#Carbapenem
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#Carbapenem#market#marketsize#marketoutlook#marketkeytrends#marketshares#marketforecast#industryanalysis#businessinsights#intelligence#marketgrowth#marketanalysis#marketdemand#marketreport#markettrend#marketresearch
0 notes
Text
Carbapenems Manufacturing | Pharma API and Raw Materials by Asymchem
Asymchem specializes in Carbapenems and pharma API manufacturing, providing high-quality raw materials for the pharmaceutical industry. Partner with us for reliable solutions.
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Researchers have identified an entirely new class of antibiotic that can kill bacteria that are resistant to most current drugs. Zosurabalpin is highly effective against the bacterium carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (Crab), which is classified as a "priority 1" pathogen by the World Health Organization due to its growing presence in hospitals.
Continue Reading.
219 notes
·
View notes
Text

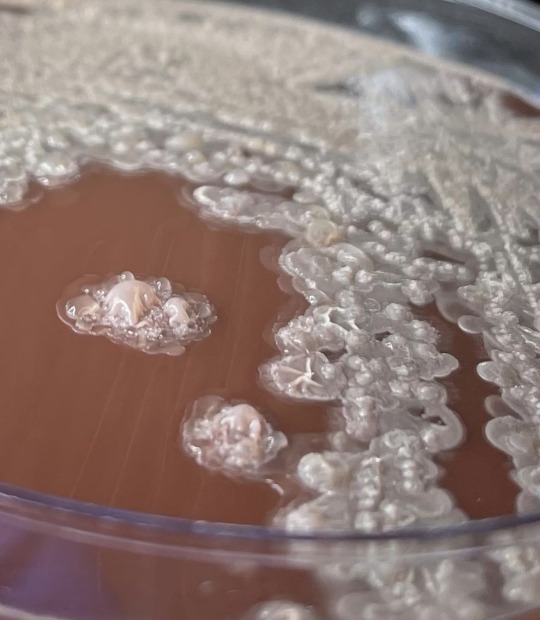
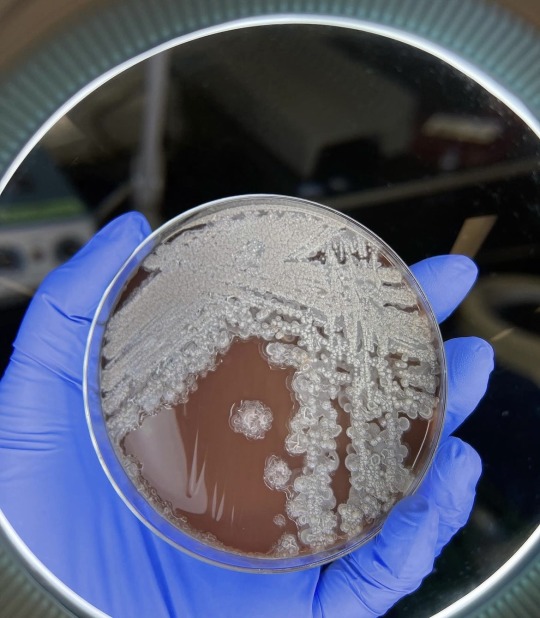

Bacillus licheniformis:
This is a gram positive bacterium commonly found in soil. It’s found on bird feathers especially chest and back plumage. It’s common in ground dwelling birds too. Is it harmful to man ? Yes it is has been found to cause infection in several cases of immunocompromised patients. It’s the causative agent of ventriculitis, ophthalmitis, bacteremia and endocarditis.
Treatment: it is sensitive to antibiotics such as cefepime, carbapenems, aminoglycosides and vancomycin.
…. Health is wealth …
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
Finegoldia magna
Cold open with a case report:
60M with a past history of previous wrist fracture presents with worsening pain and swelling, erythema and reduced range of motion, after suffering an abrasion from changing a tire.
the previous injury resulted from an MVA 9 yrs prior with a closed rist fracture
there was also a history of ETOH use and possible malnutrition, which can result in immunosuppression
Xray showed extensive changes in the wrist bones compared to past years with near loss of several, suggestive of pyogenic arthritis
Aspiration of the wrist joint grew Finegoldia magna
What is it
not actually uncommon
but is more commonly associated with post op infections or prosthetic joint infections (so case reports are harder to find in this category)

previously known as peptostreptococcus (sounds like peptobismol) but was renamed following 16S rna sequence availability, so in older texts/articles you'll still see it's old name
it's a commensal, so normal part of our microflora, but is opportunistic like so many other pathogens we usually live with and covers our body
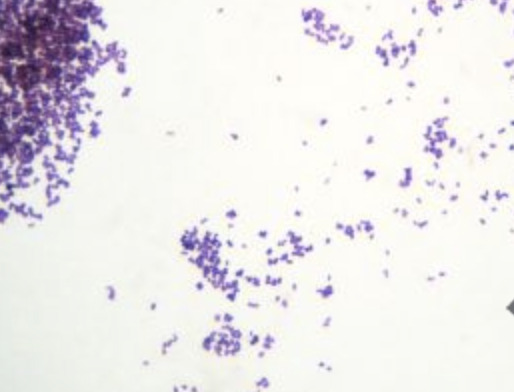
It is a Gram Positive Anaerobe, of the same flavour of clostridium. Remember there's fewer gram positive anaerobes than there are aerobes. So consider it in cultures if there's only growth in the anaerobe bottle and it's gram positive (purple). Usually it likes mucosal surfaces, such as the GI or GU tracts, but it doesn't mind skin either. It's considered a "gram positive anaerobic cocci" (GPAC) and has increasing prevalence and antibiotic resistance in the group.
Image source
Increased risk and when to think of it
chronic ulcers, diabetic ulcers
associated with biofilms (always bad, requires prolonged duration of antibiotics)
prosthetic joints
prosthetic valves
as it is opportunistic, also consider it in the immunocompromised
In the case above, the patient had septic arthritis, for which anaerobes account for 20% of cases. And Finegoldia is often the culprit in the case of post op and prosthetic joint infections. Rarely affects normal joints or healed joints from previous closed trauma years prior.
In chronic wounds it can impair healing via Protein L, which bindings to antibodies, causing immunomodulatory effect.
Bit of history
named for Sydney Finegold, an American physician who was a founding member of IDSA (infectious diseases society of American) and one of its early former presidents
but the name did make me think of 'fine gold'

Treatment
luckily susceptible to penicillin - but there is growing resistance, hence relevance of always chasing susceptibility
alternatives: metronidazole (typical class that covers anaerobes), tazocin and carbapenems
also has increasing resistance to clindamycin (a consideration in penicillin allergy or during empirical therapy for wounds)
Resources:
case report
wikipaedia
microbe canvas
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Role of Ertapenem 100 mg in Modern Antibiotic Therapy
In recent years, the growing challenge of antibiotic resistance has prompted healthcare professionals to explore newer therapeutic options. Among these, Ertapenem 100 mg has emerged as a significant player in modern antibiotic therapy. This broad-spectrum antibiotic belongs to the carbapenem class and is renowned for its effectiveness against a variety of infections, particularly those caused by Gram-negative bacteria. In this blog, we will delve into the importance of Ertapenem, its applications, and its availability through Ertapenem 100 mg injection manufacturers in India, exporters, suppliers, and distributors.

Understanding Ertapenem
Ertapenem is a synthetic beta-lactam antibiotic that offers potent activity against a wide range of bacterial pathogens. Its unique structure allows it to penetrate bacterial cell walls effectively, making it suitable for treating complex infections, including those originating from intra-abdominal sources, skin and soft tissue infections, and pneumonia. Given the rising rates of resistance to commonly used antibiotics, Ertapenem provides a vital alternative for clinicians seeking reliable treatment options.
The Need for Effective Antibiotics
The World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized antibiotic resistance as one of the most significant global health threats. With an increasing number of bacterial strains becoming resistant to traditional therapies, the role of advanced antibiotics like Ertapenem has become crucial. The ability of Ertapenem to maintain its efficacy against resistant strains makes it an essential component of modern treatment regimens.
Applications of Ertapenem 100 mg
Ertapenem is indicated for various infections, including:
Intra-abdominal Infections: It is often used to treat complicated intra-abdominal infections due to its broad spectrum of activity.
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: Ertapenem is effective against multiple pathogens commonly responsible for skin infections.
Pneumonia: This antibiotic is also a go-to treatment for community-acquired pneumonia.
Complicated Urinary Tract Infections: Ertapenem can be a critical option when dealing with complicated cases.
The versatility of Ertapenem makes it a valuable asset in a clinician's toolkit, particularly for patients who have not responded to other antibiotic therapies.
Availability in India
Ertapenem 100 mg Injection Manufacturers in India
India has a robust pharmaceutical industry, recognized for producing high-quality medications at competitive prices. Numerous Ertapenem 100 mg injection manufacturers in India are dedicated to maintaining stringent quality standards while ensuring that their products meet international guidelines. These manufacturers play a vital role in making Ertapenem accessible to healthcare facilities across the country and abroad.
Ertapenem 100 mg Injection Exporters in India
The global demand for effective antibiotics has led to an increase in Ertapenem 100 mg injection exporters in India. These exporters are crucial in supplying this essential medication to international markets, contributing to India's reputation as a leader in the global pharmaceutical landscape. The adherence to quality and regulatory standards has helped these exporters establish strong relationships with healthcare providers worldwide.
Ertapenem 100 mg Injection Suppliers in India
A reliable supply chain is fundamental for the availability of Ertapenem in hospitals and clinics. Numerous Ertapenem 100 mg injection suppliers in India ensure that healthcare institutions receive timely deliveries of this critical antibiotic. These suppliers work closely with manufacturers to maintain a steady stock, facilitating uninterrupted access to essential medications.
Ertapenem 100 mg Injection Distributors in India
The role of Ertapenem 100 mg injection distributors in India is equally important. They bridge the gap between manufacturers and healthcare providers, ensuring that the product reaches the end-users efficiently. Distributors are vital in managing logistics, handling regulatory compliance, and addressing the needs of various healthcare institutions. Their efforts ensure that doctors have immediate access to this antibiotic, particularly in emergency situations.
Best Indian Pharma Industry 2024
The best Indian pharma industry 2024 is characterized by innovation, quality, and a commitment to addressing public health challenges. With a focus on research and development, Indian pharmaceutical companies are continually improving their product offerings. The introduction of advanced antibiotics like Ertapenem is a testament to the industry’s efforts to combat antibiotic resistance. The commitment to maintaining high manufacturing standards and complying with international regulations has solidified India’s position as a trusted source for pharmaceuticals worldwide.
Conclusion
The role of Ertapenem 100 mg in modern antibiotic therapy cannot be overstated. As antibiotic resistance continues to pose significant challenges to healthcare, the importance of effective and reliable treatments like Ertapenem becomes even more critical. The collaboration among Ertapenem 100 mg injection manufacturers, exporters, suppliers, and distributors in India has made this essential antibiotic readily available to healthcare providers, ensuring that patients receive the best possible care.
In 2024, as the best Indian pharma industry continues to evolve, the ongoing development and distribution of innovative antibiotics will remain pivotal in the fight against infectious diseases. By prioritizing access to effective medications, we can work towards a healthier future and combat the ever-growing threat of antibiotic resistance.
#Ertapenem 100 mg for injection distributors in India#Ertapenem 100 mg for injection suppliers in India#Best Indian pharma industry 2024#Ertapenem 100 mg for injection exporters in India#Ertapenem 100 mg for injection manufacturers in India
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Another person has died in an outbreak of extensively drug-resistant bacteria linked to contaminated eye drops, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported in an update on Thursday.
The outbreak now totals 81 cases across 18 states. In addition to the four deaths, health officials have tallied reports of 14 people with vision loss and an additional four people who have had their eyeballs surgically removed (enucleation) due to infection.
The bacteria behind the outbreak is a strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa dubbed VIM-GES-CRPA. This unwieldy acronym stands for a carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa (CRPA) with Verona integron-mediated metallo-β-lactamase (VIM) and Guiana extended-spectrum-β-lactamase (GES). It is an extensively drug-resistant strain of bacteria that, until this outbreak, had never been seen in the US before.
US health officials have traced the bacteria's origins to contaminated eye drops, with EzriCare artificial tears being the most common product used by people infected during the outbreak. The Food and Drug Administration reported a recall of these drops in February after the CDC released a health alert about 55 cases and the link to the eye drops. The manufacturer of EzriCare eye drops, India-based Global Pharma, also recalled two other products it makes: Delsam Pharma’s Artificial Tears and Delsam Pharma’s Artificial Ointment. The CDC and the FDA advise people to stop using these products immediately if they haven't already.
Before the recalls, the eye drops were readily available nationwide and sold through Amazon, Walmart, eBay, and other retailers. Clinical samples indicate the contamination spans from at least May 2022 to April 2023, though the CDC has advised health care professionals to report any suspect clinical samples dating back to January 2022.
This week's outbreak update includes 13 new cases since the last outbreak update in March, six of which had samples collected prior to the recall and are now confirmed and added to the tally. Of the seven other newly added cases, most either resided in long-term care facilities with other known cases or reported continued use of one of the recalled artificial tears, the CDC reported. Another person has died in an outbreak of extensively drug-resistant bacteria linked to contaminated eye drops, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported in an update on Thursday.
The outbreak now totals 81 cases across 18 states. In addition to the four deaths, health officials have tallied reports of 14 people with vision loss and an additional four people who have had their eyeballs surgically removed (enucleation) due to infection.
The bacteria behind the outbreak is a strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa dubbed VIM-GES-CRPA. This unwieldy acronym stands for a carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa (CRPA) with Verona integron-mediated metallo-β-lactamase (VIM) and Guiana extended-spectrum-β-lactamase (GES). It is an extensively drug-resistant strain of bacteria that, until this outbreak, had never been seen in the US before.
US health officials have traced the bacteria's origins to contaminated eye drops, with EzriCare artificial tears being the most common product used by people infected during the outbreak. The Food and Drug Administration reported a recall of these drops in February after the CDC released a health alert about 55 cases and the link to the eye drops. The manufacturer of EzriCare eye drops, India-based Global Pharma, also recalled two other products it makes: Delsam Pharma’s Artificial Tears and Delsam Pharma’s Artificial Ointment. The CDC and the FDA advise people to stop using these products immediately if they haven't already.
Before the recalls, the eye drops were readily available nationwide and sold through Amazon, Walmart, eBay, and other retailers. Clinical samples indicate the contamination spans from at least May 2022 to April 2023, though the CDC has advised health care professionals to report any suspect clinical samples dating back to January 2022.
This week's outbreak update includes 13 new cases since the last outbreak update in March, six of which had samples collected prior to the recall and are now confirmed and added to the tally. Of the seven other newly added cases, most either resided in long-term care facilities with other known cases or reported continued use of one of the recalled artificial tears, the CDC reported.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The manufacturer of a brand of over-the- counter eye drops said that it was recalling the product, EzriCare Artificial Tears, after it was linked to a drug-resistant bacteria strain that has caused at least one person's death and vision loss in five others.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has advised people to stop using the eye drops, as the agency investigates an outbreak of a strain of the bacteria pseudomonas aeruginosa, which can cause infections in the blood, lungs and other parts of the body. This strain of the bacteria had never been identified in the United States before the current outbreak and is resistant to a class of antibiotics called carbapenems, which are generally considered a last resort.
The bacteria strain had been found in 55 people in 12 states as of Tuesday, the C.D.C. said. The agency said that the infections had caused one death, vision loss in five of 11 people who had eye infections, and some hospitalizations.
Another Note👇
They stop this but let a vaxxine known to cause multiple adverse effects and tens of thousands of deaths continue to be used. History has shown inoculations we're stopped after 25 adverse reactions and or deaths.
Does this even make sense to you?��
#pay attention#educate yourself#educate yourselves#reeducate yourself#knowledge is power#reeducate yourselves#think for yourself#think for yourselves#think about it#do your homework#do your research#do your own research#question everything#ask yourselves#ask yourself#government lies#history research#hidden history#american history#history lesson#history
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

CRE = Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Carbapenems are a newer class of beta-lactamase antibiotics; CRE bacteria may also be resistant to unrelated drugs such as fluoroquinolones. Enterobacteriaceae is the name of a family of Gram-negative bacteria (E. coli, Klebsiella, Salmonella, etc.), many of which live in the human gut. Some patients came down with CRE after being scoped with the same endoscope as another patient with CRE in their stomach, intestines, or lungs. This category includes bacteria that have certain resistance factors such as KPC , NDM-1, and VIM. Treat with old and/or toxic drugs such as polymyxins, fosfomycin, and (sometimes) aminoglycosides (susceptibility varies).
• KPC = Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase. A resistance factor that helps bacteria survive carbapenems and other beta-lactamase antibiotics. There was an outbreak in an NIH hospital.
• NDM-1 = New Delhi Metallobeta-lactamase 1. First identified in India and now in 140 countries, this plasmid moves promiscuously among different species of bacteria. Bad news for wound infections, pneumonias, meningitis, and blood infections.
• VIM = Verona Integron-Mediated Metallo-betalactamase. Like NDM-1, makes bugs resistant to beta-lactamase antibiotics such as penicillin or ceftriaxone.
4 notes
·
View notes
Link
#market research future#antibiotics market#antibiotics market size#antibiotics market trends#antibiotics market growth
0 notes
Text
Epidemiology and Insights into the Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy Market Outlook

Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy (OHE) is a severe neurological complication of advanced liver disease, particularly cirrhosis. Characterized by confusion, altered consciousness, and even coma in extreme cases, OHE arises from the accumulation of toxins like ammonia in the bloodstream due to impaired liver function. As the global prevalence of chronic liver diseases increases, the Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy market is gaining significant attention from healthcare providers and pharmaceutical companies.
Market Insight
The Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy market size is expected to grow substantially through 2032, driven by the rising prevalence of cirrhosis, aging populations, and the increased focus on liver disease management. Current treatments, such as lactulose and rifaximin, aim to reduce toxin levels and manage symptoms. However, the high recurrence rate of OHE underscores the need for novel therapies that address the underlying pathophysiology.
In recent years, pharmaceutical companies have intensified their efforts to develop advanced treatments for OHE. Innovations in precision medicine and the emergence of combination therapies are likely to reshape the market landscape. Additionally, growing awareness about the condition and improved diagnostic techniques are driving earlier interventions, which further contribute to market growth.
Epidemiology Forecast
The Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy Epidemiology Forecast indicates a steady rise in cases globally due to the increasing prevalence of liver diseases such as hepatitis and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). According to estimates, 30-40% of cirrhotic patients experience at least one episode of OHE, with recurrence rates as high as 50% within a year.
Regions with high rates of viral hepatitis, alcohol-related liver disease, and metabolic syndrome, such as Asia-Pacific and North America, are anticipated to report the largest patient populations. Enhanced screening programs and access to healthcare in these regions will likely improve diagnosis rates, further influencing epidemiological trends.
Market Forecast
Through 2032, the Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy market size is poised for significant growth, supported by ongoing clinical trials, increased research funding, and advances in therapeutics. The market is also expected to benefit from the development of targeted therapies that address ammonia metabolism and reduce systemic inflammation.
Conclusion
The OHE market represents a critical area of growth and innovation within liver disease management. With rising patient numbers and advancements in treatment options, the Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy market offers significant opportunities for improving patient outcomes and addressing a major public health challenge.
Latest Reports
Treatment Resistant Depression Market | Uveal Neoplasms Market | Vasomotor Symptoms Market | Von Willebrand Disease Market | Wet-age Related Macular Degeneration Market | Aicardi-goutières Syndrome Market | Airway Stent Market Market | Alpha Thalassemia Market | Ambulatory Arrhythmia Market | Ascites Market | Aspergillosis Market | Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market Market | B Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Market | B-cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Market | Bone Marrow Failure Market | Bunion Market | Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae Infection Market | Cardiac Amyloidosis Market | Cardiovascular Imaging Equipment Market | Charcot-marie-tooth Disease Market | Crps Market | Dilators Market | Eisenmenger Complex Market | Familial Lipoprotein Lipase Deficiency Market | Functional Constipation Market | Generalized Anxiety Disorder Gad Market | Kernicterus Market | Lambert-eaton Myasthenic Syndrome Market | Myotonic Dystrophy Market | Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency Market | Partial Seizure Market | Patent Foramen Ovale Closure Devices Market | Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor Market
0 notes
Text
DAILY DOSE: Google DeepMind Releases AlphaFold3 Code After Delay; Study Warns of Spreading Carbapenem-Resistant CRAB Strain.
DEEP MIND RELEASES FULL ALPHAFOLD3 CODE AFTER DELAY Google DeepMind has released the full code for its AI protein prediction software, AlphaFold3, after a six-month delay following criticism for initially only providing pseudocode with its May 2023 Nature paper. The delayed release followed backlash from researchers who argued it violated standards for openness and reproducibility. Despite this,…
#Africa#Antibiotic Resistance#artificial intelligence#Asia#Australia#Bacteria#Europe#Featured#North America#South America#technology
1 note
·
View note
Link
#market research future#antibiotics market#antibiotics market size#antibiotics market trends#antibiotics market growth
0 notes
Text
Antibiotic Resistance Market Size, Share, Growth, Trends and Forecast 2024-2032
Antimicrobials relate to antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, and antiparasities which are classifications of drugs administered in controlling diseases caused by microorganisms in humans, animals, and plants. Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) defines any activity of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites to known antimicrobial medicines. Drug resistance means that even antibiotics and other antimicrobial treatments are rendered ineffective and infections can become hard or even impossible to handle, leading to increased danger of disease transmission, severe disease, disability, and death. As a naturally occurring process, AMR occurs through gradual pathogen evolution over a period through mutations. It has been promoted and spread by human endeavors especially the irrational and excessive use of antimicrobials for prevention, treatment, or control of infections in man, animals, and crops.
According to the Univdatos Market Insights analysis, increasing cases of antibiotic-resistant infections and increasing investment in antibiotic research & development activities across the globe will drive the scenario of the antibiotic resistance market. As per their “Antibiotic Resistance Market” report, the global market was valued at ~USD 8.3 billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of about 5.4% during the forecast period from 2024-2032.
Request Free Sample Pages with Graphs and Figures Here - https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=66996
A GLOBAL CONCERN:
Antimicrobial medicines are the cornerstone of modern medicine. The emergence and spread of drug-resistant pathogens threaten our ability to treat common infections and to perform life-saving procedures including cancer chemotherapy and cesarean section, hip replacements, organ transplantation, and other surgeries. In addition, drug-resistant infections impact the health of animals and plants, reduce productivity in farms, and threaten food security. AMR has significant costs for both health systems and national economies overall. AMR is a concern for every country irrespective of income level. It does not respect the territorial standards or boundaries of countries. They include adequate availability and utilization of clean water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) for humans and animals; inadequate prevention, infection, and disease control in human and animal households, health care, and farming sectors; Inadequate access to proper, affordable, and effective vaccines, diagnostic tools, and medicines; poor knowledge or health literacy; and all implementing regulations. Both the driving force as well as the effect of AMR bear more influence on individuals dwelling in developing nations and at-risk communities.
Ø Drug resistance in bacteria-
The worldwide spread of antibiotic resistance remains a major concern while the effectiveness of widespread bacterial infections is reduced due to the ineffectiveness of most used antibiotics. According to the 2022 Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) report, some of the bacteria pathogens have high resistance rates and this is a big worry. The crude resistance rate of third-generation cephalosporin-resistant Escherichia coli is 42 % and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is 35% in 76 countries which is reportedly high. Klebsiella pneumoniae, which is a bacterial isolate from human intestines, has also raised its resistance to several important antibiotics. Higher levels of resistance may translate to greater adoption of the last resort drugs such as carbapenems which in turn have their resistance levels which are presently being noted across the world. As the effectiveness of the last-resort drugs diminishes, the danger of infections that can no longer be treated rises. According to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development projections, there is a predicted twofold increase in resistance to last-line antibiotics by 2035 as compared to the year 2005 implying the need to invest in effective antimicrobial stewardship and improve surveillance across the world.
KEY FACTS:
Ø AMR has been reported to threaten many advancements in modern medicine. They also prove more difficult to eliminate and increase complications attached to other medical operations and therapies including surgery, cesarean section, and cancer chemotherapy.
Ø The world faces an antibiotics pipeline and access crisis. There is an inadequate research and development pipeline in the face of rising levels of resistance, and an urgent need for additional measures to ensure equitable access to new and existing vaccines, diagnostics, and medicines.
Ø In addition to death and disability, AMR has significant economic costs. The World Bank estimates that AMR could result in USD 1 trillion in additional healthcare costs by 2050, and USD 1 trillion to USD 3.4 trillion in gross domestic product (GDP) losses per year by 2030.
For more information about this report visit- https://univdatos.com/report/antibiotic-resistance-market/
Conclusion
The gradual development of the extensive and imaginative healthcare research business is showing a new day. All these measures are changing the manner of managing the industry at the moment offering numerous varieties to the population on the international level.
#Antibiotic Resistance Market#Antibiotic Resistance Market Size#Antibiotic Resistance Market Share#Antibiotic Resistance Market Growth#Antibiotic Resistance Market Trends
0 notes