#April Woodson
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
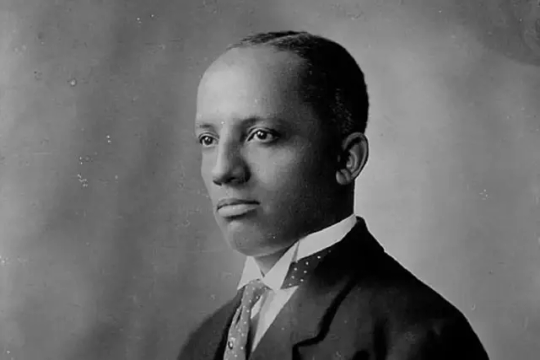
Carter Godwin Woodson (December 19, 1875 – April 3, 1950)[1] was an American historian, author, journalist, and the founder of the Association for the Study of African American Life and History (ASALH). He was one of the first scholars to study the history of the African diaspora, including African-American history. A founder of The Journal of Negro History in 1916, Woodson has been called the "father of black history." In February 1926, he launched the celebration of "Negro History Week," the precursor of Black History Month. Woodson was an important figure to the movement of Afrocentrism, due to his perspective of placing people of African descent at the center of the study of history and the human experience.
#Carter G. Woodson#black history month#melanin#black is beautiful#black is better#beautiful#love yours#black king#black kings
23 notes
·
View notes
Text

50 years ago, Julie Woodson PMOM, April 1973
225 notes
·
View notes
Text

Dr. Carter Godwin Woodson (December 19, 1875 – April 3, 1950) was born to poor, yet land-owning, former enslaved in New Canton, Virginia. He hired himself out as a farm and manual laborer, drove a garbage truck, worked in coalmines, and attended high school and college at Berea College, from which he earned a BL. He taught African American youth in West Virginia. He worked in the Philippines under the auspices of the US War Department. He traveled to Africa, Asia, and Europe and attended the Sorbonne. He received an MA in History, Romance languages, and Literature from the University of Chicago. While teaching, he earned his Ph.D. in History from Harvard University.
In 1915, he published his first book, The Education of the Negro Before 1861, and co-founded the Association for the Study of Negro Life and History. In 1916, he singlehandedly launched The Journal of Negro History, now The Journal of African American History. In 1918, he published A Century of Negro Migration and became the principal of Armstrong Manual Training School. He was the Dean of Howard University’s School of Liberal Arts and he served as a dean at West Virginia Collegiate Institute. In 1921, he published The History of the Negro Church and founded the Associated Publishers, Inc. He became active in Black organizations like the NAACP, the National Urban League, the Friends of Negro Freedom, and the Committee of 200.
He purchased a three-story, late-nineteenth-century Italianate-style row house in DC, that became his residence as well as the office for the Associated Publishers, Inc. and the national headquarters of the ASNLH. In 1926, he launched Negro History Week. He relied on African American communities throughout the country to maintain his organization’s activities. He created The Negro History Bulletin mainly for children and schoolteachers and throughout the 1930s and 1940s he spoke at countless elementary and high schools, Negro History Week events, and at the graduation ceremonies for many HBCUs. #africanhistory365 #africanexcellence #sigmapiphi #omegapsiphi
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
LEST WE FORGET... On this day in 1950
Carter G. Woodson, Ph.D.
Born: December 19, 1875, Virginia; Died: April 3, 1950 (aged 74) Washington, D.C. United States
Carter G. Woodson was born in 1875 in New Canton, Virginia. One of the first African Americans to receive a doctorate from Harvard, Woodson dedicated his career to the field of African-American history and lobbied extensively to establish Black History Month as a nationwide institution. He also wrote many historical works, including the 1933 book The Mis-Education of the Negro. He died in Washington, D.C., in 1950. Source: Biography.com

10 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Legend of Jesse James: An Outlaw's Tale from the Old West

The Wild West, with its untamed landscapes and massive-than-existence characters, has long captured the imaginations of human beings spherical the place. Among the myriad figures who rode thru this rugged terrain, one call stands proud for its aggregate of notoriety and romanticism Jesse James. An notorious outlaw, monetary institution robber, and educated bandit, Jesse James' existence is a tapestry of rebellion, crime, and the war in opposition to a changing America.
The Early Years: Roots of an Outlaw
Jesse Woodson James was born on September 5, 1847, in Clay County, Missouri. His circle of relatives, in the starting farmers, positioned themselves deeply tormented by the turbulence of the Civil War. The James circle of relatives were staunch supporters of the Confederacy, and this allegiance drastically inspired Jesse's childhood. As the conflict ravaged the kingdom, younger Jesse emerged as thrust right into a global of violence and guerilla warfare, becoming a member of pro-Confederate bushwhackers led by William Quantrill and "Bloody Bill" Anderson. These early testimonies in brutal, unusual fights laid the inspiration for his future life of crime.
The Birth of the James-Younger Gang
After the Civil War ended, the Reconstruction generation added massive discontent amongst former Confederate sympathizers, collectively with Jesse James and his older brother, Frank James. Disillusioned by the manner of the Confederacy's defeat and the cruel realities of Reconstruction, the brothers became criminals. Alongside different like-minded outlaws, they join the James-Younger Gang, which might turn out to be one of the most notorious crooks in American history.

The gang's first most important crime became the theft of the Clay County Savings Association in Liberty, Missouri, in February 1866. This heist is considered one of the first sunlight hours of armed financial institution robberies in the United States. The audacity and achievement of the robbery set the tone for a sequence of excessive-profile crimes, including educate robberies, stagecoach heists, and extra financial group jobs. The gang's sports activities quickly earned them infamy, in addition to the admiration of some who considered them as Robin Hood-like figures, resisting the encroaching forces of industrialization and authorities authority.
Jesse James: The Outlaw Legend
Jesse James has become the face of the institution, in element due to his formidable nature and in part due to the burgeoning media organization. Sensationalist newspapers and dime novels depicted him as a gallant outlaw, a folk hero in opposition to the set up order. These memories frequently exaggerated or romanticized his deeds, contributing to his legendary repute.
However, the reality of Jesse James' life ends up a protracted way much less glamorous. The robberies he led were violent and often lethal. The gang operated in a time while the burgeoning railroad organization and increasing banks have been seen as symbols of corruption and greed, making them objectives for those left in the back of with the aid of manner of monetary changes. Despite this, the collateral harm in their crimes regularly protected innocent bystanders, undermining any notion of noble banditry.

The Fall of Jesse James
As regulation enforcement intensified their efforts, the James-Younger Gang confronted growing strain. A botched robbery in Northfield, Minnesota, in 1876 brought approximately the size of numerous gang individuals and the loss of lifestyles of others. The surviving participants, which includes the James brothers, went into hiding.
Jesse James continued his crook sports, albeit more cautiously. He lived below various aliases, looking to carve out a semblance of ordinary life along with his spouse, Zee Mimms, and their youngsters. Despite those efforts, he should by no means completely escape his past.
The surrender got here on April three, 1882. Seeking the reward cash supplied via way of Missouri Governor Thomas T. Crittenden, Robert Ford, a member of Jesse's new gang, shot him in the back at the same time as he came to be dusting an image in his home in St. Joseph, Missouri. Jesse James has become 34 years vintage. Ford's betrayal marked the dramatic quit of certainly one of America's most famous outlaws.
Legacy and Cultural Impact
The existence and lack of lifestyles of Jesse James have left an indelible mark on the American way of life. He has been immortalized in endless books, films, songs, and even video games. The duality of his personality—each ruthless criminal and romanticized rebel—keeps captivating audiences.
Historians and enthusiasts nevertheless debate the actual nature of Jesse James. Was he a trifling bandit pushed via the use of greed and a penchant for violence, or became he an image of resistance against a swiftly converting America? The truth probably lies someplace in between, encapsulating the complexities of a man fashioned by means of using war, loss, and the relentless pursuit of his personal logo of justice.
Conclusion
Jesse James remains an image of the Wild West, embodying the lawlessness and rebellious spirit of an era long gone. His tale, filled with journey, crime, and a touch of myth, keeps resonating, reminding you . S.A. Time whilst the frontier emerged as a high-quality, untamed expanse, and outlaws like Jesse James roamed its wilds, hard the very cloth of American society.
#OutlawsTale#OldWest#WildWest#JesseJames#AmericanOutlaw#BankRobber#JamesYoungerGang#CivilWar#Bushwhackers#OutlawLegend#FolkHero#AmericanHistory#WesternOutlaws#InfamousCriminals#OldWestHistory#HistoricalFigures#WildWestLegends#AmericanFolklore#NotoriousOutlaw#WesternMythology#CulturalImpact#FrontierEra#LawlessWest
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Violence of Poetry
In the Q&A with Natalie Diaz called “Energy” by Jacqueline Woodson in the March/April 2020 Poets&Writers Magazine, Natalie Diaz said, “I have lived many lives. I have tried and failed at many things. I have won and lost much. I don’t know much, but I believe language lasts. In all its violence and tenderness, it lasts and lasts.” P&W Collage #22 – Violence She continues, “You and I are here…

View On WordPress
#April challenges#April PAD Challenge#blogging#Blogging A to Z Challenge#collage#dVerse#dVerse poets#homonyms#NaPoWriMo#National Poetry Month#new poem#poetry immersion#poets#prompts
0 notes
Audio
THE WOODSON MUSEUM screens Chronicles of Color Underground History April 11. https://audioboom.com/posts/8487457-the-woodson-museum-screens-chronicles-of-color-underground-history-april-11
#<Tag:0x00007f6831506248>#<Tag:0x00007f6814cf7820>#<Tag:0x00007f6814cf76e0>#<Tag:0x00007f6814cf75a0>#<Tag:0x00007f6814cf7460>#<Tag:0x00007f6814cf7320>
0 notes
Text
The Dirty Little Coward Who Shot Mr. Howard - Today In Southern History
3 April 1882 On this date in 1882… Bob Ford was the trigger man when he and his brother Charlie assassinated Jesse Woodson James in his home at St. Joseph, Missouri. The fame, money, and notoriety they sought never materialized and both died tragic deaths. Other Years: 1730 – In modern day Franklin, North Carolina, Sir Alexander Cuming performed a sham ceremony pronouncing Chief Moytoy as…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text

50 years ago, Julie Woodson PMOM April 1973
54 notes
·
View notes
Text

Robert L. Woodson Sr. (born April 8, 1937) in South Philadelphia is described as the “godfather” of the movement to empower community-based organizations to help themselves. He rose from liberal-oriented neighborhood civil rights activism in the 1960s to coordinating national community development programs in the 1970s.
He headed the National Urban League’s Administration of Justice Division, the Neighborhood Revitalization Project, and had a fellowship with the American Enterprise Institute. He founded the National Center for Neighborhood Enterprise. The name was shortened to Center for Neighborhood Enterprise and he serves as its president. The program have helped more than two thousand six hundred community groups in thirty-nine states. CNE’s approach reduced gang wars and increased opportunities for resident ownership of former public housing units.
Independent evaluations credited these initiatives with significant reductions in school absences, incidents of violence, and police arrests. He has advised the 104th Congress, the Pennsylvania Legislature, and the Wisconsin Assembly on poverty and welfare reform.
One of five children, determined not to join a gang, he dropped out of high school and joined the Air Force. He earned his GED and enrolled in Cheyney State University, where he graduated with a BS in Mathematics. He earned an MSW from the University of Pennsylvania and holds honorary doctorates from Colorado Christian University and the University of Cincinnati. He has received a John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur “Genius” Fellowship and the Lynde and Harry Bradley Foundation Prize. He was awarded the Presidential Citizens Medal.
He has authored hundreds of articles on poverty and empowerment as well as several books, including A Summons to Life: Mediating Structures and the Prevention of Youth Crime. He sits on the boards of the American Association of Enterprise Zones, the Commission on National and Community Service, and the Commonwealth Foundation. He married Ellen (1977) and they have four children. #africanhistory365 #africanexcellence
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
American Songbook 2024 Spotlights Change-Makers, Embracing Individuality Through Performance
Highlights Include: Indigo Girls, John Holiday, Justin Vivian Bond, and Nona Hendryx Celebration of Musical Theater with RENT by Deaf Broadway and Live Album Recording of Off-Broadway’s Running Man Tribute to Poet Phillis Wheatley Peters with AFROPUNK Free Performances from Jeremy Dutcher, Crys Matthews, Author Jacqueline Woodson and more March 12 – April 12, 2024 Lincoln Center for the…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
History
December 19, 1732 - Benjamin Franklin first published Poor Richard's Almanac containing weather predictions, humor, proverbs and epigrams, eventually selling nearly 10,000 copies per year.
December 19, 1946 - War broke out in French Indochina as Ho Chi Minh attacked the French seeking to oust them from Vietnam. This marked the beginning of a thirty-year conflict which eventually led to heavy U.S. involvement and ended with a Communist victory in April 1975 after U.S. withdrawal from South Vietnam.
December 19, 1998 - The House of Representatives impeached President Bill Clinton, approving two out of four Articles of Impeachment, charging Clinton with lying under oath to a federal grand jury and obstructing justice.
Birthday - British explorer William Parry (1790-1855) was born in Bath, England. He conducted Arctic expeditions and made three attempts to find a Northwest Passage.
Birthday - Historian
Carter Woodson (1875-1950) was born in New Canton, Virginia. He introduced black studies to American colleges and universities. His works included; The Negro in Our History and The Education of the Negro Prior to 1861.
0 notes
Text

Before the Ever After is a poignant and personal verse novel, told from the point of view of a young man whose father is a former professional football player. Set at the turn of the millennium, when many football players were experiencing memory loss, aggression, migraines, confusion, and other symptoms without a clearly defined cause, Ever After follows Zachariah Junior (nicknamed ZJ) as he watches his father slowly lose himself to a disease that no one wants to suggest might be linked to his former career.
Genre: Fiction, Verse Novel (Coretta Scott King Author Award)
Target Age Group:
Middle Grade – Grades 5-9
Justification:
In order to fulfil the CSK Author Award category of my project, I sought out a list of winners through the past several years; Ever After was the winner in 2021 and caught my attention because of the subject matter. Loss of a parent to mental illness, specifically dementia and other diseases which affect memory, is a very personal topic to me. I was pleasantly surprised to find that Ever After was a verse novel—after I’d already borrowed it from my library—but I chose to evaluate it for the CSK category.
Evaluation:
Every character is unique, given details to make them stand out from one another in both broad ways and subtler details. One of ZJ’s friends, Ollie, is an orphan found abandoned outside of a church; Darry loves to dance; Daniel is a risk-taker. Characters are also defined with smaller details, like ZJ’s mother, who “only eats candy bars/when she’s worrying,” because “Chocolate[…]helps her think.” (p. 88) The theme of music is woven throughout the novel as ZJ writes songs, for and about his father, and into the format of the novel itself—many of the poems are songs that ZJ writes. The pacing of Ever After is both fast and slow—looming, impending, a disaster in slow-motion. The narrative begins in 1999 and continues through the spring of 2001; two years of Zachariah’s slow unraveling, happening too quickly to stop and dragging on agonizingly slow. It reflects very accurately the feeling of watching a parent’s decline. The mood is sorrowful, hopeful, nostalgic; ZJ always hopes that there’s a way for his father to get better, and is always remembering better days. My mother passed away in April of 2020, following years of mental decline; she suffered from Lewy body dementia, which was only diagnosed after I went to college, but she first started exhibiting symptoms when I was eleven or twelve. Multiple times during this book, I had to stop reading, because it brought too much back—ZJ’s dad not remembering his name, ZJ’s confusion and feeling of being lost, the quiet fearful helplessness of not knowing what’s wrong. Ever After is a beautiful book, and I recommend it wholeheartedly, but I don’t think I can ever read it again.
References:
2021 Coretta Scott King Book Award winners and honorees. Brilliant Books. (2021, August 5). https://www.brilliant-books.net/2021-coretta-scott-king-book-award-winners-and-honorees Penguin Young Readers. (n.d.). Before the ever after by Jacqueline Woodson: 9780399545443: Penguinrandomhouse.com: Books. PenguinRandomhouse.com. https://www.penguinrandomhouse.com/books/535796/before-the-ever-after-by-jacqueline-woodson/ Woodson, J. (2020). Before the Ever After. Thorndike Press, a part of Gale, a Cengage Company.
0 notes





