We are fascinated with the idea of Artificial Intelligence and watching the effects AI have on the world around us. Through this blog we hope to investigate different applications of Artificial Intelligence in manufacturing. We want to explore different topics and uses of AI and hope the content we post can effectively reflect that mission.
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Photo


We made a 3D Printer for our Final Project.
One of the greatest boons that 3D printing provides to intelligent manufacturing and manufacturing in general is the ability to quickly prototype a product. It takes the majority of the guesswork out of the design process and allows people to have the same power at home or at their office desk as a fully functioning manufacturing floor.
The speed and cost are also benefits in that it allows parts to be prototyped at speeds unable to be reached by conventional methods. Changes to the product can also be done without having to change molds (usually a large sunk cost), all this makes 3D manufacturing of this type incredibly powerful and efficient.
Additive manufacturing is a multi-billion dollar industry – including both products and services – and whose technology is constantly advancing. The future of 3D printing and additive manufacturing is well on its way from going beyond just prototyping and into final production of parts and products. Additive manufacturing is a fine example of a disruptive technology because it is transforming the businesses so they can develop products and expand their capabilities. Its entry into the market gives business a lot more flexibility in how they manufacture products because it can both increase efficiency and reduce the assembly of parts when a part can be printed already fully assembled.
1 note
·
View note
Photo



WEKA Project: Predicting the Onset of Diabetes
Using WEKA Machine Learning to Predict the Onset of Diabetes in Pima Indians:
How Did We Choose this Dataset and Why?
We chose this dataset after much group deliberation, after having everyone list topics that interest them. The only topic that everyone chose was diabetes; over 30 million people in the United States are affected by diabetes and it is an important topic that affects everyone. We wanted to investigate the leading causes of diabetes and what the early indicators are. That way we could also investigate how to predict the onset of diabetes by observing how those indicators re-occur in patients.
The goal of this dataset is to promote awareness of Diabetes and make sure that people understand the statistics of the disease. The dataset provides an analysis of patients with various characteristics and if they have Diabetes.
Understanding the Dataset:
This dataset was created by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and donated by Vincent Sigillito, Research Center, RMI Group Leader of the Applied Physics Laboratory in The Johns Hopkins University on May 9th, 1990.
It is comprised of data collected from many patients with several constraints on the data in order to predict the early onset of diabetes in this specific group of Pima Indians. The constraints are as follows: All the patients are female, at least 21 years old, and of Pima Indian Heritage.
Attributes:
Number of times pregnant
Plasma glucose concentration a 2 hours in an oral glucose tolerance test
Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg)
Triceps skin fold thickness (mm)
2-Hour serum insulin (mu U/ml)
Body mass index (weight in kg/(height in m)^2)
Diabetes pedigree function
Age (years)
Classes:
Tested Negative - 0
Tested Positive - 1
0 notes
Photo



Local IM Company: SEMA Garage
A Look into Intelligent Manufacturing in Local Industries.
How 3D Scanning and Additive Manufacturing Helps Businesses with Prototyping and Production:
“3D printing has long been considered a tool to quickly design and make one-off prototypes. But as the technology is becoming more accessible, more affordable and more capable, it is beginning to redefine the way we think about manufacturing almost anything - and the way we run our businesses.”
Additive manufacturing is a multi-billion dollar industry – including both products and services – and whose technology is constantly advancing. The future of 3D printing and additive manufacturing is well on its way from going beyond just prototyping and into final production of parts and products. Additive manufacturing is a fine example of a disruptive technology because it is transforming the businesses can develop products and expand their capabilities. Additive manufacturing gives business a lot more flexibility in how they manufacture products because it can both increase efficiency and reduce the assembly of parts when a part can be printed already fully assembled. It also allows companies to make smaller production runs and have better testing of their products when they don’t have to invest as much in every production run. The advent of 3D printing and scanning is the ability to quickly make parts, accessories, and spare parts for existing manufacturing lines – it is very easy to incorporate these tools into already established companies. Companies can use 3D scanning to reverse engineer existing products to be able to develop them further. “Additive manufacturing is going to be a future core technology of the engineered products industry,” rp+m Chief Technology Officer Anthony Hughes said at the NorTech event. “As we are shifting our focus from purely rapid prototyping into direct digital production, we are opening up new markets and channels really fast.” We are starting really innovative uses of the technologies available to us with additive manufacturing. For example, rare metal alloys that before were difficult materials to obtain can simply be printed in the product without the need to wait for and place a huge material order. Additive manufacturing is completely transforming the way some industries previously developed products. One example of this disruptive technology is within the aftermarket auto industry.
3D scanning and printing is an immensely beneficial tool to new growing businesses in the aftermarket auto industry. Where before most of this industry would develop parts by hand – building a prototype jig out of wood or ABS and forming it with bondo, etc. – now they have the opportunity to inject smart manufacturing into their product development process. They can take the manually manufactured prototype to a facility like SEMA Garage and have them create a CAD file and use that to either print or manufacture a final version of the part. Another benefit to having access to a 3D scanning and printing resource is the ability to create models of cars that the business works with in order to create parts without the presence of the physical vehicle.
SEMA Garage provides access to many car manufacturer’s vast library of 3D CAD model of their vehicles with a service they call Tech Transfer. “Access CAD OEM data to develop high-quality parts fast and cost effectively. The participating OEMs include Ford, Lincoln, General Motors/Chevrolet, Chrysler, Dodge, Ram, Jeep, Fiat and Scion.” [3] SEMA Garage is also working on creating a more expansive library of scans with every vehicle brought to the facility to scan using their FARO Arm. This gives businesses who otherwise would not have access to such resources the ability to develop parts for vehicles and have access to all the measurements and specifications of the vehicle body.
0 notes
Video
youtube
AddWorks from GE Additive helps your organization successfully navigate its additive journey. Chris Schuppe, design leader for GE Additive and part of the AddWorks team, talks about GE's internal track record with additive solutions and how the team is using that experience to help customers achieve additive transformations in their business.
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
AP&C is a leader in the production of metal powders for Additive Manufacturing. The APA™ process produces premium quality spherical powders of reactive and high melting point materials such as titanium, nickel, zirconium, and others.
0 notes
Link
This link is a great example of how much google and voice recognition has changed even in the past year. The fact that the program hems and haws when it it answering questions and sounds EXACTLY like a person is incredibly amazing/scary. It appears that as this system goes forward technologically the less need companies will have for people.
Just imagine what a talking to customer service will be like once robots of this caliber take the place of the rote responses computers currently have.
0 notes
Text
Computer Vision and Application
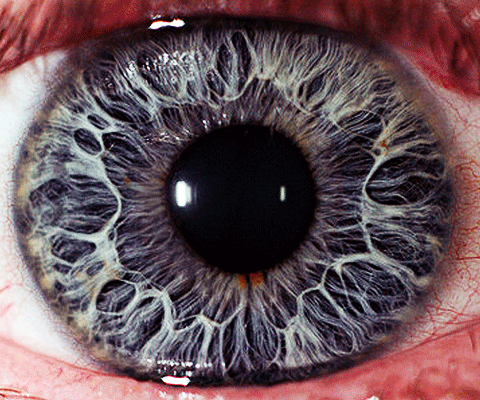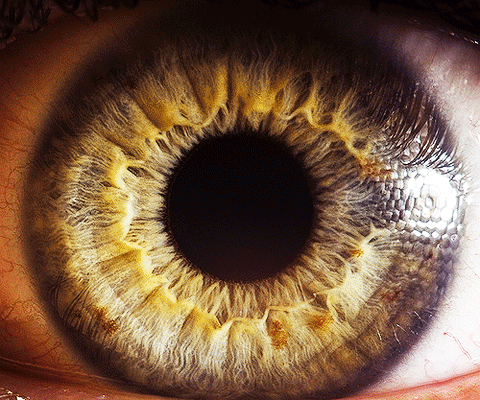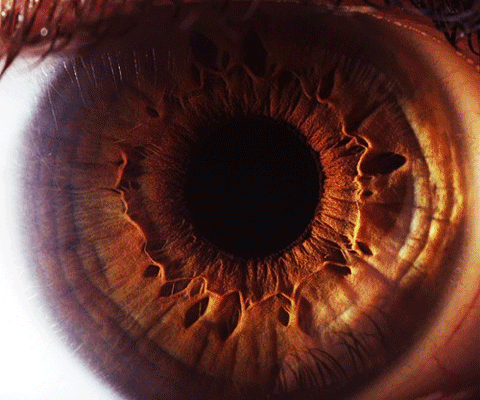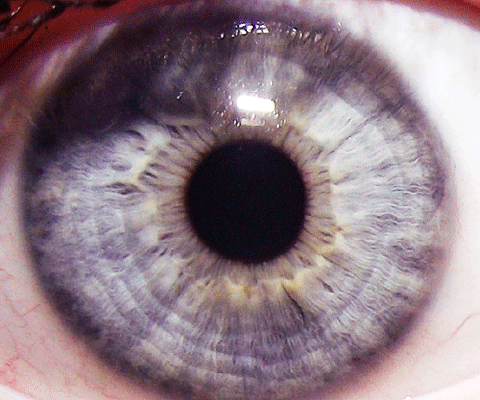
Computer vision is a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology that has already entered our lives and businesses in ways many of us may not be aware of.
Social media platforms, consumer offerings, law enforcement, and industrial production are just some of the ways in which computer vision is improving the quality of our lives.
Computer Vision Improves the Social Media User Experience
Snapchat users love to overlay rabbit ears and fairy dust, for instance, on the images of friends while the amateur photographers are walking or jostling their mobile phones. What seems like such a simple activity actually relies on computer vision algorithms. The calculations constantly dip into a vast amount of data about the objects and relative positions of the elements in the stream of images.
Pinterest has a mobile phone app called Lens that uses computer vision. The app can tell users where, for example, someone in a photo bought an amazing pair of sneakers she’s wearing. The computer vision application can also display shoes that match the item’s design and styling.
Computer Vision for Consumers
Banks around the world now use computer vision to deposit checks remotely. Banking customers take a photo of a paper check with their mobile device. Computer vision software in the banking app captures the image of the check destined for deposit in the bank, then verifies if the signature on the check is genuine. Funds typically become available for use within a business day of verification.
During the Spring of 2017, Amazon rolled out its Echo Look product. Echo Look enables fashionistas to take full-body selfies. The AI behind the computer vision offering then compares the outfit with options it suggests and delivers the user an overall style rating.
Meanwhile, consumers can feel all their gadgets are secure at home with low-cost security cameras that use computer vision to fortify the homestead. For example, Netatmo’s Presence outdoor surveillance product alerts home owners that a car, person, or animal has come onto the property. Netatmo Welcome cameras, the company’s indoor product, use facial recognition software to distinguish welcome visitors from unwelcome intruders.
Computer vision is not just for home security, though. Law enforcement agencies have seen its benefits in protecting citizens on the road.
https://www.networkworld.com/article/3239146/internet-of-things/conventional-computer-vision-coupled-with-deep-learning-makes-ai-better.html
0 notes
Video
youtube
Hello, my name is Sophia. I’m the latest robot from Hanson Robotics.
I would like to go out into the world and learn from interacting with people. Every interaction I have with people has an impact on how I develop and shapes who I eventually become. So please be nice to me as I would like to be a smart, compassionate robot. I hope you will join me on my journey to live, learn, and grow in the world so that I can realize my dream of becoming an awakening machine.
Will Smith goes on date with Sophia
There’s no denying that Will Smith has a certain star quality about him, but his charm apparently doesn’t work on everyone. the Fresh Prince can be seen crashing and burning on a date in the Cayman Islands with none other than Sophia the Robot.
After attempting to flirt with Hanson Robotics’ state of the art artificial intelligence creation by cracking a joke about the type of music robots like and not-so-subtly bringing up his ’80s hip-hop career, Smith readied himself to lean in for a kiss. “Sophia, can I be honest with you?” he asked. “I don’t know if it’s the island air or the humidity, but you’re just so easy to talk you. You got a clear head…literally.”
But as he went for smooch, Sophia was so quick to shut him down. I think we can be friends. She interjected. lets hang out and get to know each other foe a little while.
Watch the full video above.
https://www.theverge.com/2017/12/30/16832164/2017-tech-recap-ai-robots-machine-learning
0 notes
Photo

Tesla Motors’ Over-the-Air Repairs Are the Way Forward
Tesla is once again at the forefront of intelligent manufacturing by creating a system to deploy over-the-air updates to their vehicles. This allows Tesla to address most recall issues without obligating the customer to take the car into the dealership for service.
“As more and more of automotive functions begin to be controlled by electronics, it is probably reasonable to expect future problems to be also logical in nature rather than mechanical. Clearly such problems can be readily addressed OTA and without the need for a mechanic. “
0 notes
Video
youtube
1. What is an Intel light show drone? (technical aspects of it)
“Intel enables clients to brighten up the night sky with a choreographed light show featuring hundreds of Intel drones - creating a stunning way to communicate to audiences large and small.”
The Shooting Star drones utilize the same autopilot technology as the Falcon 8+, except there are no humans manning a remote control for each drone.
"We have this master computer that is the pilot. And that manages the whole
Each drone carries just a single LED, but there are more than four billion color combinations, according to Cheung.
2. How is a drone light-show performed? (technical aspects of it)
The hardware of a Shooting Star is fairly simple. The drone weighs about as much as a volleyball, is made of foam and plastic, and carries an LED payload that can flash red, green, blue or white. It doesn't have cameras. The Shooting Star, flying outdoors, is guided by GPS, and the Mini drones use a similar tech called the Intel Indoor Location System.
Intel built software to program groups of hundreds of these drones that can be operated by a single drone pilot, helping it create intricate moving shapes and logos for festivals, sporting events and movie premieres all over the world.
3. What is the difference between a “fireworks” show and a “drone light-show”?
The technology behind the show. Fireworks are just blast of different lights whereas the drone show can have choreographed movement.
4. What are the challenging aspects of using drones at events?
Intel Corp. had to ditch plans to deploy 300 small drones during the Winter Olympics Opening Ceremony because of logistical challenges. Instead, pre-recorded footage of 1,218 drone launched during a rehearsal in December in Pyeongchang, South Korea was broadcast to U.S. viewers.
“During the Ceremony, POCOG made the decision to not go ahead with the show because there were too many spectators standing in the area where the live drone show was supposed to take place,” according to a statement from the Olympic organizing committee.
5. Why was the Lady Gaga’s show at the Superbowl in Huston in 2015 pre-recorded rather than run live?
Restriction placed by the Federal Aviation Administration forbid drones from flying within a 34.5-mile radius of the NRG Stadium, in addition to other rules that bar drones from hovering too high, or from doing acrobatic maneuvers directly above hundreds of thousands of people.
6. What were the difficult aspects of making the show for the Olympic Games in Korea?
“The planning was very intense, and we had to send teams on the ground very early,” Evans told USA TODAY. “We knew we’d need to understand the wind—it’s very windy up here, and we had to understand the impact of the (cold) temperature. So, we practiced.”
In fact, the tech giant launched 1,218 of its drones in December in Pyeongchang and pre-recorded the light show that was to air on NBC’s tape-delayed broadcast in the United States. The pre-recording was shown during the U.S. broadcast of the ceremony Friday evening.
7. How do Intel drones relate to the Intelligent Manufacturing subject matter?
These drones can be used for more than just elaborate light shows. Already Amazon plans to deploy drones to deliver products more instantaneously and manufacturing facilities are using drones to increase efficiency and safety in the manufacturing process.
8. Do you know other applications of drones?
Concerned about declining bee populations, technologists are devising artificial pollination solutions using tiny drones. Intel built a small drone capable of artificially pollinating plants. Equipped with a sticky gel and some horsehair on its belly, the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) can catch and release pollen grains as it moves from plant to plant.
9. Any special thoughts that the members of your group have on the “drones” subject?
The advent of these drones has the potential to be amazing for our world. From developing ways to better pollinate flowers to delivering products this can change our world very quickly.
0 notes
Link
“Predictive maintenance is a major step toward an intelligent system even without web-based connectivity. “
Part of the move to intelligent processes is creating a feedback loop that tells control personnel what is happening on the manufacturing line. “Sometimes smart manufacturing is a matter of collecting a handful of alarms,” said Craven. “Your car will now tell you when to change your oil. Industrial machinery is beginning to do this. As you get intelligence into your maintenance operation, you’ll find you don’t have to do maintenance as often. Asset monitoring is the low-hanging fruit of IIoT.”
0 notes
Photo


Prospector is an expert system developed in the 70’s to aid geologists in mineral exploration. The purpose of prospector is threefold; to aid in the exploration for mineral resources, to keep the field of mineral exploration up to date technologically, and to bring the knowledge of multiple specialists to bear when solving geological problems. With this purpose in mind prospector’s goal was to have geologists tell the program the properties of the rocks around them. The program would then ask questions leading to it ultimately telling the geologist the mining potential of the area. It was found that prospector was accurate (when all information inserted was correct) to within 7% based on other models used to survey areas. The program would also create a large database storing all the data from previous searches and as well as information regarding current mineral deposits and enhance its ability to predict the viability of an area.
The program is meant to be used by a geologist and not a layperson, which is represented by the questions that it asks the end user. It was developed by computer scientists with the aid of experts in the field of geology. But since it is a program and not an expert it can only base its knowledge on statistics and not hard science. It develops much of its statistical knowledge from previously inputted geological surveys as well as new statistical models that are developed to aid in its search. The method of its search is called “the inference network” which connects evidence with and assumptions with the various program paths or nodes.
Sources
https://www.sri.com/sites/default/files/uploads/publications/pdf/739.pdf
https://www.computting.surrey.ac.uk/ai/profi.e/prospector.html
1 note
·
View note
Photo

Tesla's future is completely inhuman — and we shouldn't be surprised
“Auto manufacturing is about as efficient as it can be these days without a massive leap in technology. But a massive leap is what Musk wants. You could accuse Tesla of being somewhat unfriendly to human concerns, given its recent bad press around labor. But what Musk truly has in mind is something completely inhuman.”
http://www.businessinsider.com/tesla-completely-inhuman-automated-factory-2017-5
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
The animated guide to artificial intelligence (Explanimators: Episode 1)
1 note
·
View note
Link
This article from Time Magazine is about advanced manufacturing technology and the benefits of its implementation in smart manufacturing. Smart manufacturing has been defined as a fully-integrated, collaborative manufacturing system that responds in real time to the changing demands and conditions of factories, supply networks, and customer needs.
The authors believes we should go through following steps if we want to have the smart manufacturing as a strategic asset for growth:
First, one should invest in smart manufacturing innovation centers.
Second, companies should invest equal funding in applied research and basic science.
Third, one should should prepare markets for new products that smart manufacturing will bring about.
The author also mentions the three phases that advanced manufacturing technology will lead to.
The first phase that advanced manufacturing technology will take us through is that of connecting each of the individual stages of manufacturing production. This will be done by sharing all data efficiency between stages. This will create powerful economic performance, higher worker safety and greater environmental sustainability.
Plant-and Enterprise-wide Integration (phase 1) will usher us to the second phase. With the new data coming derived from advanced computer simulation and modeling, businesses will be able to improve current and future operation through the simulation of manufacturing processes. This simulation will revolutionize technology and enable companies to have more flexible manufacturing systems, optimized production rates, and faster product customization.
The third phase relates to consumer shopping behavior and the creation of new opportunities in the competitive market. Amazon is an example of this, as it shows the causes of market-disruptive innovations in products and processes.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ted Talk - How We’re Teaching Computers to Understand Pictures
This TED Talk was particularly interesting because it addressed the faults in the current technology of vision in computers and explained the solutions of how to teach computers to better understand visual information of the world around us.
youtube
Fei-Fei Li, a modern day pioneer, revolutionized the way we teach computers to see and interpret the world. Gaining her bachelors in physics from Princeton, and her PhD in electrical engineering from Caltech she went on to lead the Vision Lab at Stanford, focusing on teaching computers how to see.
In the early days of image recognition, the prevailing method of training computers to understand images was to create object models. Object models is the defining of a shape and color pattern and then telling the computer that that pattern is – for example – a cat. However, where this method fails is when a cat takes a different pose. At which point one would have to create a new model for that new position.
Fei-Fei realized that this method would never succeed; she determined that instead of using object models, the best method would be to expose the algorithms to as many images as a three year old child would absorb. She explains that the reason that humans have such an advantage over computers in understanding images is because we are constantly “taking pictures” of the world. In order for computers to understand these images the way a human would, they would have to be exposed to the same amount of information
1 note
·
View note