#Finlandfisheryzonesmap
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
maritime boundaries between Finland and Estonia

Agreement between the Republic of Estonia and the Republic of Finland on the Boundary of the Maritime Zones in the Gulf of Finland and the Northern Baltic Sea was signed in 18 October 1996. In principle, the main aim of the negotiations was not to try to establish a maritime boundary in areas· where no such boundary existed before. In fact, only a very minor part of this agreement could fit such a description. What the Estonia-Finland Agreement did rather was to provide an answer to the much more subtle question about the ·exact legal value to be attributed under international law to the previously concluded maritime boundary agreements, in casu by the former Soviet Union. For several years the parties side-Stepped the crux of the issue on a provisional basis. Indeed, in 1992 Estonia and Finland started out by concluding an interim agreement. Since no final agreement had yet been reached between the parties at the end of this first period, the latter was extended for another two years. It was clearly stressed that the agreements themselves had not entered into force between the parties, but that the latter had only agreed that the content of these agreements would be applied ad interim. Both countries now have recently terminated the interim agreement by concluding a definite agreement on the subject. The final outcome seems to indicate that the whole operation can be characterized as a storm in a teacup. Out of the 17 points listed in the agreement, 16 correspond to turning points already established by the former Soviet Union in its relations with Finland. Only the last point is totally new. But this .segment of the line is special, for it covers a maritime area in which the former Soviet Union and Finland had never been able to arrive at a delimitation. In other words, in as far as a maritime boundary line existed at the time of the dissolution of the Soviet Union, that line has now been taken over, point by point, by Estonia and Finland to form the basis of the new agreement. The only real novelty introduced by the Estonia-Finland Agreement therefore concerns the last point listed in Article 2. This turning point touches upon the most difficult problem of the exact effect to be attributed to the Bogskar island group belonging to Finland. The latter, which consis1s primarily of two uninhabited rocks with a total area of approximately 4-5 sq. km., is located close to the hypothetical tri-junction point with Sweden. In its relationship with Sweden, Finland had just arrived at a political compromise in this respect. The present agreement allowed the parties to close the remaining gap around this trijunction somewhat further from the east. Totally in line with a well-established practice in the Baltic Sea, the .agreement finally leaves the two tri-junction points open for later determination with the interested parties. it is notable the that Nevertheless, all three Baltic States have moved towards accepting the maritime boundaries negotiated on their behalf by the Soviet Union with Finland and Sweden, often through negotiating fresh agreements which serve to reconfirm the course of the relevant maritime boundaries. A good example of this trend is Estonia’s interim 1992 agreement with Finland on the provisional application of certain treaties concluded between Finland and the former Soviet Union. The 1992 agreement did not confirm the validity of the Soviet-era treaties. Instead, Estonia and Finland simply agreed to observe their provisions for practical reasons for a specified period of time. Among the treaties covered by the 1992 agreement, which was extended for an additional two years in January 1995, were four maritime boundary accords between Finland and the former USSR. Whilst the 1992 agreement was in effect Estonia and Finland were able to conduct maritime boundary delimitation negotiations leading to the conclusion of a new delimitation treaty on 18 October 1996. The turning points defined in the 1996 agreement are directly based on those previously agreed between Finland and the former Soviet Union, aside from a 30 nm long western extension of the maritime boundary. In keeping with other Baltic sea maritime boundary agreements, the treaty notes, in Article 2, that ‘the starting point of the boundary is that point in the east on which agreement will be reached with the third State concerned’ – that third state being the Russian Federation. Estonia’s unilateral definition of its territorial sea and EEZ does include qualifying ‘remarks’, however. In respect of Estonia’s territorial sea claim within the Bay of Narva it is noted that as this has not been determined in negotiations with Russia, the boundary ‘may change as a result of these negotiations’. It is similarly stated in relation to the boundary of Estonia’s continental shelf and EEZ ‘near Vaindlo Island in the Gulf of Finland’, that as the boundary has not been determined in negotiations with the Russian Federation, the boundary ‘may change as a result of the negotiations’. Once the starting point for the maritime boundary on the coast is determined, the maritime delimitation should not prove particularly problematic. An equidistance line between the parties coasts extends for approximately 65 nm in length initially westwards through the Bay of Narva before turning northwestwards towards the centre of the Gulf of Finland and the potential tripoint with Finland between the Russian island and rock of Ostrov Malyy Tyuters and Ostrov Rodsher and the Estonia islet of Vaindloo Saar. Although relatively small islands or rocks are involved in defining the seaward part of the delimitation, it is unlikely that it could be argued by either side that these should be discounted given that the delimitation predominantly concerns the territorial sea. Furthermore, a delimitation based on equidistance relies on islands and rocks as basepoints on both sides of the line, which therefore tend to balance one another out. Agreement between the Republic of Finland and the Republic of Estonia on the Boundary of the Maritime Zones in the Gulf of Finland and on the Northern Baltic Sea, 18 October 1996+mapDownload Agreement between the Republic of Finland and the Republic of Estonia on the Boundary of the Maritime Zones in the Gulf of Finland and on the Northern Baltic Sea, 18 October 1996Download

Estonia Straight baseline-internal waters-territorial waters

Finnish Exclusive Economic Zone

Finland Stright baseline-internal waters-territorial waters

Estonia Exclusive Economic Zone






Read the full article
#BayofNarva#Estonia#Estoniacontinentalshelfmap#EstoniaEEZmap#Estoniaexclusiveeconomiczonemap#Estoniainternalwatersmap#Estoniamaritimeboundaries#Estoniamaritimezone#Estoniaterritorialwatersmap#Finland#Finlandcontinentalshelfmap#FinlandEEZmap#Finlandfisheryzonesmap#Finlandinternalwatersmap#Finlandmaritimeboundaries#Finlandmaritimeclaims#Finlandstraightbaselines#Finlandterritorialseamap#VaindloIsland
0 notes
Text
maritime boundaries between Finland and Russia
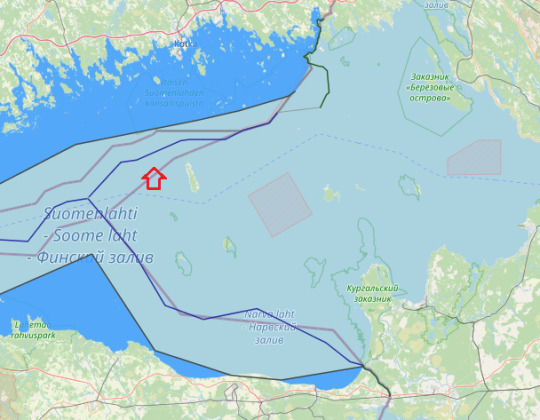
between Russia and Finland, the boundary is on the shore of Gulf of Finland, in which there is a maritime boundary between the respective territorial waters, terminating in a narrow strip of international waters between Finnish and Estonian territorial waters. In 2014, Estonia and the Russian Federation signed their land and maritime boundary agreements that are currently awaiting ratification. This study reconstructs the maritime boundary delimitation between the two States. In particular, the role of islands and pre-existing agreements for the delimitation of the territorial sea boundary in the south-eastern part of the Gulf of Finland are critically examined. It is established that the agreed maritime boundary line is a median line which was influenced by the use of the special circumstances method in the delimitation process. in relation to the first part of the Finland-USSR maritime boundary, military, strategic and related navigational considerations have had a powerful influence on the course of maritime boundaries and it had not based on equidistance method alone. In the modern period maritime delimitation was, at least initially, conducted among the communist states, together with Finland. However, from the early 1970s, and particularly in the wake of the conclusion of the Treaty on the Basis of Intra-German Relations between the two Germanys, a number of agreements were concluded between Western and Soviet bloc states, despite the profound ideological and economic divides between the littoral states. This remarkable situation has been attributed, not only to small size (the average width being about 120 miles) and semi-enclosed characteristics of the Baltic but to its shallowness (average depth being 55 m), the large number of rivers flowing into it, high coastal populations and a high degree of industrialization among the littoral states. This combination of factors dictated a clear need for cooperation’. considered chronologically, maritime boundaries in the Baltic Sea have therefore been concluded between Denmark and Germany (1965 and 1988), Finland and the USSR (1965, 1967, 1980 and 1985) and more.. Finland was the first, in 1956, when it placed the termini of its model straight baselines in the sea to link with subsequent baselines drawn by Sweden and Russia. Finland For most of length straight baselines cross water but their termini are on land and are defined by the coordinates on or near the normal baseline. It would be prudent for countries to review the coordinates defining their straight baselines at set intervals. This would ensure that any changes in the configuration of the low-water line can be recorded and the coordinates of basepoints adjusted. Finland seems to be the only country that specified in its declaration of its straight baselines that they would be reviewed every 30 years. in 1995 Finland reviewed the 1965 definition of its baselines. Finland took the opportunity to abandon its requirement that no segment of its baselines should be longer than 8 nm. The length of baselines in the previous system averaged 4.4 nm. The previous system ensured that the Finnish straight baselines conformed to the coast to a greater degree than those of any other country. The new arrangements allow the Finns to use fewer basepoints which will reduce the costs of future measurements. The 1995 definition will cover the period 1995-2024. Agreement between the Government of the Republic of Finland and the Government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics concerning the boundaries of sea areas and of the continental shelf in the Gulf of Finland, 20 May 1965Download Agreement between the Government of the Republic of Finland and the Government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics concerning the boundary of the continental shelf between Finland and the Soviet Union in the north-eastern part of the Baltic Sea, 5 May 1967 (entry into force: 15 March 1968)Download Agreement between the Government of the Republic of Finland and the Government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics regarding the delimitation of the areas of Finnish and Soviet jurisdiction in the field of fishing in the Gulf of Finland and the North-eastern Part of the Baltic Sea, 25 February 1980 (entry into force: 9 July 1980)Download Agreement between the Government of the Republic of Finland and the Government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics regarding the delimitation of the economic zone, the fishing zone and the continental shelf in the gulf of Finland and in the North-Eastern part of the Baltic Sea, 5 February 1985 (entry into force: 24 November 1986)Download

Russia Straight baseline-internal waters-territorial waters in gulf of Finland
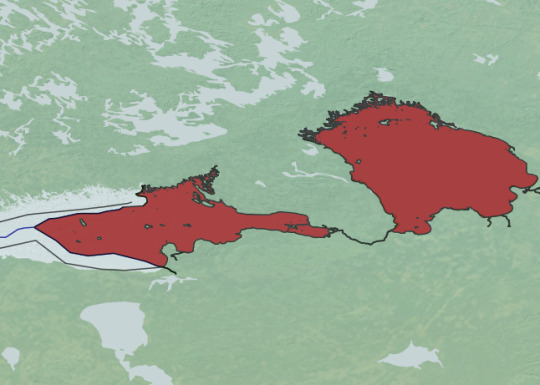
Russian Exclusive economic Zone in gulf of Finland
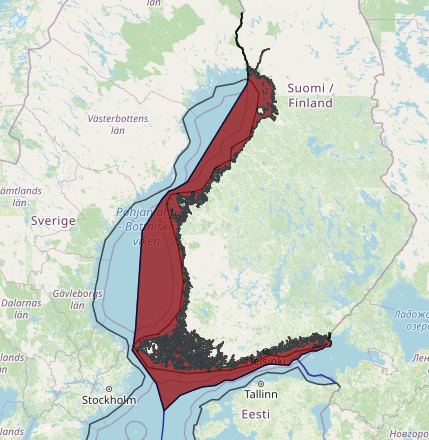
Finnish Exclusive Economic Zone
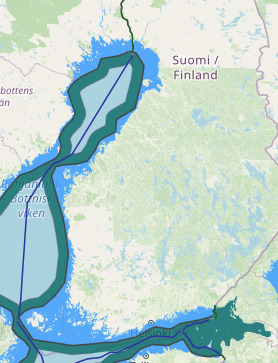
Finland Stright baseline-internal waters-territorial waters
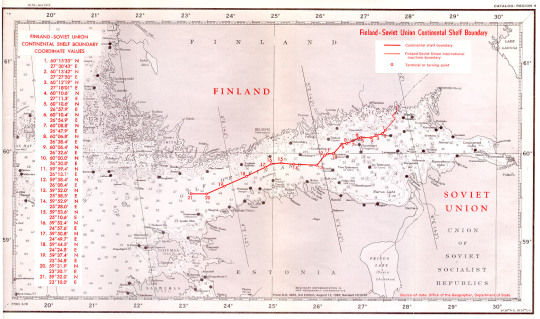
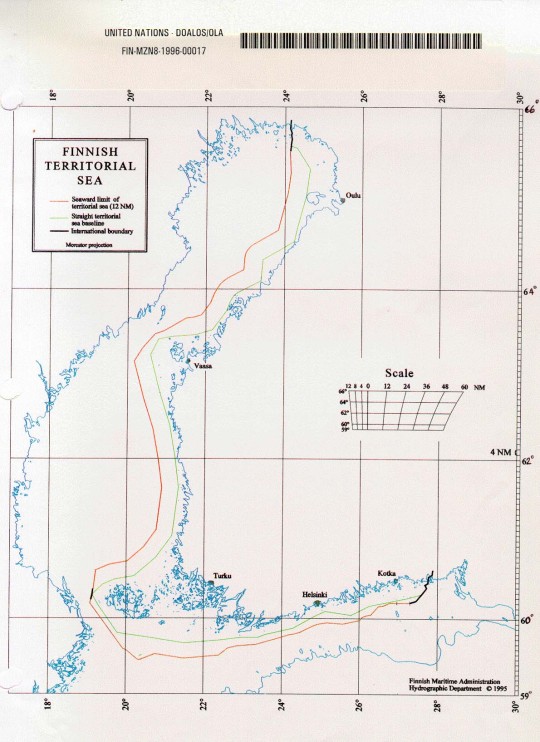
map (provisional) and of a list of geographical coordinates (straight baselines; outer limits of the territorial sea) of Finland
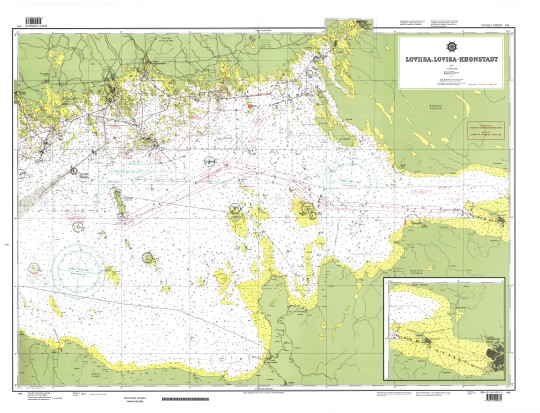
"Loviisa, Lovisa - Kronstadt", Scale 1:200,000
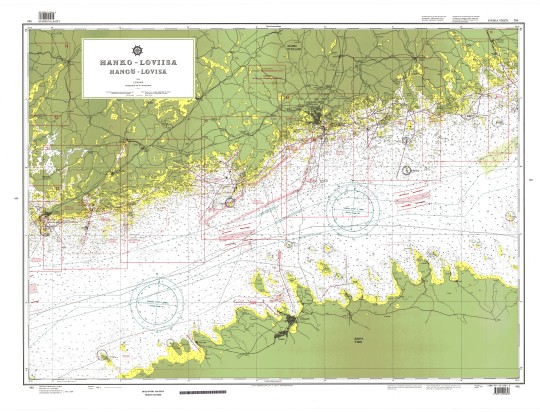
"Hanko-Loviisa/Hangö-Lovisa", Scale 1:200,000 Read the full article
#Finland#Finlandcontinentalshelfmap#FinlandEEZmap#Finlandfisheryzonesmap#Finlandinternalwatersmap#Finlandmaritimeboundaries#Finlandmaritimeclaims#Finlandstraightbaselines#Finlandterritorialseamap#russia#Russiacontinentalshelfmap#Russiaexclusiveeconomiczonemap#Russiainternalwatersmap#Russiamaritimeboundaries#Russiamaritimeclaims#Russiaterritorialwatersmap#russianfederation#TheGulfofFinland
0 notes