#Chiplet market
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
As I understand it you work in enterprise computer acquisitions?
TL;DR What's the general vibe for AI accelerating CPUs in the enterprise world for client compute?
Have you had any requests from your clients to help them upgrade their stuff to Core Ultra/Whateverthefuck Point with the NPUs? Or has the corporate world generally shown resistance rather than acquiescence to the wave of the future? I'm so sorry for phrasing it like that I had no idea how else to say that without using actual marketing buzzwords and also keeping it interesting to read.
I know in the enterprise, on-die neural acceleration has been ruining panties the world over (Korea's largest hyperscaler even opted for Intel Sapphire Rapids CPUs over Nvidia's Hopper GPUs due to poor supply and not super worth it for them specifically uplift in inference performance which was all that they really cared about), and I'm personally heavily enticed by the new NPU packing processors from both Team Red and Team We Finally Fucking Started Using Chiplets Are You Happy Now (though in large part for the integrated graphics). But I'm really curious to know, are actual corporate acquisitions folks scooping up the new AI-powered hotness to automagically blur giant pink dildos from the backgrounds of Zoom calls, or is it perceived more as a marketing fad at the moment (a situation I'm sure will change in the next year or so once OpenVINO finds footing outside of Audacity and fucking GIMP)?
So sorry for the extremely long, annoying, and tangent-laden ask, hope the TL;DR helps.
Ninety eight percent of our end users use their computers for email and browser stuff exclusively; the other two percent use CAD in relatively low-impact ways so none of them appear to give a shit about increasing their processing power in a really serious way.
Like, corporately speaking the heavy shit you're dealing with is going to be databases and math and computers are pretty good at dealing with those even on hardware from the nineties.
When Intel pitched the sapphire processors to us in May of 2023 the only discussion on AI was about improving performance for AI systems and deep learning applications, NOT using on-chip AI to speed things up.
The were discussing their "accelerators," not AI and in the webinar I attended it was mostly a conversation about the performance benefits of dynamic load balancing and talking about how different "acclerators" would redistribute processing power. This writeup from Intel in 2022 shows how little AI was part of the discussion for Sapphire Rapids.
In August of 2023, this was the marketing email for these processors:

So. Like. The processors are better. But AI is a marketing buzzword.
And yeah every business that I deal with has no use for the hot shit; we're still getting bronze and silver processors and having zero problems, though I work exclusively with businesses with under 500 employees.
Most of the demand that I see from my customers is "please can you help us limp this fifteen year old SAN along for another budget cycle?"
104 notes
·
View notes
Text
You know, if AMD combined all of the technology they've been working on or used in the last few years, They could probably make something that would absolutely Crater anything Nvidia could bring to market.
Like, their chiplet design that they use on their CPUs, The old HBCC tech from VEGA64 with the add on VRAM in a similar CAMM module as well- CAMM (obviously mix it up a little bit so you can't mount a normal CAMM module where your gcamm is supposed to go.)
They need the upcoming 9000 series to be something Nvidia cannot meet. CUDA should be dying as ROCm adoption picks up. The fourth gen AMD RT cores should be up to snuff.
Amd really hasn't had a competitor for nvidia's top of the line since the Radeon VII.
Sure, the modern 7000 series crushes Nvidia in raster until you get to the 4080 super, And even then it's damn close. But they don't have an answer for the 4090. If they get chiplet gpus working, They should absolutely go whole hog and bring back the Halo Radeons. I'd love to see a Radeon IX come in several hundred dollars cheaper than the potential 6090, and still stomp it across the board.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
US launches $1.6B bid to outpace Asia in packaging tech
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/us-launches-1-6b-bid-to-outpace-asia-in-packaging-tech/
US launches $1.6B bid to outpace Asia in packaging tech
.pp-multiple-authors-boxes-wrapper display:none; img width:100%;
The US is betting big on the future of semiconductor technology, launching a $1.6 billion competition to revolutionise chip packaging and challenge Asia’s longstanding dominance in the field. On July 9, 2024, the US Department of Commerce unveiled its ambitious plan to turbocharge domestic advanced packaging capabilities, a critical yet often overlooked aspect of semiconductor manufacturing.
This move, part of the Biden-Harris Administration’s CHIPS for America program, comes as the US seeks to revitalise its semiconductor industry and reduce dependence on foreign suppliers. Advanced packaging, a crucial step in semiconductor production, has long been dominated by Asian countries like Taiwan and South Korea. By investing heavily in this area, the US aims to reshape the global semiconductor landscape and position itself at the forefront of next-generation chip technology, marking a significant shift in the industry’s balance of power.
US Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo emphasised the importance of this move, stating, “President Biden was clear that we need to build a vibrant domestic semiconductor ecosystem here in the US, and advanced packaging is a huge part of that. Thanks to the Biden-Harris Administration’s commitment to investing in America, the US will have multiple advanced packaging options across the country and push the envelope in new packaging technologies.”
The competition will focus on five key R&D areas: equipment and process integration, power delivery and thermal management, connector technology, chiplets ecosystem, and co-design/electronic design automation. The Department of Commerce anticipates making several awards of approximately $150 million each in federal funding per research area, leveraging additional investments from industry and academia.
This strategic investment comes at a crucial time, as emerging AI applications are pushing the boundaries of current technologies. Advanced packaging allows for improvements in system performance, reduced physical footprint, lower power consumption, and decreased costs – all critical factors in maintaining technological leadership.
The Biden-Harris Administration’s push to revitalise American semiconductor manufacturing comes as the global chip shortage has highlighted the risks of overreliance on foreign suppliers. Asia, particularly Taiwan, currently dominates the advanced packaging market. According to a 2021 report by the Semiconductor Industry Association, the US accounts for only 3% of global packaging, testing, and assembly capacity, while Taiwan holds a 54% share, followed by China at 16%.
Under Secretary of Commerce for Standards and Technology and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Director Laurie E. Locascio outlined an ambitious vision for the program: “Within a decade, through R&D funded by CHIPS for America, we will create a domestic packaging industry where advanced node chips manufactured in the US and abroad can be packaged within the States and where innovative designs and architectures are enabled through leading-edge packaging capabilities.”
The announcement builds on previous efforts by the CHIPS for America program. In February 2024, the program released its first funding opportunity for the National Advanced Packaging Manufacturing Program (NAPMP), focusing on advanced packaging substrates and substrate materials. That initiative garnered significant interest, with over 100 concept papers submitted from 28 states. On May 22, 2024, eight teams were selected to submit complete applications for funding of up to $100 million each over five years.
According to Laurie, the goal is to create multiple high-volume packaging facilities by the decade’s end and reduce reliance on Asian supply lines that pose a security risk that the US “just can’t accept.��� In short, the government is prioritising ensuring America’s leadership in all elements of semiconductor manufacturing, “of which advanced packaging is one of the most exciting and critical areas,” White House spokeswoman Robyn Patterson said.
The latest competition is expected to attract significant interest from the US semiconductor ecosystem and shift that balance. It promises substantial federal funding and the opportunity to shape the future of American chip manufacturing. As the global demand for advanced semiconductors continues to grow, driven by AI, 5G, and other emerging technologies, the stakes for technological leadership have never been higher.
As the US embarks on this ambitious endeavour, the world will see if this $1.6 billion bet can challenge Asia’s stronghold on advanced chip packaging and restore America’s position at the forefront of semiconductor innovation.
(Photo by Braden Collum)
See also: Global semiconductor shortage: How the US plans to close the talent gap
Want to learn more about AI and big data from industry leaders? Check out AI & Big Data Expo taking place in Amsterdam, California, and London. The comprehensive event is co-located with other leading events including Intelligent Automation Conference, BlockX, Digital Transformation Week, and Cyber Security & Cloud Expo.
Explore other upcoming enterprise technology events and webinars powered by TechForge here.
Tags: ai, AI semiconductor, artificial intelligence, chips act, law, legal, Legislation, Politics, semiconductor, usa
#2024#5G#Accounts#Administration#ai#ai & big data expo#AI semiconductor#America#amp#applications#Art#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#Asia#automation#betting#biden#Big Data#billion#Business#challenge#China#chip#chip shortage#chips#chips act#Cloud#Commerce#competition#comprehensive
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
#reframed cisc vs risc and simplistic gpu functions scaledup in low investm ent burdens chiplet reheat old cores .@cnet @techpowerup @techpowerup @intel @amd @apple @wired @wireduk @pcwelt @debian @linux @windowsdev i speculate intel cpu s are optimised for their server market and spawned off to consumers. thebiggest flaw the reduction of energy consumption of cisc systems over risc systems and the simplistic gpu cores spawned reheate d in chiplet combinations variations to raw throughput scaled simplistic functions is why youget dozens of cpu cores reused old de signs and simpler but farmore gpu cores
#reframed cisc vs risc and simplistic gpu functions scaledup in low investment burdens chiplet reheat old cores .@cnet @techpowerup @techpowerup @intel @amd @apple @wired @wireduk @pcwelt @debian @linux @windowsdev i speculate intel cpu s are optimised for their server market and spawned off to consumers. thebiggest flaw the reduction of energy consumption of cisc systems over risc systems and…
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
The Rise of AMD: A Look at their Advancements in CPU Technology
In recent years, AMD has been making waves in the tech industry with their innovative advancements in CPU technology. From challenging competitors to pushing the boundaries of performance, AMD has solidified its position as a major player in the market. In this article, we will explore the key advancements Find out more that have propelled AMD to the forefront of the industry and examine how they are shaping the future of computing.
Introduction
AMD, short for Advanced Micro Devices, is a semiconductor company known for its cutting-edge CPUs and GPUs. Founded in 1969, AMD has a long history of innovation and has established itself as a formidable competitor to industry giants like Intel and Nvidia. With a focus on pushing the boundaries of performance and efficiency, AMD has consistently delivered products that cater to both consumers and professionals alike.
The Evolution of AMD Processors The Early Days: A Brief History of AMD
AMD vs Competition: In the early days, AMD primarily focused on manufacturing second-source microprocessors for companies like Intel. However, it wasn't until the launch of the AMD K5 processor in 1996 that they began to establish themselves as a serious contender in the market. The K5 marked the beginning of AMD's journey towards developing their own line of processors that could rival Intel's offerings.
The Athlon Era
AMD at GPU: In 1999, AMD introduced the Athlon processor, which quickly gained popularity for its impressive performance and competitive pricing. The success of the Athlon series laid the foundation for future innovations from AMD and firmly established them as a major player in the CPU market. Around this time, AMD also made significant strides in GPU technology with their Radeon graphics cards, further solidifying their position as a leading tech company.
Ryzen Revolution
Innovative Technologies of AMD: Fast forward to 2017, when AMD launched their Ryzen line of processors based on their Zen architecture. The Ryzen CPUs marked a significant leap forward in terms of performance and efficiency, offering consumers a viable alternative to Intel's offerings. With features like simultaneous multithreading (SMT) and Precision Boost technology, Ryzen processors quickly gained a reputation for being powerful yet affordable options for gamers and content creators alike.

Advancements in CPU Technology Zen 2 Architecture
The Rise of AMD: A Look at Their Advancements in CPU Technology: One of the most significant advancements from AMD in recent years has been the introduction of their Zen 2 architecture. Built on a 7nm process node, Zen 2 CPUs offer improved IPC (instructions per cycle) performance and higher clock speeds compared to previous generations. This architectural leap has allowed AMD to compete head-to-head with Intel's offerings across various market segments.
youtube
Chiplet Design
AMD and AI: Another key innovation from AMD is their chiplet design approach, which involves using multiple smaller dies interconnected on a single package. This modular design allows for greater scalability and efficiency compared to traditional monolithic designs. By leveraging chiplets, AMD can optimize performance while reducing costs associated with manufacturing larger monolithic dies.
Infinity Fabric Interconnect
One of the key technologies that enable AMD's chiplet design is their Infinity Fabric int
1 note
·
View note
Text
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Breaking Down the Differences Between AMD and ARM Processors
Introduction
In today's fast-paced technological world, the battle between AMD and ARM processors has been a hot topic of debate among tech enthusiasts and experts. Both companies have made significant advancements in their respective processor technologies, but what sets them apart? In this article, we will delve deep into the intricacies of AMD and ARM processors, exploring their differences, strengths, weaknesses, and innovative technologies.
Breaking Down the Differences Between AMD and ARM Processors What is the difference between AMD and ARM processors?
AMD (Advanced Micro Devices) is a well-known American multinational semiconductor company that primarily focuses on computer processors. On the other hand, ARM (Advanced RISC Machines) is a British semiconductor company that designs architecture for processors used in mobile devices, IoT devices, and other embedded systems.
How do AMD processors compare to the competition?
AMD has been making significant strides in recent years with its Ryzen series of processors. These chips offer excellent performance at competitive prices, giving tough competition to Intel's offerings. AMD processors are known for their multi-core performance and overclocking capabilities, making them a popular choice among gamers and content creators.

What sets AMD apart at GPU performance?
One area where AMD truly shines is in GPU performance. The company's Radeon GPUs are known for their excellent graphics capabilities, making them a preferred choice for gaming enthusiasts. With technologies like RDNA 2 powering their latest GPUs, AMD has managed to close the gap with Nvidia in terms of performance and efficiency.
What are some innovative technologies of AMD?
AMD has been at the forefront of innovation when it comes to processor technologies. From introducing chiplet architecture in their CPUs to implementing Infinity Cache in their GPUs, AMD has continually pushed the boundaries of what is possible in the world of semiconductors. Their commitment to innovation has Check out here helped them stay competitive in an ever-evolving market.
How does AMD collaborate with AI technologies?
AI (Artificial Intelligence) is a rapidly growing field that requires powerful computing capabilities. AMD has been investing heavily in AI technologies, developing solutions that cater to the needs of AI researchers and developers. With platforms like ROCm (Radeon Open Compute) and Instinct accelerators, AMD is positioning itself as a key player in the AI space.
youtube
Exploring the world of ARM processors
ARM processors are based on a different architecture compared to x86 processors like those from Intel or AMD. They are designed to be more power-efficient and are commonly used in mobile devices due to their low power consumption. ARM licenses its technology to other companies who then design their own chips based on ARM's architecture.
How do ARM processors differ from traditional CPUs?
ARM processors use a Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) architecture, which simplifies instructions for faster execution. This design philosophy allows ARM chips to be more power-efficient compared to traditional x86 CPUs. While they may not offer the same raw performance as high-end desktop CPUs, they excel in tasks that require low power consumption.
What advantages do ARM-based devices offer?
Devices powered by

1 note
·
View note
Text
The Rise of AMD: A Look at their Advancements in CPU Technology
In recent years, AMD has been making waves in the tech industry with their innovative advancements in CPU technology. From challenging competitors to pushing the boundaries of performance, AMD has solidified its position as a major player in the market. In this article, we will explore the key advancements that have propelled AMD to the forefront of the industry and examine how they are shaping the future of computing.
Introduction
AMD, short for Advanced Micro Devices, is a semiconductor company known for its cutting-edge CPUs and GPUs. Founded in 1969, AMD has a long history of innovation and has established itself as a formidable competitor to industry giants like Intel and Nvidia. With a focus on pushing the boundaries of performance and efficiency, AMD has consistently delivered products that cater to both consumers and professionals alike.
The Evolution of AMD Processors The Early Days: A Brief History of AMD
AMD vs Competition: In the early days, AMD primarily focused on manufacturing second-source microprocessors for companies like Intel. However, it wasn't until the launch of the AMD K5 processor in 1996 that they began to establish themselves as a serious contender in the market. The K5 marked the beginning of AMD's journey towards developing their own line of processors that could rival Intel's offerings.
The Athlon Era
AMD at GPU: In 1999, AMD introduced the Athlon processor, which quickly gained popularity for its impressive performance and competitive pricing. The success of the Athlon series laid the foundation for future innovations from AMD and firmly established them as a major player in the CPU market. Around this time, AMD also Additional info made significant strides in GPU technology with their Radeon graphics cards, further solidifying their position as a leading tech company.
youtube

Ryzen Revolution
Innovative Technologies of AMD: Fast forward to 2017, when AMD launched their Ryzen line of processors based on their Zen architecture. The Ryzen CPUs marked a significant leap forward in terms of performance and efficiency, offering consumers a viable alternative to Intel's offerings. With features like simultaneous multithreading (SMT) and Precision Boost technology, Ryzen processors quickly gained a reputation for being powerful yet affordable options for gamers and content creators alike.
Advancements in CPU Technology Zen 2 Architecture
The Rise of AMD: A Look at Their Advancements in CPU Technology: One of the most significant advancements from AMD in recent years has been the introduction of their Zen 2 architecture. Built on a 7nm process node, Zen 2 CPUs offer improved IPC (instructions per cycle) performance and higher clock speeds compared to previous generations. This architectural leap has allowed AMD to compete head-to-head with Intel's offerings across various market segments.

Chiplet Design
AMD and AI: Another key innovation from AMD is their chiplet design approach, which involves using multiple smaller dies interconnected on a single package. This modular design allows for greater scalability and efficiency compared to traditional monolithic designs. By leveraging chiplets, AMD can optimize performance while reducing costs associated with manufacturing larger monolithic dies.
Infinity Fabric Interconnect
One of the key technologies that enable AMD's chiplet design is their Infinity Fabric int
1 note
·
View note
Text
Semiconductor Solutions With GAA Process & 2.5D Packaging
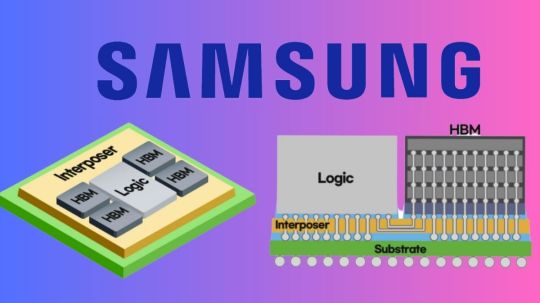
Samsung Electronics will partner with a top Japanese AI startup to develop cutting-edge AI accelerator chips. The company will provide turnkey semiconductor solutions with a 2nm GAA process and 2.5D packaging to preferred networks.
Leading global provider of advanced semiconductor technology, Samsung Electronics, today announced that it will supply Preferred Networks, a top Japanese artificial intelligence company, with turnkey semiconductor solutions utilising the 2-nanometer (nm) foundry process and the cutting-edge 2.5D packaging technology Interposer-Cube S (I-Cube S).
With the help of Samsung’s cutting-edge foundry and cutting-edge packaging goods, Preferred Networks hopes to create potent AI accelerators that will satisfy the constantly rising demand for processing capacity fueled by generative AI.
GAA Process
Samsung has successfully secured orders for the 2nm process with additional improvements in performance and power efficiency, solidifying its position as the industry leader in GAA technology since beginning mass production of the first 3nm process node using Gate-All-Around (GAA) transistor architecture.
With this partnership with Preferred Networks, Japanese firms have achieved a first in the realm of large-scale heterogeneous integrated package technologies, and Samsung intends to intensify its offensive to lead the worldwide advanced package market.
The turnkey solutions include the 2.5D packaging I-Cube S technology, a heterogeneous integration package technology that combines numerous chips into a single package to improve interconnection speed and minimize package space.
In order to achieve an ultra-fine redistribution layer (RDL) and stabilize power integrity for the best possible semiconductor performance, the silicon interposer, or Si-interposer, is essential. The chip was designed by GAONCHIPS, a specialized system semiconductor development business.
According to Junichiro Makino, vice president and chief technology officer (CTO) of computing architecture at Preferred Networks, “This solution will significantly support Preferred Networks’ ongoing efforts to build highly energy-efficient, high-performance computer gear to address generative AI’s expanding computational needs, especially for big language models.”
“This order is crucial because it demonstrates that Samsung’s 2.5D packaging technology and 2nm GAA process technology are the best options for next-generation AI accelerators,” stated Taejon Song, Corporate VP and Head of Samsung Electronics’ Foundry Business Development Team. “It’s are dedicated to working closely with our customers to ensure that our products’ high performance and low power characteristics are fully realized.”
Tokyo-based Preferred Networks vertically integrates the AI value chain from chips to supercomputers and generative AI foundation models to build cutting-edge hardware and software. It supplies industrial, transportation, healthcare, entertainment, and education products. The company is a global AI leader after topping the Green500 supercomputer list three times in five years.
As a result of their partnership, Samsung and Preferred Networks want to present ground-breaking AI chiplet solutions for the market for generative AI computing and next-generation data centers.
Introduction
With its groundbreaking discoveries, Samsung Electronics leads semiconductor technology’s rapid change. Combining 2.5D packaging technology with Samsung’s latest invention, the 2nm GAA (Gate-All-Around) process, will alter the semiconductor industry by offering Preferred Networks complete semiconductor solutions. This strategic cooperation aims to push semiconductor application performance, efficiency, and scalability.
The Development of Electronic Technology
2nm GAA Process
In the semiconductor industry, the 2nm GAA process represents a major turning point. The limitations of conventional FinFET (Fin Field-Effect Transistor) technology call for a more sophisticated strategy. Better channel management, lower leakage current, and enhanced performance are all made possible by the Gate-All-Around architecture. Samsung plans to use 2nm nodes to reach hitherto unheard-of levels of processing speed, power efficiency, and integration density.
Benefits of the Two-Nm GAA Process
Improved Efficiency: When compared to the earlier 3nm technology, the 2nm GAA process offers up to a 30% performance boost.
Energy Efficiency: It is perfect for applications requiring a longer battery life because it can reduce power usage by up to 50%.
Improved Capabilities: Integrated circuits can now have more transistors per unit area thanks to the 2nm technology.
Inventive 2.5D Packaging Methods
2.5D packaging: what is it?
2.5D packaging technique bridges 2D and 3D packaging. It entails arranging several dies side by side on an interposer, which serves as a high-bandwidth communication channel. Without the complications of complete 3D stacking, this technique lowers latency and improves performance.
Advantages of Two-Sided Packaging
Enhanced Connectivity: Data transfer between chips is made quicker and more effective by the interposer.
Better heat dissipation than 3D packaging in terms of thermal management lowers the possibility of overheating.
Scalability: Promotes the integration of many chip types such as logic and memory on a single package, hence improving functionality.
Semiconductor Solutions
Complete Integration of Samsung’s Turnkey Semiconductor Solutions
The complete semiconductor development process, from design and manufacture to packaging and testing, is covered by Samsung’s turnkey solutions. With a comprehensive package, Samsung guarantees optimal performance and a smooth integration of the finished product.
Customized for favored networks
Samsung’s cutting-edge semiconductor technologies will be extremely beneficial to Preferred Networks, a pioneer in AI and machine learning. High performance and energy efficiency are guaranteed by the partnership’s delivery of specially designed chips that cater to the unique requirements of AI applications.
Principal Elements of Samsung’s Custom Design Services: optimized for a given application by being specifically designed to match its needs.
More Complex Manufacturing Methods: achieving the highest standards of accuracy and productivity by applying cutting-edge procedures.
Thick Validation and Testing: Thorough testing guarantees dependability and functionality in practical uses.
Influence on Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Enhanced Efficiency for Artificial Intelligence Uses
AI and ML application performance is greatly improved by the combination of 2.5D packaging and the 2nm GAA technology. Deep learning models and real-time data analysis depend on quicker processing rates and higher data throughput, which these technologies make possible.
Energy-Secure Edge Computing
Samsung’s solutions offer a substantial advantage in the field of edge computing, where power economy is crucial. The 2nm process’s lower power consumption guarantees longer battery life for edge devices, allowing for more prolonged and demanding computational operations without the need for frequent recharging.
Future Innovations’ Scalability
Scalable and versatile semiconductor solutions are becoming increasingly important as AI and ML applications develop. Samsung’s strategy facilitates the seamless assimilation of novel technology and caters to the increasing needs of forthcoming advancements.
Strategic Alliance with Selected Networks
Combination of Leaders
An innovative and experienced partnership between Preferred Networks and Samsung Electronics is strategic. The alliance uses Preferred Networks’ AI experience and Samsung’s cutting-edge semiconductor technology to provide highly effective, scalable, and reliable AI solutions.
Collaborative Development Programmes
Co-development of application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) designed specifically for AI workloads is known as custom AI chips.
Improved Software Integration: Making the most of software frameworks to take full advantage of hardware capabilities.
Future Plan: Joint research and development endeavors to maintain a lead in technological breakthroughs.
In conclusion
Samsung Electronics’ 2nm GAA process and 2.5D packaging technology advanced the semiconductor industry. Samsung’s turnkey Preferred Networks solutions will revolutionize AI and ML applications with unprecedented performance, efficiency, and scalability. This strategic collaboration highlights how cutting-edge hardware and creative AI solutions may propel the next wave of technological breakthroughs.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#govindhtech#News#technologynews#technology#technologytrends#technologysolutions#SAMSUNG#SamsungElectronics#gaaprocess#semiconductor#semiconductorsolutions
0 notes
Text
The Rise of AMD: A Look at their Advancements in CPU Technology
In recent years, AMD has been making waves in the tech industry with their innovative advancements in CPU technology. From challenging competitors to pushing the boundaries of performance, AMD has solidified its position as a major player in the market. In this article, we will explore the key advancements that have propelled AMD to the forefront of the industry and examine how they are shaping the future of computing.
Introduction
AMD, short for Advanced Micro Devices, is a semiconductor company known for its cutting-edge CPUs and GPUs. Founded in 1969, AMD has a long history of innovation and has established itself as a formidable competitor to industry giants like Intel and Nvidia. With a focus on pushing the boundaries of performance and efficiency, AMD has consistently delivered products that cater to both consumers and professionals alike.
The Evolution of AMD Processors The Early Days: A Brief History of AMD
AMD vs Competition: In the early days, AMD primarily focused on manufacturing second-source microprocessors for companies like Intel. However, it wasn't until the launch of the AMD K5 processor in 1996 that they began to establish themselves as a serious contender in the market. The K5 marked the beginning of AMD's journey towards developing their own line of processors that could rival Intel's offerings.

youtube
The Athlon Era
AMD at GPU: In 1999, AMD introduced the Athlon processor, which quickly gained popularity for its impressive performance and competitive pricing. The success of the Athlon series laid the foundation for future innovations from AMD and firmly established them as a major player in the CPU market. Around this time, AMD also made significant strides in GPU technology with their Radeon graphics cards, further solidifying their position as a leading tech company.
Ryzen Revolution
Innovative Technologies of AMD: Fast forward to 2017, when AMD launched their Ryzen line of processors based on their Zen architecture. The Ryzen CPUs marked a significant leap forward in terms of performance and efficiency, offering consumers a viable alternative to Intel's offerings. With features like simultaneous multithreading (SMT) and Precision Boost technology, Ryzen processors quickly gained a reputation for being powerful yet affordable options for gamers and content creators alike.
Advancements in CPU Technology Zen 2 Architecture
The Rise of AMD: A Look at Their Advancements in CPU Technology: One of the most significant advancements from AMD in recent years has been the introduction of their Zen 2 architecture. Built on a 7nm process node, Zen 2 CPUs offer improved IPC (instructions per cycle) performance and higher clock speeds compared to previous generations. This architectural leap has allowed AMD to compete head-to-head with Intel's offerings across various market segments.

Chiplet Design
AMD and AI: Another key innovation from AMD is their chiplet design approach, which involves using multiple smaller dies interconnected on a single package. This modular design allows for greater scalability and efficiency compared to traditional monolithic designs. By leveraging chiplets, AMD can optimize performance while reducing costs associated Additional reading with manufacturing larger monolithic dies.
Infinity Fabric Interconnect
One of the key technologies that enable AMD's chiplet design is their Infinity Fabric int
1 note
·
View note
Text
Breaking Down the Differences Between AMD and ARM Processors
Introduction
In today's fast-paced technological world, the battle between AMD and ARM processors has been a hot topic of debate among tech enthusiasts and experts. Both companies have made significant advancements in their respective processor technologies, but what sets them apart? In this article, we will delve deep into the intricacies of AMD and ARM processors, exploring their differences, strengths, weaknesses, and innovative technologies.
youtube
Breaking Down the Differences Between AMD and ARM Processors What is the difference between AMD and ARM processors?
AMD (Advanced Micro Devices) is a well-known American multinational semiconductor company that primarily focuses on computer processors. On the other hand, ARM (Advanced RISC Machines) is a British semiconductor company that designs architecture Additional hints for processors used in mobile devices, IoT devices, and other embedded systems.
How do AMD processors compare to the competition?
AMD has been making significant strides in recent years with its Ryzen series of processors. These chips offer excellent performance at competitive prices, giving tough competition to Intel's offerings. AMD processors are known for their multi-core performance and overclocking capabilities, making them a popular choice among gamers and content creators.
What sets AMD apart at GPU performance?
One area where AMD truly shines is in GPU performance. The company's Radeon GPUs are known for their excellent graphics capabilities, making them a preferred choice for gaming enthusiasts. With technologies like RDNA 2 powering their latest GPUs, AMD has managed to close the gap with Nvidia in terms of performance and efficiency.
What are some innovative technologies of AMD?
AMD has been at the forefront of innovation when it comes to processor technologies. From introducing chiplet architecture in their CPUs to implementing Infinity Cache in their GPUs, AMD has continually pushed the boundaries of what is possible in the world of semiconductors. Their commitment to innovation has helped them stay competitive in an ever-evolving market.
How does AMD collaborate with AI technologies?
AI (Artificial Intelligence) is a rapidly growing field that requires powerful computing capabilities. AMD has been investing heavily in AI technologies, developing solutions that cater to the needs of AI researchers and developers. With platforms like ROCm (Radeon Open Compute) and Instinct accelerators, AMD is positioning itself as a key player in the AI space.
Exploring the world of ARM processors
ARM processors are based on a different architecture compared to x86 processors like those from Intel or AMD. They are designed to be more power-efficient and are commonly used in mobile devices due to their low power consumption. ARM licenses its technology to other companies who then design their own chips based on ARM's architecture.
How do ARM processors differ from traditional CPUs?
ARM processors use a Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) architecture, which simplifies instructions for faster execution. This design philosophy allows ARM chips to be more power-efficient compared to traditional x86 CPUs. While they may not offer the same raw performance as high-end desktop CPUs, they excel in tasks that require low power consumption.
What advantages do ARM-based devices offer?
Devices powered by


1 note
·
View note
Text
Semiconductor Packaging Materials Market - Forecast(2024 - 2030)
Semiconductor packaging materials market size is forecast to reach USD 39,600 million by 2029, after growing at a CAGR of 9.79% during 2024-2029. By supplying the materials required for the assembly and packaging of semiconductor devices, the semiconductor packaging materials market is vital to the semiconductor industry. Substrates, leadframes, encapsulants, bonding wires, and die attach materials are a few examples of these materials. Technological developments, consumer demand for more compact and energy-efficient electronics, and the emergence of new technologies like IoT, artificial intelligence, and automotive electronics all have an impact on the market. With the development of cutting-edge packaging technologies like Chip-on-Wafer-on-Substrate (CoWoS) and Integrated Fan-Out (InFO), TSMC has been in the forefront of enabling the integration of numerous chips into a single package. Samsung has made investments in the creation of System-in-Package (SiP) solutions, which provide high-performance, small-form factor packaging choices for a range of uses, such as automotive electronics and mobile devices.
United States: To improve national security and advance domestic semiconductor manufacturing capabilities, the U.S. government has funded research and development initiatives in semiconductor packaging materials through the Department of Defense (DoD) and the National Science Foundation (NSF). Japan: As part of its plan to support the nation's semiconductor industry and preserve its position as a global leader, the Japanese government has announced investments in semiconductor R&D, including packaging technology.
Request Sample
Report Coverage
The report “Semiconductor packaging materials Market– Forecast (2024-2029)”, by IndustryARC, covers an in-depth analysis of the following segments of the semiconductor packaging materials market. By Type: Substrates, Lead Frames, Bonding Wires, Mold Compounds, Liquid Encapsulants, Die Attach Materials, Solder Balls, Wafer-Level Package Dielectrics, and Plating ChemicalsBy Technology: Grid Array, System-In-Package (SIP), Quad Flat Package (QFP), Dual In-line Package, OthersBy End-User Industry: Consumer Electronics, Aerospace & Defense, Healthcare, Automotive, OthersBy Geography: North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, RoW
Key Takeaways
• Rapid technological breakthroughs are driving constant innovation in the semiconductor packaging materials market to fulfill the changing needs of the electronics sector. Chiplets and 3D stacking are two examples of cutting-edge packaging technology that businesses like Intel Corporation have been investing in. For example, Intel's "Foveros" technology allows numerous logic chips to be stacked vertically, which improves performance and power efficiency in small form factors.• The market for semiconductor packaging materials is dominated by the Asia-Pacific area, namely by nations like China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan, but new regional competitors are gaining ground on them. Packaging materials are only one area in which China's Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation (SMIC) has been growing its footprint in the semiconductor industry. SMIC's investments in cutting-edge packaging technologies are intended to strengthen homegrown semiconductor manufacturing capacities and lessen reliance on imports.• In the market for semiconductor packaging materials, sustainability is receiving more attention as businesses and governments place more emphasis on the creation and uptake of environmentally responsible packaging options. Regulations and incentives are part of the European Union's "Green Deal" plan to encourage environmentally friendly practices in the electronics sector. Businesses such as Infineon Technologies AG are allocating resources towards environmentally sustainable packaging materials and manufacturing techniques in order to meet regulatory obligations and satisfy consumer demand for sustainable products.
By Type - Segment AnalysisMold Compounds dominated the semiconductor packaging materials market in 2023. Mold compounds are essential for maintaining the dependability and durability of semiconductor devices because they shield sensitive parts from outside impurities and mechanical harm. Mold compounds are essential for a wide range of semiconductor devices since they are employed in a variety of packing technologies, such as conventional leaded packages and cutting-edge packages like chip-scale packages (CSPs), flip-chip packages, and ball grid arrays (BGAs). As sophisticated semiconductor packing technologies have become more complex, materials with increased dependability, less warpage, and higher thermal conductivity have been developed as a result of ongoing innovation in mold compound formulations. A new generation of mold compounds with improved temperature management capabilities has been developed, according to a recent announcement from prominent chemical manufacturer BASF SE. These cutting-edge materials meet the increasing need for high-performance semiconductor packages in industries including data centers, automotive electronics, and 5G infrastructure by providing exceptional thermal conductivity and dependability.
Buy Now
By Technology - Segment AnalysisSystem-in-Package (SiP) dominated the semiconductor packaging materials market in 2023. System-in-Package (SiP), one of the aforementioned semiconductor packaging technologies, has dominated the market share in recent years because of its adaptability and capacity to combine several functions into a single package. SiP is well-suited for a variety of applications in consumer electronics, telecommunications, automotive, and Internet of Things devices because it has a number of benefits over conventional packaging technologies. The development of InFO_SoW (System-on-Wafer), TSMC's sophisticated Integrated Fan-Out (InFO) packaging technology, was unveiled. This method enables high-density packing with better performance and a smaller form factor by integrating several chips and passive components on a single wafer. With its substantial cost, performance, and time-to-market benefits, InFO_SoW is a top option for upcoming electronic products.
By End User Industry - Segment AnalysisAutomotive Sector dominated the semiconductor packaging materials market in 2023. Because electronics are being integrated into cars more and more, the automobile sector has become a significant user of semiconductor packaging materials. Electric vehicle (EV) powertrains, infotainment systems, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), and vehicle connection are just a few of the many uses for semiconductor devices in modern cars. An important recent development that emphasizes the automobile sector's reliance on semiconductor technologies is Nvidia's acquisition of Arm Holdings. Nvidia, which is well-known for its proficiency with artificial intelligence (AI) and graphics processing units (GPUs), hopes to increase its market share in the car industry by utilizing Arm's chip design skills. The significance of semiconductor packaging materials in allowing cutting-edge computing systems for connected and autonomous automobiles is highlighted by this acquisition.
By Geography - Segment AnalysisAsia Pacific dominated the semiconductor packaging materials market in 2023. Due to a number of factors, including the existence of important semiconductor manufacturers, the high demand for consumer electronics, and government support for the semiconductor industry, Asia-Pacific has been the dominating region in the market for semiconductor packaging materials. Samsung Electronics made an announcement in South Korea on a large investment in its semiconductor industry, which included the creation of cutting-edge packaging technology. In order to better address the development of innovative packaging solutions for 5G, AI, and automotive applications, Samsung has expanded its System LSI division. This investment strengthens the region's standing as a global leader in the semiconductor industry and highlights its dedication to technological innovation.
Drivers – Semiconductor packaging materials Market
• Technological Advancements and MiniaturizationThe semiconductor industry's constant technological developments fuel the demand for electronic gadgets that are increasingly compact, potent, and energy-efficient. The adoption of cutting-edge packaging materials and solutions is fueled by this need for miniaturization. Manufacturers of semiconductors are under pressure to create novel packaging methods as consumers want electronic devices that are progressively more feature-rich and compact. Wafer-level packaging, 3D integration, and fan-out packaging are some of these methods that allow for increased component density and better performance in smaller form factors.Fan-out wafer-level packaging (FOWLP) has become more popular as a vital component of advanced packaging in recent years. The partnership between Advanced Semiconductor Engineering, Inc. (ASE) and Deca Technologies to create cutting-edge FOWLP solutions is an illustration of a real-time development. Through this collaboration, Deca's M-Series technology and ASE's experience in packaging technologies will be combined to provide high-performance, reasonably priced semiconductor packaging solutions for upcoming markets including 5G, AI, and Internet of Things devices.
• Increasing Demand for High-Performance ComputingThe increasing need for innovative semiconductor packaging materials that provide better electrical performance, thermal management, and durability is driven by the growing need for high-performance computing (HPC) applications, including data centers, artificial intelligence (AI), and automotive electronics. Semiconductor devices with increased processing power, memory bandwidth, and energy efficiency are needed for HPC applications. This calls for the creation of packaging materials with strong component interconnection, effective heat dissipation, and reduced signal loss. The semiconductor industry has seen a major real-time development with NVIDIA's acquisition of ARM Holdings. In order to create integrated solutions for AI, HPC, and automotive computing, NVIDIA—which is well-known for its GPUs used in HPC applications—aims to take advantage of ARM's experience in CPU and system-on-chip (SoC) design. The increasing significance of cutting-edge semiconductor packaging materials is demonstrated by this acquisition.
Challenges – Semiconductor packaging materials Market
• Miniaturization and ComplexityThe growing demand from consumers for more powerful, smaller electronic gadgets is a challenge for semiconductor packaging in terms of complexity and shrinking. Smaller semiconductor packages with the same or better performance require material and manufacturing process advances. Chiplets can now be integrated into a single package thanks to developments in Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company's (TSMC) InFO technology. This breakthrough solves the problem of shrinking while improving performance by enabling more functionality in smaller form factors.
• Thermal Management and ReliabilityAs semiconductor devices' power densities rise, reliability and thermal control have emerged as crucial packaging problems. Especially in high-performance applications, effective heat dissipation is crucial for preventing device failure and guaranteeing long-term reliability. For advanced packaging applications, Dow Inc. recently unveiled a unique mold compound with enhanced thermal conductivity and dependability. Because of this material's exceptional heat-dissipation qualities, semiconductor devices operate more dependably under hot conditions. When it comes to solving the problems associated with thermal management in semiconductor packing, this invention is a major step forward.
Market Landscape
Technology launches, acquisitions, and R&D activities are key strategies adopted by players in the semiconductor packaging materials market. Major players in the semiconductor packaging materials market are Dow Inc., Henkel AG & Co. KGaA, Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., BASF SE, Hitachi Chemical Co., Ltd., Alent plc, Kyocera Chemical Corporation, Tanaka Holdings Co., Ltd., ASM Pacific Technology Ltd., and Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. among others.
#Semiconductor Packaging Materials Market#Semiconductor Packaging Materials Market share#Semiconductor Packaging Materials Market trends#Semiconductor Packaging Materials Market size
0 notes
Text
The Rise of AMD: A Look at their Advancements in CPU Technology
In recent years, AMD has been making waves in the tech industry with their innovative advancements in CPU technology. From challenging competitors to pushing the boundaries of performance, AMD has solidified its position as a major player in the market. In this article, we will explore the key advancements that have propelled AMD to the forefront of the industry and examine how they are shaping the future of computing.
Introduction
AMD, short for Advanced Micro Devices, is a semiconductor company known for its cutting-edge CPUs and GPUs. Founded in 1969, AMD has a long history of innovation and has established itself as a formidable competitor to industry Article source giants like Intel and Nvidia. With a focus on pushing the boundaries of performance and efficiency, AMD has consistently delivered products that cater to both consumers and professionals alike.
The Evolution of AMD Processors The Early Days: A Brief History of AMD
AMD vs Competition: In the early days, AMD primarily focused on manufacturing second-source microprocessors for companies like Intel. However, it wasn't until the launch of the AMD K5 processor in 1996 that they began to establish themselves as a serious contender in the market. The K5 marked the beginning of AMD's journey towards developing their own line of processors that could rival Intel's offerings.
The Athlon Era
AMD at GPU: In 1999, AMD introduced the Athlon processor, which quickly gained popularity for its impressive performance and competitive pricing. The success of the Athlon series laid the foundation for future innovations from AMD and firmly established them as a major player in the CPU market. Around this time, AMD also made significant strides in GPU technology with their Radeon graphics cards, further solidifying their position as a leading tech company.
Ryzen Revolution
Innovative Technologies of AMD: Fast forward to 2017, when AMD launched their Ryzen line of processors based on their Zen architecture. The Ryzen CPUs marked a significant leap forward in terms of performance and efficiency, offering consumers a viable alternative to Intel's offerings. With features like simultaneous multithreading (SMT) and Precision Boost technology, Ryzen processors quickly gained a reputation for being powerful yet affordable options for gamers and content creators alike.

Advancements in CPU Technology Zen 2 Architecture
The Rise of AMD: A Look at Their Advancements in CPU Technology: One of the most significant advancements from AMD in recent years has been the introduction of their Zen 2 architecture. Built on a 7nm process node, Zen 2 CPUs offer improved IPC (instructions per cycle) performance and higher clock speeds compared to previous generations. This architectural leap has allowed AMD to compete head-to-head with Intel's offerings across various market segments.
youtube
Chiplet Design
AMD and AI: Another key innovation from AMD is their chiplet design approach, which involves using multiple smaller dies interconnected on a single package. This modular design allows for greater scalability and efficiency compared to traditional monolithic designs. By leveraging chiplets, AMD can optimize performance while reducing costs associated with manufacturing larger monolithic dies.
Infinity Fabric Interconnect
One of the key technologies that enable AMD's chiplet design is their Infinity Fabric int
1 note
·
View note
Text
Team Red (AMD) vs. Team Green (NVidia): Who Reigns Supreme in Profits for 2024?

pexels nanadua The battle between AMD and Nvidia for dominance in the graphics processing unit (GPU) market has been a fierce one for decades. Both companies constantly push the boundaries of technology, offering cutting-edge solutions for gamers, professionals, and AI enthusiasts alike. But when it comes to profitability, who stands out in 2024? Let's delve into the financial landscape of these tech titans to see which company is raking in the bigger bucks. Market Share and Growth Trajectory Nvidia currently holds a significant lead in market share, particularly in the high-end discrete GPU market. Jon Peddie Research reported Nvidia holding an impressive 80.2% share in Q2 2023. This dominance translates to substantial revenue, with Nvidia boasting a market capitalization of over $2 trillion as of April 2024. However, AMD is not going down without a fight. They've been steadily gaining ground, especially in the data center market. Analysts predict AMD's data center revenue to experience a significant jump in 2024, reaching $6.5 billion, a 38% year-over-year increase. While Nvidia might hold the current crown in terms of raw market share and revenue, AMD's growth trajectory is nothing to scoff at. Analysts expect AMD's overall revenue to increase by a healthy 21.9% in 2024, reaching $30.5 billion. This impressive growth is fueled by factors like the increasing adoption of their EPYC server CPUs and the growing demand for AI-powered solutions where AMD's products are gaining traction. Diversification and Profitability Profitability isn't just about raw revenue. It's about how efficiently a company uses its resources to generate income. Here, Nvidia takes a clear lead. Their focus on high-end GPUs translates to higher margins compared to AMD. Additionally, Nvidia's dominance in the AI training space, driven by their powerful CUDA software platform, provides another layer of profitability. While AMD is making strides in AI inference, Nvidia's current edge in this lucrative market gives them a significant advantage. However, AMD isn't a one-trick pony. Their diversification across CPU, GPU, and chiplet technologies allows them to cater to a broader market. This, coupled with their focus on improving production efficiency, could lead to a future where their profit margins become more competitive. The Evolving Landscape: New Frontiers and Challenges The landscape of chipmakers is constantly evolving. The global chip shortage that plagued 2021 and 2022 seems to be easing, but new challenges are emerging. The ongoing geopolitical tensions and the potential for a recession could impact consumer spending on electronics, which in turn would affect both AMD and Nvidia. Additionally, the rise of alternative architectures like Intel's Arc GPUs could introduce a new variable into the already competitive market. So, who wins the profitability crown in 2024? It's a close call. Nvidia, with its current market share dominance, high margins, and strong presence in the booming AI training space, holds a significant advantage. However, AMD's impressive growth trajectory, focus on diversification, and potential for improved margins paint a bright future. Ultimately, the answer might depend on your perspective. If you're looking at pure revenue figures in 2024, Nvidia likely edges out AMD. However, if you consider growth potential and future profitability, AMD's trajectory is undeniably impressive. The true victor might be determined by how both companies adapt to the ever-changing technological landscape and navigate the challenges that lie ahead. The battle between AMD and Nvidia goes beyond just profits. It's a rivalry that fuels innovation, pushing both companies to develop ever-more powerful and efficient chipsets. This competition ultimately benefits consumers by offering a wider range of choices and driving down prices in the long run. Whether you're a hardcore gamer, a data scientist, or simply someone who appreciates cutting-edge technology, the continued competition between AMD and Nvidia promises to be an exciting ride for years to come. Read the full article
0 notes