#Biosolids Market
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The global biosolids market size was valued at USD 2,321.8 million in 2023 and is poised to grow at a significant CAGR of 4.9% during the forecast period 2024-30. It also includes market size and projection estimations for each of the five major regions from 2024 to 2030.
0 notes
Text
The Middle East Biosolids Market is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 6% during the forecast period, i.e., 2022-27. The majority of the market expansion would be backed by the mounting public awareness about the benefits of biosolids, i.e., portraying their mounting utilization in different applications like agricultural, forest crop, land reclamation, landscaping, recreational fields, heat generation, incineration & gasification, oil & cement production, domestic & commercial uses, etc.
#Middle East Biosolids Market#Middle East Biosolids Market size#Middle East Biosolids Market Share#Middle East Biosolids Market Growth
0 notes
Text
We have just one day left to reach the $20,000 donation match challenge. And we’re only halfway there. Every dollar donated through midnight, December 31 will be doubled. Would you help us take advantage of this once-a-year opportunity to double your impact? Your gift of $5 will become $10. Your gift of $50 will become $100. Your gift of $250 becomes $500. Every single dollar donated helps us get closer to the full match.
Bill Gates donates to expand the GMO and pesticide industry’s grip on our food system. Are you an organic champion able to make a significant donation? If that’s you, please help us reach the full match.
Your donation will help us hit the ground running in 2025.
This is the short list of important issues we will tackle…
advocate for improvements to the National Organic Standards
fight for the accurate labeling of GMO products created with Synthetic Biology or gene-editing
promote seed companies that pledge not to sell GMO seeds
prevent GMO mosquitoes from being sold commercially in the U.S.
advocate for Monarch butterfly protections under the Endangered Species Act
advocate for organic school meals to be served in all U.S. schools
continue to hold corporations accountable for false advertising and misleading marketing through impact litigation/consumer protection lawsuits
advocate for a ban on the use of PFAS-contaminated biosolid fertilizer and compost
advocate for a ban on non-essential uses of PFAS chemicals
advocate for a ban on the use of toxic chemicals in all food packaging
advocate for a ban on the most widely used cancer-causing and endocrine-disrupting synthetic pesticides
advocate for a moratorium on animal factory farms
fight to stop the practice of pre-harvest pesticide desiccation of commodity crops
continue to educate about the toxicity of plastics/microplastics and shift consumer demand toward safe food packaging options
We’ll be educating the public about all of those issues and motivating those we reach to take action by making personal changes, sharing important issues with family and friends, contacting legislators, submitting comments on open regulatory dockets, signing petitions and more.
Our public education efforts played an important role in getting GMO salmon off the menu once and for all. But it took years of campaigning to generate awareness and consumer rejection.
Our first post on social media informing people that AquaBounty’s GMO salmon could be coming was in 2012. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved this first-ever genetically engineered animal for human consumption in 2019. Our announcement of FDA’s approval on Facebook was shared by over 29,000 people and seen by over 2 million, a critical leap toward public awareness.
It took a consistent, ongoing public education effort over many years before we announced this December that AquaBounty finally buckled. Unable to secure a market for their GMO salmon, the corporation announced it was shuttering all operations.
This was a market victory, with people raising their voices and voting with their wallets. GMO/Toxin Free USA played a critical role.
Your gift today will be doubled, ensuring that we have the funds needed to get off to a strong start in 2025. You can help us increase our impact.
We often say, “It takes a village.” That’s the truth. Help us grow our village to be bigger and stronger so we can achieve more victories.
You are very much appreciated.
@upontheshelfreviews
@greenwingspino
@one-time-i-dreamt
@tenaflyviper
@akron-squirrel
@ifihadaworldofmyown
@justice-for-jacob-marley
@voicetalentbrendan
@thebigdeepcheatsy
@what-is-my-aesthetic
@ravenlynclemens
@writerofweird
@bogleech
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text

The NY Times
By Hiroko Tabuchi
For decades, a little-known company now owned by a Goldman Sachs fund has been making millions of dollars from the unlikely dregs of American life: sewage sludge.
The company, Synagro, sells farmers treated sludge from factories and homes to use as fertilizer. But that fertilizer, also known as biosolids, can contain harmful “forever chemicals” known as PFAS linked to serious health problems including cancer and birth defects.
Farmers are starting to find the chemicals contaminating their land, water, crops and livestock. Just this year, two common types of PFAS were declared hazardous substances by the Environmental Protection Agency under the Superfund law.
Now, Synagro is part of a major effort to lobby Congress to limit the ability of farmers and others to sue to clean up fields polluted by the sludge fertilizer, according to lobbying records and interviews with people familiar with the strategy. The chairman of one of the lobbying groups is Synagro’s chief executive.
In a letter to the Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works in March, sludge-industry lobbyists argued that they shouldn’t be held liable because the chemicals were already in the sludge before they received it and made it into fertilizer.
The lobbying has found early success. A bill introduced by Senators John Boozman of Arkansas and Cynthia Lummis of Wyoming, both Republicans, would protect sludge companies like Synagro, as well as the wastewater plants that provide the sludge, from lawsuits. A House bill has also been introduced.
Ms. Lummis will “work with President Trump’s E.P.A. to ensure ‘passive receivers,’ like water utilities and others, are protected from bogus third-party lawsuits,” her office said in a statement, referring to the Environmental Protection Agency.
Synagro and Goldman Sachs declined to answer detailed questions. Synagro in its most recent sustainability reportacknowledged the risks of PFAS contamination in its fertilizer, calling it “one of our industry’s challenges.”
Widespread manufacturing of PFAS began decades ago, with some of the country’s largest chemical companies making vast quantities and downplaying the risks. Water-resistant and virtually indestructible, the chemicals have been used in everything from nonstick pans and dental floss to firefighting gear and waterproof clothing.
Even as PFAS has turned up in wastewater, the government has continued to promote the use of sewage sludge as fertilizer. And while Donald J. Trump’s election raises the prospect that PFAS restrictions might be rolled back, alongside other environmental rules, Synagro is pressing ahead in the effort to protect itself from expensive lawsuits.
The company is already facing all manner of legal challenges. This year a group of ranchers in Johnson County, Texas, stopped sending their cattle to market and sued Synagro for damages after a neighboring farm used sludge fertilizer on its fields. County investigators found 32 types of PFAS in the ranchers’ soil and water. Synagro has contested those allegations.
Residents of San Bernardino County, Calif., have also sued the company, over exposure to PFAS and other pollutants when an open-air pit of biosolids caught fire at a Synagro subsidiary. In October, a cattle farmer in Randolph County, Mo., filed an intent to sue Synagro and another biosolids company, saying the companies had acknowledged that PFAS chemicals may be present in the sludge but continued to provide it to farmers.
“I think it’s terrible,” said Donald Craig, the Missouri farmer, who alongside two local environmental groups is demanding that Synagro cease supplying sludge fertilizer in the state. He and the coalition have also petitioned the state to ban the use of the fertilizer altogether. “It’s disgusting. It needs to be outlawed.”
The current lawsuits against Synagro don’t make claims under America’s Superfund law, which requires corporations to clean up toxic contamination. But that landmark law is likely to be central to future cases, because of the E.P.A.’s decision this year to designate two major kinds of PFAS as hazardous substances under the law. The industry’s lobbying seeks to inoculate Synagro and others from lawsuits, even over decades-old contamination.
“What the biosolids companies are doing is attempting to buy themselves a ‘get out of jail free’ card,” said Mary Whittle, an attorney with Guerrero & Whittle who is representing the Texas ranchers. All this protects a business model that “makes Synagro rich while destroying America’s farmland,” she said.

How PFAS Ended Up on Farmland
The federal government has long encouraged the use of sludge as fertilizer in part because it would otherwise need to be disposed of another way — dumped in landfills, or burned — potentially releasing greenhouse gases and other pollution. In addition, sludge contains nutrients that encourage plant growth, and helps reduce use of fertilizers made from fossil fuels.
But a growing body of research shows that, unbeknown to farmers, fertilizer made from the sewage that flows from homes and factories can contain heavy concentrations of PFAS, which can then contaminate farmland.
It’s difficult to know how much fertilizer sludge is used nationwide, and E.P.A. data is incomplete. The industry says that more than two million dry tons were used on 4.6 million acres of farmland in 2018. And it estimates that farmers have obtained permits to use sewage sludge on nearly 70 million acres, or about a fifth of all U.S. agricultural land.
Researchers have found the chemicals in products as varied as milk, eggs, fruit juice and seafood.
Only one state, Maine, has begun systematically testing agricultural land for PFAS. So far, it has found 68 farms with significant contamination. In 2022, the state banned the use of sludge fertilizer and has since set up a fund to support affected farms.
Lawmakers in Washington are only starting to take notice. The Senate version of a stalled farm bill would have created a $500 million fund to be used to clean up farms, buy out farmers, monitor health, and fund testing for PFAS, essentially shifting the costs onto taxpayers. The fate of the measures, modeled on Maine’s approach, remained unclear.
“It could be that ultimately millions of acres of farmland is contaminated with biosolids, and may no longer be suitable for agriculture unless they are cleaned up,” said Scott Faber, an attorney with the Environmental Working Group and adjunct professor of law at Georgetown University. But there’s another possibility, he said: “They may simply be too expensive to clean up.”
Smelly but Profitable

Sewage sludge is a lucrative business.
When local water utilities treat sewage, and filter out the water, it leaves behind a thick sludge. Companies like Synagro take the sludge from more than 1,000 wastewater facilities in North America, which is then sold as inexpensive fertilizer.
While Synagro does not publicly report financial results, its earnings hit $100 million to $120 million last year, analysts estimated. An investment fund run by Goldman Sachs, West Street Infrastructure Partners III, acquired Synagro in 2020 in a deal reported to be worth at least $600 million.
As concerns over PFAS risks have grown, Synagro has stepped up its lobbying.
In 2022, the company set up a nonprofit, the Coalition of Recyclers of Residual Organics by Practitioners of Sustainability at Synagro’s corporate headquarters, and installed the company’s chief executive, Bob Preston, as chairman, according to the group’s tax filings. Since its founding, the group has spent $220,000 on federal lobbying, disclosure forms show.
In a statement, the nonprofit said the bills it lobbied for would “ensure liability resides with the manufacturer of these chemicals.”
Mr. Trump’s return to office introduces a new complication: The E.P.A.’s designation of some PFAS as hazardous under the Superfund law could be rolled back. Project 2025 calls for removing the hazardous-substance designation, and a major industry group has challenged the E.P.A.’s move in court.
Ryan McManus, government-affairs manager at the American Public Works Association, which represents water utilities and wastewater-treatment plants nationwide, and which has been key player in the effort to lobby Congress, said his group remained “very focused on a legislative solution because ultimately you could have another administration four years from now that decides to reverse course.”
Risks Hidden for Years

The argument that sludge companies aren’t liable because the chemicals were already in the sludge is based on the fact that PFAS manufacturers for years had minimized the dangers. Lawsuits, news articles and peer-reviewed research have chronicled how chemical giants 3M and DuPont, the original manufacturers of PFAS, for decades hid evidence of the chemicals’ dangers.
The chemicals are now so ubiquitous in the environment that nearly all Americans carry PFAS in their bloodstream. As many as 200 million Americans are exposed to PFAS through tap water.
In a statement, 3M said it was starting to exit PFAS manufacturing.
Under a sweeping settlement last year, 3M is paying $10 billion to cities and counties to test for and clean up PFAS in public water supplies. The E.P.A. has said that almost no level of exposure is safe, and this year imposed strict limits on drinking-water contamination for six types of PFAS.
Synagro and the sewage plants say they are simply at the end of that chain of contamination. We “do not manufacture or profit from PFAS,” Michael Witt, general counsel at Newark’s Passaic Valley Sewerage Commission, said at a hearing this year. “Industry did that.”
But critics point to research that for years has detected PFAS in wastewater. Recent studies have also explored how the chemicals can move from the soil into water and plants, and then to the livestock that feed on them.
Regarding Synagro, “it seems crazy to be able to say they’re a passive receiver and they shouldn’t be liable, that they know it’s harmful but they’re going to continue to sell it,” said Laura Dumais, an attorney with Public Employees for Environmental Responsibility, a group that assisted the Texas ranchers with PFAS testing. “It’s like CVS selling a tainted medicine and saying, ‘We can’t be liable and we’re just going to continue to sell it.’”
Wastewater treatment plants say they are finding it increasingly difficult to find landfills to accept sludge, partly because landfill operators are themselves wary of contamination. “They don’t want their landfill to potentially become a Superfund site,” said Mr. McManus of the public-works association.
‘They’re Not Even Aware’

The E.P.A. continues to promote sludge as fertilizer. It regulates harmful pathogens and some heavy metals in biosolids, but not PFAS. The agency is working on a risk assessment that it intends to release this year, the first step in determining whether new standards are necessary.
Some farming groups support the Senate bill, saying it would also offer them protection against potential lawsuits. “Your neighbor or anybody out there could sue you for the price of a postage stamp,” said Courtney Briggs, senior director for government affairs at the American Farm Bureau. Farmers, she said, are “victims, and often they’re not even aware” of the danger.
But experts point out that the Superfund law already exempts farmers from cleanup responsibilities. So farmers would gain little, while becoming unable to themselves sue, Mr. Faber said.
Neither can farmers easily sue the PFAS manufacturers, unless there is evidence that the manufacturer intended for the chemicals to be released onto farmland, Kate R. Bowers, legislative attorney at the Congressional Research Service, testified at a recent hearing.
That leaves ranchers like Tony Coleman, one of the plaintiffs in the Texas case against Synagro, in limbo. They have now taken legal action against the E.P.A., saying that it failed to properly regulate PFAS in fertilizer. The agency is pushing to dismiss the lawsuit.
https://www.nytimes.com/2024/12/06/climate/sludge-fertilizer-synagro-lobbying.html?searchResultPosition=2
0 notes
Text
There is a call-to-action at the end of this article. Please don’t leave without taking action! Thank you!
What Are Biosolids?
“Biosolids” is the word waste treatment industry marketers came up with to rebrand sewage sludge, the solid byproduct of wastewater treatment processes. The reason the industry needed to rebrand sewage sludge was because they planned on marketing and selling the nutrient-rich waste to farmers and home gardeners as cheap fertilizer and compost products.
But biosolids aren’t just rich in nutrients. Biosolids can contain high levels of toxic PFAS “Forever Chemicals” (perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances) that aren’t removed during the waste treatment process. And neither are the phthalates, pesticides, PCBs, antibiotics and other pharmaceuticals, microplastics, heavy metals, and innumerable other harmful substances that have been found in biosolids.
Applications of biosolids contaminate the soil with toxic PFAS and other chemicals, which are then taken up by crops grown in that soil. PFAS also migrates to contaminate groundwater and surface waters. The meat, milk and eggs of livestock become contaminated when the animals consume adulterated crops and water.
The biosolids industry and the commercial fertilizer and compost companies that use biosolids continue to claim that the products are safe and non-toxic. Even municipalities have been giving out biosolids fertilizer and compost to farmers, community gardens, and home gardeners for free, without warning about the dangers.
Unfortunately, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), though aware of the problem, still allows the commercialization of toxic biosolids. Just as alarming, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) actively promotes the use of biosolids as fertilizer to commercial farmers. We suspect this is due to the revolving door and corporate capture of our regulatory agencies and the resulting collusion, favoring corporate profits over human or environmental health.
In 2022, Sally Brown, Research Professor at the University of Washington and veteran biosolids industry lobbyist, was selected by USDA Secretary Tom Vilsack to serve on USDA’s inaugural Advisory Committee for Urban Agriculture.
Sally Brown once called environmental activists “ecoterrorists” for a successful protest on March 4, 2010, that stopped the San Francisco Public Utilities Commission from giving away sewage sludge as “organic biosolids compost” for home and school gardens.
As you’ll soon read, it’s Sally Brown that is the ecoterrorist for promoting biosolids.
Biosolids Poisoning Farms and Farmers Across America
The practice of using biosolids as fertilizer on conventional farms has been happening for decades but has, more recently, turned into a national catastrophe, creating a crisis for farmers and ranchers across the country.
Although the use of biosolids as fertilizer is prohibited in organic agriculture, even organic farms have been hit hard.
March 22, 2022, The Guardian reported:
Maine organic farmers Johanna Davis and Adam Nordell bought Songbird Farm in 2014. By 2021 the young family with their three-year-old son were hitting their stride, Nordell said. But disaster struck in December. The couple learned the farm’s previous owner had decades earlier used PFAS-tainted sewage sludge, or “biosolids”, as fertilizer on Songbird’s fields. Testing revealed their soil, drinking water, irrigation water, crops, chickens and blood were contaminated with high levels of the toxic chemicals. The couple quickly recalled products, alerted customers, suspended their operation and have been left deeply fearful for their financial and physical wellbeing. “This has flipped everything about our lives on its head,” Nordell said. “We haven’t done a blood test on our kid yet and that’s the most terrifying part. It’s f#####g devastating.” Ironwood Organic Farm, about six miles from Songbird Farm, tested its water and found high levels suspected to have migrated from a neighbors’ sludge-packed field. The small produce farm pulled its products, halted operations and is nervously awaiting more test results. “I spent my entire adult life building this farm,” said Nell Finnigan. “Everything is at stake for us, and this is a tragedy for anyone who comes up with a high [groundwater] well test.” Stoneridge Farm, a small dairy operation more than 100 miles south of Songbird Farm, discovered in 2016 that sludge and paper mill waste used as fertilizer had probably contaminated its cows and milk. Stoneridge killed most of its livestock in 2019. Co-owner Fred Stone was denied federal assistance for his tainted milk because one of its milk tests came in just below the state’s limit, but Stone didn’t feel comfortable selling it. Now his family of four, which believes PFAS is behind their health ailments from thyroid disease to reproductive problems, survives on welfare and friends’ and family’s generosity. Stone said he could have continued to sell contaminated food: “This is the cost of having a moral compass and doing the right thing.” “I don’t know how we are going to get debts paid,” he added. “I don’t know how the Christ we are going to live. I don’t know how we’re going to survive.”
...
March 11, 2024, KCUR reported:
“This is a hundred-year-old operation,” Jason Grostic said. “My grandpa milked cows, my dad milked cows, I milked cows, (then) got into the beef industry. It’s in my blood.” But Grostic may be at the end of the line. Two years ago, he was blindsided when the state of Michigan ordered him to shut down his farm, citing high levels of PFAS in both his beef and soil. Grostic had been using biosolids, a treated byproduct from wastewater plants, to fertilize his crops, which he then fed his cattle. But what he thought was a cost-effective fertilizer, turned out to be laden with PFAS. It’s a risk, Grostic said, no one warned him about — and now his 400-acre farm has been deemed unusable. “I took a fertilizer source that was recommended and was EPA-approved, and the government dropped the ball by not testing it and assuring it was a clean product,” he said.
We encourage you to watch the VICE Special Report, “The Hidden Chemicals Destroying American Farms,” a year long investigation featuring Jason Grostic and his experience with biosolids and PFAS. It will shock you.
#ecology#enviromentalism#Biosolids#Waste treatment industry#pfas#forever chemicals#farming#organic farming#farm animals#livestock industry
1 note
·
View note
Text
Agricultural Testing Market Trends, Size, Share, Growth Opportunities, and forecast 2028
The global agricultural testing market is projected to reach USD 9.8 billion by 2028 from USD 6.7 billion by 2023, at a CAGR of 7.1% during the forecast period in terms of value. The agricultural testing market encompasses the industry dedicated to analysing various agricultural products such as soil, water, compost, biosolids, manure, and seeds to assess their quality, composition, and contaminant levels. This testing is essential for ensuring food safety, optimizing crop production, and maintaining environmental sustainability within the agriculture sector. As the global population grows and concerns about foodborne illnesses increase, there is a heightened focus on ensuring the safety and quality of agricultural products. Agricultural testing helps identify contaminants, pesticides, heavy metals, and pathogens, enabling proactive measures to uphold food safety standards. Advances in testing methods and technologies, including remote sensing, DNA testing, and rapid diagnostic techniques, have enhanced the efficiency and accuracy of agricultural testing, streamlined the process and reducing turnaround times.

Agricultural Testing Market Driver: Stringent safety and quality regulations for agricultural commodities
Stringent safety and quality regulations for agricultural commodities are the rules and standards established by regulatory bodies and governments to ensure that agricultural products adhere to specific safety and quality criteria. These regulations aim to protect public health, prevent the spread of diseases, and maintain the overall quality of agricultural products. The agriculture testing market is driven by the necessity to comply with these regulations. Agricultural producers, processors, and exporters must demonstrate that their products meet the established safety and quality standards before they can be sold in domestic or international markets. This requirement generates a demand for agriculture testing services, fueling the growth of the agriculture testing market.
Agricultural Testing Market Opportunities: Technological advancements in the testing industry
The focus on reducing lead time, sample utilization, cost of testing, and drawbacks associated with several technologies has resulted in the development of new technologies such as spectrometry and chromatography. Increased adoption of these technologies is an opportunity for medium- and small-scale laboratories to expand their service offerings and compete with large market players in the industry, as these technologies offer higher sensitivity, accuracy in results, reliability, and multi-contaminant and non-targeted screening with low turnaround time, among other benefits.
The agricultural testing industry is experiencing technological innovations as major players are offering faster and more accurate technologies such as liquid chromatography (LC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) for testing the safety and quality of various agricultural samples. These methods are used in the detection of almost all targets to be tested, including pathogens, pesticides, toxins, and heavy metals, among others. One company that has made significant advancements in this area is AgroCares. In 2019, AgroCares launched the AgroCares Scanner, a handheld device that can analyze soil and crop samples on-site, providing real-time nutrient measurements. The device uses near-infrared spectroscopy to assess nutrient levels in the samples, eliminating the need for laboratory testing and reducing the time required to get results. Also, in 2021, the company Purigen Biosystems announced the launch of its new automated DNA extraction system, which is designed to help researchers and testing labs quickly and efficiently extract DNA from complex samples, including those from plants and other agricultural sources. The system uses a proprietary microfluidic technology to isolate and purify DNA and can process up to 96 samples at a time. Also in 2021, the company Eurofins announced the launch of its new "AgroSeq" DNA testing service, which is designed to help agricultural companies and researchers quickly and accurately identify and track genetic traits in crops and livestock. The service uses high-throughput sequencing technology to analyze DNA samples and provide detailed information about genetic variation, which can be used to improve breeding programs, monitor food safety, and more.
Download PDF Brochure: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=203945812
By application, safety testing is projected to have fastest growing rate during the forecast period.
Products are governed by various national and international regulations, standards, and guidelines. To comply with these regulations and ensure that products meet the specified safety criteria, safety testing is essential. Non-compliance can lead to product recalls, legal issues, reputational damage, and loss of market access. By conducting safety testing, agricultural businesses demonstrate their commitment to regulatory compliance and the provision of safe products to consumers.
Since agricultural products are frequently traded internationally, they must meet the safety standards and import regulations of different countries. Exporting agricultural products necessitates compliance with the safety requirements of the destination market. Safety testing ensures that products meet these standards, helping to avoid trade barriers or rejections. Exporters must provide evidence of safety testing to prove their products' suitability for international markets.
Asia Pacific is expected to have the fastest growing rate during the forecast period.
The Asia-Pacific region is home to a significant portion of the global population, including countries like China and India, which have the world's largest populations. This densely populated region requires extensive agricultural production to meet the growing food demand. As a result, there is a greater need for agricultural testing to ensure the safety, quality, and productivity of agricultural products. The Asia-Pacific region has experienced rapid industrialization and urbanization, leading to increased pollution and pressure on agricultural lands. This has raised concerns about the impact of industrial activities and urban expansion on agricultural productivity and safety. Agricultural testing helps identify and mitigate potential contamination risks, ensuring the safety and sustainability of agricultural practices in the face of urban development.
Top Companies in the Agricultural Testing Market
The key players covered in the study include SGS (Switzerland), Eurofins (Luxembourg), Intertek (UK), Bureau Veritas (France), ALS Limited (Australia), TUV Nord Group (Germany), Merieux (US), AsureQuality (New Zealand), RJ Hill Laboratories Limited (New Zealand), SCS Global (US), Agrifood Technology (Australia), APAL Agricultural Laboratory (Australia), Agvise Laboratories (US), LGC Limited (UK) and Water Agricultural Laboratories (US).
#Agricultural Testing Market#Agricultural Testing Market Size#Agricultural Testing Market Share#Agricultural Testing Market Growth#Agricultural Testing Market Trends#Agricultural Testing Market Forecast#Agricultural Testing Market Analysis#Agricultural Testing Market Trpoty#Agricultural Testing Market Scope#Agricultural Testing Market Overview#Agricultural Testing Market Outlook#Agricultural Testing Market Drivers#Agricultural Testing Industry#Agricultural Testing Companies
0 notes
Text
Agricultural Testing Market Growth Rate, Analysis Status, Outlook And Forecast
The agricultural testing market is projected to reach USD 9.8 billion by 2028 from USD 6.7 billion by 2023, at a CAGR of 7.1% during the forecast period in terms of value. The agricultural testing market refers to the industry involved in analyzing various agricultural products, such as soil, water, compost, biosolids, manure and seeds, to determine their quality, composition, and presence of contaminants. This type of testing is crucial for ensuring food safety, optimizing crop production, and maintaining environmental sustainability in the agriculture sector. With the growing global population and rising concerns about foodborne illnesses, there is a greater emphasis on ensuring the safety and quality of agricultural products. Testing helps identifying contaminants, pesticides, heavy metals, and pathogens, enabling proactive measures to be taken to maintain food safety standards. The development of advanced testing methods and technologies has improved the efficiency and accuracy of agricultural testing. These advancements include the use of remote sensing, DNA testing, and rapid diagnostic techniques, which have streamlined the testing process and reduced turnaround times.
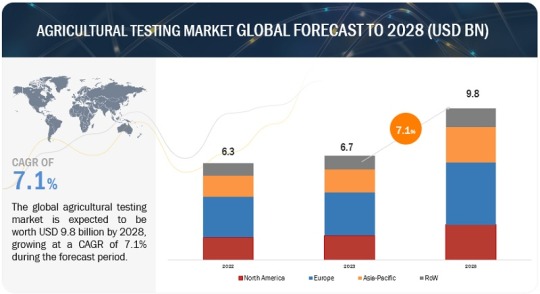
Download PDF Brochure: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=203945812
Opportunity: Technological advancements in the testing industry
The focus on reducing lead time, sample utilization, cost of testing, and drawbacks associated with several technologies has resulted in the development of new technologies such as spectrometry and chromatography. Increased adoption of these technologies is an opportunity for medium- and small-scale laboratories to expand their service offerings and compete with large market players in the industry, as these technologies offer higher sensitivity, accuracy in results, reliability, and multi-contaminant and non-targeted screening with low turnaround time, among other benefits.
By application, safety testing is projected to have fastest growing rate during the forecast period.
products are subject to various national and international regulations, standards, and guidelines. Safety testing is necessary to comply with these regulations and ensure that products meet the specified safety criteria. Non-compliance can result in product recalls, legal consequences, damage to reputation, and loss of market access. By conducting safety testing, agricultural businesses can demonstrate their commitment to meeting regulatory requirements and providing safe products to consumers. Also, agricultural products are often traded internationally, and different countries have specific safety standards and import regulations. Exporting agricultural products requires compliance with the safety requirements of the destination market. Safety testing is necessary to ensure that products meet these standards and avoid potential trade barriers or rejections. Exporters must provide evidence of safety testing to demonstrate the suitability of their products for international markets.
Make an Inquiry: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Enquiry_Before_BuyingNew.asp?id=203945812
Asia Pacific is expected to have the fastest growing rate during the forecast period.
The Asia-Pacific region is home to a significant portion of the global population, including countries like China and India, which have the world's largest populations. This densely populated region requires extensive agricultural production to meet the growing food demand. As a result, there is a greater need for agricultural testing to ensure the safety, quality, and productivity of agricultural products. The Asia-Pacific region has experienced rapid industrialization and urbanization, leading to increased pollution and pressure on agricultural lands. This has raised concerns about the impact of industrial activities and urban expansion on agricultural productivity and safety. Agricultural testing helps identify and mitigate potential contamination risks, ensuring the safety and sustainability of agricultural practices in the face of urban development.
0 notes
Text
Bonita Springs Water Reclamation Facility

Photo taken by me.
The Bonita Springs East Water Reclamation Facility is a wastewater treatment plant that is leading its industry in sustainable practices. Up to 4 million gallons of sewage are processed at this facility every day, and the sewage is turned into new products that are sold to generate revenue for the plant. The process begins when water from drains all around the Bonita Springs area reaches the water reclamation facility through underground pipes. Large materials are removed from the water using a coarse drum screen before it reaches the equalization tank. The equalization tank serves the purpose of treating the sewage at a continuous rate as well as aerating the sewage to reduce malodors. The sewage is then moved through a finer drum screen to remove smaller solids, which are taken to a landfill. Next is the denitrification stage, which occurs inside the anoxic basin. The book “Sustainability Principles and Practice” explains that “some anaerobic bacteria can metabolize some kinds of contaminants that cannot be broken down by aerobic bacteria (Alexander 1999, 369). It is anaerobes who digest food in animal digestive tracts, sewage in wastewater treatment tanks, and buried matter in landfills” (Robertson, 2021, pp. 190-191). Indeed, anaerobic microorganisms are used at the wastewater treatment plant to consume any organic material in the sewage. From the anoxic basin, the water moves into the aerobic basin, where microorganisms use the oxygen in the basin for energy to convert ammonia in the sewage into nitrate and nitrite ions. Next, the water moves through Veolia membranes, which are long fibers with microscopic pores that filter all impurities out of the water. The next steps in the process turn the reclaimed water into products that are profitable for the facility.

Photo taken by me.
According to the textbook, “One industrial ecology strategy sets up closed-loop “food webs” among industries, where output from one industry is input for another and materials are reused. These networks of exchanges are sometimes referred to as industrial symbiosis or industrial metabolism. A complex of industrial facilities that applies these principles in an industrial ecosystem is referred to as an eco-industrial park” (Robertson, 2021, p. 344). The Bonita Springs East Water Reclamation Facility is a great example of a chain in one of these eco-industrial parks. After passing through the membrane basins, the remaining biosolids in the wastewater are mixed with polymers, thickened, and heated, evaporating the remaining water and turning the biosolids into small pellets. These pellets are marketed as fertilizer and make money for the wastewater treatment plant. The recovered water is disinfected using sodium hypochlorite and sent to a water pump station, where it is sold as irrigation water to businesses such as golf courses. Wastewater facilities like this one face many challenges, including excessive amounts of nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, limiting the energy used by the plant to run its operations, and limiting the release of endocrine disruptors into the environment. Despite these challenges, the Bonita Springs East Water Reclamation Facility has found a sustainable way to turn “waste” into profitable products that are in high demand by other industries.

Photo taken by me.
References:
Robertson, M. (2021). Sustainability Principles and Practice (3rd ed.). Taylor & Francis Group.
0 notes
Text
Water and Wastewater Treatment Equipment Market: Financial Outlook, Investments, and Financing Trends 2023
The water and wastewater treatment equipment market has seen rapid growth in recent years driven by increasing global demand for clean water, more stringent regulations, and technological advancements. This market is poised for continued expansion as communities and industries seek to upgrade aging infrastructure and invest in innovative new systems.
The Global Water and Wastewater Treatment Equipment Market is expected to attain a value of USD 69.9 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to grow with a CAGR of 4.9% for the forecast period (2023-2032).
An Overview of the Water and Wastewater Treatment Industry
The water and wastewater treatment industry is vital in providing clean and safe water for drinking, agriculture, industry, recreation, and more. This sector involves complex processes to remove contaminants from water and wastewater before discharge into the environment.
Companies in this industry manufacture specialized equipment like pumps, valves, filters, membranes, disinfectants, and control systems. They also provide critical services such as system design, engineering, construction, operations, and maintenance. The water and wastewater treatment equipment market includes both municipal and industrial customers.
Key drivers of growth in this industry are:
Increasing global population and water scarcity
Aging water infrastructure in developed nations
Stringent governmental regulations on water quality and wastewater discharge
Industrialization and increased manufacturing activity
Technological improvements enabling more efficient systems
Increased environmental awareness and sustainability initiatives
Take a look at the Free Sample PDF: https://dimensionmarketresearch.com/report/water-and-wastewater-treatment-equipment-market/requestSample.aspx
Key Equipment and Technology Segments
The water and wastewater treatment equipment market can be divided into several key technology and equipment segments:
Pumps and valves control the flow of liquids through treatment systems
Filtration systems remove solids through technologies like sand filtration, microfiltration, and reverse osmosis
Disinfection systems inactivate disease-causing microorganisms and can use chlorine, UV light, or ozone
Sludge treatment reduces volume and allows for biosolids reuse through processes like digestion, dewatering, and drying
Instrumentation includes sensors, analyzers, SCADA, and control systems to monitor and automate processes
Chemical dosing systems deliver coagulants, disinfectants, pH adjusters, and other process chemicals
Membrane systems use ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis to filter contaminants
Screening systems remove large debris and solids at intake points
Market Segmentation
By Equipment
Primary Treatment
Primary Clarifier
Sludge Removal
Grit Removal
Pre-Treatment
Others
Secondary Treatment
Activated Sludge
Sludge Treatment
Others
Tertiary Treatment
Tertiary Clarifier
Filters
Chlorination systems
Others
By Application
Industrial
Municipal
Have any Queries? Talk to Research Expert: https://dimensionmarketresearch.com/enquiry/water-and-wastewater-treatment-equipment-market.aspx
Key Factors Driving Market Growth
Several important factors are contributing to the continued growth and opportunities in the global water and wastewater treatment equipment market:
Increasing Population and Water Scarcity Issues
The world's population is expected to reach 8.5 billion by 2030, intensifying demand for freshwater and wastewater treatment in both developing and developed countries. Water scarcity already affects over 1.7 billion people globally. These trends will drive infrastructure and technology investments to access new water sources and maximize reuse.
Aging Infrastructure in Developed Nations
Many drinking water and sewage systems in the U.S., Europe, and Japan are approaching or exceeding their design lifespans. Upgrading outdated equipment and pipes to meet stricter regulations will be a major market driver. The EPA estimates over $400 billion is needed to maintain and improve U.S. drinking water infrastructure over the next 20 years.
Stringent Government Regulations
Tightening regulations worldwide for safe drinking water and proper wastewater disposal require upgrades to treatment methods and systems. For example, the U.S. Clean Water Act has set higher standards for allowable wastewater discharge levels that require added treatment capacities.
Increased Industrial Water Usage
Rapid industrialization in developing nations is expanding the number of manufacturing plants which require process water treatment and wastewater management. The power industry is another major sector demanding advanced water and wastewater treatment.
Water Reuse Opportunities
As freshwater supplies become scarcer, reuse of treated wastewater is growing. Equipment that can cost-effectively treat wastewater to potable standards is a promising new market segment. Industries are also increasing on-site water reuse with closed loop recycling systems to lower costs and improve sustainability.
Advances in Treatment Technologies
New membrane materials, UV and ozone disinfection methods, automation, and data analytics are enhancing treatment efficiencies. Companies are developing smarter systems controlled with artificial intelligence, remote sensors, and software to optimize operations and lower energy use. These technologies provide sales opportunities as customers upgrade systems.
Purchase This Premium Report Now: https://dimensionmarketresearch.com/checkout/water-and-wastewater-treatment-equipment-market.aspx
Regional Outlook
The Asia Pacific region dominates the water and wastewater treatment equipment market in 2023 with a maximum share of 35.9%. This region is anticipated to further lead the market with a high compound annual growth rate by 2032. This growth is majorly driven by the rising consciousness among customers & various sectors regarding the benefit of conservation of water & protection of the environment in the Asia-Pacific region. As a result, the need & desire for water & wastewater treatment equipment is observing a substantial rise.
Leading Corporations Driving the Market
Pentair plc.
Ecolab Inc.
Xylem Inc.
Evoqua Water Technologies LLC
DuPont
Aquatech International LLC
Veolia Group
Evonik Industries AG
Calgon Carbon Corporation
Toshiba Water Solutions Private Limited
Lenntech B.V.
Other
Key Industry Challenges
While the future looks bright overall for the water and wastewater treatment equipment market, there are some persistent challenges:
High Capital Costs - Constructing modern water and wastewater plants requires major capital investments that can be prohibitive for smaller municipalities and companies. Obtaining financing and government support are crucial for many projects.
Increasing Energy Usage - More advanced treatment systems generally consume greater amounts of energy. Optimizing processes to minimize energy requirements is an ongoing focus area.
Waste Disposal Issues - Disposing of landfill waste and brines from membrane systems is becoming more difficult and costly due to regulations. Further treatment of residuals is often needed.
Lack of Trained Operators - The skilled labor needed to properly operate and maintain complex new treatment systems is lacking in some regions, especially developing countries. Better training programs are essential.
Lagging Infrastructure in Developing Nations - Many developing countries still lack basic water and wastewater infrastructure. This hampers industrial growth and public health. Financing these massive investments remains a hurdle.
Climate Change Resiliency - Making water and wastewater infrastructure more resilient to droughts, floods, and other climate change effects represents a new challenge for the sector.
Addressing these issues will be instrumental as communities work to upgrade critical water and wastewater treatment infrastructure worldwide. Technologies and designs that minimize costs and energy while maximizing reliability will be favored.
Take a look at the Free Sample PDF: https://dimensionmarketresearch.com/report/water-and-wastewater-treatment-equipment-market/requestSample.aspx
Water Treatment Equipment - Future Innovations
Engineering and technology innovations in the water treatment equipment market aim to lower costs, improve efficiencies, and expand treatment capabilities. Some key areas for future innovations include:
Hybrid membrane systems - Combining two or more membrane technologies like ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis can optimize contaminant removal and lower fouling issues.
New antifouling materials - Membrane fouling costs the industry billions annually. New nanotech and biomimetic membrane materials resist fouling better for longer membrane life.
Improved oxidation methods - Ozone, UV, and other oxidation processes minimize chemical use but have high energy demands. New catalytic oxidation methods are being developed.
** Biosorption adsorbents** - Low-cost biosorbents derived from chitosan, cellulose, algae and other renewable sources can replace activated carbon for some applications.
Mobile and modular plants - Containerized and skid-mounted systems allow for cost-effective water treatment in remote locations and decentralized facilities.
Automation and AI - Expanding real-time sensing, system controls, machine learning, and artificial intelligence improve plant performance, minimize costs, and reduce staffing needs.
Renewable energy integration - On-site renewable energy such as solar, wind, and biogas integration can offset plant energy demands to lower costs and emissions.
Improved remote monitoring - Drone and satellite data, inexpensive sensors, and cloud-based solutions help monitor source water conditions and assets across remote distribution networks.
These emerging technologies will alter the future competitive landscape as companies integrate more advanced capabilities into new equipment and services.
Outlook for Water Reuse Systems
Growing water scarcity globally is driving greater adoption of water reuse technologies allowing treated wastewater to be safely reused for irrigation, industry, potable supplies, groundwater recharge and more. The equipment market for water reuse is estimated to grow 10% yearly over the next decade, reaching over $30 billion by 2030.
Some key trends shaping technology developments in this area include:
Equipment allowing direct potable reuse with multiple treatment barriers such as membrane bioreactors, reverse osmosis, UV disinfection, and advanced oxidation.
More cost-effective and compact systems for on-site greywater reuse and rainwater harvesting.
Improved real-time sensors, automation, and data analytics for smarter operation and control of reuse systems.
New selective membranes and absorbers to remove trace contaminants and salts from reused water cost-effectively.
Hybrid centralized decentralized facilities combine large-scale reuse with localized satellite plants.
Concentrate treatment and zero liquid discharge systems to maximize recovery and minimize waste volumes.
Public outreach and regulatory initiatives to increase acceptance and expand allowable applications of reused water.
With water reuse often the most reliable and cost-effective new supply option, this sector provides excellent opportunities but also requires overcoming public perceptions and regulatory hurdles.
Have any Queries? Talk to Research Expert: https://dimensionmarketresearch.com/enquiry/water-and-wastewater-treatment-equipment-market.aspx
Key Takeaways and Market Outlook
Global demand for water and wastewater treatment equipment is forecast for steady long-term growth, driven by population increases, aging infrastructure, stringent regulations, industrialization, and water scarcity issues.
Municipal drinking water and sewage treatment represent major market segments, especially in developed nations.
Rapid urbanization and water-intensive industries will drive faster growth in developing regions like China, Southeast Asia, and Africa.
Leading multinational firms hold advantages in R&D and integrated treatment systems, but niche players still thrive in specialty segments.
Reuse equipment is an emerging high-growth segment as communities increasingly adopt recycled wastewater systems.
Technological improvements and innovative new equipment will be critical for minimizing costs while meeting tougher treatment standards.
In closing, the water and wastewater treatment equipment market offers tremendous business opportunities on a global scale for companies at the forefront of developing cost-effective, reliable and high-performance systems. With clean water scarcity being one of the defining challenges of the 21st century, the importance and growth prospects in this industry remain strong.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main segments in the water and wastewater treatment equipment market?
The main segments are pumps, valves, filters, membrane systems, disinfection equipment, instrumentation and controls, sludge treatment systems, and chemical dosing and feeding technologies. Municipal drinking water and wastewater plants represent the largest market segment, followed by industrial process water and wastewater treatment.
What regions offer the best growth opportunities?
Developing countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America have the greatest growth potential due to high population growth, rapid urbanization, and industrial expansion driving massive new investments in water and wastewater infrastructure.
What are the new technological trends in this market?
Top trends are automation, remote monitoring and control, AI-enabled smart systems, renewable energy integration, advanced membranes and filtration media, improved oxidation processes, and mobile/modular equipment. Reuse systems are also an important emerging segment.
What factors affect market competition and pricing?
Competitive factors include product differences, custom engineering capabilities, R&D investments, manufacturing costs, regional market presence, and service/support infrastructures. Pricing is also strongly influenced by raw materials and energy pricing fluctuations.
What are the main industry challenges ahead?
Challenges include aging infrastructure, high upgrade/expansion costs, increasing energy demands, climate change resiliency, lack of technical skills, and financing struggles in developing countries. Managing residuals and brines and improving public perceptions of reused water are also issues.
What role will technology and innovation play in future growth?
New technology development is essential for minimizing costs, energy and chemical use, waste volumes, and environmental impacts while maximizing reliability, reuse potential, and operational simplicity. Companies at the forefront of the latest advances will gain competitive advantages.
How big is the global water equipment market projected to be by 2025?
The Global Water and Wastewater Treatment Equipment Market is expected to attain a value of USD 69.9 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to grow with a CAGR of 4.9% for the forecast period (2023-2032). The fastest growth will be in developing countries undergoing rapid urbanization and industrialization.
Get Free Sample PDF: https://dimensionmarketresearch.com/report/water-and-wastewater-treatment-equipment-market/requestSample.aspx
Conclusion
The water and wastewater treatment equipment market is poised for steady growth in the coming decades driven by fundamental global trends of population growth, water scarcity, environmental regulations, aging infrastructure, and socioeconomic development. While expansions in developing nations represent major opportunities, replacement and upgrades of aging plants and distribution systems in developed countries also contribute significantly to market size.
Technological innovation and expertise will be key differentiators as companies compete to deliver more efficient, reliable, and cost-effective treatment solutions. Leaders able to leverage the latest advances in membrane systems, filtration media, UV disinfection, oxidation processes, automation, remote monitoring, and data analytics will be well-positioned. The market also presents opportunities to apply reuse systems and decentralized solutions for water-stressed regions.
Overall, the future remains bright for companies participating in this essential industry, although challenges like high costs, energy demands, and environmental constraints must continually be overcome. By providing clean water supply and wastewater treatment solutions, companies in this sector make invaluable contributions worldwide to public health, economic prosperity, and environmental sustainability.
Contact us:
United States 957 Route 33, Suite 12 #308 Hamilton Square, NJ-08690 Phn. No: +1 732 369 9777 Mail: [email protected]
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Mexico Biosolids Market Growth and Share 2021-2025 [ 2023 UPDATE Available – Forecast 2023-2030*]
The global biosolids market is witnessing exponential growth as it offers an effective solution for reusing waste material and addressing the challenges of wastewater treatment. According to recent statistics, the market was valued at US$1.4 billion in 2018 and is projected to reach US$1.9 billion by 2025, growing at a healthy rate of 4.7% between 2021 and 2025.
Access Full Report: https://www.fairfieldmarketresearch.com/report/global-biosolids-market

With over 35 million tonnes of biosolids produced globally in 2018, this industry is gaining momentum worldwide.
In 2018, Europe accounted for more than 25% of the global biosolids consumption, while the United States emerged as the largest producer in North America, primarily utilizing biosolids for land application. However, countries in the Asia Pacific region, such as China and India, are making significant investments in sludge management strategies and exploring alternative treatment and disposal methods to mitigate the adverse environmental impact. As a result, China is expected to surpass North America in the near future, supported by its substantial investments in wastewater treatment technologies.
Biosolids are organic materials derived from the treatment of domestic and industrial sewage sludge. They offer a valuable resource for agriculture as wastewater sewage contains nutrients that can be used for agricultural purposes. Class A and Class A (EQ) biosolids, which are pathogen-free and meet stringent standards set by regulatory bodies, are gaining popularity among customers. It is estimated that together they will account for more than 50% of the total biosolids market by the end of the forecast period.
Agriculture constitutes the largest application segment for biosolids, accounting for over 60% of the market in 2018. Biosolids are rich in micro and macro nutrients, making them an excellent source of fertilizers, soil replacement products, and soil conditioners. Additionally, biosolids find applications in forestry and landscaping, land reclamation, construction materials, and heat generation.
Governments around the world are actively supporting biosolids management programs as part of the circular economy. Strict regulations on wastewater and waste disposal, along with the phasing out of landfilling and incineration, are driving the demand for biosolids. Recycling biosolids into agriculture offers benefits such as carbon recycling and the nourishment of vegetation for CO2 capture. The United Kingdom government and the European Union recognize the recycling of biosolids into agriculture as the best environmental option.
Despite the numerous benefits of biosolids, challenges persist in terms of malodour and effective management. Odor issues have created negative publicity in recent years, necessitating public support and awareness to ensure the success of biosolids programs. Furthermore, transportation costs and capital limitations for new plants pose challenges to market growth.
Leading companies in the global biosolids market, including Cleanaway, SUEZ, Veolia, and Thames Water, have integrated their business operations and are offering comprehensive solutions in their respective regions. These companies are also exploring partnerships with fertilizer companies to develop new application avenues. The industry is witnessing the emergence of disruptive technologies, with companies like Aries Clean Energy receiving approvals for large-scale biosolids gasification plants, which convert waste into renewable energy and biochar.
As the global biosolids market continues to grow, it is evident that this industry offers an effective and sustainable solution for reusing waste material. By harnessing the potential of biosolids, we can address the challenges of wastewater treatment, reduce dependency on commercial fertilizers, and promote a circular economy.
Web: https://www.fairfieldmarketresearch.com/Email: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Obtaining The Most effective out of Dewatering Tools
Has the Dewatering Effectiveness Declined over time?
Sludge Dewatering and thickening is Among the most common procedures in H2o and Wastewater procedure plants. Belt presses, gravity tables and centrifuges are the same old machines merchandise used. In the situation of belt presses and gravity tables, the simplicity with the products can lull operators and upkeep personnel into a gradual means of letting the devices and options to deteriorate.

A modern study of press installations ranging in age from three to 18 many years has proven that many are increasingly being operated at 10 to thirty% below the first style and design capacity. There are plenty of motives, but usually lessened functionality seems for being because of a mix of factors, like staff turnover, servicing and acquiring selections, as well as a want to decrease the length of time invested adjusting the tools.
A de-tuned method could be more stable, and can tolerate far more variability within the feed problems. Additional obtainable plant potential can also inspire this approach.
General performance elements
In restoring functionality there are two procedure aspects to take into consideration. The first is the fact that sludge dewatering is actually a blended Actual physical /chemical strategy of flocculation, accompanied by a 2nd system, the mechanical stage of the actual dewatering. Efficient operation of both equally ways is important for effective dewatering.

Flocculation
Flocculation of sludges depends strongly on the character of your sludge. Throughout initial
commissioning the machines provider along with the flocculant supplier will normally
do the job alongside one another to pick out the most effective flocculation regime. This features don't just the
alternative of the right flocculant (normally a cationic polymer), but additionally the indicates
of dosing and mixing, as well as the dosage amount. If, in excess of successive many years,
the cure course of action, or even the cure plant influent, changes, these options
might require to be revisited. The dosing options, for instance closing dilution and
mixing changes also must be modified, and these configurations could be very important
to superior general performance.
Flocculant suppliers have an on-likely source of profits from the sale of
chemical compounds, and so are generally the key source of information and repair in
this regard. Nevertheless, They could not have an in-depth knowledge of the mechanical
products changes required to match The brand new circumstances. Moreover, they
Have got a vested curiosity in advertising and marketing their particular items.
The polymer flocculant is the center and soul of the biosolids dewatering
procedure. Whilst doctorate theses abound regarding the functionality and collection
of the proper polymer for an application, the truth is it is a trial and error approach,
with luck and ability associated.
Commercial Aspects
A typical challenge is H2o Authorities with more than one treatment method plant applying polymer flocculants contacting for tenders for offer of polymer flocculants for your range apps in a single massive agreement. This performs from choosing the right polymer for each application, as occasionally 1 suppliers’ polymer variety will not fit each individual circumstance.
Due to this technique, It's not at all uncommon to locate poor accomplishing polymers being used, with corresponding decreased dewatering performance of your products. This policy also brings about a flurry of screening exercise at tender time, followed by a lengthy period of time in the course of which the polymer provider focuses his interest in other places.
A serious occasional issue is often a planet –wide lack of raw resources, which has enhances the value, and alternatively encourages polymer producers to decrease the active information per kilogram of chemical.
Mechanical Troubles
Along with the method concerns you will discover mechanical upkeep difficulties. Belt presses, like a car or truck, have wear elements which should get replaced, and also demanding occasional adjustment. The principle don parts will be the filter belts, cake scraper “health care provider’ blades, and also the seals to the belt spray wash bins and aspect skirts, as well as spray nozzles.
Filter Belts
The filter belts Have got a direct impact on the process overall performance, and also the aspect skirt seals can influence course of action general performance. Unfortunately many organizations leave the purchasing of these spares to procurement departments or mechanical maintenance staff, who may purchase purely on apparent price, and the procedure general performance can go through for a consequence.
The selection of the best filter belt is really a compromise in between an open up weave to really encourage drainage, the necessity to help the cake and lessen losses with the fabric, and the opportunity to wash the belt cleanse. Belt washing might be vital, along with a worn h2o force booster pump, or worn nozzles, in combination with the incorrect option of belt, is a standard recipe for weak approach functionality.
A further component would be the mechanical strength expected, specifically the resistance of the filter belt to creasing and distortion in the seam (Which leads to a curved seam, which some phone a “smiley encounter” but All those inside the know connect with a “sad facial area”). A high quality belt press provides minimum stresses from the belt, whereas some compromise presses generate more anxiety. The incorrect choice of belt can substantially cut down throughput and capture.
Seals
Basic merchandise including wash spray seals and enclosures will often be
neglected, resulting in aerosol emissions. While some operators
have documented that they may have tolerated these aerosols for many
a long time with no sick consequences on their own staff, it is far much better to carry
out the bare minimum servicing demanded, and the advantages will include
a happier workforce. A happy operator will consider far more care of his
products and have a tendency to produce a greater method end result.
Spray Washbox
Seals will need common inspection and alternative wherever important. It is crucial they be put in place accurately in an effort to seal proficiently. A typical installation oversight is to offer insufficient flexibility in the piping to the spray headers to make sure that suitable adjustment is difficult.
Medical professional Blades
Other small mechanical locations where by faults are made, are cake launch “medical doctor” blades and gravity drainage zone skirt seals. There's a notion that if the thickness of fabric is elevated, it will eventually operate much better. Having said that, in engineering, often larger will not be often improved, and the additional stiffness of health care provider blades and aspect skirt sealing rubbers may result in mechanical difficulties which include inadequate belt monitoring, and elevated motor electric power consumption, and shorter belt daily life.
Tuning
Similar to a motor vehicle, sludge dewatering programs should be tuned by specialist personnel at common intervals. A plant with small improvements in functioning employees and approach disorders may only need to have re-tuning each individual three or four many years, While yearly tuning and reteaching might be appropriate for wastewater plants in higher development regions and with swift team turnover.
Changes to sludge age can change the characteristics from the sludge, and need a special polymer and press settings.
In tuning, the professional will evaluate the system from the biosolids conditioning substances in the mixing and flocculation routine, and correlate this Along with the belt speeds, form of filter belt weave, belt pressures, and attributes of the particular belt press. Some presses for instance are really tough within the formed floccs, Whilst Some others may need a more Light action. The specialist could also spot mechanically established course of action troubles, including bad belt washing or range.
Centrifuges
These types of aspects can also be legitimate regarding centrifuge dewatering equipment, but designed more intricate by The truth that the Visible clues provided by the belt push aren't out there Together with the centrifuge. It's also simpler to ignore very poor performance of a centrifuge procedure, as the process are all occurring In the machine, beneath a canopy. Off-tune centrifuges will consume a whole lot extra polymer, or might develop much deteriorated capture costs, as well as lowered throughput.
Summary
A thoroughly adjusted dewatering program will present Price tag financial savings by way of lessened polymer consumption, manpower for operation, and energy usage. An additional reward is often lessened disposal costs from a drier cake. As being a large proportion on the running price of a cure plant is usually attributed into the sludge dewatering and managing, a little financial investment in maintaining and tuning this equipment can result in substantial financial savings.
To know more details visit here: sludge dewatering equipments manufacturer
0 notes
Text
0 notes