#Gasdetection
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
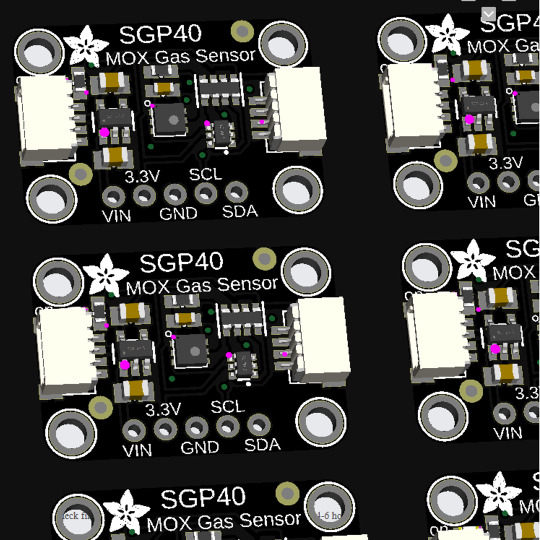
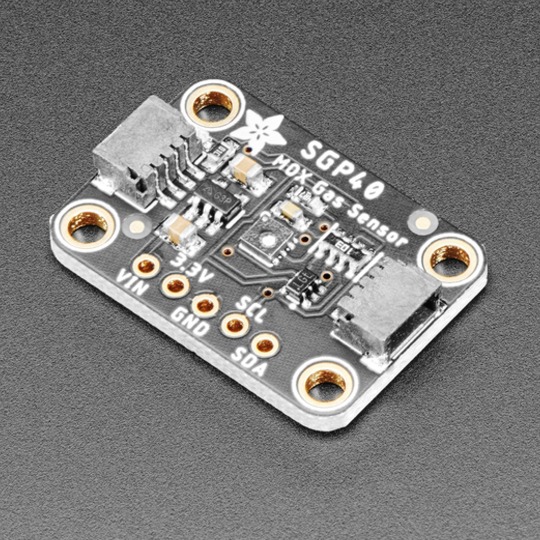
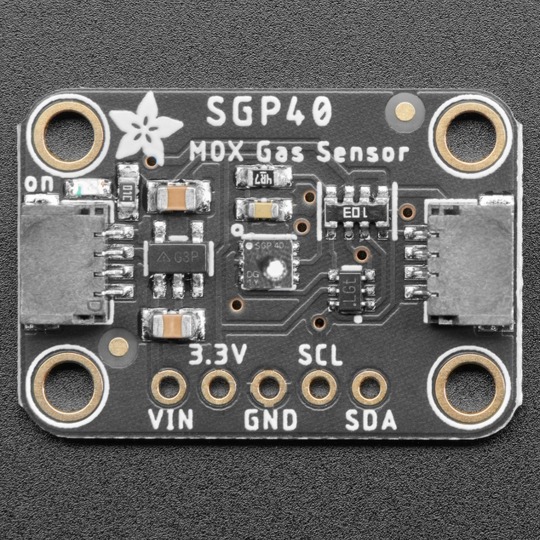

PCB of the day! SGP40 Air Quality Sensor Breakout - VOC Index - STEMMA QT / Qwiic 👃🥛🌬️
sniff sniff … do you smell that? You no longer need to stick your nose into a carton of milk; you can build a digital nose with the SGP40 Multi-Pixel Gas Sensor, a fully integrated MOX gas sensor. This is an excellent air quality sensor from the sensor experts at Sensirion, with I2C interfacing, so you don't have to manage the heater and analog reading of a MOX sensor. It combines multiple metal-oxide sensing and heating elements on one chip to provide more detailed air quality signals.
#sensirion#airquality#sensor#SGP40#adafruit#electronics#opensource#opensourcehardware#mox#digitalnose#vocindex#gasdetection#stemmaqt#qwiic#techinnovation#environmentaltech#smartsensors#iot#cleanairtech#pcb of the day#pcb
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Gas Detection Standards and Regulations in Singapore: What You Need to Know
Regarding industrial safety in Singapore, few things are as important as proper gas detection. Invisible, silent, and often deadly hazardous gases pose a significant risk in many sectors—from oil refineries and chemical plants to commercial kitchens and construction sites. Singapore has developed stringent standards and regulations surrounding gas detection to address these dangers. Whether you're an HSE officer, business owner, or worker on the ground, understanding these requirements is essential.
In this comprehensive guide, we explain gas detection standards and regulations in Singapore so you know exactly what to do to keep your operations safe and compliant.
Why Gas Detection Matters in Singapore
Singapore is a dense, urbanized nation with a robust industrial sector and tight safety regulations. With industries like petrochemicals, shipbuilding, manufacturing, and food services operating side by side, the margin for error is very small.
Hazardous gases such as carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), methane (CH₄), ammonia (NH₃), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can cause fires, explosions, or poisoning. Often, the first sign of danger is already too late. Gas detectors act as early warning systems, alerting personnel before conditions become life-threatening.
Governing Bodies and Key Regulations
1. Ministry of Manpower (MOM)
The Workplace Safety and Health (WSH) Act under MOM is the cornerstone legislation for workplace safety in Singapore. It legally requires employers to eliminate or control workers' safety and health risks, including gas hazards.
Relevant Regulations:
WSH (General Provisions) Regulations
WSH (Construction) Regulations
WSH (Shipbuilding and Ship-Repairing) Regulations
WSH (Confined Spaces) Regulations
Key Requirement: Employers must identify gas-related hazards and implement control measures such as gas detection, ventilation, and employee training.
2. National Environment Agency (NEA)
The NEA regulates environmental emissions and pollution, especially for facilities that deal with VOCs or chemical gases. Businesses must comply with air emission standards and may require fixed gas detection systems as part of their environmental controls.
3. Singapore Civil Defence Force (SCDF)
Under the Fire Safety Act, SCDF mandates that gas detection systems be installed in certain premises, particularly those storing or using flammable gases. This applies to:
Laboratories
Chemical plants
LPG storage rooms
SCDF also enforces fire safety certifications for buildings that use gas detection as mitigation systems.
Gas Detection in Confined Spaces
One of Singapore's most regulated gas detection applications is confined space entry (CSE). This includes tanks, silos, manholes, tunnels, or any enclosed space with limited ventilation.
MOM's Requirements for Confined Spaces:
Pre-entry gas testing is mandatory. The atmosphere must be tested for oxygen, flammable gases, and toxic substances.
Continuous monitoring is required during work if the atmosphere may change.
Gas testing must be done by a competent person using a properly calibrated device.
A Permit-To-Work (PTW) system must be implemented before entry.
Failure to follow these guidelines can result in heavy penalties or fatal accidents.
What Types of Gas Detectors Are Acceptable?
Regulations do not specify brands but require the equipment to be:
Fit for purpose: Appropriate for the gas being detected.
Regularly calibrated: According to the manufacturer's schedule or more frequently if required.
Used by trained personnel: Operators must understand how to use and interpret readings.
Certified: Detectors should meet international or regional standards such as:
ATEX (EU)
IECEx (International)
UL (US)
In Singapore, these certifications ensure the devices can be used in potentially explosive or high-risk environments.
Fixed vs. Portable Systems: What Regulations Apply?
Portable Gas Detectors
Used primarily for confined spaces, maintenance, or worker protection. The WSH Act mandates their use during high-risk activities like hot work, confined space entry, or tank cleaning.
Common Features Required:
Multi-gas capability (O₂, CO, H₂S, LEL)
Audible and visual alarms
Data logging (for audit and recordkeeping)
IP67 or better rating (for local weather and wet conditions)
Fixed Gas Detection Systems
Installed in locations with continuous gas emission risks, such as:
Chemical manufacturing units
Laboratories
Fuel storage rooms
SCDF and NEA may require fixed systems as part of Fire Safety or Environmental Control Plans. These systems must be maintained regularly and tested during annual inspections or audits.
Maintenance and Calibration Requirements
MOM and SCDF stress that maintenance and calibration are not optional. Regular checks ensure that sensors remain accurate and reliable.
Suggested Schedule:
Bump test: Daily or before each use
Full calibration: Every 6 months or as recommended by the manufacturer
Sensor replacement: Based on lifespan (usually 1-2 years)
Documentation of calibration and maintenance must be kept for audits.
Some employers opt to use docking stations and automated calibration tools, especially for large fleets of detectors.
Training and Competency
Gas detection is only effective if users understand what the device tells them. MOM requires that workers be trained and competent in using gas detectors, especially for confined space entry.
Training Topics:
Basic gas hazard awareness
Operation of specific detectors
Alarm responses
Pre-entry and continuous testing
Maintenance and calibration basics
Training is often available through MOM-accredited providers or equipment suppliers.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Singapore takes safety very seriously. Non-compliance with gas detection requirements can lead to:
Stop-Work Orders
Fines up to SGD 500,000 for companies
Imprisonment up to 2 years for individuals
Permanent closure of non-compliant businesses in serious cases
Besides legal consequences, the reputational damage and loss of life from an avoidable incident can destroy a business.
Industry Best Practices in Singapore
Beyond the legal minimums, many companies adopt best practices to enhance safety further:
Implement iNet or cloud-based systems for gas detector fleet management
Use real-time wireless transmission for detectors in large or complex sites
Perform third-party audits to validate gas safety procedures
Adopt integrated safety systems that combine fire alarms, gas detection, and ventilation
Many of these practices are already used in high-risk sectors like oil and gas, shipyards, and pharmaceuticals.
Where to Get Certified Equipment and Support in Singapore
Recommended Local Suppliers:
Draeger Safety Asia Pte Ltd: Known for X-am series and industrial solutions
Safetyware (Singapore): Multi-brand supplier with local calibration services
MSA Singapore: Supplies the ALTAIR series with excellent support
Honeywell Authorised Distributors: Easy access to the BW MicroClip range
Leeden National Oxygen Ltd: Strong in marine and petrochemical sectors
What to Look For:
Local service and calibration center
Training support
Spare parts availability
After-sales service agreements
Final Thoughts: What You Need to Know
Gas detection is not just a box to tick off in your safety checklist. In Singapore, where industrial activities happen near residential and commercial zones, the margin for safety error is slim.
Staying compliant with MOM, NEA, and SCDF regulations protects your team, your business, and the community. But more than just following the law, it shows that your company values human lives and takes responsibility for its impact.
Key Takeaways:
Know the regulations from MOM, NEA, and SCDF.
Use certified, regularly maintained gas detection equipment.
Train your team in proper usage and alarm response.
Document all maintenance and calibrations.
By staying proactive, informed, and compliant, you help create a safer Singapore for everyone.
0 notes
Text
Gas detection is vital for workplace safety, preventing hazards from toxic and flammable gases. Portable gas monitors provide real-time alerts for workers, while gas transmitters ensure continuous monitoring in industrial settings. Investing in reliable gas detection technology helps protect lives, maintain compliance, and prevent costly accidents in hazardous environments.
0 notes
Text
Advanced laser technology methane gas detector
Experience high-precision methane detection with our Advanced Laser Technology Methane Gas Detector. Designed for industrial and environmental safety, it ensures rapid, accurate gas leak detection with real-time monitoring. Stay compliant, efficient, and secure with cutting-edge laser-based detection technology.

0 notes
Text

Saudi Arabia Gas Sensors Market size by value at USD 24.6 million in 2024. During the forecast period between 2025 and 2031, BlueWeave expects Saudi Arabia Gas Sensors Market size to boom at a robust CAGR of 10.5% reaching a value of USD 48.9 million by 2031. The growth of Gas Sensors Market in Saudi Arabia is propelled by increased industrial automation across vital sectors like oil and gas, petrochemicals, chemicals, and manufacturing is driving demand for these critical devices. Gas sensors play a crucial role in ensuring workplace safety by detecting hazardous leaks, mitigating potential risks, and preventing environmental damage. Stringent regulatory frameworks and heightened environmental awareness are further compelling businesses to adopt advanced gas monitoring systems. Technological advancements, including IoT integration, are enabling real-time data collection and analysis, further accelerating market expansion. Regionally, Riyadh and the Eastern Province, encompassing Dammam and Jubail, represent key markets due to their robust industrial infrastructure and concentration of oil refineries and petrochemical complexes. Riyadh's smart city initiatives and rapid urbanization also contribute significantly to market growth. Furthermore, stringent air quality and safety regulations imposed by Saudi authorities like the General Authority for Meteorology and Environmental Protection (GAMEP) are fueling the demand for high-precision gas detection systems within industrial facilities.
Sample Request: https://www.blueweaveconsulting.com/report/saudi-arabia-gas-sensors-market/report-sample
Opportunity – Growing Adoption of IIoT in Industrial Environments
The growing adoption of Industrial internet of things (IIoT) in industrial environments significantly drives demand for gas sensors in Saudi Arabia. With the country’s increased focus on industrial automation and Vision 2030, IIoT integration is enhancing operational efficiency and safety in industries, such as oil and gas, manufacturing, and petrochemicals. Gas sensors integrated with IIoT provide real-time data, enabling remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and proactive responses to gas leaks. These sensors also contribute to compliance with environmental regulations, reducing operational risks and improving workplace safety. As smart factory concepts and IIoT-enabled systems expand, the need for advanced gas sensors with wireless connectivity is expected to rise. This trend will continue to shape the future of the gas sensors market in Saudi Arabia, creating new opportunities for businesses to innovate and meet the demand for smarter, more efficient gas detection solutions.
#BlueWeave#Consulting#Marketforecast#Marketresearch#GasSensors#SafetySolutions#IndustrialSafety#GasDetection#IIOT
0 notes
Text
Portable Gas Monitor LT-GM401

Labtro High-Speed Portable Gas Monitor with advanced electrochemical sensor ensures fast response. Compact, anti-static PC+TPU body suits harsh environments. Features rechargeable lithium battery, LCD display, sound/vibration alarms, and single-button operation to prevent misoperation.
0 notes
Text
Long Range Ultrasonic Sensor & Carbon Dioxide Calibration Gas: Precision for Industrial Applications
Enhance your industrial operations with the cutting-edge Long Range Ultrasonic Sensor, designed for accurate distance measurement over extended ranges. This advanced sensor provides reliable performance in harsh environments, ensuring precision in level, distance, and flow monitoring. Coupled with Carbon Dioxide Calibration Gas, your equipment will maintain top accuracy for gas detection and measurement systems. Proper calibration ensures compliance with safety standards and enhances the overall efficiency of your sensors and monitoring devices.
0 notes
Text

Labtro Gas Analyzer detects CO2, CO, CH4, NOx, and SO2 using electrochemical/infrared methods. Features include pump suction, ±3% FS accuracy, 20 sec response, LCD display, audible/visual alarms, 500 mL/min flow, sensor self-detection, and alarm record function.
0 notes
Text

Portable Single Gas Detector
Labtron Portable Single Gas Detector uses diffusion sampling and operates from -20°C to 55°C. It measures flammable gases and oxygen. Utilizing electrochemical detection for oxygen and toxins, catalytic combustion for flammable gases, and infrared for CO₂, it ensures accurate readings.
0 notes
Text

Portable Hydrogen Sulfide Gas Detector
Labmate Portable Hydrogen Sulfide Gas Detector measures H₂S gas levels from 0 to 5000 ppm accurately. It uses a built-in pump to draw in air for testing and has alarms that use sound, light, and vibration. The pump samples air at a rate of up to 1 L/min and detects gas within 10 sec. It provides precise measurements, responds quickly to gas presence, and has a long-lasting battery.
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.industryarc.com/Research/commercial-fixed-gas-detector-market.html-800678?utm_source=TumblrPost&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=vikassagar

Commercial Fixed Gas Detector Market (2024-2030)
#GasDetectors#GasDetection#SafetyFirst#IndustrialSafety#WorkplaceSafety#HazardousGas#SafetyTechnology#GasMonitoring
0 notes
Text
Understanding the Different Types of Personal Gas Detectors

Personal gas detectors are essential safety tools used to identify and measure harmful gases in the air. These devices help protect individuals from exposure to toxic, flammable, or oxygen-depleting gases that may be invisible and odourless yet pose significant health risks. Gas detectors are indispensable in various settings, from industrial workers in hazardous environments to homeowners concerned about air quality.
To ensure you choose the right detector, you must understand the different types of personal gas detectors, their functions, and the specific gases they are designed to detect. This guide will explore the most common types of personal gas detectors and their applications.
1. Single-Gas Detectors
Best for Monitoring the presence of a specific gas in the air.
As the name suggests, single-gas detectors are designed to detect and monitor the presence of one particular type of gas. These detectors are commonly used in industries where workers are exposed to a specific gas hazard, such as carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen sulphide (H₂S), or oxygen (O₂) depletion.
How They Work: Single-gas detectors use sensors calibrated to detect one specific gas. When the gas concentration exceeds the pre-set safety limits, the detector triggers an alarm, which could be audible, visual, or vibrating, alerting the user to take immediate action.
Common Applications:
Carbon monoxide (CO) detectors are often used in confined spaces, homes with gas-powered appliances, and areas where combustion occurs.
Hydrogen sulphide (H₂S) detectors are crucial in oil and gas, sewage treatment, and mining industries.
Oxygen (O₂) detectors are essential in environments where oxygen levels, such as confined spaces or laboratories, may drop below safe levels.
Single-gas detectors are typically compact, portable, and easy to use, making them ideal for workers who only need to monitor one specific gas in their work environment.
2. Multi-Gas Detectors
Best for: Detecting multiple gas hazards simultaneously.
Multi-gas detectors can detect and monitor multiple gases at once, making them ideal for industries where workers are exposed to a variety of gas hazards. These detectors can typically monitor up to four or five gases simultaneously, such as oxygen (O₂), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen sulphide (H₂S), and combustible gases(methane, propane, etc.).
How They Work: Multi-gas detectors have multiple sensors designed to detect a specific gas. The device continuously samples the air and displays the concentration of each gas. If the levels of any gas exceed safe limits, the detector triggers an alarm to alert the user.
Common Applications:
Construction and confined space entry: Workers entering confined spaces must know about oxygen levels, toxic gases, and combustible gas hazards.
Oil and gas industries: Multi-gas detectors are critical in detecting the presence of flammable gases and toxic fumes, ensuring worker safety in these high-risk environments.
Emergency response teams: Firefighters and first responders rely on multi-gas detectors to quickly assess air quality in disaster situations.
Multi-gas detectors are essential for environments with mixed gas hazards. They offer comprehensive protection and simplify gas detection tasks by combining sensors in one device.
3. Combustible Gas Detectors
Best for: Detecting the presence of flammable gases.
Combustible gas detectors are designed to identify and measure the concentration of flammable gases, such as methane (CH₄), propane (C₃H₈), and butane (C₄H₁₀), which can pose explosion hazards if they accumulate in enclosed spaces.
How They Work: Combustible gas detectors often use catalytic bead or infrared (IR) sensors to detect the presence of flammable gases. When the concentration of these gases reaches a certain percentage of the lower explosive limit (LEL), the detector sounds an alarm to warn of the danger of ignition.
Common Applications:
Residential and commercial buildings: Combustible gas detectors are commonly used in homes, kitchens, and industrial plants where natural gas or propane is used for heating and cooking.
Oil and gas industries: These detectors help prevent explosions where flammable gases are produced, stored, or transported.
Mining operations: Detecting combustible gases is critical in preventing mine explosions caused by methane accumulation.
Combustible gas detectors are essential in environments where explosive gases are present. They provide an early warning system to prevent accidents and ensure safe evacuation or containment.
4. Oxygen Detectors
Best for Monitoring oxygen levels to prevent oxygen deficiency or enrichment.
Oxygen detectors measure the concentration of oxygen in the air. Maintaining appropriate oxygen levels is critical for life safety and the prevention of combustion, especially in confined spaces or industrial environments.
How They Work: Oxygen detectors typically use electrochemical sensors to measure oxygen concentration in the air. If the oxygen levels drop below a certain threshold (usually around 19.5%), the detector sounds an alarm, indicating the risk of asphyxiation. Conversely, if oxygen levels exceed the safe limit (above 23.5%), the detector will also sound an alarm, as high oxygen levels increase the risk of fire or explosion.
Common Applications:
Confined spaces: Oxygen levels in confined spaces can drop due to poor ventilation or other gases, making oxygen detectors essential for worker safety.
Laboratories and research facilities: In areas where gases like nitrogen are used, oxygen detectors ensure that oxygen depletion doesn't pose a risk to personnel.
Mining: Oxygen levels in mines can fluctuate due to gas emissions, so continuous monitoring is critical for worker safety.
Oxygen detectors are indispensable in any environment where oxygen levels may be depleted or enriched. They provide early warnings to prevent life-threatening situations.
5. Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) Detectors
Best for Monitoring elevated levels of carbon dioxide, particularly in enclosed environments.
Carbon dioxide detectors are designed to monitor carbon dioxide concentrations (CO₂) in the air. While CO₂ is a naturally occurring gas, elevated levels can cause health problems such as headaches, dizziness, and, in extreme cases, suffocation.
How They Work: CO₂ detectors use infrared (IR) sensors to measure the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air. The detector will alert the user if CO₂ levels exceed safe limits, typically around 5,000 ppm (parts per million) for prolonged exposure.
Common Applications:
Indoor air quality monitoring: CO₂ detectors are commonly used in homes, offices, and schools to ensure proper ventilation and safe indoor air quality.
Greenhouses and agriculture: Elevated CO₂ levels can promote plant growth, but excessive levels can harm workers, making CO₂ detectors essential in these environments.
Breweries and food production: CO₂ is commonly used in fermentation and carbonation processes, so monitoring levels is crucial for worker safety.
CO₂ detectors are essential for monitoring air quality in environments where carbon dioxide can accumulate, ensuring a healthy and safe atmosphere for occupants.
6. Photoionization Detectors (PIDs)
Best for: Detecting volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and toxic gases at low concentrations.
Photoionization detectors (PIDs) detect volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and toxic gases, which may be harmful even at low concentrations. VOCs are often found in household products, paints, solvents, and industrial chemicals.
How They Work: PIDs use ultraviolet (UV) light to ionize gases, creating a measurable current that is proportional to the concentration of the VOCs. These highly sensitive detectors can detect gases in the parts-per-billion (ppb) range.
Common Applications:
Environmental monitoring: PIDs detect VOCs in air, soil, and water samples to protect the environment.
Industrial hygiene: Workers in industries that use solvents, chemicals, or petroleum products rely on PIDs to ensure they are not exposed to harmful levels of toxic gases.
Hazardous materials response: First responders use PIDs to quickly assess the presence of VOCs during chemical spills or leaks.
PIDs provide early detection of low-level toxic gases, making them invaluable for health, safety, and environmental protection industries.
Conclusion
Choosing the right personal gas detector is crucial for ensuring safety in various environments, from homes and offices to industrial worksites. Whether you're concerned about carbon monoxide in your home, toxic gases in a laboratory, or explosive gases in a manufacturing plant, understanding the different types of gas detectors can help you select the best device for your needs. By investing in the right gas detector, you can protect yourself and others from the invisible dangers that hazardous gases present.
0 notes
Text
Discover the ideal gas detection system for your industry with our detailed blog. Whether you're in manufacturing, healthcare, or energy, find insights into selecting the right technology. Learn about key factors such as sensor types, reliability, safety features, and maintenance needs. Our guide provides valuable tips to help you make an informed choice and ensure the safety and compliance of your operations. Read on for expert advice!
0 notes
Text
Precision Mercury Analysis with High-Accuracy Generator
Need accurate mercury analysis? Our high-precision Elemental Mercury Generator delivers stable and reliable performance for gas monitoring. 🚀 Trusted by industries worldwide. 📌 Get more details at: Gas Analyzer

0 notes
