#Family Property Dispute Lawyer
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Legal Mavericks: The Best Criminal Litigation Law Firm in India
In the complex tapestry of legal proceedings, a bail hearing appeal holds pivotal significance within the realm of criminal procedure. This article sheds light on the nuances of bail hearing appeals, the importance of securing legal representation from the best criminal litigation law firm in India, and the role of a proficient family property dispute lawyer.
For more information visit us: https://mbbsadmissionabroad12.blogspot.com/2024/01/legal-mavericks-best-criminal.html
#Best Criminal Litigation Law Firm in India#Family Property Dispute Lawyer#bail hearing appeal in criminal procedure
0 notes
Text
Legal Essentials: Must-Know Advice for Running a Business
In today’s competitive business environment, it’s crucial for entrepreneurs to have a solid understanding of the legal essentials required to run a successful business. From entity formation to contracts and intellectual property protection, having the right legal foundation is essential for long-term success. In this article, we will explore the must-know legal advice for running a business and…
#civil rights and protections#common legal issues and solutions#criminal law basics#family law topics#how to choose a lawyer#how to resolve legal disputes#latest legal news 2024#legal advice for businesses#legal procedures and documentation#legal rights and responsibilities#property and contract law#tips for navigating the legal system#trends in legal practice.#Understanding legal terms#updates on major legal cases
0 notes
Text
Advocate in Jaipur | Your Trusted Legal Partner in Jaipur
Whether it’s a personal matter, a business dispute, or a criminal case, the right lawyer can make all the difference. That’s where Advocate in Jaipur comes in. We offer professional, reliable, and affordable legal services to help you with whatever legal issue you're facing.
#advocate#advocate in jaipur#business issue#civil litigation#corporate law#criminal case#criminal law#family law#lawyer#lawyer in jaipur#legal services#family dispute law#property law
0 notes
Text
Advocate in Kakrola
If you're looking to find the best advocate in Kakrola for all your legal matters, it's essential to choose someone with the right expertise and experience. Kakrola is home to several skilled advocates who specialize in a variety of legal fields, including family law, property disputes, criminal defense, civil litigation, and corporate law.

#Best Lawyers in Kakrola#Legal Services in Kakrola#Experienced Advocates in Kakrola#Property Dispute Lawyer Kakrola#Family Lawyer Kakrola
0 notes
Text
https://justpaste.it/b9x1d
#civil lawyer in lucknow#top lawyer for criminal cases in lucknow#legal advisory services in lucknow#best law firm in lucknow#divorce lawyer in lucknow#best family advocate in lucknow#best advocate in lucknow high court#top criminal lawyers in lucknow#best criminal lawyer in lucknow high court#best lawyers for property disputes#criminal advocate in lucknow#family court lawyers in lucknow
0 notes
Text
#Criminal Case Lawyers in Delhi#best civil lawyers in delhi#criminal lawyers in delhi#criminal case lawyers#best civil advocates law firms in delhi ncr#civil lawyers in delhi#best law firm in delhi#top 10 civil advocates law firms delhi ncr#law firm in delhi#Criminal Case Lawyers in Delhi:#Property Dispute Lawyers in Delhi#Family Case Lawyers in Delhi#Family Case Lawyers in Delhi 2023#top Family Case Lawyers in Delhi
0 notes
Text
It's Just In My Nature (F!Reader x F!Werewolf)
Pairing: F!Reader x F!Werewolf
Genre: Human/Monster Society, Gratuitous Smut, Inspired by Chappell Roan's "The Giver" (if that wasn't obvious)
Warnings: Explicit Content Under the Cut, 18+ ONLY
Summary: Ain't got antlers on my walls But I sure know mating calls From the stalls in the bars on a Friday night And other boys may need a map But I can close my eyes And have you wrapped around my fingers like that
(AKA you get your world rocked by a hot werewolf handywoman)
Word Count: 3281 words
She’s trouble, that's the first thought you have when you see her.
It’s nothing about her personally. Your first impression isn’t nasty, not even a real impression; Just catching a glimpse of her in your neighbor's driveway, coveralls stained with grease as she looks under his mustang’s hood. A local handywoman. From pipes to engines, she’s the one to call. You’ve heard good things, commendations on her reasonable prices and her good sense. Sort of crass, but it's to be expected, a stereotype about the folks in her line of work.
No, it’s the way her shoulders bulge in the stained wife beater, glistening with sweat and muscles as she leans down to grab her tools. It's the way you see a peak of her stomach, when she raises her arms to wipe the drops off her forehead, a glimpse of a treasure trail leading straight down into her half-zipped coveralls. It’s a sweltering day, humid and miserable, it makes sense she’d strip it down halfway. But it's dangerous the way her lips wrap around her water bottle, the way her throat bobs as she sucks it down. It's dangerous the way she catches you, starting from over your coffee cup. Dangerous the way she holds up her hand, a wordless greeting, and winks.
Your heart pounds in your chest and you can hear the blood pulsing in your ears. Eyes wander down her form, down her spine and all the way to her paint-splattered steel-toe boots. They linger on her backside, too thick to be covered up by fabric. It twists your stomach, has your mouth going dry.
Yep, big trouble indeed.
You know she’s strong, it comes from her family. A big pack of werewolves, settled all over your small little town. Hardworking and dependable just like her, bastions of the community. Good stock, friendly, the kind of friends you need in a tight-knit community. You can spot them at most of the usual haunts, at almost every corner there’s an O’Connell. It’s no surprise when you bump into her at the one bar in town, still in work wear. Not her coveralls (unfortunately) but something equally as tasty; A stained flannel and solid work pants, the same set of steel-toed boots on her feet.
“Can I buy ya something?” She offers, and you're not strong enough to say no. You’re sure she gets around, sweeps sweet little things like you off their feet with a single slip of her southern drawl. It doesn’t matter to you, though, not when her hands find their way around your waist, sliding into the seat next to you at the bar. “What’s your poison?” You babble out your order and your heart flutters when she smirks. “Something sweet for something sweet.”
She asks your name, says she’s seen you around. The cute little house with the blue door, right? Always fluttering too and fro during the week, working on your humble garden out front during the weekends. Sje’d never plucked up the courage to say hi until now, which has you blushing, even though you're sure it's not true. She probably says that to all the girls, yet you’re swooning self can’t find it in yourself to care.
She asks about your job, curious where you run off to in the early mornings during the week. When you tell her you’re a lawyer, she whistles.
“Damn, smart and sexy? Darling, what don’t you got?” Your hearts sings under the praises, bashfully takes it without complaint. Not as exciting as big city lawyers, you admit, mostly dealing with property disputes and other legalese like that. “Still, gotta take up a lot of your time, negotiating and reading all them contracts. You ever need help with that old house of yours, just lemme know.” You can feel her calloused hands through your pants, her grip warm as she pats you right on the knee. It hits a certain nerve that shoots right up into your belly, scrambles your brain and shoots out any good sense.
You’re not the type to go home with strangers. But is she really a stranger, when she grabs your hips and pulls you in close on the dance floor, whispering filthy things in your ears? When those lips, the ones you saw sucking on that water bottle, just graze yours? When you practically taste the salt on her skin, still sweaty from a day's worth of work?
No, she isn’t strange to you at all. So you have no problem hopping into her pick-up truck, or spreading your legs when she places a warm hand on your inner thigh, the other still on the wheel.
Her place is small, a rough and tumble trailer in a park not too far from your neighborhood. She’s got a few garden beds of her own, small and humble, and you wonder if that's what first drew her to you. This miniscule thing in common, working with your hands when you can. You’ll ask her about it later, after.
Her skin is burning, trembling as you push up her shirt, feeling the soft plains of her stomach. She growls into your hasty kiss, grips harder onto your waist.
“Shit, d-don’t think I can hold it back.” Her laugh is cracked by a chest-deep groan, her bottom lip worried between her teeth. “Do you mind?”
You shake your head in a haste, stomach twisting at the very idea of seeing her shifted form. She smiles, gives you another wet kiss before pulling away, shaking off her shirt and pants in a haste. Her bones begin to crack, a startling sound, but it doesn’t seem to hurt. No, it seems like a release, the fur cascading down her skin as her body changes, grows bigger, grows stronger.
The minute she’s comfortable, you leap on her. It makes her chuckle again, big paws now landing on your ass, squeezing.
“Like what ya see?” She says, scooping you up right onto her forearm, your weight nothing to her superior strength. Your legs instinctually wrap around her hips, grind like the animal you are. But it's stopped when she throws you on her bed, springs squeaking as she pounces on you.
Her fur is soft, knots easily in between your fingers as she kisses down your face, your neck, your chest. Canines nip at your tits from behind your shirt, quickly pushes up so she can lick down your stomach. You wiggle compliantly once she undoes your zipper, hips thrown up to get these damn pants off as quickly as possible. You’d be embarrassed by your lack of sexy underwear, not planning on something so sexy when you stopped by the bar after work, if not for the fact she literally tears them off.
“Well well, look at you.” She purrs, thumb and forefinger spreading apart your pussy lips. You gasp, hands curling into knuckles when her hot breath blows across your sensitive entrance. “That's a mighty fine cunt, missy.”
She doesn’t give you a moment to be embarrassed by the crass observation before her tongue is on you. It licks a long stripe up your hole, the rough texture shooting sparks across your nervous system, her nose snuggling into your clit. Your head throws back, nearly hitting the cheap metal bed frame, a moan ripping out from your throat. Her ears flick when your thighs clamp around your head, and you can feel her smirking. She doesn’t stop to comment, solely focused on that mighty fine cunt and making it weep.
Her tongue is long, just as deft as her hard-working fingers, writhing against your gummy walls. She easily finds that spongy spot inside with the tip, the muscle of her jaw feathering across as she presses against your insides. Her nostrils flare, soaking in the scent of your juices, lapping at you like a dog. She’s making your whole lower half tingle, but the rubbing against your clit isn’t quite enough, now flush with blood and throbbing for more. Not until a paw pad replaces it, her rough thumb making slow circles around the sensitive button.
“Oh god!” Your fingers tangle in the fur on her head, knuckles taut against the skin, rolling your hips onto her face. She shudders as you yank, too lost to be ashamed of your desperation. It's just how she wants you, writhing and fervent. The sounds coming from her lips on your pussy squelch inside her cheap trailer, practically bouncing across the walls. It matches the squeaking of the bed springs as she ruts her hips, soaking the crotch of her boyshorts. Gosh, if she had known you’d make such pretty noises, she would have approached you sooner. Would have bent you over in that garden and made you sing.
Her coordination is expert, thumb never faltering on your clit as her tongue fucks you open. It keeps a steady pace; Never too hard, never too fast, simply riding the wave of your reactions. At one point the two appendages switch, her tongue moving upward and her fingers sliding in to fill its place. Her tongue flicks like a professional, making your mouth form a breathless ‘o’ as even moaning becomes out of your reach. Lips wrapped around your clit, the tip of her tongue just teases your entrance as her fingers scissor outward. Your juices drip down her palm, already matting down the fur on her face and staining the bed sheets. She barely has to move her fingers, thrusting them only an inch before your spasming.
It's impressive how expertly she navigates your own pussy. You don’t think you’ve ever brought yourself so close to cumming this fast, even with your favorite vibrator. It's like she knows it better than you do, knowing each nerve to press, when to go fast, when to go slow, when to go hard and when to be soft. Your orgasm hits like a thundercrack, not even giving you a moment to say “I’m-” before it shocks through you. But she knows, she knows immediately, when your whole body convulses, pelvis thrown up in the air and squealing like a stuck pig.
“That’s it.” She nips at your thigh, a smarmy smirk in her voice. “There’s my pretty girl.” She admires her handiwork, spreading open your gushing lips with two fingers. God, you might be dehydrated from how much you just came, the dim lighting of her trailer making everything seem blurry. You can barely make out her face when she climbs up on top of you, leaning in her so her snout is right next to your ear. “Think you can give me one more, princess?” She whispers, and your head is nodding before your better sense can say no. You would do dangerous things to experience that again.
She jumps off you with a grin, shimmying off her underwear as she rummages around her room for something. You’re too tired from the mind-blowing orgasm to sit up, so your head just swivels, barely making out what she’s fiddling with. It isn’t till she’s back on you when you can feel strap-on tapping against your stomach that you realize. Your pussy clenches around nothing, already aching for it.
You let your legs fall open, no words needed as she lines her strap up with your hole. Her warm paws grab onto onto your thick thighs as she slides in, meeting no resistance from your wet and eager cunt.
“Say my name.” She growls, lips curling back to reveal her canines. How badly you wish she’d dig them into you. When you don’t immediately respond, still catching a breath as the toy sinks inside, she slaps the side of your ass.
“Jo-anna!” You yelp, head turn back as the final inch fits, the tip now pressing right at your cervix. You didn’t think you could take something this big.
That snarl twists into a smug smile, only widening when a jerk of her hips makes you squeak. She chuckles, and it sounds exactly like trouble.
“Thatta girl.”
Joanna pulls her strap out to the end, not giving you a moment to complain before forcing it back, the tip bullying at your deepest part. From there she sets a punishing pace, puts those working woman muscles to work and fucking you like its her job. If only there were a mirror in here, so you can see her fine ass clench with each thrust.
“Yeah, take it.” Her voice rumbles, claws digging into the fat of your thighs for more leverage, though not enough to sting. Even now she’s in perfect control, working your body like a fiddle being tuned. She has you clawing at the bedsheets, no shame in your dirty moans. You don;t care that her trailer walls do nothing to suppress the noise, that everyone within a three mile radius can hear your caterwauling. Not when it feels this good.
“Fu-uck!” You pant, heart damn-near pounding out of your chest. Each thundering pound against your g-spot has your vision going spotty, has your brain turning to mush. Tingles buzz across your skin with each drag of the strap, like every cell has been set aflame. Your legs try to clench shut, to wrap around her hips and writhe against the toy, but she keeps them wide with pinches of her claws, her own muscled thighs filling up the space, working hard to batter at your spongy insides. “Right there! Right there!”
“I hear ya, baby.” Joanna leans a hand forward to grip onto the cheap bed frame, extra leverage allowing her to go even harder on the spot making you see stars, pinpointed on that nebulous “there” you described. “I’ve gotcha, gonna make you feel real good.”
She loves watching your tits bounce, the hard peaks pushing through your cute little blouse. So formal, what she expected from her little lawyer. All of this and she still hasn’t gotten a proper view of them tits, she should fix that.
With one hand she’s able to deftly undo all the needed buttons, never faltering in her rhythm. Your bra is cute, like you, but the real prize is underneath, so it's shoved down below your full breasts so she can get a proper look.
“Love these fucking tits.” Joanna pants, leaning down and swirling her tongue around one. You wail, chest pressing up and into her mouth. She pops off your nipple and smiles. “Been waiting to see these pretty things. Knew they’d be just so tasty.” She latches onto the other, letting the teeth just graze the sensitive skin. Your fingers quickly knot into the back of her skull, forcing her face to nuzzle in your cleavage. A purr rumbles through her.
Ahh, this is where she’s meant to be. Buried between your thighs, lips on your nipples, hearing your heartbeat out of your ribcage. She’s been needin’ this.
“Shit, Jo!” Your fingers yank on her skull, but she doesn’t give you any reprieve, still swirling her tongue around your areola. “Gonna cum again!” You pant in her ear, as if she doesn;t’ already know. As if she doesn’t feel your legs starting to shake, smells your pussy juices just gushing around her strap.
Joanna finally detaches from your chest, a long string of saliva still connecting her tongue to your boob. She leans in close, so her nose is touching yours.
“Then cum for me, baby. Give mama one more.”
“Oh, Fuck!”
Your nails dig down her back, giving Joanna’s claws a run for their money, no doubt leaving long tracks that’ll linger in her human form. Not that she minds, they’re just badges of honor, signs of a job well done.
Your thighs lock around her hips, hips rocking as you ride out your second orgasm of the night, somehow more mindblowing the last. You’re surprised you still have enough energy to clench your legs, all energy sapped from your body. You feel beads of sweat rolling down the side of your face, sticking your cheeks to the pillowcase. It’s cool against your heated skin, which is so burning hot the fabric might as well be a bag of ice.
“Shit.” You wheeze, vocal cords strained, mouth feeling cottony from all your yelling. “That was….” You struggle to form the words, both from the puddle your brain has become and just how indescribable the last hour has been, “....fucking incredible.”
“Well, aint you a flatterer.” Joanna kisses the side of your forehead, right before finally pulling her strap out of you. Your pussy feels thoroughly stretched, and while you know that's not at all how your anatomy works, you genuinely feel like it's been molded to the shape of the dildo.
“Seriously, that was-” Your breath catches, mind still fuzz, “-I think that was the best sex I’ve ever had.”
Joanna chuckles, but doesn’t deny the compliment. She definitely knows what she’s got going on.
“Lemme get you some water, sugar.” Joanna says, giving you another kiss before sliding out from between your legs. Her strap is quickly stripped off and put to the side, leaving her in the nude. Your lazy gaze admires her ass jiggling as she walks. It looks even better now than in her working uniform. Her tail swings lazily behind, looking temptingly soft to the touch.
It takes all you can to sit up and gulp down the water, your nervous system finally rebooting and firing the correct orders to your muscle groups. The hydration is exactly what you need, luke-warm tap never tasting more delicious.
“Slow down, don’t want you to choke.” Joanna laughs as she pulls the cup away, watches your mouth follow it,despite the drops coming down your jaw. She takes a long sip herself, finishing off the cup with a content sigh.
It didn’t seem like it in the moment, with how effortlessly she moved, but fucking you must’ve been a work out. Sweat clings to her fur, sticks it closer to her skin, and while she doesn’t seem too out of breath, her chest is inhaling a little deeper.
The realization gives you another boost, has you sitting up more and leaning into her space. Pressing a soft kiss onto her shoulder, you look up at her with (what you hope are) proper bedroom eyes.
“I wanna make you feel good, Jo.”
She raises one brow, a hint of that smug smile back.
“Yeah?” Her heated gaze rolls down your debauched self: bra pushed down, shirt-hall unbuttoned, bottom half bare as the day you were born. You may not be much of a vixen as she, but you know a thing or two about seduction.
Before you know it you’re on your back, Joanna’s arms wrapped around your waist. But she doesn’t have that hungry look in her eyes, her gaze softer. You both lay side by side, her big paws brushing away the wayward hairs that cling to your sweaty forehead.
“Maybe in the morning, sugar. For now, all I wanna do is hold ya.”
Your brows slightly raise, but you don’t push the subject. While you’d gladly try to bring her to the highs she just brought you too (or at least attempt to), you're more than content snuggling into her strong chest and sleeping the rest of the night away.
No doubt you’ll wake up with dry mouths, sticking to the sheets and smelling like something left out in the sun for far too long. But neither of you will care, too wrapped up in each other to think about anything else.
You had thought she’d be trouble. As it turns out, you don’t mind a little bit of trouble, now and then.
#my writing#reader insert#monster x reader#monster romance#female reader insert#x reader#werewolf x reader#wlw smut#smut#monster fucker
84 notes
·
View notes
Text
After a legal battle lasting more than eight years, Brad Pitt and Angelina Jolie have settled their divorce.
According to Jolie’s lawyers, both parties signed the settlement on December 30.
“More than eight years ago, Angelina filed for divorce from Mr. Pitt. She and the children left all of the properties they had shared with Mr. Pitt, and since that time she has focused on finding peace and healing for their family. This is just one part of a long ongoing process that started eight years ago. Frankly, Angelina is exhausted, but she is relieved this one part is over,” Jolie’s lawyer James Simon of Hersh Mannis told CNN Monday.
120 notes
·
View notes
Text

Angel Named Angel: Angel Sanz Briz
Made Them Citizens Of Spain.
Angel Sanz Briz was a Spanish diplomat in Budapest who saved over 5000 Jews from the Nazis after Germany invaded Hungary in 1944.
Born in Zaragoza in 1910, Angel trained as a lawyer and in 1933 enrolled in diplomat school in Madrid. His first posting was to Cairo, Egypt, and in 1942 he was sent to Budapest, where he served as first secretary of the Spanish legation.
In March 1944, Germany invaded Hungary and the Nazis quickly began rounding up Jews for deportation. At this point in the war, Nazi genocide of the Jews ran like a well-oiled machine, and the Jews of Hungary were arrested with shocking speed.
Horrified at what was happening, Angel came up with a clever plan to save Jews. He told the Hungarian authorities that Spain was offering citizenship to Jews “of Spanish origin” – meaning Sephardic Jews, who trace their ancestry to Jewish communities that were kicked out of Spain in 1492. It was true that Spanish dictator Miguel Primo de Rivera had issued a decree to that effect in 1924, but Angel neglected to mention that the decree was canceled in 1930.
Unwilling to risk a dispute with Spain, Hungarian authorities begrudgingly told Angel he could issue passports to 200 Jews. Cleverly, Angel changed the order to read 200 Jewish families. When he reached the 200 family limit, he discreetly falsified documents to change the number, and he did this several times.
Officially, the Jews Angel was saving were supposed to be Sephardic, descended from Spanish refugees. However, the vast majority of Hungarian Jews were Ashkenazi rather than Sephardic. Undeterred, Angel simply claimed that all the Jews he was saving were Sephardic. He used his extensive contacts in Hungary to place the Jews in safe houses, where he personally gave them lessons in basic Spanish. This was enough to convince the Hungarian authorities, most of whom did not know any Spanish, that their “Spanish heritage” was genuine. When Angel ran out of Hungarians willing to take Jews into their homes, Angel purchased inexpensive properties with his own money. He decorated the buildings with prominent Spanish flags, marking them as officially part of Spain and therefore off-limits to the Nazis and Hungarian collaborators. The Jews staying in these safe houses couldn’t leave, so Angel brought them food, medicine, and other necessary supplies. Incredibly, he persuaded the Red Cross representative in Budapest to put Spanish signs on hospitals, clinics and orphanages where Jews were hiding to make sure everybody knew the occupants were under the protection of Spain.
Between June and December 1944, Angel issued fake Spanish passports to 5200 Jews, saving them from Nazi death camps and enabling them to live safely in Spain until the war ended.
Angel continued to serve as a diplomat after the war, with postings in San Francisco, Washington DC, Lima, Brussels and China, among other places. In 1977 he was appointed Ambassador to the Holy See in Rome, where he died in 1980. In 1991, Israeli Holocaust Memorial Yad Vashem posthumously honored Angel Sanz Briz as Righteous Among the Nations, and in 1994 Hungary awarded him the Cross of the Order of Merit. A Spanish TV series about Angel Sanz Briz, called “El Angel de Budapest” aired in 2011. In 2015 a street in Budapest was named after this brave Spaniard.
For saving 5200 Hungarian Jews from Nazi death camps by making them citizens of Spain, we honor Angel Sanz Briz as this week’s Thursday Hero.
106 notes
·
View notes
Text
Some interesting news from India!
In its verdict, the court said that the wife had contributed equally towards acquiring family assets by doing domestic chores. It said that the "contribution made by either the husband by earning or the wife by serving and looking after the family and children" would mean that "both are entitled equally to whatever they earned by their joint effort". It did not matter in whose name the property was bought - the spouse who looked and cared after the family would be entitled to an equal share in them. The court also held that the woman's domestic labour contributed indirectly to earning the money that enabled the purchase of the assets and that her work allowed the husband to be gainfully employed.
The wife works for 24 hours in various roles, including that of a chef, a "home doctor" and a "home economist", the court said. In the absence of the homemaker's duties, the husband would have to pay for the services these roles provided.
Women's rights lawyer Flavia Agnes called it a "very positive judgement because it recognises women's domestic labour". Malavika Rajkotia, a family and property lawyer, said the verdict was "a very important milestone", one that women had been "trying to evolve and plead in their various cases".
"This is, for the first time, a meaningful recognition of the homemaker's right." So the hope is that the judgement could have a positive impact in future.
336 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello, bitches! I don't think I saw this in the renter's master post, but how does one go about breaking a lease in the least financially ruinous way possible? My apartment flooded for the 3rd time in 12 months due to an improper drainage system, and I am FED UP. I have family telling me to sue over it, but I'd be content if they let me break the lease without fees or penalties.
If your apartment keeps flooding and your landlord has not fixed the problem... then your LANDLORD HAS ALREADY BROKEN YOUR LEASE.
A lease is a legal contract. Which means the landlord AND tenant both have responsibilities in order to keep the contract valid. There is usually language in there about the landlord keeping the unit in good maintenance. Constant flooding is NOT good maintenance. And if your property has been damaged by the flooding, the landlord could actually owe YOU, either for temporary housing or replacement of property.
So go read your lease, find the clause about maintenance, and take it to your landlord and say "According to this clause right here, you're in violation of our rental agreement. Therefore, I am moving out without penalty. If you'd like to discuss this, I'll have my lawyer get in touch." (Note: not everyone can afford a lawyer, but if you know anyone even tangentially related to a law firm, use the line about the lawyer. My husband's uncle and aunt are lawyers and the one time I used this line to resolve a labor dispute, it scared the bastard so much that they stopped their bullshit and paid me for my work with no further argument.)
Lastly: we are not infallible. Your state government website should have a section on tenant's rights. Look up this information to see if there are any other protections you can take advantage of before going nuclear on your shitty landlord.
The Rent Is Too Damn High: The Affordable Housing Crisis, Explained
Ask the Bitches: Why Are Painted Mason Jars the Internet's Only Solution to My Tiny Apartment Woes?
If we just helped you out, tip us!
85 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Legal Side of Business: Tips for Ensuring Compliance and Success
Introduction: Starting and running a successful business involves much more than just coming up with a great idea and selling products or services. One crucial aspect that many entrepreneurs overlook is the legal side of business. Ensuring compliance with various laws and regulations is essential for long-term success and avoiding costly legal troubles down the line. In this article, we will…
#civil rights and protections#common legal issues and solutions#criminal law basics#family law topics#how to choose a lawyer#how to resolve legal disputes#latest legal news 2024#legal advice for businesses#legal procedures and documentation#legal rights and responsibilities#property and contract law#tips for navigating the legal system#trends in legal practice.#Understanding legal terms#updates on major legal cases
0 notes
Text
How do I know if I have a case that your firm can handle?
Navigating the legal world can be overwhelming, especially when you're unsure if your case is something a law firm can handle. It's essential to know that you have the right team on your side, ready to guide you through the complexities of your legal issue. This article will help you determine if your situation fits our expertise well.
At McGinn Law Firm, we handle various cases, from personal injuries to property disputes. Our goal is to help you understand the strength of your case and provide the guidance you need from the very start. We're here to ensure you have the support you need as we explore the details of your case together.
Ready to find out if we can help? Contact McGinn Law Firm today. With a proven track record of serving clients in Western Iowa and Eastern Nebraska, we offer you a free initial consultation. Contact Shawn McCann at 712-328-1566 to discuss your personal injury claim and take the first step toward resolving your legal matter.
Determining Your Legal Needs
The following key steps help you determine whether you have a case that could benefit from legal representation.
First, evaluate your situation carefully. Examine the facts and any relevant documents that might illuminate your position, such as contracts, correspondence, photos, and witness accounts. This initial evaluation will give you a provisional idea of whether your issue can be legally pursued.
Second, identify the legal domain your case falls into - family law, labor law, personal injury, or another type of practice. Law firms often specialize in particular areas, and knowing this can help you pinpoint the most qualified legal professionals to handle your specific concerns.
Third, if your query relates to the inadequacy of representation or breach of fiduciary duty, consider the potential for a legal malpractice claim against previous counsel. Such claims are particularly complex and require legal professionals with specialized experience in professional malpractice issues.
Remember, not all disputes warrant legal proceedings; some may be better resolved through mediation or alternative dispute resolution. To make the most informed decision, it's essential to align your situation with the vast expertise that a law firm offers.
Understanding the Importance of Legal Representation
The role of a law firm extends beyond merely providing legal advice; they are your advocates in navigating the intricate legal process. Skilled legal professionals offer vital assistance, from conducting thorough conflict checks to ensure there's no Potential Conflict with a current client to maintaining meticulous client relations through detailed notes and client portal interactions that factor in all relevant legal issues.
Legal representation is about more than arguing your case in court. It involves the awareness of fiduciary duty towards clients, rendering services that protect their rights and interests, especially in matters where an expert witness's insights might be crucial or in personal injury claims where experienced lawyers can significantly enhance the chances of obtaining fair compensation.
Further, law firms have an ethical duty to keep business relationships transparent, avoiding any disqualification from representation that might arise through conflicts of interest. If such disqualification occurs, a firm must ensure that a potential client's valuable time is well-spent and that their need for legal services is addressed promptly.
Factors to Consider When Assessing Your Legal Situation
In assessing whether you have a case that a law firm can handle, several factors should be considered:
Legal Viability: Is there a sound legal basis for your case? Evaluate the legal merits and potential outcomes.
Type of Practice: Does the law firm specialize in your legal issue?
Conflict of Interest: Can the firm represent you without causing a conflict with the interests of a current client?
Discover the law firm's history with similar cases where they have guided potential clients through the legal process.
Resources and Time Commitment: Does the firm have the necessary resources to take on your case, considering their current caseload?
Client-Firm Compatibility: Assess client interactions and client relations demonstrated by the firm to ensure their approach aligns with your expectations.
Expert Witnesses: Will your case require expert testimony, and can the firm provide access to these crucial resources?
Financial Considerations: Understand the fee structures and determine if the potential benefits of legal action justify the cost.
Outcome Objectives: Ensure that the firm understands your desired outcomes and has a history of achieving similar goals for their clients.
Gathering as much information as possible during the initial consultation is critical to deciding whether to proceed with legal representation. Interaction with the firm during this period will help determine whether the lawyer-client relationship will be productive and beneficial in addressing your legal needs.
Types of Legal Issues We Handle
Our law firm takes pride in offering a wide range of legal services tailored to meet the diverse needs of our clients. From individuals facing personal dilemmas to corporations dealing with complex legal hurdles, our seasoned legal professionals are equipped to handle various cases. Below is a breakdown of the types of legal issues we specialize in.
Personal Injury Cases
You may be entitled to compensation if you’ve suffered an injury due to someone else's negligence. Our team of personal injury lawyers has extensive experience in cases including, but not limited to, car accidents, slip and fall incidents, medical malpractice claims, and workplace injuries. We understand the physical, emotional, and financial toll these injuries can cause, and we are committed to fighting for the justice and compensation our clients deserve.
Business Law Matters
Businesses of all sizes encounter legal issues that require knowledgeable guidance. Our legal professionals offer invaluable advice and representation in business formation, contracts, mergers and acquisitions, intellectual property protection, and commercial disputes. Whether you're a startup or an established enterprise, we aim to support and protect your business interests with strategic legal solutions.
Criminal Defense Cases
Facing criminal charges can be a daunting experience. Our criminal defense lawyers offer robust representation, advocating fiercely for our client's rights. We handle a spectrum of criminal cases, from misdemeanors to serious felonies, including DUI/DWI, drug offenses, theft, assault, and white-collar crimes. Trust in our expertise to navigate the complexities of the criminal justice system on your behalf.
Family Law Issues
Family law encompasses some of the most sensitive legal matters, impacting the lives of loved ones. Our compassionate lawyers address various family law issues, including divorce, child custody and support, spousal maintenance, adoption, and domestic violence cases. We strive to provide considerate and practical legal assistance during these personal and often emotional times.
Real Estate Disputes
Real estate transactions and disputes can be intricate and fraught with potential pitfalls. Our firm represents clients in all facets of real estate law, from residential and commercial transactions to landlord-tenant disputes and zoning issues. We aim to safeguard your interests by handling your real estate dealings carefully and professionally.
Employment Law Matters
The employer-employee relationship can give rise to numerous legal issues. We advise and represent employers and employees in employment discrimination, wrongful termination, wage and hour claims, and workplace harassment. Our knowledgeable team is adept at ensuring the enforcement of employment rights and navigating the complexities of employment law.
Regardless of your legal challenge, our initial consultation will help clarify whether your situation aligns with our expertise. Our detailed notes, discussions, and analyses will give you a clear notion of how we can effectively represent your interests and ensure that your next steps are taken with the full backing of our legal proficiency.
Assessing the Strength of Your Case
When contemplating legal action, one of the primary queries you may have is how to assess the strength of your potential case. It's an essential aspect of the legal process, as it determines whether your situation has the merit necessary to warrant legal representation and pursue a positive outcome. The evaluation typically includes examining the evidence available, the legality of the claim, and the potential for proving fault or liability. Additionally, assessing both eligibility to file a lawsuit within the relevant statute of limitations and the likelihood of a successful resolution is crucial. Our firm's experienced legal professionals are adept at meticulously reviewing the details of your situation and offering a frank assessment of the strength of your case.
Gathering Key Information and Documentation
Initiating your legal journey requires gathering critical information and documentation pertinent to your case. This may include incident reports, contracts, communications, medical records, or any material that can substantiate your claims. Gathering this evidence is critical, as it facilitates our legal professionals' ability to evaluate the specifics of your situation. Documenting the details accurately and promptly can be highly beneficial for a more accurate case assessment. While our team will guide you through what is needed, the following is a list of that might be required:
Personal identification documents
Incident or accident reports
Relevant communication records (emails, letters, text messages)
Contracts and agreements
Medical records and bills (for personal injury claims)
Financial documents (for business-related disputes)
Evaluating Legal Claims and Potential Damages
An in-depth evaluation of your legal claims and the potential damages you may be entitled to is a vital step in understanding the scope of your case. Our seasoned lawyers will examine the facts against applicable laws to determine the validity of your claim. In addition, we will assess the extent and types of possible damages — economic (such as medical expenses and lost wages), non-economic (like pain and suffering), and, in some instances, punitive damages. This evaluation will influence the strategy we adopt for your case and also help establish realistic expectations about the compensation you could receive.
Assessing the Legal Process and Timeline
Understandably, clients are often concerned about the length of time their legal issues might take to resolve. Assessing the legal process and timeline is contingent upon the complexity of the case and the jurisdiction in which it falls. While some cases may be settled swiftly through negotiation or mediation, others may require litigation and can take months or even years. Our firm endeavors to give you a realistic timeline, factoring in stages such as the initial filing, discovery phase, settlement negotiations, trial preparations, and the possibility of an appeal. The time invested in a case should be proportional to its complexities and potential benefits to our clients, and we prioritize handling your valuable time with respect and efficiency.
By working closely with our firm, we ensure that each client receives personalized attention and that all potential legal matters are handled with due diligence. The synergy of our legal expertise and our commitment to maintaining an ethical duty within the lawyer-client relationship promises that we will strive for the best possible outcome for your case.
Initial Consultation with Our Firm
At the outset of exploring legal avenues, the initial consultation is the first significant step. Our law firm acknowledges the weight of this encounter, as it allows you to present your circumstances and allows us to evaluate your case's compatibility with our areas of practice. During this meeting, one of our skilled legal professionals will explore the particulars of your situation to discern if we can offer you the legal representation you seek. We treat every initial consultation with the confidentiality and seriousness it deserves, paving the way for a potential lawyer-client relationship.
Importance of the Initial Consultation
The initial consultation sets the foundation for your entire legal journey. This encounter is crucial for multiple reasons: it allows us to perform a conflict check to ensure there is no Potential Conflict with current clients, it enables us to understand the nuances of your case, and it helps establish expectations regarding legal processes and potential outcomes. Moreover, this stage is vital for assessing whether a legal malpractice claim or other fiduciary duty concerns must be addressed. Remember, this is a chance for you to gauge our firm's fit for your needs as much as it is for us to evaluate your case.
What to Expect During the Consultation
When you attend the initial consultation, be prepared for a thorough discussion. Here's what you can expect:
Review of your case: We’ll discuss the details of your situation, the events leading up to your legal needs, and the desired outcome you expect.
Document evaluation: If applicable, we'll examine any critical information or documentation you bring that is paramount to building your case.
Legal assessment: Our experienced lawyers will provide insight into the legal context of your circumstances, potential avenues for pursuit, and candid feedback on the viability of your case.
Discussion of next steps: If our firm can assist you, we will outline the next phases of the legal process, including the formulation of a legal strategy and timeline.
Understanding the Lawyer-Client Relationship
Initiating a lawyer-client relationship is a step that should be taken with thorough understanding and mutual agreement. This relationship is grounded in trust, confidentiality, and a commitment to pursue your legal interests with enthusiasm and integrity. Within this relationship, we uphold strict ethical standards and ensure that all interactions with our clients—from client portal communications to court representations—are conducted professionally. Understanding this dynamic can help create successful client relations and positive legal outcomes.
In summary, an initial consultation is more than a mere introduction; it’s essential to determine whether our firm can effectively handle your legal issues. Our commitment to detailed evaluation and personalized legal strategy aims to avoid wasting your valuable time and support a productive lawyer-client relationship from the outset.
Conflicts of Interest and Disqualification
Our law firm takes potential conflicts of interest very seriously, as they can affect the integrity of our legal practice and the trust of our clients. Conflicts of interest arise when a lawyer’s professional judgment or loyalty to a client could be reasonably affected by other interests or relationships. In such instances, disqualification from representation may be necessary to maintain ethical standards and protect the interests of all parties involved.
Importance of Conflict Checks
Conflict checks are integral to our intake procedure to prevent conflicts of interest before taking on a new case. This process safeguards potential clients by ensuring that prior or current firm commitments will not compromise their case. These checks are not only a necessary step in adhering to our ethical duty but also in building a solid foundation of trust with our clients.
Potential Conflicts with Current Clients
We strive to avoid potential conflicts with current clients. These conflicts occur when the interests of a new client may be directly adverse to those of an existing client or when there is a significant risk of materially limiting our duties to one or both parties. In such cases, we must carefully consider our ability to represent each party while strictly adhering to legal ethics and protecting our clients' confidential information.
Disqualification from Representation
Disqualification from representation becomes necessary if a conflict of interest is identified and cannot be resolved through informed consent or other ethical measures. We take this step to uphold the integrity of our legal practice and the trust of our clients. The disqualification helps ensure that every client receives the focused and uncompromised representation they deserve.
Ethical Duty to Avoid Conflicts
Our legal professionals have an ethical duty to avoid conflicts of interest in our lawyer-client relationship. This commitment extends to maintaining confidentiality, ensuring loyalty, and providing competent representation while avoiding situations where our professional judgment could be unduly influenced. Upholding these ethical standards is crucial for the fair administration of justice and the reputation of our practice.
In conclusion, understanding and effectively managing conflicts of interest is critical for legal professionals and is a foundational aspect of our role in serving you. Our firm's stringent conflict check processes exemplify our devotion to ethical practice and respect for the legal system and our clients.
Expert Witnesses and Supporting Evidence
Expert Witnesses and Supporting Evidence
Expert witnesses and supporting evidence are vital when building a robust legal case. Expert witnesses, with their specialized knowledge and experience, can provide clarity and understanding of complex subjects for the court. Their testimony often sheds critical light on aspects of a case that laypersons may struggle to comprehend. Supporting evidence, meanwhile, includes any material that can corroborate a claim, ranging from documents and photographs to physical objects and digital data. Together, they form the cornerstone of a persuasive legal argument, help establish facts, and often influence the outcome of a legal proceeding.
Role of Expert Witnesses in Legal Cases
Expert witnesses are vital to the legal process, offering specialized insights that can make or break a case. They are professionals with high skills or knowledge in a particular field relevant to the case. Their role is to provide objective opinions based on the evidence presented. Unlike regular witnesses, who can only testify on what they observe, expert witnesses interpret facts and give expert opinions to help judges and juries make informed decisions.
Critical Points of Expert Witness Testimony:
Expertise in a specific field (medical, engineering, financial, etc.)
Evaluation of evidence from an expert perspective
Provision of expert opinion testimony to clarify case complexities
Assistance in establishing a claim by using specialized knowledge
Gathering and Preserving Supporting Evidence
Sound legal representation involves the presentation of expert witness testimony and the meticulous gathering and preservation of supporting evidence. Properly collected and preserved evidence is paramount in substantiating the expert witness's testimony and the case as a whole.
Steps for Effective Evidence Management:
Identification: Determining what constitutes relevant evidence for the case.
Collection: Acquiring evidence while following legal protocols to ensure admissibility.
Documentation: Keeping detailed notes and records of where and how evidence was collected.
Preservation: Storing evidence in a manner that prevents tampering or degradation.
Presentation: Effectively presenting evidence during legal proceedings to support the arguments.
How Expert Witnesses Can Strengthen Your Case
Having expert witnesses contribute to your legal strategy can significantly strengthen your case. They bring authority and credibility, particularly in technical or specialized areas beyond the court's general understanding.
Advantages of Expert Witness Testimony:
Clarification of intricate details: They can distill complex information into understandable terms.
Enhancement of case credibility: The education and experience of experts can lend weight to the case representation.
Influence on jury persuasion: Expert testimonies can be persuasive and sway jury opinions.
Provision of an edge over the opponent: Well-presented expert testimony can provide a strategic advantage.
In conclusion, expert witnesses and supporting evidence are essential elements of the legal arsenal. When effectively integrated into a case, they reinforce each other and play a pivotal part in pursuing justice. Legal representation must include skilled professionals capable of selecting suitable experts and managing evidence efficiently to ensure the most favorable outcome.
Client-Lawyer Relationship and Communication
Establishing a robust client-lawyer relationship is critical to the success of a legal matter. At its core, this involves clear, consistent, and professional communication between the legal professional and the client. A solid relationship built on trust can significantly impact the efficiency and outcomes of the legal process.
Critical Elements of Effective Communication:
Honesty: Clients expect transparency regarding their cases. Likewise, lawyers should also be candid about the probable outcomes and potential challenges.
Responsiveness: Timely responses to clients' queries and concerns are essential in maintaining good client relations.
Clarity: Legal jargon can be confusing; thus, lawyers should strive to explain matters in plain language.
Regular updates: Both the lawyer and client should keep each other informed about developments in the case.
Fostering open communication channels enables lawyers and their clients to collaborate more closely. This teamwork allows them to strategize effectively and respond to legal issues. Building a robust and communicative relationship cannot be overstated, as it is the foundation of trust. A lawyer who listens to and understands their client's needs can better represent their interests in negotiations and court proceedings.
Importance of Effective Client Relations
Effective client relations are beneficial for the progression of a case and essential for the reputation and success of the law firm. Satisfied clients can lead to repeat business, referrals, and a strong professional reputation. Furthermore, managing client expectations through effective communication helps avoid misunderstandings and the potential for malpractice claims.
Benefits of Positive Client Relations:
Increased client satisfaction: Satisfaction levels rise when clients feel heard and understood.
Enhanced firm reputation: Positive client experiences contribute to the firm’s overall reputation.
Reduced risk of disputes: Clear communication minimizes the risk of conflicts.
More excellent client retention: Clients with a positive experience are likelier to return and refer others.
The law firm must invest in training staff to manage client relations effectively. This includes lawyers and support staff who may interact with clients. Implementing a client portal for efficient and secure communication or setting guidelines for client interactions, such as periodic updates on case progress, could be crucial.
In summary, the client-lawyer relationship and communication are the bedrock of mutual understanding, effective legal representation, and a case's strategic success. By prioritizing effective client relations, lawyers can ensure they meet their ethical duty to their clients while promoting their practice's well-being and growth.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

Kaianere’kó:wa as Constitution of a Stateless Polity?
Some have been tempted to submit a particular translation and transcription of the Kaianere’kó:wa to a political-science constitutional analysis. Depending on the version of the Kaianere’kó:wa, an analyst might come to the conclusions that Donald S. Lutz has: that the Rotinonshón:ni was not a participatory democratic confederacy of equal nations, but rather a hereditary oligarchy in which the Kanien’kehá:ka enjoyed a privileged position in making proposals to the council. [81] Lutz only consults the versions of the Kaianere’kó:wa published by Gawasco Waneh (Arthur Parker). In fact, his analysis focuses only on a single version written by Dayodekane (Seth Newhouse), and ignores a different version approved by the roiá:ner at Ohswé:ken, which was included in Gawasco Waneh’s volume. According to Snow, “The Newhouse version tells us as much, if not more about political conditions on the Grand River at the end of the nineteenth century than it does about the origins of the League” [82]. The Grand Council of the Haudenosaunee believe that no one version is preferred and that “many traditional leaders feel that none of the written versions have all of the known oral history included.” [83]
Atsenhaienton (Kenneth Deer) objects to the Kaianere’kó:wa even being called “the Great Law” and those that would treat it as such: “it’s not a law: it’s guidelines to help people get to harmony and coexistence... They look at the Great Law and interpret it the way a constitutional lawyer would. That’s not the way it was intended to be treated.” [84] Even if the Kaianere’kó:wa should not be given a strict legalist reading, among its principles is a metaphor for amendment: “adding to the rafters” of the long house. This includes meetings among the traditional Rotinonshón:ni involving not only the roiá:ner but all the people, as a check on their power. [85]
The influence of Lewis Henry Morgan’s study of the Rotinonshón:ni on Marx and Engels’ concept of a stateless communist society is well known. In The Origin of the Family, Private Property and the State, Engels summarized Morgan’s description of the Rotinonshón:ni society:
“No soldiers, no gendarmes or police, no nobles, kings, regents, prefects, or judges, no prisons, no lawsuits — and everything takes its orderly course. All quarrels and disputes are settled by the whole of the community affected, by the gens or the tribe, or by the gentes among themselves; only as an extreme and exceptional measure is blood revenge threatened-and our capital punishment is nothing but blood revenge in a civilized form, with all the advantages and drawbacks of civilization. Although there were many more matters to be settled in common than today — the household is maintained by a number of families in common, and is communistic, the land belongs to the tribe, only the small gardens are allotted provisionally to the households — yet there is no need for even a trace of our complicated administrative apparatus with all its ramifications. The decisions are taken by those concerned, and in most cases everything has been already settled by the custom of centuries. There cannot be any poor or needy — the communal household and the gens know their responsibilities towards the old, the sick, and those disabled in war. All are equal and free — the women included. There is no place yet for slaves, nor, as a rule, for the subjugation of other tribes.” [86]
While Engels is right to commend the communal economy, sexual equality, and horizontal political structure of the Rotinonshón:ni, he erred in claiming that there were no ranks of social prestige with political responsibilities. The anthropological definition of “egalitarian” is narrow. There are some “rank societies in which positions of valued status are somehow limited so that not all those of sufficient talent to occupy such statuses actually achieve them. Such a society may or may not be stratified. That is, a society may sharply limit its positions of prestige without affecting the access of its entire membership to the basic resources upon which life depends” [87] While the numbers of roiá:ner and iakoiá:ner were limited by the Kaianere’kó:wa to certain kahwá:tsire, positions of ohnkanetoten were open to all men on the basis of merit and selection by the roiá:ner council. As has already been explained, Rotinonshón:ni society had a communal work and consumption ethic (the communal economy of the “one bowl”), so although ranks of prestige did exist, they did not serve in a position of accumulating or redistributing wealth.
Graeber, who as an anarchist is quite suspicious of all hierarchy, says of the traditional Rotinonshón:ni, “for all the complex federative structure, society was in most respects highly egalitarian. Office-holders, male and female, were elected from among a pool of possible heirs; the offices themselves, at least the male political ones, were considered as much a responsibility as a reward as they involved no real material rewards and certainly granted the holder no coercive power.” [88]
While it is often argued that the roiá:ner were traditionally selected from certain matrilineal lines, and that not all kahwá:tsire were able to select candidates, this varied over time and location. Teiowí:sonte describes modern debates around heredity: “To some, heredity is the very essence of Haudenosaunee governance and an integral factor in leadership selection... To others, this concept represents the infiltration of European corruption into Haundenosaunee leadership selection and the fortification of a class system invading our traditional concept of democracy with notions of royalty. Likewise, advocates against the heredity concept believe it to be a non-traditional convention that is a fairly recent development resulting from colonization.” [89] Snow claims that “Each nation devised its own internal mechanism for selecting and organizing its League Chiefs”[90]; and that ohnkanetoten were created to specifically deal with the issue of empowering men who did not come from the distinct matrilineal lines eligible for becoming roiá:ner. [91] He argues further that at times, the ranks may have represented a political class distinct from the common Rotinonshón:ni, and a class of slaves made up of captives who had not been adopted [92]—a situation which would have been most pronounced during the Beaver Wars.
Graeber notes this as well. “It was around this period one reads accounts of a society effectively divided into classes, with adopted prisoners doing the bulk of the menial labor and with members of their adopted families having the right to kill them for the slightest infranctions or impertinence... [T]his exceptionally brutal period did not last long: the children of these captives were considered full members of their adoptive clans.” [93] As we have seen from the life of Thaientané:ken, the descendents of adoptees had the same political rights of common Rotinonshón:ni and could be selected as ohnkanetoten. It is seemingly without contradiction that Snow also describes how little authority came with rank: “Although men appointed by each ohwachira probably met as a village council, they had little authority beyond the force of their personalities. This in turn meant that face-to-face persuasion was the rule.” [94] Kanatiiosh emphasizes that “being a chief or a clan mother is just as important as being a person without a title, for all people are held responsible for preserving and protecting the Great Law of Peace.” [95]
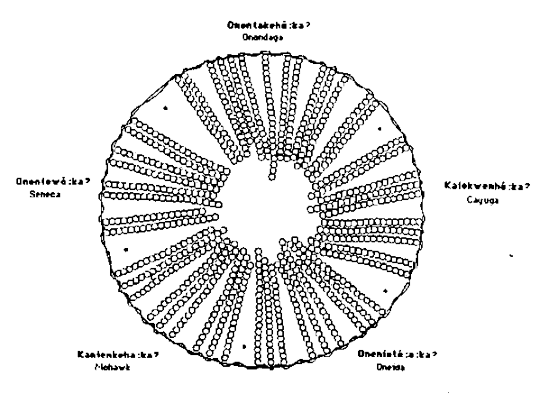
Circle Wampum [96]
Bonaparte, who himself served as a former elected chief of the Mohawk Council of Akwesasne,[97] does not even think that roiá:ner should be called “chiefs”: “a lot of our people don’t like using the term “chief” instead of “royaner,” because chief is such a generic term. You’ve got fire chiefs, police chiefs, chief of staff, etc. Those are positions where the people who have them are empowered to make decisions for a group, whereas our “royaners” are facilitators for having the group itself come to the decision, and who then act upon that decision.” [98] Indeed, the focus on decision-making among the Rotinonshón:ni was always to reach consensus. Snow has argued that the Rotinonshón:ni “emphasized consensus rather than executive authority, unanimity rather than majority rule, and equality rather than hierarchy” [99] Taiaiake goes so far as to write that “holding non-consensual power over others is contrary to tradition. Whatever the purpose behind the use of arbitrary authority, the power relationship is wrong”. [100] Richter describes a state of universal suffrage, claiming that voting in the council was open to all who had reached the age of maturity.[101]
Those familiar with the institution of consensus-based spokecouncils, used recently in the protests against corporate neoliberalism (“anti-globalization”), will notice many similarities with Kahentinetha Horn’s description of consensual decision-making among the Kanien’kehá:ka:
“[N]o one can impose their will nor make decisions for another, all must understand the viewpoint and agree of their own free will. The goal is not total agreement, but total understanding. If there is no agreement, then the consensus is to retain the status quo. If there is understanding by all then they go ahead with the decision... In entering the consensual decision-making process, whatever ideas are put into the process, the needs and attitudes of each is considered and complements the decision. Also, the individual has a duty to be directly involved, and to bring their ideas into the discussion within their clan. The final decision will be fully satisfactory to some, satisfactory to others and relatively satisfactory to the remainder, and will reflect elements from every group. This is a slow careful process requiring the reaching of a full understanding by each individual and not a decision made by a ‘leader.’ The person who explains the decision is a spokesman.” [102]
The Kaianere’kó:wa lacks the monopoly of force and the authority of coercive control that define statist polities. It is a mutual agreement of non-aggression among its participants, aimed primarily on maintaining peaceful relations among them, rather than a guiding document for the rule of elites over the rest of society. Richter has stated that “the coercive exercise of authority was virtually unknown” among the Rotinonshón:ni,[103] and that their “political values were essentially noncompetitive.” [104] Graeber believes that “the entire political apparatus was seen by its creators primarily as a way of resolving murderous disputes. The League was less a government, or even alliance, than a series of treaties establishing amity and providing the institutional means for preventing feuds and maintaining harmony among the five nations that made it up. For all their reputation as predatory warriors, the Iroquois themselves saw the essence of political action to lie in making peace.” [105]
Justice among the traditional Rotinonshón:ni was the responsibility of everyone, particularly one’s matrilineal kin. The focus was on condoling kahwá:tsire for their loss and on regulating social behavior through popular opinion, rather than through justice administered by a specialized class. While some see the offering of wampum to the family of a murder victim to as a reparational payment, comparable to the Northern European weregild, Morgan claimed that “the present of white wampum was not in the nature of a compensation of the life of the deceased, but of a regretful confession of the crime, with a petition for forgiveness. It was a peace-offering, the acceptance of which was pressed by mutual friends, and under such influences that the reconciliation was usually effect, except, perhaps, in aggravated cases of premeditated murder.” [106]
Wallace’s interpretation echoes Engel’s analysis of Rotinonshón:ni justice: “Behavior was governed not by published laws enforced by police, courts, and jails, but by oral tradition supported by a sense of duty, a fear of gossip, and a dread of retaliatory witchcraft. Theft, vandalism, armed robbery, were almost unknown. Public opinion, gently exercised, was sufficient to deter most persons from property crimes, for public opinion went straight to the heart of the matter: the weakness of the criminal.” [107] And Kanatiiosh argues that European settler “hierarchy breeds competition, and competition breeds anger, resentment, hatred, and can lead to revenge, which only continues the vicious cycle of violence. Western society is dependent on imprisonment, fines and other punishments, which are supposed to keep social order.” She contrasts that system of coercive punishment with the legal principles of the Kaianere’kó:wa, which created a “shared community where people have mutual respect for the entire group rather then interested only in one’s self. Perhaps a little spirituality, shame, guilt, and respect of self and community would be the best elements to include in a recipe for a true system of justice.” [108]
Richter repeatedly describes the traditional polity of the Rotinonshón:ni as a “nonstate society” [109] and “a system dependent upon voluntary compliance”. [110] His insistence on the difference between the Rotinonshón:ni and the colonial states it was contemporary with is worth emphasizing:
“Making and preserving peace, then was the purpose of the League, and accordingly the Grand Council apparently did not undertake the kinds of political functions of decision making and diplomacy characteristic of state-organized governments. In the early seventeenth century, the League possessed few state like characteristics: the Five nations had little in the way of common foreign policy, no effective means of devising unified strategies, and no central government in the sense that term is usually understood by Americans. Indeed, on various issues the ten or so autonomous towns of Iroquoia were often at odds with one another as they were in consensus. The League was not designed to remedy the deficit—nor, apparently, did the Iroquois people even perceive that there was any kind of deficit...” Daniel Richter, Ordeal of the Longhouse [111]
While the exact definition of a “state” is elusive, none can deny that states wield a legal monopoly of violence, and that the state therefore takes a coercive role in regards to its citizens. In respect to the degree of a given polity’s coercive control over its constituent members, we can imagine a spectrum with the totalitarian state on one end and a stateless society, an anarchy, on the other. Societies that are more ranked and stratified are more statist. Along this spectrum, the Rotinonshón:ni polity falls toward the pole of statelessness, having extremely limited ranking, and lacking in both coercive authority and economic stratification.
The anarchist historian George Woodcock believed that the Rotinonshón:ni’s polity amounted to a stateless confederation: “a common council of sachems, in whose selection the women, whose influence derived from their control of agriculture, played a great role; but this council did not interfere in the internal affairs of the tribes, so that it remained the coordinating body of a true confederation rather than the government of the state.” [112] Colonial historian Francis Jennings recognizes that it was “a league of friendship and mutual assistance, but ... a league of consultation and contract rather than a government of legislative command”. [113] Member nations “never gave up their power of individual decision. Often they struggled for dominance within the league, and sometimes (though rarely) they came to blows with each other. These phenomena were also to be observed among colonial towns and villages, but whereas the Iroquois tribes maintained local independence throughout their existence, the colonies gradually came under more and more effective central controls.” [114] All Rotinonshón:ni nations are equal, regardless of their number of clans, size of territory or numbers of population. [115] Bookchin, who so often suggested New England town-meeting democracy as a basic building block of libertarian municipalist confederation, would have done well to have taken the advice of Mitchel Cohen, and examine the Rotinonshón:ni polity as an example of the very sort of ideal of that he was advocating:
“Town meetings, according to Bookchin, are the American equivalent of the Greek polis — and why does he not seek to emulate the Iroquois tribal council instead or any of a hundred non-European forms? Linked together, local communities form the potential, according to Bookchin, for a “federated municipalism.” All other forms, particularly those created by native peoples, are seen as inferior. American Indian communities are diminished, in Bookchin’s framework, because of their lack of rational municipal debate. The framework of the colonizer informs Bookchin’s ideas despite himself, disempowering radical ecology movements and undermining their potential.”[116]
#Kaianere’kó:wa#stateless polity#precolonial#precolonial history#first nations#indigenous#Iroquois#mohawk#history#anthropology#true history#Rotinonshón:ni Polity#Rotinonshón:ni#Rotinonshon:ni Polity#us politics#us history#Native Americans#Northeastern Anarchist#Six Nations#anarchism#anarchy#anarchist society#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#resistance#autonomy#revolution#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Guardian gives biased view of Jerusalem property dispute
Another Arab family is about to be evicted from their home in East Jerusalem, reports The Guardian. But as we have come to expect, the issue is framed as rapacious ‘settlers’ stealing homes from their rightful Arab owners. In this case, the property belonged to Yemenite Jews evacuated from the Jerusaelm suburb of Silwan by the British in the 1930s. The Legal and Administrative Matters Law, passed in 1970, allows for Israeli property owners who owned properties that in 1948 were transferred to Jordanian control to claim them back from the Israeli administrator-general. (East Jerusalem is the only area where Jews are allowed to claim restitution of their property.) if the present Arab occupants have been paying rent, they are protected from eviction under the law. In this case, the court seems to have ruled that Saleem Abed Gaith’s claim to have bought his home is not valid.

Saleem Abed Gaith is facing eviction (Photo: Amnon Gutman/ The Guardian)
“In all, about 700 Palestinians in Batn al-Hawa may be threatened with displacement.
“It is our family home. It is where I was born. My family came here 60 years ago. If we had a just government then it would be given to us but instead they are trying to take our homes away,” said Nasser Rajabi, 52, whose most recent effort to prevent eviction was heard in court on Wednesday.
Saleem Abed Ghaith, whose case was heard this week, said he had lived in Batn al-Hawa since 1979, when he bought his home from a local Palestinian family.
“My health is not good. The fear of losing my home has taken complete control of me. What will I do? I have no other place to go,” he said.
The driving force behind the influx of Jewish Israelis into Batn al-Hawa is Ateret Cohanim, which describes itself as “the leading urban land reclamation organisation in Jerusalem … working for over 40 years to restore Jewish life in the heart of ancient Jerusalem”.
The group argues that much of Batn al-Hawa lies on the site of a village constructed by a philanthropic trust under Ottoman rule in the late 19th century to house poor Yemeni Jews. The community was evacuated by British authorities when tensions rose between Arabs and Jews in Palestine in the 1930s and its inhabitants were told they would be able to return when calm was restored. A 1970 law allows Jews the right to reclaim property in east Jerusalem.
Lawyers acting for the trust, which was reactivated almost 20 years ago, have successfully argued that its prior ownership of the properties in Batn al-Hawa should take precedence over any later purchases made by current inhabitants or their parents or grandparents, many of whom lost their homes during the conflict in 1967 or the wars surrounding Israel’s creation in 1948. Possession of other buildings has been obtained through deals with their owners, though the circumstances of these remains controversial.”
Read article in full
More about Jewish property claims
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
#civil lawyer in lucknow#top lawyer for criminal cases in lucknow#legal advisory services in lucknow#best law firm in lucknow#divorce lawyer in lucknow#best family advocate in lucknow#best advocate in lucknow high court#top criminal lawyers in lucknow#best criminal lawyer in lucknow high court#best lawyers for property disputes#criminal advocate in lucknow#family court lawyers in lucknow
0 notes