Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Where to do a wireless packet capture?
Close to the AP? Can see everything what the AP see? Or close to client because the client have the problem and then I can see it? Or in the middle between the AP and the client?
I like to go to the client to talk to him/her first to let them explain the issue they may have. But there is no real answers here. Because it depends. In the below scenario I describe why its better to capture close to the wireless client.
Power mismatch, and how to capture it?
We hear it allot in the wireless realm, power matching problems.
Where the AP is sending a signal on strong power and the client sending data on weak power transmission.
So where we capture the data near the AP and near the client? If we capture near the AP we only see AP traffic. We don’t see client traffic Near the client we see both traffic AP and client traffic, this indicated a problem that the AP don’t hear the client? Nope, this only indicated that my capture device near the AP doesn’t see the client.
At the packet capture near the client we see 2-way traffic, but do I see acknowledgements or do I only see retries? This I cannot see at the AP, so its better to sit at the client in this scenario and I don’t need the capture near the AP.
0 notes
Text
Update Cisco 9800-80 WLC
I want to share a quick HA software update from a Cisco 9800-80 in HA with you. In this scenario we go from version 17.3.4EWS13 to version 17.3.4cEWS1. Its always hard not to type upgrade but it isn't, this is only software and no hardware replacement is done here. I don't know why people always talk about upgrades when there is only software involved.

Maybe you thinking"EWS" releases? yes they are only available through TAC and not public available yet. This EWS13 release came out just before the public 17.3.4c release. EWS releases are like minor changes till it becomes public available. Right after that a new bug was discovered and still present in release 17.3.4EWS13. CSCvz18383 SGT Bindings for Fabric Enabled SSIDs are not seen on Fabric Edge Switch . This bug basically makes SGT segmentation unusable, since we run a fabric enabled network with SGT segmention we are in need of this EWS1 release on top of the 17.3.4c release.

Start the update First download the code and go to Administration > Softwaremanagement and upload the image through http
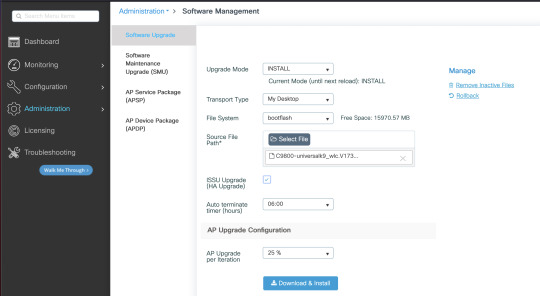
As soon as the download is complete it get copy to both nodes at the point the log will also be visible at the right side of the screen.

During this process this image will downloaded to the primary and secondary controller and to all AP's. After the image is installed on the standby it will reload and join back to the HA cluster.
Starting ISSU Install Activate Operation... install_activate: START Mon Jan 3 18:00:45 CET 2022 install_activate: Activating ISSU NOTE: Going to start Activate ISSU install process STAGE 0: System Level Sanity Check =================================================== --- Verifying install_issu supported --- --- Verifying standby is in Standby Hot state --- --- Verifying booted from the valid media --- --- Verifying AutoBoot mode is enabled --- --- Verifying Platform specific ISSU admission criteria --- Finished Initial System Level Sanity Check STAGE 1: Installing software on Standby =================================================== --- Starting install_remote --- [2] install_remote package(s) on chassis 2/R0 [2] Finished install_remote on chassis 2/R0 install_remote: Passed on [2/R0] Finished install_remote STAGE 2: Restarting Standby =================================================== --- Starting standby reload --- Finished standby reload --- Starting wait for Standby to reach terminal redundancy state ---
This will take long because approx 20-30 minutes, it will join in HA with 2 different WLC version's.
Standby update done After the standby controller comes back it will run as the active controller, you can see the correct version number in the left upper corner.
If you go to Monitor > General (header) System > Redundancy (TAB), you can see its still syncing

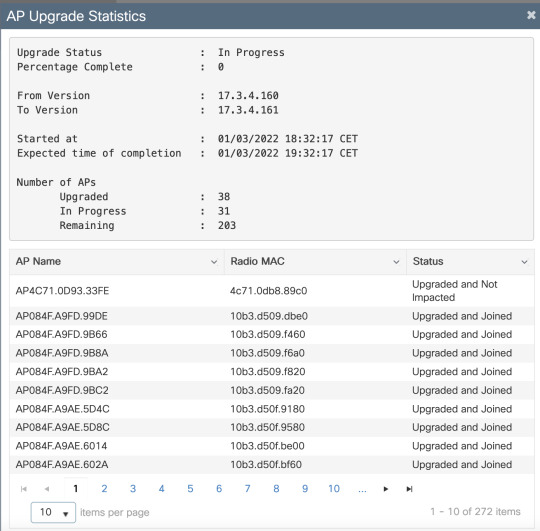
After its done syncing it will start upgrading the AP's in batches of 25% , so 4 shots.
For P = 25%, expected number of iterations for all APs to upgrade ~ 6
The AP update statistics will show the progress of the AP update
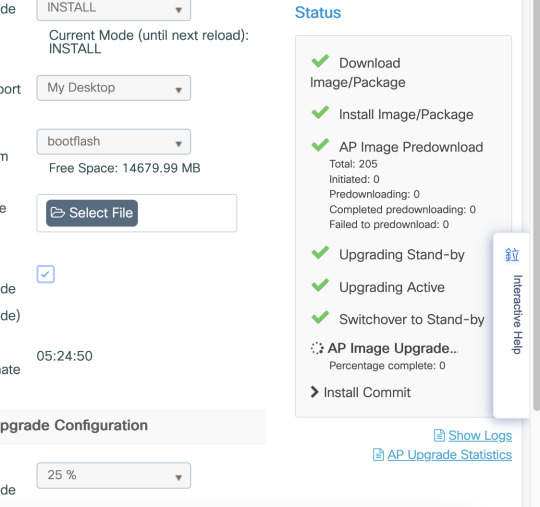
The WLC keeps track of upgrade and joined or not. If there are some AP's that have struggle joining this process can take longer
Hitless Rolling AP Upgrade Algorithm
Status: Upgraded and not impacted..
The algorithm works in three stages.
1. Candidate AP Set Selection
First, a set of candidates are selected based on nearby APs information. Rolling AP Upgrade algorithm selects the configured percentage of APs to be upgraded in each iteration while maintaining RF coverage
For serving wireless clients. maintaining coverage is important and hence, it takes precedence over selecting the required number of APs. Therefore,
For P = 25%, expected number of iterations for all APs to upgrade ~ 6 For P = 15%, expected number of iterations for all APs to upgrade ~ 12 For P = 5%, expected number of iterations for all APs to upgrade ~ 22
2. Client Steering
Clients on the candidate APs are steered to APs which are not in the candidate list prior to rebooting the candidate APs. If the clients still persist on the candidate APs, they will just be sent a de-authentication frame and the AP will reload with the new image.
3. AP Re-load and Re-join
Post the client steering stage, the AP is reloaded with the new image.
At this point, a 3-minute timer is started for the APs to join back. When this timer expires, all candidate APs are checked and marked for the WLC they have connected to (self or the peer).
If at least 90% of the candidate APs have joined back, the iteration is concluded. If not, 3 minutes window is extended and the check is repeated for two more times until the count hits at least 90%.
At the end of the 3rd try, the iteration is concluded anyway and the next iteration is initiated. Hence, each iteration may last for at most 10 mins.
Dont forget to commit
After the update is done commit it on the GUI so it doesn't rollback after the rollback timers expire. Then use the redundancy force-switchover command on the WLC CLI to make the primary controller back active
0 notes
Text
EWC on Cisco Catalyst 9130AXI-E Access Points
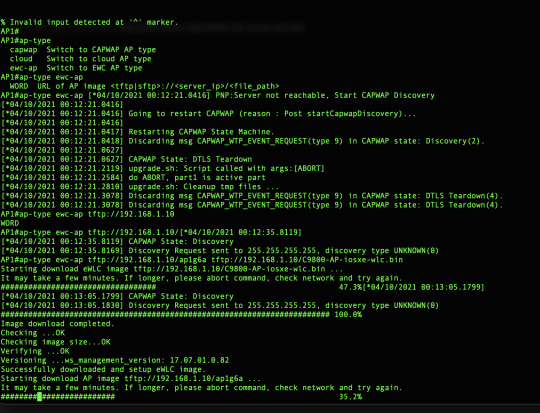
Few buildings on the campus where I work will get the privilege to install the new 9130 AP's before the underlying network will change. Because its an research environment we want to know exactly how the RF propagate with these new 9130 AP's. So we changed one AP to an EWC like AP. EWC stands for Embedded Wireless Controller, which will make the AP join onto his own controller, in this way we can use if for an Ap-On-A-Stick survey. Unpack the AP and hook it up to a power Injector ( I used the AIR-PWRINJ6). Connect the OUT to your laptop and give it the IP 192.168.1.10/24. Factory Reset Before converting the Access Point Iit is best practice to perform a factory reset, even if it is brand new: Unplug the AP from its power source Plug the console cable in and open a serial session on your PC Press and hold the Mode/Reset button on the AP Plug the AP back to its power source while still holding the Mode/Reset button Continue holding the button for 30 seconds, you can see the countdown on your terminal console.
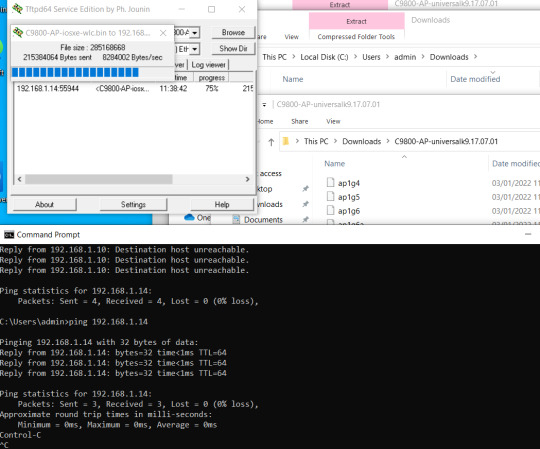
Download TFTP to your laptop and download the EWC software from the Cisco site.
Mine is called C9800-AP-universalk9.17.01.01.zip, unpack it and it contains all the AP's software image that support this and the image for the Controller.
EWC .bin image (example: C9800-AP-iosxe-wlc.bin)
AP image for all APs that can join EWC (example: ap1g4, ap1g7)
After its done downloading and booting up enter the a new enable secret password for the WLC and choice option 2 to save it.
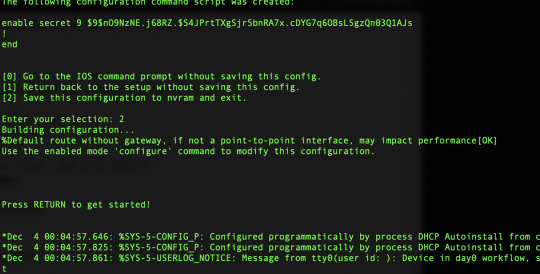
After that create an account for the GUI access and enable http in this order:
Option 1 : Initial CLI Configuration
Once the EWC partition boots up, a prompt will offer to start up an initial configuration wizard. This article will cover manual configuration from scratch, without the use of Catalyst Wireless app or web browser wizard:
######## Cteates local user admin ######## EWC(config)#user-name admin EWC(config-user-name)#privilege 15 EWC(config-user-name)#password 0 Cisco123 EWC(config-user-name)#exit ######## Specifies credentials used to log into APs joined to this EWC ######## EWC(config)#ap profile default-ap-profile EWC(config-ap-profile)#mgmtuser username admin password 0 Cisco123 secret 0 Cisco123 EWC(config-ap-profile)#exit ######## Configures management interface IP address and subnet######## EWC(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0 EWC(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.15 255.255.255.0 EWC(config-if)#exit ######## Default gateway IP address ######## EWC(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1 ######## Enables web interface of EWC ######## EWC(config)#ip http server EWC(config)#ip http secure-server ######## Write to memory ######## EWC(config)#end EWC#write memory
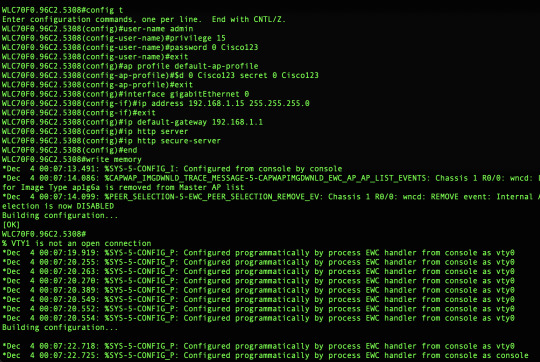
The AP will already be joined but you need to create a new WLAN profile with the corresponding tags.
First time its booting up I saw the provision SSID "CiscoAirProvision-5308" appear as SSID
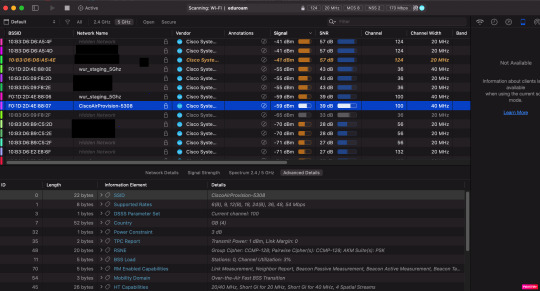
Cisco docs say it only send out by the master "the pre-defined CiscoAirProvision Service Set Identifier (SSID) is advertised only by the master AP and not by other APs" but after creating some SSID and let it run for 15minutes the provisioning SSID was gone and I didnt saw it coming back. We also dont need this because with the special SSID you can configure it trough an app on your mobile which we dont use.
Funny thing is that after a reboot the AP gets an random IP address in subnet which cannot reach the ewc so once the ewc is booted login the AP's console port and change its IP address.
Accessing AP Console From EWC (former apciscoshell)
When console cable is plugged into the AP running EWC image, an EWC prompt will be shown by default. If, for any reason, access to the underlying AP shell is required, it can be done using:
EWC#wireless ewc-ap ap shell username admin [email protected]'s password: Cisco123
Change Ip address: AP70F0.96C2.5308#capwap ap ip 192.168.1.14 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Notes That 192.168.1.15/24 is the subnet where the EWC is in. Note Internal DHCP server is not supported in EWC.
1 note
·
View note