Text
elon musk did a nazi salute twice at the inauguration, and republicans are defending him.
trump revoked executive order 11246, which prohibited discrimination.
trump put all dei employees on leave to be fired.
trump banned all lgbtq+ flags from being hung in government buildings.
trump rolled back biden’s executive order to lower prescription drug costs for people using medicare and medicaid.
trump rescinded the $35 cap on insulin, and prices are expected to rise to $1500 a month.
trump ordered the national institutes of health to cancel their review panels on cancer research.
when sean hannity asked trump about the economy, he said “i don’t care”, after campaigning with the economy as his main talking point.
trump has withdrawn the us from the world health organization.
trump is ordering health agencies to stop reporting on bird flu and halt publications of scientific reports.
trump has pardoned over 1500 people who stormed the capitol on january 6th.
trump changed mount denali back to mount mckinley.
trump signed an executive order to rename the gulf of mexico to gulf of america.
trump shut down cbp one, an app which granted legal entry to 1 million+ immigrants.
trump is allowing ice raids at churches and elementary schools.
trump announced plans to declare a national emergency at the us-mexico border.
trump signed an executive order to expand the use of the death penalty.
trump disbanded the school safety board that works to prevent school shootings. it was comprised of survivors, educators, and gun violence prevention advocates and formed after the school shooting in parkland.
trump withdrew from the paris climate act.
trump revoked all protections for transgender troops in the us military.
trump rescinded executive orders made by biden that benefited and protected women, lgbtq+ people, black americans, hispanic americans, asian americans, native hawaiians, and pacific islanders.
trump is attempting to make it legal to refuse to hire or fire pregnant women.
multiple state legislators are drafting bills to allow the punishment for abortion to be the death penalty.
trump pardoned 23 individuals convicted under the freedom of access to clinic entrances (FACE) act for their anti-abortion activism, including oftentimes violent protests at abortion clinics.
trump signed an executive order allowing deportation of foreign students who they believe express support for hamas or hezbollah.
trump announced that the us government will from here on out only recognize male and female as sexes. intersex is not legally recognized anymore.
trump refused to swear on the bible during his inauguration.
andy ogles drafted a constitutional amendment to allow trump to be president for a third term.
georgia republican congressman mike collins called for the deportation of new jersey born mariann budde, the bishop who urged trump to “have mercy” on the lgbtq+ community and immigrants during a service at the national cathedral.
amazon revoked protections for lgbtq+ and black employees.
every single republican told us we were overreacting. trump swore he had nothing to do with project 2025 yet continues implementing details outlined in it. not a single person has the right to tell us we’re being dramatic anymore.
hope the possibility of cheaper eggs and gas was worth it.
51K notes
·
View notes
Text
This all day long … Elena Kanagy-Loux's article is right-on. I myself have made it a point in recent years not to share any content that glibly uses the phrase, "not your grandma's " because it's a) lazy and b) dismisses the real fact that grandmothers and older textile artists have worked hard to keep craft traditions alive and evolving, not to mention their immense skills. We should be thanking them and looking to them for inspiration, not mocking them. via @hyperallergic ❤️
3K notes
·
View notes
Note
We don’t need a handful of people doing zero waste perfectly. We need millions of people doing it imperfectly.
Anne Marie Bonneau
do you think solarpunk is an actual political philosophy and not just an aesthetic? (not meant to be accusatory)
Tbh I learned about the aesthetic after learning about the political orientation! Like I wasn’t aware of it as a genre until later. So definitely!
Is it primarily used as an aesthetic for fiction now, rather than an axis of action? Well, yes. But that doesn’t take away from those of us who do orient our actions that way. Some great examples of folks I follow here doing such things are @solarpunkani and @justalittlesolarpunk!
Now, I’d LIKE to be a solarpunk, but…I don’t think I qualify. I’m very much a beginner and my lifestyle isn’t great for the climate. I travel a lot, shop online, buy unnecessary things, don’t have a compost, and eat a lot of foods that come in single use plastics. That said—I definitley have made changes since trying to become solarpunk!
I thrift more and have learned to sew, crochet, and darn, even if I rarely use those skills. My most recent cosplay I bought nothing new for! I’ve started actively turning down when people offer me rides to take public transit (not every time but often), and I have plants in my room now. I started a little free zine library for my dorm community and donated a bunch of toys I’d bought for gifts to a little free library at a K-8 school. I painted over a wall in my parents house that had some not-great symbols with bright paint and hearts and polka dots. We call it the cheer up closet. I’ve started masking again in classes, meetings, and on public transit. I buy biodegradable gloves, trash bags, cotton tips, and so on. When I thrift, I buy cheap books, books I enjoyed, or books that might be banned to put in lottle free libraries. It’s motivated me to spend more time in Libraries, community spaces, and to get involved with organizing on my campus. So at least in my personal life, it leads me in the right direction!
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
I want you to remember:
The fascists hate you too and they just will pretend otherwise until after they've killed the rest of us, before they turn on you.
181K notes
·
View notes
Text






























Our world shall be more open and equal. All of us shall have the freedom to be ourselves and express our love. Marriage shall be accepted both socially and legally regardless of our gender.
Love is far beyond definition. It should not be restricted.
The law comes into effect today January 23, 2025
*names of shows are listed in replies.
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
"On his first day back in the White House, president Donald Trump signed a series of executive orders, including rescinding Biden-era executive actions and withdrawing the US from the Paris climate accord.
Trump told Fox News host Sean Hannity during his campaign that he would be a dictator only on “day one” and use his presidential powers to close the southern border with Mexico and expand oil drilling.
“After that, I’m not a dictator,” he said.
As executive orders rolled in on Monday, the accelerated pace amounted to a shock-and-awe campaign. Trump promised in his inaugural speech that these orders would amount to a “complete restoration of America”.
Here’s what we know so far about themost significant executive orders and actions Trump signed on Monday.
Ending birthright citizenship
The order: Along with a slew of immigration-focused orders, Trump is targeting automatic citizenship for US-born children of immigrants in the country illegally, to begin 30 days from today.
What Trump said: The order specifies that it would limit birthright citizenship if a person’s “mother was unlawfully present in the United States and the father was not a United States citizen or lawful permanent resident at the time of said person’s birth”, or “when that person’s mother’s presence in the United States at the time of said person’s birth was lawful but temporary”.
What it means: Birthright citizenship, which guarantees citizenship to anyone born on US soil, is protected by the 14th amendment and any attempt to revoke it will likely bring immediate legal challenges. The order attempts to deny documents recognizing US citizenship for individuals who meet that criteria and are born in the US 30 days after the order was signed.
-via The Guardian, January 20, 2025. Article continues below.
Leaving the World Health Organization
The order: Trump signed an order to have the US exit the World Health Organization (WHO).
What Trump said: “World Health ripped us off, everybody rips off the United States. It’s not going to happen anymore,” Trump said at the signing. He accused the WHO mishandled the Covid-19 pandemic and other international health crises.
What it means: The US will leave the WHO in 12 months’ time and stop all financial contributions to its work. The US is biggest financial backer to the United Nations health agency.
Renaming the Gulf of Mexico
The order: Trump ordered two name changes: the Gulf of Mexico and Alaska’s Mount Denali.
What Trump said: “President Trump is bringing common sense to government and renewing the pillars of American Civilization,” the executive order said in part.
What it means: Trump ordered the Gulf of Mexico to be renamed the “Gulf of America”, something he promised earlier this month at a press conference. He will rechristen Alaska’s Mount Denali as Mount McKinley, a change first made by former president Barack Obama in 2015 to reflect the traditions of Alaska Natives as well as the preference of many Alaska residents.
It will have no bearing on what names are used internationally.
Revoking electric vehicle targets
The order: Trump revoked a non-binding executive order signed by Biden aimed at making half of all new vehicles sold in 2030 electric.
What Trump said: “The United States will not sabotage our own industries while China pollutes with impunity,” Trump said on Monday afternoon.
What it means: Part of an effort to repeal Biden’s environmental protections, Trump has also promised to roll back auto pollution standards finalized by Biden’s administration last spring.
Reclassifying federal employees, making them easier to fire
The order: Trump’s executive order reclassified thousands of federal employees as political hires, making it much easier for them to be fired.
What Trump said: Aides to the president have long heralded mass government firings as part of an attack on the so-called “administrative” or “deep” state.
What it means: Trump effectively reinstates “Schedule F”, an executive order he signed in the last year of his first term, seeking to reclassify tens of thousands of federal workers. (Biden rescinded the order.)
Key aides to Trump have called for mass government firings. Project 2025 made attacks on the deep or administrative state a core part of Trump’s second term. The rightwing playbook called for civil servants deemed politically unreliable to be fired and replaced by conservatives.
Declaring a national energy emergency
The order: Trump declared a national energy emergency as part of a barrage of pro-fossil fuel actions and efforts to “unleash” already booming US energy production that included also rolling back restrictions in drilling in Alaska and undoing a pause on gas exports.
What Trump said: The order means “you can do whatever you have to do to get out of that problem and we do have that kind of emergency,” Trump said at the White House late on Monday.
What it means: The declaration would allow his administration to fast-track permits for new fossil fuel infrastructure. It is likely that the order, part of a broader effort to roll back climate policy, will face legal challenges.
Creating a policy recognizing only two genders
The order: Trump signed an order to remove “gender ideology guidance” from federal government communication, policies and forms. The order makes it official policy that there are “only two genders, male and female”.
What Trump said: “Agencies will cease pretending that men can be women and women can be men when enforcing laws that protect against sex discrimination,” the order states.
What it means: The order reverses a Biden-era executive action on the acceptance of gender identity.
Pausing the TikTok ban
The order: Trump signed an executive order temporarily delaying the enforcement of a federal ban on TikTok for at least 75 days.
What Trump said: “I guess I have a warm spot for TikTok that I didn’t have originally,” Trump said at the White House, as he signed executive orders according to the New York Times.
What it means: Trump ordered his attorney general to not enforce the law requiring TikTok’s sale. Trump says the pause allows for time to chart an “appropriate course forward” to protect national security and not abruptly shut down the popular app. In his first term, Trump favored a TikTok ban, but has since changed his position due to factors including his own popularity on the app.
Rescinding 78 Biden-era executive actions
The order: Trump ordered 78 Biden-era executive actions to be rescinded, including at least a dozen measures supporting racial equity and combating discrimination against gay and transgender people.
What Trump said: “I’ll revoke nearly 80 destructive and radical executive actions of the previous administration,” Trump told a crowd in Washington after his inaugural speech. He also said he would end policy “trying to socially engineer race and gender into every aspect of public and private life” and push for a “color blind and merit-based” society.
What it means: The orders signal a reversal of Biden-era policy that prioritized implementing diversity measures across the federal government. Trump repealed orders signed by Biden advancing racial equity for underserved communities and the aforementioned order combating discrimination based on gender identity or sexual orientation.
Declaring a national border emergency
The order: Trump signed an order at the White House declaring an emergency at the southern US border, along with several other immigration-related policies.
What Trump said: “All illegal entry will immediately be halted, and we will begin the process of returning millions and millions of criminal aliens back to the places from which they came,” Trump said in his inauguration speech.
What it means: The executive action paves the way to send US troops to the southern border and makes good on campaign promises to implement hardline immigration policies. There are limited details about how the administration planned to execute its sprawling set of immigration actions that were all but certain to face legal and logistical challenges.
Immigrant communities across the country are bracing for Trump’s promise to carry out the “largest deportation program in American history”, beginning as early as Tuesday morning.
Issuing pardons for January 6 defendants
The order: Trump issued pardons for offenders and commutations related to the January 6 attack on the Capitol. He will direct the Department of Justice to dismiss cases currently in progress.
What Trump said: “I’m going to be signing on the J6 hostages, pardons, to get them out,” Trump said during his rally speech. “We’ll be signing pardons for a lot of people, a lot of people.” Trump said he has pardoned about 1,500 defendants charged in the January 6 attack on the US Capitol and issued six commutations.
What it means: Trump made his pledge to issue pardons for those with convictions related to the January 6 Capitol attack a core part of his re-election campaign. On the campaign trail, Trump often featured the national anthem sung by prisoners in a Washington DC jail. There are more than 1,500 people federally charged with associated charges.
With Trump back in the White House, justice department investigations into January 6 crimes are expected to cease.
Withdrawing from the Paris climate agreement
The order: Trump issued executive action withdrawing the US from the 2015 Paris agreement, along with a letter informing the United Nations of the decision.
What Trump said: “I am immediately withdrawing from the unfair, one-sided Paris Climate Accord rip off” Trump said during a rally at the Capital One Arena. In his inaugural speech, Trump said he would use executive action to “end the Green New Deal”.
What it means: In 2017, Trump exited the Paris agreement. Upon taking office in 2021, Biden rejoined. Monday’s order makes good on a Trump election promise to withdraw from the 2015 global treaty seeking to avoid the worst impacts of the climate crisis.
Exiting the Paris agreement is part of Trump’s broader efforts to roll back climate protections and policy. Trump has described Biden’s efforts to grow the US’s clean energy sector as “the green new scam”.
-via The Guardian, January 20, 2025
113 notes
·
View notes
Text
Just a thought- is there any reason why you like having spells that use a half a mana slot, rather than doubling the cost and supply for everything and using only whole numbers?
the ttrpg I am making is going well so far



81 notes
·
View notes
Text
mercy seems like a long shot here, so my prayer for inauguration day 2025: may they be incompetent. may they just be really bad at implementation. may their egos choke their effectiveness. may they drown themselves week by week with infighting and selfish posturing. may they be easily distracted. may the very governors and senators and agencies and religious leaders that the new administration expects to be friendly force endless stalemates to preserve their own power. may every delay turn into a three ring blame circus so chaotic that no one remembers what they were doing. may the good and necessary parts of government be too boring to draw attention and keep running quietly in the background. may the next four years be full of sound and fury and signify nothing.
45K notes
·
View notes
Text
I need your help with a hypothesis!
For context: My linguistics professor and I got into a discussion after a test she did with us, and I was of the opinion that the reason for the results was different from the one she offered, so she encouraged me to test my theory.
What I need
All you need to do is draw a coffee cup (with a handle, not the disposable stuff) and then answer three questions.
I don't need to see the coffee cup. You can draw it wherever you like; on a piece of paper, digitally, in the sand, on a foggy window. Anything works. It does not have to be good. A doodle is fine.
You have to draw the coffee cup before you see the questions. This is very important. If you decide to help me with this, please doodle the coffee cup before you keep reading.
Assuming you have drawn the coffee cup, I now need you to answer these three questions:
On which side did you draw the handle?
Are you right-handed or left-handed?
Do you primarily write using the Latin alphabet or a different one? (please specify which)
More context
Most people will draw the handle on the right side. My professor says it's because most people are right-handed, so they draw the handle in the direction that would be comfortable for them to pick up.
I said drawing it on the right side just felt more comfortable to my hand and argued it's probably because we write a bunch of letters like that. B, b, D, P, p, R all look like a tiny "handle on the right side" and are all a straight line followed by a round one (so "cup first, handle second," like most people draw cups). The Latin alphabet doesn't have letters like that that face the other way, except maybe d, depending on how you write it, so it makes sense to me that people writing mostly Latin letters would go with the handle on the right side.
Which means that I need to know what Asians, Arabs and Greeks do and if the distribution of left and right sides of handles differs from the Latin alphabet group. Cyrillic seems to favor right, too, though it'd be interesting to see if there are differences.
If there are, my theory is right. Doubly so if there is a sizeable increase in a group whose alphabet has letters that benefit the left side choice.
So feel free to spread this to as many people as you like and put the answers in the comments or the tags of a reblog. The more answers I get, the better I can assess whose theory is better.
Thank you for your help!
8K notes
·
View notes
Text
Re the last part, don't sweat it! You wanted to share something you are proud of with people who also like looking at the thing. If there's a kind of social media sharing that's the least harmful, it's this 😊
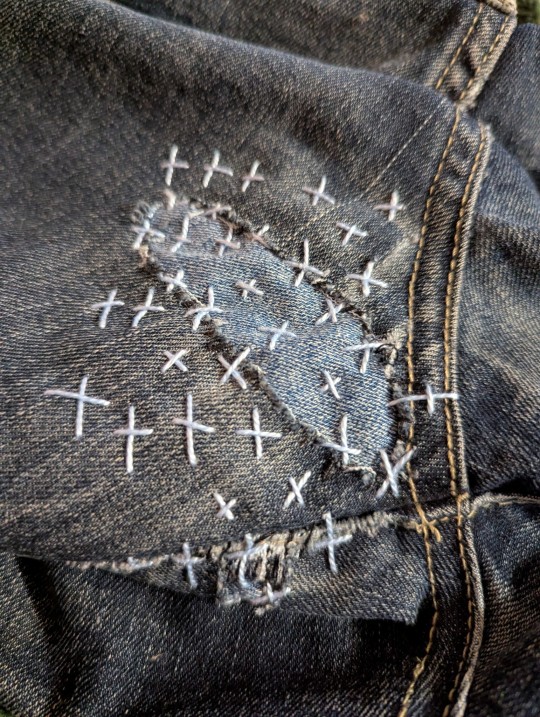
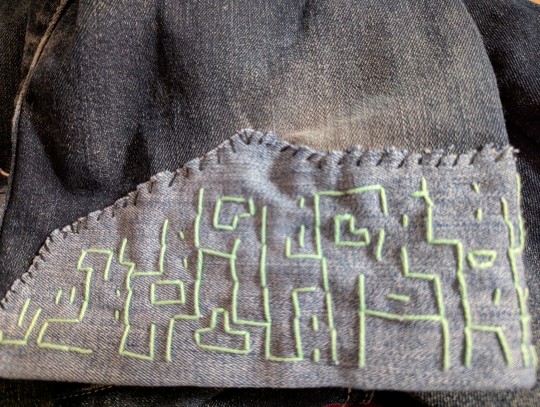
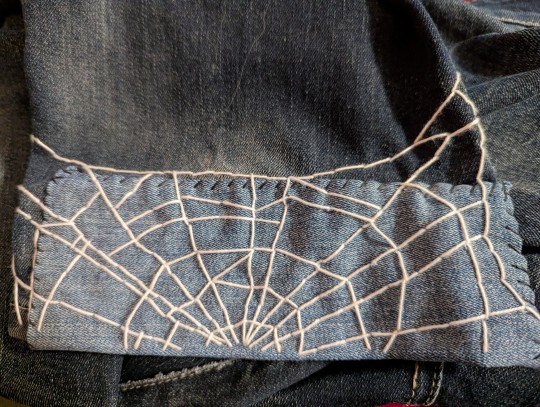




Been mending my partner's pants while listening to an audiobook that is kicking my ass. Like damn, I fell for so much of the capitalist scam down to my core. I DO look for ways to hack my brain for productivity and how I can min-max my life 😬
Even posting on here the writer of the book was talking about how every time we do something we wanna optimize it, share it on social media etc etc. I'm giving myself a pass cause I don't share the stuff I do much these days.
Anyways, feeling proud of how my visible mending is going, found my thimble way too late in the game though haha.
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
This might suck to hear, but if you're a people pleaser that is motivated by praise and avoids disagreements, you are easy to manipulate.
When I was in therapy after surviving years of domestic violence, my therapist had to tell me that my personality was primed for abuse and we needed to work on that so I would be better equipped to see the red flags and respond appropriately in the future.
I'm still working on this, and it's been 8 years. If you tell someone how you want to be treated, what behaviors you don't tolerate in your life, what you're looking for in that relationship, and they react negatively, don't compromise yourself. Just move on.
This one's for all the praise-kink girlies: differentiate, self-actualize, stay sexy
63K notes
·
View notes
Text
My boyfriend is trying to explain cricket to me again. “He’s only got two balls to make 48 runs”, he says. The camera focuses on a man. Underneath him it says LEFT ARM FAST MEDIUM. A ball flies into the stands and presumably fractures someone’s skull. “There’s a free six”, my boyfriend says. 348 SIXES says the screen. A child in the audience waves a sign referencing Weet-Bix
121K notes
·
View notes
Text
tbt the time Terry Pratchett's German publisher inserted a soup ad into The Light Fantastic
Did I miss something or are they doing product placement in novels now? Both my partner and I recently each read a new (ie, published in the last few years) fiction book. Normally he and I tend to read non-fiction or fiction that is a bit older, so maybe we're both just not used to tropes and commonalities in modern pulp fiction, but the fact that each of the books we read - written by different authors, and ostensibly different genres - featured pivotal scenes set in a Dunkin' Donuts just feels like weird product placement. Again, maybe its just that we both tend towards older fiction and aren't used to more modern writing styles (although I should caveat here that my fiance is a writer so maybe this doesn't apply to him as much), but we both had trouble taking either of our books seriously after noticing how much modern product placement was featured for no apparent reason. Apparently there was a whole scene in my partner's novel where the character was comparing prices of furniture at IKEA before having a problem resolved by using the Starbucks app on their phone.
Idk, maybe its just us being old and pretentious, but I do find it a little distracting to be in the center of a pivotal scene only for the book to take a quick little aside to remind me this is all happening at a Dunkin' Donuts.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
i have a fever. let's imagine pokemon world dash discourse together.

🤳🏻 pokestopit reblogged team-sprocket

👻 gengaydar Follow
For the last fucking time owning a gengar is NOT graverobbing. what is actually wrong with you people
#gengar #why am i even still on this site #i don't have a gengar but like. what's even going on over there #is marowak graverobbing now too??

💅 deerlinguist reblogged

👩❤️👩 lightscreend Follow
farfetch'd is like the most edible pokemon just because he comes with his own aromatics. pop that bad boy in the oven with some oran berries.... don't mind if i do

⚧ feministforcepalm Follow

@dyketraining tags pass peer review

🚣🏼♂️ magicarpaltunnel reblogged haxorsus

🐦⬛ corvikite Follow
I love to hate things and people. And when I turn out to be RIGHT and that person is a DICK? All parasocial relationships are bad and evil unless I am right about hating someone and then parasocial relationships are good actually

🪐waterbubbil Follow
We all thought about the same person let's just be honest here....

🎀 contest-winrar Follow
For me it's always going to be people who keep Pokémon without any thought as to their enrichment and needs. You do not need a fucking Arcanine, you live in a studio apartment and don't walk more than a block a day. You think you want a Gardevoir but are you okay with having an unknowable creature reading your thoughts every waking moment of the day? Even while you do... the nasty?
It drives me crazy because people see a Champion and think they have the time, energy, money, and space necessary to raise a Dragon type. Unless you have generational wealth, let me spell it out for you: you do not have the funds for a Dragon type. And yes! Charizard is on that list, guys! You can't even afford to feed yourself!

📯 jessiejustlickme Follow
local tumblr user declares the poors only get rat pokemon. maybe a bug pokémon if we are very good. we must grovel in the streets amen

🎀 contest-winrar Follow
Laugh all you want but I'm serious. I have heard of someone who is living with a MR. MIME like it's her HUSBAND!!!! That's fucking GROSS. These are creatures that TRUST us and NEED us.
Did you know that most Ponyta prefer to be in a herd? Are you going to have the space for that? Did you know that if you don't properly care for certain fire species their flame goes out? Sure, they're cute when they're small: but unless you're a rancher or a Gym Leader... I'm sorry. You're gross to me if you think otherwise. I hate people like that.
And for the record, rat and bug Pokémon are very valuable from an ecological standpoint. They hold an extremely important niche. People like you would rather they be hunted to extinction because they're pests, not pretty. It's disgusting.

🐦⬛ corvikite Follow
anybody in this thread smoke weed
#NOT THE RATS FOR THE POOR PEOPLE... GIRLLLLLL #the thing is they're not like... wrong.... #like i agree with the sentiment #my friend tried to get a slyveon just by like. playing catch a few times #.... like you do need to try.... #also fyi i have a large species so i'm biased #grovyle my baby . my man. u are costing me like so much in pokepuffs per month

👁🗨 badsol
why are we all talking about what pokemon to eat tonight lmafo
#.... obviously jigglypuff. homegirl is 90% cotton candy

🪅 feebassguitar reblogged metrognome

🫖 sinisteacher Follow
Like okay I got into science because I love to learn but the more I find out about how we've classified Pokémon types the more insane I feel. What do you mean there's no singular true indicator? What do you mean that there are several conditions which completely alter their base type?
Literally today my lab partner and I got into a very serious discussion about Luxray. That thing is a fuckking dark type!!!!! I'm sorry!!! I don't care what Bulbapedia says!!!! anyway i threw a pokeball at him and it swallowed him whole and now i'm going to jail for unlawful imprisonment of a TA

🍙 thesandwichking Follow
there's something, like, very dystopian about the idea that if u put an ugly hat on ur favorite little creature it changes like. the DNA. like. do other pokemon look at what you've done and cower? that's their friend... similar but changed... forever having known a life that is entirely alien to them...

🐳 wailordsupreme Follow
.... Are we going to ignore that OP swallowed a human into a ball???
#yes we are. #my friend loves those hats but I think they're so ugly. #and stupid. #if i wanted a specific type imma get that type..... #typesetting #show james

🧗♀️ backpacksandcavesnacks reblogged eevee-lotion

👑 lemmegrabmyballs Follow
ROUND 5 of 6 (see blog for more)
PLEASE REBLOG FOR VISIBILITY:

✍️ dreepydrabbles reblogged ash-hole

☠️ marrowhackoff Follow
just saw someone say writing omegaverse fanfic of your pokemon is bestiality. ma'am this is the monster fucking site. you should be grateful that it's only omegaverse.
#the things i've seen would melt your eyebrows clean off your face. #..... typhlosion they could never make me hate you baby. #i know that's not what's in your heart

🪽 honey-tree-skies reblogged gymcrawler

🐛 youngstirjoey Follow
Okay say what you will. But shorts really are comfy and easy to wear

🛀🏽 intimidatecutsyourattack Follow
Sorry bud. But. Investing at 3 notes

🐛 youngstirjoey Follow
don't do this to me. i h avue a wife . and chi ld
3K notes
·
View notes