also develop due to certain medications or genetic factors.
2. Can fatty liver disease be reversed?Yes, with proper lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight, fatty liver disease can often be reversed in its early stages.
3. What foods should I avoid if I have fatty liver disease?Avoid processed foods, refined carbohydrates, added sugars, and foods high in saturated fats. Limiting alcohol intake is also crucial.
4. Are there medications to treat fatty liver disease?There is no specific medication that directly cures fatty liver disease. However, doctors may prescribe medications to manage associated conditions such as high cholesterol, diabetes, or obesity.
5. How can I tell if my fatty liver disease is getting worse?Signs that your condition may be worsening include persistent fatigue, abdominal pain, jaundice, and swelling in the abdomen. Regular medical checkups and liver function tests can help track your condition.
6. Is fatty liver disease life-threatening?While early stages of fatty liver disease are usually manageable, severe progression can lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer. Early diagnosis and proper care can prevent life-threatening complications.
7. How often should I have my liver checked if I'm at risk?If you're at risk due to obesity, diabetes, or other factors, it's advisable to have liver function tests annually or as recommended by your doctor.
0 notes
Text
Alcoholic Liver Disease: Signs, Symptoms, and Treatment Options

Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is a serious condition caused by excessive alcohol consumption over time. It damages the liver, leading to inflammation, scarring, and, in severe cases, liver failure. The liver plays a crucial role in detoxification, metabolism, and overall bodily function, so liver damage can have life-threatening consequences.
Understanding the signs, symptoms, and treatment options for ALD is essential for early detection and management. We brought in the best stomach specialists in Surat from Vedam gastro hospital to help you understand the different stages of alcoholic liver disease, its warning signs, and available treatments.
What Is Alcoholic Liver Disease?
Alcoholic liver disease is a progressive condition that develops due to long-term alcohol abuse. The liver processes alcohol, but excessive consumption over time can lead to inflammation, fat accumulation, and scarring. ALD generally progresses through three main stages:
Fatty Liver (Steatosis):
The earliest stage of ALD, where fat accumulates in liver cells.
Often reversible if alcohol consumption stops.
Usually asymptomatic but may cause mild discomfort in the upper right abdomen.
Alcoholic Hepatitis:
Inflammation of the liver due to prolonged alcohol use.
Can range from mild to severe and may cause serious complications.
Symptoms include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite.
Cirrhosis:
The most severe stage, where scar tissue replaces healthy liver cells, leading to liver failure.
This condition is irreversible, though treatment can slow progression.
Symptoms include severe fatigue, fluid buildup in the abdomen (ascites), mental confusion, and bleeding disorders.
Signs and Symptoms of Alcoholic Liver Disease
Our experts at Vedam Gastro Hospital, one of the best gastro hospitals in Surat, say that ALD symptoms vary depending on the stage and severity of the disease. Many people may not notice symptoms until significant liver damage occurs. Common signs include:
● Early Symptoms:
o Loss of appetite
o Nausea and vomiting
o Fatigue and weakness
o Abdominal discomfort
o Unexplained weight loss
● Advanced Symptoms:
o Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
o Swelling in the legs and abdomen (edema and ascites)
o Dark-colored urine and pale stools
o Easy bruising and bleeding
o Confusion, memory problems, and difficulty concentrating (hepatic encephalopathy)
o Severe itching due to bile buildup
If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, especially after long-term alcohol use, seeking medical attention from one of the best gastro hospitals in Surat is crucial.
Risk Factors for Alcoholic Liver Disease
Several factors increase the risk of developing ALD, including:
● Heavy Alcohol Consumption: Regular, excessive alcohol intake is the primary cause of ALD. The liver can only process a limited amount of alcohol, and exceeding this capacity leads to damage.
● Gender: Women are more susceptible to ALD than men because their bodies metabolize alcohol differently, leading to higher alcohol levels in the bloodstream, explain our liver specialists at Vedam Gastro Hospital, one of the best stomach hospitals in Surat.
● Genetics: Some people may be genetically predisposed to liver damage due to alcohol.
● Obesity and Poor Diet: Being overweight and consuming a high-fat, low-nutrient diet increases the risk of fatty liver disease and worsens ALD progression.
● Coexisting Liver Conditions: Conditions like hepatitis B or C can accelerate liver damage in people who consume alcohol excessively.
Diagnosis of Alcoholic Liver Disease
Doctors diagnose ALD using a combination of medical history, physical exams, and diagnostic tests, including:
● Blood Tests: Liver function tests (LFTs) measure enzyme and protein levels to detect liver damage.
● Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI scans help assess liver size, fat deposits, and scarring.
● Liver Biopsy: A small sample of liver tissue is examined under a microscope to confirm the severity of liver damage.
Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention and better outcomes.
Treatment Options for Alcoholic Liver Disease
The most effective treatment for ALD is stopping alcohol consumption completely. Continued drinking worsens liver damage and reduces treatment effectiveness. Here are the main treatment options:
1. Lifestyle Changes and Alcohol Cessation
● Complete alcohol abstinence is the only way to stop ALD progression.
● Rehabilitation programs and support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) can help with alcohol dependency.
● A healthy diet rich in vitamins and proteins supports liver function and repair.
2. Medications
● Corticosteroids: Used to reduce inflammation in severe alcoholic hepatitis cases.
● Pentoxifylline: An anti-inflammatory drug that may help in some patients with alcoholic hepatitis.
● Liver Supplements: Vitamin and mineral supplements, such as vitamin B and thiamine, help address nutritional deficiencies.
3. Managing Complications
● Diuretics: Reduce fluid buildup (ascites) in the abdomen.
● Lactulose: Helps treat hepatic encephalopathy by reducing toxins in the blood.
● Endoscopic Treatment: Used for variceal bleeding in cirrhosis patients.
4. Liver Transplant
● For end-stage ALD, a liver transplant may be the only option.
● Patients must be alcohol-free for at least six months before being considered for a transplant.
Preventing Alcoholic Liver Disease
Prevention is key to avoiding ALD and its complications. Here’s how you can protect your liver:
● Limit Alcohol Intake: Follow recommended guidelines — no more than 1 drink per day for women and 2 drinks per day for men.
● Eat a Balanced Diet: Include fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains in your meals.
● Exercise Regularly: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of fatty liver disease.
● Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help the liver flush out toxins.
● Get Regular Check-Ups: Routine liver function tests can detect problems early.
Conclusion
Alcoholic liver disease is a serious yet preventable condition. Recognizing the early warning signs and seeking medical help from the best gastro hospital in Surat can improve outcomes. The most important step in treatment is quitting alcohol completely. With the right lifestyle changes, medications, and medical interventions, it is possible to slow down or even reverse liver damage in the early stages.
If you or a loved one struggles with alcohol use, seek medical advice and support to protect liver health and overall well-being. Early action can save lives.
0 notes
Text
Impact of Alcohol on Liver Health

When we think of the liver, we often imagine it as the body's filter—working tirelessly to detoxify and process the substances we put into our bodies. However, one common substance that poses a serious threat to liver health is alcohol. Many people don’t realize just how harmful alcohol can be when consumed in excess over time. In this article, we will explore the impact of alcohol on liver health, shedding light on what happens inside the body when we drink and how to safeguard your liver.So, let’s dive into the details and discover why it's crucial to be mindful of our drinking habits.
Introduction to the Liver and its Vital Role
The liver is an important organ in the body. The liver is responsible for filtering toxic substances, producing bile to aid digestion, and storing vital nutrients. Our bodies would not be able handle vital processes without a healthy liver.
Alcohol is a leading cause of liver disease worldwide. We can better protect ourselves if we know how alcohol affects our liver health.
What happens to your liver when you drink alcohol?
Your liver will work overtime to metabolize alcohol. The liver converts alcohol to acetaldehyde which is toxic and can harm liver cells. The liver can only process so much alcohol at once, despite its efficiency. When you drink alcohol, the liver's ability detoxify your body is compromised. This can lead to liver inflammation and scarring.
The liver is like a factory, processing all kinds of materials. The production line becomes clogged when it is overloaded. The more damage is done the longer it continues.
The Stages of Alcohol Related Liver Disease
Alcohol-related liver diseases progress in stages. Understanding these stages is crucial to identifying early risks. The stages include:
Alcoholic Steatosis This is the first stage of liver damage where fat deposits in liver cells. If alcohol consumption is stopped, it can be reversed.
Alcoholic Hepatitis. Continued heavy drinking can lead to liver inflammation. This stage can include symptoms such as fever, jaundice and pain in upper abdomen.
Cirrhosis This is the last stage of liver damage where liver tissue scars and becomes unable to perform properly. Cirrhosis can be irreversible, and lead to liver failure.
It is important to note that the sooner you detect the problem, you have a better chance of reversing the damage.
How much alcohol is too much for your liver?
Understanding what is "too much alcohol" can be difficult. The liver is at risk for most people who binge drink or drink heavily every day. Women should drink no more than one glass of alcohol per day according to health guidelines. Men should limit themselves to two glasses per day.
Note that "one drink", which is 14 grams of pure ethanol, equals approximately a 5-ounce glass of wine or beer (12 oz) or 1.5-ounces of distilled spirit. The risk of liver damage increases significantly if you drink more than these limits.
Liver Damage Symptoms from Alcohol
Alcohol-induced liver damage doesn't always present with immediate symptoms. Early liver damage is often not noticed. As the damage worsens, certain symptoms can begin to show up, such as:
Fatigue
Loss of appetite
Nausea and vomiting
Pain in the abdomen, particularly on the upper right side
Jaundice is the yellowing of skin or eyes.
Swelling of the legs or abdomen
You should consult your doctor immediately if you have any of these symptoms and a history that includes heavy drinking.
Alcohol and Fatty Liver Disease
Alcohol is the leading cause of fatty liver disease. Fat builds up inside liver cells and affects the ability of the liver to function. Although fatty liver disease may not have any symptoms, it could progress to more serious conditions such as alcoholic hepatitis or cirrhosis if you continue drinking.
Alcohol consumption can disrupt the liver's ability to process fats and nutrients. This leads to fat accumulation.
Alcohol Effects on Liver Function and Enzymes
Alcohol is broken down by liver enzymes. Alcohol can affect the liver enzyme levels in your blood when you drink a lot. Elevated liver enzyme levels may indicate inflammation or injury.
Chronic alcohol consumption over time can damage liver cells, reducing liver regeneration ability. This can lead to long-term health issues, such as liver failure.
The Dangers of Heavy Drinking: Cirrhosis, and Beyond
Cirrhosis can be a severe consequence of excessive alcohol consumption. Cirrhosis is a permanent scarring of the liver. Cirrhosis may lead to liver cancer, internal bleeding and infections.
A liver transplant can be the only way to survive in some situations. You could save your life by finding the best liver transplant surgeon in India. India has renowned liver surgeons who have exceptional success rates.
How long does it take to recover from alcohol-related liver damage?
The severity of alcohol-related liver disease will determine the recovery time. When liver damage is detected early, it can be reversed in a matter of weeks or even months by stopping alcohol consumption. For those with severe liver disease or cirrhosis, a recovery may not be possible and a liver-transplant may be necessary.
Early intervention is key, as are steps taken to protect the liver.
What you need to know about the best liver transplant surgeon in India
A liver transplant is sometimes required in cases of liver failure caused by alcohol. If you are looking for the Best Liver Transplant Surgery in India look for surgeons with extensive experience and a track record of successful liver surgeries. India is a medical tourism destination because it has world-class surgeons and hospitals that specialize in liver transplants.
The right surgeon will increase your chances of having a successful organ transplant, and can improve your life quality.
Tips to Drink Healthily and Avoid Liver Damage
Moderation is the best way to avoid liver damage caused by alcohol. Here are some tips on how to maintain a healthy liver while enjoying alcohol:
Limit your alcohol intake to the daily recommended limit.
Avoid binge drinking.
Eat a healthy diet and stay hydrated.
Regularly take breaks from alcohol so that your liver can recover.
Is Alcohol Detox Safe?
Alcohol detoxification is the process by which alcohol is removed from your body, typically after excessive or prolonged drinking. Detoxing from alcohol can be harmful if it is not done correctly. Alcohol detox should be done under medical supervision, especially if heavy drinking is a part of your past.
Diet and liver health
A healthy diet is important for liver function. Eating foods high in antioxidants and vitamins can reduce inflammation of the liver and promote healing. For liver health, foods like leafy vegetables, turmeric, garlic and berries can be very beneficial.
To prevent liver damage, it is important to avoid excessive alcohol and fatty food.
When should you seek help for liver issues?
Consult a medical professional immediately if you notice any symptoms of liver disease. It is important to detect liver damage early in order to prevent further complications. A doctor can assess your liver function and prescribe appropriate treatment if you are concerned about alcohol-induced liver damage.
Conclusion - Protect Your Liver to Ensure a Healthier Tomorrow
Alcohol can cause liver damage. The liver is vital to maintaining your health, but alcohol can also harm it. You can reduce your risk of liver disease by understanding how alcohol affects liver health, and taking measures to protect it.
Consult the Best Transplant Surgeons in India if you have severe liver damage. By taking care of your liver, you can live a longer and healthier life.
FAQs
What are the early signs of liver damage caused by alcohol?
Fatigue, nausea, and loss of appetite are often the first symptoms. Jaundice and abdominal discomfort may be present in more severe cases.
Does a liver recover after quitting alcohol?
If the damage to the liver is not severe, it can regenerate and heal after stopping alcohol consumption.
How do I protect my liver against alcohol damage?
Moderation is the key. Drink in moderation, adhere to the recommended limits and stay hydrated.
Is liver surgery the only option for treating cirrhosis of the liver?
Early treatment and lifestyle modifications can help manage this condition.
How should I act if I suspect I may have liver issues?
Ask your doctor to perform tests on the liver and to discuss possible treatment options. Early intervention can help prevent further damage.
0 notes
Text
Which Ayurvedic Medicine is Best For Fatty Liver
Fatty liver disease is a growing concern among many people worldwide. The liver, one of the most important organs in our body, helps filter toxins, store energy, and perform several essential functions. When the liver accumulates excess fat, it can lead to fatty liver disease. But did you know that Ayurveda offers several natural ways to support liver health? In this blog, we will explore the best Ayurvedic medicine for fatty liver, its symptoms, causes, and five powerful herbs that can help detox your liver.
What is Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition where too much fat accumulates in the liver cells. It’s a common condition and can be caused by factors like poor diet, obesity, alcohol consumption, and certain medications. Although fatty liver might not show obvious symptoms in its early stages, it can eventually lead to serious health issues if not managed properly.
There are two main types of fatty liver:
Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) – caused by excessive alcohol consumption.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) – caused by factors such as obesity, poor diet, and lack of exercise.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver
Many people with fatty liver disease do not experience symptoms in the early stages. However, as the condition progresses, the following symptoms may appear:
Fatigue and tiredness
Unexplained weight loss
Pain or discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen
Swelling in the abdomen or legs
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes)
Nausea or loss of appetite
Dark-colored urine
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Fatty Liver
Fatty liver disease can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Obesity: Excess fat in the body can contribute to fat buildup in the liver.
Poor Diet: Diets high in fats, sugars, and processed foods can increase the risk of fatty liver.
Excess Alcohol Consumption: Drinking alcohol excessively can lead to liver damage and fatty liver disease.
Diabetes and High Blood Sugar: People with diabetes or high blood sugar levels are more likely to develop fatty liver.
High Cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels can lead to the accumulation of fat in the liver.
Medications: Some medications may have side effects that cause fat buildup in the liver.
Best Ayurvedic Medicine for Fatty Liver
Ayurveda, the ancient system of medicine from India, focuses on balancing the body’s natural energies (doshas) to maintain health. According to Ayurveda, fatty liver disease occurs due to an imbalance in the digestive system, often caused by poor diet, lifestyle choices, and toxins. Ayurvedic medicine offers several herbal remedies that can help detoxify the liver and promote its natural healing process.
One of the most effective ways to support liver health is by using liver detox tablets Ayurvedic that contain a combination of powerful herbs. These herbs work together to support liver function, reduce inflammation, and promote detoxification.
5 Powerful Ayurvedic Herbs for Fatty Liver
Kutki (Picrorhiza kurroa): Kutki is a well-known herb in Ayurveda for its ability to detoxify the liver. It helps improve liver function, reduce liver inflammation, and promote bile production. It is also known for its antioxidant properties, which protect the liver from damage caused by free radicals.
Bhumyamalaki (Phyllanthus niruri): Bhumyamalaki is a highly effective herb used in Ayurvedic liver detox formulas. It is known to support liver health, cleanse the liver, and reduce the risk of liver damage. This herb is particularly beneficial for people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Triphala: Triphala is a combination of three fruits—Amla, Haritaki, and Bibhitaki—that are well-known for their detoxifying properties. Triphala helps in flushing out toxins from the liver and improving digestion. It is also known to reduce fat accumulation in the liver and improve overall liver health.
Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum): Milk Thistle is a powerful herb widely used for liver health. It contains silymarin, a compound that helps protect the liver from toxins, regenerate liver cells, and reduce inflammation. Milk Thistle is particularly useful for people with alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia): Guduchi is an Ayurvedic herb that has been used for centuries to support liver health. It helps reduce inflammation, fight infections, and detoxify the liver. Guduchi also strengthens the immune system, which can further help the liver in its healing process.
Kayashree Liver Detox: A Natural Solution for Fatty Liver
When looking for fatty liver medicine, it's important to choose products that contain a combination of these potent Ayurvedic herbs. One such product is Kayashree Liver Detox. This supplement combines all the above-mentioned herbs, making it an excellent choice for liver detox and overall liver health.

Kayashree Liver Detox is a natural, herbal solution designed to help detoxify the liver, reduce fat accumulation, and improve liver function. It is a powerful combination of Kutki, Bhumyamalaki, Triphala, Milk Thistle, and Guduchi, all working together to cleanse the liver, protect it from toxins, and reduce inflammation. The regular use of this supplement can help improve liver health, boost digestion, and support the body's natural detoxification process.
How to Use Kayashree Liver Detox
To get the maximum benefits from liver detox tablets Ayurvedic, it's essential to follow the recommended dosage. Typically, the dosage for Kayashree Liver Detox is one or two tablets per day, preferably after meals, or as directed by a healthcare professional. Along with taking this supplement, it is also advisable to follow a healthy diet and lifestyle, which can further enhance the detox process.
Lifestyle Tips for a Healthy Liver
While fatty liver medicine like Kayashree Liver Detox can help support liver health, it’s equally important to make lifestyle changes to prevent and manage fatty liver disease:
Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid processed foods, excess sugar, and fatty foods.
Exercise Regularly: Physical activity helps reduce fat accumulation in the liver and improves overall health.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps the body flush out toxins and supports liver function.
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol can damage the liver and worsen fatty liver disease.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing excess weight can help reduce fat in the liver and improve liver health.
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease is a serious condition that can lead to severe health problems if left untreated. The good news is that Ayurveda offers effective, natural solutions to support liver health. By using the best Ayurvedic medicine for fatty liver, such as Kayashree Liver Detox, and making lifestyle changes, you can help your liver detoxify, reduce fat accumulation, and promote overall health. Remember, a healthy liver is key to a healthy body, and with the right support, you can achieve optimal liver health!
#ayurvedic medicine for fatty liver#best ayurvedic medicine for fatty liver#liver detox tablets ayurvedic#fatty liver medicine
0 notes
Text
Skin Signs of Fatty Liver You Shouldn’t Ignore
Fatty liver, also called hepatic steatosis, develops when fat accumulates in the liver, causing inflammation and severe health complications. Although lifestyle and dietary changes can reverse fatty liver, recognizing early signs is crucial. Doctors emphasize that many symptoms of fatty liver are on your skin, offering visible clues to the condition. From puffiness to jaundice, here are seven…
0 notes