#Digitalhealth
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
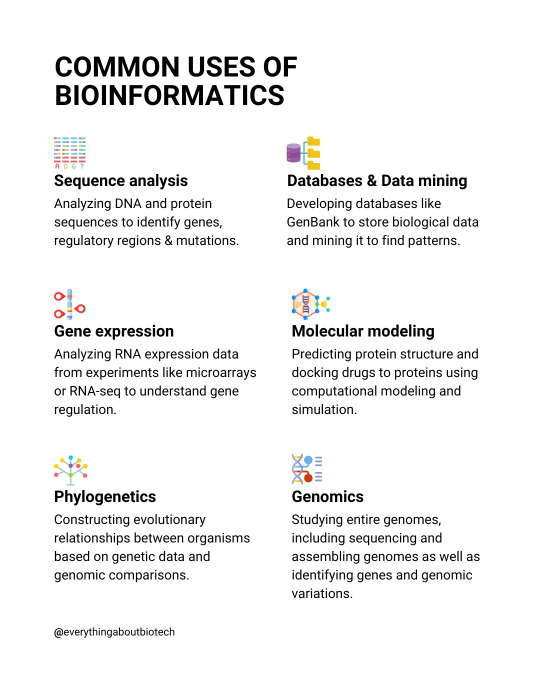
Common uses of bioinformatics
💡Sequence analysis Analyzing DNA and protein sequences to identify genes, regulatory regions & mutations.
💡Gene expression Analyzing RNA expression data from experiments like microarrays or RNA-seq to understand gene regulation.
💡Phylogenetics Constructing evolutionary relationships between organisms based on genetic data and genomic comparisons.
💡Molecular modeling Predicting protein structure and docking drugs to proteins using computational modeling and simulation.
💡Databases & Data mining Developing databases like GenBank to store biological data and mining it to find patterns.
💡Genomics Studying entire genomes, including sequencing and assembling genomes as well as identifying genes and genomic variations.
Follow @everythingaboutbiotech for useful posts.
#bioinformatics#genomics#proteomics#sequencing#PCR#biodata#bioIT#precisionmedicine#digitalhealth#biotech#DNA#healthtech#medtech#biostatistics#bioinformaticsjobs#BLAST#microarray#GenBank
53 notes
·
View notes
Text

In a world filled with big-name players in the smart wearables industry, TikTik Global LLP is an up-and-coming bootstrapped startup poised to change the game with its highly anticipated Aether X smartwatch, launching this December. TikTik Global LLP has leveraged its startup culture and local manufacturing approach to bring advanced, AI-driven smartwatches that blend functionality with fashion, offering a unique, user-focused experience that rivals any global tech leader.
Innovating with TikTik AI and Infinity OS
At the core of TikTik’s groundbreaking wearable is TikTik AI, an intelligent system that sets the Aether X apart with unique features tailored for a more intuitive user experience. Built on the company’s proprietary Infinity OS, this AI-enhanced operating system transforms the Aether X into more than just a smartwatch; it’s a lifestyle tool that integrates seamlessly into daily life. Users can expect fast and responsive real-time notifications, push alerts, and an intuitive user interface that adapts based on usage. The Aether X not only supports essential smartphone connectivity but also boasts an array of exclusive wellness and fitness features designed for everyone, from health-conscious individuals to fitness enthusiasts.
A Lifestyle-First Approach with Customizable Design
TikTik Global LLP aims to make smartwatches accessible, stylish, and suitable for every occasion. The Aether X is designed as a unisex lifestyle accessory with a variety of interchangeable options, including premium leather, durable silicon, and sleek metallic straps. The patented, sophisticated watch design and color-customizable crown allow users to personalize their style for any setting—whether it’s a gym session, formal meeting, or casual outing.
Advanced Health and Fitness Tracking
What truly sets Aether X apart from other smartwatches in its category is its advanced health and fitness tracking capabilities. Equipped with top-tier features like VO2 max monitoring, MET score tracking, and SpO2 levels, the Aether X enables users to maintain comprehensive health insights at their fingertips. Additionally, TikTik’s Health Tricycle provides an overview of daily fitness progress, including steps taken, calories burned, and active duration, allowing users to set achievable goals and stay motivated.
Other innovative metrics include sleep and stress analysis to monitor physical and mental health, as well as waist-to-hip ratio, cadence, and stride length for a holistic view of one’s health profile. These analytics, combined with the intuitive TikTik AI, empower users to understand and improve their overall well-being.
A Commitment to Make in India and Accessible Pricing
Aligned with the Make in India initiative, TikTik Global LLP champions local manufacturing, ensuring every aspect of the Aether X is crafted with high standards and optimized for the Indian consumer. In a market where most smartwatches are produced abroad, TikTik stands out by leveraging local resources, which not only supports the national economy but also allows for superior quality control and customization.
TikTik Global LLP’s bootstrapped approach means it’s committed to affordability and accessibility without compromising quality. With pricing structured around Purchasing Power Parity (PPP), the Aether X is set to provide cutting-edge technology at a price point that meets the Indian market’s needs—making high-tech, feature-rich smartwatches available to a wider demographic.
A December Launch: Shaping the Future of Smart Wearables
With its December launch around the corner, TikTik Global LLP’s Aether X is more than a smartwatch; it’s a revolution in wearable tech. As a bootstrapped startup, TikTik has overcome resource constraints through innovation, local partnerships, and a user-first design approach. This launch promises to not only introduce a new product to the market but also set a new standard for Indian-made wearables.
TikTik Global LLP’s mission to deliver affordable, high-quality smartwatches that cater to diverse lifestyles is a testament to the power of innovation and determination. As the December release date approaches, Aether X is expected to capture the interest of consumers and industry experts alike, placing TikTik Global LLP on the map as a formidable player in the wearables market.
#AetherX#PoweredByTikTik#TikTikSmartwatch#TikTikAI#InfinityOS#Smartwearable#MakeInIndia#BootstrappedStartup#TikTikGlobal#WearableInnovation#TechForIndia#HealthTracking#VO2Max#SmartFitness#FitnessWearable#UnisexSmartwatch#LifestyleWearable#IndiaTech#WearableAI#SmartwatchFashion#AffordableLuxury#MadeForIndia#ActivityTracker#HealthTech#InnovationInIndia#InfinityStore#TikTikGlobalLLP#AetherXSmartwatch#DigitalHealth#HealthMetrics
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
About Lifespark Technologies

Lifespark Technologies creates solutions for care in chronic neurological conditions such as Stroke, Parkinson's Disease . We are based at the Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay, India. Our solutions are designed for individuals, caregivers and the entire family; because these conditions don't just affect the lives of individuals.
Our solutions span the domains of AI/ML, medical devices, mobile applications and web applications. Lifespark Technologies aims to create the basic intelligence that will one day solve health issues at the earliest stage before they have damaging results. One day, a 60-year-old will look like today's 30-year-old.
Lifespark Technologies is among the top health-tech startups in the country and count many prominent business leaders and academics as our mentors. We have deployed our solutions in partnership with some of the largest healthcare organizations in India and are looking to establish ourselves as the go-to innovator globally.
Our Core Team Members :
CEO & Founder - Amey Desai

He has research experience in Machine Learning, Electronics, AI and their application in healthcare .
Research Head - Dr. Devendra Desai

Dr. Desai heads the research team at Lifespark. With extensive experience in research and over a hundred publications, Dr. Desai's skills and medical acumen are instrumental to the research at Lifespark .
Chief Scientific Advisor & Mentor - Dr. Samit Chakrabarty

Dr. Chakrabarty is our chief scientific advisor and mentor. His expertise in Neurophysiology and multidisciplinary research provide deep and meaningful insights into the research at Lifespark .
Our Partners :


Awards and Recognition :
Shark Tank Season 3
youtube
Times of India

Prosus SICA Award 3rd place Winner
National Bio Entrepreneurship Competition Winner

#ParkinsonsDisease#ParkinsonsCare#NeurologicalDisorders#NeuroRehabilitation#MovementDisorders#ParkinsonsAwareness#StrokeRecovery#ParkinsonsSupport#ParkinsonsResearch#PDWarriors#CareForParkinsons#WalkDevice#LifesparkTechnologies#HealthTech#NeuroCare#ChronicCareSolutions#InnovationInHealthcare#MedicalDevices#FutureOfHealth#IITBombay#IndianStartups#HealthcareInnovation#CaregiverSupport#DigitalHealth#Youtube
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
From Wait Times to Wellness:
Transforming OPD Visits with hashtag#SelfServiceKiosks
Transform the patient experience and cut wait times with Achala Health Services Private Limited's self-service kiosks. With over 50+ kiosks installed across Hyderabad hospitals, we're revolutionizing patient care and boosting operational efficiency.
🔹 Front office staff efficiency is up by 10-15% 🔹 Over 50% of new patients register via kiosks 🔹 Wait times slashed by 80% (45 minutes to 9 minutes) 🔹 85%+ of patients use kiosks to collect reports 🔹 Report collection wait times cut from 25 minutes to under 5 minutes 🔹 Nurse administrative workload reduced by 20-30% 🔹 Manual processes & errors eliminated by 25-40%
Join us in enhancing healthcare with innovative solutions! https://lnkd.in/geQ54BMy





#HealthcareInnovation#OperationalEfficiency#PatientExperience#SelfServiceKiosks#AchalaHealth#HealthcareTechnology#PatientCare#HospitalInnovation#DigitalHealth#HealthTech#MedicalInnovation#PatientFlow#OPDManagement#EfficiencyInHealthcare#HealthcareTransformation#SelfCheckIn#HospitalEfficiency#HealthCareAutomation#SmartHospitals#PatientSatisfaction
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Analysis of: "From Brain to AI and Back" (academic lecture by Ambuj Singh)
youtube
The term "document" in the following text refers to the video's subtitles.
Here is a summary of the key discussions:
The document describes advances in using brain signal recordings (fMRI) and machine learning to reconstruct images viewed by subjects.
Challenges include sparseness of data due to difficulties and costs of collecting extensive neural recordings from many subjects.
Researchers are working to develop robust models that can generalize reconstruction capabilities to new subjects with less extensive training data.
Applications in medical diagnosis and lie detection are possibilities, but risks of misuse and overpromising on capabilities must be carefully considered.
The genre of the document is an academic lecture presenting cutting-edge neuroscience and AI research progress to an informed audience.
Technical content is clearly explained at an advanced level with representative examples and discussion of challenges.
Ethical implications around informed consent, privacy, and dual-use concerns are acknowledged without overstating current capabilities.
While more information is needed, the presentation style and framing of topics skews towards empirical science over opinion or fiction.
A wide range of stakeholders stand to be impacted, so responsible development and governance of emerging neural technologies should involve multidisciplinary input.
Advancing both basic scientific understanding and more human-like machine learning is a long-term motivation driving continued innovation in this important field.
Here is a summary of the key points from the document:
The speaker discusses advances in using brain signal recordings (fMRI) to reconstruct images that a person is viewing by training AI/machine learning models.
An example is shown where the top row is the actual image viewed and the bottom row is the image reconstructed from the person's brain signals.
Larger datasets with brain recordings from multiple subjects are allowing better models to be developed that may generalize to new subjects.
Challenges include the sparseness of brain signal data due to the difficulty and costs of collecting it from many subjects.
A model is presented that maps brain signals to a joint embedding space of images and text, allowing reconstruction of novel images from new brain signals.
Examples are shown where the reconstructed images match fairly well or not as well depending on image details and semantics.
Issues around ethics, risks of misuse, and questions of explaining and improving the models are discussed.
Ongoing work aims to address challenges around transferring models between subjects and measuring reconstruction performance.
Based on the content and style of the document, it appears to be an academic lecture or presentation.
Key evidence points include:
The document consists primarily of a speaker talking and presenting slides/examples to an audience, as indicated by phrases like "Let me just start with this" and an applause at the end.
Technical topics from neuroscience and machine learning/AI are discussed in detail, such as fMRI brain recordings, reconstructing images from brain signals, modeling approaches, dataset descriptions, and challenges/questions in the field.
Academic concepts like human subjects studies, building models, transferring learning, and measuring performance are referred to.
The presentation of information is intended to educate the audience on the state of the field and cuttting edge research, not just entertain.
There are no narratives, characters or creative storytelling elements - it adheres strictly to explaining complex technical content.
Therefore, based on the instructive/educational style and focus on explaining advanced technical research, I would classify the genre of this document as an academic lecture/presentation intended to inform an audience about progress in the domain of neuroscience and artificial intelligence.
Here are some of the key stakeholders that could be affected by the content and topics discussed in this document:
Neuroscience researchers - Directly interested and impacted by advances reported from their field of study. Progress informs future research directions.
AI/machine learning researchers - Models and challenges discussed could inspire new research at the intersection of AI and neuroscience. Transfer of model techniques.
Medical/clinical communities - Potential applications to diagnosis, personalized medicine if models can accurately reconstruct brain states. Raises ethical issues.
Government research agencies - Fund future related research based on understanding of opportunities and challenges conveyed. Evaluates societal impacts.
General public - Increased understanding of science helps engagement but topics like brain reading raise public concerns around privacy, consent if translated beyond research.
Research participants - Summary does not disclose identities but motivates others to contribute data for progress. Well-being depends on responsible use of data.
Technology companies - Commercial opportunities from real-world applications but also reputational risks if misused. Data ownership questions.
Academic institutions - Collaborations, education of next generations of researchers on cutting-edge topics is enabled through open dissemination of knowledge.
Overall the document provides value to a wide range of stakeholders by communicating the state and potential implications of this multidisciplinary area of neuroscience and AI research. Responsible stewardship is important given several ethical considerations.
Here is a summary of the key points about advances in using brain signal recordings from the document:
Researchers are using fMRI to record brain signals as people view images, in order to reconstruct the viewed images from the brain activity patterns alone.
Machine learning models, especially neural networks, are allowing researchers to train mappings from brain signals to representations of semantic content like images and text.
Examples show the capability of reconstructing fairly accurate images that a person viewed, based solely on their brain activity recordings during viewing.
Larger datasets with multiple subjects are important to develop models that may generalize beyond individual subjects. However, fMRI data is very difficult and expensive to collect at scale.
Advances now allow reconstruction of more complex stimuli like full stories a person reads, not just static images.
Ongoing work aims to better understand brain learning processes and apply those principles to more human-like machine learning architectures.
Analyzing brain recordings also has potential applications for medical diagnosis, lie detection, personalized medicine as models improve.
Ethics must be carefully considered to ensure technologies for reading neural signals are developed and applied responsibly and avoid misuse or privacy violations.
So in summary, the document outlines significant progress using machine learning on brain recordings to reconstruct sensory experiences, with applications and open questions that can further both neuroscience and AI.
Here is a summary of the key points about the sparseness of brain signal data:
Collecting fMRI brain signal recordings from large numbers of subjects is extremely challenging and costly due to the resources and time required.
Each recording session with a single subject takes considerable time, as the number of images/stimuli that can be presented is limited within a session.
Collecting data from a single subject sufficient for training complex models may require recording sessions over multiple days or weeks.
As a result, publicly available datasets typically contain recordings from only a small number of subjects, often under 10.
The sparseness of data makes it difficult to develop robust models that will generalize well to new subjects that lack extensive recordings.
Researchers aim to better leverage smaller datasets by training models that can reconstruct novel stimuli from just a subset of training data per subject.
If successful, this could enable more efficient data collection, such as obtaining usable models from a subject after a single shorter session rather than many long sessions.
However, overcoming the sparseness of brain signal data remains a major challenge holding back progress in the field. Larger collaborative datasets are needed.
So in summary, sparse data severely limits progress but also motivates techniques to optimize learning from limited samples per subject.
Here is a summary of key points regarding risks of misuse from the document:
Advances in reconstructing cognitive states like images viewed from brain recordings raise potential dual-use concerns if technologies are not regulated.
Applications in medical diagnosis and lie detection could help many, but lead to issues if used without consent or for non-medical surveillance.
Overly ambitious claims about capabilities need to be avoided to prevent misleading expectations that could fuel inappropriate usage assumptions.
Privacy and security of sensitive neural data must be prioritized to prevent potential misuse for profiling, identification or manipulation without oversight.
Commercial pressures may incentivize premature deployment before understanding implications, so continued research is important.
Public education about limitations and complexities involved can help curb fears that fuel misuse if capabilities are overestimated.
Multidisciplinary cooperation ensures societal and ethical issues are considered proactively rather than reactively addressed later.
Governance frameworks may be needed to steer applications toward public benefit rather individual or state abuse of personal mental information.
The speaker acknowledges misuse risks to inform discussion and underscore the importance of ongoing examination of new neural technologies through multidisciplinary lens including ethics.
Based on the content and style of presentation, my evaluation of the document status is:
Science vs Fiction: Clearly grounded in science as it discusses ongoing empirical research studies using neuroimaging and machine learning techniques. No fictional or hypothetical elements.
Empirical vs Anecdotal: Empirical in nature, rooted in dataset collection from human subjects and quantitative modeling/evaluation, not personal experience. While data quantities are limited, research follows scientific method.
Fact vs Opinion: Primarily presents technical details and research findings as established facts from the literature. Does not advance strong personal opinions beyond realistic discussion of challenges. Maintains an objective tone.
Objective vs Subjective: Remains objective in explaining research accomplishments and questions objectively without emotive language or bias. Any subjective experience like dataset limitations are clearly labeled as such. Presentation aims for factual information transfer.
In summary, while farther research is still ongoing, the document presents the current state of a scientific research domain factually based on empirical evidence and quantitative analysis published in the field. It does not intermingle non-factual elements or stray from an objective reporting of the topic at hand. The status therefore skews heavily toward science, empiricism, fact and objectivity.
I did not identify any logical fallacies in the content or arguments presented in this document.
The speaker objectively summarizes established research results and proposals, without making assertions that require logical scrutiny.
Some key reasons why logical fallacies are not present include:
No causal claims are made without proper evidence or empirical support from published studies. Progress is tied to concrete research efforts.
No arguments are constructed through flawed reasoning or non sequiturs. Concepts are explained clearly and build upon each other logically.
Comparisons to other approaches are fair without strawman misrepresentations of opposing ideas. Related work is acknowledged.
Limitations and open challenges are candidly outlined rather than ignored or obscured through fallacious defense.
No emotional, exaggerated or politically motivated language is used that could constitute emotional appeals. Tone remains factual.
No false dilemmas or false attributions of complexity are presented. Discussions appropriately scope multi-factor research questions.
No hasty generalizations are made from limited evidence. Data constraints are clearly communicated.
Overall, through objectively summarizing established neuroscience and AI research domains and techniques, without engaging in argument or debate, I did not find any logical fallacies employed in this academic information-sharing document. The focus appears to be factual reporting of progress and issues, avoiding fallacious reasoning.
Here is an evaluation of the ethics addressed and considered in the document:
Informed consent is implied but not explicitly discussed for research participants. Given the sensitivity of brain data, proper protocols were likely followed.
Privacy and anonymity of participants is a concern, but cannot be fully assessed without more details on the dataset and review process.
Potential dual-use issues around brain reading/reconstruction technologies are identifed by discussing applications but also worries about misuse or lack of oversight. This shows awareness of ethical implications.
Limitations and challenges and openly discussed, avoiding overpromising on capabilities. This establishes credibility and sets appropriate expectations.
Societal impacts and usage beyond research (e.g. diagnostics) are flagged as requiring careful consideration of risks like surveillance, discrimination if not regulated properly.
No claims are made without empirical evidence, showing results are driven by facts rather than desires which can bias judgment. Objectivity helps ethical analysis.
Multidisciplinary collaboration is emphasized , suggesting diverse viewpoints were incorporated into the research process.
Overall, while full review details are not provided, the document demonstrates an awareness of important ethical considerations around privacy, consent and responsible development for these sensitive types of neural data and technologies. A balanced assessment of opportunities and risks is conveyed.
Here are the usual evaluation criteria for an academic lecture/presentation genre and my evaluation of this document based on each criteria:
Clarity of explanation: The concepts and technical details are explained clearly without jargon. Examples enhance understanding. Overall the content is presented in a clear, logical manner.
Depth of technical knowledge: The speaker demonstrates thorough expertise and up-to-date knowledge of the neuroscience and AI topics discussed, including datasets, modeling approaches, challenges and future directions.
Organization of information: The presentation flows in a logical sequence, with intro/overview, detailed examples, related work, challenges/future work. Concepts build upon each other well.
Engagement of audience: While an oral delivery is missing, the document seeks to engage the audience through rhetorical questions, previews/reviews of upcoming points. Visuals would enhance engagement if available.
Persuasiveness of argument: A compelling case is made for the value and progress of this important multidisciplinary research area. Challenges are realistically discussed alongside accomplishments.
Timeliness and relevance: This is a cutting-edge topic at the forefront of neuroscience and AI. Advances have clear implications for the fields and wider society.
Overall, based on the evaluation criteria for an academic lecture, this document demonstrates strong technical expertise, clear explanations, logical organization and timely relevance to communicate progress in the domain effectively to an informed audience. Some engagement could be further enhanced with accompanying visual/oral presentation.
mjsMlb20fS2YW1b9lqnN
#Neuroscience#Brainimaging#Neurotechnology#FMRI#Neuroethics#BrainComputerInterfaces#AIethics#MachineLearning#NeuralNetworks#DeepLearning#DataPrivacy#InformationSecurity#DigitalHealth#MentalHealth#Diagnostics#PersonalizedMedicine#DualUseTech#ResearchEthics#ScienceCommunication#Interdisciplinary#Policymaking#Regulation#ResponsibleInnovation#Healthcare#Education#InformedConsent#Youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Explore your choice...
The statement “Health is Wealth” is a Nice and Wonderful statement that illustrates the value of health benefits of human body. Every human body consists of so many nerves, muscles, bones and organs associated with continuous flow of blood…
If a person had healthy body, then he/she will enjoy pleasures and joy in every aspect of life. A healthy body will give physical pleasures and internal joy that will lead to a peaceful mind and joyful soul…
Read more...
#Healthcare#HealthTech#HealthcareTechnology#MedicalInnovation#DigitalHealth#HealthcareIndustry#HealthcareSolutions#HealthcareIT#HealthcareServices#HealthcareManagement#HealthcareProviders#HealthcareSystems#HealthcareLeadership#MPMTechnologies#MPMTech#HealthcareSoftware#MedicalDevices#HealthcareAnalytics#HealthcareAutomation#Telehealth#medicare#telehealth
2 notes
·
View notes
Link
Mobile apps are transforming the #healthcare industry, from improving #patientcare to streamlining medical processes. Stay ahead of the game and learn more about the impact of mobile apps on healthcare
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hybrid Technology – Works Anywhere, Access Everywhere!
In the modern healthcare landscape, technology continues to reshape how care is delivered and experienced. One of the most significant advancements is the introduction of hybrid healthcare platforms — intelligent systems that integrate various medical devices and digital interfaces to provide seamless, real-time care across multiple touchpoints. With patient outcomes at the forefront, hybrid technology is proving to be a game-changer for healthcare providers and patients alike.

What is a Hybrid Healthcare Platform?
A hybrid healthcare platform combines software and hardware components to deliver a unified healthcare experience. By connecting different monitoring systems like intensive care (IC) monitors, ventilator monitors, and electronic data handling systems, the platform creates a cohesive environment where all patient data is centralized and accessible in real time.
This interconnectivity allows healthcare professionals to monitor, analyze, and act on patient data from virtually any location, making it possible to respond faster and more effectively to a patient's needs.
youtube
Key Features of Hybrid Technology in Healthcare
Device Integration
The hybrid model integrates devices from various manufacturers into one coherent platform.
Real-time data is collected from ICU equipment, ventilators, and other monitoring tools.
Data is transmitted securely, ensuring HIPAA compliance and patient privacy.
Mobile Accessibility
Doctors and nurses can access data via a secure mobile application.
Critical results, alerts, and trends are available at the fingertips of authorized personnel.
This promotes faster diagnostics and interventions, regardless of location.
Electronic Data Handling
The system utilizes advanced electronic data handling equipment (EDHE) to compile and manage vast volumes of patient information.
Automation ensures that data is accurate, up-to-date, and immediately accessible.
Real-Time Updates
Live updates help healthcare providers respond promptly to changes in patient conditions.
Reduces response time during emergencies, potentially saving lives.
Cloud and On-Premise Hybrid Storage
Combining cloud-based storage with on-premise infrastructure ensures data security, scalability, and accessibility.
Facilitates remote work and telemedicine services while maintaining strong control over local data.
Why Hybrid Platforms Matter
In a post-pandemic world, telemedicine and digital healthcare are no longer optional — they’re essential. Hybrid technology plays a vital role in enabling remote care while still leveraging the power of traditional, in-hospital systems. With the ability to collect and share data across departments and devices, healthcare providers benefit from a more comprehensive view of the patient's condition.
Imagine a scenario where a patient in an intensive care unit is being monitored with multiple devices. With a hybrid platform, all readings — heart rate, oxygen levels, blood pressure, and ventilator settings — are integrated into a single dashboard. A specialist, even off-site, can immediately access this dashboard through their smartphone or tablet, review trends, and provide consultation. This enhances communication, collaboration, and patient care dramatically.
Benefits for Healthcare Providers
Faster Decision-Making Access to real-time data reduces delays in diagnosis and treatment.
Improved Communication Doctors, nurses, and specialists can collaborate more efficiently.
Reduced Administrative Burden Automated data capture and reporting mean less manual paperwork and more time for patient care.
Remote Monitoring Enables clinicians to monitor patients without being physically present, a crucial benefit in resource-limited or quarantine situations.
Benefits for Patients
Enhanced Monitoring Continuous data collection ensures that no detail is missed, improving diagnosis accuracy.
Faster Response Times Medical staff can intervene more quickly, reducing complications and improving outcomes.
Accessible Health Records Patients can view their own health information through companion apps, promoting transparency and engagement.
Applications of Hybrid Healthcare Platforms
Hybrid technology isn't limited to ICU or emergency settings. Its applications include:
Primary Care Clinics – For quick diagnostics and patient tracking.
Home Healthcare – Monitor chronic conditions like diabetes, COPD, or hypertension.
Telehealth Services – Provide virtual consultations and follow-ups.
Rural & Remote Clinics – Deliver high-quality care even in underserved areas.
Security and Compliance
Data security is a major concern in digital healthcare. Hybrid systems are designed with robust encryption protocols, user access controls, and compliance standards to protect sensitive information. With built-in logs and audit trails, they help meet regulatory requirements like HIPAA, GDPR, and other national healthcare data laws.
The Future of Hybrid Healthcare
The future of healthcare lies in interconnected, intelligent systems. With advancements in AI, machine learning, and Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), hybrid platforms are set to become even smarter. Predictive analytics could soon anticipate health issues before they occur, and voice-activated systems could allow for hands-free operation in sterile environments.
As technology continues to evolve, hybrid platforms will remain at the heart of smart hospitals, bridging gaps between care providers and enabling a higher standard of personalized, efficient healthcare.
Conclusion
The hybrid healthcare platform is a revolutionary approach that ensures access everywhere and functionality anywhere. It breaks down silos between departments, improves communication, and delivers real-time insights that empower healthcare professionals to act swiftly and confidently.
As we move forward in this digital age, hybrid technology will not only optimize workflows but also redefine what it means to deliver patient-cantered care. It’s not just about innovation—it’s about creating a smarter, more responsive, and compassionate healthcare system.
For more Click The Link below : Best Hospital Management Software
#HybridHealthcare#DigitalHealth#HealthTech#MedTech#Telemedicine#RemoteMonitoring#PatientCare#SmartHospitals#HealthcareInnovation#IoMT#MobileHealth#HealthcareIT#HospitalTechnology#RealTimeData#MedicalDevices#HealthMonitoring#EHealth#HealthcareSolutions#CloudHealthcare#HealthInformatics#DataDrivenCare#MobileHealthApp#VirtualCare#ICUMonitoring#HealthcareIntegration#SmartCare#Youtube
0 notes
Text

CALL FOR SPEAKERS Welcome to top professionals at the 15th American Healthcare, Hospital Management, Nursing, and Patient Safety Summit, May 14–16, 2025, in San Francisco. Connect, share insights, and help shape the future of healthcare. Early Bird Registration Deadline: April 15th, 2025 We are offering a 20% discount on registration. Register here: https://healthcare.utilitarianconferences.com/discounted-registration
#Healthcare#MedicalSummit#HealthConference#DigitalHealth#HealthTech#MedTech#InnovativeCare#SmartHealthcare#HealthcareLeaders#MedicalManagement#LeadershipInMedicine#HospitalAdmin#ExecutiveHealthcare#OneHealth#GlobalMedicine
0 notes
Text
#HealthScore#DigitalHealth#HealthcareInnovation#PatientOutcomes#PreventiveCare#HealthData#ValueBasedCare#HealthMonitoring
0 notes
Text
#CloudNative#HealthcareIT#DigitalHealth#MedTech#CloudComputing#HealthTech#WebDevelopment#AIinHealthcare#FutureofHealthcare#TechInnovation
0 notes
Text
Large Language Models (LLMs) have been trained to understand intricacies of human language, which made them a powerful tool that can act as virtual assistants and be incredibly helpful. Let us look at details on 5 Best Techniques to Control Hallucination in LLMs.
#AI#ArtificialIntelligence#MachineLearning#LLM#TechInnovation#USATech#HealthcareAI#AIinHealthcare#DigitalHealth#FutureOfAI#AIforBusiness#DataScience#NLP#DeepLearning#AIConsulting#AIStartups#MedTech#AIinMedicine#SiliconValleyTech#AIResearch#MITTech#SmartAI#AIRegulations#USHealthcare#TechForGood#AITransformation
0 notes
Text







The collaboration between WHO and HL7 International brings together their respective expertise and resources to drive the adoption and appropriate use of interoperability standards globally.
This collaboration has the potential to harmonize digital health systems, improve data exchange and continuity of care, and contribute to the overall goal of achieving universal health coverage.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Rise of Telemedicine in Pediatrics: How Virtual Care is Changing Child Health

The healthcare industry has seen a rapid shift toward digital solutions, and pediatrics is no exception. With the increasing accessibility of telemedicine, virtual care is transforming the way children receive medical attention. Parents, pediatricians, and healthcare providers are leveraging digital tools to ensure that young patients receive timely and efficient care, reducing hospital visits and making healthcare more accessible.
The Growing Need for Telemedicine in Pediatric Care
The demand for telemedicine in pediatrics has surged due to various factors:
Accessibility: Families in remote areas or those with limited access to healthcare facilities can now consult pediatricians without the need for long travel hours.
Convenience: Parents no longer have to take time off work or disrupt their child’s routine to visit a clinic for minor illnesses.
Infection Control: Telehealth has played a crucial role in minimizing exposure to contagious diseases, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Specialist Reach: Children with rare conditions can now access expert opinions without geographical constraints.
How Telemedicine is Transforming Pediatric Care
1. Remote Consultations and Diagnosis
Telemedicine allows pediatricians to assess symptoms, provide medical advice, and even prescribe treatments via video calls and online consultations. Parents can discuss concerns such as fever, cough, rashes, and minor injuries without stepping into a clinic.
2. Managing Chronic Conditions
Children with chronic illnesses like asthma, diabetes, or epilepsy require frequent monitoring. Telemedicine enables regular check-ups and medication adjustments without unnecessary hospital visits.
3. Mental Health Support
With rising concerns over children’s mental health, virtual therapy and counseling services are making it easier for young patients to access professional help. Teletherapy has proven effective in managing anxiety, ADHD, depression, and behavioral disorders.
4. Pediatric Emergency Guidance
While telemedicine cannot replace emergency care, it helps parents make informed decisions about when a child needs immediate medical attention versus when symptoms can be managed at home.
5. Post-Surgical Follow-ups
For children recovering from surgery, virtual follow-ups reduce stress and the risk of complications by allowing pediatric surgeons to monitor healing progress remotely.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its benefits, telemedicine in pediatrics faces challenges such as:
Technology Barriers: Not all families have access to reliable internet and digital devices.
Regulatory and Insurance Issues: Varying telehealth policies and insurance coverages can affect adoption.
Limitations in Physical Exams: Some conditions require in-person assessments that telemedicine cannot fully replace.
Looking ahead, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), wearable health monitors, and improved telehealth regulations will further enhance virtual pediatric care. Telemedicine is not just a temporary trend—it is paving the way for a more efficient, accessible, and patient-centered approach to child healthcare.
Conclusion
Telemedicine is revolutionizing pediatric healthcare, making it easier for children to receive timely medical attention while reducing the burden on families. As technology continues to evolve, virtual care will play an even more significant role in ensuring better health outcomes for children worldwide. Parents and healthcare providers must embrace this digital transformation to enhance pediatric well-being in the years to come.
#Telemedicine#Pediatrics#ChildHealth#VirtualCare#HealthcareInnovation#PediatricCare#DigitalHealth#Telehealth#MedicalTechnology#RemoteHealthcare
0 notes
Text
Revolutionizing Healthcare with Natural Language Processing (NLP)!
Medical data is complex, unstructured, and often overwhelming. That’s where Natural Language Processing in healthcare is making a difference—turning scattered medical records, doctor’s notes, and patient interactions into meaningful insights.
How Can NLP Transform Healthcare? ✅ Faster & Accurate Diagnoses – AI-powered data extraction from clinical notes ✅ Enhanced Patient Care – Voice-assisted documentation reduces physician burnout ✅ Automated Medical Coding & Billing – Minimizing errors & improving efficiency ✅ Personalized Healthcare – AI-driven chatbots & virtual assistants for better patient engagement
For healthcare providers, hospitals, and MedTech innovators, adopting Natural Language Processing in healthcare is a game-changer. Are you ready to optimize workflows and improve patient outcomes with AI?
#HealthcareAI#NLPinHealthcare#MedicalTech#DigitalHealth#AIinMedicine#HealthTech#PatientCareInnovation
0 notes