#16S rRNA
Text
Lobster shell microbes, epizootic shell disease, and climate change manuscript is published!
A collaborative paper on lobster shell bacteria has just been published in the journal iScience: “Water temperature and disease alters bacterial diversity and cultivability from American Lobster (Homarus americanus) shells.” This paper investigates what happens to bacterial communities on healthy and sick lobsters as they experience different water temperatures for a year.
You can read the paper…

View On WordPress
#16S rRNA#aquaculture#climate and microbes#climate change#epizootic shell disease#Lab Work#lobsters#maine#preprint#shell bacteria#UMaine#Updates
1 note
·
View note
Photo

A new resource has been released that enables the comparison of microbial 16S rRNA and shotgun metagenomics data. The resource is a web-based tool that allows users to upload and compare two datasets, and to visualize the results as a heat map. The tool is designed to help researchers identify microorganisms that are present in different samples.
#Featured#News#OMICs#Topics#Translational Medicine#fault#microbial 16S rRNA#shotgun metagenomics#web-based tool#compare datasets#visualize results
0 notes
Text

Limestone jewel: A new colourful karst-dwelling pitviper (Serpentes: Viperidae: Trimeresurus) from the poorly explored borderlands of southern peninsular Thailand
Sabira S. Idiiatullina, Parinya Pawangkhanant, Tanapong Tawan, Thanawut Worranuch, Bunyarit Dechochai, Chatmongkon Suwannapoom, Tan Van Nguyen, Lawan Chanhome, Nikolay A. Poyarkov
Abstract
We describe a new species of pitvipers from Trang Province of Thailand, near the Thailand–Malaysian border, based on morphological and molecular (2427 bp from cyt b, ND4, and 16S rRNA mitochondrial DNA genes) lines of evidence...
The new species is currently known from a small karstic area in the Nakawan Range spanning the border of Thailand and Malaysia, in particular in limestone forests in Trang and Satun provinces (Thailand); it likely also occurs in the adjacent parts of Perlis State (Malaysia).
Our study also suggests that the taxonomy of T. kanburiensis species complex requires further studies; in particular our study suggests that the status of populations from Chumphon Province of Thailand and Pulau Langkawi Island of Malaysia should be re-assessed.
Read the paper here:
Limestone jewel: A new colourful karst-dwelling pitviper (Serpentes: Viperidae: Trimeresurus) from the poorly explored borderlands of southern peninsular Thailand (arphahub.com)
118 notes
·
View notes
Text
Eukaryogenesis
Presently, it is understood that there are three domains of life. There is the eukarya, which is the domain consisting of the highest degree of complexity per cell and constitutes organisms such as plants, animals, and fungi. The other two are sub-branches of the prokarya, wherein the individual cells are less complex than the eukarya, and these are the bacteria and the archaea. Archaea, specifically, are a relatively new discovery (in terms of the scientific timescale) as their existence was first reported by Dr. Carl Woese in 1977.
Over time, the tree of life has undergone many changes, but the current most popular form is the below image, which was published in Nature Microbiology in 2016 and is based on 16S rRNA sequences (these ribosomal RNAs are ubiquitous in all life, and thus are a solid candidate for tracking evolutionary lineages)
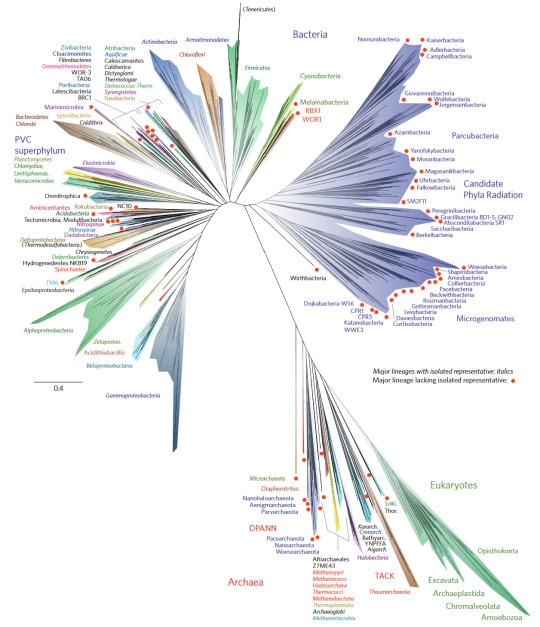
There are two interesting features of this tree. The first is the upper right branch, which consists entirely of candidatus bacterial species. Candidatus indicates the the organism has been identified, but it has not been isolated and grown in a homoculture. Some species may never escape this category as it stands as some are obligate syntrophs, meaning that they cannot be grown without a co-culture that provides necessary nutrients. The second feature is the bottom right corner, in which the archaea and eukarya are located on the same arm, with the eukaryotes branching off just after the Asgard archaea.
An interesting feature of archaeal species is that they are a sort-of middle ground between the bacteria and the eukarya. What I mean by this is that, despite being prokaryotes like bacteria, they contain proteins that are more eukaryote-like. Additionally, the rRNA of some Asgard archaea actually contains elongation segments, something previously considered a trait exclusive to eukaryotes.
With these cursory points in mind, a current hypothesis for an aspect of eukaryogenesis (the origin of eukarya), specifically the aquisition of the mitochondria and/or the chloroplast, is that an archaeal species and a bacterial species were closely symbiotic to the point that the archaea engulfed the bacteria and fully incorporated it into its metabolism and replication cycle. This hypothesis is called "endosymbiosis."
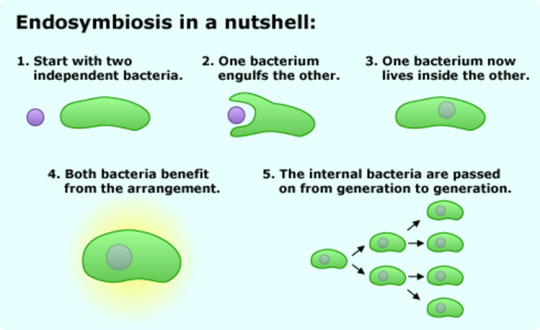
Evidence for the mitochondria and chloroplast having their origins as bacterial species is the presence of a double membrane (one would have been the bacteria's, and one would have been the proto-eukaryote's), their own distinct ribosomes, and their own DNA.
How exactly this occurred is hotly debated, but two methods of engulfment include standard phagocytosis, and the other involves filaments of cytoplasm-containing membrane called "blebs" that could slowly build up around the symbiote. An example of the latter has been observed in the species Candidatus Prometheoarchaeum syntrophicum, strain MK-D1, which is an example of Lokiarchaeota (a subsection of the Asgard archaeota). In the paper "Isolation of an archaeon at the prokaryote-eukaryote interface" by Itachi et al. (2020), it was observed to grow blebs around its syntrophs, namely Halodesulfovibrio bacteria and Methanagenium archeaon.
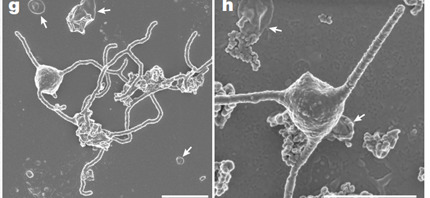
As might be gathered by its classification as Candidatus, it was incapable of growth without its syntrophs due to an "incomplete" metabolism where the syntrophs covered the crucial gaps.
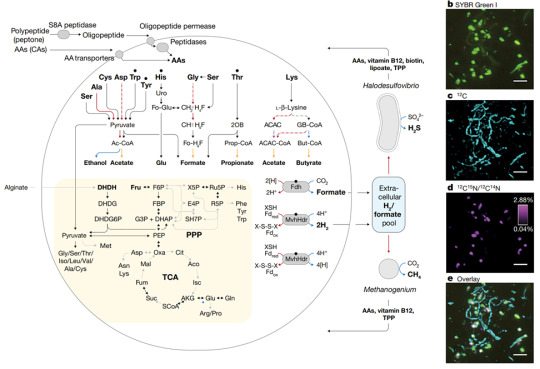
Based on their results, they proposed their own model for Endosymbiotic Eukaryogenesis, which they dubbed "Entangle, Engulf, Endogenize."
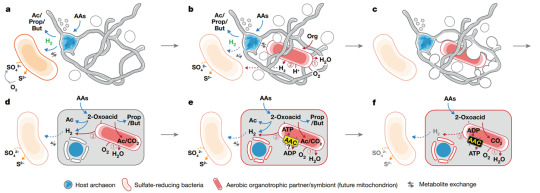
However, it is important to note that these cells were grown in optimized growth conditions. Originally, these cells came from a deep-sea sediment core, meaning that they are more accustomed to minimal nutrient conditions. As such, the optimized growth conditions may have resulted in the formation of these blebs as the cells struggled to self-regulate under overly nutrient-rich conditions. So, as always, more research would need to be done on these cells to make sure the bleb formation was not simply a side-product of lab growth conditions. Furthermore, this only accounts for one aspect of eukaryogenesis and does not account for the formation of the nucleus.
#If you need help accessing any of the sources just lmk#If you have any questions on the subject also feel free to ask#microbiology#eukaryogenesis#eukaryotes#cells#biochemistry#science#literature review
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bactéries en chasse - Une équipe de recherche découvre un organisme unicellulaire "impossible"
See on Scoop.it - EntomoNews
Une équipe de chercheur·euses découvre un organisme unicellulaire "impossible"
03.09.2024
"... « Le séquençage du génome d'Uabimicrobium helgolandensis nous a également permis de formuler de nouvelles hypothèses sur le mécanisme moléculaire de l'absorption des bactéries proies », explique Jogler. Il considère les planctomycètes prédateurs comme l'Archaeopteryx microbien, un organisme pont entre les procaryotes et les eucaryotes, et est convaincu que les planctomycètes ont joué un rôle dans l'eucaryogenèse, peut-être même dans l'origine de la vie elle-même."
Note: Cet article a été traduit à l'aide d'un système informatique sans intervention humaine. LUMITOS propose ces traductions automatiques pour présenter un plus large éventail
------
NDÉ
L'étude
“Candidatus Uabimicrobium helgolandensis”—a planctomycetal bacterium with phagocytosis-like prey cell engulfment, surface-dependent motility, and cell division | mBio, 27.08.2024 https://journals.asm.org/doi/full/10.1128/mbio.02044-24
Carmen E. Wurzbacher Jonathan Hammer, Tom Haufschild, Sandra Wiegand, Nicolai Kallscheuer, Christian Jogler
Image : Overview on the cell biology and phylogeny of “Ca. U. amorphum” SRT547 as well as the novel isolate “Ca. U. helgolandensis” HIEnr_7. Phagocytosis-like uptake of surrounding prey bacteria by “Ca. U. amorphum” (large cell) (a); white arrows indicate the prey bacterium being internalized. Cell division of “Ca. U. amorphum” (b), and “Ca. U. helgolandensis” HlEnr_7 (c). Two opposite cell poles move apart until only a thin, thread-like connection remains (red arrows) that finally disrupts. 16S rRNA gene sequence- (d) and multi-locus sequence analysis (MLSA)- (e) based phylogenies showing the deep branching of the “Ca. Uabimicrobium” clade within the phylum Planctomycetota.
0 notes
Text
Microorganisms, Vol. 12, Pages 1820: Profile of Bacterial Communities in Copper Mine Tailings Revealed through High-Throughput Sequencing
Mine-tailing dumps are one of the leading sources of environmental degradation, often with public health and ecological consequences. Due to the complex ecosystems generated, they are ideal sites for exploring the bacterial diversity of specially adapted microorganisms. We investigated the concentrations of trace metals in solid copper (Cu) mine tailings from the Ovejería Tailings Dam of the National Copper Corporation of Chile and used high-throughput sequencing techniques to determine the microbial community diversity of the tailings using 16S #rRNA gene-based amplicon sequence analysis. The concentrations of the detected metals were highest in the following order: iron (Fe) > Cu > manganese (Mn) > molybdenum (Mo) > lead (Pb) > chromium (Cr) > cadmium (Cd). Furthermore, 16S #rRNA gene-based sequence analysis identified 12 phyla, 18 classes, 43 orders, 82 families, and 154 genera at the three sampling points. The phylum Proteobacteria was the most dominant, followed by Chlamydiota, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, and Firmicutes. Genera, such as Bradyrhizobium, Aquabacterium, Paracoccus, Caulobacter, Azospira, and Neochlamydia, showed high relative abundance. These genera are known to possess adaptation mechanisms in high concentrations of metals, such as Cd, Cu, and Pb, along with nitrogen-fixation capacity. In addition to their tolerance to various metals, some of these genera may represent pathogens of amoeba or humans, which contributes to the complexity and resilience of bacterial communities in the studied Cu mining tailings. This study highlights the unique microbial diversity in the Ovejería Tailings Dam, including the discovery of the genus Neochlamydia, reported for the first time for heavy metal resistance. This underscores the importance of characterizing mining sites, particularly in Chile, to uncover novel bacterial mechanisms for potential biotechnological applications. https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/12/9/1820?utm_source=dlvr.it&utm_medium=tumblr
0 notes
Text
Metagenomics Market - Forecast(2024 - 2030)
Metagenomics Market Overview
Metagenomics Market size is estimated to reach $1.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 16.2% during the forecast period 2022-2027. Metagenomics is the examination of genetic material reclaimed directly from environmental samples. The expansive field may also be specified as environmental genomics, eco-genomics or community genomics. Shotgun metagenomic sequencing is a comparatively novel environmental sequencing technique utilized to analyze thousands of organisms in parallel and completely sample all genes, offering acumen into community biodiversity and function. 16S rRNA gene sequencing is typically restricted to recognizing bacteria at the genus level (e.g. Bifidobacteria). De novo assembly has been a necessary instrument in current investigations in metagenomics viral analysis. Glycoside hydrolases (GHs) are amidst the industrially significant enzymes that are widely explored by way of metagenomics owing to their very great expedience and significance in food and additional industrial sectors. Whole-genome sequencing offers added information on the nature and localization of antimicrobial resistance factors and on their dissemination possibility by horizontal gene delivery, and on genes connecting to virulence and biological fitness. Interoperable data will play a principal role in the forthcoming utilization of whole genome sequencing and metagenomic data.
The COVID-19 pandemic is set to drive the Metagenomics Market owing to the extensive utilization of technologies like Metagenomics in pandemic hazard computations to detect the molecular alterations in pathogens at the time of their worldwide rise, which could help in the forecast of rising hotspots, populations at risk, and the pathogens under genetic evolution as per the research article issued in Future Science, 2021. The burgeoning interest of researchers in related new research fields like metatranscriptomics, metaproteomics, and metabolomics has inspired microbiologists to investigate related workflows` in conjunction with novel techniques like shotgun metagenomic sequencing and is set to propel the growth of the Metagenomics Market during the forecast period 2022-2027. This represents the Metagenomics Industry Outlook.
Report Coverage
The report: “Metagenomics Market Forecast (2022-2027)”, by Industry ARC, covers an in-depth analysis of the following segments of the Metagenomics Market.
By Product: Sequencing And Data Analytics Services, Kits And Reagents, Others.
By Technology: Sequencing Driven, Function Driven.
By Application: Human Health, Environmental, Others.
By Geography: North America (the U.S, Canada, and Mexico), South America (Brazil, Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Rest of South America), Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Russia, and Rest of Europe), Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia & New Zealand, and Rest of Asia-Pacific), and Rest Of The World (Middle East, Africa).
Request Sample
Key Takeaways
Geographically, North America Metagenomics Market accounted for the highest revenue share in 2021 and it is poised to dominate the market over the period 2022-2027 owing to the existence of a soaring count of pharmaceutical and biotechnological firms developing new and effective metagenomic platforms in conjunction with novel techniques like shotgun metagenomic sequencing in the North American region.
Metagenomics Market growth is being driven by the technological advancements in DNA sequencing in conjunction with the development of novel techniques like shotgun metagenomic sequencing. However, the soaring cost of complete metagenomics is one of the major factors hampering the growth of the Metagenomics Market.
Metagenomics Market Detailed Analysis on the Strength, Weakness, and Opportunities of the prominent players operating in the market will be provided in the Metagenomics Market report.
Metagenomics Market Segment Analysis – By Product:
The Metagenomics Market based on products can be further segmented into Sequencing And Data Analytics Services, Kits And Reagents, and Others. The Kits And Reagents Segment held the largest market share in 2021. This growth is owing to the considerable count of kits and reagents being introduced and utilized to back the increasing demand for library preparation workflows from research laboratories. The boost in the rate of application and the great infiltration in conjunction with the extensive application of shotgun metagenomic sequencing is further propelling the growth of the genome engineering segment.
Furthermore, the Sequencing And Data Analytics Services segment is estimated to grow with the fastest CAGR of 16.9% during the forecast period 2022-2027 owing to the accelerated and considerable cost minimization in next-generation sequencing which has productively expedited the growth of sequence-based metagenomics in conjunction with the soaring application of shotgun metagenomic sequencing.
Inquiry Before Buying
Metagenomics Market Segment Analysis – By Technology:
The Metagenomics Market based on technology can be further segmented into Sequencing Driven and Function Driven. The Sequencing Driven Segment held the largest market share in 2021. This growth is owing to the soaring application of this technology. The burgeoning acceptance of this technology may be ascribed to the onset of new bioinformatics-associated solutions, which make workflows easy and offers accelerated outcomes. shotgun metagenomic sequencing permits researchers to exhaustively sample all genes in all organisms existing in a given complex sample. Surging endeavors to keep up a standard database and increase in the count of metagenome samples accumulated at data repositories are further propelling the growth of this segment.
Furthermore, the Function Driven segment is estimated to grow with the fastest CAGR of 17.1% during the forecast period 2022-2027 owing to the increasing application of function-driven metagenomics for protein screening applied to antibiotic resistance and vitamin manufacture in conjunction with the proliferating application of shotgun metagenomic sequencing.
Metagenomics Market Segment Analysis – By Geography:
The Metagenomics Market based on geography can be further segmented into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and the Rest of the World. North America (Metagenomics Market) held the largest share with 36% of the overall market in 2021. The growth of this region is owing to the surging spend on R&D. The extensive acceptance of metagenomic diagnostic, an expanding count of next-generation sequencing(NGS) based research endeavors in conjunction with increased application of shotgun metagenomic sequencing and the existence of key players like Illumina Inc., in the region are propelling the growth of the Metagenomics market in the North American region.
Furthermore, the Asia-Pacific region is estimated to be the region with the fastest CAGR rate over the forecast period 2022-2027. This growth is owing to factors like consistent developments performed to build up the bioinformatics infrastructure and genomic landscape in nations like India and China. The considerable fluctuation in climate and environment in the region together with the heightening application of shotgun metagenomic sequencing is fuelling the progress of the Metagenomics market in the Asia-Pacific region.
Schedule a Call
Metagenomics Market Drivers
Increased Application Of Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing Is Projected To Drive The Growth Of Metagenomics Market:
Shotgun metagenomic sequencing developed by Illumina Inc., permits researchers to completely sample all genes in all organisms existing in a given complex sample. The technique allows microbiologists to assess bacterial diversity and discover the profusion of microbes in different environments. Shotgun metagenomics also offers a means to investigate unculturable microorganisms that are otherwise hard or impossible to evaluate. Unlike capillary sequencing or PCR-based techniques, next-generation sequencing (NGS) permits researchers to sequence thousands of organisms in parallel. With the capability to integrate abundant samples in a single sequencing run and acquire high sequence coverage per sample, NGS-based metagenomic sequencing can discover very low abundance members of the microbial community that may be unnoticed or are too high-priced to recognize utilizing additional techniques. The surging application of shotgun metagenomic sequencing is fuelling the growth of the Metagenomics Market during the forecast period 2022-2027.
Benefits Of 16S rRNA Sequencing Are Expected To Boost The Demand Of Metagenomics:
16S rRNA Sequencing is a typical amplicon sequencing technique utilized to recognize and compare bacteria existing within a given sample. The prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene is almost 1500 bp long, with nine variable regions integrated between conserved regions. Variable regions of the 16S rRNA gene are generally utilized for the phylogenetic classification of genus or species in different microbial populations. An essential advantage of 16S rRNA Sequencing is that it offers an affordable method to recognize strains that may not be discovered utilizing conventional techniques. Unlike capillary sequencing or PCR-based techniques, next-generation sequencing (NGS) is a culture-free technique that allows investigation of the complete microbial community within a sample. 16S rRNA NGS permits microbiologists to accomplish genus-level sensitivity for metagenomic examinations of bacterial populations. The advantages of 16S rRNA Sequencing are driving the growth of the Metagenomics Market during the forecast period 2022-2027.
Metagenomics Market Challenges
Databases For Metagenomic Data Present Challenges To The Growth Of The Metagenomics Market:
Absorbing the sequence that will be produced by metagenomics projects will be demanding for the nucleic acid sequence data archive. Adding to the archiving challenge, it is evident that the community will need novel, secondary databases if the data are to be utilized efficiently. Only a specially-designed database will be able to provide constant storage and querying of the abundant metadata that metagenomic sequences require. The investigation of metagenomic sequences will need computational programs that are best provided in the context of a specially-designed database, for example, programs for the clustering of metagenomic sequence reads or for time-series analysis. And metagenomic data must be combined with data from distinct projects, like satellite data on ocean temperatures and time-series data on alterations in ocean salinity. This issue is hampering the growth of the Metagenomics Market.
Buy Now
Metagenomics Market Landscape:
Product launches, technological advancements, collaborations, mergers and acquisitions, financing in R&D activities, partnerships, and joint ventures are key strategies adopted by players in this Market. Metagenomics top 10 companies include:
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
QIAGEN
Illumina, Inc.
Promega Corporation
Novogene Co., Ltd.
Takara Bio, Inc
Oxford Nanopore Technologies
Arc Bio, LLC.
Eurofins Scientific
Zymo Research
Acquisitions/Product Launches:
In November 2021, QIAGEN declared the inclusion of StableScript™ to the OEM portfolio. The versatile reverse transcriptase is planned for application in one-step RT-qPCR and long-range RT-PCR and is accessible to order in bulk amounts. The launch of reverse transcriptases has permitted polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to be adapted to RNA and the establishment of cDNA libraries from mRNA.
In October 2021, QIAGEN N.V. declared the introduction and CE marking of QIAreach® QuantiFERON®-TB test for tuberculosis (TB) infection, to assist in accomplishing TB removal targets worldwide by boosting access to effortless and trustworthy TB testing, specifically in great burden countries, low-resource regions. A breakthrough in the battle against a pathogen estimated to be carried by over two billion people globally established on the proven QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus technology, QIAreach® QuantiFERON®-TB is a portable instrument that allows the ultrasensitive digital discovery of TB infection with an end-to-end workflow that is clear and cost-efficient and raises access to trustworthy Interferon Gamma Release Assay (IGRA) testing. QIAGEN will target regions that encounter a huge burden of the ailment, and where procuring access to laboratory infrastructure and resources for testing is restricted.
In July 2021, QIAGEN N.V. declared the introduction of the Workflow Configurator, allowing researchers in the life sciences to effortlessly and speedily discover the best solutions to make their experiments perfect. Purchasers simply select their application, biological starting material, analyte, and analysis type. In seconds, the configurator arranges by way of hundreds of possible products to detect the most appropriate workflow and related products.
#Metagenomics Market#Metagenomics Market size#Metagenomics industry#Metagenomics Market share#Metagenomics top 10 companies#Metagenomics Market report#Metagenomics industry outlook
0 notes
Text
Can Alterations in Gut Microbiota Serve as Biomarkers for Predicting Mental Health Disorders?
The gut-brain axis mediated by gut microbiota represents bidirectional communication network in gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system this link suggests that changes in gut microbiota could serve as biomarkers for mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety highlighting its vital function and potential impact (Duan et al., 2022; Jia et al., 2020).
Likewise, significant effect has been discovered through recent studies that individuals with mental health disorders have experienced faster recovery compared to the control sample suggesting high value of impact through supplementation and balance of microbiota (Duan et al., 2022; Järbrink-Sehgal & Andreasson, 2020), forming high potential in predictive value of specific microbial taxa as modification in gut microbiota has been linked to positively affect mental health and recovery time compared to individual with an unbalanced microbiota (Yan et al., 2021). Therefore, active manipulation of microbiota levels provider can support individuals in faster and more efficient recovery.
youtube
Although specific role of gut microbiota in mental health is not well understood nor can be predicted due to individual differences or response; this research aims to further investigate and explore this topic through active alteration of gut microbiota via introduction of probiotics and prebiotics within participant’s daily diet. This can offer an opportunity to observe participants response to therapy and its respond marked as a predictor of mental health recovery time and state particularly when considering anxiety and depression.
A groundbreaking understanding of gut and mental health
This understanding can be a groundbreaking step for therapists and psychologist to incorporate its finding within their treatment planning and work collaboratively with nutritionist to formulate a more effective and personalized treatment plan making informed decisions with an integrated treatment plan effective for long-term mental health management and recovery time, potentially helping individuals shorten therapy with less reliant on medication through a holistic treatment plan that incorporated a multidimensional perspective incorporating both body and mind.
Formulating this collaboration can be the ground for a new personalized treatment plan. This study theorizes that a balance gut microbiota can serve as a supportive factor for individuals to progress their mental health recovery journey and achieve a desired response through therapy with a lower medication dependency. Therefore, the focuses will be set to explore the potential role of gut microbiota alterations in daily diets seeking to understand its interaction and/or involvement when exploring disorders such as anxiety and depression in via gut microbiota manipulation through supplementation.
youtube
Variables Definition
The variables in this study are defined as follows:
Independent variable (IV): Given the state of this research in this study the IV has been set as the dietary intervention with and without probiotic and prebiotic supplementation. These conditions will be explored in two set levels:
Control condition: Through standard diet Participants carry their regular daily diet without any added supplementation.
experimental condition: Participants diet will be supplemented with probiotics and prebiotics adjusted by a nutritionist to ensure proper supplementation.
Dependent variables (DV): Three primary DVs have been set for this study that will be measured and monitored throughout the study:
Gut microbiota composition: The gut microbiota composition will be measured through 16S rRNA sequencing of stool samples defined by changes within the microbial taxa.
Mental health status: To assess participants mental health status the researcher will utilize standardized scales such including Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) and Beck Depression Inventory (BDI).
Physiological stress markers: The physiological stress markers will include cortisol levels and inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein, measured through blood samples.
Set conditions will be defined throughout the study by participants adherence to dietary protocols assigned.
Theoretical Framework and Literature Review
Halverson and Alagiakrishnan (2020) explored gut-brain axis as a well-established pathway impacting mental health through gut microbiota influencing brain function and behavior a process in how gut microbes interact with central nervous system demonstrating significant effect on mental health by neural, endocrine, and immune pathways. Highlighting the modulation of neurotransmitters and other neuroactive compounds through gut bacteria leading to changes in mental and behavioral state.
youtube
Likewise, dietary components offer therapeutic approach through altering gut microbiota with potential in improving mental health disorders via healthy diet (Xiong et al., 2023). This study explored the positive effects of diet and its components via gut microbiota by alleviating and/or reducing symptoms of mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. Xiong et al. (2023) highlights the importance of a healthy dietary plan in support of having a healthy gut microbiota composition an important factor in maintaining a healthy mental health as Implementing a healthy and positive interventions, a promising approach to treat mental health disorders.
Chang et al. (2024) mini review employed faecal microbiota transplants to emphasize the significant progress via mechanistic pathway involved in rebalancing gut microbiota showcasing the positive impact in mental health. Gates et al. (2022) also examined changes in diet and its effects by modifying gut microbiota emphasizing positive impact on mental health suggesting a healthy alteration indicating noteworthy response with Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Boscaini et al. (2023) explored whey proteins consumption affecting microbiota with positive impact on mental health. Boscaini et al. (2023) highlights mechanisms through which whey protein can enhances the production of beneficial gut bacteria and the production of neuroactive substances that positively affect mental health.
youtube
Gut microbiota and mental health
Collective evidence from current research suggests strong link between gut microbiota and mental health. However, as stated by Grajek et al. (2022) the current body of research lacks an understanding on how mental health professionals can utilize such knowledge in formulating treatment plans.
Furthermore, Vindegaard et al. (2021) and Moqbil et al. (2021) highlighted the need for targeted research on predictive value of gut microbiota alterations for a better and more efficient mental health recovery. Madison and Kiecolt-Glaser (2019) in their study emphasized the role of stress and depression in regard to gut microbiota with the inclusion of cortisol and C-reactive protein as dependent variables, Merlo et al. (2024) additionally supported the positive effect of probiotic and prebiotic supplementation with positive impact on mental health.
Thus, this study aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how alteration in gut microbiota can serve as mean to support individuals who are suffering from mental health disorders and support them in their treatment. This study hypothesizes that incorporating probiotic and prebiotic to daily diet can support individuals in a faster and more personalized recovery from mental health disorders and support positive changes in microbiota composition correlating with mental health improvement. This research has the potential to revolutionize mental health treatment offering a new pathway for therapist to work collaboratively with nutritionist providing scientific basis for the integration of nutritional interventions to not replace traditional treatment but rather to enhance and personalize treatment planing and reduce the possible dependency of medication.
Therefore this study seeks to bridge the gap by allowing therapist and other mental health professionals to better understand the existing link among body and mind, supporting individuals with long-term mental disorders with the hope of more effective response to treatment and recovery creating the foundation for a true personalized treatment plan link with both body and mind.
Existing research limits the connection of gut microbiota and mental health in supporting mental health professionals working collaboratively with nutritionist to support individuals in their recovery journey; therefore, filling a crucial gap by investigating direct impact of targeted gut microbiota manipulation though supplementation of proper probiotic and prebiotic while observing the changes in mental health recovery outcomes.
Although past research established correlation between gut microbiota and mental health disorders (Vindegaard et al., 2021; Moqbil et al., 2021; Merlo et al., 2024) though very limited research has been conducted on its predictive value by intentional alteration of gut microbiota for a faster mental health recovery. Previous research has established correlations between gut microbiota and mental health; though, there is limited research on the predictive value of intentional microbiota alterations for mental health disorder recovery. This study aims to provide a foundation for integrating nutritional interventions into psychological treatment plans, an area that remains underexplored in current clinical practice.
youtube
Research Design and Hypotheses
Research Design
Utilizing randomized controlled trial (RCT) design participants are randomly selected and assigned. The selection of this design helps assess the impact of specialized dietary intervention impacting gut microbiota and mental health outcomes. Both groups will also receive cognitive behavioral therapy as an intervention on a weekly basis to support their specific needs such as anxiety or depression.
youtube
Methods and Systems
Participant Recruitment
For this study all participants will be recruited through social media platforms such as Instagram and the utilization of advertisement. This can benefit the study by allowing the researcher to be specific in criteria and target their audience. The age group for participants will be 18-65 clinically diagnosed with anxiety and/or depression.
Exclusion criteria: Individuals that are currently and actively taking antibiotics and/or Individuals who are diagnosed with either gastrointestinal diseases and/or individuals with any form of past gut surgery.
Intervention
The intervention group will receive specialized diet rich in probiotics and prebiotics for three months. This diet will be reviewed and administered by a nutritionist to ensure accuracy. The control group will continue with usual diet without receiving supplements.
Data Collection
The gut microbiota composition will be analyzed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing sampled through stool collection at the beginning of the experiment and at the end of the study after the 3-month duration of the study.
Psychological testing and assessments will also be conducted by a mental health providers at the beginning of the study to measure beginning levels of anxiety and depression utilizing standardized scales and at the end of the treatment duration to indicate the beginning and the ending of the levels. This study will incorporate the Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) and Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) as an assessment for this research
Physiological stress markers for this study will be measured via cortisol levels and C-reactive protein measured through blood samples at the beginning and the end of treatment.
Data Analysis
The changes in psychological and physiological markers of mental health will be correlated with changes in gut microbiota composition of participants. Statistical analyses will include t-tests and ANOVA to compare changes also regression analysis will be utilized to predict mental health outcomes based on gut microbiota.
Hypothesis
This study proposes the following hypotheses:
H₁: Participants who are supplemented with probiotic and prebiotic will show more beneficial gut microbiota revealing a lower levels of stress markers and an improved scores on psychological assessments with a faster recovery time vs the participants who are not receiving the probiotic and prebiotic.
H₂: Positive alterations in gut microbiota composition will positively correlate with improvements in mental health that can suggesting specific changes in microbial taxa is an effective biomarker for not only predicting but also managing mental health disorders.
Method
Participants
This study will have 100 adult participants who are between the age of 18 and 55 years. This sample size was selected due to several factors. First to understand the proper number of participants a power analysis was conducted while assuming medium effect size (d=0.5), an alpha level of 0.05, and desired power of 0.80 using G*Power software for our analyses suggesting minimum sample size of 84; therefore, the sample size was increased to 100 to support the study and count for potential attrition and to further enhance statistical power. Likewise this sample size aligns with the possibility of participants dropping out. Furthermore, the larger sample also allows for a more diverse representation of participants, enhancing the external validity of our results.
Furthermore the sample size can support the study in detecting significant differences among each group the experimental and the control group creating balance and the need for rigorous statistical analysis while accounting for potential dropout and non-compliance typically seen in dietary intervention studies.
Participants Selection
The selection of participants for this study will be through the use of social media platform. The researchers will utilize Instagram as a mean to recruit participants by incorporating advertisement. Utilizing advertising campaign will allow the researcher to fine tone their criteria and target the correct audience who fall into the participants criteria and are targeted to have a higher chance of interaction with the advertisement. This process will emphasize on the voluntary aspect of this study with all its potentials informing the participants thoroughly on all potential risks and the benefits of the study prior to giving written informed consent.
To support the diversity of the study and achieve balance within the desired demographic the recruitment advertisement and the consent form will be available in multiple language including but not limited to English, Spanish, and Mandarin. Further efforts will be made to incorporate underrepresented groups.
Sampling Procedure
For this study the participants are recruited via non-probabilistic, convenience sampling method. Although, this may limit generalizability of the finding vs random sampling; however, due to its feasibility and effectiveness for online settings this method has been chosen. After the completion of the initial response all participants for this study will undergo a screening process to better verify current diagnoses and their suitability based on inclusion and exclusion criteria.
youtube
Group Assignment
Upon successful screening of all active participants, they will be randomly assigned to one of two groups helping the study to achieve and ensure equal distribution within each active groups. The control group will be instructed to maintain their diet without any modification or alteration throughout the study. However, the experimental group will be instructed to adhere a diet supplemented with probiotics and prebiotics selected for them based on their levels provided to them by a nutritionist. To ensure randomization this study will utilized Microsoft Excel and create a computer-generated table to ensure unbiased assignment this code will be created by the research team to ensure ability of replication.
Group Assignment Code: =IF(B2<MEDIAN($B$2:$B$n), "Control", "Experimental")
youtube
Apparatus/Materials and Procedure
Apparatus: The device that will be utilized for this study will be centrifuge Model AC-234 for blood samples processing and stool samples the study will utilize a microbiota analysis system 16S rRNA sequencing kit provided by GenTech Labs.
Materials: The study will utilize two main forms of data collection instruments:
Dietary Intake Questionnaire: The dietary intake questionnaire will be primarily built for the use of this study to support the study in tracking adherence of the participants to the provided diet intervention provided in Appendix A.
Psychological Measures: The use of Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) and Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) also will be utilized in this study to assess participants mental health state both at the beginning of the experiment and at the end of the study. and end of the study period.
Procedure: The specific procedure for this study has been developed in 4 steps to ensure clarity and replicability of future studies.
Initial Screening and Group Assignment: upon completion of informed consent by the participants all active participants will be screened via BAI and BDI to confirm current diagnoses of anxiety or depression which then allows the researcher to randomly assign participants to one of two groups, control or experimental.
Dietary Intervention: The participants who are within the experimental group will be provided a diet enriched with probiotic and prebiotics vs the participants in control group who will receive their usual diet. During the study all participants will be monitored on a weekly basis via Zoom meeting to ensure compliance and will have access to a direct line to the researcher in case of any needed adjustment or intervention.
Biological and Psychological Assessments: At the end of the 3-month period of this study the researcher will collect biological samples from the participants that include a blood and stool sample the blood sample is analyzed for cortisol and C-reactive protein levels and stool samples will be analyzed for microbiota composition; also during this time the researcher with conduct psychological assessment.
Data Analysis: The provided data from this study will then be analyzed using a t-test to compare the mean between the two group and analyzed for the difference, the researcher will then utilize ANOVA for a more in-depth analysis within each given groups. Finally, regression analysis will be utilized to explore the predictive relationship of gut microbiota changes and mental health outcome.
Follow-Up: To ensure participants engagement and active participation weekly Zoom meetings will be conducted to follow up with participants and ensure the need if any adjustment is needed to be made or any support during the study. Likewise, this can support participants to increase motivation.
Ethical Considerations and Informed Consent
Prior to the start of the study all participants will be required to sign an informed consent that covers the purpose, procedures, potential risks and benefits. This can ensure full involvement of participants and acknowledgment of all aspects of this study while addressing all questions that participants may have in regard to their participations and their participation reequipment and how their data will be collected and furthermore protected while being used solely for the research. The consent form also assures all participants of their voluntary involvement and ability to withdraw at any point of the study.
youtube
All data will be protected and saved in a local computer that is in a secure location and will only be handled by the researchers to comply with all HIPPA criteria ensuring that all participants information is and will remain confidential. Upon the completion of the study all names and identifying information will be removed.
youtube
Original Paper and Presentation:
References
Boscaini, S., Skuse, P., Nilaweera, K. N., Cryan, J. F., & Cotter, P. D. (2023). The ‘Whey’ to good health: Whey protein and its beneficial effect on metabolism, gut microbiota and mental health. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 133, 1-14. 10.1016/j.tifs.2022.12.009
Duan, Y., Wu, X., Yang, Y., Gu, L., Liu, L., Yang, Y., Zhou, J., Wu, C., & Jin, F. (2022). Marked shifts in gut microbial structure and neurotransmitter metabolism in fresh inmates revealed a close link between gut microbiota and mental health: A case-controlled study. International Journal of Clinical and Health Psychology, 22(3), 100323. 10.1016/j.ijchp.2022.100323
Chang, M., Chang, K. T., & Chang, F. (2024). Just a gut feeling: Faecal microbiota transplant for treatment of depression – A mini-review. SAGE Publications. 10.1177/02698811241240308
Gates, E. J., Bernath, A. K., & Klegeris, A. (2022). Modifying the diet and gut microbiota to prevent and manage neurodegenerative diseases. Reviews in the Neurosciences, 33(7), 767-787. 10.1515/revneuro-2021-0146
Grajek, M., Krupa-Kotara, K., Białek-Dratwa, A., Sobczyk, K., Grot, M., Kowalski, O., & Staśkiewicz, W. (2022). Nutrition and mental health: A review of current knowledge about the impact of diet on mental health. Frontiers in Nutrition (Lausanne), 9, 943998. 10.3389/fnut.2022.943998
Halverson, T., & Alagiakrishnan, K. (2020). Gut microbes in neurocognitive and mental health disorders.Annals of Medicine (Helsinki), 52(8), 423-443. 10.1080/07853890.2020.1808239
Järbrink-Sehgal, E., & Andreasson, A. (2020). The gut microbiota and mental health in adults. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 62, 102-114. 10.1016/j.conb.2020.01.016
Jia, W., Zhen, J., Liu, A., Yuan, J., Wu, X., Zhao, P., Zhao, L., Li, X., Liu, Q., Huang, G., & Xu, A. (2020). Long-Term Vegan Meditation Improved Human Gut Microbiota. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2020, 9517897. 10.1155/2020/9517897
Madison, A., & Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K. (2019). Stress, depression, diet, and the gut microbiota: human–bacteria interactions at the core of psychoneuroimmunology and nutrition. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 28, 105-110. 10.1016/j.cobeha.2019.01.011
Merlo, G., Bachtel, G., & Sugden, S. G. (2024a). Gut microbiota, nutrition, and mental health. Frontiers in Nutrition (Lausanne), 11, 1337889. 10.3389/fnut.2024.1337889
Moqbil, S., Niedobylski, S., Laszczak, K., Warchoł, K., & Mikos, E. (2021). The gut microbiota and mental health. Journal of Education, Health and Sport, 11(9), 304-309. 10.12775/JEHS.2021.11.09.037
Vindegaard, N., Speyer, H., Nordentoft, M., Rasmussen, S., & Benros, M. E. (2021). Gut microbial changes of patients with psychotic and affective disorders: A systematic review. Schizophrenia Research, 234, 1-10. 10.1016/j.schres.2019.12.014
Xiong, R., Li, J., Cheng, J., Zhou, D., Wu, S., Huang, S., Saimaiti, A., Yang, Z., Gan, R., & Li, H. (2023). The Role of Gut Microbiota in Anxiety, Depression, and Other Mental Disorders as Well as the Protective Effects of Dietary Components. Nutrients, 15(14), 3258. 10.3390/nu15143258
Yan, R., Andrew, L., Marlow, E., Kunaratnam, K., Devine, A., Dunican, I. C., & Christophersen, C. T. (2021). Dietary Fibre Intervention for Gut Microbiota, Sleep, and Mental Health in Adults with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Scoping Review. Nutrients, 13(7), 2159. 10.3390/nu13072159
#Gut Microbiota#eating for mental health#foods for mental health#Gut-Brain Axis#Probiotics#Prebiotics#Holistic Health#Nutritional Therapy
0 notes
Text
Alcanivorax borkumensis and Bioremediation: The Actual Perspective of a Vintage Bacteria

Opinion
Approximately twenty-six years after its discovery, Alcanivorax borkumensis and the hydrocarbonclastic bacteria present themselves as one of the most efficient microbiological tools offered by nature to be used in the environmental recovery processes (bioremediation) of areas contaminated by oil and its derivatives. However, the careful study of the physiological and metabolic properties of this bacterium and the development of modern technologies for environmental recovery are of primary importance for achieving increasingly better performance (maximum degradation in the shortest possible time). Twenty-six years ago, in 1998 Yakimov et al. reported the isolation and characterization from a sediment collected in the island of Borkum (Germany), of a new bacterium strain named Alcanivorax borkumensis, an unusual marine microorganism able to grow using as only carbon and energy sources a highly restricted spectrum of substrates, predominantly alkanes [1]. This discovery of this bacterium is the beginning of an important advancement in microbiological research and at the same time, in the technology for the development of strategies for bio-recovery of environments polluted by hydrocarbons (bioremediation). The isolation of Alcanivorax correspond to the identification a one eco-physiologically unusual group of marine hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria named Obligate Hydrocarbonoclastic Bacteria (OHCB) comprising, overtime, different bacterial genera, such as Cycloclasticus, Oleiphius, Oleispira, Thalassolituus and clearly Alcanivorax. Within a short period of time, was massive the isolation of bacteria related to Alcanivorax, or detection of its 16S rRNA gene sequences, from samples taken from surface water, shallow and deep sea water bodies, sediments, hydrothermal vents and mud volcanoes, ridge flank crustal fluids and grey whale carcass, in corals, sponges and aquaculture-poisoning dinoflagellates. Sequences of Alcanivorax like bacteria have also been detected in a few terrestrial environments that share relevant properties (salinity, presence of hydrocarbons) with marine ecosystems.
Read more about this article: https://crimsonpublishers.com/eimbo/pdf/EIMBO.000643.pdf
Read more Crimson Publishers Google Scholar Articles: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=5CwCZSMAAAAJ&citation_for_view=5CwCZSMAAAAJ:j8SEvjWlNXcC
#marine biology#crimson publishers#oceanography crimson#marine crimson#crimsonpublishers#water#ocean
1 note
·
View note
Text
Lobster shell microbes, epizootic shell disease, and climate change preprint manuscript is now online
Lobster shell microbes, epizootic shell disease, and climate change preprint manuscript is now online
It’s been a few years in the making, but our draft manuscript on lobster shell microbes, epizootic shell disease, and climate change is available online as a preprint (not yet peer reviewed)! You can read the preprint here, and the summary is below.
I joined this project back in the summer of 2020, when I was given a large 16S rRNA gene sequence dataset of bacterial communities from the shells…

View On WordPress
#16S rRNA#aquaculture#climate and microbes#climate change#epizootic shell disease#lobsters#maine#preprint#shell bacteria#UMaine#Updates
1 note
·
View note
Text
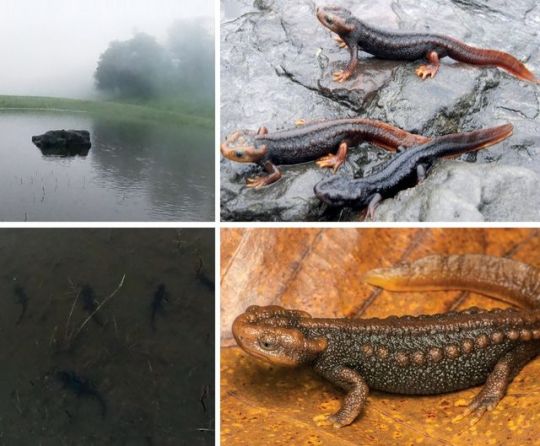

A new cryptic species of Tylototriton (Amphibia, Caudata, Salamandridae) from mysterious mountain lakes in Manipur, north-eastern India
Ht. Decemson, Hmar Tlawmte Lalremsanga, Premjit Singh Elangbam, Mathipi Vabeiryureilai, Parag Shinde, Jayaditya Purkayastha, Dmitriy V. Arkhipov, Andrey M. Bragin, Nikolay A. Poyarkov
An integrative taxonomic analysis combining molecular and morphological lines of evidence revealed a new cryptic species in the Tylototriton verrucosus species group from Manipur, north-eastern India.
The new species was previously confused with T. himalayanus and T. verrucosus. Tylototriton zaimeng sp. nov. can be distinguished from its congeners by medium body size, head massive and wide with rounded snout and very wide and protruding supratemporal bony ridges and a well-developed sagittal ridge, short limbs not overlapping when adpressed along body, wide and not segmented vertebral ridge distinct, 13–14 pairs of rib nodules, brown colouration with dull orange to yellowish-brown markings on head, vertebral ridge, rib nodules, palms, soles, vent and ventral tail ridge and by vomerine teeth organised in two distinctly curved bell-shaped series.
Phylogenetic analysis of the ND2 and 16S rRNA mtDNA genes confirmed the placement of the new species to the Clade I of the subgenus Tylototriton and suggested it is a sister species of T. panwaensis and T. houi (p-distance 3.0% in ND2 gene).
The range of the new species is restricted to the Khongtheng Mountain Range and is isolated from the range of T. panwaensis and T. houi in northern Myanmar and southern China, respectively. We suggest the new species to be considered as Vulnerable (VU) in the IUCN Red List.
Read the paper here:
A new cryptic species of Tylototriton (Amphibia, Caudata, Salamandridae) from mysterious mountain lakes in Manipur, north-eastern India (pensoft.net)
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
Whole genome sequence and 16S rRNA gene amplicon metagenomics of enhanced in-situ reductive dechlorination at a tetrachloroethene-contaminated superfund site
The application of environmental DNA analysis techniques to guide the bioremediation strategy for tetrachloroethene-contaminated groundwater is exemplified by the North Railroad Avenue Plume (NRAP) Superfund site located in New Mexico, USA. Enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) was selected as the remedy due to the presence of tetrachloroethene biodegradation byproducts, organohalide respiring genera Dehalococcoides and Dehalobacter, and associated reductive dehalogenase genes detected prior to remediation. DNA extracted from groundwater samples collected prior to remedy application and after four, 23 and 39 months was subjected to 16SrRNA gene amplicon and whole genome sequencing (WGS). The goals were to compare the potential of these methods as tools for environmental engineers and to highlight how advancements in DNA techniques can be used to understand ERD. The response of the indigenous NRAP microbiome to the injection and recirculation of electron donors and hydrogen sources is consistent with results obtained from microcosms, dechlorinating consortia, and other contaminated sites. WGS detects three times as many phyla and six times as many genera as 16S rRNA gene amplicons. Both techniques reveal abundance changes in Dehalococcoides and Dehalobacter that reflect organohalide form and availability. No methane was detected before remediation, its appearance after biostimulation corresponds to the increase in methanogenic Archaea. Assembly of WGS reads produced scaffolds containing reductive dehalogenase genes from Dehalococcoides, Dehalobacter, Dehalogenimonas, Desulfocarbo, and Desulfobacula. Anaerobic and aerobic cometabolic organohalide degrading microbes that increase in abundance at NRAP include methanogenic Archaea, methanotrophs, Dechloromonas, and Xanthobacter, some of which contain hydrolytic dehalogenase genes. Aerobic cometabolism may be supported by oxygen gradients existing at the aquifer-soil interface or by microbes that have the potential to produce O2 via chlorite dismutation. Results from next-generation sequencing-based methods are consistent with current hypotheses regarding syntrophy in environmental microbiomes and reveals novel taxa and genes that may contribute to ERD. http://dlvr.it/T8kS3l
0 notes
Text
Fwd: Workshop: SapeloIsland_US.eDNA_SciComm.Aug4-10
Begin forwarded message:
> From: [email protected]
> Subject: Workshop: SapeloIsland_US.eDNA_SciComm.Aug4-10
> Date: 31 May 2024 at 05:12:37 BST
> To: [email protected]
>
>
>
> "Telling Stories Through Data" Workshop
> August 4-10, 2024
> UGA Marine Institute on Sapelo Island
>
> Workshop Website: https://bit.ly/TSTD2024
>
> Apply to participate (form closes on Friday June 14, 2024):
> https://ift.tt/iDcBuUx
>
> The TSTD workshop series is designed to foster practical skills in both
> bioinformatics and science communication, training participants in how
> to "tell stories through data." Each weeklong workshop will be centered
> around two overarching questions: How do you find the story? and What
> do you do with the story? Morning sessions (led by Holly Bik, Associate
> Professor at the University of Georgia) will focus on how these questions
> are applied to bioinformatics data analyses, guiding participants in how
> to visualize data, conduct appropriate statistical analyses, and build
> narratives for scientific manuscripts. Afternoon sessions (led by Virginia
> Schutte, freelance science communicator) will provide complementary
> training on storytelling for public audiences, teaching participants how
> to identify compelling public narratives and prepare science outreach
> products using a variety of digital media tools. This workshop is
> targeted towards graduate students and postdoctoral researchers, and
> participants are expected to have some basic familiarity with command
> line tools and scientific programming (e.g. Unix, R, and/or Python). The
> 2024 TSTD workshop will be focused on analysis of eDNA Metabarcoding data
> (e.g. 16S/18S rRNA environmental amplicons). Please refer to workshop
> website for a full description and preliminary schedule.
>
> This workshop is targeted towards graduate students and
> postdoctoral researchers, although we will consider applications
> from other early-career scientists who would especially benefit
> from participating. All participants are expected to have some
> basic familiarity with command line tools and scientific programming
> (e.g. Unix, R, and/or Python) in order to fully benefit from the workshop
> trainings. This is NOT an introductory programming course; we will be
> focusing on -Omics workflows and downstream data visualizations of target
> datasets. The 2024 TSTD workshop will be focused on eDNA Metabarcoding
> data (e.g. 16S/18S rRNA environmental amplicons).
>
>
> Holly Bik
> Associate Professor
> Department of Marine Sciences
> and Institute of Bioinformatics
> University of Georgia
> 102B Marine Sciences Bldg
> 325 Sanford Drive
> Athens, GA 30602
>
> Email: [email protected]
> Office: (+1) 706-542-2844
> Lab: (+1) 706-542-2037
>
> Lab: https://www.biklab.org/
> Personal: https://ift.tt/KUM0orR
> Twitter: https://twitter.com/hollybik
>
>
>
>
> [email protected]
>
> (to subscribe/unsubscribe the EvolDir send mail to
> [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Cannabis Bust in Route 72 Minibus, DEA's New Hemp Rules & Anti-Aging Hemp Oil Discoveries
Green Nexus News Brief Welcome back to Green Nexus News Brief, your go-to source for quick updates on everything cannabis. Here’s what we’ve got for you today: - Recent DEA statements suggest that THCA, which converts to delta-9 THC upon heating, may now be considered in legal thresholds under the 2018 Farm Bill. This could potentially affect the compliance status of many hemp-derived products and shift the regulatory landscape, raising concerns among industry leaders. - A groundbreaking study reveals that hemp seed oil might have significant anti-aging properties. Utilizing advanced techniques like 1H NMR metabolomics and 16S rRNA gene sequencing, researchers found that this oil could positively impact metabolic phenotypes in aging, offering new possibilities for anti-aging therapies. - In a chilling discovery, explorers in Chernobyl encounter a mummified corpse clutching survival rules, signaling potential horrors in the area. This find leads them deeper into the forest, where grotesque mutations and a menacing cult challenge their survival, blurring the lines between nightmare and reality. That's all for today. Connect with us at greennexus.academy. Don't forget to hit subscribe and come back tomorrow for more quick cannabis news from Green Nexus News Brief. - visit https://greennexus.academy for more!
0 notes
Text
Applied Microbiology, Vol. 4, Pages 1268-1282: Addition of Chicken Litter Compost Changes Bacteriobiome in Fallow Soil
Composting is an environmentally friendly process, turning animal waste into fertilizer. Chicken litter compost (CLC) improves soil properties, increasing crop yields. However, the CLC effect on the soil microbiome is understudied. This study aimed to compare bacteriobiome diversity in fallow arable Chernozem with and without CLC addition in a field experiment in the Novosibirsk region, Russia, using 16S #rRNA gene metabarcoding. Pseudomonadota, Actinomycetota and Acidobacteriota were the most OTU-rich phyla, together accounting for >50% of the total number of sequence reads. CLC-related shifts in the bacteriobiome structure occurred at all taxonomic levels: the Bacillota abundance was 10-fold increased due to increased Bacilli, both being indicator taxa for the CLC-soil. The main Actinomycetota classes were the indicators for the CLC-soil (Actinobacteria) and no-CLC soil (Thermoleophilia, represented Gaiella). Both Bacillota and Actinomycetota phyla were the ultimate constituents of the CLC added, persisting in the soil for five months of fallowing. The no-CLC soil indicator phyla were Acidobacteriota (represented by Acidobacteria_Group3) and Verrucomicrobiota. Future metabarcoding studies of chicken litter application in agricultural soils, including cropped studies, should address the soil microbiome at the species/strain levels in more detail, as well as how it is affected by specific crops, preferably accompanied by a direct methodology revealing the microbiota functions. https://www.mdpi.com/2673-8007/4/3/87?utm_source=dlvr.it&utm_medium=tumblr
0 notes
Text
Using short-read 16S rRNA sequencing of multiple variable regions to generate high-quality results to a species level.
bioRxiv: http://dlvr.it/T6rMn9
0 notes