#Black holes
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
A black hole is a region of space where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. There are two main types of black hole; stellar mass and supermassive black holes, and they differ in size, formation, and impact on their host galaxy. Stellar mass black holes, a few to dozens of times the mass of the sun, form from collapsing massive stars. Supermassive black holes, on the other hand, are millions to billions of times more massive and tend to live in the center of galaxies and grow through accretion and mergers.
Continue Reading.
40 notes
·
View notes
Text

Love Letters from Space
Love is in the air, and it’s out in space too! The universe is full of amazing chemistry, cosmic couples held together by gravitational attraction, and stars pulsing like beating hearts.
Celestial objects send out messages we can detect if we know how to listen for them. Our upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will help us scour the skies for all kinds of star-crossed signals.
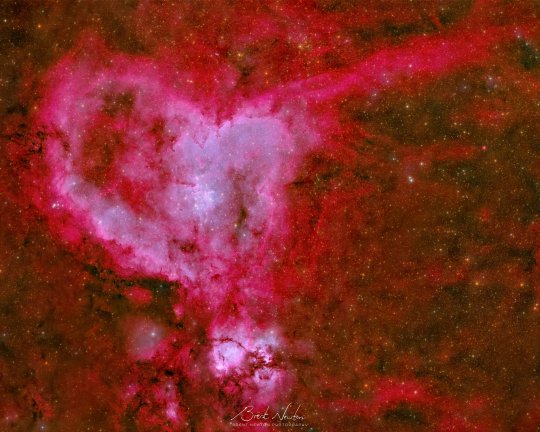

Celestial Conversation Hearts
Communication is key for any relationship – including our relationship with space. Different telescopes are tuned to pick up different messages from across the universe, and combining them helps us learn even more. Roman is designed to see some visible light – the type of light our eyes can see, featured in the photo above from a ground-based telescope – in addition to longer wavelengths, called infrared. That will help us peer through clouds of dust and across immense stretches of space.
Other telescopes can see different types of light, and some detectors can even help us study cosmic rays, ghostly neutrinos, and ripples in space called gravitational waves.
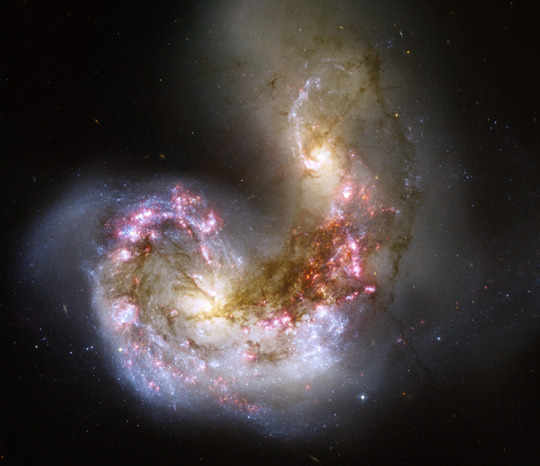

Intergalactic Hugs
This visible and near-infrared image from the Hubble Space Telescope captures two hearts locked in a cosmic embrace. Known as the Antennae Galaxies, this pair’s love burns bright. The two spiral galaxies are merging together, igniting the birth of brand new baby stars.
Stellar nurseries are often very dusty places, which can make it hard to tell what’s going on. But since Roman can peer through dust, it will help us see stars in their infancy. And Roman’s large view of space coupled with its sharp, deep imaging will help us study how galaxy mergers have evolved since the early universe.
Cosmic Chemistry
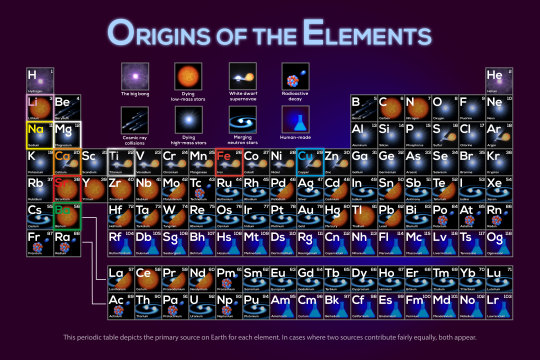
Those stars are destined to create new chemistry, forging elements and scattering them into space as they live, die, and merge together. Roman will help us understand the cosmic era when stars first began forming. The mission will help scientists learn more about how elements were created and distributed throughout galaxies.
Did you know that U and I (uranium and iodine) were both made from merging neutron stars? Speaking of which…

Fatal Attraction
When two neutron stars come together in a marriage of sorts, it creates some spectacular fireworks! While they start out as stellar sweethearts, these and some other types of cosmic couples are fated for devastating breakups.
When a white dwarf – the leftover core from a Sun-like star that ran out of fuel – steals material from its companion, it can throw everything off balance and lead to a cataclysmic explosion. Studying these outbursts, called type Ia supernovae, led to the discovery that the expansion of the universe is speeding up. Roman will scan the skies for these exploding stars to help us figure out what’s causing the expansion to accelerate – a mystery known as dark energy.

Going Solo
Plenty of things in our galaxy are single, including hundreds of millions of stellar-mass black holes and trillions of “rogue” planets. These objects are effectively invisible – dark objects lost in the inky void of space – but Roman will see them thanks to wrinkles in space-time.
Anything with mass warps the fabric of space-time. So when an intervening object nearly aligns with a background star from our vantage point, light from the star curves as it travels through the warped space-time around the nearer object. The object acts like a natural lens, focusing and amplifying the background star’s light.
Thanks to this observational effect, which makes stars appear to temporarily pulse brighter, Roman will reveal all kinds of things we’d never be able to see otherwise.

Roman is nearly ready to set its sights on so many celestial spectacles. Follow along with the mission’s build progress in this interactive virtual tour of the observatory, and check out these space-themed Valentine’s Day cards.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
#NASA#astronomy#telescope#Roman Space Telescope#Valentine’s Day#space#science#STEM#nebula#chemistry#galaxies#black holes#rogue planets#exoplanets#Hubble Space Telescope#tech
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

[REDACTED] if you agree
8K notes
·
View notes
Text

When I get mad, I like to draw black holes
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

AND I LOOKED, AND BEHOLD A PALE HORSE: AND HIS NAME THAT SAT ON HIM WAS DEATH
#art#my art#artists on tumblr#oc#horror#horror art#cosmic horror#black holes#chalk pastel#traditional art#fine art#also i'm not religious i just think the quote goes hard
928 notes
·
View notes
Text



about black holes
#homestuck#alternate calliope#jade harley#alt calliope#homestuck beyond canon#homestuck epilogues#homestuck epilogue#black holes#comic#my art
919 notes
·
View notes
Text

198 notes
·
View notes
Text

I honestly didn't ever expect that I'd be in the position where I'd be using this blog not just to analyse what has come before in Homestuck, but to look toward the comic's future and do some real old-fashioned theorycrafting. but the time has come. so here goes; lime-bloods' Beyond Canon theories as of the July 6th 2024 update:
Vriska's Going to Hell

were all gonna help you! / whether you like it or not
a select few eagle-eyed readers already noticed that the sound used in last month's (Vriska: Figure shit out yourself.) is called "hell_tierwav". while it was easy to dismiss this as irrelevant composer shenanigans at the time, it's now become clear exactly what this was foreshadowing. whether it would be more apt to call this "Hell" or "Purrgatory" is probably up for debate - but whatever you call it, Vriska's been placed in a dimension seemingly tailored specifically for her personal torment.
while Vriska characteristically interprets the recreation of her childhood home as a symbol of how badass she was, the ghosts of her past - both literal, as the shades of the trolls she killed as Mindfang, and figurative, in the form of sprites wearing the faces of her dead friends - show us in no uncertain terms that Vriska's childhood home is the stage where traumas play out.
Erisolsprite puts it succinctly with his welcome to hell, but pay close attention to what exactly we're being welcomed to: this update ends on page 665. so as of this next update, we'll be starting on page 666.
Does Homestuck Have Hell?
the exact bubble of reality Vriska's currently found herself in seems to be an entirely new construction of the likes we've not yet seen in Homestuck - but that doesn't mean this kind of cosmic torment is without precedent. because while 666 is a number with Satanic connotations in the broader cultural context, it also has a very particular meaning of its own within the world of Homestuck. indeed, the latter half of the comic almost revolves around it, culminating in a climax in Act 6 Act 6 Act 6.
specifically, this repetition of a single digit is emblematic of recursive storytelling. to summarise what you can already read about in detail in my essay The World / The Wheel: when Caliborn is 'gifted' the Act 6 Act 6 supercartridge, which he is told is an "expansion" of Homestuck, it's a trick. there is no "expansion"; he's going to be trapped in a story that never ends because it keeps dividing into smaller and smaller versions of itself forever. the only way to truly beat the devil who trapped the heroes within a story is to trap him in his own story.
that's what Caliborn's "Hell" is, and that's also exactly what the Alternate Calliope achieved in Act 7 by creating the black hole which Vriska knocked Lord English into, ending Homestuck's story - something that Calliope even hints at in this very update, when she refers to the black hole as "containment"; not an accident, but a deliberately crafted prison. black holes are a symbol of recursion and regression; being sucked into one means being forced to live out your whole life over and over again, forever. so really, this is all we ever could have expected to happen when Vriska stepped into a black hole within a black hole! the presentation of the narrative even subtly hints at this; events in Beyond Canon that take place in the black hole are enclosed (in brackets), and now events that take place in a black hole-within-a-black-hole are contained within {curly brackets}, because you should always use a different kind of brackets to differentiate nested parenthesis from each other!
it is absolutely no coincidence that when Caliborn closes the curtains on his appearances in Homestuck, thinking he's won when really he's been condemned to a hell of his own making forever more, it's with a tribute to this exact same Sweet Bro and Hella Jeff strip.

IF YOU REMEMBER JUST ONE THING I SAY, OF SO MANY GREAT THINGS SAID BY ME, THEN PLEASE REMEMBER THIS. I WANTED TO PLAY A GAME.
So What Does That Mean?
one of Beyond Canon's central missions is expanding upon Homestuck's exploration of the relationships between author, text, and audience. as discussed above, a large part of Homestuck's thesis is the evil of forcing characters to live the same lives and the same stories over and over without the chance to grow or move on, and Beyond Canon picks up on this by placing Dirk in the position of trying to keep Homestuck going forever purely to appease its fans, while the Alternate Calliope continues to oppose this ideology. and while the alpha Calliope outwardly seems not to have taken a hard position on where she stands in this cosmic battle, the question posed by her device seems to be an entirely new one: can it actually be a good thing to regress, to return to ground that the story has already covered? can this path lead to something new, rather than merely stagnation?
it's so relevant that Vriska is being confronted with the crimes of her past, not only in the form of all the trolls she was personally responsible for killing but also in the form of the exact same punishment she condemned Lord English to with her heroism - complete with the herd of horses that are always present at Caliborn's demise! but where being condemned to an eternal cycle was fitting punishment for Caliborn, someone who refuses to break free of cycles of abuse and instead chooses to enact that same abuse on the world around him... if Vriska is someone who can break free of these cycles, who can change and become a better person despite what happened to her, will this punishment have the same effect? or, as Davepeta seems to believe, is forcing Vriska to reckon with her own past and traumas exactly what will allow her to break free of that cycle?

DAVE: [...] ill just be over here in the hyper gravity chamber training to beat lord english KARKAT: WE HAVE A HYPER GRAVITY CHAMBER???
it's hard not to be struck by the parallels in design and purpose between the Plot Point and Dragon Ball's Hyperbolic Time Chamber, and not just because of the Dragon Ball enthusiasts present on Beyond Canon's writing and art teams: albeit in typically Strider-bastardised form, the Time Chamber got a shoutout in Andrew Hussie's own Homestuck (see quote above), in a reference that was even picked up on by prolific theorist bladekindeyewear at the time. for the uninitiated: the Hyperbolic Time Chamber allowed its users to train for extended stretches of time, sometimes even spanning years, while a significantly smaller time period passed in the world outside - something that is actually true of real-life black holes! and with the Plot Point's own emphasis on time, represented by the hourglass included among its mechanisms, it seems to me that an essential part of making the 16-year-old Vriska ready for the trials ahead will be giving her the time to undergo the same growth her adult friends have experienced.
considering that Beyond Canon is already playing in the Ultimate Self space, where there are levels of power beyond merely the "god tiers", it also doesn't seem too farfetched to speculate that Vriska, forced to reckon with the fact that becoming a powerful Thief of Light isn't the be-all and end-all of personal growth, will take another leaf out of Dragon Ball's book here and ascend "beyond Super Saiyan". perhaps this is even the "hell tier" so cheekily alluded to in the Plot Point flash? certainly this kind of evolution would be the perfect way to challenge Dirk's belief that the Ultimate Self is the only logical final step for a character's development.
whatever the case, I believe we can take Davepeta at their word here. I don't think it's just a joke that by the end of this ordeal Vriska Serket is going to be fucking RIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIPPPPPPPPPED!
#homestuck#beyond canon#upd8#vriska#vriska serket#davepetasprite#caliborn#black holes#theory#< apparently ive used this tag before but i cant say what for. will have to check later
438 notes
·
View notes
Text


AU where Keith and Lance get sucked into a black hole for eternity.
I have some more stuff about this, like writing ideas about maybe a future fanfic if you wanna read those
#klance#lance mcclain#keith kogane#voltron#voltron legendary defender#vld#vld keith#vld lance#klance fanfiction#black holes#space#outer space#astronomy#cosmos#solar system
164 notes
·
View notes
Text
265 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the constellation of Cygnus, some 7,800 light-years from Earth, lurks a real space oddity. There, a black hole in a system named V404 Cygni repeatedly engages in behavior that has simultaneously baffled and delighted scientists. Now it's whipped a brand new trick out of its seemingly endless arsenal: an unseen binary companion, a star on a wide orbit of around 70,000 years. Since V404 Cygni already has a companion – a star on a close, 6.5-day orbit, on which the central black hole is leisurely feasting – the newly discovered third object makes the system a trinary.
Continue Reading.
260 notes
·
View notes
Text
Before we get into black holes, there are a few myths about them that deserve to be addressed.
First off, they don’t “suck stuff in.” They exert gravity on objects the same as anything else with mass. In fact, if our sun were to be magically replaced, instantly, with a black hole of equal mass, our orbit around it wouldn’t change at all!
Second, that they’re black because their gravitational pull is so large that not even light can escape. This one’s more complicated. Around the singularity, there is a region of space where an observer cannot see “in”, which is called the event horizon. If you’re curious, this region’s size is defined by the black hole’s “Schwarzchild Radius” (Rs), which is defined by the equation Rs = 2GM / (c^2) where G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the black hole, and c is the speed of light.
In simple terms, let’s say we send an astronaut into the black hole. As they approach the event horizon, they experience time passing normally. From their perspective, they fall toward the black hole, through the event horizon, and observe whatever is happening beyond it. But from our perspective as an observer, the astronaut appears to slow down. Gravity affects spacetime, and the farther down a gravity well one goes, the slower time moves. This is actually something that GPS satellites need to account for, because this difference is observably present even for Earth’s gravity!
So as observers, the astronaut’s progress continues to slow as they approach the event horizon, to the point that their progress appears to just stop when they arrive at the edge of it. This is where the astronaut will appear to be, forever…if we could still see them. Light is also affected: it appears to slow down too and its frequency decreases. This decrease of its frequency is called redshift, and as the light approaches the event horizon it redshifts out of observable frequencies. So the astronaut, and the light with which we’d observe them, disappear without ever passing the event horizon from our perspective as observers. Remember, from the astronaut’s perspective they’re moving as normal and they pass through the event horizon just fine. So while, yes light can’t escape the event horizon, we’d never see it pass into it in the first place, and that’s why black holes appear black.
The last misconception, which I’m guilty of spreading in my last post, is that all black holes are infinitely dense. This is true in some cases, but supermassive black holes can actually have very low density! When I can find a satisfying answer as to why, I will be sure to share it lol.
This has become another one of my Very Long Posts, so if you would rather absorb this information in video or audio format, PBS Space Time has an excellent video here which I found very helpful in my understanding. All the material I’ve covered in this post is in this video, actually.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text


A black hole is much more than just an empty void in space—it's a complex structure with distinct regions that define its behavior. Here's an excerpt showing some properties of this celestial body.


Here's a close-up for those who can't see (me)
112 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Dark Matter - Natasha Nanook
128 notes
·
View notes
Text
What if "predator of the universe" were a chill dude?

a small comic below :3 <3 <3 <3🕳🕳🕳


My baby Earth is so cute omg ❤❤❤😭💕
#giant/tiny#g/t#sfw g/t#g/t community#digital art#planet earth#planet humans#black holes#earth chan#wholesome#size difference#gentle giant#g/t fluff
71 notes
·
View notes