#But salamanders are 1) not lizards 2) AMPHIBIOUS
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text


Why am I not a Vulkan fanblog actually, I'm literally dragon flavor autism. And I'm obsessed with drawing skeletal dragons.
This thing literally lives on my TV his name is Vaal Hazak

I need to get weirder about giant warm dragon man
#I only dislike them being called salamanders#I KNOOOWWW its like all fantasy does this#But salamanders are 1) not lizards 2) AMPHIBIOUS#Why we keep making them desert/ fire lizards??? Thats a bearded dragon! A hornytoad! A gila monster!!! OPPOSITE OF WET AMPHIBIAN#Besides that tho why am i sleepin on vulkan#My art#vulkan#I am not well in the brain at 1:30am 🐉#Dragon posting on main /j
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
Triadobatrachus massinoti

By Scott Reid
Etymology: Triassic frog
First Described By: Piveteau, 1936
Classification: Biota, Archaea, Proteoarchaeota, Asgardarchaeota, Eukaryota, Neokaryota, Scotokaryota Opimoda, Podiata, Amorphea, Obazoa, Opisthokonta, Holozoa, Filozoa, Choanozoa, Animalia, Eumetazoa, Parahoxozoa, Bilateria, Nephrozoa, Deuterostomia, Chordata, Olfactores, Vertebrata, Craniata, Gnathostomata, Eugnathostomata, Osteichthyes, Sarcopterygii, Rhipidistia, Tetrapodomorpha, Eotetrapodiformes, Elpistostegalia, Stegocephalia, Temnospondyli, Euskelia, Dissorophoidea, Xerodromes, Amphibamiformes, Lissamphibia, Batrachia, Salientia, Triadobatrachidae
Referred Species: T. massinoti
Status: Extinct
Time and Place: Approximately 251–250 million years ago, in the late Induan to early Olenekian of the Early Triassic.

Triadobatrachus is only known from the Sakamena Formation in Northern Madagascar.
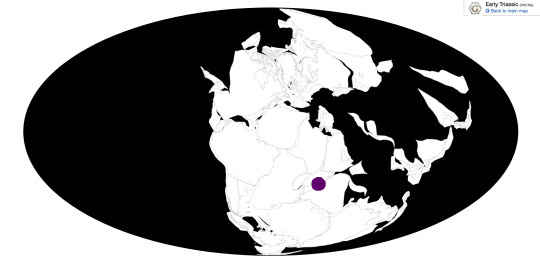
Physical Description: Triadobatrachus superficially resembles modern frogs, it was only around 10 cm long, had a broad head and a very reduced tail. Its skeleton had many features associated only with frogs among amphibians, including a very frog-like skull with big eyes and their characteristically elongated hips. Soft tissues preserved around the fossil even show that it had the wide, round body of frogs too. However, the skeleton of Triadobatrachus differed from living frogs in a few major ways. It had much more vertebrae than living frogs, 26 compared to the maximum 4–9 of frogs alive today, giving it a much longer body, and these vertebrae had ribs, unlike living frogs. Its legs were shorter and more squat, especially its back legs, which were hardly any longer than its front ones, making Triadobatrachus incapable of hopping despite its derived hips. Even the stumpy tail was still more prominent than in living frogs, and may have even retained some degree of mobility. To sum it up, Triadobatrachus more or less looked like a stretched out frog with short legs. Think of a horned toad lizard but with more of the toad part and less horned.
Diet: Like other frogs, Triadobatrachus was probably carnivorous, likely feeding on invertebrates like insects and other arthropods, molluscs, worms, and perhaps even any small vertebrates it could fit in its mouth.
Behavior: One of the most standout features of Triadobatrachus is that it couldn’t have hopped like modern frogs. Instead, Triadobatrachus would have walked around on land more like a salamander, although it is unknown just how much time it would have spent on land in the first place anyway. It was clearly amphibious, and it probably swam by kicking its back legs like frogs, unlike the undulation of newts and salamanders. It would have spawned like living amphibians too, laying shell-less eggs in water that hatched into tadpoles and underwent metamorphosis just like modern frogs. Otherwise, its behaviour is a mystery. We don’t even know if it would have croaked or not.
Ecosystem: Not much is directly known about the ecosystem Triadobatrachus inhabited, as the only known fossil had been washed out to sea along the coast. The intact body at least implies the body wasn’t transported far, so Triadobatrachus probably lived in coastal floodplain rivers and swamps. Various other temnospondyl amphibians are known from the area, including Edingeralla, Deltacephalus, Mahavisaurus, Wantzsosaurus and Tertremoides. Despite being amphibians, many of these temnospondyls were likely euryhaline, meaning they could tolerate salt water and inhabited the coastline, something only a few living amphibians are even remotely capable of standing. The peculiar aquatic reptile Hovasaurus lived along the coasts, although it’s unknown if it ever crossed paths with the freshwater frogs, and terrestrial procolophonid parareptiles were also present. Plant remains suggest the environment was tropical and semi-arid with a monsoonal climate that supported conifer forests along with seed ferns, horsetails and clubmosses.
Other: Triadobatrachus is one of the only known stem-frogs, along with the polish Czatkobatrachus, and is certainly the oldest. The early evolution of Lissamphibia (all living amphibians) is poorly understood, particularly whether their ancestry lies in the temnospondyls or some other “amphibians”. Triadobatrachus doesn’t solve this debate, although it does show similarities to the Permian amphibamiforms like Gerobatrachus, supporting the temnospondyl affinity for batrachians (the frogs and salamanders) amongst dissorophoids.
Before they were considered to be temnospondyls, lissamphibians were often thought to be lepospondyls, a probably paraphyletic or even polyphyletic (i.e. unnatural) collection of “amphibians” on the tetrapod tree more derived than temnospondyls (some may even be honest to goodness amniotes!). This picture is complicated by caecilians, which at one point were suggested to be lepospondyls while batrachians were temnospondyls, making Lissamphibia polyphyletic! The story got even stranger after a little Triassic amphibian, Chinlestegophis, was discovered in 2017 and was considered to be a stem-caecilian. Chinlestegophis pulled caecilians back into temnospondyls with the other lissamphibians, but at almost opposite ends of the temnospondyl tree—batrachians in amphibamiforms and caecilians in with the stereospondyls related to the giant metoposaurs! So lissamphibians may all be temnospondyls...but also polyphyletic, unless nearly all of Temnospondyli is classed as lissamphibians and becomes part of the crown group. This would also mean our small modern amphibians both independently miniaturised from the much larger, classic predatory amphibians of the Palaeozoic and Triassic. What a concept.
Regardless of temnospondyl taxonomic troubles, Triadobatrachus is a perfect transitional form from more generalised amphibians to the highly specialised anatomy of frogs. Particularly, it shows that some of their unique anatomical adaptations evolved before they were able to hop, and may have functioned for other activities like swimming. The almost complete preservation of a skeleton as delicate as one of a small amphibian is a remarkable find, let alone one that represents a perfect transitional form for a group of animals whose evolutionary history is shrouded in mystery, and makes Triadobatrachus a fantastic find, no matter how unassuming it may be.
~ By Scott Reid
Sources under the Cut
Ascarrunz, Eduardo; Rage, Jean-Claude; Legreneur, Pierre; Laurin, Michel (2016). "Triadobatrachus massinoti, the earliest known lissamphibian (Vertebrata: Tetrapoda) re-examined by µCT-Scan, and the evolution of trunk length in batrachians". Contributions to Zoology. 58 (2): 201–234.
Lires, A. I., Soto, I. M., & Gómez, R. O. (2016). Walk before you jump: new insights on early frog locomotion from the oldest known salientian. Paleobiology, 42(4), 612-623.
Maganuco, S., Steyer, J.S., Pasini, G., Boulay, M., Lorrain, S., Bénéteau, A., Auditore, M. (2009). “An exquisite specimen of Edingerella madagascarensis (Temnospondyli) from the Lower Triassic of NW Madagascar; cranial anatomy, phylogeny, and restorations”. Società italiana di scienze naturali.
Pardo, Jason D.; Small, Bryan J.; Huttenlocker, Adam K. (2017-07-03). "Stem caecilian from the Triassic of Colorado sheds light on the origins of Lissamphibia". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 114 (27): E5389–E5395
Piveteau, J. (1936). "Une forme ancestrale des amphibiens anoures dans le Trias inférieur de Madagascar". Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Séances de l'Académie des Sciences. 202: 1607–1608.
Rage,J-C; Roček, Z. (1989). "Redescription of Triadobatrachus massinoti (Piveteau, 1936) an anuran amphibian from the Early Triassic". Palaeontographica Abteilung A. 206: 1–16.
Roček , Z., Rage, J-C. (2000). "13. Proanuran Stages (Triadobatrachus, Czatkobatrachus)". In Heatwole, H.; Carroll, R. L. (eds.). Amphibian Biology. Paleontology: The Evolutionary History of Amphibians. 4. Surrey Beatty & Sons. pp. 1284–1294.
Ročková, H., Roček Z. (2005). “Development of the pelvis and posterior part of the vertebral column in the Anura”. Journal of Anatomy. 206(1): 17–35.
Xing, L., Stanley, E. L., Bai, M., & Blackburn, D. C. (2018). “The earliest direct evidence of frogs in wet tropical forests from Cretaceous Burmese amber”. Scientific reports, 8(1), 8770.
#Triadobatrachus#Triadobatrachus massinoti#Frog#Palaeoblr#Triassic Madness#Triassic March Madness#Triassic#Prehistory#Paleontology#Prehistoric life
157 notes
·
View notes
Text
Aitvaras (3-Point Quality)
Prerequisite: Dragon
Some dragons can transform into a small, mundane animal to better hide themselves among humans. This could be a bird (like a chicken, kestrel, or duck), a large lizard, a large toad, ferret, cat, bat, snake, large salamander, or similar animal. While in this form, they retain their armor and natural weapons, but the new form should reflect all the Dragon can do in some respect (IE: An “Amphibious” snake might pass muster, but if the new form loses limbs, it can’t use those abilities). In this form, they are roughly 2-3ft tall, or twice that in overall length for snakes and fish. Their weight from ‘human’ size becomes 1/8th normal. Damage from falls is reduced by ½. However, their normal damage for their hand-to-hand attacks is also reduced by ½. Their Life Points is halved as well. Ranged attacks have a -1 penalty against them. They gain a +3 to Stealth tasks, as well as a +1 to hit normal sized targets.
1 note
·
View note