#B2B Invoice QR Code
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Future of USDT Payments and Stablecoin in Global Commerce

In a global financial ecosystem where speed, transparency, and accessibility are becoming non-negotiables, stablecoins—particularly Tether (USDT)—have carved out a powerful niche. Once seen merely as trading instruments on crypto exchanges, stablecoins are now evolving into vital tools for cross-border commerce, payroll, lending, and global remittances. But what does the future of USDT payments hold in the context of expanding digital economies? This in-depth guide explores the emerging role of USDT and stablecoins in global commerce, including current trends, technological shifts, regulatory evolution, and their potential to disrupt legacy finance. The Future of USDT Payments and Stablecoin in Global Commerce Why USDT Has Become the Stablecoin of Choice Market Dominance and Liquidity As of 2025, USDT remains the most widely used and liquid stablecoin in the world, with over $90 billion in circulation. Its integration into thousands of platforms—ranging from centralized exchanges and DeFi protocols to merchant payment systems—gives it an unmatched level of acceptance and interoperability. Blockchain Interoperability USDT operates on multiple blockchains, including Ethereum (ERC-20), Tron (TRC-20), Binance Smart Chain (BEP-20), Solana (SPL), and Polygon. This cross-chain deployment enables businesses to select the protocol that best balances speed, cost, and network activity. For example: - TRC-20 USDT is popular in Asia due to low fees. - ERC-20 USDT is favored in institutional DeFi platforms. For a step-by-step breakdown on how to integrate USDT payments into your online store or digital platform, check out our in-depth guide on the best USDT payment gateway for business at XAIGATE. USDT in Real-World Payments: Current Use Cases International Payroll Companies hiring remote workers now use USDT to pay salaries globally in a matter of seconds, avoiding high bank fees and currency conversion losses. B2B Cross-Border Trade Manufacturers and wholesalers in emerging markets use USDT to settle international invoices, eliminating the delays and costs of SWIFT or traditional remittance services. Merchant Adoption Retailers in crypto-friendly jurisdictions are increasingly accepting USDT via gateways like XAIGATE. It offers customers a fast, private, and irreversible payment option without currency volatility. Technological Trends Shaping the Future of USDT Payments Layer-2 Scaling and Gas Efficiency As congestion and fees on mainnets like Ethereum persist, the rise of Layer-2 networks—such as Arbitrum, zkSync, and Optimism—presents a promising future for USDT microtransactions. Gas fees drop from dollars to cents, enabling everyday retail and online purchases. Integration With Web3 Wallets and dApps USDT is being integrated into decentralized apps and Web3 wallets like MetaMask, Phantom, and Trust Wallet, enabling users to pay or receive funds across borders without intermediaries. AI and Smart Routing in Stablecoin Payments Emerging smart contract-based payment systems can automatically route USDT across chains and protocols for the lowest fees and fastest confirmations, optimizing both B2B and retail usage. Technological Trends Shaping the Future of USDT Payments Future Projections: What Will the Next 5 Years Look Like? Widespread Retail Adoption We’re likely to see more POS systems and eCommerce platforms natively support USDT, especially in crypto-forward countries. QR code payments and one-click checkout via stablecoin wallets could rival traditional credit cards. Embedded Finance and API-Based Payment Flows As XAIGATE and other platforms improve API flexibility, businesses can build USDT payments directly into their apps, games, and services—without needing custodial gateways. Real-Time Global Settlement With blockchain interoperability, future USDT payment systems will support atomic swaps and real-time settlements between fiat and crypto. This could revolutionize supply chains, freelance platforms, and gig economies. Challenges to Address in the Future of USDT Payments Centralization and Reserve Transparency Despite Tether’s regular attestations, concerns persist over the composition and liquidity of reserves backing USDT. Increasing regulatory pressure will likely push for more frequent and detailed disclosures. On/Off Ramp Friction The success of USDT in commerce depends on efficient fiat on/off ramps. While platforms like MoonPay and Binance Pay are filling the gap, local regulations and KYC requirements still pose barriers in many countries. Volatility of Stablecoin Pegs While USDT is pegged to the USD, black swan events or market manipulations can threaten stability. Future implementations may involve algorithmic safeguards or dynamic collateralization to enhance resilience. To stay ahead in the evolving world of crypto commerce, businesses should explore robust solutions like XAIGATE. Learn how to streamline your stablecoin integration with our expert insights on the future-proof USDT gateway for global businesses:🔗 https://www.xaigate.com/usdt-payment-gateway-for-business/ Institutional Integration Will Accelerate the Future of USDT Payments Financial Giants Are Embracing Stablecoin Infrastructure Traditional finance players—including Visa, Mastercard, and major regional banks—are increasingly exploring blockchain-based payments. In this shift, USDT stands out due to its deep liquidity and global reach. Financial service providers in Asia, Europe, and Latin America are testing cross-border settlements using USDT, bypassing the SWIFT system. This momentum signals that the future of USDT payments is not just driven by crypto-native startups, but also by global institutions that recognize its potential for efficiency, transparency, and accessibility. Corporate Adoption for Treasury and Payroll Large corporations are beginning to hold USDT in their treasury reserves to hedge against fiat currency instability in emerging markets. Additionally, USDT is being used for real-time international payroll in industries such as freelance tech, BPO services, and logistics—where bank transfers are costly and slow. These use cases are critical in shaping the future of USDT payments for operational finance. Compliance-Ready Stablecoin Payments: A New Era for Global Businesses Web3 Identity Layers and zk-KYC Protocols One of the most critical enablers of mainstream USDT adoption is the emergence of on-chain compliance tools. Web3-native identity solutions—like decentralized identifiers (DIDs), verifiable credentials, and zero-knowledge KYC—allow payment processors to meet local regulations without exposing sensitive customer data. As these tools integrate with crypto payment gateways like XAIGATE, businesses can comply with regulatory requirements while preserving the privacy of their users, expanding the future of USDT payments into regulated sectors such as healthcare, education, and insurance. Tiered Risk and Regulatory Models Instead of a one-size-fits-all KYC process, the next generation of USDT payment systems will offer tiered access levels: P2P payments under a certain threshold may remain KYC-optional, while enterprise-level transactions can trigger automated compliance protocols. This model not only aligns with global regulatory trends but also preserves accessibility—a crucial factor in the future of USDT payments for borderless commerce. Conclusion: From Trading Tool to Global Payment Standard The trajectory of USDT is transitioning from speculative asset to utilitarian digital dollar. As global commerce grows increasingly borderless, USDT’s stability, speed, and availability give it a unique advantage over both fiat and crypto rivals. With innovations in scalability, regulation, and user experience on the horizon, the future of USDT payments looks more like a core pillar of the new digital economy than a temporary crypto trend. Businesses that integrate USDT payments today are not only improving efficiency—they are future-proofing for a financial system in transformation. FAQs – Future of USDT Payments Q1: Is USDT legal to use in global payments?Yes, in many jurisdictions. However, legality depends on local financial regulations and whether stablecoins are recognized under digital asset laws. Q2: How does USDT avoid volatility compared to Bitcoin or Ethereum?USDT is pegged to the US Dollar and backed by reserves, maintaining a near 1:1 price ratio with minimal fluctuation. Q3: Can I use USDT for recurring payments?Yes. Some platforms offer programmable USDT-based subscriptions using smart contracts or API-based invoicing systems. Q4: Which industries benefit most from USDT payments?E-commerce, remote work platforms, SaaS, logistics, and cross-border trade benefit greatly due to instant global transfer and low fees. Q5: How do I integrate USDT payments on my website?You can use gateways like XAIGATE to integrate no-login, low-fee USDT payment plugins into your eCommerce or business website. FAQs – Future of USDT Payments We may also be found on GitHub, and X (@mxaigate)! Follow us! Don’t miss out on the opportunity to elevate your business with XAIGATE’s Future of USDT Payments and Stablecoin. The three-step process is designed to be user-friendly, making it accessible for all businesess. Embrace this modern payment solution to provide customers with a secure and efficient way to pay. Take the first step towards a competitive edge in the digital realm and unlock the benefits of cryptocurrency payments for online casino today. Read the full article
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Ensure Compliance with ZATCA Phase 2 Requirements
As Saudi Arabia pushes toward a more digitized and transparent tax system, the Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority (ZATCA) continues to roll out significant reforms. One of the most transformative changes has been the implementation of the electronic invoicing system. While Phase 1 marked the beginning of this journey, ZATCA Phase 2 brings a deeper level of integration and regulatory expectations.
If you’re a VAT-registered business in the Kingdom, this guide will help you understand exactly what’s required in Phase 2 and how to stay compliant without unnecessary complications. From understanding core mandates to implementing the right technology and training your staff, we’ll break down everything you need to know.
What Is ZATCA Phase 2?
ZATCA Phase 2 is the second stage of Saudi Arabia’s e-invoicing initiative. While Phase 1, which began in December 2021, focused on the generation of electronic invoices in a standard format, Phase 2 introduces integration with ZATCA’s system through its FATOORA platform.
Under Phase 2, businesses are expected to:
Generate invoices in a predefined XML format
Digitally sign them with a ZATCA-issued cryptographic stamp
Integrate their invoicing systems with ZATCA to transmit and validate invoices in real-time
The primary goal of Phase 2 is to enhance the transparency of commercial transactions, streamline tax enforcement, and reduce instances of fraud.
Who Must Comply?
Phase 2 requirements apply to all VAT-registered businesses operating in Saudi Arabia. However, the implementation is being rolled out in waves. Businesses are notified by ZATCA of their required compliance deadlines, typically with at least six months' notice.
Even if your business hasn't been selected for immediate implementation, it's crucial to prepare ahead of time. Early planning ensures a smoother transition and helps avoid last-minute issues.
Key Requirements for Compliance
Here’s a breakdown of the main technical and operational requirements under Phase 2.
1. Electronic Invoicing Format
Invoices must now be generated in XML format that adheres to ZATCA's technical specifications. These specifications cover:
Mandatory fields (buyer/seller details, invoice items, tax breakdown, etc.)
Invoice types (standard tax invoice for B2B, simplified for B2C)
Structure and tags required in the XML file
2. Digital Signature
Every invoice must be digitally signed using a cryptographic stamp. This stamp must be issued and registered through ZATCA’s portal. The digital signature ensures authenticity and protects against tampering.
3. Integration with ZATCA’s System
You must integrate your e-invoicing software with the FATOORA platform to submit invoices in real-time for validation and clearance. For standard invoices, clearance must be obtained before sharing them with your customers.
4. QR Code and UUID
Simplified invoices must include a QR code to facilitate easy validation, while all invoices should carry a UUID (Universally Unique Identifier) to ensure traceability.
5. Data Archiving
You must retain and archive your e-invoices in a secure digital format for at least six years, in accordance with Saudi tax law. These records must be accessible for audits or verification by ZATCA.
Step-by-Step Guide to Compliance
Meeting the requirements of ZATCA Phase 2 doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Follow these steps to ensure your business stays on track:
Step 1: Assess Your Current System
Evaluate whether your current accounting or invoicing solution can support XML invoice generation, digital signatures, and API integration. If not, consider:
Upgrading your system
Partnering with a ZATCA-certified solution provider
Using cloud-based software with built-in compliance features
Step 2: Understand Your Implementation Timeline
Once ZATCA notifies your business of its compliance date, mark it down and create a preparation plan. Typically, businesses receive at least six months’ notice.
During this time, you’ll need to:
Register with ZATCA’s e-invoicing platform
Complete cryptographic identity requests
Test your system integration
Step 3: Apply for Cryptographic Identity
To digitally sign your invoices, you'll need to register your system with ZATCA and obtain a cryptographic stamp identity. Your software provider or IT team should initiate this via ZATCA's portal.
Once registered, the digital certificate will allow your system to sign every outgoing invoice.
Step 4: Integrate with FATOORA
Using ZATCA’s provided API documentation, integrate your invoicing system with the FATOORA platform. This step enables real-time transmission and validation of e-invoices. Depending on your technical capacity, this may require support from a solution provider.
Make sure the system can:
Communicate securely over APIs
Handle rejected invoices
Log validation feedback
Step 5: Conduct Internal Testing
Use ZATCA’s sandbox environment to simulate invoice generation and transmission. This lets you identify and resolve:
Formatting issues
Signature errors
Connectivity problems
Testing ensures that when you go live, everything operates smoothly.
Step 6: Train Your Team
Compliance isn’t just about systems—it’s also about people. Train your finance, IT, and sales teams on how to:
Create compliant invoices
Troubleshoot validation errors
Understand QR codes and UUIDs
Respond to ZATCA notifications
Clear communication helps avoid user errors that could lead to non-compliance.
Step 7: Monitor and Improve
After implementation, continue to monitor your systems and processes. Track metrics like:
Invoice clearance success rates
Error logs
Feedback from ZATCA
This will help you make ongoing improvements and stay aligned with future regulatory updates.
Choosing the Right Solution Provider
If you don’t have in-house resources to build your own e-invoicing system, consider working with a ZATCA-approved provider. Look for partners that offer:
Pre-certified e-invoicing software
Full API integration with FATOORA
Support for cryptographic signatures
Real-time monitoring dashboards
Technical support and onboarding services
A reliable provider will save time, reduce costs, and minimize the risk of non-compliance.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with ZATCA Phase 2 can result in financial penalties, legal action, or suspension of business activities. Penalties may include:
Fines for missing or incorrect invoice details
Penalties for not transmitting invoices in real-time
Legal scrutiny during audits
Being proactive is the best way to avoid these consequences.
Final Thoughts
As Saudi Arabia advances toward a fully digital economy, ZATCA Phase 2 is a significant milestone. It promotes tax fairness, increases transparency, and helps modernize the way businesses operate.
While the technical requirements may seem complex at first, a step-by-step approach—combined with the right technology and training—can make compliance straightforward. Whether you're preparing now or waiting for your official notification, don’t delay. Start planning early, choose a reliable system, and make sure your entire team is ready.
With proper preparation, compliance isn’t just possible—it’s an opportunity to modernize your business and build lasting trust with your customers and the government.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ship the Product, Receive Payment Instantly—No Waiting Around
When you run an online store, speed isn’t just nice—it’s survival. Customers want fast shipping, sure. But on your side? You want to receive payment fast. Because every delay in getting paid means tighter cash flow, stretched budgets, and slower growth. You’ve done the hard part. You built a product, packed the orders, and shipped them out the door. Now comes the final mile—the one that really matters: collecting your money. And in the DTC (Direct-to-Consumer) and eCommerce game, you don’t have time to chase invoices or worry about when that payment will finally land in your account.
So how do you ship it and immediately start collecting cash? Let’s talk.

Late Payments, Big Problems—Here’s the Fix
Delayed payments don’t just hurt your accounting reports. They hit your operations in real time:
You can’t restock your bestsellers.
Ad budgets stay frozen while you wait.
Freelancers and fulfillment partners get cranky when their checks don’t show up.
And let’s not forget the ripple effect. If your supplier doesn’t get paid, your restock timeline slows. If your ad agency isn’t paid, your campaigns pause. Suddenly, your whole momentum gets hijacked by one unpaid invoice.
Even worse, if you’re growing fast, every unpaid invoice slows you down. And in the eCommerce world, being slow is being left behind. Let’s turn things around. Discover faster, smarter ways to collect payments—minus the stress.
Make It Easy for Customers to Pay (So They Actually Do)
You know what doesn’t help? Sending a PDF invoice and hoping someone reads it. Or asking your customer to log in somewhere, find a routing number, and figure it out on their own. People want to pay the way that works for them—credit card, ACH, eCheck, you name it. The easier you make it to pay, the harder it is for them to stall. And that’s the beauty of flexible payment platforms today—especially with Zil Money. Instead of dictating how someone should pay you, you let them choose. And guess what? When you do that, you get paid faster.
Here’s what works:
Accept credit cards and eChecks without a fancy setup.
Offer ACH for B2B buyers or repeat clients.
Send quick payment links by email or text—no login, no fuss.
Make it so easy to pay that even your most distracted customers can’t mess it up.
Make Invoicing the Easiest Part of Your Day
You know how it goes—create an invoice, send it out, then wait… follow up… and follow up again… just to get paid. That’s the old way. The smart way? Let your invoice do the chasing.
Zil Money lets you:
Build and send invoices without breaking your flow.
Attach payment links with the invoice
Send invoices via email or mail
While you’re busy handling new orders or planning your next product drop, your invoice is out there doing the work—nudging customers to pay, collecting the cash, and syncing everything for your records.
Send. Pay. Done.
Quick Payment Links = Instant Gratification (and Instant Cash)
Let’s be honest: no one wants to open an invoice, scan a QR code, go to a payment portal, and enter details across five screens.
What they do want is a link.
A clean, direct, no-nonsense payment link sent via SMS or email. Tap, pay, done. Zil Money let you create and customize these links in seconds. Add the amount, pick the payment method, and hit send. You’ll be surprised how fast customers pay when it’s that frictionless.
And if you’re doing product drops or flash sales? These links are gold. You can move product and collect payment instantly, even before your competitors realize what just happened.
The Money Should Move as Fast as You Do
You’re building something. Maybe it’s a small DTC brand or the next breakout eCommerce success. Either way, you can’t afford to be stuck waiting on payments. Every minute your money sits in limbo is a missed chance to invest, restock, or reinvest in growth. It’s not just about faster payments—it’s about unlocking freedom. Financial freedom to run your business your way, without constantly checking your balance or playing the “did they pay yet?” game. So stop slowing down your success. Use payment tools that move at your speed.
0 notes
Text
Types of Automated Direct Mail
Automated direct mail has revolutionized how businesses communicate with their audiences. By integrating data-driven technology with traditional mail, marketers can now launch campaigns faster, cheaper, and more effectively. But not all direct mail is created equal. Understanding the different types of automated direct mail helps businesses select the most suitable format for their goals.

1. Postcards
Overview: One of the most popular forms of automated direct mail, postcards are cost-effective, quick to produce, and visually impactful.
Best for:
Promotions and coupons
Event announcements
Product launches
Automation Features:
Personalization with customer names or location-based offers
QR code and PURL tracking
Pre-designed templates for quick deployment
2. Letters
Overview: Letters provide a more formal, personal touch. They're often used in B2B, finance, and healthcare communications.
Best for:
Renewal notices
Policy updates
Donation requests
Automation Features:
Variable data printing for personalized content
Dynamic letterheads and signatures
Double-window envelope printing
3. Catalogs and Booklets
Overview: Larger-format direct mail pieces like catalogs and booklets offer an immersive experience with detailed product or service information.
Best for:
Seasonal product guides
Luxury goods
High-ticket items
Automation Features:
Page personalization based on user data
SKU-specific printing
Dynamic pagination and layout tools
4. Self-Mailers
Overview: A self-mailer is a folded piece with no envelope, offering more space than a postcard and lower costs than letters.
Best for:
Announcements
Lead generation
Informational content
Automation Features:
Fold and seal automation
Integrated tear-off reply cards
Personalized headlines and CTAs
5. Dimensional Mailers
Overview: These are 3D packages or bulky envelopes that grab attention through shape and size.
Best for:
VIP customer outreach
Product samples
High-value B2B campaigns
Automation Features:
Automated fulfillment and kitting
CRM-triggered gift mailers
Personalized gift notes
6. Thank You and Welcome Cards
Overview: These are transactional or relationship-building pieces sent automatically after customer actions.
Best for:
New sign-ups
Completed purchases
Customer milestones
Automation Features:
Event-triggered mailing
Handwritten-style fonts
Loyalty program integrations
7. Invoices and Statements
Overview: Businesses can automate operational mail like invoices or statements while including marketing messages.
Best for:
Financial institutions
Utility companies
Subscription services
Automation Features:
API integration with billing systems
Payment QR codes
Security and compliance tools
8. Holiday and Seasonal Campaigns
Overview: These are themed campaigns sent around holidays or seasonal events.
Best for:
Christmas greetings
New Year promotions
Black Friday deals
Automation Features:
Scheduled mailing calendar
Festive templates
Holiday-specific personalization
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of automated direct mail helps marketers plan better campaigns based on their goals. Whether it's a promotional postcard, a detailed catalog, or a personalized thank-you card, automation makes it easier to deliver impactful mail at scale. By choosing the right format and leveraging automation tools, businesses can maximize their ROI and customer satisfaction.
youtube
SITES WE SUPPORT
Automated HIPAA Mails – Wix
0 notes
Text
Best Practices for Sharing Payment Links with Customers
In today’s digital-first world, businesses—big or small—are constantly looking for ways to simplify the payment process. One of the most effective tools to collect payments quickly and securely is payment links. Whether you're a freelancer, a retail shop, or running a home-based business in the UAE, payment links offer a fast, no-fuss way to get paid.
But just sending a link isn’t enough. The way you share it matters. If done right, it builds trust, ensures faster payments, and keeps your customers happy.
In this blog, let’s explore the best practices for sharing payment links with customers, so you can boost your success and leave a lasting impression.
1. Choose a Reliable Payment Link Platform
First things first—reliability matters. Always use a secure and trusted payment platform when generating and sharing links. This assures your customers that their information is safe.
Look for platforms that offer:
PCI DSS compliance (industry standard for secure payments)
Real-time tracking
Multiple payment options like card, Apple Pay, and more
Easy integration and refund options
In the UAE, solutions like Foloosi are widely trusted for providing secure, easy-to-use payment links tailored for local businesses.
2. Customize the Payment Link Details
When sending a payment link, add as much clarity as possible. A customized message makes a difference. Include:
Customer’s name
Invoice number or order ID
Amount due
Purpose of the payment
For example: “Hello Ahmed, here’s your payment link for Order #F12345 - AED 120.00. Kindly complete the payment at your earliest convenience. Thank you!”
This not only looks professional but also avoids confusion for both you and the customer.
3. Use the Right Communication Channels
The success of your payment link depends a lot on where and how you send it. Choose a channel that your customer uses regularly.
Here are some commonly used methods:
WhatsApp: Popular in the UAE and very effective for instant communication.
SMS: Good for quick notifications, especially when customers don’t use messaging apps.
Email: Ideal for formal invoicing or B2B transactions.
Social Media DMs: Great for small businesses selling on Instagram or Facebook.
QR Codes: Perfect for in-person interactions—just print and place it at your counter or table.
Use the platform that best matches your customer’s preferences to improve response times.
4. Keep the Language Clear and Polite
Avoid sounding robotic or too pushy. Your message should sound human, polite, and friendly. Here's a sample:
“Hi Sara! Hope you’re doing well. Please find your payment link below for AED 75.00. Let us know if you have any questions. Thank you!”
This kind of message not only prompts quicker payments but also builds customer loyalty.
5. Set a Due Date or Expiry for the Link
One smart practice is to set a validity period for the payment link. This encourages timely payment and also helps you keep your records clean.
Mention the expiry in your message, like:
“Please note: This link will be valid for 3 days.”
Some platforms like Foloosi allow you to auto-expire links after a specific time frame, adding a layer of control and professionalism.
6. Send Gentle Reminders if Needed
Customers can be forgetful. If someone hasn’t paid yet, send a gentle reminder. Don’t sound aggressive—just give a nudge.
Example:
“Hi again! Just a friendly reminder about your pending payment. Here’s the link in case you missed it. Let us know if you need any help.”
Tip: Use automation tools to send reminders without having to follow up manually each time.
7. Enable Multiple Payment Options
Customers love choices. Make sure your payment link allows payments through:
Credit/debit cards
Apple Pay or Samsung Pay
Wallets or bank transfers
Offering multiple options increases the chances of faster payment, especially in a diverse market like the UAE where different people prefer different payment modes.
8. Ensure Mobile-Friendly Experience
Most people open messages and payment links on their phones. If the link opens to a slow, confusing page, they may exit. Always choose a platform that offers a smooth, mobile-optimized experience for your customer.
This means:
Fast load time
Clear CTA (Pay Now button)
Minimal steps to complete the payment
Foloosi’s payment links, for example, are designed to be mobile-first, making it easy for customers to complete the process in seconds.
9. Add a Personal Touch with Branding
Add your business name, logo, or color scheme if possible. This builds trust and makes the link feel more legitimate.
A payment page that shows your brand increases the likelihood of payment completion, especially from new customers who may be cautious of unknown links.
10. Track and Analyze Link Performance
Lastly, don’t just send links and forget. Use platforms that allow you to track payment status, see who paid, and when.
This helps in:
Managing your cash flow better
Following up only when needed
Understanding customer payment behavior
Foloosi provides real-time tracking, making it easier for UAE-based businesses to stay on top of payments.
Final Thoughts
Sharing payment links is more than just sending a URL. It’s about providing a smooth, secure, and professional payment experience for your customer. By following these best practices, you not only make it easier for them to pay—but also strengthen your brand’s trust and credibility.
Whether you're a small boutique in Dubai or a delivery service in Sharjah, adopting these practices will help you collect payments faster and more efficiently.
Want to create and share secure payment links in seconds? 👉 Try Foloosi’s Payment Links in UAE
#payment solutions#payment link in sharjah#best payment link in dubai#online payment link in uae#business uae#abudhabipaymentsolutions
0 notes
Text
How To Generate E-Invoice In TallyPrime 6.0? | Enable E-Invoicing in Tally | Latest Tally Updates
Are you looking for an easier way to manage E-Invoicing in TallyPrime?
In this video, we break down the E-Invoicing process in TallyPrime—a must-know feature for GST compliance that eliminates manual errors and automates digital invoicing. Whether you’re handling B2B transactions or meeting the ₹5 Cr turnover mandate, Antraweb Technologies makes it seamless and hassle-free!
Contact Us: +91 8448449099 Mail Us: [email protected] Visit Our Website: www.antraweb.com
What you’ll learn in this video: ✅ What is E-Invoicing and its importance for GST ✅ How to enable E-Invoicing in TallyPrime ✅ Step-by-step guide to generating E-Invoices with QR codes ✅ Mandatory details for error-free E-Invoice creation
📌 Timestamps: 00:00 - Introduction 00:05 - What is E-Invoice? 00:40 - Enable E-Invoice In Tally 01:21 - Create E-Invoice In Tally 03:35 - Invoice On Screen 04:00 - E-Invoice Basic Mandatory Details 04:55 - Antraweb's Tally E-Invoice Solution 05:10 - Need Help (Visit - www.tallyhelp.com) 05:24 - Like, Share & Subscribe
Want to Know More - Here's the full webinar on E-Invoice and E-Way Bill in Tally Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-7agUoP6S2c
Need help with E-Invoicing? Our expert support team at Antraweb is here to ensure a smooth experience. Visit https://www.tallyhelp.com for instant assistance!
Stay Updated with Tally Tips & Tricks!
✅ LIKE this video if you found it helpful! 👍 ✅ COMMENT below with any queries! 💬 ✅ SUBSCRIBE for more insightful tutorials! 🚀 ✅ Hit the notification bell to never miss an update!
0 notes
Text
Poland E-Invoicing Mandate: What you need to know

Poland is rolling out a mandatory e-invoicing system known as KSeF (Krajowy System e-Faktur), which obligates businesses in the country to create, receive, and archive invoices electronically using a centralized platform managed by the government.
SAF-T System for Poland e-invoicing
Companies are required to submit their accounting data through the SAF-T (Standard Audit File for Tax) system. This system is used by the Polish Tax Authority (Urzad Skarbowy) to collect and review financial information electronically.
Timelines and Requirements
Under Poland e-invoicing mandate, B2B transactions will require mandatory e-invoicing starting February 1, 2026, for large taxpayers with annual revenues over 200 million PLN. The requirement will extend to all other taxpayers from April 1, 2026.
Format: B2B: XML FA(2) – current version; FA(3) – draft version , B2G: UBL 2.1, Peppol BIS 3.0
Digital Signature: Not mandatory
Archiving: Invoices must be archived for 5 years
Scope of e-invoicing
At present, e-invoicing is applicable to Business-to-Government (B2G) transactions. Additionally, the government introduced e-invoicing for Business-to-Business (B2B) transactions on a voluntary basis starting in January 2022. However, beginning 1 July 2024, it will become mandatory to issue e-invoices for B2B transactions. Enforcement through fines and penalties is set to commence from January 2025. Issuing invoices to consumers (B2C) through KSeF is optional. When used, consumers can retrieve their invoices by scanning a QR code.
Exemptions from e-invoicing:
In Poland e-invoicing is not mandatory for certain types of transactions. These include Business-to-Consumer (B2C) transactions, dealings with parties that do not have a Fixed Establishment (FE) in Poland, and transactions conducted under the EU One Stop Shop (OSS) or Import One Stop Shop (IOSS) schemes. Additionally, e-invoices are not required for toll receipts and railway tickets.
KseF – Poland e-invoicing portal
In Poland, the government has appointed the Krajowy System e-Faktur (KSeF) as the official Poland e-invoicing portal responsible for receiving, issuing, and storing structured electronic invoices. KSeF, also known as the National e-Invoice System, is Poland’s dedicated Electronic invoicing System and was developed by a state treasury-established firm called “Critical Applications.” The system validates e-invoices by checking the XML file structure for compliance with the logical template defined in the XSD format and verifying the authorisations to use the platform. However, it does not verify the factual correctness of the data, focusing solely on structural accuracy. KSeF has successfully passed a security audit, ensuring its compliance with security standards.
Everything You Need to Know About Poland E-Invoicing Process with KSeF
With Poland e-invoicing mandate rolling out via the Krajowy System e-Faktur (KSeF), businesses are navigating a new digital landscape for compliance. Whether you’re just getting started or looking for clarity on some finer points, here’s a simplified breakdown of how the system works and what you need to keep in mind.
Do I need to sign invoices before sending them to KSeF?
No digital signature is required when submitting invoices to KSeF. However, digital authentication is mandatory to access the KSeF portal. This ensures that the individual submitting the invoice has the appropriate authorization to act on behalf of the company.
What is considered the invoice date in KSeF?
The invoice date is the date the e-invoice is received and accepted by the KSeF system—not the date it was created.
Do I need to submit invoices to KSeF immediately after issuing them?
Not immediately. You have until the 15th day of the month following the taxable supply to submit the invoice.
Should the KSeF invoice number appear on printed invoices?
No, including the KSeF identifying number on the printout is not mandatory.
Can I attach supporting documents to the e-invoice?
No, attachments aren’t allowed in KSeF invoices. However, you can include a link within the invoice content pointing to external resources if needed.
What could cause an invoice to be rejected by KSeF?
Two common reasons for rejection are:
Incorrect invoice structure that doesn’t align with the system’s logical format.
Unauthorized submission, i.e., the person sending the invoice lacks the necessary permissions.
What happens if KSeF rejects an invoice?
If your invoice is rejected, it’s considered not issued. You’ll need to recreate and resubmit it with the corrected information. You cannot cancel or issue a correction for a rejected invoice.
Can I download multiple e-invoices at once?
Yes, bulk downloading is possible, but only in XML format.
Can I issue multiple corrective invoices for one sales invoice?
Yes, one can issue as many corrective invoices as needed for a single sales invoice.
Can I issue a proforma invoice through KSeF?
No. Proforma invoices aren’t recognized as official invoices under Poland’s VAT law, so they can’t be issued via KSeF
Can I use self-invoicing under KSeF?
Yes, self-invoicing is allowed—but the buyer must receive authorization from the seller, and this must be formally registered within KSeF.
Can invoices be shared with customers outside of KSeF?
Yes, once an invoice is approved by KSeF, you can send it to your customers directly. Just make sure the format and method of delivery are agreed upon between buyer and seller. Tools like ClearTax can help automate this.
What if KSeF is temporarily unavailable?
In case of a system outage, you must submit your e-invoice to KSeF within seven days after the system comes back online.
Do I still need to submit the JPK_VAT file if I’m using KSeF?
If you’re issuing all invoices via KSeF, there’s no need to submit the JPK_VAT file separately.
Navigating Poland e-invoicing system may seem complex at first, but once you understand the key rules, it becomes much more manageable. Staying compliant is not just about meeting deadlines—it’s also about understanding the logic of the system and using the right tools to streamline the process.
Preparing your business:
Businesses must thoroughly understand the KSeF mandate and ensure they are prepared to comply by the relevant deadlines. Technical readiness plays a key role, particularly in adapting internal systems to accommodate the FA_VAT format. To support a smooth transition, it is important to utilize available training and support resources. The requirement to include the KSeF number in payment references will have direct implications for accounting and payment processes, necessitating adjustments. While the optional use of offline mode and B2C e-invoicing offers additional flexibility, these options also demand careful evaluation. Ongoing monitoring of regulatory updates and official clarifications is essential to remain compliant. Moreover, it is important to consider that the National Revenue Administration (Krajowa Administracja Skarbowa, KAS) may use data from the KSeF system during their proceedings.
What next?
Analyze KSeF’s impact on existing invoicing processes.
Update ERP and accounting systems to align with FA_VAT schema requirements.
Train relevant teams on compliance procedures.
Track regulatory updates from the Polish Ministry of Finance.
Enable system capability for handling KSeF e-invoice attachments.
Prepare for QR code certificate issuance and retrieval.
Contribute to public consultations on the draft Act and technical specs, if applicable.
How can we help?
Anusaar is a certified Peppol Access Point, equipped to support businesses in seamlessly integrating and automating electronic invoices and other business documents. With extensive experience in integration and automation, our team of seasoned professionals offers expert assessment and gap analysis to identify your specific needs. We provide tailored solutions designed to enhance efficiency, ensure compliance, and streamline your invoicing processes. Let us help you navigate the path of Poland e-invoicing with ease.
0 notes
Text
E-Invoicing in Saudi Arabia

E-invoicing is becoming an important part of doing business in Saudi Arabia. It involves creating and storing invoices digitally, ensuring efficiency, security, and compliance with regulations. In this blog, we will explore what e-invoicing is, why it matters, and how businesses can adapt to the new requirements set by the Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority (ZATCA). We will also explain the transition to ZATCA Phase 2, which focuses on integration with the government’s system.
What is E-Invoicing?
It is a digital system where businesses issue and store invoices electronically instead of on paper. These invoices are created through special software and cannot be manually edited once issued. However, corrections can be made using electronic credit or debit notes linked to the original invoice.
For VAT-registered businesses in Saudi Arabia, e-invoicing ensures that all transactions are recorded digitally, making it easier to track and report sales. This system applies to various transactions, including domestic sales, exports, and advance payments for goods or services.
However, e-invoices are not required for:
VAT-exempt supplies.
Imports into Saudi Arabia.
Transactions subject to the reverse charge mechanism.
Why is E-Invoicing Important?
It is more than a technical update; it’s a step towards modernizing how businesses operate. The Saudi government introduced this system to improve efficiency, transparency, and security.
Here are some key benefits:
Fraud Prevention: Digital records make it harder to issue fake invoices, ensuring fair competition.
Streamlined Audits: Tax authorities can easily access standardized data, reducing the need for frequent audits.
Faster Processing: Buyers and sellers benefit from quicker transactions and tax refunds.
Reduced Errors: Digital systems minimize mistakes compared to handwritten invoices.
Ease of Storage: Storing invoices electronically saves space and simplifies retrieval.
By transitioning to e-invoicing, businesses can align with global best practices, enhancing their credibility and operational efficiency.
E-Invoicing in Saudi Arabia: The Two Phases
Phase 1: Issuing and Storing E-Invoices (Effective December 4, 2021)
This phase required all VAT-registered businesses to start generating and storing e-invoices and related notes electronically. The invoices must include all mandatory fields such as:
Seller’s name and VAT number.
Invoice issue date and time.
VAT amount.
Total invoice value, including VAT.
However, businesses were not required to share invoices with ZATCA during this phase. They could use any compliant e-invoicing software to meet these basic requirements.
Phase 2: Integration with ZATCA’s System (Effective January 1, 2023)
Zatca e-invoicing Phase 2 introduced more advanced requirements for e-invoicing. Businesses now need to integrate their systems with ZATCA to share invoices electronically. Here’s what Phase 2 integration involves:
Invoice Formats: E-invoices must be in XML or PDF/A-3 format with embedded XML.
Authentication: Each invoice must have a digital signature, a unique identifier (UUID), and a cryptographic stamp to prevent tampering.
API Connectivity: Systems must connect with ZATCA through APIs to enable real-time validation and submission.
Mandatory Reporting: Simplified invoices for B2C transactions must be reported within 24 hours, while standard invoices for B2B transactions must be authenticated before sharing with the buyer.
ZATCA informs businesses about their integration deadlines at least six months in advance.
Types of E-Invoices
There are two main types of e-invoices in Saudi Arabia:
Standard E-Invoice: Used for B2B and B2G (Business-to-Government) transactions. These invoices must meet VAT requirements and, in Phase 2, need ZATCA authentication before being sent to buyers.
Simplified E-Invoice: Used for B2C (Business-to-Consumer) transactions at the point of sale. These invoices include a QR code for validation and must be reported to ZATCA within 24 hours during Phase 2.
How to Prepare for ZATCA E-Invoicing Phase 2
Transitioning to ZATCA E-Invoicing Phase 2 might seem challenging, but with proper preparation, businesses can meet the requirements smoothly. Here are some steps to help you get started:
Choose a Compliant System: Select e-invoicing software that meets ZATCA’s technical and security requirements. The system should support API integration, digital signatures, and anti-tampering features.
Train Your Team: Ensure that employees involved in invoicing understand the new process. Training them on using the e-invoicing system will reduce errors and delays.
Test Your System: Before the deadline, test your system to ensure it meets all requirements for generating and sharing e-invoices.
Stay Updated: Regularly check ZATCA’s website for updates and guidelines. They provide detailed technical specifications for compliance.
Work with Experts: If you’re unsure about compliance, consider consulting with accounting or software experts who can guide you through the transition.
Dos and Don’ts for Businesses
Dos
Use a ZATCA-compliant e-invoicing system.
Train your staff on using the system effectively.
Issue all invoices in Arabic (you can add translations if needed).
Store invoices securely for future reference.
Don’ts
Avoid using manual or handwritten invoices.
Do not edit or delete issued e-invoices. Use credit or debit notes instead.
Avoid using systems that allow tampering or unauthorized access.
Why Act Now?
Compliance with ZATCA’s e-invoicing regulations is mandatory for VAT-registered businesses. Failure to comply could result in penalties or interruptions to your operations. By adopting a robust e-invoicing system now, you can ensure a seamless transition, improve your business processes, and avoid last-minute hassles.
To sum up
The move to e-invoicing in Saudi Arabia is a significant step toward transparency, efficiency, and secure business operations. As ZATCA Phase 2 requirements come into full effect, preparing your business with the right tools and knowledge is essential.
By adopting a ZATCA-compliant solution and staying informed about the latest regulations, you can ensure smooth transitions and maintain compliance with ease.
Ready to streamline your invoicing process? Choose a ZATCA-compliant solution today and stay ahead in the digital era of business!
0 notes
Text
Real-Time Proof of Delivery: A Game-Changer in Last Mile Delivery

The last mile of delivery is often the most critical and complex part of the logistics process. As the demand for faster, more reliable deliveries grows, managing proof of delivery (POD) in real time has become a key differentiator for businesses aiming to offer exceptional customer experiences. Real-time POD not only enhances customer satisfaction but also addresses common issues like billing disputes, settlement delays, and inaccurate tracking of goods, making it essential for both B2B and B2C logistics.
In this blog, we explore the challenges in last mile delivery, the significance of real-time proof of delivery, and how leveraging advanced last mile SaaS platforms can revolutionize logistics operations.
What are the Challenges in Last Mile Delivery
The last mile delivery process — where goods are delivered from a transportation hub to the final destination — faces several hurdles that impact both operational efficiency and customer satisfaction:
⦁ Inconsistent Proof of Delivery:
Inaccurate or missing POD can lead to disputes over delivery status, particularly in cases of lost or damaged goods. This is especially problematic for high-value deliveries or industries requiring precise tracking, such as pharmaceuticals or retail.
⦁ Delayed Billing and Settlements:
Without timely proof of delivery, the billing process is often delayed, leading to cash flow issues and operational inefficiencies. Real-time POD can expedite these processes by confirming deliveries as soon as they occur.
⦁ Lack of Transparency and Visibility:
Customers and businesses alike expect real-time updates on the status of their deliveries. Without an efficient system in place, providing accurate tracking and delivery confirmation becomes difficult, reducing customer trust.
⦁ Manual Errors:
In many logistics operations, proof of delivery is still managed using paper-based systems. This can lead to errors, delays, and even loss of important documents, further complicating the billing and settlement processes.
Why Real-Time Proof of Delivery Matters
Real-time proof of delivery (POD) is a critical component in ensuring smooth logistics operations and delivering a superior customer experience. Here’s why it has become so significant:
⦁ Enhanced Customer Experience
In both B2B and B2C segments, customers demand instant notifications and transparency throughout the delivery process. With real-time proof of delivery, businesses can provide immediate confirmation upon delivery completion, often with electronic signatures, photos, or QR codes. This enhances trust, reduces the risk of disputes, and boosts overall customer satisfaction.
⦁ Operational Accuracy and Accountability
Real-time POD eliminates manual errors and ensures that every delivery is documented accurately. Whether it’s capturing a recipient’s signature or documenting the condition of goods upon arrival, digital POD provides an indisputable record, minimizing the risk of disputes and costly delays.
⦁ Streamlined Billing and Settlements
For B2B businesses, especially those dealing with large volumes of transactions, real-time proof of delivery accelerates the billing and settlement processes. The moment a delivery is confirmed, it triggers automatic invoicing and settlement workflows, reducing the need for manual intervention and eliminating bottlenecks in revenue collection.
⦁ Increased Operational Efficiency
Real-time POD provides logistics teams with full visibility over delivery operations. This allows them to quickly identify and resolve issues such as missed or delayed deliveries, ensuring that operations run smoothly and efficiently. The integration of POD with last mile TMS software also provides valuable data that can be used for performance monitoring and optimization.
Impact of Real-Time Proof of Delivery for B2B and B2C Segments
Real-time proof of delivery (POD) has transformed both B2B and B2C logistics by providing instant confirmation and transparency. For B2B, it ensures seamless operations with reduced disputes and faster billing, while in B2C, it meets consumer expectations for real-time updates and reliable deliveries. Across both segments, real-time POD enhances efficiency and customer satisfaction.
B2B Benefits
In the B2B logistics space, where multiple stakeholders are involved in the supply chain, real-time POD ensures transparency and accountability at every stage. It allows companies to:
⦁ Track the movement of goods with precision. ⦁ Reduce disputes over delivery accuracy or condition. ⦁ Expedite billing cycles by confirming deliveries instantly. ⦁ Improve relationships with clients by providing a seamless delivery experience.
B2C Benefits
For B2C logistics, real-time proof of delivery is essential to meet the growing expectations of tech-savvy consumers. Whether it’s a same-day delivery or a scheduled drop-off, real-time POD:
⦁ Provides customers with real-time updates and delivery confirmation. ⦁ Reduces customer inquiries about delivery status. ⦁ Builds trust and reduces the anxiety often associated with online shopping. ⦁ Increases transparency by providing evidence of delivery, including signatures and photos.
Leveraging Last Mile SaaS Platforms for Real-Time Proof of Delivery
Advanced last mile SaaS platforms are transforming the way businesses manage proof of delivery. These platforms integrate seamlessly with existing logistics operations, offering a suite of tools that enhance real-time visibility, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
Here’s how they do it:
1. Mobile POD Solutions
Delivery agents can use mobile devices to capture electronic signatures, photos, and barcodes at the point of delivery. This data is instantly uploaded to the cloud, giving businesses and customers real-time access to proof of delivery. This reduces paperwork and minimizes the risk of errors.
2. AI and Predictive Analytics
Modern last mile SaaS platforms often include AI-powered route optimization and predictive analytics tools that anticipate delivery issues before they happen. These insights allow businesses to communicate proactively with customers, preventing delays and improving overall satisfaction.
3. Integration with ERP and Billing Systems
Seamless integration with ERP systems ensures that once a delivery is confirmed, billing and invoicing processes are triggered automatically. This not only speeds up the settlement process but also improves cash flow and reduces the risk of delayed payments.
About nuVizz
nuVizz is a market leader in providing innovative Last Mile TMS solutions that enable real-time visibility and proof of delivery, empowering businesses to enhance their operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. nuVizz’s cutting-edge technology offers seamless integration of route optimization, automated billing, and real-time tracking, making it the ideal choice for shippers and carriers looking to excel in the logistics industry.
Conclusion
Real-time proof of delivery is more than just a logistical necessity — it’s a strategic advantage for businesses looking to thrive in the competitive world of last mile delivery. By embracing cutting-edge last mile SaaS platforms, companies can improve transparency, reduce operational inefficiencies, and provide their customers with a superior delivery experience.
As the logistics industry continues to evolve, real-time POD will play an increasingly important role in driving customer satisfaction, operational excellence, and revenue growth. Businesses that invest in advanced last mile solutions will be well-positioned to lead in this rapidly changing landscape.
Original content is published at www.nuvizz.com
0 notes
Text
Best GST Invoice Software
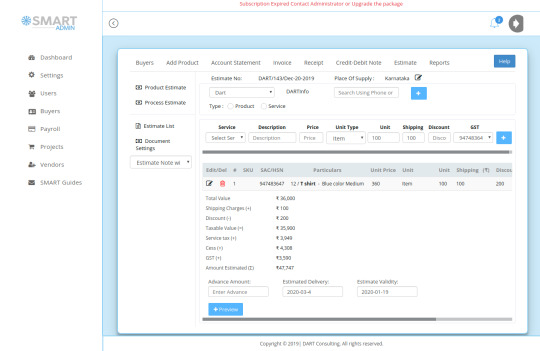
The invoicing option of Smart Admin links estimate/quote, invoice, receipt, and Credit/Debit to ensure accurate flow of data points in the overall invoicing process. This will ensure zero error in all statutory filings connected with invoicing. The invoice management software captures data points associated with each of the documents and numbers it properly. The Import and Export transactions as well as SEZ transactions of both products and services are listed in the process.
Need for using GST Invoice Software
GST Invoice Software has been designed to meet the challenges as posed by GST implementation and its frequent updates. The implementation of GST has brought multitude of challenges to small and medium business owners. The larger businesses were fully equipped to meet challenges because of their affordability to invest in costly software whereas for small businesses, it turned out to be a nightmare. The organized sector with its regular stream of tax payment process was least affected by GST and the need for GST invoice generator. The small and medium segments were bogged down by the burden of generating GST Compliant Invoice and fear of reporting wrong data. In addition, there were compelled to route transactions through banking channels to meet the requirement of large suppliers. This posed additional challenges of keeping record of each and every transaction and its proper reporting.
Smart Admin stepped into this need and developed invoice management software to match up with the requirements of GST filing and minimize errors in transactions. The billing software has been designed taking into account of the level of expertise of common man. The Smart Admin Invoice Software can be operated by anyone who can handle Gmail and WhatsApp.
Further, Smart Admin has been configured to handle the future requirements of e-invoicing as if it is going to be implemented by GST Council for B2B transaction at any time in future. With such implementation, the e-invoice generated needs to be validated at Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). This will generate a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and digitally sign the e-invoice and also generate a QR code. The QR Code will contain vital parameters of the e-invoice and return the same to the taxpayer who generated the document in first place. The IRP will also send the signed e-invoice to the recipient of the document on the email provided in the e-invoice. Smart Admin GST invoice software has the option to update the invoice with IRN as generated and send the same to buyers once the feature has been implemented at any time .
The options as given for GST Invoicing Software India are expected to speed up the filing process and minimize errors. With Smart Admin, users can go for multiple GST invoice formats, receipt and cr/dr vouchers according to requirements for generating Tax Invoices under GST.
The invoice management software is linked with all other transactions to avoid duplication of efforts and missing of entries. Once you subscribe for the mobile app, then invoice can be generated on the go. Invoice will be sent to the recipients over email or SMS instantly. If you are looking for best GST Invoice Software, then we can confirm that Smart Admin is one of the best invoicing software India, a solution for you.
0 notes
Text
Navigate the New Rules of ZATCA e-Invoicing Phase 2
The digital shift in Saudi Arabia’s tax landscape is picking up speed. At the center of it all is ZATCA e-Invoicing Phase 2—a mandatory evolution for VAT-registered businesses that brings more structure, security, and real-time integration to how invoices are issued and reported.
If you’ve already adjusted to Phase 1, you’re halfway there. But Phase 2 introduces new technical and operational changes that require deeper preparation. The good news? With the right understanding, this shift can actually help streamline your business and improve your reporting accuracy.
Let’s walk through everything you need to know—clearly, simply, and without the technical overwhelm.
What Is ZATCA e-Invoicing Phase 2?
To recap, ZATCA stands for the Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority in Saudi Arabia. It oversees tax compliance in the Kingdom and is driving the movement toward electronic invoicing through a phased approach.
The Two Phases at a Glance:
Phase 1 (Generation Phase): Started in December 2021, requiring businesses to issue digital (structured XML) invoices using compliant systems.
Phase 2 (Integration Phase): Began in January 2023, and requires companies to integrate their invoicing systems directly with ZATCA for invoice clearance or reporting.
This second phase is a big leap toward real-time transparency and anti-fraud efforts, aligning with Vision 2030’s goal of building a smart, digital economy.
Why Does Phase 2 Matter?
ZATCA isn’t just ticking boxes—it’s building a national infrastructure where tax-related transactions are instant, auditable, and harder to manipulate. For businesses, this means more accountability but also potential benefits.
Benefits include:
Reduced manual work and paperwork
More accurate tax reporting
Easier audits and compliance checks
Stronger business credibility
Less risk of invoice rejection or disputes
Who Must Comply (and When)?
ZATCA isn’t pushing everyone into Phase 2 overnight. Instead, it’s rolling out compliance in waves, based on annual revenue.
Here's how it’s working:
Wave 1: Companies earning over SAR 3 billion (Started Jan 1, 2023)
Wave 2: Businesses making over SAR 500 million (Started July 1, 2023)
Future Waves: Will gradually include businesses with lower revenue thresholds
If you haven’t been notified yet, don’t relax too much. ZATCA gives companies a 6-month window to prepare after they're selected—so it’s best to be ready early.
What Does Compliance Look Like?
So, what exactly do you need to change in Phase 2? It's more than just creating digital invoices—now your system must be capable of live interaction with ZATCA’s platform, FATOORA.
Main Requirements:
System Integration: Your invoicing software must connect to ZATCA’s API.
XML Format: Invoices must follow a specific structured format.
Digital Signatures: Mandatory to prove invoice authenticity.
UUID and Cryptographic Stamps: Each invoice must have a unique identifier and be digitally stamped.
QR Codes: Required especially for B2C invoices.
Invoice Clearance or Reporting:
B2B invoices (Standard): Must be cleared in real time before being sent to the buyer.
B2C invoices (Simplified): Must be reported within 24 hours after being issued.
How to Prepare for ZATCA e-Invoicing Phase 2
Don’t wait for a formal notification to get started. The earlier you prepare, the smoother the transition will be.
1. Assess Your Current Invoicing System
Ask yourself:
Can my system issue XML invoices?
Is it capable of integrating with external APIs?
Does it support digital stamping and signing?
If not, it’s time to either upgrade your system or migrate to a ZATCA-certified solution.
2. Choose the Right E-Invoicing Partner
Many local and international providers now offer ZATCA-compliant invoicing tools. Look for:
Local support and Arabic language interface
Experience with previous Phase 2 implementations
Ongoing updates to stay compliant with future changes
3. Test in ZATCA’s Sandbox
Before going live, ZATCA provides a sandbox environment for testing your setup. Use this opportunity to:
Validate invoice formats
Test real-time API responses
Simulate your daily invoicing process
4. Train Your Staff
Ensure everyone involved understands what’s changing. This includes:
Accountants and finance officers
Sales and billing teams
IT and software teams
Create a simple internal workflow that covers:
Who issues the invoice
How it gets cleared or reported
What happens if it’s rejected
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Transitioning to ZATCA e-Invoicing Phase 2 isn’t difficult—but there are a few traps businesses often fall into:
Waiting too long: 6 months isn’t much time if system changes are required.
Relying on outdated software: Non-compliant systems can cause major delays.
Ignoring sandbox testing: It’s your safety net—use it.
Overcomplicating the process: Keep workflows simple and efficient.
What Happens If You Don’t Comply?
ZATCA has teeth. If you’re selected for Phase 2 and fail to comply by the deadline, you may face:
Financial penalties
Suspension of invoicing ability
Legal consequences
Reputation damage with clients and partners
This is not a soft suggestion—it’s a mandatory requirement with real implications.
The Upside of Compliance
Yes, it’s mandatory. Yes, it takes some effort. But it’s not all downside. Many businesses that have adopted Phase 2 early are already seeing internal benefits:
Faster approvals and reduced invoice disputes
Cleaner, more accurate records
Improved VAT recovery processes
Enhanced data visibility for forecasting and planning
The more digital your systems, the better equipped you are for long-term growth in Saudi Arabia's evolving business landscape.
Final Words: Don’t Just Comply—Adapt and Thrive
ZATCA e-invoicing phase 2 isn’t just about avoiding penalties—it’s about future-proofing your business. The better your systems are today, the easier it will be to scale, compete, and thrive in a digital-first economy.
Start early. Get the right tools. Educate your team. And treat this not as a burden—but as a stepping stone toward smarter operations and greater compliance confidence.
Key Takeaways:
Phase 2 is live and being rolled out in waves—check if your business qualifies.
It requires full system integration with ZATCA via APIs.
Real-time clearance and structured XML formats are now essential.
Early preparation and testing are the best ways to avoid stress and penalties.
The right software partner can make all the difference.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Crossed the e-invoicing turnover limit? Here are 5 things to do next!

E-Invoicing Turnover Limit is the base criteria on the basis of which a company falls under the E-Invoice Mandate. Recently, the government has further reduced the e-invoicing turnover limit covering companies with Annual Aggregate Turnover of Rs. 5 Cr. and above.
As per the GST notification 10/2023, from August 1, 2023 companies having AATO of Rs 5 Cr and above need to register their B2B invoices and other specific documents on IRP and get Invoice Registration Number in return. This is an attempt to accommodate MSMEs under e-invoicing and streamline the process while bringing in transparency and reducing tax evasion.
This article will help you to know if you have crossed the e-invoicing turnover limit and if you have recently crossed or are about to cross the e-invoicing threshold limit, then what are the next steps you need to carry from here on…
What is the turnover limit for e-invoicing?
Introduced in a phased manner, e-invoice under GST is based on the Aggregate Annual Turnover (AATO) of companies and businesses in India.
The first phase addressed companies with a turnover of over INR 500 crores. This went live from 1st October 2020. The next was for the ones that turned a revenue over of more than INR 100 crores. This went live from 1st January 2021. The third phase, which went live in April 2021, was for the companies with a revenue of over INR 50 crores. Earlier this year, the fourth phase, launched in April 2022, was effective for companies that have turnover over INR 20 crores. Finally, the fifth phase was for companies with a turnover of over INR 10 crores going live from 1st October 2022.
Steps to take after your business crosses the e-invoice turnover limit
1. Familiarize your Accounts Department with E-invoicing
Prior to the e-invoice applicability, all your B2B and B2C invoices may have had a similar common format that is followed by Indian businesses across the country with the required data fields. However, after crossing the e-invoicing turnover limit, you cannot carry out generating invoices in your usual manner. There is a standard procedure that needs to be followed. There are rules regarding the data fields and most importantly the IRN (Invoice Reference Number) and QR Code.
So, the first step will be to familiarize your accounts department with the e-invoicing mandate, its rules and regulations, about e-invoice printing, data fields etc. The change is massive and thus, a dynamic implementation will be made possible by having a thorough understanding of the e-invoice issuance, e-way bill production, and GST return filing processes.
2. Register yourself on the Invoice Registration Portal
Once your business crosses the e-invoicing threshold, you will automatically get enabled on the official GSTN portal. After the enablement, you need to register yourself on an IRP (Invoice Registration Portal) like IRIS IRP.
Note: In some cases, your business may not get automatically enabled on the official GSTN website. In that case, you need to create an account and enable yourself on the GSTN portal if your business falls under the e-invoicing threshold.
3. Verify and Prepare your Systems
Now that you have registered yourself on the invoice registration portal, it is also super important to check if your accounting and billing systems are ready for e-invoicing under GST. Before sending your invoice data to the IRP, you need to check if all the data is correct in order to avoid errors.
So, make sure your tax rates, HSN code etc. are updated in your systems. All the mandatory e-invoice data fields should be filled appropriately. Another major activity is that you will have to have a separate set-up for your B2B and B2C invoices. This is because e-invoicing is applicable to only B2B and export invoices so you must segregate your B2B and B2C invoices in your billing systems so as to avoid confusion.
Read This Full Article at e-invoice turnover limit
0 notes
Text
GST E Invoicing, Process and Its Benefits
What is e-invoicing under GST
GST e-invoicing is a system that electronically authenticates B2B invoices through the Goods & Services Network (GSTN). Under the system, an identification reference number (IRN) will be issued against every invoice by the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP).
This system is not built to prepare and generate invoices on the GST portal. Instead, it involves submitting already generated invoices on a common e-invoice portal.
Information from the invoices will be transferred from IRP to the GST portal in real-time. This will eliminate the need for manual inputs while filing GST returns.
Process of getting a GST e-invoice
‘e-Invoicing under GST’ does not mean invoice generation by a government portal. Taxpayers will continue to create GST invoices through their preferred method. These invoices will be uploaded to IRP. This portal will generate a unique IRN, digitally sign it, add a QR code, and return the invoice.
Benefits of e-invoicing under GST
Technological advancements, increased internet penetration with the availability of computer systems at economical prices will make e-invoice – a popular choice for businesses.
e-Invoicing has many advantages for businesses in India.
Reporting B2B invoices in the e-invoice form will reduce reporting of the same in multiple forms like GSTR-1, e-way bill, etc
No tax evasion as a complete trail of B2B invoices will be available
System-level reconciliation of input credit and output tax
Auto-population of invoice details into GST return and other forms (like an e-way bill)
Mitigation of fraud invoices
Reduction in processing costs and disputes
Improvement in payment cycles, and
Advancement in overall business efficiency
0 notes
Photo

QR Code: The new identity of a B2B invoice
0 notes
Text
Complete F&Q All e-Invoicing Software
Q-1: What is e-Invoicing?
Answer: Electronic invoicing or e-invoicing is an invoicing process that allows other software to access invoices generated by software, eliminating the need for re-entry of data or errors. In less difficult words, it is an invoice created in a standard format, whereby the electronic information of the invoice can be shared with other people, which guarantees the compatibility of the information.
Q-2: What is the electronic invoicing process?
Answer: There aren't many changes; Companies can continue to generate their invoices from their existing software. To ensure a certain level of standardization, only one standard format is used, the e-invoicing schema. These systematic invoices are prepared by the taxpayer. When creating the invoices, you must report them to the GST Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). The portal then generates a unique invoice reference number and adds the digital signature along with the QR code to the e-invoice. The QR code contains all the information required for the electronic invoice. After this process, the electronic invoice is sent back to the taxpayer via the portal. IRP will also send a copy of the signed invoice to the seller's registered email address.
Q-3: Will the electronic invoice format be the same for all categories?
Answer: All companies/taxpayers that must pay GST must issue electronic invoices using the same scheme established by GSTN. The format has required and non-required fields. All taxpayers must complete the required fields and non-required fields are used as required.
Q-4: Is e-invoicing mandatory?
Answer: Electronic invoicing is mandatory for all companies with an annual turnover of Rs. Rs. 100 crores or more from 1st January 2021. Previously it applied to companies with a turnover above the limit of Rs. 500 million crores.
However, e-invoicing does not apply to the categories listed below, regardless of commercial invoicing, as per CBIC Notice No. 13/2020- Central Rate:
. An insurance company or a banking company or financial institution, including an NBFC . A Freight Transport Company (GTA) . A registered person offering passenger transportation services. . A registered person who provides services by way of admission to the exhibition of motion pictures in multiplex services . One SEZ unit (excluded by CBIC Report No. 61/2020 – Central Tax)
Q-5: What are the advantages of electronic invoicing? Answer: These are some of the benefits of electronic invoicing:
. Report B2B invoices once during generation, reducing reporting in multiple formats. . Most of the data on the GSTR-1 form can be kept ready to send while using the electronic billing system. . E-Way invoices can also be easily created with electronic invoice data. . There is a minimal data reconciliation between the books and the GST returns submitted. . Real-time tracking of invoices generated by a supplier can be enabled, along with faster availability of input tax credits. It will also reduce input tax credit verification problems. . Better management and automation of the tax declaration process. . Reduced fraud as tax authorities also has real-time access to data. . Elimination of false GST invoices that are generated.
Q-6: What deliveries are currently covered by e-invoicing? Answer: Electronic invoicing currently applies to:
. Deliveries to registrants (i.e. B2B deliveries), . Deliveries to ZEE (with/without payment of taxes), . Exports (with/without payment of taxes) and exports considered,
made by the Class of Notified Taxpayers.
Q-7: How will the e-invoicing model work? Answer: Under the e-invoicing model, companies will continue to issue invoices in their respective ERPs, as has been the case in the past. Only the standard, schema, and format for creating invoices are specified to ensure a certain level of standardization and machine-readability of these invoices. The preparation of the invoice is the responsibility of the taxpayer.
As it is generated, it must be reported to the GST Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). The IRP generates a unique invoice reference number (IRN) and adds the digital signature for the e-invoice along with the QR code. The QR code contains important parameters of the electronic invoice and sends it back to the taxpayer who created the document. The IRP also sends the signed e-invoice to the seller to the registered email id.
Q-8: What types of fields are there in an electronic invoice? Answer: The data of the fields marked as "required" must be entered.
. A required field that has no value can be reported as null. . Fields marked as "Optional" may or may not be filled out. They are only relevant to certain companies and only relate to certain scenarios. . Some sections of the electronic invoice marked as "Optional" may contain mandatory fields. For example, the E-Way Billing Details section is marked as Optional. However, in this section, the Transport Type field is required.
Q-9: Does the e-invoice need to be signed again by the supplier? Answer: The provisions of Rule 46 of the Central Goods and Services (CGST) Rules, 2017 apply here. According to Rule 46, the signature/digital signature of the supplier or his authorized representative is required while issuing invoices. However, a proviso to Rule 46 states that the signature/digital signature shall not be required in the case of issuance of an electronic invoice that is by the provisions of the InformationTechnology Act, 2000. Hence, it has been interpreted that in the case of e-invoices, a supplier will not be required to sign/digitally sign the document.
Q-10: What are the options for receiving electronic invoices registered in the IRP?
Answer: Several ways to record electronic invoices are provided in the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). Some of the suggested modes are-
. Web-based, . API based, . Based on offline tools and . based on GSP.
Q-11: What is the final threshold for e-invoicing?
Answer: In a bid to step up measures against tax evasion, the government announced last week that GST e-invoicing will be mandatory for companies with a turnover of more than Rs 10 crore from October 1, down from the current Rs 20 crore, which will bring in another 0.36 million businesses in digital reporting.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
E-Invoicing Malaysia

1. E-invoicing Malaysia
e-invoicing is a form of electronic billing. This term is used to define the process by which a transaction between two parties (a buyer and seller) is documented electronically, in order to ensure their trading agreements are being met. The e-invoices are sent through government portals for validation and recordkeeping.
For Malaysia, the e-invoice must be created in the format as mentioned by the IRBM (Inland revenue board of Malaysia), which is usually XML or JSON.
2. Rules – e-invoicing Malaysia.
The IRBM had announced in March 2023, that all businesses that are listed in Malaysia must generate e-invoices for B2B, B2C transactions. However, the issuance of e-invoices is not just limited to transactions in Malaysia, it relates to cross border transactions as well. As of now, no industries are exempted from e-invoice implementation.
An e-invoice for Malaysia consists of 55 fields, which encompass details of the buyer, seller, kind of transaction, product, price, time etc. An e-invoice that is validated successfully, consists of a Unique Identification number (UIN) and a QR code.
3. Implementation timeline for e-invoicing Malaysia
In order to ensure smooth implementation, e-invoicing Malaysia, will be executed in phases based on the revenue threshold of the company.
The implementation of e-invoices began in August 2024, for companies of annual revenue more than 100 million.
For taxpayers with an annual turnover or revenue of more than RM25 million and up to RM100 million, the implementation date is January 1, 2025.
All other taxpayers except the ones whose annual turnover is less than 150 million need to implement e-invoice from July 1, 2025.
4. Penalty:
In Malaysia, failing to issue an e-invoice is considered an offence under Section 120 (1)(d) of the income tax act, 1967. The penalty of non-compliance includes a fine ranging from RM 20O to RM 20,000 or imprisonment for 6 months, or both, for each instance of non-compliance.
5. Benefits of e-invoicing Malaysia:

a. Digitalizing the reporting process
All the data is stored by leveraging digital tools to create optimized solutions that promote greater efficiency. Thereby reducing chances of error and misinterpretation of data.
b. Enhanced security
Improved security measures to protect against unauthorized entry and potential threats.
c. Legal compliance
Makes it easier to adhere to the law and regulations of the state and maintain the legal standards that are applicable to the business.
d. Increased efficiency and productivity
Getting substantial work done, with the least amount of resources. Both are important for effective time and resource management in any industry.
e. Improved accuracy and compliance
– It helps in being compliant with the state’s laws and regulations in order to avoid any discrepancies in the future, thereby reducing any legal mishaps.
f. Greater cost saving by streamlining the operations
By providing a structured process flow, that includes validation of the e-invoice, any chance of erroneous transactions is highly minimized. This ensures better recordkeeping and ease of operations.
Conclusion:
e-invoicing Malaysia showcases an important step towards modernizing the country’s business and tax processes. As domestic and cross-border transactions are required to maintain electronic billing, the system improves compliance, reduces manual errors and results in improved efficiency. Implementation is in phases based on the revenue thresholds. This ensures a smooth transition by adhering to the regulations and thereby, avoiding penalties. e-invoicing Malaysia, offers multiple advantages such as enhanced security, cost savings and streamlined operations. These advantages allow businesses to maintain a strong framework and optimize their financial management. All this, while being tax-compliant. We at Lenorasoft, through our custom solution, Anusaar, through e-invoicing Malaysia, aim to align with Malaysia’s efforts for a transparent, efficient and digitalized economy.
0 notes