#Anterior cervical discectomy and plating
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Understanding Cervical Bone Fracture: Causes, Treatments, and Advanced Implant Solutions by Bonetech Medisys
Cervical bone fractures, often referred to as neck fractures, are serious injuries that require prompt medical attention. These fractures occur in the cervical spine, which consists of seven vertebrae (C1 to C7) at the top of the spinal column. Here, we delve into the causes, treatment options, and advanced implant solutions offered by Bonetech Medisys, a leader in orthopedic innovations.
Causes of Cervical Bone Fractures Cervical fractures are typically caused by high-energy trauma or degenerative conditions. Common causes include:
Trauma from Accidents:Motor vehicle collisions are a leading cause of cervical spine injuries.Falls, especially in elderly individuals or athletes, can lead to fractures. Sports Injuries:Contact sports such as rugby, football, or wrestling may result in cervical fractures due to sudden, forceful impacts. Osteoporosis:Weakening of bones due to age or disease makes individuals more susceptible to fractures, even with minor trauma. Pathological Conditions:Conditions like bone cancer or infections can weaken the cervical vertebrae, leading to fractures.
Symptoms of Cervical Fractures Severe neck pain, especially after an accident or trauma Limited range of motion in the neck Swelling and tenderness around the injured area Neurological symptoms such as tingling, numbness, or paralysis in limbs (in severe cases)
Treatment Options The treatment of cervical bone fractures depends on the severity and type of the injury. Options range from conservative management to advanced surgical interventions:
Conservative Treatment:Mild fractures without spinal cord involvement may be treated with immobilization using a cervical collar or brace.Physical therapy is essential for restoring mobility and strength after healing. Surgical Treatment:Severe fractures often require surgery to stabilize the cervical spine and prevent further complications. Techniques include:Spinal Fusion: Joining two or more vertebrae to eliminate movement at the fracture site.Internal Fixation: Using plates, screws, or rods to stabilize the fracture.
Advanced Implant Solutions by Bonetech Medisys Bonetech Medisys offers an array of advanced cervical spine implants, both for anterior and posterior applications. These state-of-the-art products are designed to address various complexities of cervical fractures, ensuring optimal stability, patient safety, and effective recovery.
Anterior Implant Solutions SYMPLEX II Anterior Cervical PlateA highly durable and anatomically contoured plate for stabilizing cervical fractures.Ensures secure fixation with advanced locking mechanisms. AVIATION - Peek Cervical CageMade of biocompatible PEEK material, promoting bone fusion and maintaining disc height.Lightweight yet robust, suitable for anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) procedures. DUO - Anterior Cervical CageCombines superior fusion capabilities with ease of implantation.Designed for versatile application in multi-level cervical procedures. AVIATION-P Cervical Cage with PlateA combined system with an integrated plate for enhanced stability.Reduces the need for additional hardware, simplifying surgical procedures. PRIME PLUS-Expandable Jack Cage with PlateAn innovative jack cage that allows controlled expansion to restore spinal alignment.Integrated with a plate for immediate stabilization. C-Xpan™ Cervical Interbody Expandable Peek CageA cutting-edge expandable cage for precise restoration of disc height and alignment.Crafted with PEEK material to facilitate fusion and reduce postoperative complications.
Posterior Implant Solutions NOVA PLUS™ - Posterior Cervical ScrewOffers high pull-out strength and stability for posterior cervical fixation.Engineered for ease of use and accurate placement. NOVA™ Posterior Cervical Screw SystemA comprehensive system for multi-level fixation, ensuring optimal load distribution.Features advanced screw designs for enhanced grip in cortical and cancellous bone. NOVA™ Posterior Cervical C1-C2 SpacerDesigned for challenging upper cervical procedures.Provides stability and promotes fusion in the atlantoaxial region. NOVA™ Adjustable Occipital Fixation SystemA modular system designed to address occipital-cervical fusion challenges.Ensures precise alignment and stabilization of the occipital region.
Why Choose Bonetech Medisys? With a strong focus on research and development, Bonetech Medisys delivers products that align with the latest advancements in orthopedic care. Their implants undergo rigorous testing to ensure reliability and safety. The company's commitment to innovation, coupled with its global presence, makes it a trusted name among healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Conclusion Bonetech Medisys’ comprehensive portfolio of anterior and posterior cervical implants empowers surgeons with the tools needed to handle complex cervical spine injuries. Whether addressing a single-level fracture or a multi-level stabilization challenge, these advanced implants offer solutions tailored to diverse surgical needs, ensuring improved outcomes for patients worldwide.
For more information on Bonetech Medisys and their orthopedic innovations, visit their website or contact their team of experts.
#bonetechmedisys hashtag#spineimplants hashtag#cervicalimplants hashtag#Anteriorimplants hashtag#Posteriorimplants hashtag#orthopedicimplants hashtag#surgeon hashtag#spinespecialist
1 note
·
View note
Text
CDF Surgery in Mumbai: Expert Care at Synapse Spine

Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) surgery is a highly effective procedure for treating conditions such as cervical herniated discs, nerve compression, and degenerative disc disease. For patients suffering from chronic neck pain, tingling, or weakness in the arms, ACDF surgery in Mumbai offers a solution to restore quality of life. At Synapse Spine, we specialize in providing expert surgical care for spine-related issues, including ACDF surgery, under the guidance of Dr. Abhishek Kulkarni, a renowned spine surgeon in Mumbai.
What is ACDF Surgery?
ACDF surgery involves the removal of a damaged disc from the cervical spine (neck region) and replacing it with a bone graft or implant. This procedure is typically performed through a small incision at the front of the neck, allowing the surgeon to remove the disc with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues. After the disc is removed, the vertebrae are fused together to stabilize the spine.
Minimally invasive technique for quicker recovery
Relieves nerve compression and chronic neck pain
Why Choose ACDF Surgery?
ACDF surgery is considered the gold standard for patients with severe cervical spine issues. Whether it's degenerative disc disease, herniated discs, or nerve compression, ACDF surgery in Mumbai offers a safe and effective treatment option. At Synapse Spine, we take a personalized approach to ensure each patient receives the best care tailored to their specific condition.
High success rates in pain relief and mobility restoration
Suitable for patients with cervical disc herniation and nerve compression
Benefits of ACDF Surgery in Mumbai
Choosing ACDF surgery in Mumbai at Synapse Spine provides numerous benefits. Dr. Abhishek Kulkarni and his team ensure that each procedure is performed with precision and care. The surgery not only alleviates pain but also improves spinal stability, which is crucial for long-term recovery.
Pain relief from chronic neck issues
Increased mobility and improved quality of life
Shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times
What to Expect During ACDF Surgery?
During the procedure, Dr. Abhishek Kulkarni will make a small incision in the front of the neck to access the spine. The damaged disc is removed, and a bone graft is inserted to promote fusion between the vertebrae. A titanium plate may also be used to provide additional support while the bones heal.
Performed under general anesthesia
Minimally invasive approach for reduced scarring and faster healing
Recovery After ACDF Surgery
Recovery from ACDF surgery generally takes a few weeks to a couple of months, depending on the patient’s overall health. At Synapse Spine, we provide comprehensive post-operative care, including physical therapy, to help you regain strength and mobility. Dr. Abhishek Kulkarni will work closely with you to monitor your progress and ensure a smooth recovery.
Post-surgery physical therapy for quicker recovery
Regular follow-up visits to track healing and fusion progress
Why Choose Synapse Spine for ACDF Surgery?
At Synapse Spine, we prioritize patient care and safety. With Dr. Abhishek Kulkarni's expertise in spine surgery and a state-of-the-art facility, we are dedicated to delivering the best outcomes for our patients. Our team is highly experienced in ACDF surgery in Mumbai, providing both surgical excellence and compassionate care.
Expert surgeon with years of experience in spine surgeries
Cutting-edge technology for accurate diagnosis and treatment
Contact Us for ACDF Surgery in Mumbai
If you're suffering from chronic neck pain or cervical spine issues, ACDF surgery in Mumbai at Synapse Spine can offer lasting relief. Contact us today to schedule a consultation with Dr. Abhishek Kulkarni and start your journey towards a pain-free life.
Address:Eye & Neuro Clinic, 291, Jyoti Avenue, Next to Sherepunjab Chemist, Opposite Titanic Bunglow, near Tolani College, Andheri E, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400093 Phone: +91 93726 71858 | +91 93211 24611 Email: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
ACDF: Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion

What is ACDF Surgery?
ACDF, or Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion, is a surgical procedure performed on the neck to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots caused by a damaged disc. It's often used to treat:
Cervical Disc Herniation
This occurs when the inner gel-like material of a disc bulges out and puts pressure on the nerve.
Cervical Stenosis
This is a narrowing of the spinal canal that compresses the spinal cord or nerve roots.
Myelopathy
This is damage to the spinal cord caused by compression.
Radiculopathy
This is pain, weakness, or numbness caused by compression of a nerve root.
Synopsis
Who needs an ACDF?
What all happens in ACDF?
Benefits of ACDF
Risks Of ACDF
Who needs an ACDF?
ACDF surgery is only needed in specific situations where other less invasive treatments haven't provided sufficient relief or where the damage to the discs and nerves is severe enough to warrant surgery. Here are some key reasons why an
ACDF might be considered:
Persistent and Debilitating Pain
If you're experiencing severe neck pain that radiates down to your arm or hand, and hasn't been effectively managed with conservative measures like physical therapy, medication, or injections, ACDF can offer significant pain relief by decompressing the affected nerve.
Neurological Symptoms
When cervical disc herniation or stenosis compresses the nerve roots or spinal cord, it can lead to neurological symptoms like numbness, weakness, tingling, or difficulty controlling bowel or bladder function. If these symptoms are severe and impacting your daily life, ACDF can offer a solution by relieving the pressure and potentially reversing the nerve damage.
Myelopathy
Myelopathy, which is damage to the spinal cord itself, is a serious condition that can worsen without intervention. ACDF can decompress the spinal cord and prevent further damage if other treatments haven't been successful.
Instability of the Cervical Spine
In some cases, severe disc damage or trauma can lead to instability of the vertebrae in the neck. ACDF can provide stabilization by fusing the affected vertebrae, reducing pain and preventing further deterioration.
Failure of other Treatments
If conservative treatments like physical therapy and medication haven't provided adequate relief after a reasonable period, and the symptoms are significantly impacting your quality of life, ACDF might be considered as a next step.
It's important to note that ACDF is a major surgery with potential risks and complications, so it's always recommended to discuss all options and risks thoroughly with a certified neurosurgeon before making any major decisions. Manipal Hospitals Delhi has the best neurosurgeon and neurologist to help you find the correct diagnosis for your neurological symptoms, and find the apt treatment plans for the same as well.
What all happens in ACDF?
The surgeon makes an incision in front of the neck to access the affected disc.
Removing the damaged disc (discectomy) under a microscope
Inserting a graft into the empty disc space to promote bone growth and fusion of the two adjacent vertebrae.
Placing a metal plate and screws (if needed) to stabilise the fusion while it heals.
Benefits of ACDF
Effective in relieving pain, weakness, numbness, and tingling in the arm or hand.
Long-term pain relief for most patients.
Restores the normal anatomical height and curvature of cervical spine.
Minimally invasive with a shorter recovery time than some other spine surgeries.
Patients are typically discharged after 2 days of surgery in most cases.
Early discharge and quick recovery leading to early start of normal lifestyle routine and work.
Book an appointment now at the best neursurgery hospital in Delhi to get the finest treatment.
Risks Of ACDF
In safe hands and with the latest technological advances the risks involved are very minimal, however, one should be aware of them before planning surgery. Some of them are:
Difficulty swallowing due to temporary irritation of nerves- resolves within a day or two.
Infection.
Injury to blood vessels or nerves.
Recurrence of symptoms.
Before considering ACDF surgery, it's important to discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor and explore other treatment options, such as physical therapy, medication, or injections. Manipal Hospitals Delhi believes in holistic healing and encourages patients to consult with their doctors and go for regular health check ups to help diagnose conditions in the early phase and find correct treatment in a timely manner.
0 notes
Text
types of cervical spine surgery
There are several types of cervical spine surgery, including:
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF): This surgery involves removing a damaged or herniated disc in the cervical spine from the front of the neck, then fusing the adjacent vertebrae together to stabilize the spine.
Posterior cervical laminectomy: In this procedure, the bony arches of the vertebrae, known as the lamina, are removed from the back of the neck to relieve pressure on the spinal cord and nerves.
Artificial disc replacement: This surgery involves replacing a damaged or herniated disc with an artificial disc to restore normal function and mobility.
Spinal fusion: This surgery is used to fuse two or more vertebrae together using bone grafts or metal plates and screws to stabilize the spine.
Foraminotomy: This procedure involves removing part of the bone or tissue that is obstructing the nerve root to alleviate pressure on the nerve and reduce pain.
Corpectomy: This surgery involves removing the entire vertebral body, including the disc and adjacent vertebral bones, to treat conditions such as tumors or fractures.
Cervical laminoplasty: This procedure is used to relieve pressure on the spinal cord by creating more space within the spinal canal.
The type of cervical spine surgery recommended will depend on the underlying condition and the individual patient's needs and circumstances. It is important to discuss the options with a qualified medical professional to determine the best course of treatment.
0 notes
Text
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion is the commonest used surgical procedure for the treatment of symptomatic cervical herniated disc which is not responding to medical management.
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion is a surgery performed for a herniated intervertebral disc in cervical spine. This surgery remains the most widely done and preferred procedure for symptomatic cervical disc herniations. Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion(short form ACDF) is the commonest procedure performed for herniated cervical discs. Anterior refers to front, as the surgery is…

View On WordPress
#ACDF#acdf surgery cost in india#Anterior cervical discectomy#Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion#Anterior cervical discectomy and plating#best hospital for cervical spine surgery in india#Best Neurosurgeon in Gurugram#Best Neurosurgeon in India#Cervical disc surgery#Cervical discectomy cost in India#cervical myelopathy surgery cost in india#Cervical radiculopathy discectomy#cervical surgery cost in india#Discectomy and fusion#Endoscopic spine surgeon in Gurugram
0 notes
Text
Clerkship thread
Day 1 - Ortho
Got to assist Dr. Bundoc for a cervical spine surgery (Anterior C4 Vertebrectomy, Anterior Column Reconstruction C5-C6, Interbody Discectomy and Fusion, Anterior Cervical Plating)!!! <3 It was SOO COOOOLL <3 Pinaka-idol spine surgeon ever since LU1!
Met buddy Ria today and she gave me a very pretty necklace as grad gift T_T waah my heart is fuuulll!
Also got to have 7 patients today as SIC :) Super upgrade na po tayo ;)
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is three level cervical fusion surgery?

What is three level cervical fusion surgery? Cervical fusion surgery joins more than one spinal bone by employing screws, bolts and plates, corrects deformities and removes discs which are replaced with bone graft or spacer. Three level fusion surgery replaces three discs with hardware to stabilize the neck. Indications of three level cervical fusion Three level surgery is performed in instances like tumors, spinal bone fractures, osteomyelitis infection, stenosis, trauma, spinal cord injury, scoliosis and severe arm pain accompanied by numbness and tingling. Types of three level cervical fusion Three level fusion surgery may be performed in anterior or posterior region and is referred to as Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion or Posterior Cervical Fusion respectively. The anterior approach provides direct visualization of cervical discs and access to the entire cervical spine and is preferred owing to its uncomplicated pathway. It also has lesser incision compared to the posterior approach. Types of bone grafting in cervical fusion Surgeons may take one’s own bone cells from the hip, known as autograft, since it has a high rate of fusion, though it causes more pain in the hip region. Bone obtained from a donor is known as allograft, which does not have bone growing cells and yet averts harvest of hip bone. Bone graft substitute is made from plastic, ceramic and is packed with shavings of live bone tissues. Post cervical fusion surgery After surgery, range of motion depends on the number of bones fused where single level fusion has better mobility. Post surgery, one must avoid lifting, pushing and pulling of heavy objects and keep the spine in neutral position besides maintaining good posture. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
The Anterior Cervical Plate is used to remove a herniated or damaged disc. To treat neck and arm discomfort, ACDF surgery replaces damaged discs with bone grafts. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion is a surgical treatment that involves removing a damaged cervical spinal disc and fusing the affected bone.
0 notes
Text
Adjacent Segment Disease after Anterior Cervical Inter body Fusion using Conventional Plate versus Zero-Profile Implant - A Preliminary Report

Abstract
Background: Anterior cervical discectomy and interbody fusion is a common surgical method used for treatment of single or 2 level cervical lesion. Recently, zero-profile implant, which lessened irritation of adjacent structures by preventing the contact with them, was design for anterior cervical fusion, and was assumed that it would reduce the occurrence of adjacent segment disease. Thus, authors compared the occurrence of adjacent segment disease after using conventional plate or zero-profile for anterior cervical interbody fusion.
Methods: 48 consecutive cases that underwent single-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion for lesions of cervical spine that did not respond to nonsurgical treatment and were able to follow up for at least 1 year were included in this study. Clinical and radiologic features of 25 cases (group A) that used conventional plate from April 2007 to January 2011 and 23 cases (group B) that used zero-profile plate from March 2011 to February 2014 were retrospectively compared.
Results: Adjacent segment degeneration was present in 10 cases in group A and 6 cases in group B. The occurrence of the degeneration was statistically insignificant. In aspect of grade of ossification, group A consisted of 6 cases of grade 1, 2 cases of grade 2, and 1 case of grade 3 while group B consisted of 5 cases of grade 1, 1 case of grade 2, and no case of grade 3.
Conclusion: It is considered rather than the insult to adjacent structures by implants, natural degeneration or increased loading to the adjacent segment after interbody fusion are more important factors for occurrence of adjacent segment degeneration.
Keywords: Adjacent segment disease; Anterior cervical inter body fusion; Zero-profile implant
Introduction
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion is a widely used technique for cervical spine disease and trauma such as herniation of intervertebral disc, cervical spondylotic radiculopathy, cervical fracture, and etc [1]. The technique requires relatively short operation time, has less blood loss and complication, shows immediate symptom relief, and high union rate of over 90% compared to lumbar spine [2]. Though the technique has become popular due to such merits, there are a few possible complications at risk, for example, dysphagia and adjacent segment disease. Adjacent segment disease refers to a radiologic degeneration on the segment adjacent to previous arthrodesis with accompanied symptom due to such degeneration and adjacent segment degeneration refers to only radiologic degeneration. However, the correlation between the degree of degeneration and occurrence of symptom due to degeneration is not well established [3,4]. According to Hilibrand et al, the annual occurrence of adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical discectomy and interbody fusion is about 2.5% [3]. In the other hand, some clinical and mechanical studies reveal that there are no increased motion or pressure of adjacent level after interbody fusion [5,6].
Another study showed that cases with postoperative kyphotic angulation are more likely to have adjacent segment disease [7,8]. As indicative above, numerous studies reported that various factors influence the occurrence of adjacent segment disease and results whether it is brought about due to trauma by surgery or natural history is inconsistent. Based on studies that concluded that adjacent segment degeneration was more frequently occurred and accelerated by insult of tissue due to surgery [9-11], authors investigated the occurrence of adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion using zero-profile plate and conventional plate hypothesizing that group using zero-profile plate will show lower occurrence.
Materials and Methods
The study was conducted after the approval of the institutional review board (IRB file no. 2015-08-015). All patients signed consent that they will be enrolled in clinical study. Medical records and radiologic evaluation of 48 consecutive cases that underwent a single level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion due to degenerative change from April 2007 to February 2014 were retrospectively analyzed. All cases had been followed up for at least 12 months clinically and radiologically. Surgery was performed for cases refractory to adequate nonsurgical treatment of at least 6 weeks with a diagnosis of single level cervical radiculopathy or myeloradiculopathy with subtle myelopathy symptoms such as mild numbness on the hand. Patients’ symptoms were well correlated with the conventional radiograph and magnetic resonance images with evident stenosis (Figure 1). The senior author (JS Ahn) performed every surgery and Smith-Robinson technique was used for surgical approach for all patients.
Before the introduction of zero-profile plate on February 2011, a conventional plate (Vectra-T plate, Synthes, Switzerland) was used and ever since, zero-profile plate (Zero-P plate, Synthes, Switzerland) was used for degeneration cases (Figure 2). For postoperative care, soft cervical collar (Philadelphia brace) was applied for 1 day and then all neck motion was allowed without brace. Conventional radiograph was performed on the final follow up for each case (Figure 3). To eliminate the difference of loading due to difference numbers of fused segment, multi segment fusion cases were excluded from the study. In addition, since compromised soft tissues such as anterior longitudinal ligament and bony structures could accelerate degeneration of the adjacent segment, trauma or tumor cases were also excluded [11,12]. Also, cases without radiological follow up at least 12 months after surgery were not included.
Clinical factors such as sex, age, alcohol, smoking, and index level of every patient were checked. The preoperative and postoperative curvature of the index level was measured using simple radiograph. Diagnosis of adjacent segment degeneration and classification of ossification was made according to Katsuura et al. and Nassr et al. [8,9]. Patient was diagnosed as adjacent segment degeneration if at least 1 of the following findings was present:
Evident intervertebral disc space narrowing
Newly developed instability on flexion-extension radiographs
Vertebral anterior or posterior spur formation. Cases were also were classified by the degree of ossification as following:
Grade 0: no ossification
Grade 1: extending across less than 50% of adjacent disc space
Grade 2: extending across more than 50% of adjacent disc space
Grade 3: complete bridging of adjacent disc space [13].
For evaluate the clinical judgment after surgery, Odom’s criteria along with symptom and sign of each patient were investigated. Odom’s criteria are as follows:
Excellent: all preoperative symptoms relieved; abnormal findings improved
Good: minimal persistence of preoperative symptoms; abnormal findings unchanged or improved
Fair: definite relief of some preoperative symptoms; other symptoms unchanged or slightly improved
Poor: symptoms and signs unchanged or exacerbated.
1 for Excellent,
2 for Good,
3 for Fair, and
4 for Poor
As a result, group A showed 1.96±0.73 points while group B showed 1.65±0.88 points which showed no significant difference between 2 groups (p=0.092). Authors emphasized to keep
For the comparison of diverse clinical factors between two groups, the Mann-Whitney U and chi-squared tests were used. Various pre and postoperative findings were analyzed using the Mann-Whitney U-test, Chi-square test, and Fisher’s exact test. All statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS analytical software version 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, Ill., USA). In all analyses differences were considered significant at a level of p < 0.05.
Results
Total of 48 cases were included in the study. 25 cases used conventional plate with cage insertion (group A) and 23 cases used zero-profile plate (group B) for cervical interbody fusion. The demographic data of both groups are descripted on (Table 1). All factors mentioned above showed no statistically significant difference between the 2 groups. Cases’ clinical improvements were graded according to Odom’s criteria:
lordosis of the index level, and as a result, postoperatively, sagittal angle was maintained as a lordotic curve (group A: 5.19±6.00, group B: 5.38±4.96) (+; lordosis, -; kyphosis). Adjacent segment degeneration was present in 10 cases in group A and 6 cases in group B. Specifically, spur formation, disc space narrowing, and instability was found in 9 cases, 2 cases, and 1 case in group A and 6 cases, 0 case, and 2 cases in group B.
The occurrence of the degeneration was statistically insignificant. (p=0.307) In aspect of grade of ossification, group A consisted of 6 cases of grade 1, 2 cases of grade 2, and 1 case of grade 3 while group B consisted of 5 cases of grade 1, 1 case of grade 2, and no case of grade 3. There were 1 cases of each group that had new radiculopathic symptom (tingling sensation) apart from preoperative symptoms, however, both cases were able to be managed non-surgically (Tables 2 & 3). Each clinical and radiological factor (age, sex, smoking, alcohol drinking, index level, and preoperative and postoperative sagittal angle of the index level) were statistically analyzed for influence to the adjacent segment degeneration. As a result, cases that have smoked and regular alcohol drinker showed a statistically significantly higher occurrence rate of adjacent segment degeneration.
Discussion
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion is a common procedure for single or two level cervical spondylotic changes or disc disease. Rarely, however, complications of the technique such as postoperative dysphagia, hematoma, recurrent laryngeal nerve, and adjacent segment disease could occur. Specifically, 58.4% of the patients that underwent anterior cervical discectomy and fusion suffered from symptoms related to swallowing difficulty immediately after surgery [2] and among them, 6.6% had the symptom continued until 2 years follow up, [14,15] and adjacent segment disease is reported that the annual occurrence is about 3% [6]. It is assumed that anterior cervical plating bring about dysphagia and adjacent segment disease [16].
However, even with such evidence, most of the anterior cervical discectomy cases are augmented with plating rather than using cage alone since plate augmentation shows higher union rate and preservation of intervertebral disc height [6,17,18]. Thus, to minimize complications while maintain firm fixation with plate, recently a zero-profile plate has been developed and promising results, especially in aspect of dysphagia, are being reported [19-22]. Though the causes of adjacent segment disease is multivariate, however, the issue is that whether it is a result of natural course of degeneration or due to insult after interbody fusion of the cervical spine. Some reports are conflicting with the theory of accelerated adjacent segment degeneration after fusion surgery.
Biomechanical studies by Reitman et al. [5] reported no increased motion of cephalad segment after anterior cervical interbody fusion, and Fuller et al. [23] found that sagittal rotation of the immediately adjacent segment of arthrodesis was not statistically significantly increased. However, there are other studies show contrary results with accelerated degeneration and motion of the adjacent segment after fusion, for example, Eck et al. [24] reported significantly higher intervertebral pressure and motion of the segments adjacent to arthrodesis. Since Park et al. [10] reported that adjacent segment degeneration is prone to occur when the distance of plate end and adjacent disc is less than 5mm and Mahrling [25] reported accelerated degenerative change after wider resection of anterior longitudinal ligament, zero-profile plate was considered to minimize such problems which in order will decrease the occurrence of adjacent segment disease.
However, against to our expectation, according to the result of our study, the difference of occurrence rate between cases using conventional plate and zero-profile plate was statistically insignificant. In view of such result, it is considered that rather than insult to the adjacent segment caused by plating, increased loading to the adjacent segment due to interbody fusion is the major factor for degeneration. In addition, since there are some reports of accelerated degeneration after postoperative kyphotic sagittal alignment [8,26], postoperative sagittal balance should be carefully considered.
There are some limitations of this study, which are small numbers of cases and the results are obtained after a shortterm follow up. Since there is chance of development of adjacent segment problems in longer follow up, which is necessary to make a final conclusion of our study? In addition, as Cherubino et al. [27] described, the degree of degeneration and clinical symptom showed no correlation thus, factors influencing clinical symptoms of adjacent segment was not established. Further evaluation to investigate the factors that cause symptoms due to adjacent segment degeneration is necessary. However, the strength of our study is that, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study comparing the zero-profile plate with conventional plate in aspect of adjacent segment disease.
Contrary to our expectation, surgery using both implants showed similar results in aspect of adjacent segment degeneration. It is considered rather than the insult to adjacent structures by implants, other factors such as natural degeneration or increased loading to the adjacent segment after interbody fusion might be more important factors for occurrence of adjacent segment degeneration. In short-term after surgery, adjacent segment disease is not a frequently complication, however, longer term follow up is necessary since degeneration of adjacent segment is accelerated.
To Know More About Orthopedics and Rheumatology Open Access Journal Please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/oroaj/index.php For more Open Access Journals in Juniper Publishers please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/oroaj/index.php
For more about�� Juniper Publishers Please click on: https://juniperpublishers0.wixsite.com/juniperpublishers
0 notes
Text
Anterior Cervical Discectomy And Fusion- Dr. Anil Kesani -MySpineMD
Discectomy actually signifies "removing the plate." A discectomy can be performed anyplace along the spine from the neck (cervical) to the low back (lumbar). The specialist arrives at the harmed circle from the front (foremost) of the spine through the throat zone. By clearing out the neck muscles, trachea, and throat, the circle and hard vertebrae are uncovered. Medical procedure from the front of the neck is more open than from the (back) in light of the fact that the plate can become to without irritating the spinal rope, spinal nerves, and the solid neck muscles. Contingent upon your specific side effects, one circle (single-level) or more (staggered) might be evacuated.
After the circle is evacuated, the space between the hard vertebrae is vacant. To keep the vertebrae from falling and scouring together, a spacer bone unite is embedded to fill the open plate space. The unite fills in as a scaffold between the two vertebrae to make a spinal combination. The bone unite and vertebrae are fixed set up with metal plates and screws. Following the medical procedure, the body starts its common mending procedure and new bone cells develop around the join. Following 3 to a half year, the bone unite should join the two vertebrae and structure one strong bit of bone. The instrumentation and combination cooperate, like fortified cement.
0 notes
Text
Comprehensive approach to cervical spine spondylosis
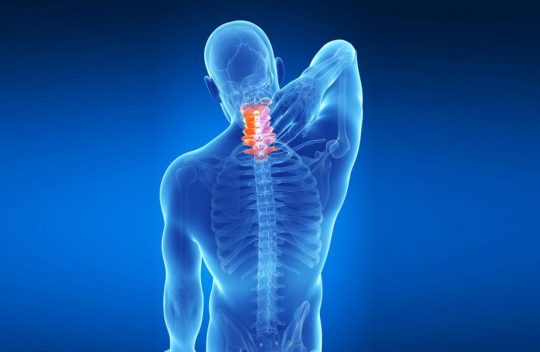
Degeneration of bones and discs in the neck are referred to as cervical spine disease or cervical spondylosis. As age progresses, bones and cartilages in this region face wear and tear which results in problems such as herniated discs and bone spurs. How to detect cervical spine spondylosis? Neck pain, nagging soreness in the neck, muscle spasms, clicking or grinding sound while rotating or moving the head, dizziness and headaches might suggest presence of cervical spine spondylosis. Since spondylosis invokes pressure on the neighbouring nerves, pain could be felt at chest, ribs and abdomen areas. Cervical spine spondylosis narrows the space around spinal cord and results in numbness, strain and lack of coordination in walking and loss of bladder and bowel control. Imaging tests like neck x-ray, CT scan, MRI and Myelography would confirm the ailment. Nerves affected by cervical spine spondylosis First three cervical spines namely C1, C2 and C3 control head and neck and movements around them while C4 controls upward shoulder movements. Decompression surgery suggestions Spondylosis surgery includes removal of pain agent and fusion of spine. To remove the tissue that evokes nerve pressure, surgeon conducts decompression surgery and to conduct fusion, stabilization surgery is done. Before going into decompression surgery let’s familiarize with terms such as ‘ectomy’ which means removal and ‘otomy’ which refers to opening. Facetectomy and Laminoectomy removes facet joint and lamina or part of lamina (bony plate that protects spinal cord) respectively. Foraminotomy creates an opening in the vertebra exit also known as foramen, so that nerve can exit smoothly. Laminotomy creates or enlarges opening in the bony plate so that the lamina does not press the nerve structure. Laminoplasty is performed to create a hinge to lift lamina and mitigate compression. Surgical approaches The spine is accessed from the front to reach the abdomen and is known as anterior approach. Incision in the back enables posterior approach and access through the sides is lateral approach. However, anterior and posterior approaches are risky. Risks associated with cervical spine spondylosis surgery Complications associated with cervical spine spondylosis surgery include paralysis, inability to walk, anesthetic complications, infections associated with improper handling of wounds and complications associated with related injuries. Non surgical suggestions for cervical spine spondylosis Non surgical remedies include acupuncture, bed rest, using brace, muscle relaxants, physical therapy, spinal injections. Chiropractic methods like employing ice, heat, ultrasound, massage, spinal manipulation can also be employed to cure the ailment. About Dr Karunakaran Dr Karunakaran, spine specialist for more than two decades, has performed more than 3000 surgeries for various complications including scoliosis, cervical spine diseases, thoracotomies, laparotomy and disc replacement surgeries, to name a few. Dr Karunakaran is also a pioneer in Tamil Nadu to perform percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy under local anesthesia for disc prolapse and INSPACE-interspinous implant for lumbar canal stenosis-key hole spine surgery local anesthesia besides being fluent in pain management techniques of spine such as foraminal epidural steroid injection, facetal blocks and discography. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
The Anterior Cervical Plate is used to remove a herniated or damaged disc. To treat neck and arm discomfort, ACDF surgery replaces damaged discs with bone grafts. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion is a surgical treatment that involves removing a damaged cervical spinal disc and fusing the affected bone.
#arthroscopic knee#arthroscopy#c2cspinesystem#mjsurgical#polyaxial screw#knee arthroscopy implants#monoaxial screw#knotless suture anchor
0 notes
Text
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF)
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) is a surgical procedure to treat nerve root or spinal cord compression by decompressing the spinal cord and nerve roots of the cervical spine with a discectomy, followed by inter-vertebral fusion to stabilize the corresponding vertebrae.This procedure is used when other non-surgical treatments have failed.
Medical uses
ACDF is used to treat serious pain from a nerve root that has become inflamed. This can be caused by:
1. a herniated disc when other non-surgical treatments have failed. The nucleus pulposus (the jelly-like center of the disc) of the herniated disc bulges out through the annulus (surrounding wall) and presses on the nerve root next to it.
2. degenerative disc disease (spondylosis). The disc consists of about 80% water. When one grows older, the disc starts to dry out and shrink, causing small tears in the annulus and inflammation of the nerve root.

Technique
The neurosurgeon or orthopedic surgeon enters the space between two discs through a small incision in front (= anterior) of and at the right or left side of the neck. The disc is completely removed, as well as arthritic bone spurs. The disc material, pressing on the spinal nerve or spinal cord, is then completely removed. The intervertebral foramen, the bone channel through which the spinal nerve runs, is then enlarged with a drill giving the nerve more room to exit the spinal canal.
To prevent the vertebrae from collapsing and to increase stability, the open space is often filled with a graft. That can be a bone graft, taken from the pelvis or cadaveric bone; or an artificial implant. The slow process of the bone graft joining the vertebrae together is called “fusion”. Sometimes a titanium plate is screwed on the vertebrae or screws are used between the vertebrae to increase stability during fusion, especially when there is more than one disc involved.
0 notes
Text
The Inevitable Role Of Cervical Disc In Human Body

To get an idea about cervical disc surgery, we must first understand the cervical spine and its functions. The spinal column is made up of twenty-four vertebrae, sacrum and coccyx is the protective casing of the spinal cord. Cervical spine, behind the neck, is the uppermost portion of the entire spinal column that runs from the skull to the pelvis. There is a cartilaginous disc each between every two vertebrae. These shock absorbing discs provide flexibility to the spine and ease movements. There are nerves branching out of the spinal cord which passes through openings in the vertebrae to other parts of the body. The intervertebral discs may get damaged due to strain, injury or arthritis and may result in muscle inflammation and spasms.
Know Your Vertebral Column
Any instability of the vertebral column because of stress, trauma, injury or old age can strain the spinal cord or the nerves. This may result in constricted nerves which cause pain and numbness of neck, shoulders, and arms. Though neck and shoulder pain could be for a variety of reasons like arthritis or herniated disc or stressed nerves, it is for your doctor to find out if you need surgery. You will need some x-rays and MRI and maybe some more scans to determine exactly where and how much the damage is. It is only after you have taken medication and physical therapy for some time without any relief that you may be advised surgery. A cervical disc surgery may be required for a number of cervical spine troubles. With age, the discs between the vertebrae may wear away and get herniated. You may feel pain, numbness and tingling sensations on your neck, shoulders, and arms when the spinal nerves of the cervical region are under pressure. Cervical disc surgery can also be helpful for people who have cervical deformities like hyper lordosis or swan neck. The spine gets straightened with this surgery.
Need For Cervical Disc Surgery
An injury to the neck is possible because the neck is so flexible and subject to so much movement. If an injury results in a fracture or dislocation of the cervical vertebrae, surgery can help stabilize the spine. Cervical disc surgery can help relieve pain, numbness, and weakness of the cervical spine. It also helps restore nerve function which may be because of unstable vertebral column. This is done either by removing a disc or a bone. The vertebrae are then fused together with the help of a bone graft. This can be done in front or back of the spine. Sometimes, instead of a bone, metal plate, screw or wire is used to stabilize the spine.
Anterior cervical discectomy is performed to remove the damaged disc through an incision at the front of the neck. This is done with or without spinal fusion. In the case of posterior cervical discectomy, the surgery is carried out on the back of the neck.
After surgery, you will need to wear a neck brace to keep your spine stable. The duration and type of brace will be decided by your doctor. You may also be advised to have limited physical activity for some time.
Reference Box:
A swift movement of head and neck is very necessary, and if anyone of them stiffs or anything which hampers the movement, can be troublesome for the person then you need to get the best Cervical Disc Treatment in Delhi, the person should be free to consult Dr. Shailesh Jain for the same. Being an expert in his field and rich in his experience, he gains a high repute in his are and amongst his patients.
Content Source: https://drshaileshjainneurosurgeon.home.blog/2019/06/18/the-inevitable-role-of-cervical-disc-in-human-body/
#Cervical Disc Treatment in Delhi#Cervical Disc Treatment#cervical disc surgery#Role Of Cervical Disc
0 notes