#Africa agri-food systems
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How Kenya’s Investment in Macadamia Nuts is Driving Regional Export Growth
Discover how Kenya’s investment in macadamia farming and digital innovation has propelled the country to become a leading exporter, overcoming regulatory challenges and boosting agricultural growth. Explore the role of MSMEs and digital platforms in transforming Kenya’s macadamia sector, driving productivity, and enhancing market access for sustainable economic growth. Learn how Kenya’s macadamia…
#Africa agri-food systems#African food economy#AGRA 2024 report#agricultural financing Kenya#agricultural infrastructure investment#agricultural value chains#cash crops in kenya#digital agriculture Kenya#digital farming innovations#digital platforms for farmers#farm input distribution#food systems transformation#Hello Tractor Kenya#Kenya export diversification#Kenya macadamia farming#Kenya macadamia success#Kenyan agricultural exports#Kenyan farm management#M-Kulima platform#M-Pesa agriculture#macadamia exports#macadamia industry growth#macadamia market challenges#macadamia productivity#macadamia regulatory challenges#mechanization in farming#MSMEs economic growth#MSMEs in agriculture#private sector in agriculture#sustainable agriculture
1 note
·
View note
Text
Agritech Market: Trends, Growth, and Future Insights
What Is the Agritech Market?
Agritech (Agricultural Technology) refers to the use of advanced technologies like AI, IoT, drones, and precision farming to enhance agricultural productivity, sustainability, and efficiency. It helps optimize resource use, improve crop yields, and reduce environmental impact.
The global Agritech market is projected to grow from USD 22.1 billion in 2023 to USD 45.4 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 10.8%, driven by the need for food security, climate change challenges, and digital transformation in farming.

What Are the Key Applications of Agritech?
Precision Farming: Uses AI and IoT sensors for real-time monitoring and data-driven decision-making.
Vertical & Urban Farming: Maximizes space efficiency and reduces water usage.
Agricultural Drones & Robotics: Automates planting, spraying, and crop health monitoring.
Smart Irrigation Systems: Optimizes water use with AI-powered scheduling.
Agri-Biotechnology: Improves crop resilience with genetically enhanced seeds and bio-fertilizers.
Where Is the Agritech Market Growing the Fastest?
North America: A leader in smart farming innovations and agri-tech startups.
Europe: Strong government support for sustainable agriculture and food security.
Asia-Pacific: The fastest-growing market, driven by precision farming in India and China.
Latin America & Africa: Rising adoption due to increasing agribusiness investments.
What Are the Challenges in This Market?
High Initial Investment: Advanced technologies can be costly for small farmers.
Lack of Digital Infrastructure: Connectivity issues in rural areas slow adoption.
Regulatory & Data Privacy Concerns: Compliance issues with agricultural data usage.
What’s Next for the Agritech Market?
Expansion of AI & Blockchain in Agriculture: Enhancing transparency and efficiency in supply chains.
Growth in Alternative Protein & Agri-Biotech: Boosting food security with lab-grown and plant-based innovations.
Advancements in Climate-Resilient Farming: Developing adaptive solutions for changing weather patterns.
Conclusion
The Agritech Market is revolutionizing farming through AI, automation, and biotechnology. As agriculture embraces digital transformation, the industry is set for rapid growth, improving food production efficiency worldwide.
Looking to explore innovations in Agritech? Mark & Spark Solutions can help you stay ahead in this evolving sector. Visit our website for more details.
0 notes
Text
Tech for Good: How Startups Are Solving Critical Social Problems
Technology is becoming not just about being convenient or fun to use; today, in a fast-moving world, technology becomes a power for solving some of the most severe challenges facing this global community. Usually, they come from young innovators and socially-conscious entrepreneurs with start-ups and take on tasks as diverse as battling global hunger and poverty, isolation, cyberbullying, among many others. Take a look at how impactful these companies drive changes.

1. Innovation to Combat Global Hunger
Despite the strides the world has made, hunger remains a big problem. Many parts of the world still face the lack of access to food and a significant waste of food. Start-ups are now changing this narrative by leveraging technology to combat hunger and increase food sustainability.
Too Good To Go connects consumers with surplus food from restaurants and grocery stores to help reduce food waste and make affordable meals available.
Innovating agricultural technologies with an aim at maximizing crop yield while reducing loss are agri-tech startups; such innovations end up feeding many with a lesser resource.
Such efforts are not merely feeding the hungry but are transforming how the global food systems work.
2. Eradication of Poverty through Education and Employment
Poverty is not a simple problem, but startup companies have been quite creative with finding solutions to the root causes of poverty. Breaking the cycle of poverty involves several things: accessing good education or stable jobs, and new ventures are serving both ends.
Andela trains talented software developers from Africa and connects them with companies around the world. It empowers the individuals while boosting the local economy.
Kiva directly impacts the microloans that are provided to small businesses in developing countries. It helps entrepreneurs lift themselves and their communities out of poverty.
These startups show that tech and education can be used as a good force against poverty.
3. Social Isolation Among the older people
For many old people, loneliness is the real danger risk for the health, resulting in isolation and depression. Fortunately, startups come up with solutions to bridge this gap between old people and the rest of their communities.
Papa connects college students with older adults for companionship and help with daily tasks to reduce loneliness and provide a much-needed support system.
ElliQ, an artificial intelligence-powered robot, is also a companion to the older people, reminding them of things and entertaining them while also giving them health tips.
The new startups use technology to really change the lives of older people, making sure they are not lonely in their older years.
4. Combating Cyberbullying and Online Dangers
With the introduction of digital forums, cyberbullying and general online safety are increasing. More innovative tools offered by startups that help make online environments safer have become a response to this problem to safeguard young ones in particular.
Bark identifies the presence of cyberbullying or online hazards in text messages, emails, and social media by using Artificial Intelligence and thereby warns parents that something harmful might be present.
ReThink is the application and device that tackles teen texting, encouraging teens to think before they text, mainly avoiding sending upsetting or harassing messages.
These tech solutions are proactive in ensuring that the internet remains a safer, more respectful space.
5. Empowering Local Communities
Startups are realizing the potential need for giving local communities all the tools and resources available to them. These small businesses help people and communities in bringing about self-sufficiency and betterment in their lives.
iDE is focused on creating affordable, innovative tools for small-scale farmers across developing countries, thereby increasing productivity levels and improving livelihoods.
Impact Hub is a global network that equips entrepreneurs within local communities with mentorship, resources, and collaborative spaces in which to grow their businesses and solve societal challenges.
These startups are not just providing resources; they are actually empowering the locals and bringing sustainable, long-term change.
Tech for a Better Tomorrow
The power of startups to address social issues is beyond doubt. They are using technology not only for innovation but for making a real difference in the lives of people. They have reduced global hunger, stopped cyberbullying, and a lot more – redefining the role of business in society. A brighter future for an increasingly connected, compassionate, and sustainable world lies ahead as entrepreneurship focuses more and more on critical problems and solving them through innovation.
0 notes
Text
Triazole Fungicides Market Forecast, Size and Share by 2025-2033

The Reports and Insights, a leading market research company, has recently releases report titled “Triazole Fungicides Market: Global Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2025-2033.” The study provides a detailed analysis of the industry, including the global Triazole Fungicides Market share, size, trends, and growth forecasts. The report also includes competitor and regional analysis and highlights the latest advancements in the market.
Report Highlights:
How big is the Triazole Fungicides Market?
The global triazole fungicides market was valued at US$ 4.0 Billion in 2024 and is expected to register a CAGR of 4.5% over the forecast period and reach US$ 5.9 Billion in 2033.
What are Triazole Fungicides?
Triazole fungicides are a class of systemic fungicides widely used in agriculture to protect crops from fungal diseases by inhibiting the biosynthesis of ergosterol, an essential component of fungal cell membranes. Known for their broad-spectrum activity, triazoles are effective against a variety of fungal pathogens, including rusts, powdery mildew, and leaf spots, making them vital for the cultivation of cereals, fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants. These fungicides offer long-lasting protection due to their curative and preventive properties and are valued for their ability to enhance crop yield and quality. Common examples include tebuconazole, propiconazole, and difenoconazole, which are favored for their efficacy, versatility, and role in integrated pest management programs.
Request for a sample copy with detail analysis: https://www.reportsandinsights.com/sample-request/2552
What are the growth prospects and trends in the Triazole Fungicides industry?
The triazole fungicides market growth is driven by various factors and trends. The triazole fungicides market is experiencing steady growth driven by the increasing demand for effective crop protection solutions to combat fungal diseases in agriculture. The market benefits from the widespread use of triazoles in cereals, fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants, owing to their broad-spectrum efficacy, long-lasting protection, and ability to enhance crop yield and quality. Key market drivers include the growing need for food security, the rising adoption of integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, and the expansion of global agricultural production. However, concerns regarding resistance development and regulatory pressures related to pesticide residues are prompting the development of new formulations and alternative products. Overall, the market is expected to expand as innovation continues, with an emphasis on sustainable agricultural practices and the adoption of advanced fungicide technologies. Hence, all these factors contribute to triazole fungicides market growth.
What is included in market segmentation?
The report has segmented the market into the following categories:
By Product Typе
Epoxiconazolе
Triadimеnol
Propiconazolе
Prothioconazolе
Mеtconazolе
Cyproconazolе
Tebuconazolе
Flusilazolе
Paclobutrazol
By Crop Typе
Cеrеals and Grains
Oilsееds and Pulsеs
Fruits and Vеgеtablеs
Othеr Crop Typеs
By Application
Sееd Trеatmеnt
Soil Trеatmеnt
Foliar Spray
Chеmigation
Post-Harvеst
By Formulation Typе
Suspеnsion Concеntratе (SC)
Emulsifiablе Concеntratе (EC)
Wеttablе Powdеr (WP)
Solublе Liquid (SL)
Granulеs
North America
United States
Canada
Europe
Germany
United Kingdom
France
Italy
Spain
Russia
Poland
Benelux
Nordic
Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
China
Japan
India
South Korea
ASEAN
Australia & New Zealand
Rest of Asia Pacific
Latin America
Brazil
Mexico
Argentina
Middle East & Africa
Saudi Arabia
South Africa
United Arab Emirates
Israel
Rest of MEA
Who are the key players operating in the industry?
The report covers the major market players including:
BASF SE
Bayеr AG
DuPont
NIPPON SODA CO., LTD.
FMC Corporation
Sumitomo Chеmical Co., Ltd.
Vеrdеsian Lifе Sciеncеs
Cortеva Agrisciеncе
FMC Corporation
Syngеnta AG
Nufarm Limitеd
View Full Report: https://www.reportsandinsights.com/report/Triazole Fungicides-market
If you require any specific information that is not covered currently within the scope of the report, we will provide the same as a part of the customization.
About Us:
Reports and Insights consistently mееt international benchmarks in the market research industry and maintain a kееn focus on providing only the highest quality of reports and analysis outlooks across markets, industries, domains, sectors, and verticals. We have bееn catering to varying market nееds and do not compromise on quality and research efforts in our objective to deliver only the very best to our clients globally.
Our offerings include comprehensive market intelligence in the form of research reports, production cost reports, feasibility studies, and consulting services. Our team, which includes experienced researchers and analysts from various industries, is dedicated to providing high-quality data and insights to our clientele, ranging from small and medium businesses to Fortune 1000 corporations.
Contact Us:
Reports and Insights Business Research Pvt. Ltd. 1820 Avenue M, Brooklyn, NY, 11230, United States Contact No: +1-(347)-748-1518 Email: [email protected] Website: https://www.reportsandinsights.com/ Follow us on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/report-and-insights/ Follow us on twitter: https://twitter.com/ReportsandInsi1
0 notes
Text
ATLAS Launches Groundbreaking 2×30 Challenge at Davos: Doubling Investments in Africa’s Agri-Food Systems by 2030
Press Release – Paris, France – 20 January, 2025 – At this year’s World Economic Forum, ATLAS (Agricultural Transitions Lab for African Solutions, an initiative of the Paris Peace Forum) is unveiling the 2×30 Challenge, which calls for doubling annual investments in Africa’s agri-food systems by 2030 – from $50 billion to $100 billion. This is a transformative step toward building more productive…
0 notes
Text
Oxfam Calls on African Leaders to push for Inclusive Agricultural Policies at AU CAADP Summit in Kampala
AU CAADP Kampala Summit to Transform Agri-food Systems. The African Union Kampala Summit of the Comprehensive Africa Agriculture Development Program (CAADP) will be held from January 9 to 11, 2025 at the Speke Resort. Women constitute the majority of actors in Africa’s agricultural value chains but continue to face barriers such as unequal access to resources, limited policy representation, and…
0 notes
Text
Africa Agritech Market: Trends, Drivers, and Opportunities
The Africa agritech market is experiencing a transformative wave as technology meets agriculture, unlocking new potential for farmers and agribusinesses across the continent. With a rapidly growing population and increasing demand for food security, this market is ripe for innovation. This report explores the current landscape, highlighting key trends, challenges, opportunities, and market drivers.
Full Report At: https://www.xinrenresearch.com/regional-reports/africa-agritech-market/
Market Dynamics of Agritech in Africa
The agritech market in Africa is evolving due to a confluence of factors, including advancements in technology, changing consumer preferences, and the urgent need for sustainable agricultural practices. As African nations strive for food security and improved agricultural productivity, agritech solutions are stepping in to bridge the gap.
Innovations such as precision agriculture, mobile apps for farming advice, and automated farming equipment are gaining traction. These technologies not only enhance productivity but also contribute to sustainable farming practices that are vital for the continent's future.
Key Market Drivers
Population Growth and Urbanization Africa's population is projected to reach 2.5 billion by 2050, leading to increased food demand. Urbanization further drives the need for efficient agricultural practices to ensure food security for growing urban populations.
Technological Advancements The rise of digital technology, including mobile phones and the internet, is revolutionizing agriculture in Africa. Farmers now have access to valuable information, market prices, and weather forecasts, enabling better decision-making and increased productivity.
Government Initiatives Many African governments are implementing policies to promote agritech adoption. These initiatives include funding for research and development, subsidies for technology adoption, and partnerships with private sector players to foster innovation.
Investment from Private Sector There is a surge in investment from venture capital firms and agribusinesses looking to tap into the African agritech space. This influx of funding supports startups and established companies in developing innovative solutions tailored to local agricultural challenges.
Climate Change and Sustainability As climate change poses significant threats to agriculture, there is a pressing need for sustainable practices. Agritech solutions, such as drought-resistant crops and efficient water management systems, help farmers adapt to changing conditions while promoting environmental sustainability.
Key Trends in the Africa Agritech Market
Precision Agriculture The adoption of precision agriculture technologies is on the rise. Farmers are utilizing data analytics, satellite imagery, and IoT devices to monitor crop health, optimize resource use, and increase yields.
Digital Platforms for Market Access Digital platforms are connecting farmers with consumers, enabling direct sales and reducing reliance on middlemen. These platforms enhance transparency and improve farmers’ income by giving them access to broader markets.
Agri-Fintech Solutions Financial technology tailored for agriculture is gaining momentum. Innovative financing solutions, such as microloans and insurance products, are helping farmers access capital and manage risks effectively.
Challenges Facing the Market
Despite its potential, the Africa agritech market faces several challenges. Limited access to technology and infrastructure in rural areas can hinder adoption. Additionally, regulatory hurdles and lack of awareness among farmers about available technologies can slow market growth. Ensuring that solutions are affordable and accessible to smallholder farmers remains a significant challenge.
Opportunities for Growth
The future of the Africa agritech market is promising. As technology continues to evolve and investment increases, the potential for agritech solutions to transform the agricultural landscape is immense. Companies that focus on developing affordable, scalable, and user-friendly technologies will likely thrive in this emerging market.
Conclusion
The Africa agritech market is at a critical turning point. With a growing population, increasing demand for food security, and the rise of innovative technologies, the potential for growth is substantial. By embracing agritech solutions and fostering collaboration among stakeholders, Africa can revolutionize its agricultural sector and pave the way for a sustainable future.
This market represents more than just agricultural innovation; it embodies the hope for a food-secure Africa. Those who seize the opportunities and address the challenges will play a crucial role in shaping the continent's agricultural landscape for generations to come.
More Reports At : https://www.xinrenresearch.com/
0 notes
Text

Unlock the Nutritional Power of Pigeon Peas with Sahel Agri-Sol
September 18, 2024
Sahel Agri-Sol is pleased to invite global food and beverage manufacturers to explore the superior quality and versatility of our sustainably sourced pigeon peas from the fertile soils of Malawi and Tanzania. Headquartered in Abidjan, Ivory Coast, we bridge global markets with the rich agricultural products of the Sahel and East Africa, ensuring every ingredient reflects the traditions and sustainable practices of our partner communities.
By partnering with Sahel Agri-Sol, you’re investing in more than just ingredients. You’re supporting a supply chain founded on fair trade, ethical sourcing, and sustainable agriculture. Our pigeon peas enable you to create nutritious, high-value products that meet the needs of today’s health-conscious consumers while making a positive impact on smallholder farmers.
Why Choose Sahel Agri-Sol’s Pigeon Peas?
1. Nutrient-Rich & Versatile
Packed with protein, fiber, and essential amino acids, our pigeon peas are ideal for manufacturers focused on health and nutrition. Whether you're developing protein-rich snacks, gluten-free alternatives, or plant-based meals, pigeon peas provide the nutrition and adaptability today’s consumers’ demand. From pastas and flour to soups, canned goods, and even fermented products, pigeon peas can transform your product line.
2. Meeting the Growing Demand for Plant-Based Products
As the demand for plant-based proteins and healthier alternatives grows, pigeon peas are emerging as a key ingredient in meat substitutes, protein isolates, and bars. Incorporating pigeon peas into your products positions you to capture a growing market of vegan, vegetarian, and health-focused consumers.
3. Superior Quality, Grown with Care
Our pigeon peas are cultivated by smallholder farmers in Malawi and Tanzania using environmentally friendly practices. These regions offer optimal conditions, producing peas with a rich, earthy flavor and exceptional nutritional value. Sahel Agri-Sol’s dedication to sustainable farming means you’re sourcing responsibly while delivering premium quality to your consumers.
4. Ethical Sourcing & Inclusive Economic Growth
When you work with Sahel Agri-Sol, you support a fair-trade supply chain. Through direct partnerships with agricultural cooperatives, we ensure equitable compensation for farmers, empowering communities and promoting long-term growth. Choosing our pigeon peas means contributing to a socially responsible and ethical food system.
5. Endless Innovation Opportunities
Pigeon peas are a versatile base for a variety of innovative food products. From high-protein pasta to gluten-free baked goods and ready-to-eat meals, the possibilities are endless. Whether you’re entering new markets or enhancing your current product line, our pigeon peas offer endless potential for product differentiation and premium appeal.
Why Global Manufacturers Trust Sahel Agri-Sol
At Sahel Agri-Sol, sustainability and social responsibility are central to our mission. By choosing us, you gain access to high-quality, sustainably sourced pigeon peas while contributing to the well-being of rural farming communities in Africa. Our transparent supply chain guarantees the traceability of every ingredient, giving your customers confidence in your commitment to quality and ethical sourcing.
As the demand for health-conscious and sustainable food options grows, manufacturers need reliable partners who can deliver high-quality ingredients that meet these evolving needs. With Sahel Agri-Sol, you get both superior ingredients, and a partner dedicated to making a global impact.
Let’s Build a Healthier, More Sustainable Future Together
At Sahel Agri-Sol, we’re more than just suppliers—we’re your partners in innovation. By incorporating our pigeon peas into your products, you can offer consumers nutritious, versatile, and sustainable options while empowering farmers in Malawi and Tanzania. Our commitment to premium quality, sustainability, and inclusive growth makes us the ideal partner for your manufacturing needs.
Contact us today to discover how Sahel Agri-Sol’s pigeon peas can elevate your product line. Together, we can bring nutritious, sustainably sourced products to tables worldwide while making a lasting impact on the communities we support.
Sahel Agri-Sol
Hamdallaye ACI 2 000,
« BAMA » building 5th floor APT 7
Bamako
Mali
Phone: +223 20 22 75 77
Mobile: +223 70 63 63 23, +223 65 45 38 38
WhatsApp/Telegram global marketing and sales: +223 90 99 1099
Email: [email protected]
Web sites
English https://sahelagrisol.com/en
Français https://sahelagrisol.com/fr
Español https://sahelagrisol.com/es
简体中文 https://sahelagrisol.com/zh
عربي https://sahelagrisol.com/ar
Social media
Facebook https://www.facebook.com/sahelAgri-Sol
LinkedIn https://www.linkedin.com/company/sahel-agri-sol
BlueSky @sahelagrisol.bsky.social https://bsky.app/profile/sahelagrisol.bsky.social
YouTube https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCj40AYlzgTjvc27Q7h5gxcA
Sahel Agri-Sol, an agribusiness group headquartered in Abidjan, Ivory Coast, with operations spanning West and East Africa, is committed to bringing the finest agricultural products from the Sahel and surrounding regions to the global marketplace. Our mission is rooted in promoting inclusive economic growth, fostering sustainable development for farming communities, and preserving their cultural and environmental heritage.
By partnering closely with agricultural cooperatives and local producers across the Sahel, West, and East Africa, we guarantee fair compensation for their premium crops, driving prosperity and resilience in rural areas.
Photo: Pigeon Peas (Sahel Agri-Sol / public domain)
0 notes
Text
Top Fintech Companies in Kenya: Pioneering Financial Innovation
Kenya has emerged as a global leader in the fintech sector, driven by a robust ecosystem of innovative companies that are revolutionizing financial services. With a tech-savvy population and high mobile penetration, Kenya's fintech landscape is vibrant and rapidly evolving. Here, we spotlight some of the top fintech companies in Kenya making significant strides in financial inclusion, digital payments, and financial technology.

1. M-Pesa
Overview: Launched in 2007 by Safaricom, M-Pesa is the most well-known and widely used mobile money service in Kenya. It has revolutionized how Kenyans send and receive money, pay bills, and access financial services.
Key Features:
Mobile money transfers
Bill payments
Microfinancing
Integration with banks and financial institutions
Impact: M-Pesa has dramatically increased financial inclusion in Kenya, allowing millions of unbanked individuals to participate in the formal financial system. It is estimated that over 90% of Kenyans use M-Pesa, making it a crucial part of everyday life.
2. Tala
Overview: Tala is a mobile lending app that offers small, short-term loans to individuals who may not have access to traditional banking services. Using alternative data points like mobile phone usage and social connections, Tala assesses creditworthiness and provides instant loans.
Key Features:
Quick loan approval and disbursement
Flexible repayment options
No need for a formal credit history
Impact: Tala has empowered many Kenyans by providing quick and accessible credit. This has helped individuals manage emergencies, invest in small businesses, and improve their financial stability.
3. PesaPal
Overview: PesaPal is a leading online payment platform in East Africa, offering businesses and individuals a seamless way to conduct transactions online. It supports a wide range of payment methods, including mobile money, credit cards, and bank transfers.
Key Features:
Secure online payments
Integration with e-commerce platforms
Merchant services and invoicing
Event ticketing and booking services
Impact: PesaPal has facilitated the growth of e-commerce in Kenya by providing reliable and secure payment solutions. It supports thousands of businesses and has played a crucial role in the digital transformation of the Kenyan economy.
4. Cellulant
Overview: Cellulant is a pan-African fintech company providing mobile payments and banking solutions. It offers a suite of products designed to streamline digital payments for consumers, businesses, and governments.
Key Features:
Mobile banking and payment solutions
Digital payment gateway
Agri-tech solutions for farmers
Merchant and consumer financial services
Impact: Cellulant has enhanced financial access and convenience across Africa. Its innovative solutions in agriculture have also supported farmers by providing timely payments and market access, contributing to food security and economic growth.
5. Jumo
Overview: Jumo is a technology company that partners with banks and mobile network operators to provide financial services to underserved markets. It uses machine learning and AI to offer savings, lending, and insurance products.
Key Features:
Data-driven financial services
Savings and lending products
Financial education and literacy
Impact: Jumo has reached millions of people who previously had limited access to financial services. By leveraging technology, it has created a more inclusive financial ecosystem, helping individuals save, borrow, and protect themselves financially.
6. Branch
Overview: Branch is a mobile app that provides personal loans to individuals with a smartphone and a Facebook account. It uses smartphone data to assess creditworthiness and offer loans with flexible terms.
Key Features:
Instant loan approval
Flexible repayment terms
No collateral required
Credit score building
Impact: Branch has made borrowing more accessible and convenient for Kenyans, particularly those without access to traditional banking services. Its user-friendly app and quick loan disbursement have made it a popular choice for personal financing.
Conclusion
Kenya's fintech industry is a beacon of innovation, demonstrating how technology can transform financial services and enhance inclusion. Companies like M-Pesa, Tala, PesaPal, Cellulant, Jumo, and Branch are at the forefront of this revolution, providing solutions that are not only innovative but also impactful. As these companies continue to grow and evolve, they are set to further solidify Kenya's position as a global fintech hub.
0 notes
Text
The Future is Now: Exploring Modern Technology in Today's Agriculture

The agricultural sector is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by technological innovations that are reshaping how food is grown, monitored, and harvested. Technology's role in agriculture is more critical than ever as it helps tackle some of the most pressing challenges such as increasing productivity, managing resources efficiently, and ensuring sustainability. The integration of advanced tools and techniques promises to revolutionize the agricultural landscape, making it smarter and more resilient against the backdrop of global food demand and environmental concerns.
The intersection of technology and agriculture brings forth a promising synergy that balances productivity with sustainability. By leveraging technologies like precision farming, IoT, and artificial intelligence, modern farms can optimize resource use—such as water and fertilizers—reduce waste, and minimize their environmental impact. This not only boosts productivity but also ensures that agricultural practices are sustainable, preserving ecosystems and biodiversity while feeding the world.
This article aims to delve deep into the latest technological advancements in agriculture, highlighting how these innovations can be transformed into viable business opportunities for aspiring entrepreneurs. By exploring a range of modern tools and methodologies, we provide practical advice on navigating the agri-tech landscape, fostering innovation, and building sustainable agricultural enterprises that can thrive in today's competitive market.
Climate-Smart Agricultural Practices
Overview of Climate-Smart Technologies and Their Importance in Sustainable Farming
Climate-smart agriculture (CSA) encompasses a plethora of technologies and practices designed to increase productivity in an environmentally sustainable way. CSA technologies are crucial for adapting to and mitigating climate change impacts while improving farm yield and resilience. Innovations such as enhanced crop varieties, precision irrigation systems, and carbon capture methodologies are pivotal in making farming more sustainable and productive. These technologies not only help in reducing greenhouse gas emissions but also in optimizing the use of water and energy, crucial for the long-term sustainability of agriculture.
Examples of Innovative Solutions from the Smarter Climate Farmers Challenge
The Smarter Climate Farmers Challenge has spotlighted several groundbreaking initiatives that merge agricultural needs with sustainability. For instance, Alkama's biological crop treatment utilizes a consortium of soil microbiology to enhance crop resilience and productivity without synthetic chemicals. This approach not only boosts yield but also enriches soil health and captures carbon, aligning with both economic and environmental goals.
Another notable innovation is AMINI’s development of a digital infrastructure for smallholder farmers in Africa. By integrating satellite technology, AI, and machine learning, AMINI provides critical data on crop management and climate resilience, empowering farmers with the tools needed for better decision-making and improved agricultural outcomes.
Advanced Farming Technologies
Exploration of Cutting-Edge Tools
The agricultural sector is rapidly adopting advanced technologies that enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of farming practices. Key among these are AI-driven decision aids, satellite monitoring, and drone technology. AI-driven tools analyze vast amounts of data to provide insights on the best farming practices, predict crop diseases, and optimize resource allocation. Satellite monitoring offers a macro-view of agricultural lands, providing critical data on crop health, soil conditions, and environmental impacts. Drones complement these technologies by delivering micro-level insights such as crop surveillance, pest detection, and precise application of inputs like water, fertilizers, and pesticides.
Enhancing Resource Efficiency and Crop Management
These technologies play a crucial role in enhancing resource efficiency and improving crop management. For instance, satellite and drone imagery can detect areas of a field that are under stress due to lack of nutrients or water, allowing farmers to apply resources precisely where they are needed, thus minimizing waste. AI algorithms can process this data to make predictive analyses about the best times to plant and harvest, leading to better crop yields and reduced resource expenditure. The integration of these tools into farming operations leads to smarter, more sustainable agricultural practices that can respond dynamically to changing environmental conditions.
Indoor and Urban Farming Innovations
The Rise of Indoor Vertical Farming
Indoor vertical farming is revolutionizing the concept of farming within urban environments by using significantly less space and water than traditional farming methods. This technique involves stacking crops in vertical layers in a controlled environment, where factors such as light, temperature, and nutrients are precisely managed. The benefits are substantial, including higher yields due to the ability to grow crops year-round under optimal conditions, up to 70% less water usage compared to conventional methods, and the elimination of agricultural runoff.
Potential of Urban Farming Technologies
Urban farming technologies extend beyond just vertical farming. Innovations like rooftop gardens, hydroponics (growing plants in a water-based, nutrient-rich solution), and aquaponics (combining fish farming with hydroponics) are transforming unused urban spaces into productive agricultural hubs. These technologies not only help in making fresh produce more accessible in urban areas but also contribute to the sustainability of cities by reducing food transport distances, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and enhancing local food security.
Integration of Robotics and Automation
Application of Robotics in Agriculture
Robotics technology is increasingly becoming integral to modern farming operations. Robots are employed for a variety of tasks such as harvesting, planting, and monitoring crops. For example, autonomous tractors can plant seeds with precise spacing and depth, robotic harvesters can pick fruits without damaging them, and drone fleets can monitor crop health across large areas. These robots are equipped with sensors and cameras to perform their tasks efficiently and effectively.
Benefits of Automation
The automation of agricultural processes through robotics offers significant benefits. It reduces the need for manual labor, which can help address labor shortages and reduce the physical toll on workers. Automation also increases operational efficiency, as machines can work faster, for longer hours, and with greater precision than human laborers. This not only boosts productivity but also lowers production costs over time, providing a competitive edge to farms adopting these technologies.
Data Management and Predictive Analytics
Transforming Farming Decisions with Big Data and Analytics
The role of big data and analytics in agriculture cannot be overstated. By harnessing vast amounts of data—from soil sensors, weather stations, drone imagery, and more—farmers and agribusinesses are revolutionizing the way decisions are made across the agricultural spectrum. Predictive analytics tools process this data to forecast weather conditions, pest invasions, crop yields, and even market demands, enabling farmers to plan better and react more swiftly to changing conditions. This technology allows for the optimization of everything from planting schedules to irrigation systems, ensuring resources are used efficiently and crops grow under the best possible conditions.
Impact of Real-Time Data on Yields and Efficiency
The advent of real-time data collection in agriculture has dramatically improved operational efficiencies and crop yields. By continuously monitoring conditions on the ground, farmers can immediately adjust their strategies to address any emerging issues, such as altering irrigation levels in response to real-time weather changes or adjusting nutrient applications based on real-time soil feedback. This level of precision farming reduces waste, lowers costs, and increases the quantity and quality of agricultural output, proving essential for modern agribusinesses striving to meet global food demands sustainably.
Challenges and Opportunities for Entrepreneurs
Navigating High Costs and Technological Adaptation
While the benefits of modern agri-tech are clear, significant challenges remain, particularly regarding the high costs associated with implementing advanced technologies and the barrier of technological adaptation. For many farmers, especially those in developing regions or small-scale operations, the initial investment in high-tech equipment and the ongoing maintenance can be prohibitive. Additionally, there is often a steep learning curve associated with deploying new technologies, requiring significant training and support.
Future Trends and Entrepreneurial Opportunities in Agri-Tech
Looking forward, the potential for 5G technology in agriculture offers exciting possibilities for enhancing connectivity and data transfer speeds, which could revolutionize remote monitoring and management of agricultural operations. Similarly, cloud computing is set to play a pivotal role in farm management by allowing agribusinesses to efficiently store, process, and analyze vast amounts of data, driving further innovations and efficiencies. Entrepreneurs have the opportunity to lead the way in developing solutions that address these challenges and harness these advanced technologies, positioning themselves at the forefront of the agricultural sector's future.
In Conclusion
The journey through modern agricultural technologies reveals a landscape brimming with transformative potential. Innovations in robotics, data analytics, indoor farming, and climate-smart practices are not just reshaping how food is produced—they are redefining the very essence of farming. For entrepreneurs, the message is clear: there lies immense opportunity in leveraging these technologies to innovate and drive sustainability in agriculture. By embracing these tools, visionary leaders can help ensure a resilient, efficient, and sustainable agricultural future, meeting global food needs while protecting our planet.
0 notes
Text
Global Digital Agriculture Market Size Expected To Reach USD 41.48 Billion With CAGR 11% By 2030
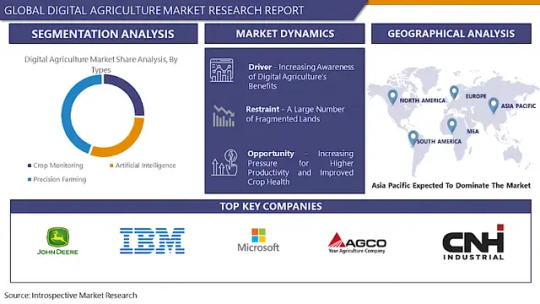
The Global Digital Agriculture Market size is expected to grow from USD 18 billion in 2022 to USD 41.48 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 11% during the forecast period (2023-2030).
Digital Agriculture also known as e-agriculture or smart farming is a tool that collects, stores, analyzes, and shares electronic data and information in agriculture digitally. It is the integration of digital technology into crop management and livestock and other processes related to managing food resources and cultivating activities. Digital agriculture includes precision agriculture. Unlike precision agriculture, digital agriculture impacts the entire agri-food value chain before, during, or after on-farm production.
Top Key Players for Digital Agriculture Market:
Deere & Company (U.S.), IBM Corporation(U.S.), CNH Industrial (U.S.), Microsoft Corporation (U.S.), AGCO Corporation (U.S.), Raven Industries (U.S.), COFCO International (Switzerland), Agrofy (South Africa),Eden Farm (Indonesia), HummingBird Technologies (England), Cranswick PLC (U.K) and Other Major Key Players.
To Understand Business Strategies, Request For a Sample Report @
https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/checkout/?user=1&_sid=16588
Updated Version 2024 is available our Sample Report May Includes the:
Scope For 2024
Brief Introduction to the research report.
Table of Contents (Scope covered as a part of the study)
Top players in the market
Research framework (structure of the report)
Research methodology adopted by Worldwide Market Reports
Moreover, the report includes significant chapters such as Patent Analysis, Regulatory Framework, Technology Roadmap, BCG Matrix, Heat Map Analysis, Price Trend Analysis, and Investment Analysis which help to understand the market direction and movement in the current and upcoming years.
Segmentation Analysis of the Digital Agriculture Market:
By Type
Crop Monitoring
Artificial Intelligence
Precision Farming
By Technology
Peripheral
Core
By Application
Field Mapping
Crop Scouting
Weather Tracking
Drone Analytics
Others
Inquire for a Discount on this Premium Report @
https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/inquiry/16588
Regional Analysis of the Digital Agriculture Market:
North America (US, Canada, Mexico)
Eastern Europe (Bulgaria, The Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Rest of Eastern Europe)
Western Europe (Germany, UK, France, Netherlands, Italy, Russia, Spain, Rest of Western Europe)
Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, The Philippines, Australia, New Zealand, Rest of APAC)
Middle East & Africa (Turkey, Bahrain, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, UAE, Israel, South Africa)
South America (Brazil, Argentina, Rest of SA)
Key Industry Development:
In November 2022, AGCO Corporation launched a brand new online tool called Geo-Bird to help farmers around the world independently plan and optimize their global navigation satellite system (GNSS) machine guidance lines.
In October 2021, CNH Industrial launched an innovative platform named AGXTEND for digital agriculture solutions in Brazil. AGXTEND develops and provides ground-breaking technologies that allow farmers to extend their efficiency, and sustainability of agribusiness by precision farming, and thereby their economic success.
For in-depth competitive analysis, buy now @
https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/checkout/?user=1&_sid=16588
About us:
Introspective Market Research (introspectivemarketresearch.com) is a visionary research consulting firm dedicated to assisting our clients to grow and have a successful impact on the market. Our team at IMR is ready to assist our clients to flourish their business by offering strategies to gain success and monopoly in their respective fields. We are a global market research company, that specializes in using big data and advanced analytics to show the bigger picture of the market trends. We help our clients to think differently and build better tomorrow for all of us. We are a technology-driven research company, we analyze extremely large sets of data to discover deeper insights and provide conclusive consulting. We not only provide intelligence solutions, but we help our clients in how they can achileve their goals.
Contact us:
Introspective Market Research
3001 S King Drive,
Chicago, Illinois
60616 USA
Ph no: +1-773-382-1049
Linkedin| Twitter| Facebook
Email:[email protected]
0 notes
Text
Building Africa’s Agricultural Resilience in the Face of Climate Change
Africa’s food systems hold global significance, impacting both worldwide food security and climate resilience. However, ensuring food resilience in Africa presents undeniable challenges. The connection between climate resilience and food systems becomes evident as climate change poses threats to agri-food systems, resulting in crop failures, increased food prices, loss of job opportunities, and…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Agritech Market Size, Growth Trends, and Future Outlook (2024-2032)
Introduction
The Agritech market is transforming the global agricultural landscape by integrating technology into traditional farming practices. From precision farming and farm management software to IoT-based solutions and vertical farming, Agritech innovations are revolutionizing how we grow, harvest, and distribute food. Rising global demand for sustainable food production and advancements in agri-biotechnology are further driving the growth of this dynamic market.

Market Overview
Current Market Size and Growth Trends
The global Agritech market was valued at USD 19.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 11.7% from 2024 to 2032, reaching approximately USD 52.8 billion by 2032. The market’s rapid growth is fueled by increasing adoption of smart agriculture solutions, rising investments in agricultural technology startups, and the growing need to address food security challenges.
Regional Market Insights
North America: A leading region, driven by the rapid adoption of precision farming, IoT solutions, and automation technologies in agriculture.
Europe: Strong growth due to supportive government policies for smart farming and the increasing focus on sustainable agricultural practices.
Asia-Pacific: The fastest-growing market, with countries like China, India, and Japan investing heavily in Agritech solutions to boost agricultural productivity.
Latin America & Africa: Emerging markets with significant potential, driven by the growing need for food security and advancements in smart irrigation and crop monitoring.
Key Market Drivers
Rising Demand for Food Security: With a growing global population, the need for efficient and sustainable food production systems is increasing.
Technological Advancements in Agriculture: IoT, drones, AI, and robotics are transforming the agricultural sector, making it more efficient and productive.
Government Initiatives and Subsidies: Governments worldwide are promoting Agritech solutions to boost productivity and reduce environmental impact.
Increased Investment in Agritech Startups: Venture capital firms are actively funding innovations in the agricultural sector, driving growth and new solutions.
Leading Players in the Agritech Market
Several key players are transforming the Agritech space with innovative solutions and technologies:
John Deere (USA) – A leader in precision agriculture and advanced farm machinery solutions.
Trimble Inc. (USA) – Specializes in precision farming technology and IoT-based solutions.
Corteva Agriscience (USA) – Focuses on seed technologies, crop protection, and digital agriculture solutions.
AgriNext (India) – Known for smart irrigation and farm automation solutions.
FarmLogs (USA) – Provides farm management software and data-driven insights for farmers.
Challenges and Roadblocks
Despite the significant potential, the Agritech market faces several challenges:
High Initial Investment: The cost of implementing Agritech solutions can be prohibitive for small and medium-sized farmers.
Limited Awareness and Technical Skills: In developing regions, many farmers lack the knowledge and resources to adopt Agritech.
Connectivity Issues in Rural Areas: Limited internet connectivity and infrastructure remain barriers to adopting smart farming solutions.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns: The increasing use of IoT and data-driven solutions raises concerns about data security and privacy.
Future Outlook
The Agritech market is poised for substantial growth, with key trends shaping its future:
Increased Adoption of Vertical and Indoor Farming: Reducing land dependency and increasing year-round crop production.
Growth of Blockchain in Agriculture: Ensuring transparency and traceability in the food supply chain.
AI and Machine Learning for Predictive Analysis: Helping farmers make data-driven decisions for better crop management.
Sustainability and Climate-Smart Agriculture: Focusing on reducing environmental impact and adapting to climate change.
Conclusion
The Agritech market is on the brink of a technological revolution, driven by advancements in precision agriculture, smart farming, and data analytics. Companies that invest in innovation and sustainability will be at the forefront of this transformation, paving the way for a more efficient and resilient agricultural sector.
About Us
Mark & Spark Solutions is committed to providing cutting-edge market insights and business solutions. Visit our website at https://marksparksolutions.com/ to learn more about our services and how we can help your business thrive in this evolving landscape.
0 notes
Text
An Overview of Southern Africa Agriculture: Challenges and Opportunities

An Overview of Southern Africa Agriculture: Challenges and Opportunities Introduction Southern Africa is a region that faces various challenges and opportunities in the field of agriculture. With a diverse climate and fertile lands, the region has the potential to be a major player in the global agricultural industry. However, there are several obstacles that need to be addressed for the agricultural sector to reach its full potential. This article will provide an overview of the challenges faced by Southern Africa and the opportunities that lie ahead. Challenges in Southern Africa Agriculture One of the main challenges faced by Southern Africa agriculture is the lack of access to modern technology and farming techniques. Many farmers in the region still rely on traditional methods of farming, which are often inefficient and unsustainable. The lack of infrastructure, including proper irrigation systems and storage facilities, further exacerbates the issue. Anoher challenge is the climate change impact. With increasing temperatures and unpredictable rainfall patterns, farmers in Southern Africa are faced with significant challenges in maintaining crop productivity. Droughts and floods have become more frequent, causing considerable crop losses and hindering food production. Furthermore, the prevalence of pests and diseases poses a constant threat to agriculture in the region. Inadequate pest control measures and limited access to quality fertilizers and pesticides further hamper agricultural productivity. Forest fire. Burned trees after forest fires and lots of smoke Opportunities in Southern Africa Agriculture Despite the challenges, there are several opportunities for the agricultural sector in Southern Africa. One of the key opportunities is the growing demand for agricultural products both within the region and globally. With a rapidly increasing population, there is a higher demand for food, creating a market for Southern African farmers. Moreover, the region's proximity to major export markets, including Europe, provides a favorable opportunity for agricultural exports. Another opportunity lies in the diversification of crops. Southern Africa has the potential to grow a wide variety of crops, including grains, fruits, vegetables, and cash crops. By embracing crop diversification, farmers can mitigate the risks associated with climate change and market fluctuations, as well as tap into new markets. Furthermore, the development of agri-businesses and value-added processing can also contribute to the growth of the agricultural sector. By adding value to raw agricultural products through processing and packaging, farmers can increase their income and create employment opportunities. Middle aged caucasian farmer stands at canola field Conclusion The agricultural sector in Southern Africa presents significant challenges, but also great potential for growth and development. By addressing the issues related to technology adoption, infrastructure development, climate change adaptation, and pest control, Southern African countries can harness the opportunities available to them. With proper investment in research and development, infrastructure, and farmer education, Southern Africa can transform its agricultural sector and become a key player in global food production. By working towards sustainable and inclusive agriculture, the region can alleviate poverty, enhance food security, and contribute to economic growth. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Q: What are the main challenges faced by the agricultural sector in Southern Africa? A: The main challenges include limited access to modern farming techniques, inadequate infrastructure, climate change impact, and pests and diseases. Q: What opportunities exist for the agricultural sector in Southern Africa? A: Opportunities include growing demand for agricultural products, crop diversification, and development of agri-businesses and value-added processing. Q: How can Southern Africa overcome the challenges in agriculture? A: Addressing technology adoption, improving infrastructure, implementing climate change adaptation measures, and enhancing pest control practices are essential steps. Q: What potential benefits can Southern Africa gain by developing its agricultural sector? A: The development of the agricultural sector can lead to poverty reduction, improved food security, increased income for farmers, and economic growth. Q: Are there specific policies or initiatives in place to support Southern Africa agriculture? A: Yes, there are various policies and initiatives, such as the Southern African Development Community (SADC) Agricultural Policy, aimed at supporting agriculture in the region. References: - Climate Change Impact on Agriculture in Southern Africa Read the full article
0 notes
Text
50 African female policy practitioners joins fellowship to work on gender-responsive agri-food policies
50 female policy practitioners from Burkina Faso, Ethiopia, Madagascar, Mozambique, Rwanda and Senegal join a Fellowship designed to help catalyze the design and implementation of gender-responsive policies in Africa’s agri-food systems. 2009 AWARD Fellow, prof Fetien Abera on the left, with barley farmers in Ethiopia: Photo credit AWARD African Women in Agricultural Research and Development…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Link
#ACRIFA#AdaptingtoClimateChangeAfrica#AfricaClimateSummitNairobi#AfricanDevelopmentBank#AfricanDevelopmentBankACRIFA#AfricanRiskCapacityACRIFA#AfricanUnionClimateInitiative#AgricultureResilienceInsuranceAfrica#AkinwumiAdesinaClimateInsurance#ClimateDisasterManagementAfrica#ClimateRiskInsuranceAfrica#ComorosClimateResilience
0 notes