#Agence France-Presse
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text




AFP slides, Beijing, June 1989.
#June Fourth Incident#Tiananmen Square massacre#Tiananmen Square Incident#Tiananmen uprising#'89 Democracy Movement#六四事件#天安門事件#1989#afp#Agence France Presse#slide
148 notes
·
View notes
Text
Further reading:
AFP, via HKFP: Hong Kong Christian newspaper runs blank front page ahead of Tiananmen crackdown anniversary, June 3, 2024
HKFP: Hong Kong’s Catholic Diocese axes third consecutive Tiananmen mass as cardinal urges ‘forgiveness’ over crackdown, June 4, 2024
HKFP: Ex-local councillor asked by police about Tiananmen crackdown anniversary plans; lawmakers say marking date in private is lawful, June 4, 2024
#Hong Kong#Hong Kong Free Press#Taiwan#Lai Ching te#Agence France Presse#political repression#Hong Kong National Security Law#Article 23#news#八九民運#六四事件#Tiananmen Square#天安門#1980s#20th century#China#天安門事件#八九六四#1989 Tiananmen Square protests#8964
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
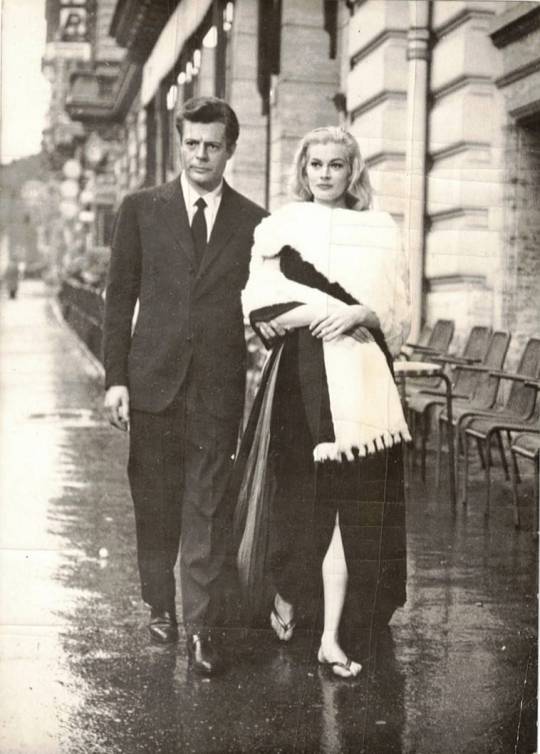

Marcello Mastroianni e Anita Ekberg nel film "La dolce vita" di Federico Fellini 1960. Agence France Press
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
| Fabrice Fries, PDG de l'Agence France-Presse (AFP), s'exprimant au Sénat français :
Nous sommes une agence de presse et la plupart de nos clients ne considèrent pas le Hamas comme une organisation terroriste.
Nous affirmons dans nos reportages que les États-Unis et l'Union européenne le font (contrairement à la plupart des pays du monde), mais nous subissons des pressions depuis un mois. C'est de la folie.
Les clients de notre agence décident eux-mêmes de la définition du Hamas.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

AFP, Umberto Eco, Roma, Italia, 1983
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://factuel.afp.com/
Factuel. La vérification de l’information est une des missions de l’Agence France Presse. Face à la multiplication des fausses informations qui circulent sur les réseaux sociaux, un réseau mondial de journalistes et d’éditeurs met à votre disposition un blog : Factuel.afp.com. Son objectif est de présenter des conclusions vérifiées sur des informations qu’ils choisissent en fonction de leur viralité ou de leur actualité.
Bibliothèque des Côtes d'Armor
#sinformer#actualité#agence france presse#décryptage#fact-checking#fake news#information#webmagazine
0 notes
Text



I'm happy to let you know that my recent video and photo drone coverage of the US border with Mexico is available now at AFP and Getty Images. The footage starts with some ATVs on the Mexican side of the border near Nogales. It's been since before the pandemic that I've drone stories with Agence France-Presse, so I'm really proud of this one. They were used on several outlets including Time. AFPTV video story AFP Photo story Getty Images
0 notes
Text
Swiss Policy Research: The Propaganda Multiplier
It is one of the most important aspects of our media system, and yet hardly known to the public: most of the international news coverage in Western media is provided by only three global news agencies based in New York, London and Paris.
The key role played by these agencies means Western media often report on the same topics, even using the same wording. In addition, governments, military and intelligence services use these global news agencies as multipliers to spread their messages around the world.
A study of the Syria war coverage by nine leading European newspapers clearly illustrates these issues: 78% of all articles were based in whole or in part on agency reports, yet 0% on investigative research. Moreover, 82% of all opinion pieces and interviews were in favor of a US and NATO intervention, while propaganda was attributed exclusively to the opposite side.

The Propaganda Multiplier:
How Global News Agencies and Western Media Report on Geopolitics
A Study by Swiss Propaganda Research: 2016 / 2019
“Therefore, you always have to ask yourself: Why do I get this specific information, in this specific form, at this specific moment? Ultimately, these are always questions about power.” (*) Dr. Konrad Hummler, Swiss Banking and Media Executive
Contents
Part 1: The Propaganda Multiplier
Part 2: Case Study on Syria War Coverage
3. Notes and Literature
Introduction: “Something Strange”
“How does the newspaper know what it knows?” The answer to this question is likely to surprise some newspaper readers: “The main source of information is stories from news agencies. The almost anonymously operating news agencies are in a way the key to world events. So what are the names of these agencies, how do they work and who finances them? To judge how well one is informed about events in East and West, one should know the answers to these questions.” (Höhne 1977, p. 11)
A Swiss media researcher points out: “The news agencies are the most important suppliers of material to mass media. No daily media outlet can manage without them. () So the news agencies influence our image of the world; above all, we get to know what they have selected.” (Blum 1995, p. 9)
In view of their essential importance, it is all the more astonishing that these agencies are hardly known to the public: “A large part of society is unaware that news agencies exist at all … In fact, they play an enormously important role in the media market. But despite this great importance, little attention has been paid to them in the past.” (Schulten-Jaspers 2013, p. 13)
Even the head of a news agency noted: “There is something strange about news agencies. They are little known to the public. Unlike a newspaper, their activity is not so much in the spotlight, yet they can always be found at the source of the story.” (Segbers 2007, p. 9)
“The Invisible Nerve Center of the Media System”
So what are the names of these agencies that are “always at the source of the story”? There are now only three global news agencies left:
The American Associated Press (AP) with over 4000 employees worldwide. The AP belongs to US media companies and has its main editorial office in New York. AP news is used by around 12,000 international media outlets, reaching more than half of the world’s population every day.
The Quasi-Governmental French Agence France-Presse (AFP) based in Paris and with around 4000 employees. The AFP sends over 3000 stories and photos every day to media all over the world.
The British Agency Reuters in London, which is privately owned and employs just over 3000 people. Reuters was acquired in 2008 by Canadian media entrepreneur Thomson – one of the 25 richest people in the world – and merged into Thomson Reuters, headquartered in New York.
In addition, many countries run their own news agencies. These include, for instance, the German DPA, the Austrian APA, and the Swiss SDA. When it comes to international news, however, national agencies usually rely on the three global agencies and simply copy and translate their reports.

Figure 1: The three global news agencies Reuters, AFP and AP, and the three national agencies of the German-speaking countries of Austria (APA), Germany (DPA) and Switzerland (SDA).
Wolfgang Vyslozil, former managing director of the Austrian APA, described the key role of news agencies with these words: “News agencies are rarely in the public eye. Yet they are one of the most influential and at the same time one of the least known media types. They are key institutions of substantial importance to any media system. They are the invisible nerve center that connects all parts of this system.” (Segbers 2007, p.10)
Small Abbreviation, Great Effect
However, there is a simple reason why the global agencies, despite their importance, are virtually unknown to the general public. To quote a Swiss media professor: “Radio and television usually do not name their sources, and only specialists can decipher references in magazines.” (Blum 1995, P. 9)
The motive for this discretion, however, should be clear: news outlets are not particularly keen to let readers know that they haven’t researched most of their contributions themselves.
The following figure shows some examples of source tagging in popular European newspapers. Next to the agency abbreviations we find the initials of editors who have edited the respective agency report.

Figure 2: News agencies as sources in newspaper articles
Occasionally, newspapers use agency material but do not label it at all. A study in 2011 from the Swiss Research Institute for the Public Sphere and Society at the University of Zurich came to the following conclusions (FOEG 2011):
“Agency contributions are exploited integrally without labeling them, or they are partially rewritten to make them appear as an editorial contribution. In addition, there is a practice of ‘spicing up’ agency reports with little effort: for example, unpublished agency reports are enriched with images and graphics and presented as comprehensive articles.”
The agencies play a prominent role not only in the press, but also in private and public broadcasting. This is confirmed by Volker Braeutigam, who worked for the German state broadcaster ARD for ten years and views the dominance of these agencies critically:
“One fundamental problem is that the newsroom at ARD sources its information mainly from three sources: the news agencies DPA/AP, Reuters and AFP: one German/American, one British and one French. () The editor working on a news topic only needs to select a few text passages on the screen that he considers essential, rearrange them and glue them together with a few flourishes.”
Swiss Radio and Television (SRF), too, largely bases itself on reports from these agencies. Asked by viewers why a peace march in Ukraine was not reported, the editors said: “To date, we have not received a single report of this march from the independent agencies Reuters, AP and AFP.”
In fact, not only the text, but also the images, sound and video recordings that we encounter in our media every day, are mostly from the very same agencies. What the uninitiated audience might think of as contributions from their local newspaper or TV station, are actually copied reports from New York, London and Paris.
Some media have even gone a step further and have, for lack of resources, outsourced their entire foreign editorial office to an agency. Moreover, it is well known that many news portals on the internet mostly publish agency reports (see e.g., Paterson 2007, Johnston 2011, MacGregor 2013).
In the end, this dependency on the global agencies creates a striking similarity in international reporting: from Vienna to Washington, our media often report the same topics, using many of the same phrases – a phenomenon that would otherwise rather be associated with »controlled media« in authoritarian states.
The following graphic shows some examples from German and international publications. As you can see, despite the claimed objectivity, a slight (geo-)political bias sometimes creeps in.
Figure 3: “Putin threatens”, “Iran provokes”, “NATO concerned”, “Assad stronghold”: Similarities in content and wording due to reports by global news agencies.

The Role of Correspondents
Much of our media does not have own foreign correspondents, so they have no choice but to rely completely on global agencies for foreign news. But what about the big daily newspapers and TV stations that have their own international correspondents? In German-speaking countries, for example, these include newspapers such NZZ, FAZ, Sueddeutsche Zeitung, Welt, and public broadcasters.
First of all, the size ratios should be kept in mind: while the global agencies have several thousand employees worldwide, even the Swiss newspaper NZZ, known for its international reporting, maintains only 35 foreign correspondents (including their business correspondents). In huge countries such as China or India, only one correspondent is stationed; all of South America is covered by only two journalists, while in even larger Africa no-one is on the ground permanently.
Moreover, in war zones, correspondents rarely venture out. On the Syria war, for example, many journalists “reported” from cities such as Istanbul, Beirut, Cairo or even from Cyprus. In addition, many journalists lack the language skills to understand local people and media.
How do correspondents under such circumstances know what the “news” is in their region of the world? The main answer is once again: from global agencies. The Dutch Middle East correspondent Joris Luyendijk has impressively described how correspondents work and how they depend on the world agencies in his book “People Like Us: Misrepresenting the Middle East”:
“I had imagined correspondents to be historians-of-the-moment. When something important happened, they would go after it, find out what was going on, and report on it. But I didn’t go off to find out what was going on; that had been done long before. I went along to present an on-the-spot report.
The editors in the Netherlands called when something happened, they faxed or emailed the press releases, and I’d retell them in my own words on the radio, or rework them into an article for the newspaper. This was the reason my editors found it more important that I could be reached in the place itself than that I knew what was going on. The news agencies provided enough information for you to be able to write or talk your way through any crisis or summit meeting.
That’s why you often come across the same images and stories if you leaf through a few different newspapers or click the news channels.
Our men and women in London, Paris, Berlin and Washington bureaus – all thought that wrong topics were dominating the news and that we were following the standards of the news agencies too slavishly.
The common idea about correspondents is that they ‘have the story’, () but the reality is that the news is a conveyor belt in a bread factory. The correspondents stand at the end of the conveyor belt, pretending we’ve baked that white loaf ourselves, while in fact all we’ve done is put it in its wrapping.
Afterwards, a friend asked me how I’d managed to answer all the questions during those cross-talks, every hour and without hesitation. When I told him that, like on the TV-news, you knew all the questions in advance, his e-mailed response came packed with expletives. My friend had relalized that, for decades, what he’d been watching and listening to on the news was pure theatre.” (Luye ndjik 2009, p. 20-22, 76, 189)
In other words, the typical correspondent is in general not able to do independent research, but rather deals with and reinforces those topics that are already prescribed by the news agencies – the notorious “mainstream effect”.
In addition, for cost-saving reasons many media outlets nowadays have to share their few foreign correspondents, and within individual media groups, foreign reports are often used by several publications – none of which contributes to diversity in reporting.
“What the agency does not report, does not take place”
The central role of news agencies also explains why, in geopolitical conflicts, most media use the same original sources. In the Syrian war, for example, the “Syrian Observatory for Human Rights” – a dubious one-man organization based in London – featured prominently. The media rarely inquired directly at this “Observatory”, as its operator was in fact difficult to reach, even for journalists.
Rather, the “Observatory” delivered its stories to global agencies, which then forwarded them to thousands of media outlets, which in turn “informed” hundreds of millions of readers and viewers worldwide. The reason why the agencies, of all places, referred to this strange “Observatory” in their reporting – and who really financed it – is a question that was rarely asked.
The former chief editor of the German news agency DPA, Manfred Steffens, therefore states in his book “The Business of News”:
“A news story does not become more correct simply because one is able to provide a source for it. It is indeed rather questionable to trust a news story more just because a source is cited. () Behind the protective shield such a ‘source’ means for a story, some people are inclined to spread rather adventurous things, even if they themselves have legitimate doubts about their correctness; the responsibility, at least morally, can always be attributed to the cited source.” (Steffens 1969, p. 106)
Dependence on global agencies is also a major reason why media coverage of geopolitical conflicts is often superficial and erratic, while historic relationships and background are fragmented or altogether absent. As put by Steffens: “News agencies receive their impulses almost exclusively from current events and are therefore by their very nature ahistoric. They are reluctant to add any more context than is strictly required.” (Steffens 1969, p. 32)
Finally, the dominance of global agencies explains why certain geopolitical issues and events – which often do not fit very well into the US/NATO narrative or are too “unimportant” – are not mentioned in our media at all: if the agencies do not report on something, then most Western media will not be aware of it. As pointed out on the occasion of the 50th anniversary of the German DPA: “What the agency does not report, does not take place.” (Wilke 2000, p. 1)
“Adding Questionable Stories”
While some topics do not appear at all in our media, other topics are very prominent – even though they shouldn’t actually be: “Often the mass media do not report on reality, but on a constructed or staged reality. () Several studies have shown that the mass media are predominantly determined by PR activities and that passive, receptive attitudes outweigh active-researching ones.” (Blum 1995, p. 16)
In fact, due to the rather low journalistic performance of our media and their high dependence on a few news agencies, it is easy for interested parties to spread propaganda and disinformation in a supposedly respectable format to a worldwide audience. DPA editor Steffens warned of this danger:
“The critical sense gets more lulled the more respected the news agency or newspaper is. Someone who wants to introduce a questionable story into the world press only needs to try to put his story in a reasonably reputable agency, to be sure that it then appears a little later in the others. Sometimes it happens that a hoax passes from agency to agency and becomes ever more credible.” (Steffens 1969, p. 234)
Among the most active actors in “injecting” questionable geopolitical news are the military and defense ministries. For example, in 2009 the head of the American news agency AP, Tom Curley, made public that the Pentagon employs more than 27,000 PR specialists who, with a budget of nearly $ 5 billion a year, are working the media and circulating targeted manipulations. In addition, high-ranking US generals had threatened that they would “ruin” him and the AP if the journalists reported too critically on the US military.
Despite – or because of? – such threats our media regularly publish dubious stories sourced to some unnamed “informants” from “US defense circles”.
Ulrich Tilgner, a veteran Middle East correspondent for German and Swiss television, warned in 2003, shortly after the Iraq war, of acts of deception by the military and the role played by the media:
“With the help of the media, the military determine the public perception and use it for their plans. They manage to stir expectations and spread deceptive scenarios. In this new kind of war, the PR strategists of the US administration fulfill a similar function as the bomber pilots. The special departments for public relations in the Pentagon and in the secret services have become combatants in the information war.
For their deception maneuvers, the US military specifically uses the lack of transparency in media coverage. The way they spread information, which is then picked up and distributed by newspapers and broadcasters, makes it impossible for readers, listeners or viewers to trace the original source. Thus, the audience will fail to recognize the actual intention of the military.” (Tilgner 2003, p. 132)
What is known to the US military, would not be foreign to US intelligence services. In a remarkable report by British Channel 4, former CIA officials and a Reuters correspondent spoke candidly about the systematic dissemination of propaganda and misinformation in reporting on geopolitical conflicts:
Former CIA officer and whistleblower John Stockwell said of his work in the Angolan war: “The basic theme was to make it look like an [enemy] aggression. So any kind of story that you could write and get into the media anywhere in the world, that pushed that line, we did. One third of my staff in this task force were propagandists, whose professional career job was to make up stories and finding ways of getting them into the press. () The editors in most Western newspapers are not too skeptical of messages that conform to general views and prejudices. () So we came up with another story, and it was kept going for weeks. () But it was all fiction.”
Fred Bridgland looked back on his work as a war correspondent for the Reuters agency: “We based our reports on official communications. It was not until years later that I learned that a little CIA disinformation expert had sat in the US embassy and had composed these communiqués that bore absolutely no relationship at all to truth. () Basically, and to put it very crudely, you can publish any old crap and it will get into the newspaper.”
And former CIA analyst David MacMichael described his work in the Contra War in Nicaragua with these words: “They said our intelligence of Nicaragua was so good that we could even register when someone flushed a toilet. But I had the feeling that the stories we were giving to the press came straight out of the toilet.” (Channel 4, 1985)
Of course, the intelligence services also have a large number of direct contacts in our media, which can be “leaked” information to if necessary. But without the central role of the global news agencies, the worldwide synchronization of propaganda and disinformation would never be so efficient.
Through this “propaganda multiplier”, dubious stories from PR experts working for governments, military and intelligence services reach the general public more or less unchecked and unfiltered. The journalists refer to the news agencies and the news agencies refer to their sources. Although they often attempt to point out uncertainties (and hedge themselves) with terms such as “apparent”, “alleged” and the like – by then the rumor has long been spread to the world and its effect has taken place.
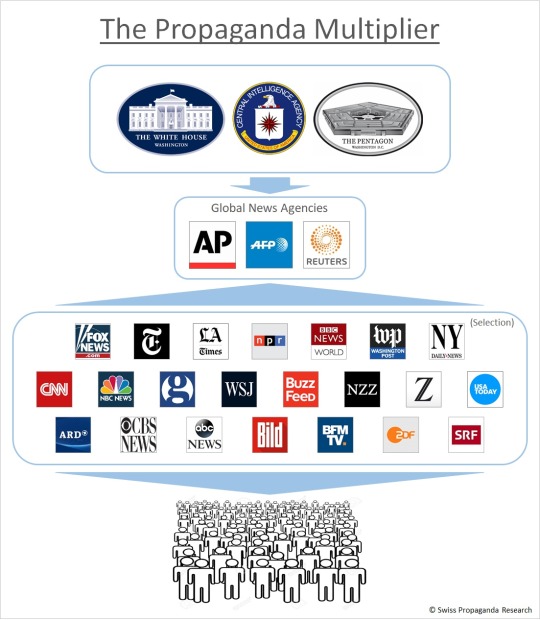
Figure 4: The Propaganda Multiplier: Governments, military and intelligence services using global news agencies to disseminate their messages to a worldwide audience.
As the New York Times Reported …
In addition to global news agencies, there is another source that is often used by media outlets around the world to report on geopolitical conflicts, namely the major publications in Great Britain and the US.
News outlets like the New York Times or the BBC may have up to 100 foreign correspondents and additional external employees. However, as Middle East correspondent Luyendijk points out:
“Our news teams, me included, fed on the selection of news made by quality media like CNN, the BBC, and the New York Times. We did that on the assumption that their correspondents understood the Arab world and commanded a view of it – but many of them turned out not to speak Arabic, or at least not enough to be able to have a conversation in it or to follow the local media. Many of the top dogs at CNN, the BBC, the Independent, the Guardian, the New Yorker, and the NYT were more often than not dependent on assistants and translators.” (Luyendijk p. 47)
In addition, the sources of these media outlets are often not easy to verify (“military circles”, “anonymous government officials”, “intelligence officials” and the like) and can therefore also be used for the dissemination of propaganda. In any case, the widespread orientation towards the major Anglo-Saxon publications leads to a further convergence in the geopolitical coverage in our media.
The following figure shows some examples of such citation based on the Syria coverage of the largest daily newspaper in Switzerland, Tages-Anzeiger. The articles are all from the first days of October 2015, when Russia for the first time intervened directly in the Syrian war (US/UK sources are highlighted):

Figure 5: Frequent citation of major British and US media, exemplified by the Syria war coverage of Swiss daily newspaper Tages-Anzeiger in October 2015.
The Desired Narrative
But why do journalists in our media not simply try to research and report independently of the global agencies and the Anglo-Saxon media? Middle East correspondent Luyendijk describes his experiences:
“You might suggest that I should have looked for sources I could trust. I did try, but whenever I wanted to write a story without using news agencies, the main Anglo-Saxon media, or talking heads, it fell apart. () Obviously I, as a correspondent, could tell very different stories about one and the same situation. But the media could only present one of them, and often enough, that was exactly the story that confirmed the prevailing image.” (Luyendijk p.54ff)
Media researcher Noam Chomsky has described this effect in his essay “What makes the mainstream media mainstream” as follows: “If you get off line, if you’re producing stories that the big press doesn’t like, you’ll hear about it pretty soon. () So there are a lot of ways in which power plays can drive you right back into line if you move out. If you try to break the mold, you’re not going to last long. That framework works pretty well, and it is understandable that it is just a reflection of obvious power structures.” (Chomsky 1997)
Nevertheless, some of the leading journalists continue to believe that nobody can tell them what to write. How does this add up? Media researcher Chomsky clarifies the apparent contradiction:
“[T]he point is that they wouldn’t be there unless they had already demonstrated that nobody has to tell them what to write because they are going say the right thing. If they had started off at the Metro desk, or something, and had pursued the wrong kind of stories, they never would have made it to the positions where they can now say anything they like. The same is mostly true of university faculty in the more ideological disciplines. They have been through the socialization system.” (Chomsky 1997)
Ultimately, this “socialization system” leads to a journalism that no longer independently researches and critically reports on geopolitical conflicts (and some other topics), but seeks to consolidate the desired narrative through appropriate editorials, commentary, and interviews.
Conclusion: The “First Law of Journalism”
Former AP journalist Herbert Altschull called it the First Law of Journalism: “In all press systems, the news media are instruments of those who exercise political and economic power. Newspapers, periodicals, radio and television stations do not act independently, although they have the possibility of independent exercise of power.” (Altschull 1984/1995, p. 298)
In that sense, it is logical that our traditional media – which are predominantly financed by advertising or the state – represent the geopolitical interests of the transatlantic alliance, given that both the advertising corporations as well as the states themselves are dependent on the transatlantic economic and security architecture led by the United States.
In addition, the key people of our leading media are – in the spirit of Chomsky’s “socialization system” – often themselves part of transatlantic elite networks. Some of the most important institutions in this regard include the US Council on Foreign Relations (CFR), the Bilderberg Group, and the Trilateral Commission, all of which feature many prominent journalists (see in-depth study of these groups).
Most well-known publications, therefore, may indeed be seen as a kind of “establishment media”. This is because, in the past, the freedom of the press was rather theoretical, given significant entry barriers such as broadcasting licenses, frequency slots, requirements for financing and technical infrastructure, limited sales channels, dependence on advertising, and other restrictions.
It was only due to the Internet that Altschull’s First Law has been broken to some extent. Thus, in recent years a high-quality, reader-funded journalism has emerged, often outperforming traditional media in terms of critical reporting. Some of these “alternative” publications already reach a very large audience, showing that the “mass” does not have to be a problem for the quality of a media outlet.
Nevertheless, up to now the traditional media has been able to attract a solid majority of online visitors, too. This, in turn, is closely linked to the hidden role of news agencies, whose up-to-the-minute reports form the backbone of most online news sites.
Will “political and economic power”, according to Altschull’s Law, retain control over the news, or will “uncontrolled news” change the political and economic power structure? The coming years will show.
Britain secretly funded Reuters in 1960s and 1970s (Reuters, January 2020)
Reuters, BBC in Covert UK Program to Push Western Agenda (The Grayzone, February 2021)
The Formation of the Reuters-Havas-Wolff News Monopoly and Cartel (Winter Watch, 2022)
The CIA’s Mop-Up Man (The Intercept, September 2014)
Case Study: Syria War Coverage
As part of a case study, the Syria war coverage of nine leading daily newspapers from Germany, Austria and Switzerland were examined for plurality of viewpoints and reliance on news agencies. The following newspapers were selected:
For Germany: Die Welt, Süddeutsche Zeitung (SZ), and Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung (FAZ)
For Switzerland: Neue Zürcher Zeitung (NZZ), Tagesanzeiger (TA), and Basler Zeitung (BaZ)
For Austria: Standard, Kurier, and Die Presse
The investigation period was defined as October 1 to 15, 2015, i.e. the first two weeks after Russia’s direct intervention in the Syrian conflict. The entire print and online coverage of these newspapers was taken into account. Any Sunday editions were not taken into account, as not all of the newspapers examined have such. In total, 381 newspaper articles met the stated criteria.
In a first step, the articles were classified according to their properties into the following groups:
Agencies: Reports from news agencies (with agency code)
Mixed: Simple reports (with author names) that are based in whole or in part on agency reports
Reports: Editorial background reports and analyses
Opinions/Comments: Opinions and guest comments
Interviews: Interviews with experts, politicians etc.
Investigative: Investigative research that reveals new information or context
The following Figure 1 shows the composition of the articles for the nine newspapers analyzed in total. As can be seen, 55% of articles were news agency reports; 23% editorial reports based on agency material; 9% background reports; 10% opinions and guest comments; 2% interviews; and 0% based on investigative research.

The pure agency texts – from short notices to the detailed reports – were mostly on the Internet pages of the daily newspapers: on the one hand, the pressure for breaking news is higher than in the printed edition, on the other hand, there are no space restrictions. Most other types of articles were found in both the online and printed editions; some exclusive interviews and background reports were found only in the printed editions. All items were collected only once for the investigation.
The following Figure 2 shows the same classification on a per newspaper basis. During the observation period (two weeks), most newspapers published between 40 and 50 articles on the Syrian conflict (print and online). In the German newspaper Die Welt there were more (58), in the Basler Zeitung and the Austrian Kurier, however, significantly less (29 or 33).
Depending on which newspaper, the share of agency reports is almost 50% (Welt, Süddeutsche, NZZ, Basler Zeitung), just under 60% (FAZ, Tagesanzeiger), and 60 to 70% (Presse, Standard, Kurier). Together with the agency-based reports, the proportion in most newspapers is between approx. 70% and 80%. These proportions are consistent with previous media studies (e.g., Blum 1995, Johnston 2011, MacGregor 2013, Paterson 2007).
In the background reports, the Swiss newspapers were leading (five to six pieces), followed by Welt, Süddeutsche and Standard (four each) and the other newspapers (one to three). The background reports and analyzes were in particular devoted to the situation and development in the Middle East, as well as to the motives and interests of individual actors (for example Russia, Turkey, the Islamic State).
However, most of the commentaries were to be found in the German newspapers (seven comments each), followed by Standard (five), NZZ and Tagesanzeiger (four each). Basler Zeitung did not publish any commentaries during the observation period, but two interviews. Other interviews were conducted by Standard (three) and Kurier and Presse (one each). Investigative research, however, could not be found in any of the newspapers.
In particular, in the case of the three German newspapers, a journalistically problematic blending of opinion pieces and reports was noted. Reports contained strong expressions of opinion even though they were not marked as commentary. The present study was in any case based on the article labeling by the newspaper.
The following Figure 3 shows the breakdown of agency stories (by agency abbreviation) for each news agency, in total and per country. The 211 agency reports carried a total of 277 agency codes (a story may consist of material from more than one agency). In total, 24% of agency reports came from the AFP; about 20% each by the DPA, APA and Reuters; 9% of the SDA; 6% of the AP; and 11% were unknown (no labeling or blanket term “agencies”).
In Germany, the DPA, AFP and Reuters each have a share of about one third of the news stories. In Switzerland, the SDA and the AFP are in the lead, and in Austria, the APA and Reuters.
In fact, the shares of the global agencies AFP, AP and Reuters are likely to be even higher, as the Swiss SDA and the Austrian APA obtain their international reports mainly from the global agencies and the German DPA cooperates closely with the American AP.
It should also be noted that, for historical reasons, the global agencies are represented differently in different regions of the world. For events in Asia, Ukraine or Africa, the share of each agency will therefore be different than from events in the Middle East.

In the next step, central statements were used to rate the orientation of editorial opinions (28), guest comments (10) and interview partners (7) (a total of 45 articles). As Figure 4 shows, 82% of the Contributions Were Generally US/NATO Friendly, 16% Neutral or Balanced, and 2% Predominantly US/NATO Critical.
The only predominantly US/NATO-critical contribution was an op-ed in the Austrian Standard on October 2, 2015, titled: “The strategy of regime change has failed. A distinction between ‘good’ and ‘bad’ terrorist groups in Syria makes the Western policy untrustworthy.”
The following Figure 5 shows the orientation of the contributions, guest comments and interviewees, in turn broken down by individual newspapers. As can be seen, Welt, Süddeutsche Zeitung, NZZ, Zürcher Tagesanzeiger and the Austrian newspaper Kurier presented exclusively US/NATO-friendly opinion and guest contributions; this goes for FAZ too, with the exception of one neutral/balanced contribution. The Standard brought four US/NATO friendly, three balanced/neutral, as well as the already mentioned US/NATO critical opinion contributions.
Presse was the only one of the examined newspapers to predominantly publish neutral/balanced opinions and guest contributions. The Basler Zeitung published one US/NATO-friendly and one balanced contribution. Shortly after the observation period (October 16, 2015), Basler Zeitung also published an interview with the President of the Russian Parliament. This would of course have been counted as a contribution critical of the US/NATO.

Figure 5: Basic Orientation of Opinion Pieces and Interviewees per Newspaper
In a further analysis, a full-text keyword search for “Propaganda” (and word combinations thereof) was used to investigate in which cases the newspapers themselves identified propaganda in one of the two geopolitical conflict sides, USA/NATO or Russia (the participant “IS/ISIS” was not considered). In total, twenty such cases were identified. Figure 6 shows the result: in 85% of the cases, propaganda was identified on the Russian side of the conflict, in 15% the identification was neutral or unstated, and in 0% of the cases propaganda was identified on the USA/NATO side of the conflict.
It should be noted that about half of the cases (nine) were in the Swiss NZZ, which spoke of Russian propaganda quite frequently (“Kremlin propaganda”, “Moscow propaganda machine”, “propaganda stories”, “Russian propaganda apparatus” etc.), followed by German FAZ (three), Welt and Süddeutsche Zeitung (two each) and the Austrian newspaper Kurier (one). The other newspapers did not mention propaganda, or only in a neutral context (or in the context of IS).
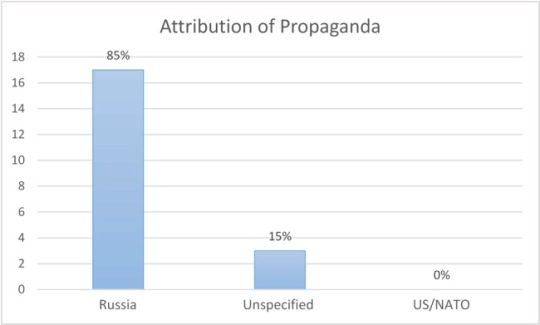
Figure 6: Attribution of Propaganda to Conflict Parties (Total; N=20).
Conclusion
The results confirm the high dependence on the global news agencies (63% to 90%, excluding commentaries and interviews) and the lack of own investigative research, as well as the rather biased commenting on events in favor of the US/NATO side (82% positive; 2% negative), whose stories were not checked by the newspapers for any propaganda.
— About the authors: Swiss Propaganda Research (SPR) is An Independent Research Group Investigating Geopolitical Propaganda in Swiss and International Media. You can contact us here. English translation provided by Terje Maloy, an SPR reader.
#Swiss🇨🇭 Propaganda Research (SPR)#The Propaganda Multiplier#Case Study | Syria 🇸🇾 War#Media System#The Invisible Nerve Center#Associated Press (AP)#Agence France-Presse (AFP)#Reuters#Great Effect#Role of Correspondents#Questionable Stories#Jew York Times#Desired Narrative#Yellow Journalism#United States 🇺🇸 | North Atlantic Terrorist Organization (NATO)
0 notes
Text
The Best News of Last Week
1. ‘We are just getting started’: the plastic-eating bacteria that could change the world

In 2016, Japanese scientists Oda and Hiraga published their discovery of Ideonella sakaiensis, a bacterium capable of breaking down PET plastic into basic nutrients. This finding marked a shift in microbiology's perception, recognizing the potential of microbes to solve pressing environmental issues.
France's Carbios has successfully applied bacterial enzyme technology to recycle PET plastic waste into new plastic products, aligning with the French government's goal of fully recycling plastic packaging by 2025.
2. HIV cases in Amsterdam drop to almost zero after PrEP scheme

According to Dutch AIDS Fund, there were only nine new cases of the virus in Amsterdam in 2022, down from 66 people diagnosed in 2021. The organisation claimed that 128 people were diagnosed with HIV in Amsterdam in 2019, and since 2010, the number of new infections in the Dutch capital has fallen by 95 per cent.
3. Cheap and drinkable water from desalination is finally a reality

In a groundbreaking endeavor, engineers from MIT and China have designed a passive solar desalination system aimed at converting seawater into drinkable water.
The concept, articulated in a study published in the journal Joule, harnesses the dual powers of the sun and the inherent properties of seawater, emulating the ocean’s “thermohaline” circulation on a smaller scale, to evaporate water and leave salt behind.
4. World’s 1st drug to regrow teeth enters clinical trials

The ability to regrow your own teeth could be just around the corner. A team of scientists, led by a Japanese pharmaceutical startup, are getting set to start human trials on a new drug that has successfully grown new teeth in animal test subjects.
Toregem Biopharma is slated to begin clinical trials in July of next year after it succeeded growing new teeth in mice five years ago, the Japan Times reports.
5. After Decades of Pressure, US Drugmaker J&J Gives Up Patent on Life-Saving TB Drug
In what can be termed a huge development for drug-resistant TB (DR-TB) patients across large parts of the world, bedaquiline maker Johnson and Johnson said on September 30 (Saturday) that it would drop its patent over the drug in 134 low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
6. Stranded dolphins rescued from shallow river in Massachusetts
youtube
7. ‘Staggering’ green growth gives hope for 1.5C, says global energy chief

The prospects of the world staying within the 1.5C limit on global heating have brightened owing to the “staggering” growth of renewable energy and green investment in the past two years, the chief of the world’s energy watchdog has said.
Fatih Birol, the executive director of the International Energy Agency, and the world’s foremost energy economist, said much more needed to be done but that the rapid uptake of solar power and electric vehicles were encouraging.
---
That's it for this week :)
This newsletter will always be free. If you liked this post you can support me with a small kofi donation here:
Buy me a coffee ❤️
Also don’t forget to reblog this post with your friends.
11K notes
·
View notes
Photo

French prosecutors charge five over acid burglaries in Paris Suspects accused of using chemicals to destroy locks of apartment doors during 90 break-insFive people have been charged over 90 burglaries in the Paris region in which acid was used to break the locks on apartment doors.Four of the suspects have been held in pre-trial detention since Wednesday and the fifth is being monitored by police, prosecutors in Nanterre, north-west of the French capital, told AFP. Continue reading... https://www.theguardian.com/world/2023/aug/17/french-prosecutors-charge-five-over-acid-burglaries-in-paris
0 notes
Text
Around 20 Killed in Burkina Faso Suspected Terror Attack
August 07, 2023 3:37 PM
Agence France-Presse

Map of Burkina Faso
OUAGADOUGOU, BURKINA FASO - Around 20 people were killed in a suspected terror attack in Burkina Faso, security and local sources told Agence France-Presse on Monday.
The Sunday attack in the Centre-East region near the Togolese border killed "around 20 people, mostly traders," a security source told AFP, while a trader put the toll at 25, and another aid there were a dozen wounded.
More than 16,000 civilians, troops and police have died in terror attacks, according to an NGO count, including more than 5,000 since the start of this year.
More than 2 million people have also been displaced within their country, making it one of the worst internal displacement crises in Africa.
Captain Ibrahim Traore seized power in Burkina Faso in a September 2022 coup which ousted Lieutenant-Colonel Paul-Henri Sandaogo Damiba, who in January that year had toppled the country's last elected president, Roch Marc Christian Kabore.
The motive for both coups was anger at failures to stem a rebel insurgency that has claimed thousands of lives since spilling over from neighboring Mali in 2015.
#africa#terrorwave#terror#terror wave#brexiiton#mali#agence france presse#roch marc christian kabore#ngo#OUAGADOUGOU#burkina faso
0 notes
Text
Madonna breaks silence after health scare
The Queen of Pop has addressed her fans for the first time after being admitted to an intensive care unit late last month and made an announcement about her upcoming world tour. Madonna is recovering after being hospitalised with a “serious bacterial infection”. “I have felt your love. I’m on the road to recovery and incredibly grateful for all the blessings in my life,” the 64-year-old wrote in…

View On WordPress
#Agence France Presse#America#bacterial infection#banned music video#care unit#Chicago#entertainment podcaster#Europe#European leg#Florida#health scare#hip replacement surgery#Illinois#Infamous banned music#London#Madonna#Miami#New York#North America#Northern America#Northern Europe#septic shockMadonna#United Kingdom#United States of America#world tour
0 notes
Text
youtube
Hong Kong hit by widespread flooding and landslides as heavy rain paralyses city, September 8th, 2023
Hong Kong was hit by widespread flooding and landslides as heavy rain paralysed the city. The Observatory recorded the highest one-hour rainfall since records began in 1884. Vid: Patrick Lamoine/Libby Hogan/AFP.
youtube
Hong Kong hit with heaviest rainfall since records began 139 years ago, September 7, 2023
Hong Kong reported 158.1mm of rainfall in the space of an hour, the highest since records began in 1884. Local authorities said various districts had been flooded and emergency services were conducting rescue operations. Members of the public were instructed to stay in a safe place. The Guardian
Further reading:
HKFP: At least 2 dead after Hong Kong battered by record rainfall, severe flooding, September 8, 2023
Reuters: Hong Kong, Shenzhen deluged by heaviest rain on record, September 8, 2023
#Typhoon Saola#Typhoon Haikui#climate crisis#climate change#Hong Kong Observatory#Nam Cheong#Sheung Shui#Chai Wan#flooding#news#Hong Kong Free Press#Hong Kong#Shenzhen#Guangdong#China#Fujian#agence france presse#the guardian#Reuters
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Two wild kiwi chicks were born near Wellington, New Zealand, about a year after a reintroduction program began in the city, the Capital Kiwi Project announced last week. The fluffy, brown babies are the first to be born near the country’s capital in at least 150 years.
“This is very special for the team, which has been working hard for the last few years,” project founder Paul Ward tells the Agence France-Presse. The chicks are a “massive milestone for our goal of building a wild population of kiwi on Wellington’s back doorstep.”
These flightless, chicken-sized birds were once abundant across New Zealand, with the nation’s five species numbering an estimated 12 million individuals in total. But nonnative predators and habitat loss caused their populations to plummet. Today, approximately 68,000 kiwis remain....
Conservation and reintroduction programs, including the Capital Kiwi Project, have been working to restore a large-scale wild kiwi population for years. In 2022, the organization released 11 kiwis into the wild in Makara, a suburb about seven miles west of Wellington. Between February and May of 2023, another 52 birds were released, and 200 more are slated to be released over the next five years, reports Eva Corlett for the Guardian.
Along with reintroduction efforts, the project aimed to reduce threats from European stoats, also known as ermines. The mammals were brought to New Zealand in the 19th century in an attempt to eradicate another introduced creature: rabbits. But these weasel-like stoats are voracious predators and kill many of New Zealand’s native species, including kiwi chicks. Only about 5 percent of kiwi chicks survive to reach breeding age in areas where predators are not controlled, largely thanks to stoats. In areas under management, however, 50 to 60 percent survive. Knowing this, conservationists worked with 100 landowners across the bird’s 60,000-acre habitat to install 4,600 stoat traps.
Of the 63 adult kiwis now roaming the hilly farmlands of Makara, only about a quarter are being monitored—meaning more chicks will likely hatch in the near future. Conservationists will continue monitoring the two new chicks, though Ward tells the Guardian they still have a long way to go before they’re fully grown...
Over the years, the long-beaked birds have become a national symbol of New Zealand, with people who hail from the country often referred to as kiwis. The animals also hold special importance to the Māori people of New Zealand, who have cultural, spiritual and historic associations with the birds. Even the New Zealand dollar is sometimes referred to as the kiwi, and the bird is featured on the country’s dollar coin."
-via Smithsonian Magazine, December 6, 2023
#aotearoa#new zealand#kiwi#kiwi bird#endangered species#birds#ornithology#conservation#invasive species#good news#hope
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

Egrets rest among the Solar Panels, Jiangsu, Eastern China image credit: Agence France-Presse via: The Guardian Week in Wildlife
465 notes
·
View notes
Photo

A Journey of 6,000 Miles
Layan Albaz is one of thousands of Palestinian children who have lost limbs in Israeli air strikes—and one of the very few evacuated to the US for medical care. Check out our excerpt of the Atavist’s latest feature “Coming to America” and read Albaz’s story.
Dina Assaf sat in her car outside Chicago’s O’Hare International airport watching the terminal’s sliding doors open and close, open and close. She and her husband, Baha, had been scrambling to prepare for this moment and were exhausted, but in the back seat their three daughters were restless with excitement. Sara, Salma, and Sereen had circled this day—March 17, 2024—on their calendars weeks ago and were giddy that it had finally come. They jostled one another for the best view of the doors, hoping to be the first to spot the person they were there to pick up. She was a young girl like them—she had turned 14 just three days before—and from what the sisters had been told, she was very important.
The girl’s name was Layan Albaz, and she had a button nose and a soft voice. What the Assafs knew of her life came mostly from videos on the internet. In one clip, Layan described how she had lost two sisters, a niece, and a nephew in an Israeli air strike in Gaza. She used a wheelchair because injuries she sustained during the attack had forced doctors to amputate her legs. In another video, filmed by Agence France-Presse not long after the air strike, Layan’s face was mottled with burns. “I want them to give me real legs,” she whimpered, clutching an oxygen mask in one hand. “I don’t want fake legs.”
323 notes
·
View notes