#Atal Pension Scheme
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Atal Pension Yojana: Financial Freedom for All Indians
Looking for a reliable way to secure your future? The Atal Pension Yojana Scheme offers financial freedom to all Indians! With guaranteed pension benefits, the APY Scheme is designed to support the unorganized sector. Whether you're self-employed or working, start contributing today for a better tomorrow! The APY Yojana provides options for varying pension amounts, ensuring you receive benefits based on your contribution. See how the progress of Atal Pension Yojana has impacted millions of lives across the country! Ready to plan your retirement? Learn more and take the first step toward financial security.
0 notes
Text

Atal Pension Yojana के अंतर्गत मिलेंगे 5000 रुपए प्रति माह की पेंशन, जाने कैसे मिलेगा लाभ
Atal Pension Yojana: https://combonews.in/under-atal-pension-yojana-you-will-get-a-pension-of-rs-5000-per-month-know-how-to-get-the-benefit/
0 notes
Text
#Atal Pension Yojana#Pension Scheme#Financial Security#Unorganized Sector#Retirement Planning#Social Security#Government Scheme#Old Age Pension#Financial Inclusion
0 notes
Text
How Accurate Is the Atal Pension Yojana Calculator?
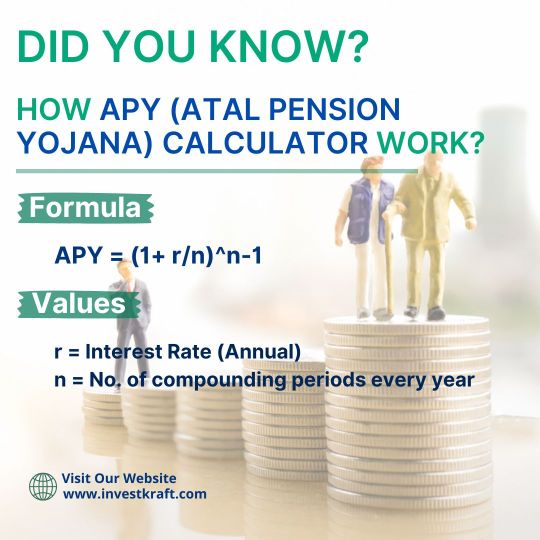
The accuracy of the Atal Pension Yojana (APY) Calculator, particularly on the Investkraft website, is generally reliable. This online tool estimates the pension amount one can receive under the APY scheme based on inputs like age, contribution amount, and the chosen pension plan. While it provides a useful estimate, it's essential to understand that the final pension amount may vary slightly due to factors such as changes in government regulations or economic conditions. However, Investkraft strives to keep its calculator updated to reflect any such changes, ensuring users get as accurate a prediction as possible. Overall, while the APY Calculator offers valuable insights into potential pension benefits, it's advisable to consult with financial experts for a comprehensive retirement planning strategy.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The NPS Administrators Association is set up to regulate the pension sector
After the Association of Mutual Funds of India (AMFI), the Association of NPS Intermediaries (ANI) has been set up to regulate the pension sector. This comes at a time when the total subscribers in the pension sector are more than 80 million, including 64 million in the Atal Pension Yojana, where there are about 16 million subscribers in the NPS, and the corpus of the pension scheme is Rs 13.8…
0 notes
Text
Association of NPS Intermediaries formed to regulate pension sector
An Association of NPS Intermediaries (ANI) has been formed to regulate the pension sector after the Association of Mutual Funds of India (AMFI). This comes at a time when the pension sector has a total of over 80 million subscribers, including 64 million in Atal Vishrama Yojana, out of which NPS has about 16 million subscribers and the pension scheme has a reserve of Rs 13.8 lakh. A crore.…
0 notes
Text
Association of NPS Intermediaries formed to regulate pension sector
An Association of NPS Intermediaries (ANI) has been formed to regulate the pension sector after the Association of Mutual Funds of India (AMFI). This comes at a time when the pension sector has a total of over 80 million subscribers, including 64 million in Atal Vishrama Yojana, out of which NPS has about 16 million subscribers and the pension scheme has a reserve of Rs 13.8 lakh. A crore.…
0 notes
Text
Association of NPS Intermediaries formed to regulate pension sector
An Association of NPS Intermediaries (ANI) has been formed to regulate the pension sector after the Association of Mutual Funds of India (AMFI). This comes at a time when the pension sector has a total of over 80 million subscribers, including 64 million in Atal Vishrama Yojana, out of which NPS has about 16 million subscribers and the pension scheme has a reserve of Rs 13.8 lakh. A crore.…
0 notes
Text
Revolutionizing Financial Inclusion with Winsoft Technologies
In today’s digital age, financial services are no longer confined to traditional brick-and-mortar setups. The integration of technology has paved the way for Digital Financial Services, making banking and financial solutions accessible to a wider audience, particularly in underserved regions. Winsoft Technologies, a pioneer in the BFSI sector, plays a pivotal role in driving this transformation with its innovative digital solutions, including specialized platforms for government initiatives like the Digital Solution for Pradhan Mantri Yojana.
The Rise of Digital Financial Services
Digital Financial Services encompass a broad range of financial products delivered through digital platforms. These services include mobile banking, online payments, digital wallets and investment tools, which enhance convenience, speed and transparency. Winsoft’s robust offerings address the growing demand for seamless digital experiences, providing customized solutions for banks, insurers and wealth managers.
By leveraging advanced technology, Winsoft empowers financial institutions to serve a broader audience while reducing operational costs. Their platforms enable quick transactions, secure data handling and efficient customer onboarding, which are critical in achieving financial inclusion.
Winsoft’s Digital Solution for Pradhan Mantri Yojana
The Indian government has introduced numerous schemes under the Pradhan Mantri Yojana umbrella to promote financial inclusion, support entrepreneurship and encourage savings. Winsoft has developed a specialized Digital Solution for Pradhan Mantri Yojana, ensuring smooth implementation and accessibility for these initiatives.
One of their flagship products, SmartAPY, is designed to simplify the distribution and management of government financial products such as the Atal Pension Yojana. This platform offers a seamless experience for beneficiaries, financial advisors and regulatory bodies, ensuring that the benefits of these schemes reach the intended audience effectively.
By streamlining processes like enrollment, transaction management and compliance reporting, Winsoft’s solutions help financial institutions deliver government schemes with efficiency and transparency.
Key Benefits of Winsoft’s Solutions
Enhanced Accessibility: Winsoft’s digital platforms eliminate geographical barriers, enabling users from remote areas to access financial services.
User-Friendly Interfaces: Their solutions prioritize customer experience with intuitive designs that cater to both tech-savvy and first-time users.
Secure Transactions: Winsoft’s ISO 27001-certified systems ensure robust security measures, safeguarding sensitive financial data.
Scalable Technology: Whether it’s catering to a growing customer base or expanding service offerings, Winsoft’s platforms are designed to scale with ease.
Driving Financial Inclusion
Winsoft’s focus on Digital Financial Services aligns with India’s vision of a cashless economy and broader financial inclusion. By collaborating with government programs and private enterprises, Winsoft has made significant strides in bridging the gap between urban and rural financial ecosystems.
Their digital solutions not only enhance efficiency for institutions but also empower individuals to take control of their finances. Whether it’s through mobile banking, pension management, or investment advisory platforms, Winsoft remains at the forefront of India’s digital transformation journey.
Conclusion
Winsoft Technologies has established itself as a leader in delivering innovative solutions for the BFSI sector. With its expertise in Digital Financial Services and its dedicated Digital Solution for Pradhan Mantri Yojana, the company is driving significant progress toward financial inclusion. By harnessing the power of technology, Winsoft continues to transform the financial landscape, ensuring a brighter and more accessible future for all.
0 notes
Text
[ad_1] Public Sector Banks (PSBs) in India have achieved a remarkable milestone by recording their highest-ever aggregate net profit of ₹1.41 lakh crore in the financial year 2023-24. This landmark achievement reflects the sector’s robust turnaround, underpinned by a significant improvement in asset quality. The Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) ratio steeply declined, dropping to 3.12% in September 2024. Demonstrating continued momentum, they registered a net profit of ₹ 85,5206,000 crore in the first half of 2024-25. In addition to their stellar performance, PSBs have contributed significantly to shareholder returns, paying a total dividend of ₹61,964 crore over the past three years. This remarkable financial growth underscores the sector’s operational efficiency, improved asset quality, and stronger capital base. Beyond their financial achievements, these banks have played a key role in promoting financial inclusion. They have implemented crucial government schemes like the Atal Pension Yojana and Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana, to name a few. These efforts have ensured that vital benefits reach underserved sections of society. The government of India has actively supported the sector with reforms, welfare measures, and strong policies. This has strengthened the banking system, fostering greater transparency, stability, and inclusivity. Decline in GNPA: Strengthening PSB Resilience The Gross NPA ratio of Public Sector Banks (PSBs) has witnessed a remarkable improvement, declining to 3.12% in September 2024 from a peak of 14.58% in March 2018. This significant reduction reflects the success of targeted interventions aimed at addressing stress within the banking system. A turning point came in 2015 when the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) initiated the Asset Quality Review (AQR). This exercise aimed to identify and address hidden stress in banks by mandating the transparent recognition of NPAs. It also reclassified previously restructured loans as NPAs, resulting in a sharp increase in reported NPAs. The heightened provisioning requirements during this period impacted the financial parameters of banks, restricting their ability to lend and support productive sectors of the economy. To address these challenges, the Government introduced a comprehensive 4R’s strategy: Another indicator of the improved resilience of Public Sector Banks (PSBs) is their Capital to Risk (Weighted) Assets Ratio (CRAR), which rose by 3983 basis points to 15.43% in September 2024, up from 11.45% in March 2015. This substantial improvement not only highlights the renewed stability and robustness of India’s banking sector but also positions PSBs to better support economic growth. Notably, this CRAR far exceeds the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) minimum requirement of 11.5%, underscoring the strengthened financial health of these institutions. Expanding Financial Inclusion PSBs continue to expand their reach across the nation, deepening financial inclusion. Their strengthened capital base and improved asset quality have enabled them to access markets independently, reducing reliance on government recapitalisation. Here’s how PSBs are deepening financial inclusion: 54 crore Jan Dhan accounts and more than 52 crore collateral-free loans have been sanctioned under various flagship financial inclusion schemes (PM Mudra, Stand-Up India, PM-SVANidhi, PM Vishwakarma). The number of bank branches has increased from 1,17,990 in March 2014 to 1,60,501 in September 2024; out of which 1,00,686 branches are in Rural and Semi-Urban (RUSU) areas. The Kisan Credit Card (KCC) Scheme aims to provide short-term crop loans to farmers. Total operative KCC accounts as of September 2024 stood at 7.71 crore with a total outstanding of Rs. 9.88 lakh crore. The Government of India (GoI) has consistently supported the MSME sector with a flow of credit at affordable rates through various initiatives. MSME advances registered
a CAGR of 15% over the last 3 years, with total advances as on March 31, 2024, standing at Rs. 28.04 lakh crore, posting an annual growth of 17.2%. The gross advances of Scheduled Commercial Banks grew from Rs. 8.5 lakh crore to 61 lakh crore during 2004-2014, which has significantly increased to Rs. 175 lakh crore in March 2024. Strengthening PSBs through EASE Framework The Government has implemented a series of measures to enhance the financial condition of Public Sector Banks (PSBs) through the Enhanced Access & Service Excellence (EASE) framework. This framework institutionalises an objective process of incremental reforms aligned with the evolving banking ecosystem, focusing on governance, prudent lending, risk management, technology- and data-driven banking, and outcome-centric human resources. Key highlights of the steps taken under EASE to strengthen the financial condition of PSBs include: Conclusion Public Sector Banks in India have made remarkable strides in recent years, achieving unprecedented financial milestones and contributing significantly to the nation’s economic stability and growth. The decline in Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) and improved Capital to Risk (Weighted) Assets Ratio (CRAR) reflect the sector’s resilience and sound risk management practices. The EASE framework has been crucial in institutionalising reforms, promoting prudent lending, and leveraging technology for better banking services. The focus on financial inclusion has expanded access to banking, empowering millions with affordable credit and insurance. With a stronger financial base and improved asset quality, PSBs are well-positioned to support India’s development agenda and drive inclusive economic growth. [ad_2] Source link
0 notes
Text
Atal Pension Yojana Crosses 7 Crore Subscribers, Strengthening Retirement Security In India
The Ministry of Finance recently announced a significant milestone for the Atal Pension Yojana (APY), with over 7.15 crore subscribers enrolled under the scheme as of December 2, 2024. Highlighting the program’s success, the Ministry posted on X, “With more than seven crore subscribers under Atal Pension Yojana #APY, offers secure retirement with guaranteed #PensionBenefits, ensuring peace of…
0 notes
Text
Creating Your Personalized Retirement Plan: A Step-by-Step Guide
Retirement is a significant phase of life where financial stability is crucial to enjoy peace of mind and independence. Planning for retirement involves evaluating your financial goals, estimating future expenses, and investing wisely. This article will guide you on how to create a robust retirement plan tailored to your needs, with a focus on the best retirement pension plans in India, available retirement policies, and the importance of using a retirement calculator.
Why is Retirement Planning Important?
Retirement planning ensures that you have sufficient financial resources to maintain your lifestyle and cover expenses after you stop working. In India, with changing family dynamics and increasing life expectancy, having a well-structured retirement plan is more important than ever. It helps you:
Achieve financial independence.
Cover medical and other unforeseen expenses.
Provide a legacy for your family.
Avoid being a financial burden on loved ones.
Steps to Build Your Retirement Plan
1. Assess Your Current Financial Situation
Begin by understanding your current financial position. Calculate your savings, investments, and liabilities. Knowing your net worth helps in setting realistic retirement goals.
2. Determine Your Retirement Goals
Think about the kind of lifestyle you want after retirement. Consider factors like:
Age of retirement
Desired monthly expenses
Travel plans
Medical needs
3. Estimate Future Expenses
Account for inflation while estimating future expenses. A retirement calculator can help you determine the corpus needed to sustain your post-retirement lifestyle.
4. Choose the Right Retirement Plans
Selecting suitable retirement plans is key to building a secure future. In India, you can explore various options, such as pension plans, retirement-focused mutual funds, and government schemes. These plans help in systematic savings and provide a steady income post-retirement.
5. Invest Early and Regularly
Starting early gives your investments more time to grow due to the power of compounding. Make consistent contributions towards your retirement fund to ensure financial security.
6. Diversify Your Investments
Spread your investments across different asset classes like equities, fixed deposits, and real estate. This minimizes risks and maximizes returns.
7. Review and Adjust Your Plan Regularly
Life circumstances and market conditions change over time. Regularly review your retirement plan and make adjustments as needed to stay on track.
Best Retirement Pension Plans in India
India offers several pension plans that cater to diverse needs. Here are some of the top options:
1. National Pension System (NPS)
A government-backed voluntary retirement scheme.
Allows contributions during your working years and provides a pension after retirement.
Offers tax benefits under Section 80C and 80CCD(1B) of the Income Tax Act.
2. Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF)
A retirement savings scheme for salaried individuals.
Both employer and employee contribute a percentage of the salary to the EPF account.
Provides a lump sum and interest at retirement.
3. Public Provident Fund (PPF)
A long-term investment plan with a lock-in period of 15 years.
Offers tax-free returns and government-guaranteed security.
Suitable for individuals seeking safe investment options.
4. LIC Jeevan Akshay VII
An immediate annuity plan from LIC that provides regular income.
Offers multiple annuity options to suit individual needs.
5. HDFC Life Click 2 Retire
A unit-linked pension plan with market-linked returns.
Offers flexibility in premium payments and tax benefits.
6. Atal Pension Yojana (APY)
A government initiative aimed at unorganized sector workers.
Provides a fixed monthly pension post-retirement based on contributions.
Retirement Policies in India
India has implemented several policies to encourage retirement savings and provide social security. Here are some key policies:
Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA): Governs pension schemes like NPS to ensure transparency and efficiency.
Senior Citizen Savings Scheme (SCSS): A government-backed savings scheme with a fixed interest rate, ideal for senior citizens.
Gratuity Act: Ensures employees receive a lump sum gratuity payment after completing a certain number of years with an employer.
These policies provide a strong framework to support individuals in planning their retirement.
Using a Retirement Calculator
A retirement calculator is a handy tool that helps you plan systematically. It allows you to:
Estimate the corpus required for retirement based on your expenses and lifestyle.
Calculate monthly savings needed to achieve your goal.
Factor in inflation, investment returns, and life expectancy.
Many online retirement calculators are available for free. By inputting details like your age, income, and savings, you can create a customized retirement plan.
Good Retirement Plans for Different Needs
For Early Starters
Opt for NPS or ULIPs, which offer long-term growth potential.
Start a SIP (Systematic Investment Plan) in equity mutual funds.
For Salaried Employees
Maximize contributions to EPF and consider opening a PPF account.
Explore employer-provided pension plans.
For Senior Citizens
Invest in SCSS or LIC’s annuity plans for stable income.
Maintain a mix of low-risk investments and liquid assets.
For the Self-Employed
Open an NPS account or invest in retirement-focused mutual funds.
Set aside a fixed percentage of income monthly towards retirement.
Tips to Strengthen Your Retirement Plan
Avoid Premature Withdrawals: Early withdrawals from retirement funds can derail your savings plan.
Plan for Medical Expenses: Consider purchasing health insurance to cover rising healthcare costs.
Minimize Debt: Pay off loans and avoid taking on new debts as retirement approaches.
Create an Emergency Fund: Maintain a separate fund to handle unexpected expenses without dipping into your retirement corpus.
Conclusion
Building your own retirement plan is a crucial step toward ensuring financial independence and a comfortable lifestyle in your golden years. With a range of retirement plans, policies, and tools like retirement calculators available in India, planning is simpler than ever. Start early, invest wisely, and regularly review your plan to secure your future. Your retirement should be a time to relax and enjoy, not worry about finances!
0 notes
Text
BJP’s 2024 Maharashtra Manifesto Highlights Plans for Economic Growth and Enhanced Social Welfare
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) has officially released its manifesto for the upcoming Maharashtra Assembly elections in 2024, laying out a series of ambitious promises aimed at benefiting the state’s grassroots population. Among the major proposals is a direct annual deposit of Rs 25,000 into the bank accounts of every woman in Maharashtra. In addition, under the Kisan Samman Yojana, farmers will see their annual support increased to Rs 15,000, up from the current Rs 12,000.
The manifesto also includes promises for senior citizens, with a proposed monthly pension of Rs 2,100, equating to an annual sum of approximately Rs 25,000. The BJP has also outlined plans to support education, with a monthly stipend of Rs 10,000 for one lakh students across the state. As part of its rural development focus, the BJP plans to improve infrastructure by building water roads in 45,000 villages, enhancing connectivity and access to resources.
Rural Development and Education Focus
For workers in rural areas, particularly Anganwadi and Asha workers, the BJP has committed to raising their monthly salary to Rs 15,000. Additionally, the Mahayuti government has already removed farmers’ agricultural electricity pump bills and plans to further reduce electricity costs by 30%, with an emphasis on promoting solar energy solutions.
The BJP’s vision extends to the future of Maharashtra’s economy. Within 100 days after the election, the party plans to unveil “Vision Maharashtra 2029,” a roadmap to transform the state into a trillion-dollar economy. Technology will play a crucial role in this vision, with plans to connect cities like Nagpur, Pune, and Nashik through initiatives like “Make in Maharashtra,” which will leverage artificial intelligence to boost industrial growth.
Economic Development and Technological Innovation
In terms of agricultural support, the BJP has promised a guaranteed price of Rs 6,000 per quintal for soybeans, alongside concessions on fertilizers through State and Goods and Services Tax (GST) reductions. To further empower women, the party proposes the creation of a Rs 1,000 crore revolving fund to support self-help groups, with the goal of turning 50 lakh women into “lakhpati didis” (millionaire women) over the next three years.
Additionally, free food grains will be provided to poor families through the Akshay Anna Yojana. The BJP has also pledged to introduce robotics and AI training programs for students in government schools, with initiatives like the Maharathi and Atal Tinkrig Lab schemes. A skill census will be conducted across Maharashtra to ensure skill development aligns with industry demands.
Empowering Women and Youth
A major highlight of the BJP’s manifesto is its plan to create one million entrepreneurs through the establishment of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Aspiration Centers in every district. Furthermore, the party aims to fully waive education and examination fees for students from economically disadvantaged categories, such as OBCs, SEBCs, ECs, EWS, and VJNT groups.
In health, the BJP has promised the issuance of Swami Vivekananda Youth Health Cards and annual health check-ups for youth and senior citizens alike. The manifesto also emphasizes the preservation of Maharashtra’s historic forts and the introduction of Aadhaar-enabled services in government hospitals to improve senior citizens’ welfare.
Social Welfare and Legal Protections
The BJP’s manifesto also outlines a strong stance on social issues, including the implementation of laws to prevent forced conversions and address fraudulent conversions. Additionally, the party has pledged to use modern technology to reduce human-wildlife conflicts, aiming to minimize fatalities caused by wild animals. The welfare measures span multiple communities, targeting women, youth, senior citizens, farmers, and marginalized groups.
This comprehensive manifesto reflects the BJP’s commitment to inclusive growth, focusing on key sectors such as agriculture, education, and technology, while ensuring that social justice and welfare remain central to the party’s policy agenda. As the party prepares for the 2024 Maharashtra Assembly elections, these promises serve as a framework for their vision of a prosperous and equitable Maharashtra.
source : newspatrolling.com
0 notes
Text
Atal Pension Yojana - Atal Pension Scheme : Tax Exemptions, Eligibility, And Contribution
Senior citizens require some sort of support from the government to spend their old age comfortably. While the government has started many pension schemes and saving schemes, Atal Pension Yojana (APY) is a leading saving scheme that helps the elderly get a fixed pension amount after the age of 60. Let us learn more details about this pension scheme of the government.
https://www.jaagrukbharat.com/atal-pension-yojana-apy-for-senior-citizens-in-india-details-eligibility-and-more-1404157

0 notes
Text
Padma Jaiswal IAS — Senior Administrative Secretary

Padma Jaiswal IAS is An Indian Administrative Service (IAS) officer of 2003 batch AGMUT cadre . She is the native of Chandigarh , completed her school & college education in Commerce and Management . She did her Masters degree in Business Administration from Panjab University Business School Chandigarh . She cleared the exam of University Grants Commission Research fellow, holds a degree of Company Secretary. She is a Marathon Participant and her interests are Reading books on social & psychological subjects, gardening, pottery , yoga .
Padma Jaiswal IAS is currently working as Secretary to Government to the state & Union Territories , is a civil servant who holds a key position in the Indian government and is responsible for implementing the government schemes, programs, projects during the allocation of responsible tasks assigned by the Government.
The role of Padma Jaiswal IAS is Policy formulation and implementation within the sphere & jurisdiction allotted to her at the federal and state levels. She contribute towards making final decisions on government matters. with the agreement of the minister concerned or the council of ministers.

Padma Jaiswal IAS is a highly respected officer and has held significant positions in the Indian government. IAS officers are protected by the Constitution of India from arbitrary action.
Padma Jaiswal IAS has held key positions in the Union Government, State governments, Public-sector Companies and other Statutory regulatory institutions and in Election Commission through deputation.
Padma Jaiswal IAS is also deployed to various government establishments such as, staff and line agencies, auxiliary bodies, public sector undertakings, regulatory bodies, statutory bodies and autonomous bodies like Secretary to the Commission for Protection of Child Rights Goa ,Commission of Backward Classes Goa.
Padma Jaiswal IAS is a part of the permanent bureaucracy of the nation which is the the executive of the Government of India.
Padma Jaiswal IAS while delivering the work as a DeputyCommissioner acted as an agent of the government in the field,as an intermediary between the public and the government. Padma Jaiswal IAS during her field posting as Deputy Commissioner performed the task of maintaining law and order in their assigned areas. To collect revenue and function as revenue court, handle the administration and daily proceedings of the government, manage government funds and supervise the expenditure of public funds, supervise the implementation of developmental schemes. act as an intermediary between the public and the government.

Padma Jaiswal IAS When posted in the district administration of a State Government, is primarily responsible for implementing the various projects and plans of the Central Government and the State Government as well as for maintaining the overall law and order situations in the district. They work as and preside over as court officials in various matters related to tax collection, general administration, civil administration, and criminal activities.
Padma Jaiswal IAS When posted with the various directorates, departments, and Ministries of a State or the Central Government, is responsible for the formulation of Government policies, formulating plans, planning various projects, schemes, and programs as well as implementation of the policies, plans, projects, and programs.
Padma Jaiswal IAS has vast & rich experience & expertise in the implementation of various projects and schemes like Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana, Atal Pension Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Gramin Awaas Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojna, etc..Beti Bachao-Beti Padhao, Swachh Bharat Mission, PM Mudra Yojna, Atal Pension Yojna, Smart City Scheme, and Make in India.AMRUT Strategy , Mission for Digital India , Gold Monetization Plan.
Padma Jaiswal IAS is often posted in leadership positions in various Government organizations such as municipal corporations, metropolitan and city development corporations, development bureaus, and even in Government-owned educational and healthcare organizations. Padma Jaiswal IAS played a significant role to ensure that the organizations function efficiently and achieve their goals.
Padma Jaiswal IAS while as Secretary to Government in Goa played a prominent role in implementing The Sagarmala project, a national program in India that aims to develop the country’s coastline and river network to boost economic growth. The project includes several initiatives in Goa, such as A new international cruise terminal , A dedicated berth for passenger and cruise vessels is being constructed at MPT. Nine coastal passenger jetties are being redeveloped. The state of Goa is included in the South Konkan-Maharashtra CEZ, which is mapped to the Mormugao major port.
Padma Jaiswal IAS during the tenure in Goa as Secretary to Government played a significant role in both The Sagarmala and Bharatmala projects which are the infrastructure development initiatives in India that aim to improve the country’s transportation and maritime sectors,to reduce logistics costs for domestic and export-import (EXIM) cargo. The program includes projects like port modernization, fishing harbor development, and coastal community skill enhancement.
Whereas Bharatmala is a program to construct highways, including new highways anbypasses.regions based on the following four pillars: Port Modernization & New Port Development. Port Connectivity Enhancement. Port-linked Industrialization.
The programme envisages development of Ring Roads / bypasses and elevated corridors to decongest the traffic passing through cities and enhance logistic efficiency; 28 cities have been identified for Ring Roads; 125 choke points and 66 congestion points have been identified for their improvements. Further, in order to reduce congestion on proposed Corridors, enhance logistic efficiency and reduce logistics costs of freight movements, 35 locations have been identified for development of Multimodal Logistics Parks.
Padma Jaiswal IAS while working as Deputy Commissioner in the Municipal Corporation of Delhi for Rohini , Civil Lines ,City Zone discharged the responsibilities associated with the Municipal Commissioner role for the overall administration of the municipality or municipal corporation in ensuring the efficient functioning of various municipal departments.
Urban Planning and Development: activities., to work towards the improvement of infrastructure, public amenities, and overall urban development within the municipality.
Padma Jaiswal IAS played a key role in local governance and work closely with elected representatives and municipal councils to implement policies and programs for the welfare of the residents.
Padma Jaiswal IAS performed the task to oversee the delivery of essential public services such as water supply, sanitation, waste management, and other civic amenities and to ensure that these services are provided efficiently to the residents . She did budgeting, financial planning, and resource allocation for municipal projects and services , to manage municipal finances effectively to meet the needs of the community.
Padma Jaiswal IAS ensured that the municipality adheres to all legal and regulatory requirements by participating & being involved in drafting and implementing local bylaws and policies.
Padma Jaiswal IAS has a rich experience in Community Engagement, She has performed the tasks of Engaging with the local community with empathy , sensitivity , resilience and high emotional intelligence.Padma Jaiswal IAS participated in community events, addressed public grievances, and worked towards building a positive relationship with residents,
Coordination with Other Agencies , collaborated with various government departments, agencies, and non-governmental organizations to implement development projects and address urban challenges.
Padma Jaiswal IAS while working as Secretary to Gov’t of UT of Puducherry INDIA for departments
Information technology,entrepreneurship, Planning ,Economic and Statistics, Stationery & printing ,EX servicemen welfare of Army ,Navy ,Airforce ,Freedom implemented the Digital India campaign which is a flagship programme launched by the Government of India to make its services available to citizens electronically via improved online infrastructure and by increasing Internet connectivity.The initiative includes plans to connect rural areas with high-speed internet networks. It consists of three core components: the development of secure and stable digital infrastructure, delivering government services digitally, and universal digital literacy.

The Digital India uses and supports other Government of India schemes, such as BharatNet, Make in India, Startup India, Standup India, industrial corridors, Bharatmala Sagarmala and Amrit Bharat Station Scheme, Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Some of the facilities which will be provided through this initiative are Bharat, digital locker, e-education, e-health, e-sign, e-shopping and the National Scholarship Portal. As part of Digital India, Indian Government planned to launch Botnet cleaning centers.
National e-Governance Plan aimed at bringing all the front-end government services online.
MyGov.in is a platform to share inputs and ideas on matters of policy and governance.It is a platform for citizen engagement in governance, through a “Discuss”, “Do” and “Disseminate” approach.
UMANG (Unified Mobile Application for New-age Governance) is a Government of India all-in-one single unified secure multi-channel multi-platform multi-lingual multi-service freeware mobile app for accessing over 1,200 central and state government services in multiple Indian languages over Android, iOS, Windows and USSD (feature phone) devices, including services such as AADHAAR, DigiLocker, Bharat Bill Payment System, PAN EPFO services, PMKVY services, AICTE, CBSE, tax and fee or utilities bills payments, education, job search, tax, business, health, agriculture, travel, Indian railway tickets bookings, birth certificates, e-District, e-Panchayat, police clearance, passport, other utility services from private companies and much more.
Padma Jaiswal IAS acted as Secretary coordination for BRICS & ASEAN summit held in Goa during her tenure in the year 2016. The FOREIGN OFFICIAL / GOVERNMENT VISITS PERFORMED are 15 days Visit to South Korea for Study tour at Seoul and Bushan during August 2012.7days visit to Manhattan New York city for study tour at Syracuse University for Public Policy during November 2019.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Income Tax Deductions List - FY 2023-24 (AY 2024-25) | Kotak Life
It is essential to understand the exemption in income tax to maximize your savings. While many are familiar with Section 80C, numerous other allowances can significantly reduce your tax liability. This extensive blog post takes you through various exemptions available under the Income Tax Act in a simple manner, making it easy to plan your taxes effectively.
What are Tax Deductions? Tax deductions are specific expenses or investments that reduce an individual’s taxable income, thus lowering the amount of income tax they are required to pay. The government allows these deductions to encourage individuals to save and invest, purchase insurance policies, and contribute to specific funds and schemes.
Income Tax Deductions on Investments Under Section 80C Investment instruments offer tax-saving opportunities under the provisions of the Income Tax Act of 1961. Every financial year, taxpayers can potentially reduce their taxable income by up to ₹1.5 lakh through deductions available under Section 80C.
Section 80C deductions apply to individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), allowing them to claim a maximum deduction of ₹1.5 lakh from their total income. As per the latest budget reforms, individuals adhering to the old tax regime can continue to benefit from deductions amounting to ₹1.5 lakhs under Section 80C.
It Is important to note that these deduction rules do not apply if taxpayers have opted for the new tax regime.
Income Tax Deductions List in India Understanding the various deductions available under the Income Tax Act is essential for taxpayers to optimize their tax planning strategies effectively. Here is the list of income tax deductions available in India:
Income Tax Deduction Under Section 80C Section 80C is one of the most popular tax-saving provisions in India. Under this section, taxpayers can claim deductions up to ₹1.5 lakhs in a financial year. Some eligible investments and expenditures under Section 80C include:
a. Employee Provident Fund (EPF)
b. Public Provident Fund (PPF)
c. Equity-Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS)
d. National Savings Certificate (NSC)
Income Tax Deduction Under Section 80CCC Under Section 80CCC of the Income Tax Act, individuals can claim annual deductions of up to ₹1.5 lakh for contributions to designated pension plans offered by term life insurance companies. However, this deduction is subject to the overall limit specified under Section 80C of the Act.
Income Tax Deduction Under Section 80CCD This section includes the contribution to the Atal Pension Yojana. It allows a contribution of up to 10% of the total salary of salaried employees and 20% of the gross income of non-salaried employees to the government-notified pension schemes. The contribution can be deducted from the taxable income under Section 80 CCD (1). If the employer also contributes to the scheme, the entire contribution amount can be claimed as a tax deduction under Section 80CCD (2).
It is important to remember that the complete deduction under Section 80C, Section 80CCC, and Section 80CCD (1) cannot exceed ₹15,00,000 in aggregate. However, the additional tax deduction amounting to ₹50,000 under Section 80CCD (1B) is above this limit.
0 notes