#Bioenergy Industry
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
US renewable energy market size is projected to exhibit a growth rate (CAGR) of 10.31% during 2024-2032. The growing concerns towards conserving resources, improving air quality, protecting biodiversity, and mitigating the adverse impact of climate change are primarily driving the market growth across the country.
#US Renewable Energy Market Report by Type (Hydro Power#Wind Power#Solar Power#Bioenergy#and Others)#End User (Industrial#Residential#Commercial)#and Region 2024-2032
0 notes
Text
Global Bioenergies starts a new phase in its collaboration with Shell to develop low-carbon road fuels
Marc Delcourt, co-founder and CEO of Global Bioenergies Global Bioenergies, France-headquartered company which is a key player in industrial biotechnology, signed a new development contract with Shell Global Solutions (Deutschland) GmbH to further develop low carbon road fuels. While the previous phases of the collaboration, starting at the end of 2022, were dedicated to exploring different…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Brazilian researchers work to transform agave into the ‘sugarcane of the sertão’
The goal is to develop an alternative for bioenergy production that can be grown in semi-arid regions, which are advancing in Brazil and worldwide; results were presented during FAPESP Week Italy.

Climate change has caused an increase in the semi-arid climate region in Brazil. Data from the National Center for Monitoring and Warning of Natural Disasters (CEMADEN) and the National Institute of Space Research (INPE) in the South American country indicate an expansion of 7,500 square kilometers per year since 1990, which is equivalent to five times the area of the city of São Paulo. A similar phenomenon has been observed in some regions of Europe and North Africa.
With this in mind, and with the desire to find solutions to mitigate climate change, a group of Brazilian researchers began searching for plants with the potential to be used to generate bioenergy and that could be grown where the climate is not favorable for sugarcane. They decided to study Agave, a genus of succulent plants that includes more than 200 species and is widely used in Mexico to make tequila.
The work is being carried out with the support of FAPESP within the Brazilian Agave Development (BRAVE) project, a partnership involving the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP), the company Shell and other teaching and research institutions such as Senai CIMATEC (the Integrated Manufacturing and Technology Campus of the National Industry Service, the non-profit initiative of the CNI, the National Confederation of Industry), the Federal University of Recôncavo da Bahia (UFRB), the University of São Paulo (USP), and São Paulo State University (UNESP). The latest results were presented on October 14th during FAPESP Week Italy by Marcelo Falsarella Carazzolle, professor at the UNICAMP’s Institute of Biology (IB) who coordinates the initiative alongside Gonçalo Pereira, also from IB-UNICAMP. The event, which ended on October 15th, was held in partnership with the Alma Mater Studiorum - Università di Bologna (UNIBO).
Continue reading.
#brazil#science#environmentalism#climate change#farming#image description in alt#mod nise da silveira
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
In a breakthrough for environmentally friendly chemical production, researchers at the Center for Advanced Bioenergy and Bioproducts Innovation (CABBI) have developed an economical way to make succinic acid, an important industrial chemical, from sugarcane. The team of University of Illinois and Princeton University researchers created a cost-effective, end-to-end pipeline for this valuable organic acid by engineering a tough, acid-tolerant yeast as the fermenting agent, avoiding costly steps in downstream processing. Succinic acid is a widely used additive for food and beverages and has diverse applications in agricultural and pharmaceutical products. This same pipeline can be used to produce other industrially important organic acids targeted by CABBI in its work to develop sustainable biofuels and biochemicals from crops, said co-author Huimin Zhao, CABBI's Conversion Theme Leader and Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (ChBE) at Illinois. To reduce reliance on fossil fuels, Conversion researchers are deploying microbes to convert plant biomass into chemicals used in everyday products as an alternative to conventional petroleum-based production.
Continue Reading
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Indian rice manufacturers are shaping the global market

Indian rice has long held a place of pride in global kitchens, from the aromatic basmati grains that grace royal banquets to the nutritious non-basmati varieties that make up everyday meals worldwide. India is the world’s largest rice exporter, meeting over 40% of global rice demand (Source: FAO). Behind this success is the dedication and innovation of rice manufacturers in India, who are constantly adapting to meet international standards and market needs.
In this blog, we explore how Indian rice manufacturers are shaping the global market, promoting sustainability and securing India’s position as a rice exporting powerhouse.
Key factors driving Indian rice exports
Quality and Variety Rice manufacturers offer a diverse range of rice, from aromatic basmati to versatile non-basmati rice varieties. Each variety caters to different cuisines and preferences, ensuring steady demand in countries such as the United States, the Middle East, and Africa.
Competitive Pricing India's favorable agricultural conditions and cost-effective manufacturing processes enable competitive pricing. Combined with bulk export capabilities, this ensures that India remains a preferred supplier for global buyers.
Government policies and support Supportive government policies such as export incentives and trade agreements have contributed significantly to India's global dominance. For example, the recent removal of export restrictions on certain Indian rice varieties has boosted international trade opportunities.
Technological advances in rice manufacturing
Technology is transforming rice production in India, increasing efficiency and quality while reducing waste.
Modern milling equipment: Automated milling units maintain uniform grain size, texture and polish, which are critical to meeting international quality standards.
AI-powered sorting: Advanced sorting systems powered by artificial intelligence help eliminate impurities, ensuring that premium-grade rice reaches global markets.
Packaging innovations: Innovative vacuum-sealing and biodegradable packaging materials have made Indian rice more attractive to environmentally conscious buyers.
Rice manufacturers in India are adopting these advancements to maintain their competitive edge while meeting global priorities.
Sustainability initiatives by Indian manufacturers
As environmental concerns grow, rice exporters in India are adopting sustainable practices to meet global expectations.
Water-efficient farming: Techniques such as alternate wetting and drying (AWD) reduce water consumption, which is crucial for regions facing water scarcity.
Low carbon footprint: Adoption of renewable energy in processing units and adoption of eco-friendly logistics have reduced emissions in the rice supply chain.
Waste Utilization: By-products such as rice husk are being reused for bioenergy and building materials, thereby reducing waste and generating additional revenue streams.
These initiatives not only enhance India’s reputation but also align with the sustainability goals of global buyers.
Conclusion: The future of Indian rice on the global stage
The success of rice manufacturers in India is not just about meeting current demands, but also about shaping the future of the global rice trade. By prioritizing quality, leveraging technology, and adopting sustainable practices, Indian manufacturers have solidified their position as reliable partners in the global food supply chain.
As international markets evolve, India’s ability to adapt and innovate will continue to drive its leadership in the rice export industry, ensuring that Indian rice remains a staple in households around the world.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Quebec government has unveiled the list of 11 companies whose projects were given the go-ahead for large-scale power connections of 5 megawatts or more, for a total of 956 MW. The announcement was made in a press release Friday evening. Five of the selected projects relate to the battery sector, and two to the bioenergy sector. TES Canada's plan to build a green hydrogen production plant in Shawinigan, announced on Friday, is on the list. Hydro-Québec will also supply 5 MW or more to the future Northvolt plant at its facilities in Saint-Basile-le-Grand and McMasterville. Other industrial projects selected are those of Air Liquide Canada, Ford-Ecopro CAM Canada S.E.C, Nouveau monde Graphite and Volta Energy Solutions Canada.
Continue Reading.
Tagging @politicsofcanada
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
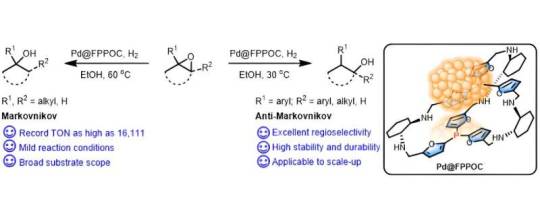
Palladium nanocluster catalyst supports highly efficient and regioselective hydrogenation of epoxides
Alcohols are widely applied in life sciences and the chemical industry. Selective hydrogenation of epoxides using hydrogen molecules as a reductant is considered to be one of the most facile and atom-economical strategies for alcohol synthesis. However, controlling the regioselective ring opening of epoxides remains a challenge. Significant progress has been made in the selective hydrogenation of epoxides using homogeneous catalysis. However, challenges remain in the difficult separation and recovery of the catalyst, as well as the drawbacks of requiring expensive and sophisticated ligands, which severely limit their practical potential. Therefore, the development of efficient and highly regioselective heterogeneous catalysts for epoxide hydrogenation is particularly important. A palladium (Pd) nanocluster catalyst for the selective hydrogenation of epoxides has been developed by Yang Yong from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Read more.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

"Prior to the events of Pokémon Omega Ruby and Alpha Sapphire, Mr. Stone's grandfather, the previous president of the Devon Corporation, learned of the ultimate weapon and wished to use the same energy to help people and Pokémon. This led to Devon developing Infinity Energy. The use of this energy made Devon one of the top industries in Hoenn."
"Confidential documents can be found in Sea Mauville stating that Dock investigated the Devon Corporation, finding that they had used Pokémon bioenergy to create Infinity Energy."
Still not over the Infinity Energy article on Bulbapedia. The ultimate weapon made you, Devon.
#(this is what inspires most of my lore for infinity energy btw!!)#(sea mauville remains one of the most underrated plot points in pokemon i will stand by that)#(time to bother muses with this info hee hoo)#reconstruction. (hcs)
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Robert Habeck, Germany’s minister for industrial policy and climate protection, has ruminated that the job of astute leaders is to unknot the contradictions of politics—the kind that can stop policymakers cold and run administrations aground. Germany’s coalition government of Social Democrats, Greens, and Free Democrats have barreled into a thicket of contradictions that illustrate just how confounding energy and climate policy—and the larger endeavor of obtaining climate neutrality—will prove as the sacrifices it demands of society grow.
Polls, for example, show that Germans are earnestly worried about the climate crisis and in favor of more climate action. The fallout of global warming is one of their most pressing concerns, indeed as it is across Europe. And yet, when it comes to modifying their lifestyles or paying higher prices to curb emissions, most say they’re not willing, or only as much as it doesn’t sting.
Habeck’s ministry is weathering this contradiction in the form of a nasty backlash against its efforts to transform Germany’s heating sector, which accounts for 15 percent of the country’s emissions and has recently become a geopolitical red-button conundrum in light of Russia’s attack on Ukraine. (Germany had previously relied on Russia for about half of its natural gas; in September 2022, Russia cut off its gas exports to Germany until Berlin lifts sanctions against Russia.)
In contrast to the electricity sector, which Germany has been decarbonizing for decades, heating is practically virgin territory—in the form of hundreds of thousands of buildings, offices, homes, and factories, too, that heat their rooms and power their furnaces with gas. Insulating the country’s building stock is treacherously slow: It happens building by building, and the likes of wood pellets, solar thermal, deep geothermal, and bioenergy are not considered sufficiently scalable.
These deficient options explain why the preferred plan is to electrify heating, primarily through the mass installation of heat pumps. An energy-efficient alternative to furnaces, heat pumps—like an air conditioner in reverse—use electricity to transfer heat from a warm space to a cool space. The most common pump is an air-source heat pump, which moves heat between a building and the outside air. By replacing gas boilers, the newest generation of heat pumps can reduce energy costs by as much as 90 percent, and cut emissions by about a quarter relative to gas and three-quarters relative to an electric fan or panel heater. As carbon prices climb higher, gas will become ever more expensive, and in the long run, heat pumps will be the less costly buy.
But the sticking point that the front guard of climate action—to which the Green politician Habeck definitely belongs—must confront is the mindset of his countrymen as the ecological modernization of their society and economy advances. The challenge is to get better at anticipating the degree of sacrifice the everyday German is willing to bear—and ready them for it, one way or another. In Germany, nearly two-thirds of households still heat with fossil fuels, and in a time of inflation and uncertainty, heat pumps are a hefty investment for households on a budget. An air-source pump—about the size of a travel trunk—will run $20,000 to $30,000, including installation, which is about twice as much as a new gas boiler.
This is why hell broke loose when the Habeck ministry’s draft law was leaked to the press (reflecting points agreed upon by all three parties in their 2021 governance treaty). It stipulated that old oil and gas heaters that break down after 2024 must be replaced with modern heating systems, namely units that rely on renewable energy for 65 percent of their energy use. This disqualifies gas and oil systems, and amounts to a de facto ban on new fossil fuel heating systems. In the draft plan, the government agreed to subsidize 30 percent of all heat pump installations.
This pronouncement jarred many people, and the government began to see before its eyes nightmare visions of the 2018 “yellow jacket” protests in France, when working-class French people took to the streets en masse in opposition to fuel taxes. Not only Germany’s boulevard press but even the Green Party’s coalition partners turned on Habeck, thundering that this measure wasn’t in the coalition contract (though it was) and that this was far too great a burden to impose on working Germans from one day to another (which the Greens had tried to address but were stifled by their partners.) According to a poll conducted by the arch-populist Bild-Zeitung, which led the charge, 61 percent of Germans were worried about the cost impact. Somewhat fewer respondents thought the ban of gas and oil heating was wrong-headed in the first place.
In hindsight, the Greens should have known better than to so flagrantly expose their Achilles’ heel: the perception that German Greens are elitist snobs with no feeling for ordinary folk with ordinary problems. But the party came around quickly on the snafu, introducing measures to subsidize boiler replacement for low-income people by 80 percent. The size of the subsidy is staggered by income, starting from the original 30 percent for the well-off. Middle-class earners (about $65,000 a year) would qualify for a 40 percent subsidy. People older than 80 are exempt from the law, according to the Green proposal.
The takeaway from the fiasco is that political leaders must test the waters and prepare the ground for the dramatic changes that are around the corner. “One era is drawing to an end—another is beginning,” said Habeck. “Because we’ve waited so long to act, these wide-ranging changes will impose on people’s day-to-day lives.”
“Today, it is becoming increasingly clear that virtually everything must change as soon as possible: housing, driving, heating,” writes Die Zeit editor Petra Pinzler. “The energy transition is no longer something that is negotiated at distant climate conferences or in political circles in Berlin and that can be avoided. It has arrived in everyday life. Many people are now realizing that something also has to change in their own boiler room.”
Veit Bürger of the Öko-Institut think tank told Foreign Policy that the changes in store for Germany and all countries seriously involved in decarbonization will affect society’s strata unevenly. “It won’t be win-win-win,” he said. “There will be new winners in the long run, sure, but those hit in the short run, like people with lower incomes, they have to be brought along, too.”
The law still isn’t in the bag: it has to pass both houses of parliament. Perhaps by Jan. 1, 2024, when it should take effect, Germans will have warmed up to a brave, new future of electrical heating. It is, though, as Habeck intoned, a harbinger of much greater changes to come.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
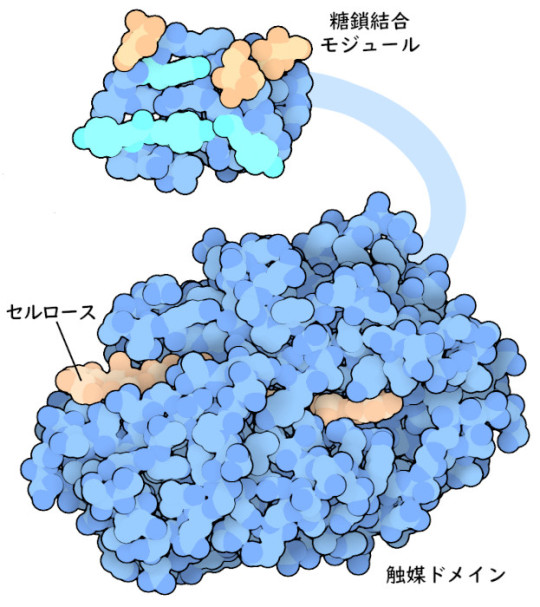
持続可能で食料と競合しない原料としてセルロールが着目されていて、セルロースの分解にはある真菌がつくる酵素が利用されている、というお話。
詳しくは今月の分子「281: セルラーゼとバイオエネルギー(Cellulases and Bioenergy)」にて
日本語訳(PDBj)
#バイオエネルギー #セルロース
This article refers to cellulose which is focused on as a sustainable and non-competing energy resource, and the enzymes produced by fungi are utilized to degrade it.
For details, please refer to the Molecule of the Month article: Cellulases and Bioenergy
Original English Article(RCSB PDB)
#bioenergy #cellulose
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Brazil Poised To Lead In Green Iron And Steelmaking With Renewable Energy Advantage

Brazil is set to emerge as a global leader in green iron and steelmaking, driven by its extensive renewable energy resources and high-quality iron ore reserves, according to a new report from Global Energy Monitor (GEM).
Currently, about 75% of Brazil’s steel production relies on coal-based processes, presenting challenges for decarbonization. However, Brazil’s abundant renewable energy resources, including its substantial hydropower, wind, and solar capacities, offer a pathway to producing green hydrogen, which is crucial for the low-emissions direct reduced iron (DRI) process. This shift could enable Brazil to develop a green iron export industry while also reducing domestic steel sector emissions.
The report highlights Brazil’s significant position in the renewable energy sector. The country ranks second globally in operating hydropower and bioenergy capacity, seventh in utility-scale wind capacity, and ninth in solar capacity. Brazil’s future prospects are even more promising, with 180 gigawatts (GW) of wind projects and 139 GW of solar projects in various stages of development, placing Brazil among the top global leaders.
Continue reading.
#brazil#brazilian politics#politics#environmentalism#economy#renewables#image description in alt#mod nise da silveira
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Global Furfural Market Strategy: From Agricultural Waste to Industrial Gold
Expanding Applications in Resins, Solvents, and Bio-Based Chemicals Drive Growth in the Furfural Market.

The Furfural Market Size was valued at USD 595.7 million in 2023, and is expected to reach USD 1095.2 million by 2032, and grow at a CAGR of 7.0% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
The Furfural Market is gaining significant traction as the global demand for bio-based and sustainable chemicals continues to rise. Furfural, a versatile organic compound derived from agricultural residues such as corn cobs, oat hulls, and sugarcane bagasse, is primarily used in the production of resins, solvents, and specialty chemicals. Its application across industries including petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and food processing positions it as a critical ingredient in the transition toward greener industrial processes.
Key Players:
Cayman Chemical Company
Furfural Company
Hongye Holding Group Corporation
Kraton Corporation
Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
Penn A Kem LLC
Segetis Inc.
Shandong Fuyuan Chemical Co., Ltd.
Sundow Polymers Co., Ltd.
Zhangjiagang Huasheng Chemical Co., Ltd.
Future Scope & Emerging Trends:
The furfural market is projected to expand robustly in the coming years, driven by rising interest in eco-friendly alternatives to petroleum-based chemicals. Innovations in green extraction technologies and improved feedstock utilization are enhancing production efficiency. Additionally, the surge in demand for furfuryl alcohol—a derivative of furfural used in foundry resins and biofuels—is creating new market opportunities. Governments and industry stakeholders are increasingly investing in biorefineries and circular economy initiatives, further supporting the furfural sector. Regions such as Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to be key growth hotspots due to abundant agricultural waste and growing industrial demand.
Key Points:
Furfural is a bio-based chemical made from agricultural by-products.
Widely used in solvents, resins, lubricants, and fungicides.
Demand is driven by the shift toward green and sustainable chemicals.
Growth in furfuryl alcohol demand boosts market prospects.
Asia-Pacific dominates production due to raw material availability.
Technological innovations are improving yield and sustainability.
Increasing adoption in bioenergy and bioplastics sectors.
Conclusion:
The Furfural Market stands at the intersection of sustainability, innovation, and industrial application, making it a vital component in the bio-based chemical revolution. With growing investments, evolving technologies, and expanding end-use sectors, furfural is well-positioned to meet the rising demand for renewable and environmentally responsible alternatives in the global chemical industry.
Read Full Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/furfural-market-4632
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave — Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1–315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
#Furfural Market#Furfural Market Size#Furfural Market Share#Furfural Market Report#Furfural Market Forecast
0 notes
Text
Wood Pellets Market Overview: Revenue, Segmentation, Future Growth and More

Wood Pellets Marketresearch report by Delvens focuses on primary sections such as – market segments, market outlook, competitive landscape, and company profiles. The segments provide details in terms of various perspectives such as end-use industry, product or service type, and any other relevant segmentation as per the market’s current scenario which includes various aspects to perform further marketing activity, the Wood Pellets market size is projected to reach a CAGR of 9.7% to 2030.
Get Free Sample Report: https://www.delvens.com/get-free-sample/wood-pellets-market
Wood Pellets is one of the most common types of pellet fuel and is a biofuel made usually from saw dust and industrial waste like coconut fibre & shell, wood remains and old furniture. These are more environment friendly in comparison to the conventional used fossil fuels and thus are an eco-friendly power generation alternative to them. They also have higher combustion ability.
Favourable governmental policies along with the environmental advantages offered by wood pellets over the conventional fuel generation methods are some of the factors that have supported long-term expansion for Wood Pellets Market.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific is the most rapidly growing market and offers a huge opportunity for the industry, whose growth is driven by the favourable governmental policies and the raised environmental concerns in the region.
Recent Developments
Drax a UK based power plant announced to become the first carbon-free business by the year 2030.
Key Players
Canfor
Schweighofer
Enviva LP
Pinnacle Renewable Energy Group
Pacific BioEnergy
Wood Pellets Marketis segmented into application and region.
On the basis of Application
Power Plants
Residential Heating
Commercial Heating
Combined Heat and Power (CHP)
On the basis of Region
Asia Pacific
North America
Europe
South America
Middle East & Africa
Access Full Report: https://www.delvens.com/report/wood-pellets-market
In addition to the market data for Wood Pellets Market, Delvens offers client-centric report and customized according to the company’s specific demand and requirement.
More Related Reports:
Coffee market
On-board Charger market
About Us:
Delvens is a strategic advisory and consulting company headquartered in New Delhi, India. The company holds expertise in providing syndicated research reports, customized research reports and consulting services. Delvens qualitative and quantitative data is highly utilized by each level from niche to major markets, serving more than 1K prominent companies by assuring to provide the information on country, regional and global business environment. We have a database for more than 45 industries in more than 115+ major countries globally.
Delvens database assists the clients by providing in-depth information in crucial business decisions. Delvens offers significant facts and figures across various industries namely Healthcare, IT & Telecom, Chemicals & Materials, Semiconductor & Electronics, Energy, Pharmaceutical, Consumer Goods & Services, Food & Beverages. Our company provides an exhaustive and comprehensive understanding of the business environment.
Contact us:
Unit No. 01, 3rd Floor, Plot No. 56, Block B
Sector 2 Noida, Near Noida Sector 15 Metro Station 201301, IN
+44 20 3290 6466
+0120- 4903958
0 notes
Text
Explore the Future of Renewable Trade with the Leading Biomass Energy Marketplace

Discover Peleti Ltd., a leading biomass energy marketplace connecting global stakeholders in the sustainable bioenergy industry. Explore, list, and network with producers, innovators, and eco-advocates worldwide in one powerful platform driving green energy solutions.
0 notes
Text
Sustainable Manufacturing in Heavy Industries: A Path Toward a Greener Future

Heavy industries such as steel production and foundries have long been recognized for their high energy consumption and environmental impact. Today, however, the shift toward sustainable manufacturing is transforming the way these sectors operate. Through innovative technologies and eco-friendly practices, businesses are not only minimizing their carbon footprint but also boosting efficiency and profitability.
Strategies for Sustainable Manufacturing in Steel and Foundry Sectors
1. Upgrading to Energy-Efficient Machinery
Modern manufacturing equipment is designed with sustainability in mind. These machines offer advanced features that reduce energy consumption without sacrificing performance.
Smart Furnaces: Leveraging AI, these systems adjust heating patterns in real-time, cutting down on energy waste.
Hydraulic Pushers by LeisterTech: Built for precision and minimal power usage, these pushers exemplify how smart engineering supports sustainable operations.
2. Transitioning to Renewable Energy
Steel plants and foundries are increasingly turning to solar, wind, and bioenergy solutions. Integrating solar panels or tapping into wind power grids can drastically offset traditional energy consumption.
3. Embracing Recycling and Circular Economy Models
Recycling metal scrap and reusing industrial byproducts reduces dependency on raw materials and curbs waste.
Scrap Transfer Trolleys from LeisterTech: These trolleys streamline internal logistics and enable efficient scrap recycling, supporting a closed-loop manufacturing model.
4. Water Conservation Innovations
Technologies like closed-loop cooling systems are becoming common in manufacturing, enabling companies to recycle water and reduce environmental discharge.
5. Automation and Process Optimization
IoT-enabled systems and smart automation ensure that production processes operate at peak efficiency, minimizing material and energy waste.
Eco-Friendly Equipment by LeisterTech
LeisterTech is at the forefront of sustainable innovation in the heavy manufacturing sector. The company offers a variety of machines engineered for environmental efficiency:
Energy-Efficient Shearing Machines: Delivering high output with low energy usage.
Smart Material Handling Systems: Advanced lifting magnets reduce emissions by optimizing internal transport and handling tasks.
Lining Vibrators with Minimal Waste Design: Built to reduce both energy and material waste during operations.
Benefits of Sustainability in Heavy Manufacturing
Adopting green technologies in heavy industry isn't just about compliance—it’s a smart business decision:
Lower Carbon Emissions: Energy-efficient systems and renewables drastically reduce greenhouse gas output.
Operational Cost Savings: Eco-friendly machines typically offer long-term savings through lower energy consumption.
Regulatory Compliance: Staying ahead of environmental standards helps avoid penalties and enhances corporate reputation.
Stronger Brand Image: Companies committed to sustainability appeal to environmentally conscious customers and stakeholders.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Sustainable Industry
The evolution of heavy manufacturing is only just beginning. Emerging technologies like green hydrogen in steelmaking, carbon capture systems, and AI-powered waste management are set to redefine industry norms. Companies like LeisterTech are leading this transformation by continuously developing forward-thinking equipment tailored to the green future.
Final Thoughts
Sustainable manufacturing is no longer optional—it's essential. By adopting eco-friendly equipment, optimizing resource use, and investing in renewable energy, companies can significantly reduce their environmental impact while staying competitive. Leaders like LeisterTech are proving that innovation and sustainability can go hand in hand in shaping the next generation of heavy industry.
#SustainableManufacturing#HeavyIndustryInnovation#EcoFriendlyMachinery#IndustrialAutomation#GreenSteel#CarbonFootprintReduction#SmartManufacturing#LeisterTech#CircularEconomy#EnergyEfficientSolutions
0 notes
Text
U.S. Sugar Prices 2025, Size, Trend, Graph, News and Forecast
North America
In the final quarter of 2024, sugar markets in North America experienced mixed trends influenced by seasonal demand, weather conditions, and production costs. By December, U.S. sugar prices had stabilized following earlier gains, supported by steady retail demand and ample inventories. The USDA raised the U.S. sugar ending stocks-to-use ratio to 13.5%, indicating a healthy supply outlook. Although domestic beet sugar production declined, strong import flows from Mexico and Brazil helped offset the shortfall.
Meanwhile, Brazil faced significant production setbacks due to El Niño-driven droughts, which severely impacted sugarcane yields and raised global supply concerns. Rising NPK fertilizer costs—particularly from U.S. exports—further inflated production expenses, adding upward pressure to sugar prices. Globally, the FAO Sugar Price Index registered a 6.7% year-on-year increase, reflecting constrained supplies from major exporters, although month-to-month pricing began to ease.
The contrast between North America’s relatively stable market and Brazil’s production struggles underscores the ongoing influence of climate variability, global trade flows, and seasonal consumption patterns on the sugar industry.
Get Real time Prices for sugar : https://www.chemanalyst.com/Pricing-data/sugar-1607
Asia-Pacific
In Q4 2024, sugar prices across the Asia-Pacific region remained largely stable with slight declines, shaped by production challenges, fluctuating input costs, and modest retail demand. India, the region’s key producer, faced a notable downturn due to adverse weather—unseasonal rains and record November temperatures—which reduced yields in major sugarcane-growing states like Uttar Pradesh. Production for the first quarter of the 2024–25 marketing year fell to 3.28 million tonnes, down from 3.43 million tonnes the previous year. The Indian Sugar and Bioenergy Manufacturers' Association (ISMA) projected a 2.24% annual production decline.
Despite inflationary pressures weakening consumer demand in the FMCG sector, strong demand from the food processing industry provided partial support. Global supply concerns intensified as India increased sugarcane diversion toward ethanol production, compounding supply tightness alongside Brazil's drought-driven output issues. However, the impact of these pressures was moderated by stable NPK fertilizer prices and a steady pace of sugarcane crushing, which ensured adequate market availability.
Europe
During Q4 2024, European sugar prices continued their upward climb, fueled by domestic supply shortfalls and rising regulatory uncertainty. A key driver was the shortage of locally produced sugar, as weather-related disruptions impacted beet harvests. Further compounding supply challenges were proposed revisions to EU deforestation regulations, which risked limiting sugar imports if not resolved by the upcoming compliance deadline.
Logistical issues also played a role—port congestion in Hamburg due to modernization efforts and shipping delays from Red Sea disruptions tightened supply chains, especially in Germany. These constraints pushed prices above 22 cents per pound, reaching a near two-week high despite consistent demand from the food and beverage sector.
Unseasonably warm autumn weather in northwestern Europe, driven by an amplified jet stream, offered temporary support for agriculture. However, rising production and logistical costs, including fertilizer expenses, continued to apply upward pressure. With regulatory ambiguity and logistical bottlenecks still unresolved, sugar prices are expected to remain volatile in the near term.
South America
In Q4 2024, Brazilian sugar markets were marked by volatility, primarily driven by extreme weather and tight supply conditions. Severe drought and record heat, especially in São Paulo, led to a sharp drop in sugarcane yields. Around 80,000 hectares were affected by wildfires, further reducing output.
Despite these setbacks, Brazil achieved a record sugar export volume of 38.24 million tonnes for the year, highlighting its resilience and global market strength. Robust international demand maintained upward pressure on prices, even as domestic availability tightened. El Niño conditions persisted, prolonging drought stress and compounding agricultural and water resource challenges.
Rising NPK fertilizer costs further strained producers, pushing production costs higher. Still, strong export performance helped Brazil sustain its role as a leading global supplier. As a result, sugar prices remained elevated, reflecting a mix of domestic production difficulties and unrelenting global demand.
Get Real time Prices for sugar : https://www.chemanalyst.com/Pricing-data/sugar-1607
Our Blog:
Packaging Materials Prices: https://www.chemanalyst.com/Industry-data/packaging-materials-7
Personal Care Chemicals Prices: https://www.chemanalyst.com/Industry-data/personal-care-chemicals-8
Contact Us:
ChemAnalyst
GmbH - S-01, 2.floor, Subbelrather Straße,
15a Cologne, 50823, Germany
Call: +49-221-6505-8833
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://www.chemanalyst.com
#Sugar Price Monitor#Sugar Database#Sugar Price Chart#Sugar Price Trend#India#united kingdom#united states#Germany#business#research#chemicals#Technology#Market Research#Canada#Japan#China
0 notes