#Banana Puree Market Analysis
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Banana Puree Market Royale: A Regal Feast of Bananas Fit for Culinary Connoisseurs

Banana puree is a thick paste made from ripe bananas which has a smooth and creamy texture. It is used as a flavoring ingredient in food products such as baby food, ice cream, yogurt, and bakery items. Banana puree offers numerous nutritional and health benefits such as being a good source of potassium, Vitamin C and fibers. It also helps in improving digestion and maintaining a healthy heart. The growing awareness about these benefits has been driving the demand for banana puree from the food processing industry. The global banana puree market is estimated to be valued at US$ 381.07 Mn in 2024 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 9.2% over the forecast period 2024-2031, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights. Market Opportunity: The rising demand for convenience food products represents a major market opportunity for banana puree. Consumers today lead a fast-paced lifestyle with little time for elaborate meal preparations at home. This has significantly boosted the demand for ready-to-eat and on-the-go food options. Banana puree is widely used as a key ingredient in various convenience foods such as baby food, ice cream, yogurt and other snack bars due to its nutritional profile and ability to impart unique flavor. Its long shelf life also allows food manufacturers to easily incorporate it into packaged food products without compromising on taste and texture. The market players are expected to leverage this growing demand for convenience foods by launching more such products containing banana puree. Porter's Analysis Threat of new entrants: Low barrier for new players to enter the market, however established brands have access to wider distribution channels and economies of scale. Bargaining power of buyers: Large buyers such as supermarkets have significant power to negotiate lower prices from suppliers. Bargaining power of suppliers: A few multinational companies dominate banana production limiting supplier power. Threat of new substitutes: Substitutes exist such as other fruit purees but banana puree has established demand for its taste and nutrition. Competitive rivalry: Intense competition among key global players to capitalize on high growth prospects. SWOT Analysis Strengths: High demand for banana puree in various food and beverage products. Emerging economies offer vast untapped potential. Weaknesses: Seasonal supply of raw bananas leads to price volatility. Banana crops susceptible to diseases necessitating costly production practices. Opportunities: Innovative product launches catering to on-the-go lifestyles and health trends. Rising incomes in developing nations to boost consumption. Threats: Strict food quality and safety regulations increase compliance costs. Climate change impacts on banana yields. Key Takeaways The global banana puree market is expected to witness high growth over the forecast period driven by burgeoning demand across major emerging economies.
Regional analysis for Asia Pacific comprises over 60% market share led by India, China and Southeast Asian countries where bananas are a staple food. Rising health consciousness and shift to convenience foods are driving banana puree demand. Further economic growth and urbanization are expected to continue propelling the Asia Pacific banana puree market over the forecast period.
Key players operating in the banana puree market are Symrise AG, Döhler GmbH, Kiril Mischeff, Riviana Foods Pty Ltd, Nestlé S.A., The Hain Celestial Group Inc, The Kraft Heinz Co., Ariza B.V., Newberry International Produce Limited, Grünewald Fruchtsaft GmbH, Tree Top Inc., Hiltfields Ltd., Shimla Hills Offerings Pvt. Ltd., Antigua Processors S.A. and SunOpta Grains and Foods Inc. These players are focusing on new product innovations, manufacturing capacity expansion and strategic collaborations to gain a competitive edge.
#Banana Puree Market Share#Banana Puree Market Growth#Banana Puree Market Demand#Banana Puree Market Trend#Banana Puree Market Analysis
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Video
youtube
How to make Chung Cake and bring it to the market to sell - Gardening | ...
Banh Chung is one of the indispensable traditional dishes during the Lunar New Year of the Vietnamese people. However, with the trend of modernization and increasing market demand, the production and business of chung cakes does not only stop at serving families but also expands to the retail market. Here is a detailed guide from making banh chung to how to put the product on the market for sale.
Part 1: How to Make Banh Chung
Ingredients to prepare:
Gạo nếp: 2 kg
Pork belly: 1 kg
Green beans: 500g
Roasted peanuts (optional): 200g
Green onions, garlic, spices: Salt, pepper, fish sauce
Dong leaves or banana leaves: For wrapping cakes
Lanyard: By natural rope or braided rope
Steps:
Prepare glutinous rice:
Rinse the glutinous rice, soak it in water for at least 4-5 hours or overnight.
After soaking, drain.
Pork preparation:
Choose pork belly with only fat and balanced meat.
Marinate the meat with salt, pepper, chopped green onions and fish sauce for at least 2 hours.
Preparation of green beans:
Rinse the green beans clean, soak in water for 4-5 hours.
Steam or boil the chickpeas, then puree.
Banh Chung Package:
Wash the dong leaves, seal them with fire so that the leaves are flexible and easy to wrap.
Start by laying out the dong leaves flat, laying out a layer of glutinous rice, then meat and green beans, continuing the layer of glutinous rice.
Wrap your hands tightly, tie the cord to fix the shape.
Cooking Banh Chung:
Bring the water to a boil in a large pot, drop the banh chung into the cooker.
Cook for about 6-8 hours so that the cake is soft and evenly absorbed with spices.
Complete:
Once cooked, allow the cake to cool naturally before removing it for use or packaging.
Part 2: Bringing Products to Market
1. Market Research:
Identify your target audience: Families, food stores, supermarkets, and individual customers.
Competitive Analysis: Consider regional competitors in terms of quality, price, and service.
2. Product Development:
Quality Assurance: Using fresh ingredients, ensuring food hygiene and safety.
Product Diversification: Providing a variety of banh chung in different sizes and flavors to suit the diverse needs of customers.
3. Packing and Packaging:
Attractive Packaging: Use beautiful, eco-friendly packaging, easy to store.
Product Information: Specify the ingredients, date of manufacture, expiration date and storage instructions.
4. Pricing Strategy:
Competitive Pricing: Research market prices and determine the right price, ensuring profits and attracting customers.
Discount Policy: Apply promotions and discounts on special occasions such as Tet.
5. Distribution Channel:
Direct Sales: Set up stalls at traditional markets, supermarkets, convenience stores.
Online Sales: Create a website, use social networks (Facebook, Instagram) and e-commerce platforms (Shopee, Lazada) to reach a wider range of customers.
Cooperation with Partners: Connect with distributors and agents to expand the sales network.
6. Marketing and Promotion:
Branding: Create unique, easy-to-remember logos and slogans for customers to identify the brand.
Online and Offline Advertising: Use social media ads, Google Ads, as well as traditional ads such as flyers and billboards.
Promotions: Organize discounts, giveaways, or prototypes to attract customers.
Reviews and Feedback: Encourage customers to evaluate products and listen to feedback to improve quality.
7. Operation and Management:
Production Management: Ensure efficient production process, quality control from raw materials to final products.
Financial Management: Track production costs, marketing costs, and revenue to ensure profits.
Customer Service: Build a good customer support system, resolve complaints and respond quickly.
8. Legal and License:
Business Registration: Make sure to register your business in accordance with the law.
Food Safety License: Ensure compliance with food safety regulations and have the necessary certifications.
0 notes
Text
How to Start Fruit Export Business from India?

India's fruit sector is experiencing significant growth, presenting vast opportunities for exporters. From exotic kiwis to delectable mangoes, a world of flavors awaits discovery. India, with its diverse climate and long agricultural history, stands as a powerhouse in fruit production.
Why Export Fruits from India?
The high demand for premium fruits in countries like the US, Europe, Hong Kong, and Vietnam makes fruit export from India a lucrative business opportunity. Despite the challenges of navigating the fruit export industry, it remains a promising venture due to India's capacity to produce various fruits at competitive prices.
Fruit Export from India: Key Statistics and Facts
India is a major player in the global fruit export market. In the fiscal year 2022-2023, the country exported 674,291.70 MT of fresh fruits (excluding grapes and mangoes), generating revenue of Rs. 2,736.99 crores, equivalent to 339.00 USD million. Projections suggest that by 2024, India's fruit export industry will achieve a gross production value of USD 41.19 billion.
Top Fruits Exported from India
Mangoes:
India's mangoes, especially the Alphonso variety, are renowned worldwide for their rich, creamy texture and sweet, citrusy flavor. The demand for these mangoes is high in India and the Middle East, Europe, and the US.
Bananas:
As the world's largest producer of bananas, India's share in banana exports is steadily increasing. Besides fresh bananas, India also exports processed banana products like dried bananas, chips, and puree, catering to diverse culinary uses globally.
Pomegranates:
Known as the "jewels of winter," Indian pomegranates dominate over half of the world's production. Major export destinations include Greece, Israel, Russia, the UAE, and Italy.
Apples:
Indian apples, appreciated for their crispness and nutritional value, are exported primarily to Bangladesh, Nepal, and the Middle East. Varieties such as Green Apple, Pink Lady, Fuji, Gala, Honeycrisp, Envy, and Red Apple are well-known.
Oranges:
Indian oranges are versatile and in high demand for their use in food, perfumes, and cosmetics. Popular export varieties include Dancy, Nagpur Santra, Coorg Santra, Kinnow Mandarin, and Darjeeling Mandarin.
Leading Fruit Exporters in India
Prominent fruit exporters in India include:
Pisum Foods
Indian Farmers Export (IFE Fruits & Vegetables)
Radha Krishan Fruit Company
Jadli Foods India
Mahindra Agri
Balaji Foods Pvt Ltd
Dhanuka Agritech Ltd
Vardhan Exports Pvt Ltd
Golden Agri Exports Pvt Ltd
Vajreshwari Enterprises And Corp
Strategies for Successful Fruit Export from India
Establish an Export Firm:
Company Registration: Choose a suitable business structure (private limited, partnership, or sole proprietorship) and register with the Registrar of Companies (ROC).
Import Export Code (IEC): Obtain an IEC from the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT), certifying your business as an approved exporter.
Select Fruits for Export: Choose fruits with high export potential, considering factors like shelf life, export quantities, and market demand. Access real-time data from platforms like Eximpedia for insights.
Compliance and Documentation:
Registration and Licensing: Register with APEDA and secure necessary licenses.
Documentation: Ensure all export documents, including commercial invoices, origin certificates, and phytosanitary certifications, meet importing country specifications.
Access Reliable Export Data: Utilize platforms like Eximpedia to access market trends, competitor analysis, and potential buyer connections. This information is crucial for making informed export decisions.
Conclusion
India's fruit export industry is booming, driven by a diverse range of fruits and robust international trade relations. For new exporters, leveraging resources like Eximpedia can provide valuable insights and help establish a foothold in the global market. Whether you need updated fruit export data, a list of top fruit exporters, or information on fruit HS codes, Eximpedia offers comprehensive support to navigate the fruit export landscape. Connect with Eximpedia today for a free live demo and take the first step towards successful fruit exporting from India.
#fruit export from india#fruit exporters in india#fruit export companies in india#list of fruits exported from india#fruit exporters#fruit export data
0 notes
Text
Banana Puree Market: Exploring Market Segmentation

Banana puree is a smooth pureed version of banana fruit obtained by pressing and sieving the flesh of ripe bananas. It has various advantages as a food ingredient such as high nutritional value, pleasant taste, and smooth texture. Banana puree is widely used in baby food products due to its nutritional profile and easy digestibility. It is also utilized in various food and beverage applications like dairy products, bakery products, desserts, juices, and smoothies to enhance flavor and texture. The growing demand for convenience and ready-to-eat foods has fueled the usage of banana puree in packaged food items. The global banana puree market is estimated to be valued at US$ 381.7 Mn in 2024 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 9.2% over the forecast period from 2023 to 2030. Key Takeaways Key players operating in the banana puree market include Symrise AG, Döhler GmbH, Kiril Mischeff, Riviana Foods Pty Ltd, Nestlé S.A., The Hain Celestial Group Inc, The Kraft Heinz Co., Ariza B.V., Newberry International Produce Limited, Grünewald Fruchtsaft GmbH, Tree Top Inc., Hiltfields Ltd., Shimla Hills Offerings Pvt. Ltd., Antigua Processors S.A., and SunOpta Grains and Foods Inc. The rising demand for healthy and nutritious baby food products is a major factor propelling the consumption of banana puree globally. Banana puree offers several health benefits and is easily digestible, making it suitable for babies and young children. Emerging economies in Asia Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness significant growth in the banana puree market over the forecast period. Growing health awareness and rising disposable incomes in developing nations are fueling the demand for high-quality banana puree in these regions. Market Key Trends The increasing usage of banana puree as a substitute for refined sugar in various foodstuff is one of the key trends being witnessed in the global market. Banana puree has a mildly sweet flavor and acts as a natural sweetener in food products like yogurt, ice cream, and cereal bars. This helps reduce sugar content and provides associated health benefits. Banana puree blends well in recipes for baby foods and breakfast cereals as its sweet taste and smooth texture make the final products more palatable for infants and children. The trend of using banana puree instead of sugar is expected to continue thus propelling the market growth.
Porter’s Analysis Threat of new entrants: New entrants cannot easily enter the market as they require high initial investments in machinery, land and raw materials. Bargaining power of buyers: Buyers have moderate bargaining power since banana puree has substitutes like apple sauce and there are many established players in the market. Bargaining power of suppliers: Suppliers have low to moderate bargaining power since bananas can be sourced from various countries and there are many suppliers. Threat of new substitutes: Substitutes like apple sauce pose moderate threat since they are not perfect substitutes for banana puree. Competitive rivalry: Fierce competition exists among key players to gain market share. Geographical Regions In terms of value, the banana puree market is currently concentrated in North America and Europe. The per capita consumption of banana puree is higher in these regions. Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest growing region during the forecast period owing to rising disposable incomes, growing health consciousness, and expanding retail sector in major countries like India and China. Increased usage of banana puree in infant food and beverages will support the market growth in Asia Pacific.
0 notes
Text
Banana Puree Market CAGR Status, Emerging Trends and Forecast till 2030

The banana puree market refers to the global industry involved in the production, distribution, and consumption of banana puree, which is a smooth and thick paste made from mashed bananas. Banana puree is commonly used as an ingredient in various food and beverage products, including baby food, desserts, smoothies, and baked goods.
Here is some information about the banana puree market:
Market Overview: The banana puree market has been experiencing steady growth due to the increasing demand for convenient and healthy food products. Banana puree is valued for its natural sweetness, nutritional benefits, and versatility in culinary applications.
Key Players: Several companies are involved in the production and supply of banana puree. Major players in the global market include Dohler GmbH, Nestlé S.A., Symrise AG, Kerr Concentrates Inc., and SunOpta Inc., among others.
Production Process: Banana puree is typically made by peeling aand mashing ripe bananas, followed by filtration to remove any undesirable solids. The puree is then pasteurized to ensure food safety and maintain product quality. Some manufacturers may add preservatives or other ingredients to extend the shelf life or enhance flavor.
Applications: Banana puree is used in a wide range of food and beverage applications. It is a popular ingredient in baby food products due to its nutritional content and smooth texture. It is also used in the production of ice creams, yogurts, smoothies, juices, sauces, bakery products, and confectionery items.
Market Trends: The banana puree market is influenced by various trends, including the growing consumer preference for natural and organic food products. There is an increasing demand for banana puree without added sugars or preservatives. Moreover, manufacturers are focusing on developing innovative banana-based products to cater to changing consumer tastes and preferences.
Regional Market Analysis: The banana puree market is geographically diverse, with key regions including North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa. Each region has its own production capabilities, consumption patterns, and market dynamics. For example, Latin America is a significant producer of bananas and is a major contributor to the global banana puree market.
Growth Drivers: The market growth is driven by factors such as increasing consumer awareness about the nutritional benefits of bananas, rising disposable incomes, changing dietary preferences, and the expansion of the food and beverage industry. Additionally, the demand for natural and organic products and the growing popularity of plant-based diets are also contributing to market growth.
Challenges: The banana puree market faces challenges such as fluctuating banana prices, limited shelf life of the product, and the need for efficient supply chain management due to the perishable nature of bananas.
Regulatory Landscape: The production and sale of banana puree are subject to various regulations and quality standards imposed by regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in the European Union. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for manufacturers to ensure food safety and meet consumer expectations.
Future Outlook: The banana puree market is expected to continue its growth trajectory in the coming years. The increasing popularity of healthy and natural food products, along with the rising demand for convenience foods, is anticipated to drive market expansion. Additionally, the development of new banana varieties, product innovations, and the exploration of untapped regional markets could further boost market growth.
Please note that the above information is based on the current understanding of the banana puree market up until September 2021, and the market dynamics may have evolved since then.
0 notes
Text
1.Executive Summary
Burger King Corporation was founded by James McLamore and David Edgerton in Miami, Florida (USA) in 1954. Just like any other businesses, it only started with a few chains until it expanded and continued to cater its consumers up until today. As time goes by, it has expanded their menu but still managed to maintain their low costs but the quality menu. For as low as PHP 64.00 you can already get to taste Buger King’s flame-Grilled burger and with PhP 59.00, you can already enjoy having their rice meal. Up until this day, Burger King is one of the most popular, top-grossing, and flavorful fast-food chains not just locally but also internationally.
We all know that the fast-food chain industry is one of the reasons why the hospitality industry continues to arise and operational due to its high demand. People love it because it offers convenience, affordability and time-saving. Fast-food chains such as KFC, McDonald's, Jack in the Box, Wendy's and Popeyes are the top 5 competitors of Burger King. Its wide variety, effective strategy, strong franchising model, delicious taste, and etc. is what makes it keep up in competing its rivalries. Whopper, Chicken Sandwiches, Cheeseburgers are some of its product offerings and that is why Burger King is dubbed as "Home of the Whopper". In year 2018, Burger King has a total revenue of 388.74 crore in which it was the least revenue they got between the year 2018-2021. In 2019, they got 644.13 crore while in 2020, they have accumulated the highest revenue they have so far that has a total of 846.83 crore amidst the global pandemic that is happening. Today, year 2021, during the first quarter of the year, they have earned a total of 151.65 crore revenue.
This paper discussed Burger King's internal assessment wherein it states the company's corporate profile, mission and vision, product line, and its internal factor evaluation matrix. Next, external assessment has porter's model analysis, external factor evaluation matrix, competitive profile matrix and the key external factor. Moreover, it also discussed the strategy formulation wherein it has BCG matrix, SPACE matrix, GS matrix, IE matrix, and the SWOT analysis. Additionally, the researchers also provided the strategy recommendation, action plan, as well as its financial projection.
It analyzed how Burger King Corporation operates on how it managed to make it to the top and how it maintained the quality of their products. Each part of this paper is a helpful tool and contributes to the success of this paper itself. Also, it is where we will recognise how significant each role is to discuss the outcome of the paper. With that, this paper aims to elaborate, explain, and discuss the story behind the fast-food chain named Burger King.
2. Internal Assessment
2.1. Corporate Profile
5505 Blue Lagoon Drive
Miami, Florida 33126
U.S.A
According to Trefis Team (2019), Burger King is the second largest fast-food chain in the United States and Routley (2019) also states that Burger King was ranked fourth as one of the biggest fast-food chains in America. It has over 10,400 business franchised restaurant. 50 states and 56 countries, Burger King has 1000 chains of stores that totaled for more than 11,455. The company has served almost 16 million customers a day and 2.4 billion Burger King’s hamburgers are sold annually across the world.
In 1954, Burger King Corporation was founded by the two entrepreneurs James McLamore and David Edgerton. It is originally owned by Keith Kramers and his wife’s uncle Mathew Burns. Burger King was inspired by McDonald’s and formerly named as Insta-Burger King during 1953. Even with the rapid success of the Insta-Burger it experienced financial trouble that led James McLamore and David Edgerton to buy the entire company from Keith Krammers and Mathew Burns. McLamore and Edgerton decided to widen their menu in 1957 with Whopper, a burger for big appetites, but still a lower price and they took the power of the popular medium which is television. The first T.V commercial of Burger King was aired in 1958 on Miami’s V.H.F Station and after 5 years by 1959, Burger King was able to expand their outlets outside Florida by establishing its franchise system. The system worked allowing Burger King to increase quickly. Burger King Company was also pursuing to reach out children and establish Kids Club but then by 2015 Burger King had no longer focused on this area.
Despite having trouble times, Burger King still became a well-known fast-food hamburger chain. Through the years, Burger King grew as they use different strategies and form a different and unique characteristics from their competitors.
2.2. Company Vision and Mission
Vision
Burger King’s vision statement is “to be the most profitable QSR business, through a strong franchise system and great people, serving the best burgers in the world.”
Mission
Burger King’s mission statement is to “offer reasonably priced quality food, served quickly, in attractive, clean surroundings.”
2.3. Corporate Officers
Daniel S. Schwartz
Chief Executive Officer
JOSHUA KOBZA
Chief Financial Officer
AZEL SCHWAN
Global Chief Marketing Officer
HEITOR GONCALVES
Chief Information Performance & People Officer
ALEXANDRE MACEDO
President of Burger King North America
JOSE E CIL
President of Burger King Europe
JOSE DIAS
President of Burger King Latin America & Global Development VP
ELIAS DIAZ SESE
President of Burger King Asia Pacific
RODRIGO MUSIELLO
Global Operations
JILL GRANAT
Secretary & General Counsel
JACQUELINE FRIESNER
Chief Accounting Officer & Controller
2.4. Product Line
Burger King operates as a quick service restaurant business focusing on burgers as its main product.
•Burgers
•Salad & veggies
•Chicken & fish
•Sides
•Sweet/desserts
•Beverages
BURGERS
Burger King is a family of different kinds of hamburgers consisting of patties, bacon, king sauce and their american cheese. Their burgers have lettuce, tomato, onion, pickles and it is the main product of their store because of its taste, quality, as well as affordability.


SALAD AND VEGGIES
Burger King salad is totally vegetarian and comes with tomatoes, lettuce, cheese, and croutons. They have different types of salad so that the customers can pick which one is their preferred salad for their side dish. The vegetable used in Burger King salads are always served fresh.

SIDES
Burger king offers frings which is the combination of onion rings and their french fries.

CHICKEN & FISH
Burger King’s chicken & fish sandwiches are pure white alaskan pollock and it also comes with lettuce.

SWEETS/ DESSERTS

BEVERAGES
Burger King’s fruit smoothies are freshly made with low fat yogurt, real fruits and juices were blended to create tropical mango, raspberry, and strawberry banana. The coffee frappes are also made with real arabica bean coffee and blended until it’s smooth and creamy.

2.5. Internal Factor Evaluation Matrix
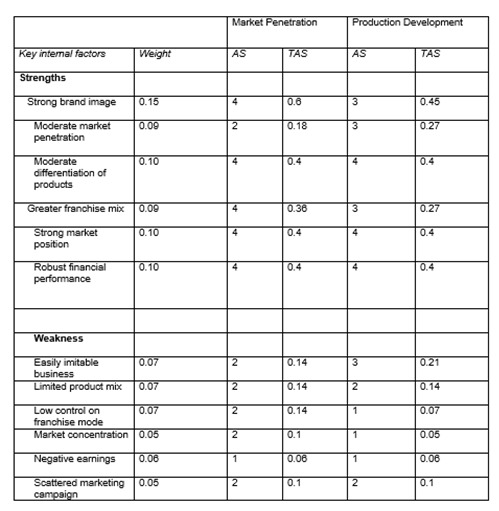
As you can see from the table, the strong point of Burger King is the strong brand image that they have which is equivalent to 15% in weight, 4 in rating and has a total of .60 in the weighted score; while their weak point is the market concentration which is at 5% in weight and 1 in rating that got a total of .5 in weighted score. In conclusion, Burger King’s weighted score is at 3.02 shows that Burger King internally performs well.

3.External Assessment
3.1. Porter’s Model Analysis
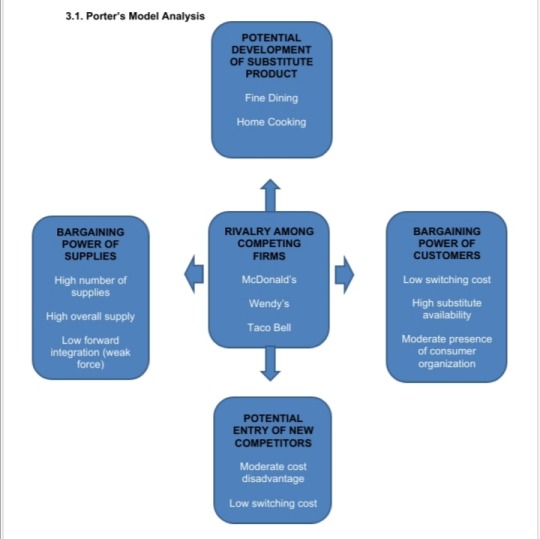
In the rivalry among competing firms, you can see that Burger King competes with major firms like McDonald’s, Wendys, and Taco Bell. In the potential development of substitute products, Burger King’s customers can transfer to another dining because they will have the choice to go to fine dining or prefer to just cook at home. Next, the factors such as the high number of supplies, high overall supply and low forward integration are what makes the bargaining power of supplies. Additionally, the potential of new competitors and new entrants are what Burger King should look after because that’s where they should perform low costs since they should be competing in the market. Lastly, in the bargaining power of customers, it is where high substitute availability, moderate presence of consumer organization, and etc. takes place.
3.2 External Factor Evaluation Matrix

External Analysis
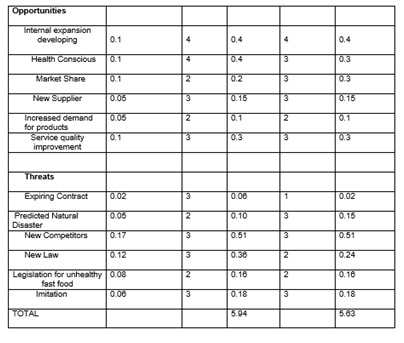
As we can see in the opportunities, market share has the highest weight compare to the others and the lowest for the weighted is New supplier and Increased demand for products. The rating of Internal Expansion, Developing Health-conscious & Market share got the highest rating, “while Increased demand for products got the lowest rating." The average of opportunities only indicate the total weighted score of opportunities.
In the table of threats, we can see that New Competitors have the highest threat in Burger King while the lowest threats are Expiring of contract. As for the rating of the threats, Predicted natural disaster and Legislation for unhealthy fast food got the lowest rate while the highest are New Competitors, New Law & Expiring contract. Total threats only indicate the average of weighted score of threats.
According to the EFE Matrix of Burger King, the total weighted score of the opportunities and threats is 2.92, which indicates the organization is responding in an above-average way to existing opportunities and threats in the industry.
3.3 Competitive Profile Matrix
Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM)
Competitor’s Analysis
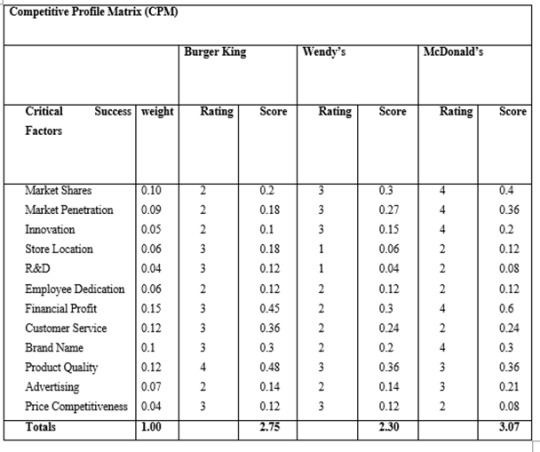
As seen in the CPM analysis, McDonald's is the most competitive in the industry with a total score of 3.07, leading in the critical factors market share, market penetration, innovation, financial profit, brand name, and advertising. Burger King, having a total of 2.75, has a relative strength in store location, Research & Development (R&D), product quality, and price competitiveness, tied with Wendy's. With the equal score of 0.12, all food chains in the matrix need to value their employees more as their employee's dedication is low in rating. Burger King should maximize their strengths and improve in market share, market penetration, innovation, and advertising because these are the factors where Burger King has the lowest rating. Financial profit has the greatest value of weight as it can really drive the business to followed by product quality and customer service, both are crucial in the fast-food chain industry.
3.4. Key External Factor
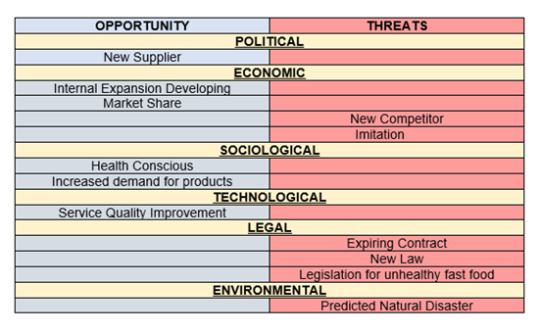
According to the chart above, External Factors are divided into six (6) forces that influence and affect Burger King externally. Both opportunities and threats are equally dividing, which shows that Burger King has balanced forces externally which means they could still be able to control and identify what forces are in need of improvements, solutions or changes in a way that would not have a bad effect to the company or negative forces that they might face in the future but still be able to strategize a plan. This PESTEL ANALYSIS would help Burger King to have a good global performance that would have long-term effectiveness to the business for future decision making.
4. Strategy Formulation
4.1. Boston Consulting Group Matrix
Boston Consulting Group Matrix of Burger king
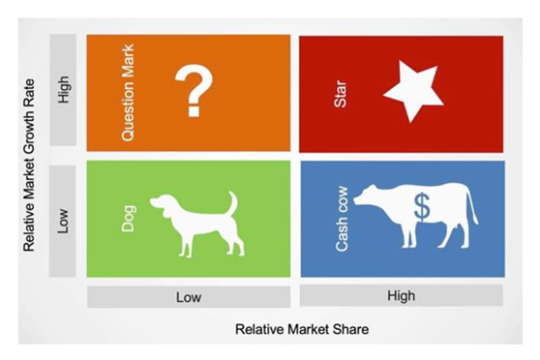
Figure 2. BCG Matrix of Burger King
● Star: Whopper Products, franchise owned outlet business
● Cash Cows: Supplier Management Service, International food strategic business unit
● Question Mark: Local Foods, confectionery market
● Dog: Ineffective market, Plastic bags, Synthetic fiber products, artificially flavored products strategic business units
In this figure, a strategic management tool will be used by Burger King to analyze the position of their strategic business unit and its market potential to offer their target markets. This BCG matrix would be helpful in a way that it will have a significant presence on deciding whether what kind of strategies can be implemented for Burger King to grow more, invest to their strengths and most especially is to consider the things that hinder their growth and success in the market.
● Star (High Growth, High Market Share)
In this aspect, it has a relatively high growth rate and high market share. The Burger King products, especially their Original Whopper Burgers have rapid growth and dominant market share. It also has 13,000 franchise-owned outlet businesses around the world and its presence in every country makes it a strong brand that is why it earned a lot of significant revenue from that strategy. However, to support their high growth and high market share, careful consideration should be given especially to their product development strategy to develop innovation in this intensive competition of the fast-food restaurants and tap the untapped areas to increase the sales or else, it will become a cash cow.
● Cash Cows: (Low Growth, High Market Share)
In this aspect, it has a relatively high market share but low growth. It is said to be high in market share, but the growth rate is declining and their competitive advantage because they manage their supplier with their own rather than outsourcing it. For them not to go beyond the decline stage, it must be taken into careful consideration of the innovation of their products, investing in research and development to be able to turn this cash cow into a star again. It will surely benefit the sales of the Burger King. In addition to this, the international food strategic business unit is a cash cow of Burger King. Within its category, it has a high market share of 30%. However, the target markets are now shifting their taste and now inclined less to the foods internationally that is why it affected the growth rate of Burger King. They must invest thoroughly to stabilize it, and if it no longer works, this strategy will now be divesting.
● Question Mark: (High Growth, Low Market Share)
In this aspect, it is relatively high growth but low in market share. Some products of Burger King are immensely consumed. However with the strong competition in the market, some customers are like the other restaurants that sells burgers as well. In this way, it is difficult to know if some of the Burger King will prosper and become a star of the brand. And most likely, it requires a significant amount of investment, especially in marketing and maintaining its market share. In line with this, the local foods strategic business unit of Burger King is considered a question mark because consumers are now inclined toward local foods. And burger king is having a low market share in this aspect. In this case, Burger King is most likely to consider and invest in this strategy in order to bring a high market share. Another thing is that Burger King is poor in reaching some areas, the confectionery market is growing for some years now. With that, Burger King needs to penetrate the market because not everybody is being targeted by their current strategy. If they include the confectionery market, surely, it will increase their sales and make it into a cash cow.
● Dog: (Low Growth, Low Market Share)
In this aspect, it has relatively low growth rate and market share. Many of their products have gone through their declining stage due to their marketing strategies and its rivals. Over the years, Burger King incurred losses and one of the reasons is the use of plastic bags. In this era where environmental concerns are being considered. They should divest this and move into an eco-friendly way. Another thing that made them in the dog category is their synthetic fiber products. It resulted from low market share and with that, it must be divested to not incur more losses. And last but not the least, is their use of artificial flavors in their products. Having to innovate products with artificial flavorings does not grow as expected because people nowadays are more health-conscious and as a result, their growth rate and market share dropped. With this, it must call back this product and free it from artificial flavorings.
4.2. Strategic Position and Action Evaluation Matrix
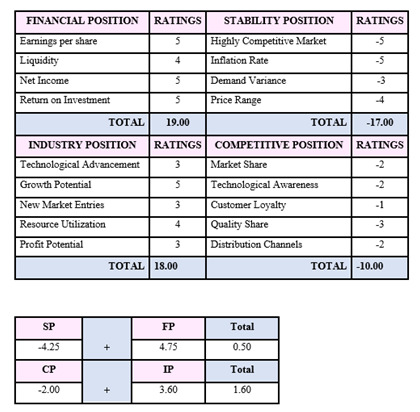

4.3. Grand Strategy Matrix
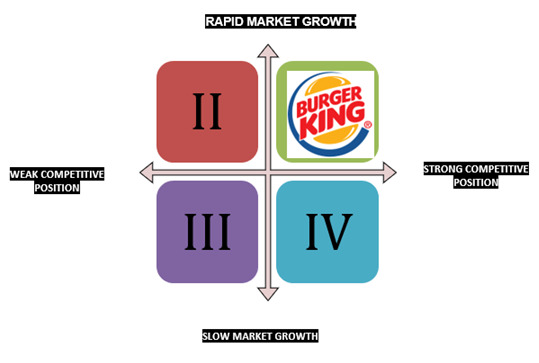
Burger King is internationally known and because of that, it is acknowledged as the 2nd largest Food chain in the industry, and that is how Burger Kind gained their competitive position. Burger King's strategy shows us how they gain their competitive advantage and the growth of its organization by producing and developing their products and resources. It indicates that Burger King is placed in quadrant I and reveals the Strong Competitive Position in the industry and their Rapid Market Growth. Burger King will grow and aim to continue growing their market environment and developing their products and markets to the industry and applying the integration strategies to have a great opportunity and to make the organization more successful in the industry.
4.4. Internal - External Matrix
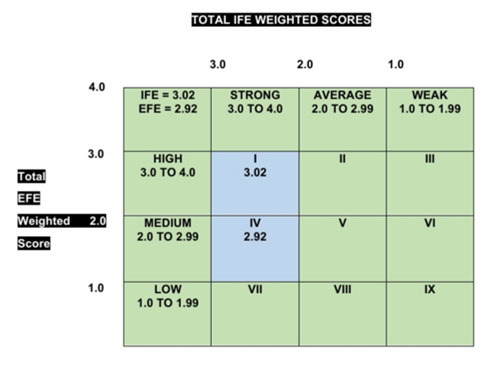
The score of Burger King’s Internal Factor Evaluation has a total weighted score of 3.02 and placed in a cell I which reveals that Burger King’s internal environment has a strong IFE outcome of strength and weakness that represents the internal firm. While External Factor Evaluation has a total weighted score of 2.92 that place in cell IV which reveals that the external environment of Burger King identified as a medium outcome score in EFE when it comes to the external opportunities and threats.
The results of IFE and EFE weighted scores are placed under cell I and cell IV, which is the Grow and Build strategies. This segment has a division of Market penetration, Product Development, and Related Diversifications and from the other point of view, backward integration, forward integration, and horizontal integration are also strategies that can be considered and reasonable on this division.
4.5. Strength - Weaknesses- Opportunities - Threats Analysis
Strengths
1. Strong brand image
Burger King takes advantage of its well-known brand. Since 1969, the logo has hardly changed. The famous terms "Burger King," squashed between two drawn hamburger buns, can still be recognized.
2. Moderate market penetration
Market penetration is Burger King's primary expansion strategy. The objective of this comprehensive approach is to increase sales from current customers or markets in which the company already operates.
3. Moderate differentiation of products
Burger King was among the most well-known brands in the business. The company would be able to open new restaurants and introduce new products more easily. Because of the large number of Burger King restaurants around the world, higher market penetration is a strength. Burger King's mild differentiation is also an asset, allowing the company to ensure that some of its products are unique.
4. Greater franchise mix
With over 18 thousand franchised restaurants, the business has almost exclusively become a franchised chain in recent years. Just 52 units are still owned by the company. Even though Burger King has decreased the number of company-owned franchises, the total number of locations has increased every year over the last decade.
5. Strong market position
Market positioning is the method of presenting a brand to potential customers in such a way that they can easily see how it compares to competing products. Burger King targeted the young adult market, especially young males, and positioned itself as a provider of high-quality, great-tasting, and affordable food.
6. Robust financial performance
Burger King's income statement has been strong in recent years, increasing year after year, making them very competitive in their industry as compared to other fast-food restaurants.
Weakness
1. Easily imitable business
Some fast-food restaurants that also has Burger on their menu can easily imitate the Burger King’s best-seller which is the “grilled burger”. They can produce similar products and lower their price because they are the one of the most saleable products in the market when it comes to burgers.
2. Limited product mix
Burger King maintains a limited approach which is shown in its limited product portfolio. Nonetheless, by economies of scale from large-scale sales of a limited range of product lines, this product mix helps Burger King's generic strategy.
3. Low control on franchise model
Acquiring a franchise entails entering a legally binding arrangement with the franchisor. Since franchise agreements determine how you run your company, you will have a little control over the franchise model, leaving little space for innovation. There are usually limitations on where you can operate, what items you can sell, and who you can work with. You would also have a lack of privacy in addition to these issues.
4. Market concentration
This can be a flaw because high concentration means that the top companies have a lot of influence over the market's products and services. It will result in higher prices and lower consumer security because just like Burger King, which is owned by Jollibee. The top firm Jollibee can set price rules and set certain services that can affect small firms.
5. Negative earnings
Full-service restaurants dominate the Philippines fast food industry, with a 31.8 percent market share in 2017. The 100 percent home service delivery sub-segment is the fastest-growing segment, followed by street stalls/kiosks, during the forecast period.
6. Scattered marketing campaign
The scattered marketing used by Burger King can affect current and potential customers. This could result in a low return on marketing campaign investment
and the loss of existing consumers, who would turn to brands with clear and insightful messaging.
Opportunities
1. Internal expansion developing
Burger King's intensive approach has a strategic goal of targeting new consumers in new markets by offering low prices. This intensive strategy entails entering new markets or targeting new consumer segments to support business growth.
2. Health conscious
Consumers are increasingly turning away from unhealthy foods high in fat and calories, therefore introducing healthy options is a smart strategic move. Burger King Worldwide believes that by combining culinary creativity with improved operations, guest satisfaction will be enhanced, as well as the company's profitability.
3. Market shares
Full-service restaurants dominate the Philippines fast food industry, with a 31.8 percent market share in 2017. The 100 percent home service delivery sub-
segment is the fastest-growing segment, followed by street stalls/kiosks, during the forecast period.
4. New supplier
Because of expansion they will seek new supplier with lesser delivery price and product cause
5. Increased demand for products
When the price of meat and vegetables decreases, the price of the meal tends to fall as well, which increases the demand for burgers. A satisfied customer is higher, which is a major factor in the rise in demand.
6. Service quality improvement
Burger King's service quality, the use of quality dimensions such as tangible, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy is used to effectively and assess the quality service of the restaurant.
Threats
1. Expiring contract
If there was a contract it is short term only for the employees, it not a lifetime work because it is a contractual basis.
2. Predicted natural disaster
Climate and its effects around the globe can impact negatively on companies' bottom lines in several ways. Extreme weather, both in the Philippines abroad, can damage factories, supply chain operations, and other infrastructure, as well as disrupt transportation.
3. New Competitors
A company's competitive advantage is compromised when new companies enter an industry offering the same services or goods. As a result, the threat of new entrants applies to a company's ability to enter a market.
4. New Law
Implementation of tax increase because Tax cuts can boost business demand by increasing firms' after-tax cash flow, which can be used to pay dividends and expand activity, and by making hiring and investing more attractive.
5. Legislation for unhealthy fast food
If there is regulation restricting the production of unhealthy foods, the cost of food will increase so there will be an increase in nutritional value, leading to increased cost to the company.
6. Imitation
Product imitation has a significant impact on the financial results, lagged asset return, and having a good marketing campaign will significantly influence market share for the sins that people can prioritize imitation with nearly the same quality as the original product with glass market value does the aim for the great return of us it slow.
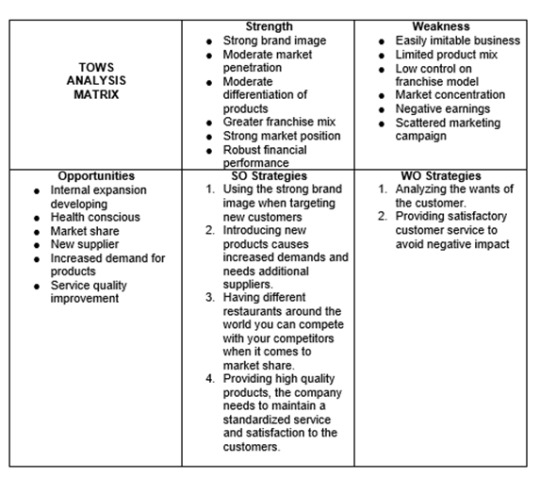

Two strategies were formulated from the TOWS Matrix: Market penetration and Production Development. Burger King needs to advertise or promote their business to stay competitive with other companies, they must improve their production and adapt to new trends in the industry.
4.6 Quantitative Strategy Planning (QSP) Matrix
The findings revealed that production development is preferable over market penetration. The two methods have similar ratings, indicating that they can both be applied by the company.
5. Strategy Recommendation
New strategy recommendations are vital for a company, especially when they are aiming for more success. These are the strategies that Burger King can use, and this includes Market Penetration, Market Development, and Product Development.
Strategy 1- Market Penetration
It is said that Burger King’s weaknesses are Market Concentration and Scattered Marketing Campaign, so the strategy of market penetration will be able to help with these weaknesses. Market Penetration will help when it comes to Burger King’s presence, and it will also help in improving their influence. Market Penetration focuses on the brand’s image like partnering with other brands, companies or even with people who have a very great image. It will help in having better marketing or branding strategies and it can also result in the company’s opportunities in the future. Market Penetration will also improve the company’s sales and it will be more recognized by more potential customers since they also need to improve their advertisement skills. Market penetration also helps when it comes to improving the company’s pricing.
Strategy 2- Market Development
Market Development is a strategy that is helpful when it comes to introducing a company’s products to new locations. Market Development will help in developing the business or market through expansions. This is a great strategy since we can see that Burger King is already very successful in their field so opening in more locations will not be that complicated for their company. Market Development is a strategy that can help Burger King in gaining more competitive advantage and it makes the business to be locally, and internationally known. The market development will help burger king to be known in every area in our country and all around the world. This can also help when it comes to improving Burger King’s Marketing Skills and Location development. If the company also focuses on opening more branches in different locations, they will have more control and it can lessen the issue that is related to their franchise models. Having more locations can also lead to the company’s increased earnings and it is a great way to compete with their major competitors which are also opening more branches in every location that is possible.
Strategy 3- Product Development
Product Development is a strategy that involves the development of the existing products, and it may also be used to develop new products that Burger King can release. This can give a new life to the company’s existing products, and this can also help with their new marketing skills that their customers will be curious about. Product development is a strategy that can provide satisfaction to the customers, improve the company’s reputation, improve competitiveness, and improve their quality and performance. Product Development is also one of the best strategies when it comes to improving burger king’s weakness which is having a limited product mix.
6. Action Plan
The action plan includes the steps or suggestions that the company can do to be successful. The action plan will help when it comes to the steps that the company needs to consider so that it can lead to the business’ improvements.
Action Plan 1- Market Penetration
This plan will involve better Marketing and Pricing Skills that Burger King should implement. It is said that Burger King’s market concentration can be seen as a flaw to the business so the best thing to do is to adjust their price range. They also have a scattered marketing campaign which can lead to losing existing and potential customers. Burger King can make their products more known or recognized, and they can compete with other companies by lowering the prices of their products and at the same time it still has a great quality. They can also partner or collaborate with famous influencers so that their sales would increase, their marketing and advertising skills will improve, and their business will be more known so it can result in higher consumer security. Burger King can also improve their location to be more known by the customers and in the market field.
Action Plan 2- Market Development
Market Development will help in maximizing Burger King’s full potential in the business industry. They already have a lot of locations that are operating but they still have a lot of potentials when it comes to opening more branches in different locations so that it will be more known, and it can also lead to their control over their products and service. Burger King can search for more great locations for their business since this will be a great advantage to be able to compete with their major competitors which has a lot of branches in different locations. Unlike their other competitors in the country, Burger King does not have a lot of branches when it comes to provincial areas so having more expanding their business in more locations will be beneficial. When they already have more locations, then they will also have more target markets who are their new potential customers. Market Development can also help when it comes to improving their weakness that is related with negative earnings since when a business is already well known and successful, then there is a high possibility that this will lead to an improvement with the company’s sales and earnings.
Action Plan 3- Product Development
Product Development will be helpful since we can also see in this paper that one of Burger King’s weaknesses is that they have a limited product mix. They have a limited range of product lines like burgers or rice meals. The action that Burger King should consider is to provide new packaging for their products and this also works for other brands. They can provide limited edition products with great packaging and when this becomes successful, they can keep this new product on their portfolio or menu. They can also release more rice meals, drinks, desserts, and new flavors of their famous burgers which they are famous for. Adding healthier options can also be a great improvement for their business because this will be perfect for the customers who are into the healthy lifestyle trends. Through product development, they can also improve the demands, and quality of their products which can result in more customers who will be loyal with their brand.
7. Conclusion
To summarize everything that has been stated so far, we therefore, conclude that Burger King Corporation is performing above the average. Meaning, this food chain is very well operating and competing with its competitors. As the years go by, it is constantly keeping up to cater its market, to meet the needs of its customers, and to be one of the top food chains in the industry.
As you have seen, the Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) Matrix shows that the Burger King Corporation has a total of 3.02 weighted score which means that it is internally strong. Also, the External Factor Evaluation (EFE) Matrix proves that the total weighted score of opportunities and threats are equal to 2.92 which indicates that Burger King Corporation is an above-average level. Moving on, Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM) stated that Burger King is only on the second spot in competing with McDonald's which has a total score of 3.17 while Burger King Corporation has only 2.75, and lastly, the Wendy's at the third spot having a 2.30 total score.
Moreover, in the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix, you have seen that what makes that Burger King have high growth and high market at the same time is their whopper products and franchise-owned outlet business. Also, the reason why Burger King Corporation falls to this quadrant is that they have rapid growth, dominant market shares as well as 13, 000 franchises around the world. Furthermore, the Strategic Position and Action Evaluation (SPACE) Matrix of this food chain shows that Burger King falls in the "aggressive" quadrant since it has a total of 0.50 in Financial Position (FP) and Stability Position (SP) while a total of 1.00 in Industry Position (IP) and Competitive Position (CP). Additionally, the Grand Strategy (GS) Matrix proved that Burger King Corporation has a strong competitive position in which strategies such as product development as well as integration strategies will best suit this food industry. To add up, the Internal-External (IE) Matrix shows that the Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) falls in cell I which has 3.02 and the External Factor Evaluation (IFE) falls under cell II because it has a total weighted score of 2.92.
As you have seen, the Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) Matrix shows that the Burger King Corporation has a total of 3.02 weighted score which means that it is internally strong. Also, the External Factor Evaluation (EFE) Matrix proves that the total weighted score of opportunities and threats are equal to 2.92 which indicates that Burger King Corporation is an above-average level. Moving on, Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM) stated that Burger King is only on the second spot in competing with McDonald's which has a total score of 3.17 while Burger King Corporation has only 2.75, and lastly, the Wendy's at the third spot having a 2.30 total score.
Moreover, in the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix, you have seen that what makes that Burger King have high growth and high market at the same time is their whopper products and franchise-owned outlet business. Also, the reason why Burger King Corporation falls to this quadrant is that they have rapid growth, dominant market shares as well as 13, 000 franchises around the world. Furthermore, the Strategic Position and Action Evaluation (SPACE) Matrix of this food chain shows that Burger King falls in the "aggressive" quadrant since it has a total of 0.50 in Financial Position (FP) and Stability Position (SP) while a total of 1.00 in Industry Position (IP) and Competitive Position (CP). Additionally, the Grand Strategy (GS) Matrix proved that Burger King Corporation has a strong competitive position in which strategies such as product development as well as integration strategies will best suit this food industry. To add up, the Internal-External (IE) Matrix shows that the Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) falls in cell I which has 3.02 and the External Factor Evaluation (IFE) falls under cell II because it has a total weighted score of 2.92.
Besides these matrices, we therefore, conclude that the Strengths-Weaknesses-Opportunities-Threats (SWOT) also come up to consider the strategies Market Penetration and Product Development to remain competitive as well as to adopt new concepts that will surely fit the trends in the industry. That is why in the (QSPM) Matrix, the methods or strategies Market Penetration and Product Development can be applied to Burger King Corporation for the food chain company to keep in the right track. To successfully achieve these goals the strategy recommendation comes up with an action plan on how these strategies will work and will help the company to be competitive as well as to perform better than usual. And so, this is the findings that this paper found.
8. Financial Projection
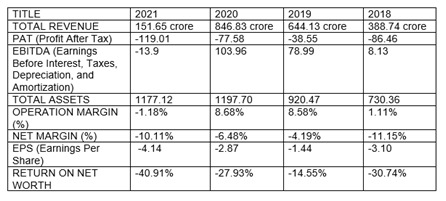
As shown in the chart Burger King’s revenue has a huge step up from the year 2018 which only shows that it is the best year of Burger King because their income has drastically risen and it continues to grow up until 2020 despite the current pandemic crisis situation, it somehow shows that Burger King wasn’t that much affected by the Crisis.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Covid 19 and the New Era
Initially published on the OA blog here.
Part 1: Goodbye to the end of History
31 years ago, US political writer Francis Fukuyama wrote an essay titled The end of history. In it, he summed up what many were feeling at the conclusion of the Cold War: without a grand historical conflict between world superpowers, what further challenges could there be to the system we live under today: capitalist liberal-democracy? In this essay, and his later books, he wrote that with the collapse of the Soviet Union, most world governments would shift towards a liberal democracy, with an emphasis on transnational government much like the European Union, and with this new epoch would come a period of unparalleled peace. Events might still occur, he said, but the overall trend of civilisation would be towards endless peace, endless profit, and endless technological advancement that would eventually lead to humans having control over their own evolution.
What Fukuyama might not have predicted is that his simple thesis would become one of the most criticised essays of all time. Barely had the ink dried on his paper when scores of writers poked holes in his analysis – something very easy to do, for Fukuyama wasn’t much of a philosopher, but rather a political hack who summed up the dominant view among liberal thinkers at the time. In this, he was wholly successful, but he also ended up being correct in ways his critics couldn’t have predicted.
The next 31 years of history were some of the most uneventful, in terms of real movement, of any decades that had passed before – sure, not all countries became liberal democracies, and sure, history continued to chew up innocent lives and spit them back out, and sure, a few terrorists showed up here and there – but it seemed that no single event could ever truly change things beyond occupying the evening news for a few weeks. We have just emerged from the one of the most viscerally boring periods in human history, at least for the more sheltered populations in the west, and it’s important to recognise this.
Fukuyama’s end of history was not a new thesis: as the postmodernist Jaques Derrida, was quick to point out, Fukuyama had simply regurgitated some of the most turgid liberal philosophies of the early Cold-War era; the idea that liberal-democracy had emerged victorious, and that socialism had been proved wrong once and for all through the many perceived failures of Soviet societies. All that had changed was that Fukuyama said it at the right time: it truly was the end, capitalism had found its perfect justification in neoliberalism, a set of ideologies based in the idea that capitalism was a perfect, trans-historical goal of humanity, that only needed to be sufficiently untethered from regulation and sufficiently protected by a growing military and police forces in order to function properly. In this proper version of capitalism, untethered from the need to legitimise itself in the face of opposing ideologies, there was no need for capitalist societies to change to face new threats, for what can challenge an ideology that is so totalising it can convince people that it’s the only thing that exists? The only thing that has ever existed. A universal default.
In that sense, Fukuyama was perfectly right. History did grind to a halt for three decades. Not just the history of those decades, but all history, for every society throughout history could be painted as nothing but a stepping stone to this universal conclusion. There was no challenge to neoliberalism in that time, no great ideological foe to defeat, no workers’ movement to crush, and the best that the neoliberal states could offer up as some immense civilisational enemy was a pitiful force of Wahhabi terrorists – a by-product of the previous era, and therefore hardly a new historical agent. All that was left for the world to do was to reckon with the leftovers of the Cold-War period (the Wahhabis, remnant socialist societies, and shrinking unions), products of the last true period of historical movement, and wait for whatever technological innovation that would come next and inject some feeling of forward momentum into an otherwise stagnant society.
In time, even technology failed to deliver a feeling of progress. Each new technology of the period wasn’t truly new: all that capitalism could deliver was slightly faster and more powerful versions of technologies based in the previous era of major public scientific investments. Internet, wi-fi, cell phones, miniaturised processors, satellite communications – every single one of these technologies was a product of Cold-War era military or public scientific investment, albeit with a better marketing team. It is almost as if capitalists could produce no new innovation whatsoever, other than a faster, slimmer version of existing tech, that broke more often.
In this sense, one of the two defining features of the past 30 years that gave life a sense of movement and progress, communications technology, proved to be nothing but a latent product of the previous era, that came up against a wall as soon as the legacy technologies it relied upon reached the limits of exploitability. The same would soon be proven true of the other great symbol of neoliberal progress: economic growth.
Since the beginning of the end of history, economic growth has skyrocketed. Only part of this was due to imperialism – the ability for strong states with financial capital to spare to offload their surpluses onto the global south. That would have been a source of actual value were it the primary cause of this continuous economic boom, since it would have meant greater exploitation of labour. Instead capitalism developed along the much easier route – pure speculation in financial markets and tech companies, both of which are largely phantasmal.
Capital was creating a bubble – not of any one market, such as the late 90s tech bubble or the late 2000s housing bubble, but rather it was making a bubble out of capitalism as a whole. Who could have guessed what would pop it?
Part 2: What the fuck is going on?
Sometime around December 1, 2019, a few people got sick in the Chinese city of Wuhan. Many writers have spent thousands of hours speculating about the potential causes of transmission. Was it from a shopper at the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market? Did the disease come from the actual produce at this market? Was it a bioweapon? Was it a bat? A Pangolin? Was everyone at the market just too weird and Chinese to not get the disease? What comparatively few news sites have focused on was how on earth a virus could cause an economic crisis so great that we have nothing to truly compare it to.
This is because it could have been anything. It could have been a completely different virus in a completely different country, it could have been a sudden war erupting, it could have been a plane crash, it could have been a Wall Street Executive slipping on a banana peel. The system of global financial markets had been systematically hollowed out and prepared in every possible way to collapse at the drop of a hat sooner or later. To understand how, we need to understand three things: the underlying philosophy of neoliberalism, the way a modern financial market operates, and the general theory of economic crisis put forward by Karl Marx in his unfinished third volume of Capital.
Under neoliberalism, austerity is everything. The existence of everything, often including human life, has to be justified in terms of cost-effectiveness, self-reliance, and interoperability with the rest of the system. This is why social welfare, such as Work & Income New Zealand, operates by giving the absolute bare minimum to beneficiaries, and why all government departments, with the exclusion of Defence, Police, and Corrections, have to operate on paper-thin budgets, constantly needing to justify any expenditure whatsoever in terms of net-benefits to the economy. It is also not a rational ideology, in that in pursuing its goals of profitability and lean government, the means are much more important than the ends. A health system stretched thin (the “ambulance-at-the-bottom-of-the-cliff model”) might actually be more costly to society than a health system which is budgeted to act preventatively and deal with unexpected crises, but this doesn’t really matter. Likewise, stockpiling, preemptively initiating spending, or even paying for proper maintenance can come to be seen as unnecessary luxuries in a system in which everything must be justified in terms of short-term profitability.
This is why the richest country in the world ended up with a shortage of basic medical supplies. Under ideal circumstances, each hospital should have had just enough masks, gloves and smocks to last a normal week, just in time for a new shipment. The same is true of most systems of logistics and supply under neoliberalism – things enter the warehouse, the shipping container, or the truck, just in time for them to leave. If anything stays in the warehouse, or is stockpiled, then that is an inefficiency in the system. Every minute those hospital gowns spend in the warehouse means a surplus is developing, which means profits lost for the manufacturer and shipping company.
The same logic rings true for financial markets. Each sector of the economy deals in just enough liquid assets (money) to operate under normal circumstances. If too much money circulates in the economy at any one time, then we get inflation – the decline in the value of currency. In a crisis, excess liquidity can be a good thing, which is why the US markets are being flooded with trillions of dollars, but under normal circumstances, these simple laws of financial supply and demand create an incentive for capitalists to invest their cash assets as soon as possible, never leaving anything in reserve in the event of a crisis.
But all of this, supply and demand, surplus and shortage, is somewhat obsolete under late capitalism. Contrary to popular belief, most microeconomic problems are pretty easy to solve using the microeconomic levers most accessible to capitalists such as changing prices, production or wages. Capitalists make them out to be huge, complex issues so that price regulation can be painted as naive meddling in the arcane market, but really, these simple problems like overproduction, underproduction, low demand, and the like, can all be fixed using the tools of the private sector. Larger systemic problems (macroeconomic issues), such as sovereign debt, low competitiveness, trade deficits, and poor consumer buying power, can also be fixed, but through the financial levers available to the state, such as bailouts, stimulus packages, elimination of reserve requirements, and massive liquidity injections. What can’t be fixed, at least not permanently, is the general downward trend in profits relative to investment.
The more serious problems of late capitalist economics – wafer-thin profit margins, constantly slowing rates of growth, and constant fears that consumers are “killing” various industries – are all products of one phenomenon that Karl Marx identified as far back as 1857, the discovery of which he called his “greatest triumph” but which remains a lesser known Marxian theory. This is the tendency of the rate of profit to fall, a hypothesis which explains why capitalism is doomed to perpetually swing between boom and bust, until it reaches a crisis from which it can’t recover.
Central to Marx’s theory of crisis is a much more famous theory – the labour theory of value. Put simply this is the idea that all the value that capitalist society places on a commodity comes from the workers who harvested the raw materials, worked in the factory that made it, and built the machines that filled the factory. The work being done by living workers is supplemented by the machines that other workers have made to assist them in their work.
The living people involved in this system are the organic component, while the machines, products, and other lifeless objects are the inorganic component. Taken together, the ratio between these components is the organic composition of capital (OOC). When there are few workers but many machines in a factory, the OOC is lower, and so the productivity of these workers is very high because the machines allow them to multiply their efforts. But high productivity creates a problem – if all of this work can be done by fewer workers, then unemployment will surely rise, wages will go down, and fewer people will be able to pay for the products from the factories. Eventually this leads to a crisis of consumption, which is what we are currently experiencing, and unless you’re over 50 or so, you’ve probably been experiencing one your entire life.
In a consumption crisis, wages are far too low for people to buy commodities or easily reproduce their capacity to work. Since the 1970s, wages have stagnated in most Western countries, but until now capitalists had many ways they could “kick the can down the road,” delaying the crisis for another few years and making higher and higher profits in the meantime. For example, to absorb the huge surpluses generated by an economy undergoing a consumption crisis, Capitalist states could offload their surplus values onto colonies and nations in the global south by creating new markets, or waging wars and thereby investing in weapons and reconstruction. A good example of this was the 2003 Invasion of Iraq, which ended up costing trillions of dollars, allowed for billions to be invested in weapons manufacturers, and opened up a handful of new markets in the bombed out ruins of Baghdad or Fallujah.
This is one way to offset a major crisis, which we might call the “fuck the rest of the world” method. The other method is a bit harder for the capitalists, which is to massively increase consumer buying power through various measures. The most straightforward of these is the one capitalists are most loath to do, since it undermines neoliberal ideology, which is to simply give people money. This was done in Australia in 2008, when each Australian was given $300 and ordered to spend it immediately. Many other countries, even the US, are now rushing to copy this method of stimulus. Another method, which has been growing since mid last century, is by artificially raising a stratum of consumers through employing people in “bullshit jobs,” a term used by economist David Graeber to refer to people engaged in work that doesn’t seem to do anything. This includes a lot of professionals: secretaries of secretaries, managers of managers, supervisors of supervisors and the like. Finally there is another method which is gaining traction among some of the more far-sighted capitalist technocrats, the Universal Basic Income (UBI), which would give people a flat rate of just enough money to fulfil their duty to the economy as consumers. Such a move would represent a last-ditch effort by capital to avoid the looming consumer crisis, which at time of writing appears to be a tsunami whose waters have only reached chest-height.
However, all of these means can only delay the inevitable. A capitalist system undergoing crisis can only offset the real crunch for so long. In 2008, the global capitalist system experienced a major shock when a speculative housing bubble popped in US financial markets. If the crisis continued, the capitalist class would have had to sell off huge amounts of assets, including industrial machinery. This would have solved the underlying productivity crisis for a time by restoring the huge imbalance between the organic and inorganic composition of capital. But this imbalance had been building for decades. Could the capitalist system survive the shock? Mass sell-offs are nothing new – the first response of the US government to the 1929 Wall Street Crash was to encourage these sell-offs, only to find out that doing so would massively increase public unrest from both capital and workers.
In the end, the crisis was instead offset through fiscal policy, as the US federal reserve removed barriers to debt and artificially preserved the value of assets by paying off capitalists with sums that often exceeded the value of their entire business. For this reason, the recovery from the 2008 crisis was slow, but the crisis itself was short-lived. The speculative bubbles weren’t quite popped, but enough air was let out to delay the inevitable, for about 12 years, as it turned out.
Part 3: Infinite new era
It is still entirely possible that the capitalists will be able to kick the can further down the road, and avert the current crisis through arcane fiscal finagling or through truly barbaric methods like forcing US and UK workers back into the workplace well before it is safe to do so.
But it seems equally possible that the world as we know it is over. By this I don’t mean that we’ll soon be living in a Mad Max-style apocalypse, but rather that period of “the end of history” is finally over. Capitalism will probably recover, either through solving the crisis through the above means before it gets worse, or it will allow the crisis to reach its conclusion and engage in massive selloffs of fixed capital, which might extend its rule by several decades by restoring some degree of profitability relative to investments. What that could mean for our people and ecology is anyone’s guess.
But whatever the results of this crisis are, one thing seems very clear. For the first time in our lives, workers have been forced to sit at home and think – not between shifts, or under the endless stress of being a beneficiary expected to look for work that often doesn’t exist, but just thinking, and getting bored. I don’t remember a time when capitalism gave an entire class of people the opportunity to get truly bored, apart from the upper classes, who get to call it ennui.
The politics of idleness are interesting. A few thousand years ago, the backbreaking labour of slaves, poor citizens, and women created the opportunity for the first truly idle class – the Ancient Greek philosophers who are credited with the entire foundation of our moral and political systems. For the next few thousand years, the only people who were allowed to be idle were the sons of rich nobles and merchants, and only with the birth of capitalism did common people find themselves idle – the unemployed newly-displaced rural folk who waited outside the great cities of Europe, waiting for jobs at the new textile factories to open up. Many of these people became the backbone of the first workers’ parties, often millenarian Christian-socialists and underground brotherhoods like the Chartists, Luddites, or League of the Just, which Marx and Engels would later co-opt and rename The Communist League.
Idleness in these times was feared greatly by those in power, and rightly so. Nothing worried them more than huge surplus populations growing restless, organising in their idle time, and realising their position somewhere near the bottom of a great social pyramid. From time to time these surplus populations grew so great that entire nations had to be set up just to get rid of them: the unemployed and wretched masses of the British Isles found themselves criminalised and subject to transportation to the penal colonies of the Caribbean, the Americas, and later New South Wales. Luckier surplus citizens found themselves in the free colonies, such as Perth, or New Zealand.
But are we truly surplus to requirements? Surely after the crash we’ll get our jobs back?
Many economists aren’t so sure. Unemployment modelling already shows rates are going to grow higher than during the great depression, and that’s without a much more pessimistic Marxian analysis of the crisis. To be surplus is a new experience to many of us. Idleness will force us to reckon with our position in the pyramid of society, just as those 19th century oligarchs were afraid of all those years ago.
The ideological backbone of capitalism as it currently exists has been broken. Neoliberalism has shown itself incapable of dealing with Covid-19. But what we make of this realisation is up to us. The ideological backbone might be broken, but the real nuts and bolts of the system: the police and politicians, bosses and workplaces, will still remain. Given enough time, they will use this crisis of legitimacy to forge a new kind of capitalism: maybe a society with a UBI? Or a form of eco-capitalism? Or maybe they’ll go the other direction, and lead us down a road to fascism, or Trumpian nationalistic fervor? If I had to place bets, I’d put it on a mix of all of the above, as usually seems to happen in a crisis of legitimacy. After all, the last great crisis of legitimacy happened during the Great Depression, leading to both the social-democratic compromise of the New Deal and Michael Joseph Savage’s welfare state, as well as the horrors of Nazism.
In truth I don’t think it matters so much what path capitalism chooses to take in order to legitimise itself in this new era, because unless the agency of that choice lies with working people – with beneficiaries, Māori, migrants, the multitude, the proletariat – it will leave us worse off. It might end the crisis, but we’ll live with the knowledge that the next one will be worse, and once again our lives will be utterly beyond our control.
So agency should be our watchword in this new era. So long as we lack agency, we are only a few years from collapse. So long as we lack agency, the response to crises will be arbitrary. New Zealanders got lucky in getting a rational response to the crisis, but next time we might be more like the US or UK – sending thousands more people to die in the name of profits. Taking power, then, is the only way to ensure that this total lack of agency never happens again.
So far in the things I’ve written for this blog, I’ve not actually included a call to join Organise Aotearoa. In a system built on broken promises, who am I to make a promise to readers that things will get better if only we fight for a revolutionary overthrow of the bosses, police and markets that put us in crisis again and again? As an organisation, we are young, and we are emerging from a very beaten-down, hollowed-out, and disparate left-wing movement. Revolution doesn’t seem realistic to many people, but then, neither did capitalism being crushed by a virus a few weeks ago. Socialism will never just happen – it takes work, and a sense of realism. We have a lot of work to do, but only in this period of transition can we see the possible futures laid out before us – apocalyptic misery, or social and economic justice. To fight for this is always worth the effort.
The best summary of the times we’re living in come from this quote I’m quite fond of:
“There are decades where nothing happens; and there are weeks where decades happen”
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
Banana Puree Market: Luxuriate in the Finest Pureed Bananas

Market Overview:
Banana puree is made from fully ripened banana which is finely mashed or sieved to obtain a smooth consistency. It is widely used in baby food products, yogurt, ice cream and other desserts due to its sweet taste and high nutritional profile.
Market Dynamics:
The banana puree market is expected to witness significant growth over the forecast period owing to high nutritional profile of bananas and growing demand for plant-based and organic baby food products. Banana puree is rich in potassium, vitamin C and fiber which make it healthier option for baby food products compared to other fruits. Additionally, increasing number of working women and dual income households have boosted the demand for convenient and ready-to-mix baby food products, thereby propelling the banana puree market growth.
Growing demand from processed food industry is driving the banana puree market
The processed food industry has been witnessing significant growth in demand for banana puree. Banana puree finds wide application in making baby food, ice creams, yogurt, baked goods and other processed snacks. It helps enhance the flavor and nutritional profile of processed foods. With rising health consciousness, consumers are increasingly preferring food products containing natural and organic ingredients like banana puree. Moreover, busy lifestyles have fueled the demand for convenient packaged food items where banana puree is used as a key ingredient. Many food manufacturers are introducing new product lines incorporating banana puree to cater to consumer demand. This growing demand from the processed food sector remains the primary driver propelling the banana puree market.
Increasing demand from confectionery industry is fueling the banana puree market
Confectionery products like candies, gums and chocolates have been experiencing growing demand globally. Banana puree is widely employed in manufacturing confectionery items owing to its sweetness and ability to enhance taste and texture. Moreover, banana puree aids in moisture retention and improves shelf life of confectionery products. Many confectioners are focusing on launching new banana flavors in candies, gums and other products. Additionally, banana puree extracted from organic bananas is gaining traction from health-conscious consumers. This rising demand from confectionery manufacturers continues to bolster growth of the banana puree market.
High dependency on weather conditions is posing a challenge for banana puree market
Supply and quality of bananas are heavily dependent on climatic conditions like rainfall, temperature and humidity levels during cultivation and harvesting. Any abnormal weather fluctuations can significantly damage banana crops, leading to low yield and reduced availability of raw materials for banana puree production. Climate change has also increased frequency and intensity of natural disasters disrupting banana cultivation. Droughts or excessive rains negatively impact banana crop growth and harvests. Furthermore, pest infestations aggravated by changing weather patterns pose quality issues in banana production. This high dependency on favorable weather conditions poses a major challenge for consistent supply and stable prices in the banana puree market.
Growing demand for organic banana puree presents a lucrative opportunity
Increasing health awareness has fueled demand for organic and natural food ingredients without artificial preservatives, colors or flavors. This rising trend represents a huge opportunity for organic banana puree market. Organic farming practices avoid use of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers to produce pesticide-residue free bananas. Since banana puree is widely used in baby food and other products targeting health-conscious customers, demand for its organic variant is expected to surge. Moreover, preferences for sustainable and eco-friendly products also promote organic banana puree market. Banana producers can capitalize on this favorable opportunity by obtaining organic certifications and catering to premium segment demand.
Manufacturers are innovating with banana puree to tap evolving trends
The banana puree market players are innovating with product development leveraging latest industry trends. They are introducing banana puree in various formats like freeze-dried powder to increase shelf life and suit customized applications. Moreover, different flavors obtained from blending banana puree with other fruits are gaining traction. Banana puree infused with functional ingredients like probiotics and prebiotics have also emerged addressing health trend. Similarly, private label brands are employing banana puree in convenient packs aligned with on-the-go snacking trend. Such innovations help tackle industry challenges and cater to dynamic consumer needs. This innovation with products and packaging remains a key trend shaping the future growth dynamics of banana puree market.
#Banana Puree Market Share#Banana Puree Market Growth#Banana Puree Market Demand#Banana Puree Market Trend#Banana Puree Market Analysis
0 notes
Text
Global Banana Puree Production and CAGR (%) Comparison by Type (Product Category) 2012–2022
In this report, the global Banana Puree market is valued at USD XX million in 2016 and is expected to reach USD XX million by the end of 2022, growing at a CAGR of XX% between 2016 and 2022.

Geographically, this report is segmented into several key Regions, with production, consumption, revenue (million USD), market share and growth rate of Banana Puree in these regions, from 2012 to 2022 (forecast), covering North America Europe China Japan Southeast Asia India
Request a sample of this report @ https://www.reporthive.com/enquiry.php?id=1140030&req_type=smpl
Global Banana Puree market competition by top manufacturers, with production, price, revenue (value) and market share for each manufacturer; the top players including Sunrise Naturals Newtown Foods USA Jadli Foods Shimla Hills Galla Foods Jain Irrigation Systems Ltd Gehrke Company, Inc.
On the basis of product, this report displays the production, revenue, price, market share and growth rate of each type, primarily split into Organic Conventional
On the basis of the end users/applications, this report focuses on the status and outlook for major applications/end users, consumption (sales), market share and growth rate for each application, including Beverages Infant Food Ice Cream & Yoghurt Dressings & Sauces Bakery & Snacks Personal Care Others
If you have any special requirements, please let us know and we will offer you the report as you want.
Enquiry For Discount @ https://www.reporthive.com/enquiry.php?id=1140030&req_type=disc
Table of Contents
1 Banana Puree Market Overview 1.1 Product Overview and Scope of Banana Puree 1.2 Banana Puree Segment by Type (Product Category) 1.2.1 Global Banana Puree Production and CAGR (%) Comparison by Type (Product Category)(2012–2022) 1.2.2 Global Banana Puree Production Market Share by Type (Product Category) in 2016 1.2.3 Organic 1.2.4 Conventional 1.3 Global Banana Puree Segment by Application 1.3.1 Banana Puree Consumption (Sales) Comparison by Application (2012–2022) 1.3.2 Beverages 1.3.3 Infant Food 1.3.4 Ice Cream & Yoghurt 1.3.5 Dressings & Sauces 1.3.6 Bakery & Snacks 1.3.7 Personal Care 1.3.8 Others 1.4 Global Banana Puree Market by Region (2012–2022) 1.4.1 Global Banana Puree Market Size (Value) and CAGR (%) Comparison by Region (2012–2022) 1.4.2 North America Status and Prospect (2012–2022) 1.4.3 Europe Status and Prospect (2012–2022) 1.4.4 China Status and Prospect (2012–2022) 1.4.5 Japan Status and Prospect (2012–2022) 1.4.6 Southeast Asia Status and Prospect (2012–2022) 1.4.7 India Status and Prospect (2012–2022) 1.5 Global Market Size (Value) of Banana Puree (2012–2022) 1.5.1 Global Banana Puree Revenue Status and Outlook (2012–2022) 1.5.2 Global Banana Puree Capacity, Production Status and Outlook (2012–2022)
2 Global Banana Puree Market Competition by Manufacturers 2.1 Global Banana Puree Capacity, Production and Share by Manufacturers (2012–2017) 2.1.1 Global Banana Puree Capacity and Share by Manufacturers (2012–2017) 2.1.2 Global Banana Puree Production and Share by Manufacturers (2012–2017) 2.2 Global Banana Puree Revenue and Share by Manufacturers (2012–2017) 2.3 Global Banana Puree Average Price by Manufacturers (2012–2017) 2.4 Manufacturers Banana Puree Manufacturing Base Distribution, Sales Area and Product Type 2.5 Banana Puree Market Competitive Situation and Trends 2.5.1 Banana Puree Market Concentration Rate 2.5.2 Banana Puree Market Share of Top 3 and Top 5 Manufacturers 2.5.3 Mergers & Acquisitions, Expansion
Read More…
Enquiry For Report Purchase @ https://www.reporthive.com/enquiry.php?id=1140030&req_type=purch
About Us
We are a leading repository of market research reports and solutions catering to industries like Comm & Technology, Energy & Power, Food And Beverages, Automotive & Transportation, Healthcare & Life Science etc. This large collection of reports assists organizations in decision-making on aspects such as market entry strategies, market sizing, market share analysis, competitive analysis, product portfolio analysis and opportunity analysis among others. We also assist in determining the best suited and targeted report from our large repository of global reports, company-specific reports and country-level reports.
Contact Us
Mike Ross Marketing Manager [email protected] http://www.reporthive.com Phone: +1 312–604–7084 Sainath Nagar, Vadgaon Sheri, Pune, Maharashtra 411014
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
How to Start Successful Fruit Export Business from India

The fruit sector in India is thriving, offering immense opportunities for exporters. From exotic kiwis to delectable mangoes, a world of flavors awaits. Thanks to India's diverse climate and rich agricultural history, the nation has become a catalyst in fruit production.
With high demand for premium fruits in countries such as the US, Europe, Hong Kong, and Vietnam, exporting fruits from India can be a lucrative business. However, navigating the fruit export industry can be challenging.
Fear not, fellow traders! This guide outlines 10 essential steps to kickstart your fruit export business from India, provides the latest industry insights, and shares fruit export data, top Indian fruit exporters, and an analysis of the top 10 fruit-exporting nations.
Is the Fruit Export Business Profitable?
India stands as a major fruit-exporting nation, offering a diverse array of premium exotic and sweet fruits. Ranking second globally in fruit and vegetable production, only behind China, India consistently proves to be a profitable venture for fruit exports. The country grows a variety of fruits including mangoes, bananas, papayas, oranges, apricots, grapes, strawberries, apples, guavas, and litchis.
India's ability to produce fruits at relatively lower costs compared to other countries enhances its success as an investment.
Fruit Export from India: Key Stats & Facts
Let's delve into the key statistics for fruit export from India!
In the fiscal year 2022-2023, India exported 674,291.70 MT of fresh fruits (excluding grapes and mangoes), totaling Rs. 2,736.99 crores (USD 339.00 million). Fruit export data indicates that India plays a significant role in the global fruit export market, with a projected gross production value of USD 41.19 billion by 2024. Major exported fruits include bananas, pomegranates, grapes, and mangoes.
Which Fruits Does India Export the Most?
Here is a list of India's top-exported fruits:
Mangoes
Indian mangoes, known for their diverse varieties and unique flavors, are highly sought after. The Alphonso mango, or "Hapus," is particularly prized for its rich, creamy texture and sweet, citrusy flavor. This variety is in high demand not only in India but also in the Middle East, Europe, and the US.
Bananas
Despite being the world's largest banana producer, India's export share continues to grow. India also exports processed banana products such as dried bananas, chips, and puree, which are popular in various global cuisines.
Pomegranates
Referred to as the "jewels of winter," pomegranates are among India's most widely exported fruits. India produces over half of the world's pomegranates, with major export markets in Greece, Israel, Russia, the UAE, and Italy.
Apples
Indian apples, known for their crisp texture and nutritional value, are popular domestically and internationally. Varieties such as Green Apple, Pink Lady Apple, Fuji Apple, Gala Apple, Honeycrisp Apple, Envy Apple, and Red Apple are exported primarily to Bangladesh, Nepal, and the Middle East.
Oranges
Indian oranges are in high demand worldwide due to their versatility. Popular varieties include Dancy, Nagpur Santra, Coorg Santra, Kinnow Mandarin, and Darjeeling Mandarin. These are used in perfumes, cosmetics, food flavorings, and more.
Major Fruit Exporters in India
Several key players dominate the Indian fruit export market. Here are some of the major fruit exporters in India:
Pisum Foods
Indian Farmers Export (IFE Fruits & Vegetables)
Radha Krishan Fruit Company
Jadli Foods India
Mahindra Agri
Balaji Foods Pvt Ltd
Dhanuka Agritech Ltd
Vardhan Exports Pvt Ltd
Golden Agri Exports Pvt Ltd
Vajreshwari Enterprises And Corp
These companies, supported by government initiatives, position India as a significant player in the global fruit market.
Key Strategies to Export Fruit from India
Here are crucial strategies to start exporting fruit from India:
1. Establish an Export Firm
Setting up a proper export company is vital. Choose a suitable business structure (private limited, partnership, or sole proprietorship) and register with the Registrar of Companies (ROC). Obtain an Import Export Code (IEC) from the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT).
2. Select the Fruits for Export
Choose the fruits you want to export, considering factors such as export quantities, values, and up-to-date fruit export data. Use data-driven platforms to obtain real-time insights on fruit export trends and market demands. Opt for fruits with a longer shelf life for smoother export processes.
3. Compliance and Documentation
Register with agencies like APEDA and ensure all necessary licenses and documentation are in place. Ensure that commercial invoices, certificates of origin, and phytosanitary certifications meet the importing nation's requirements.
4. Obtain a Reliable Fruit Exporter List
Access reliable fruit export data to make informed decisions. Platforms like Eximpedia offer valuable insights into market trends, competitor analysis, and potential buyers, helping you navigate the global fruit trade effectively.
Final Words
India exports a wide variety of fruits, with a high global demand for pineapples, dragon fruits, strawberries, guavas, litchis, papayas, sapotas (chikoo), jackfruits, pears, ber, amla, and coconuts. The country's flourishing fruit export industry, bolstered by its diverse fruit offerings and strong international trade relations, provides a lucrative opportunity for new exporters.
If you're looking to explore the Indian fruit export market, platforms like Eximpedia can help you access updated fruit export data, connect with top fruit export companies in India, and navigate the complex world of fruit trade. Connect today and book a free live demo!
#fruit export from india#fruit exporters in india#fruit export companies in india#list of fruits exported from india#fruit exporters#fruit export data#top fruit export companies in india#largest fruit exporter in india
0 notes
Text
Banana Puree Market SWOT Analysis by Leading Key Players

Banana puree is a processed form of mashed bananas that can be used in a variety of food and beverage applications. The global banana puree market has been experiencing steady growth in recent years due to the increasing demand for processed fruits and the rising popularity of banana-based products.
Market Drivers:
Increasing demand for processed fruits: Consumers are increasingly looking for convenience and ready-to-use food products that are easy to prepare and consume. Banana puree is a perfect fit for this trend as it is a convenient and versatile ingredient that can be used in a variety of food and beverage applications.
Growing popularity of banana-based products: Bananas are a widely popular fruit around the world and are used in a variety of products such as smoothies, baby food, ice creams, and bakery products. Banana puree is an essential ingredient in many of these products, which has increased the demand for banana puree in the market.
Health benefits of bananas: Bananas are known for their high nutritional value and are a rich source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals. The growing awareness among consumers about the health benefits of bananas has led to an increased demand for banana-based products, including banana puree.
Market Segmentation:
The global banana puree market can be segmented based on source, application, and distribution channel.
Based on source, the market can be segmented into organic and conventional banana puree. Organic banana puree is made from organically grown bananas, which are free from pesticides and chemicals.
Based on application, the market can be segmented into baby food, beverages, bakery & snacks, dairy & frozen desserts, and others. Banana puree is used as an ingredient in these applications to enhance the taste and nutritional value of the final product.
Based on distribution channel, the market can be segmented into direct and indirect channels. The indirect channels can be further classified into supermarkets/hypermarkets, online retailers, and others.
Regional Analysis:
The global banana puree market can be segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa.
Asia Pacific is the largest market for banana puree due to the high consumption of bananas in countries such as India, China, and Indonesia.
Europe and North America are also significant markets for banana puree due to the growing demand for natural and healthy food products.
Key Players:
The key players operating in the global banana puree market are Döhler GmbH, SVZ Industrial Fruit & Vegetable Ingredients, Nestlé S.A., Ariza B.V., AGRANA Beteiligungs-AG, Symrise AG, Diana Food (Part of Symrise), The Hain Celestial Group, Inc., and Kerry Group plc. These players are focusing on product innovation and development to expand their product portfolio and gain a competitive edge in the market.
0 notes
Link
“Fruit Puree Market ”gives detailed outlook by Type, by Application, by Segmentation and Regional Forecasts.
0 notes
Photo

Fruit Puree Market Revenue, Trends, Regional & Country Share, Key Factors, Trends & Analysis, To 2023
The fruit puree market revenue is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.4% during the forecast period. As per the fruit puree market research report, the global market for fruit puree is projected to grow swiftly by US$14,549.8 million by 2023. According to analysts, rising health concerns among consumers as well as growing demand for the natural and healthy food products will drive the market growth during the forecast period. The fruit puree market research report offers a comprehensive analysis of the global fruit puree market and its application, category, and fruit type segments. The concerns regarding sweeteners along with artificial flavors are the elements that could influence the fruit puree market advancement throughout the forecast period. The fruit puree market research report by expert analysts is developed to assist organizations in the fruit puree market.
Market Segmentation
The global fruit puree market has been segmented based on application, category, and fruit type. On the basis of application, the market for fruit puree is segmented based on bakery, beverages, baby food, and others. Additionally, the market on the basis of category, is segmented into conventional and organic. The global market for fruit puree is also covered based on the fruit type segment which is further split into banana puree, plum puree, strawberry puree, apple puree, and others.
Major elements such as availability of substitutes could obstruct the fruit puree market growth. However, according to the fruit puree market research report, the demand for food products made from natural and healthy ingredients along with fruit puree emerging as a suitable substitute will propel growth throughout the forecast period. The fruit puree market is set to register growth at a high CAGR owing to these key factors. The exploration of application, category, and fruit type segments along with regional markets has been given in the global fruit puree market research report. The research analysts studying the fruit puree market have put out market forecasts in the fruit puree market research report in order to support fruit puree market-based companies. The fruit puree market research report provides an extensive understanding of the fruit puree market based on the information and forecasts till 2023.
To get more info: https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/press-release/fruit-puree-industry
Regional Overview
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific and the rest of the world regional market for fruit puree are predominantly covered in the global fruit puree market research report. Country-level fruit puree markets spread across North America – the United States, Canada, and Mexico are also covered in the report. In South America – Brazil and other country-level fruit puree markets are covered in the report. In Asia-Pacific (APAC) region, the country-level fruit puree markets covered are Japan, India, China, and others. The fruit puree market research report also explores the regional market for fruit puree present in Europe in the United Kingdom, France, Italy, Spain, and Germany, etc. The fruit puree market research report also covers regional markets from the rest of the world alongside fruit puree markets of Africa and the Middle East.
Competitive Landscape
Growing applications of fruit puree in baby food and bakery & confectionery sectors are presumed to drive the fruit puree market growth worldwide. The global fruit puree market could be challenged by health related concerns, nevertheless, organizations in the fruit puree market will carry the growth rate forward. The fruit puree market research report presents company profiles of major companies active in the fruit puree market globally. Furthermore, the global fruit puree market report offers an all-inclusive analysis of the market collected from the fruit puree market’s primary and secondary sources covering both decision makers and thought leaders. The fruit puree market research report highlights such key areas assisting businesses operating in the fruit puree market to build better growth strategies.
Industry News
A producer of fruit purees for the craft beverage industry, Oregon Fruit Products has just announced the introduction of 16 newly branded Canned Fruit Purees packaged for the home or small-scale beverage manufacturing market. The Canned Fruit Puree line from Oregon Fruit adds beer, wine, spirits, kombucha, soda or any number of fermented or flavored drinks to the taste, aroma and texture of real fruit. They are available in 49-oz shelf-stable purees. Cans and can be bought from the Country Malt Party.
0 notes
Text
Fruit Puree Market Is Expected to Grow at A CAGR Over 5.5% during the forecast period
Market Synopsis
Market Research Future (MRFR) expects the fruit puree market 2020 to secure a growth rate of 4.4% from 2018 to 2023 (review period). The market size by 2023 is estimated to be USD 14,549.8 million, indicating favorable prospects for fruit puree worldwide. We will provide COVID-19 impact analysis with the report, along with an in-depth review post the coronavirus disease outbreak.
Primary Boosters and Restraints
The lockdown following the COVID-19 outbreak has negatively impacted farming practices across the world, leading to weaker supply of fruits. This has had a domino effect on the prices of raw materials used in the manufacturing of fruit puree. The COVID-19 impact on logistics has also boosted the prices of raw materials, which has slowed down the market growth to a large extent. With bans on cross-border commodities’ transportation in the pandemic era, manufacturers are now relying on local suppliers to maintain their operations and prevent revenue losses.
Since the SARS-CoV-2 infection affects the immunity, people are now more inclined towards food products that claim to be healthy and organic. The novel coronavirus has also induced a major shift towards products and goods that facilitate hygiene and ensure strong immunity. The fact that World Health Organization has also been encouraging the consumption of immunity-boosting foods seems to be working in favor of the fruit puree market. The demand for fruit purees is especially high in the food industry, with extensive applications in segments like dairy & frozen desserts, bakery & confectionery, baby food as well as beverages, to mention a few.
Access Report Details @
https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/fruit-puree-market-5281
Furthermore, rising adoption of advanced food-processing technologies by top manufacturers to boost their production capacities could also foster fruit puree’s demand in the upcoming period. Strict guidelines imposed by authorities pertaining to the use of chemicals and artificial ingredients in food products can open promising avenues for the renowned firms in the market. Additionally, many of the reputed players are engaged in acquisition and merger strategies, while also introducing better featured products, with the aim to clinch a higher position in the global market.
To cite a reference, in August 2020, Beavertown (London) launched a passion fruit Berliner Weisse –Passion Phantom. The brewery’s latest beer has been infused with passion fruit purée and made using malted wheat and extra-pale barley along with kettle-soured lactobacillus.
Market Segmentation
Fruit type, category and application are the top segments analyzed in the MRFR study.
The primary fruit puree types considered in the report are plum puree, banana puree, strawberry puree, apple puree, and more. Banana puree has secured the leading position in the global market and is all set to procure the fastest CAGR to touch USD 2,935.1 million by 2023-end. Banana puree has gained high traction as an essential ingredient in smoothies, baby food, to mention a few. On the other hand, apple puree remains in the second place, trailed by strawberry puree, which can hit a valuation of USD 2,340.1 million by 2023.
Depending on category, the report has reviewed segments like organic as well as conventional.
Baby food, beverages, bakery (cakes as well as pastries and other baked items) and many more are the key application areas of fruit puree.
Regional Study
The regional study of the fruit puree market size in the MRFR report covers APAC or Asia Pacific, Europe along with North America as well as RoW or Rest of the World.
APAC is brimming with a host of business opportunities, since the region encapsulates some of the fastest emerging countries in the world that are characterized by rapid urbanization and fast economic growth. Considering this aspect and many more, APAC successfully established itself as the leading market with a share of 40.21% in 2017 and can even accrue the fastest CAGR of 4.9% over the conjectured period. The regional market’s outstanding performance is the result of the soaring demand for nutritious baby food and the rising consumption of smoothies. Accelerated purchasing power of consumers and their growing preference for yogurts, snacks, ice creams and infused with fruit puree in the wake of mounting health consciousness can also add to the market attractiveness in the following years.
North America is all set to surpass USD 4,635.6 million by 2023 and has emerged as the second biggest gainer in the global market. The US has been the top performer since 2017, having captured a total share of 63.8% in the region, thanks to the growing health awareness among consumers that is encouraging food manufacturers to integrate healthy and natural food ingredients like fruit puree in their offerings. Also, an increasing number of vendors in the region are introducing fruit purees that are citrus in nature, in light of the escalating demand for the latter. To illustrate, in March 2020, Oregon Fruit Products introduced its Lemon Puree in the US market, which has a smooth consistency, bright flavor and is pale-yellow. This new offering is projected to appeal to manufacturers of beer, cider, sodas, spirits, wine, kombucha and mead.
Request a Sample Report @
https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/sample_request/5281
NOTE: Our Team of Researchers are Studying Covid19 and its Impact on Various Industry Verticals and wherever required we will be considering Covid19 Footprints for Better Analysis of Market and Industries. Cordially get in Touch for More Details.
0 notes