#Elevate Your Website's Visual Appeal With These Effective Techniques For Centering Elements Using CSS
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Elevate Your Website 's Visual Appeal with these Effective Techniques for Centering Elements Using CSS
In today’s fast-paced digital world, having a visually appealing website is essential to stand out from the crowd. One effective way to achieve this is by centering elements using CSS. Not only does it make your website look more professional, but it also enhances user experience.

In this blog post, we will introduce you to 11 effective techniques for centering elements using CSS that will elevate the visual appeal of your website and take it to the next level! So get ready to enhance your design skills with these simple yet powerful techniques.
WHAT IS CENTERING ELEMENTS IN CSS?
Centering elements in CSS is a technique for positioning HTML elements on a web page. There are several ways to center elements in CSS, and the most common method is to use the “margin: 0 auto” property.
Other methods of centering elements in CSS include using the “text-align: center” property, or setting the element’s position to “absolute” and using the “left: 50%” and “transform: translate(-50%)” properties.
The method you choose will depend on the type of element you’re trying to center, and whether or not you want that element to be responsive.
WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO CENTERING ELEMENTS IN CSS?
It’s important to center elements in CSS because it helps create a more balanced and symmetrical look for your web page. When elements are properly centered, they can add visual appeal and help direct a user’s eye toward the most important information on the page.
There are a number of different techniques that can be used to center elements in CSS. The most common method is to use the text-align property with a value of “center.” This will align all the text within an element to the center of that element.
Another popular technique is to use the margin property with auto values for both the left and right margins. This will cause the browser to automatically calculate equal margins on both sides of an element, effectively centering it within its containing element.
One can also use absolute positioning to center an element within its containing element. This involves setting the position property to “absolute” and then using either top or bottom and left or right properties to adjust the position of the element until it is perfectly centered.
HOW TO CENTER DIV OR TEXT IN DIV USING CSS?
If you’re working on a web design project and want to center either a div or text within a div, there are a couple of ways you can do it using CSS.
If you want to center a block level element like a div, you can use the CSS property “margin: 0 auto”. This will set the margins on the left and right sides of the element to be equal, thereby centering it.
If you want to center text or inline elements within a div, you can use the “text-align: center” property. This will align all the text within the div to be centered.

8 EFFECTIVE TECHNIQUES FOR CENTERING ELEMENTS USING CSS
In order to center elements using CSS, there are a few different techniques that can be employed. One popular technique is to use the “text-align” property with a value of “center.” This can be applied to any block level element, such as a paragraph, and will cause the contents of that element to be centered within the overall width of the containing element.
Another common technique is to set the width of the element to be centered to a specific value, then use the “margin” property with a value of “auto.” This will cause the element to be horizontally centered within its containing element, regardless of the width of that container.
It’s also possible to center elements vertically within their containing elements using CSS. This can be accomplished by setting the height of the container to a specific value, then using the “line-height” property with a value that is equal to or greater than the height of the container. The element will then be vertically centered within its containing element.
These are just a few of the many techniques that can be used for centering elements using CSS. By employing one or more of these techniques, you can easily improve the visual appeal of your website.
– FLEXBOX
When it comes to centering elements using CSS, there is no better option than flexbox. Flexbox provides a simple way to center elements horizontally and vertically within their container. In addition, flexbox can be used to create responsive layouts that automatically adjust to the size of the screen.
To use flexbox for centering, you must first set the display property of the container to flex. Then, you can use the justify-content property to center the elements horizontally, and the align-items property to center them vertically. For example, if you want to center an element horizontally and vertically within its container, you would use the following code:
container { display: flex; justify-content: center; align-items: center; }
– GRID LAYOUT
When it comes to CSS, there are a few different techniques that can be used to center elements on a page. The most common technique is known as the grid layout. This technique involves using a series of nested dives to create a grid of boxes that can then be used to position elements within that grid.
The first step in using the grid layout is to create a series of divs that will act as the columns of your grid. These divs should be given a class name so that they can be easily targeted with CSS. Once you have your column divs in place, you’ll need to add some content to them. This can be done by adding more divs or by using other HTML elements such as paragraphs or headings.
Once you have your columns and content in place, you can start positioning elements within the grid. To do this, you’ll need to use the CSS properties “float” and “clear”. The float property allows you to specify how an element should float within its parent container. By default, elements float to the left side of their container. However, if you want an element to be centered within its container, you’ll need to set the float property to “none”.
The clear property specifies what side of an element’s container other elements are not allowed to float on. So, if you want all subsequent elements after a centered element to also be centered, you would set the clear property to “both”.
App lying the grid layout technique is a great way to create a visually appealing design that is easy to understand and maintain. It also allows you to easily define how elements should be positioned within the grid, making it simple to adjust as needed.
– ABSOLUTE POSITIONING
When it comes to CSS, there are a few different methods that can be used to center elements on a web page. The most common method is to use the text-align property, which can be applied to both block-level and inline elements. However, this method only works if the width of the element is explicitly set.
Another method that can be used is the margin: auto; technique. This can be applied to block-level elements that have a set width, and will cause the element to be centered within its containing element.
If you want to center an element that is not a block-level element, or if you don’t want to set a width, then you can use the absolute positioning technique. With absolute positioning, you can specify exactly where you want an element to appear on the page using the left and top properties. You also need to set the position property to “absolute” for this technique to work.
– RELATIVE POSITIONING
When it comes to CSS, there are a few different ways to center elements on a web page. The most common method is to use the “text-align” property. This can be applied to either the entire page or to individual elements. For example, to center all of the text on your page, you would add the following CSS rule to your stylesheet:
body { text-align: center; }
You can also use the “text-align” property to center specific elements on your page, like images, blockquote, etc. For example, if you want to center an image that’s inside a div element, you would add the following CSS rule:
div { text-align: center; } img { /* this is for centering images */ display: block; margin: 0 auto; /* important */ /* top and bottom margins are 0 */ width: 50%; /* image width can be anything less than or equal to container width */ }
Another way to center elements is by using the “margin” property. You can set the left and right margins to “auto”, which will evenly distribute them within the containing element. This works for both block level and inline elements. For example, if you want to center a div element on your page, you would add the following CSS rule:
div { margin-left: auto; /* important */ margin-right: auto; /* important */ width: 50%; /* div width can be anything less than or equal to its parent container width */ }
Finally, you can use the “position” property with the “relative” value. This will set an element’s position relative to its containing element and then center it using margins. For example, if you want to center a div element on your page, you would add the following CSS rule:
div { position: relative; /* important */ left: 50%; /* important */ top: 50%; /* important */ margin-left: -25%; /* important */ margin-top: -25%; /* important */ width: 50%; /* div width can be anything less than or equal to its parent container width */ }
– TRANSLATE METHOD
When it comes to centering elements using CSS, there are a few different methods you can use. The ‘translate’ method is one of the more popular and effective techniques.
With the translate method, you can essentially move an element around on the page until it’s perfectly centered. To do this, you’ll need to set the element’s ‘transform’ property to ‘translate(X, Y)’. X and Y represent the amount of pixels you want to move the element horizontally and vertically, respectively.
For example, if you wanted to center an element horizontally on a page, you would set the X value to ‘50%’ and leave the Y value at ‘0px’. This would cause the element to be positioned 50% from the left side of the page (the exact center).
You can also use negative values for X and Y if you want to move an element up or left from its current position. So, if you wanted to move an element 10px to the left and 5px up from its current position, you would set the X value to ‘-10px’ and the Y value to ‘-5px’.
Once you have your desired position set, all that’s left is to add some vendor prefixes (-webkit-, -moz-, etc.) so that your CSS will work across all browsers.
– MARGIN AUTO METHOD
When it comes to CSS, there are a number of different methods that can be used to center elements on a web page. One popular method is known as the margin auto technique. This approach is relatively simple and only requires a few lines of code.
Here’s how the margin auto method works:
First, you need to set the width of the element that you want to center. This can be done using the width property in CSS. Next, you need to set the left and right margins to auto. This will cause the browser to automatically calculate equal margins for the element, effectively centering it on the page.
And that’s all there is to it! The margin auto method is a quick and easy way to center elements using CSS. Give it a try next time you’re working on a web project.
– TEXT ALIGN PROPERTY METHOD
The text-align property is a CSS method for centering elements on a web page. This can be done horizontally, vertically, or both.
To center horizontally, you would use the text-align: center; property. This is probably the most common way to center elements on a web page.
To center vertically, you need to use a different method. One way to do this is by setting the element’s height and width properties to 100%. Then, set the top and bottom margins to auto. This will make the element centered vertically on the page.
You can also use the flexbox model to center elements vertically. The flexbox model is powerful and has many other applications beyond centering elements. If you’re not familiar with flexbox, there are plenty of tutorials online that can help you get started.
– TRANSFORM PROPERTY METHOD
When it comes to centering elements using CSS, the transform property method is one of the most effective. This is because it allows you to center an element horizontally and vertically at the same time.
To use this method, you first need to add the following CSS code to your element:
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
This will cause your element to be positioned 50% from the top and 50% from the bottom of its containing element. As a result, it will be horizontally and vertically centered.
CONCLUSION
CSS centering elements is a simple but effective way to improve the visual appeal of your website. By implementing these techniques, you can create attractive and well-balanced designs that are both eye-catching and easy to read. With the help of CSS, you can add custom styles to your webpages in no time at all.
So don’t wait any longer – get started with centering elements using CSS and elevate your website’s visual appeal today!
#Elevate Your Website 's Visual Appeal with these Effective Techniques for Centering Elements Using CSS#software development#digital marketing#web development#web design#web design agency in toronto canada#app development#digital marketing agency canada#graphic design#multimedia / flash animation services#web devlopment#web design company in mississauga
0 notes
Text
Styling Excellence: Mastering Button Designs with CSS

Introduction
Welcome to a journey into the world of styling excellence! In this blog post, we'll delve into the art of mastering button designs using the power of CSS. Buttons are a fundamental aspect of web design, playing a crucial role in user interaction and navigation. Understanding how to style buttons effectively not only enhances the visual appeal of your website but also contributes to a seamless user experience. We'll explore the basics of button styling, advanced techniques to elevate your designs, and the importance of responsiveness. Additionally, we'll dive into creating interactive buttons and optimizing performance to ensure your styles not only look great but also load efficiently. Whether you're a beginner looking to grasp the fundamentals or an experienced developer aiming to refine your skills, this blog post has something for everyone. Let's embark on this journey to unlock the secrets of crafting visually stunning and highly functional buttons with the magic of CSS!
The Basics of Button Styling
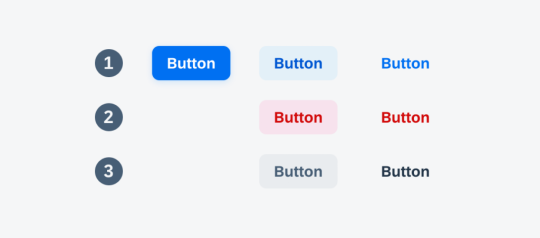
Button styling forms the foundation of creating visually appealing and user-friendly interfaces. In this section, we'll cover the fundamental CSS properties and techniques that lay the groundwork for crafting beautiful button designs. 1. Background and Color: The background-color property is essential for defining the base color of your button. Consider using a color palette that aligns with your website's overall design. Experiment with different shades to find the perfect match. Additionally, the color property determines the text color within the button, ensuring readability and contrast. 2. Border and Border-radius: The border property allows you to define the border style, width, and color of the button. Adding rounded corners is achieved through the border-radius property, providing a modern and softer aesthetic. Combining these properties allows for versatile button shapes and styles. 3. Padding and Margin: Adjusting the padding inside the button influences its size and spacing, contributing to a balanced and well-proportioned design. Meanwhile, the margin property controls the space between buttons and other elements, preventing overcrowded layouts. 4. Text Styling: Customize the font, size, and weight of the text within the button to enhance its visual appeal. Employ the text-align property for proper alignment, ensuring a polished and professional look. 5. Hover Effects: Introduce interactive elements by incorporating hover effects. This can include changes in color, shadow, or other visual cues to provide feedback to users when they interact with the button. Utilize the :hover pseudo-class for these effects. Now, let's explore a simple example to illustrate the application of these basic styling principles: HTMLClick me CSS.basic-button { background-color: #3498db; color: #ffffff; border: 1px solid #3498db; border-radius: 5px; padding: 10px 20px; text-align: center; } .basic-button:hover { background-color: #2078b4; border-color: #2078b4; } This example creates a button with a blue background, white text, and subtle hover effects. Feel free to experiment with these basic properties to craft buttons that align with your website's style and enhance the overall user experience.
Advanced Techniques for Button Designs
Take your button designs to the next level by exploring advanced CSS techniques that add sophistication and visual flair. These techniques allow you to create buttons that stand out, capturing the attention of your website visitors. 1. Gradient Backgrounds: Replace solid colors with gradient backgrounds to add depth and dimension to your buttons. Gradients can be simple two-color transitions or more complex combinations, providing a modern and vibrant aesthetic. Experiment with linear and radial gradients to achieve different effects. 2. Box Shadows: Introduce depth and realism to your buttons by utilizing box shadows. The box-shadow property allows you to cast shadows around the button, creating a lifted or floating appearance. Adjust the shadow's color, blur radius, and offset for varied visual effects. 3. Icon Integration: Enhance button designs by incorporating icons. Icons provide visual cues and can complement the button's purpose. Use the ::before or ::after pseudo-elements along with the content property to insert scalable vector icons into your buttons, ensuring a clean and modern look. 4. Custom Transitions: Implement smooth transitions to enhance the user experience. The transition property allows you to control the speed and timing function of changes in properties like color, background, or size. This creates a polished effect, especially when users interact with your buttons. 5. Border Gradients: Go beyond simple borders by applying gradients to border properties. This technique adds a dynamic and eye-catching element to your buttons. Experiment with different color combinations and gradient styles to achieve unique and visually appealing results. Let's explore an example that combines these advanced techniques: HTMLClick me CSS.advanced-button { background: linear-gradient(to right, #ff6b6b, #ffe66d); color: #ffffff; border: none; border-radius: 8px; box-shadow: 0 4px 6px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1); padding: 15px 30px; position: relative; overflow: hidden; transition: background 0.3s ease; } .advanced-button:hover { background: linear-gradient(to right, #ff8e6e, #ffec8b); } .icon::before { content: url('icon.svg'); margin-right: 10px; } This example showcases a button with a gradient background, a subtle box shadow, and an integrated icon. Feel free to customize and combine these techniques to create buttons that align with your design goals and captivate your audience.
Responsive Button Designs
Ensuring that your buttons look and function well across various devices is essential for providing a seamless user experience. Responsive button designs adapt to different screen sizes and orientations, catering to the diverse ways users access your website. 1. Media Queries: Start by incorporating media queries into your CSS to apply specific styles based on the device characteristics. Media queries allow you to set breakpoints where different styles take effect, ensuring a smooth transition between desktop, tablet, and mobile views. 2. Flexible Sizing: Utilize relative units like percentages or ems instead of fixed pixel sizes for your button dimensions. This ensures that buttons scale proportionally when viewed on different devices, preventing issues like buttons appearing too small or too large on certain screens. 3. Fluid Typography: Extend responsive design principles to text within buttons. Instead of using fixed font sizes, consider using relative units for font size, such as vw (viewport width) or ems. This ensures that text scales appropriately, maintaining readability on all devices. 4. Touch-Friendly Design: Recognize the prevalence of touchscreens on mobile devices. Adjust button sizes and spacing to accommodate touch interactions. Ensuring that buttons are large enough and well-spaced prevents accidental taps and enhances the overall user experience. 5. Hidden Elements: In certain situations, you may need to hide or rearrange elements for smaller screens. Use the display property and visibility property along with media queries to hide non-essential elements or present them in a more condensed form on smaller screens. Let's examine a practical example of a responsive button design: HTMLClick me CSS.responsive-button { background-color: #4caf50; color: #ffffff; padding: 10px 20px; font-size: 16px; border: none; border-radius: 5px; cursor: pointer; transition: background-color 0.3s; } @media (max-width: 600px) { .responsive-button { font-size: 14px; } } .responsive-button:hover { background-color: #45a049; } This example demonstrates a responsive button that adjusts its font size when viewed on screens smaller than 600 pixels wide. Implementing responsive designs ensures that your buttons remain visually appealing and functional across a spectrum of devices, contributing to a positive user experience.
Creating Interactive Buttons with CSS
Elevate user engagement on your website by making buttons interactive and visually appealing. In this section, we'll explore CSS techniques that add a dynamic touch to your buttons, making them responsive to user interactions. 1. Hover Effects: Implementing hover effects is a simple yet effective way to make buttons interactive. Use the :hover pseudo-class to define styles that activate when users hover over the button. This can include changes in background color, text color, or even subtle animations to provide visual feedback. 2. Transitions and Animations: Go beyond static styles by incorporating transitions and animations. The transition property allows for smooth changes in specified styles over a set duration. For more complex and dynamic effects, animations can be defined using the keyframes rule. Experiment with different easing functions and durations to achieve the desired impact. 3. Click Effects: Provide visual feedback when users click on a button. This can be achieved using the :active pseudo-class to define styles that activate during the click event. Consider incorporating effects like a change in background color or a slight shadow to simulate a button press. 4. Focus Styles: Enhance accessibility by styling the focus state of your buttons. When users navigate your site using the keyboard, a clear focus style ensures they know which button is currently selected. Use the :focus pseudo-class to define styles for the focused state, such as an outline or box shadow. 5. Interactive Icons: Integrate interactive icons within your buttons to convey additional meaning or functionality. Use pseudo-elements like ::before or ::after to insert icons into the button. Apply styles and animations to these icons to make them respond to user interactions. Let's dive into an example that combines hover effects and transitions: HTML Hover over me CSS.interactive-button { background-color: #3498db; color: #ffffff; padding: 10px 20px; border: none; border-radius: 5px; cursor: pointer; transition: background-color 0.3s; } .interactive-button:hover { background-color: #2078b4; } This example showcases a button with a smooth color transition on hover. Experiment with these techniques to create interactive buttons that not only capture user attention but also enhance the overall user experience on your website.
Optimizing Performance
Efficient button styling goes beyond aesthetics; it also plays a crucial role in the overall performance of your website. In this section, we'll explore best practices for optimizing CSS to ensure your button designs not only look great but also load quickly, contributing to a seamless user experience. 1. Minimize CSS File Size: Reduce the size of your CSS files by eliminating unnecessary code and comments. Utilize tools like minifiers to automatically remove whitespace and compress your stylesheets. Smaller file sizes lead to faster loading times, especially crucial for users on slower internet connections. 2. Use CSS Sprites: Combine multiple button images into a single sprite sheet. By doing so, you reduce the number of server requests needed to load individual images. This optimization technique is particularly beneficial when working with icon sets or buttons with diverse states. 3. Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading for background images or other non-essential assets within your buttons. Lazy loading delays the loading of off-screen images until they are needed, reducing initial page load times. This is especially beneficial for pages with multiple buttons or images. 4. Optimize Background Gradients: If using gradients, consider simplifying them to reduce the load on the browser. Complex gradients can contribute to slower rendering times. Experiment with simpler gradient styles or use solid colors where possible to achieve a balance between aesthetics and performance. 5. CSS Hardware Acceleration: Leverage hardware acceleration for smoother animations and transitions. This is achieved by offloading graphics rendering to the device's GPU. Apply the transform property with 3D translations to trigger hardware acceleration, enhancing the performance of interactive elements like buttons. 6. Browser Caching: Configure your server to set appropriate cache headers for your CSS files. This enables browsers to cache the styles locally, reducing the need to download them on subsequent visits. Users will experience faster load times when returning to your site. Let's explore an example that incorporates some of these performance optimization techniques: HTML CSS/* Minimized and optimized CSS */ .optimized-button {background-color: #4caf50;color: #ffffff;padding: 10px 20px;border: none;border-radius: 5px;cursor: pointer; transition: background-color 0.3s;}.optimized-button:hover{background-color: #45a049;} Implementing these performance optimizations ensures that your button styles contribute to a fast and responsive web experience. By adopting these best practices, you enhance both the visual appeal and efficiency of your website's button designs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Explore answers to common queries about button styling with CSS. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, these FAQs provide insights into various aspects of creating stylish and functional buttons for your website. - Q: How can I create a basic button with CSS? A: To create a basic button, define the background color, text color, padding, and border properties in your CSS. You can customize these properties to achieve the desired style. Consider using the :hover pseudo-class for interactive effects. - Q: What are the key properties for advanced button designs? A: Advanced button designs often involve gradient backgrounds, box shadows, icon integration, custom transitions, and border gradients. These properties add depth, interactivity, and visual appeal to your buttons. - Q: How can I make buttons responsive to different devices? A: Use media queries to apply specific styles based on device characteristics. Ensure flexible sizing, fluid typography, and touch-friendly design. Consider hiding or rearranging elements for smaller screens to maintain a responsive layout. - Q: What techniques can I use to make buttons interactive? A: Buttons can be made interactive through hover effects, transitions, animations, click effects, and focus styles. These techniques add dynamism and engagement to your buttons, enhancing the overall user experience. - Q: How do I optimize the performance of CSS for button styling? A: Optimize CSS performance by minimizing file size, using CSS sprites, implementing lazy loading for images, simplifying background gradients, leveraging hardware acceleration, and enabling browser caching. These practices contribute to faster loading times. Feel free to refer to these FAQs as you embark on your journey to master button styling with CSS. If you have additional questions, don't hesitate to reach out for further assistance!
Conclusion
Congratulations on completing your exploration of button styling excellence with CSS! In this comprehensive guide, we've covered a range of topics, from the basics of button styling to advanced techniques, responsive designs, interactive elements, and performance optimization. Let's recap the key takeaways from our journey: - Mastering the Basics: Understanding fundamental CSS properties such as background, border, padding, and text styling lays the groundwork for crafting visually appealing buttons. - Advanced Techniques: Elevate your button designs with advanced techniques like gradient backgrounds, box shadows, icon integration, custom transitions, and border gradients, adding depth and sophistication. - Responsive Design: Ensure your buttons look and function well across different devices by employing media queries, flexible sizing, fluid typography, touch-friendly design, and hidden elements for smaller screens. - Interactive Elements: Enhance user engagement by incorporating hover effects, transitions, animations, click effects, and focus styles, making your buttons dynamic and responsive to user interactions. - Performance Optimization: Optimize CSS for better performance by minimizing file size, using CSS sprites, lazy loading, simplifying background gradients, leveraging hardware acceleration, and enabling browser caching. Armed with these skills, you have the tools to create buttons that not only look visually stunning but also contribute to a seamless and efficient user experience on your website. Remember to experiment, iterate, and stay informed about evolving web design trends and best practices. Thank you for joining us on this journey to become a master of button styling with CSS. Keep pushing the boundaries of creativity, and may your buttons captivate and delight users across the digital landscape! Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Elevate Your Website's Visual Appeal With These Effective Techniques For Centering Elements Using CSS
In today’s fast-paced digital world, having a visually appealing website is essential to stand out from the crowd. One effective way to achieve this is by centering elements using CSS. Not only does it make your website look more professional, but it also enhances user experience.

In this blog post, we will introduce you to 11 effective techniques for centering elements using CSS that will elevate the visual appeal of your website and take it to the next level! So get ready to enhance your design skills with these simple yet powerful techniques.
WHAT IS CENTERING ELEMENTS IN CSS?
Centering elements in CSS is a technique for positioning HTML elements on a web page. There are several ways to center elements in CSS, and the most common method is to use the “margin: 0 auto” property.
Other methods of centering elements in CSS include using the “text-align: center” property, or setting the element’s position to “absolute” and using the “left: 50%” and “transform: translateX(-50%)” properties.
The method you choose will depend on the type of element you’re trying to center, and whether or not you want that element to be responsive.
WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO CENTERING ELEMENTS IN CSS?
It’s important to center elements in CSS because it helps create a more balanced and symmetrical look for your web page. When elements are properly centered, they can add visual appeal and help direct a user’s eye toward the most important information on the page.
There are a number of different techniques that can be used to center elements in CSS. The most common method is to use the text-align property with a value of “center.” This will align all the text within an element to the center of that element.
Another popular technique is to use the margin property with auto values for both the left and right margins. This will cause the browser to automatically calculate equal margins on both sides of an element, effectively centering it within its containing element.
One can also use absolute positioning to center an element within its containing element. This involves setting the position property to “absolute” and then using either top or bottom and left or right properties to adjust the position of the element until it is perfectly centered.
HOW TO CENTER DIV OR TEXT IN DIV USING CSS?
If you’re working on a web design project and want to center either a div or text within a div, there are a couple of ways you can do it using CSS.
If you want to center a block level element like a div, you can use the CSS property “margin: 0 auto”. This will set the margins on the left and right sides of the element to be equal, thereby centering it.
If you want to center text or inline elements within a div, you can use the “text-align: center” property. This will align all the text within the div to be centered.
8 EFFECTIVE TECHNIQUES FOR CENTERING ELEMENTS USING CSS
In order to center elements using CSS, there are a few different techniques that can be employed. One popular technique is to use the “text-align” property with a value of “center.” This can be applied to any block level element, such as a paragraph, and will cause the contents of that element to be centered within the overall width of the containing element.
Another common technique is to set the width of the element to be centered to a specific value, then use the “margin” property with a value of “auto.” This will cause the element to be horizontally centered within its containing element, regardless of the width of that container.
It’s also possible to center elements vertically within their containing elements using CSS. This can be accomplished by setting the height of the container to a specific value, then using the “line-height” property with a value that is equal to or greater than the height of the container. The element will then be vertically centered within its containing element.
These are just a few of the many techniques that can be used for centering elements using CSS. By employing one or more of these techniques, you can easily improve the visual appeal of your website.
– FLEXBOX
When it comes to centering elements using CSS, there is no better option than flexbox. Flexbox provides a simple way to center elements horizontally and vertically within their container. In addition, flexbox can be used to create responsive layouts that automatically adjust to the size of the screen.
To use flexbox for centering, you must first set the display property of the container to flex. Then, you can use the justify-content property to center the elements horizontally, and the align-items property to center them vertically. For example, if you want to center an element horizontally and vertically within its container, you would use the following code:
container { display: flex; justify-content: center; align-items: center; }
– GRID LAYOUT
When it comes to CSS, there are a few different techniques that can be used to center elements on a page. The most common technique is known as the grid layout. This technique involves using a series of nested divs to create a grid of boxes that can then be used to position elements within that grid.
The first step in using the grid layout is to create a series of divs that will act as the columns of your grid. These divs should be given a class name so that they can be easily targeted with CSS. Once you have your column divs in place, you’ll need to add some content to them. This can be done by adding more divs or by using other HTML elements such as paragraphs or headings.
Once you have your columns and content in place, you can start positioning elements within the grid. To do this, you’ll need to use the CSS properties “float” and “clear”. The float property allows you to specify how an element should float within its parent container. By default, elements float to the left side of their container. However, if you want an element to be centered within its container, you’ll need to set the float property to “none”.
The clear property specifies what side of an element’s container other elements are not allowed to float on. So, if you want all subsequent elements after a centered element to also be centered, you would set the clear property to “both”.
App lying the grid layout technique is a great way to create a visually appealing design that is easy to understand and maintain. It also allows you to easily define how elements should be positioned within the grid, making it simple to adjust as needed.
– ABSOLUTE POSITIONING
When it comes to CSS, there are a few different methods that can be used to center elements on a web page. The most common method is to use the text-align property, which can be applied to both block-level and inline elements. However, this method only works if the width of the element is explicitly set.
Another method that can be used is the margin: auto; technique. This can be applied to block-level elements that have a set width, and will cause the element to be centered within its containing element.
If you want to center an element that is not a block-level element, or if you don’t want to set a width, then you can use the absolute positioning technique. With absolute positioning, you can specify exactly where you want an element to appear on the page using the left and top properties. You also need to set the position property to “absolute” for this technique to work.
– RELATIVE POSITIONING
When it comes to CSS, there are a few different ways to center elements on a web page. The most common method is to use the “text-align” property. This can be applied to either the entire page or to individual elements. For example, to center all of the text on your page, you would add the following CSS rule to your stylesheet:
body { text-align: center; }
You can also use the “text-align” property to center specific elements on your page, like images, blockquote, etc. For example, if you want to center an image that’s inside a div element, you would add the following CSS rule:
div { text-align: center; } img { /* this is for centering images */ display: block; margin: 0 auto; /* important */ /* top and bottom margins are 0 */ width: 50%; /* image width can be anything less than or equal to container width */ }
Another way to center elements is by using the “margin” property. You can set the left and right margins to “auto”, which will evenly distribute them within the containing element. This works for both block level and inline elements. For example, if you want to center a div element on your page, you would add the following CSS rule:
div { margin-left: auto; /* important */ margin-right: auto; /* important */ width: 50%; /* div width can be anything less than or equal to its parent container width */ }
Finally, you can use the “position” property with the “relative” value. This will set an element’s position relative to its containing element and then center it using margins. For example, if you want to center a div element on your page, you would add the following CSS rule:
div { position: relative; /* important */ left: 50%; /* important */ top: 50%; /* important */ margin-left: -25%; /* important */ margin-top: -25%; /* important */ width: 50%; /* div width can be anything less than or equal to its parent container width */ }
– TRANSLATE METHOD
When it comes to centering elements using CSS, there are a few different methods you can use. The ‘translate’ method is one of the more popular and effective techniques.
With the translate method, you can essentially move an element around on the page until it’s perfectly centered. To do this, you’ll need to set the element’s ‘transform’ property to ‘translate(X, Y)’. X and Y represent the amount of pixels you want to move the element horizontally and vertically, respectively.
For example, if you wanted to center an element horizontally on a page, you would set the X value to ‘50%’ and leave the Y value at ‘0px’. This would cause the element to be positioned 50% from the left side of the page (the exact center).
You can also use negative values for X and Y if you want to move an element up or left from its current position. So, if you wanted to move an element 10px to the left and 5px up from its current position, you would set the X value to ‘-10px’ and the Y value to ‘-5px’.
Once you have your desired position set, all that’s left is to add some vendor prefixes (-webkit-, -moz-, etc.) so that your CSS will work across all browsers.
– MARGIN AUTO METHOD
When it comes to CSS, there are a number of different methods that can be used to center elements on a web page. One popular method is known as the margin auto technique. This approach is relatively simple and only requires a few lines of code.
Here’s how the margin auto method works:
First, you need to set the width of the element that you want to center. This can be done using the width property in CSS. Next, you need to set the left and right margins to auto. This will cause the browser to automatically calculate equal margins for the element, effectively centering it on the page.
And that’s all there is to it! The margin auto method is a quick and easy way to center elements using CSS. Give it a try next time you’re working on a web project.
– TEXT ALIGN PROPERTY METHOD
The text-align property is a CSS method for centering elements on a web page. This can be done horizontally, vertically, or both.
To center horizontally, you would use the text-align:center; property. This is probably the most common way to center elements on a web page.
To center vertically, you need to use a different method. One way to do this is by setting the element’s height and width properties to 100%. Then, set the top and bottom margins to auto. This will make the element centered vertically on the page.
You can also use the flexbox model to center elements vertically. The flexbox model is powerful and has many other applications beyond centering elements. If you’re not familiar with flexbox, there are plenty of tutorials online that can help you get started.
– TRANSFORM PROPERTY METHOD
When it comes to centering elements using CSS, the transform property method is one of the most effective. This is because it allows you to center an element horizontally and vertically at the same time.
To use this method, you first need to add the following CSS code to your element:
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
This will cause your element to be positioned 50% from the top and 50% from the bottom of its containing element. As a result, it will be horizontally and vertically centered.
CONCLUSION
CSS centering elements is a simple but effective way to improve the visual appeal of your website. By implementing these techniques, you can create attractive and well-balanced designs that are both eye-catching and easy to read. With the help of CSS, you can add custom styles to your webpages in no time at all.
So don’t wait any longer – get started with centering elements using CSS and elevate your website’s visual appeal today!
#Elevate Your Website's Visual Appeal With These Effective Techniques For Centering Elements Using CSS#Multimedia / Flash Animation Services#Reliable seo consultant#Best Web Design Company In Toronto
0 notes