Title is from the opening line of Sholem Aleichem's railroad stories -- "I am a passenger". I have a Merlin sideblog now! @camelotluteguild
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
this is a long shot, but does anyone know of any immigration lawyers who are familiar with the issues facing palestinians and willing to help, or may know someone who does? and ideally speak arabic too? my palestinian-american friend is trying to get her partner out of the west bank rn and is open to marrying him, but they def need legal help. it’s urgent as the west bank is now being bombed by israel as well.
125 notes
·
View notes
Text
for US citizens: call and email your reps about the genocide of Gaza
^ this is a script and also an auto-call thing that makes it very simple to call
^ here’s an easy email form
this action is organized by a Jewish organization but you don’t need to be Jewish to use this site to contact your reps
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo
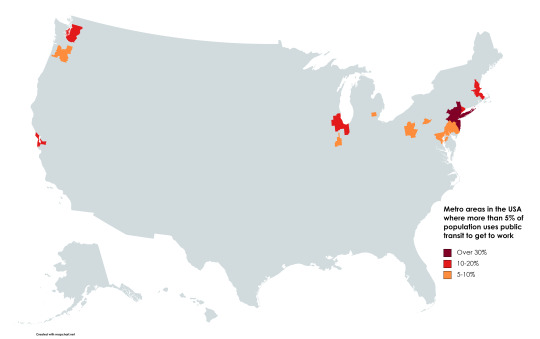
Metro areas in the USA where more than 5% of population uses public transit to get to work.
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
leonard cohen's you want it darker should be remixed and played in clubs like if i heard "hineni hineni....i'm ready my lord" and then the most insane beat drop of my life i'd see god on the dance floor
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
Translation thoughts on the greatest poem of our time, “His wife has filled his house with chintz. To keep it real I fuck him on the floor”
It’s actually quite tricky to translate. Because it’s so short, each word and grammatical construction is carrying a lot of weight. It also, as people have noted, plays with registers. “Chintz” is a word with its own set of associations. Chintz is a type of fabric with its origins in India. The disparaging connotation is from chintz’s eventual commonality. Chintz was actually banned from England and France because the local textile mills couldn’t compete.
Keep it real” is tremendously difficult to translate – it’s a bit difficult to even define. It means to be authentic and genuine, but it also has connotations of staying true to one’s roots. Like many English slang words, it comes first from AAVE. From this article on the phrase:
“[K]eeping it real meant performing an individual’s experience of being Black in the United States. As such, it became a form of resistance. Insisting on a different reality, one that wasn’t recognized by the dominant culture, empowered Black people to ‘forge a parallel system of meaning,’ according to cultural critic Mich Nyawalo…The phrase’s roots in racialized resistance, however, were erased when it was adopted by the mostly-White film world of the 1970s and ’80s….Keeping it real in this context indicated a performance done so well that audiences could forget it was a performance.This version of keeping it real wasn’t about testifying to personal experience; it was about inventing it.”
One has to imagine that jjbang8 did not have the origins of these phrases in mind when composing the poem, but even if by coincidence, the etymological and cultural journeys of these two central lexemes perfectly reflect the themes of the poem. The two words have themselves traveled away from the authenticity they once represented, and, in a new context, have taken on new meanings – the hero of our poem, the unnamed “him”, is, presumably, in quite a similar situation.
Setting aside the question of register, of the phonology, prosody, and meter of the original, of the information that is transmitted through bits of grammar that don’t necessarily exist in other languages – a gifted translator might be able to account for all of these – how do you translate the journey of the words themselves?
In my translations, I decided to go for the most evocative words, even if they don’t evoke the exact same things as in the original. The strength of these two lines is that they imply that there’s more than just what you see, whether that’s the details of the story – what’s happening in the marriage? how do the narrator and the husband know each other? – or the cultural background of the very words themselves. I wanted to try and replicate this effect.
Yiddish first:
זייַן ווייַב האָט אָנגעפֿילט זייַן הויז מיט הבלים
צו בלייַבן וויטיש, איך שטוף אים אופֿן דיל. zayn vayb hot ongefilt zayn hoyz mit havolim.
tsu blaybn vitish, ikh shtup im afn dil
This translation is pretty direct. There is a word for chintz in Yiddish – tsits – but, as far as I can tell, it refers only to the fabric; it doesn’t have the same derogatory connotation as in English. I chose, instead, havolim, a loshn-koydesh word that means “vanity, nothingness, nonsense, trifles”. In Hebrew, it can also mean breath or vapor. I chose this over the other competitors because it, too, is a word with a journey and with a secondary meaning. Rather than imagining the bright prints of chintz, we might imagine a more olfactory implication – his wife has filled his house with perfumes or cleaning fluids. It can carry the implication that something is being masked as well as the associations with vanity and gaudiness.
Vitish – Okay, this is a good one. Keep in mind, of course, that I’ve never heard or seen it used before today, so my understanding of its nuances is very limited, but I’ll explain to you exactly how I am sourcing its meaning. The Comprehensive Yiddish-English Dictionary (CYED) gives this as “gone astray (esp. woman); slang correct, honest”. I used the Yiddish Book Center’s optical character recognition software, which allows you to search for strings in their corpus, to confirm that both usages are, in fact, attested. It’s a pretty rare word in text, though, as the CYED implies, it might have been more common in spoken speech. It appears in a glossary in “Bay unds yuden” (Among Us Jews) as a thieves cant word, where it’s definted as נאַריש, שרעקעוודיק, אונבעהאלפ. אויך נישט גנביש. אין דער דייַטשער גאַונער-שפראַך – witsch – נאַריש, or “foolish, terrible, clumsy/pathetic. not of the thieves world. in the German thieves cant witsch means foolish”. A vitishe nekeyve (vitishe woman) is either a slacker or a prostitute. I can’t prove this for sure, but my sense is that it might come from the same root as vitz, joke (it’s used a couple of times in the corpus to mention laughing at a vitish remark – which makes it seem kind of similar to witty). I assume the German thieve’s cant that’s being referred to is Rotwelsch, which has its own fascinating history and, in fact, incorporates a lot of Yiddish. In fact, for this reason, some of the first Yiddish linguists were actually criminologists! What an excellent set of associations, no? It has the slangy sense of straightforward of honest; it has a sense of sexual non-normativity (we might use it to read into the relationship between the narrator and the husband) – and a feminized one at that; it was used by an underground subculture, and, again, the meaning there was quite different – like the “real” in “keeping it real” it was used to indicate whether or not someone was “in” on the life (tho “real” is used to mean that the person is in, while “vitish” is used to mean they’re not). It’s variety of meanings are more ambiguous than “keep it real”, which can pretty much only be read positively, and it also brings in a tinge of criminality. Though it doesn’t have the same exact connotations as “keep it real”, I think it’s about as ideal of a fit as we’ll get because it’s equally evocative of more below the surface. I also chose “tsu blaybn vitish”, which is “to stay vitish”, as opposed to something like “to make it vitish” to keep the slight ambiguity of time that “keep it real” has – keeping it real does< I think, imply that there is a pre-existing “real” to which one can adhere, so I wanted to imply the same.
The rest is straight-forward. “Shtup” is one of a few words the Comprehensive English-Yiddish Dictionary (CEYD) gives for “fuck”, and I think it has a nice sound.
Ok, now Russian
женой твой дом наполнен финтифлюшками
чтоб не блудить с пути, ебемся на полу
zhenoy tvoy dom napolnin fintiflyushkami.
shtob ne bludit’ s puti’, yebyomsya na polu
In order to preserve, more or less, the iambic meter, I made a few more changes here – since Russian, unlike Yiddish, is not a Germanic language, it’s harder to keep the same structure + word order while also maintaining the rhythm. I would translate this back to English as:
“Your house is filled with trifles by your wife. To not stray off the path, we’re fucking on the floor”
So a few notes before we get into the choice of words for “chintz” and “keep it real”. To preserve the iamb, I changed “his” to “your”. This changes the lines from a narration of events to some outside party to a conversation between the two men at the center. Russian also has both formal and informal you (formal you is also the plural form, as is the case in a number of other languages). I went with informal you because I wanted to preserve the fact that his wife has filled his house not their house, as someone pointed out in the original chain (though I don’t think that differentiation is nearly as striking in the 2nd person) and because it’s unlikely you’d be on formal you with someone you’re fucking (unless it’s, like, a kink thing). I honestly didn’t even consider making it formal, but that would actually raise a lot of interesting implications about the relationship between the speaker and the husband, as well as with what that means about the “realness” of the situation. Is, in fact, the narrator only creating a mirage of a more real, more meaningful encounter, while the actual truth – that there is a woman the husband has made promises to that he’s betraying – is obscured? that this intimacy is just a facade? Is there perhaps some sort of power differential that the narrator wishes to point out? Or perhaps is the way that the narrator is keeping it real by pointing out the distance between the two of them? there is no pretense of intimacy, the narrator is calling this what it is – an encounter without deeper significance?
Much to think about, but I actually think the two men do have history – i think the narrator remembers the house back when it was actually only “his house” and was as yet unfilled with chintz. We also don’t know what they were calling each other prior to this moment. This could be the first time they switched to the informal you.
Ok moving on, I originally translated it as “твой дом наполнен финтифлюшками жены”. Honestly, this sounds more elegant than what I have now, but I ultimately though removing the wife from either a subject or agent position (grammatically, I mean) was too big a betrayal of the original. The original judges the wife. She took an active role in filling the house. If she were made passive, that read is certainly a possible one – perhaps even the dominant one – but it could also read more like “we are doing this in a space filled with reminders of his wife and the life they share” – the action of filling is no longer what’s being focused on. Why do I say the current translation is inelegant? I feel you stumble over it a little, because it’s almost a garden path sentence. This is also an assset though. “Zhenoy tvoy dom napolnen” is a fully grammatical sentence on its own, and it means “Your house is filled by your wife” – as in English, the primary read is that the wife is what the house is full of. If the sentence makes you stumble, perhaps that’s even good – we focus, for good reason, on the relationship between the two men, but in a translation, the wife is able to draw more attention to herself.
Ok, chintz: I chose the word “финтифлюшки” (fintiflyushki), meaning trifle/bobble/tchotchke, because it, allegedly, comes from the german phrase finten und flausen, meaning illusions and vanity/nonsense. Once again, I like that the word has a journey, specifically a cross-linguistic one.
Keep it real: this one, frankly, fails to capture the impact of the original, in my opinion, but allow me to explain the reasoning. “Stray off the path” implies, again, that there is some sort of path that both the narrator and the husband were on before the wife and the chintz – and one they intend to continue taking, one that this act is a maintenance of. It brings in a little irony, since the husband very much is straying from the path of his marriage. “Bludit’“ can also mean to be unfaithful in a marriage (as, in fact, can “stray”). The proto-slavic word it comes from can mean to delude or debauch – they want to do the latter but not the former.
As for register – “shtob” is a bit informal. I would write the full version (shto by) in an email, for example. The word for fuck, yebyomsa, is from one of the “mat” words, the extra special top tier of russian swears, definitely not to be said in polite company (and, if you are a man of a certain generation or background, not in front of women; it’s not that the use of mat automatically invokes a male-only environment, but if we’re already thinking that deeply about it. But while we’re on the topic, i will say that in my circles in the US, women use mat much more actively than men (at least in front of me, who was, up until recently, a woman and also a child).)
Ok i think that’s all the comments i have!
#french speakers are really holding up this post. glad this resonated with the French community#chintzhouse translations#long post#also i know no French unfortunately but is Google translate correct in telling me that the 2nd line means#'i fuck him on the ground to keep his feet there'#bc if so that's very clever#it might be that others have already played around with the idea of using an equivalent of 'grounded'#to both convey 'keep it real' and evoke the specific physical space#which honestly -- if your language does that that might be the best way to go
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
Translation thoughts on the greatest poem of our time, “His wife has filled his house with chintz. To keep it real I fuck him on the floor”
It’s actually quite tricky to translate. Because it’s so short, each word and grammatical construction is carrying a lot of weight. It also, as people have noted, plays with registers. “Chintz” is a word with its own set of associations. Chintz is a type of fabric with its origins in India. The disparaging connotation is from chintz’s eventual commonality. Chintz was actually banned from England and France because the local textile mills couldn’t compete.
Keep it real” is tremendously difficult to translate – it’s a bit difficult to even define. It means to be authentic and genuine, but it also has connotations of staying true to one’s roots. Like many English slang words, it comes first from AAVE. From this article on the phrase:
“[K]eeping it real meant performing an individual’s experience of being Black in the United States. As such, it became a form of resistance. Insisting on a different reality, one that wasn’t recognized by the dominant culture, empowered Black people to ‘forge a parallel system of meaning,’ according to cultural critic Mich Nyawalo…The phrase’s roots in racialized resistance, however, were erased when it was adopted by the mostly-White film world of the 1970s and ’80s….Keeping it real in this context indicated a performance done so well that audiences could forget it was a performance.This version of keeping it real wasn’t about testifying to personal experience; it was about inventing it.”
One has to imagine that jjbang8 did not have the origins of these phrases in mind when composing the poem, but even if by coincidence, the etymological and cultural journeys of these two central lexemes perfectly reflect the themes of the poem. The two words have themselves traveled away from the authenticity they once represented, and, in a new context, have taken on new meanings – the hero of our poem, the unnamed “him”, is, presumably, in quite a similar situation.
Setting aside the question of register, of the phonology, prosody, and meter of the original, of the information that is transmitted through bits of grammar that don’t necessarily exist in other languages – a gifted translator might be able to account for all of these – how do you translate the journey of the words themselves?
In my translations, I decided to go for the most evocative words, even if they don’t evoke the exact same things as in the original. The strength of these two lines is that they imply that there’s more than just what you see, whether that’s the details of the story – what’s happening in the marriage? how do the narrator and the husband know each other? – or the cultural background of the very words themselves. I wanted to try and replicate this effect.
Yiddish first:
זייַן ווייַב האָט אָנגעפֿילט זייַן הויז מיט הבלים
צו בלייַבן וויטיש, איך שטוף אים אופֿן דיל. zayn vayb hot ongefilt zayn hoyz mit havolim.
tsu blaybn vitish, ikh shtup im afn dil
This translation is pretty direct. There is a word for chintz in Yiddish – tsits – but, as far as I can tell, it refers only to the fabric; it doesn’t have the same derogatory connotation as in English. I chose, instead, havolim, a loshn-koydesh word that means “vanity, nothingness, nonsense, trifles”. In Hebrew, it can also mean breath or vapor. I chose this over the other competitors because it, too, is a word with a journey and with a secondary meaning. Rather than imagining the bright prints of chintz, we might imagine a more olfactory implication – his wife has filled his house with perfumes or cleaning fluids. It can carry the implication that something is being masked as well as the associations with vanity and gaudiness.
Vitish – Okay, this is a good one. Keep in mind, of course, that I’ve never heard or seen it used before today, so my understanding of its nuances is very limited, but I’ll explain to you exactly how I am sourcing its meaning. The Comprehensive Yiddish-English Dictionary (CYED) gives this as “gone astray (esp. woman); slang correct, honest”. I used the Yiddish Book Center’s optical character recognition software, which allows you to search for strings in their corpus, to confirm that both usages are, in fact, attested. It’s a pretty rare word in text, though, as the CYED implies, it might have been more common in spoken speech. It appears in a glossary in “Bay unds yuden” (Among Us Jews) as a thieves cant word, where it’s definted as נאַריש, שרעקעוודיק, אונבעהאלפ. אויך נישט גנביש. אין דער דייַטשער גאַונער-שפראַך – witsch – נאַריש, or “foolish, terrible, clumsy/pathetic. not of the thieves world. in the German thieves cant witsch means foolish”. A vitishe nekeyve (vitishe woman) is either a slacker or a prostitute. I can’t prove this for sure, but my sense is that it might come from the same root as vitz, joke (it’s used a couple of times in the corpus to mention laughing at a vitish remark – which makes it seem kind of similar to witty). I assume the German thieve’s cant that’s being referred to is Rotwelsch, which has its own fascinating history and, in fact, incorporates a lot of Yiddish. In fact, for this reason, some of the first Yiddish linguists were actually criminologists! What an excellent set of associations, no? It has the slangy sense of straightforward of honest; it has a sense of sexual non-normativity (we might use it to read into the relationship between the narrator and the husband) – and a feminized one at that; it was used by an underground subculture, and, again, the meaning there was quite different – like the “real” in “keeping it real” it was used to indicate whether or not someone was “in” on the life (tho “real” is used to mean that the person is in, while “vitish” is used to mean they’re not). It’s variety of meanings are more ambiguous than “keep it real”, which can pretty much only be read positively, and it also brings in a tinge of criminality. Though it doesn’t have the same exact connotations as “keep it real”, I think it’s about as ideal of a fit as we’ll get because it’s equally evocative of more below the surface. I also chose “tsu blaybn vitish”, which is “to stay vitish”, as opposed to something like “to make it vitish” to keep the slight ambiguity of time that “keep it real” has – keeping it real does< I think, imply that there is a pre-existing “real” to which one can adhere, so I wanted to imply the same.
The rest is straight-forward. “Shtup” is one of a few words the Comprehensive English-Yiddish Dictionary (CEYD) gives for “fuck”, and I think it has a nice sound.
Ok, now Russian
женой твой дом наполнен финтифлюшками
чтоб не блудить с пути, ебемся на полу
zhenoy tvoy dom napolnin fintiflyushkami.
shtob ne bludit’ s puti’, yebyomsya na polu
In order to preserve, more or less, the iambic meter, I made a few more changes here – since Russian, unlike Yiddish, is not a Germanic language, it’s harder to keep the same structure + word order while also maintaining the rhythm. I would translate this back to English as:
“Your house is filled with trifles by your wife. To not stray off the path, we’re fucking on the floor”
So a few notes before we get into the choice of words for “chintz” and “keep it real”. To preserve the iamb, I changed “his” to “your”. This changes the lines from a narration of events to some outside party to a conversation between the two men at the center. Russian also has both formal and informal you (formal you is also the plural form, as is the case in a number of other languages). I went with informal you because I wanted to preserve the fact that his wife has filled his house not their house, as someone pointed out in the original chain (though I don’t think that differentiation is nearly as striking in the 2nd person) and because it’s unlikely you’d be on formal you with someone you’re fucking (unless it’s, like, a kink thing). I honestly didn’t even consider making it formal, but that would actually raise a lot of interesting implications about the relationship between the speaker and the husband, as well as with what that means about the “realness” of the situation. Is, in fact, the narrator only creating a mirage of a more real, more meaningful encounter, while the actual truth – that there is a woman the husband has made promises to that he’s betraying – is obscured? that this intimacy is just a facade? Is there perhaps some sort of power differential that the narrator wishes to point out? Or perhaps is the way that the narrator is keeping it real by pointing out the distance between the two of them? there is no pretense of intimacy, the narrator is calling this what it is – an encounter without deeper significance?
Much to think about, but I actually think the two men do have history – i think the narrator remembers the house back when it was actually only “his house” and was as yet unfilled with chintz. We also don’t know what they were calling each other prior to this moment. This could be the first time they switched to the informal you.
Ok moving on, I originally translated it as “твой дом наполнен финтифлюшками жены”. Honestly, this sounds more elegant than what I have now, but I ultimately though removing the wife from either a subject or agent position (grammatically, I mean) was too big a betrayal of the original. The original judges the wife. She took an active role in filling the house. If she were made passive, that read is certainly a possible one – perhaps even the dominant one – but it could also read more like “we are doing this in a space filled with reminders of his wife and the life they share” – the action of filling is no longer what’s being focused on. Why do I say the current translation is inelegant? I feel you stumble over it a little, because it’s almost a garden path sentence. This is also an assset though. “Zhenoy tvoy dom napolnen” is a fully grammatical sentence on its own, and it means “Your house is filled by your wife” – as in English, the primary read is that the wife is what the house is full of. If the sentence makes you stumble, perhaps that’s even good – we focus, for good reason, on the relationship between the two men, but in a translation, the wife is able to draw more attention to herself.
Ok, chintz: I chose the word “финтифлюшки” (fintiflyushki), meaning trifle/bobble/tchotchke, because it, allegedly, comes from the german phrase finten und flausen, meaning illusions and vanity/nonsense. Once again, I like that the word has a journey, specifically a cross-linguistic one.
Keep it real: this one, frankly, fails to capture the impact of the original, in my opinion, but allow me to explain the reasoning. “Stray off the path” implies, again, that there is some sort of path that both the narrator and the husband were on before the wife and the chintz – and one they intend to continue taking, one that this act is a maintenance of. It brings in a little irony, since the husband very much is straying from the path of his marriage. “Bludit’“ can also mean to be unfaithful in a marriage (as, in fact, can “stray”). The proto-slavic word it comes from can mean to delude or debauch – they want to do the latter but not the former.
As for register – “shtob” is a bit informal. I would write the full version (shto by) in an email, for example. The word for fuck, yebyomsa, is from one of the “mat” words, the extra special top tier of russian swears, definitely not to be said in polite company (and, if you are a man of a certain generation or background, not in front of women; it’s not that the use of mat automatically invokes a male-only environment, but if we’re already thinking that deeply about it. But while we’re on the topic, i will say that in my circles in the US, women use mat much more actively than men (at least in front of me, who was, up until recently, a woman and also a child).)
Ok i think that’s all the comments i have!
#chintzhouse translations#long post#i like how people have been playing with the implications of the 'fill' in the first line
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
Translation thoughts on the greatest poem of our time, “His wife has filled his house with chintz. To keep it real I fuck him on the floor”
It’s actually quite tricky to translate. Because it’s so short, each word and grammatical construction is carrying a lot of weight. It also, as people have noted, plays with registers. “Chintz” is a word with its own set of associations. Chintz is a type of fabric with its origins in India. The disparaging connotation is from chintz’s eventual commonality. Chintz was actually banned from England and France because the local textile mills couldn’t compete.
Keep it real” is tremendously difficult to translate – it’s a bit difficult to even define. It means to be authentic and genuine, but it also has connotations of staying true to one’s roots. Like many English slang words, it comes first from AAVE. From this article on the phrase:
“[K]eeping it real meant performing an individual’s experience of being Black in the United States. As such, it became a form of resistance. Insisting on a different reality, one that wasn’t recognized by the dominant culture, empowered Black people to ‘forge a parallel system of meaning,’ according to cultural critic Mich Nyawalo…The phrase’s roots in racialized resistance, however, were erased when it was adopted by the mostly-White film world of the 1970s and ’80s….Keeping it real in this context indicated a performance done so well that audiences could forget it was a performance.This version of keeping it real wasn’t about testifying to personal experience; it was about inventing it.”
One has to imagine that jjbang8 did not have the origins of these phrases in mind when composing the poem, but even if by coincidence, the etymological and cultural journeys of these two central lexemes perfectly reflect the themes of the poem. The two words have themselves traveled away from the authenticity they once represented, and, in a new context, have taken on new meanings – the hero of our poem, the unnamed “him”, is, presumably, in quite a similar situation.
Setting aside the question of register, of the phonology, prosody, and meter of the original, of the information that is transmitted through bits of grammar that don’t necessarily exist in other languages – a gifted translator might be able to account for all of these – how do you translate the journey of the words themselves?
In my translations, I decided to go for the most evocative words, even if they don’t evoke the exact same things as in the original. The strength of these two lines is that they imply that there’s more than just what you see, whether that’s the details of the story – what’s happening in the marriage? how do the narrator and the husband know each other? – or the cultural background of the very words themselves. I wanted to try and replicate this effect.
Yiddish first:
זייַן ווייַב האָט אָנגעפֿילט זייַן הויז מיט הבלים
צו בלייַבן וויטיש, איך שטוף אים אופֿן דיל. zayn vayb hot ongefilt zayn hoyz mit havolim.
tsu blaybn vitish, ikh shtup im afn dil
This translation is pretty direct. There is a word for chintz in Yiddish – tsits – but, as far as I can tell, it refers only to the fabric; it doesn’t have the same derogatory connotation as in English. I chose, instead, havolim, a loshn-koydesh word that means “vanity, nothingness, nonsense, trifles”. In Hebrew, it can also mean breath or vapor. I chose this over the other competitors because it, too, is a word with a journey and with a secondary meaning. Rather than imagining the bright prints of chintz, we might imagine a more olfactory implication – his wife has filled his house with perfumes or cleaning fluids. It can carry the implication that something is being masked as well as the associations with vanity and gaudiness.
Vitish – Okay, this is a good one. Keep in mind, of course, that I’ve never heard or seen it used before today, so my understanding of its nuances is very limited, but I’ll explain to you exactly how I am sourcing its meaning. The Comprehensive Yiddish-English Dictionary (CYED) gives this as “gone astray (esp. woman); slang correct, honest”. I used the Yiddish Book Center’s optical character recognition software, which allows you to search for strings in their corpus, to confirm that both usages are, in fact, attested. It’s a pretty rare word in text, though, as the CYED implies, it might have been more common in spoken speech. It appears in a glossary in “Bay unds yuden” (Among Us Jews) as a thieves cant word, where it’s definted as נאַריש, שרעקעוודיק, אונבעהאלפ. אויך נישט גנביש. אין דער דייַטשער גאַונער-שפראַך – witsch – נאַריש, or “foolish, terrible, clumsy/pathetic. not of the thieves world. in the German thieves cant witsch means foolish”. A vitishe nekeyve (vitishe woman) is either a slacker or a prostitute. I can’t prove this for sure, but my sense is that it might come from the same root as vitz, joke (it’s used a couple of times in the corpus to mention laughing at a vitish remark – which makes it seem kind of similar to witty). I assume the German thieve’s cant that’s being referred to is Rotwelsch, which has its own fascinating history and, in fact, incorporates a lot of Yiddish. In fact, for this reason, some of the first Yiddish linguists were actually criminologists! What an excellent set of associations, no? It has the slangy sense of straightforward of honest; it has a sense of sexual non-normativity (we might use it to read into the relationship between the narrator and the husband) – and a feminized one at that; it was used by an underground subculture, and, again, the meaning there was quite different – like the “real” in “keeping it real” it was used to indicate whether or not someone was “in” on the life (tho “real” is used to mean that the person is in, while “vitish” is used to mean they’re not). It’s variety of meanings are more ambiguous than “keep it real”, which can pretty much only be read positively, and it also brings in a tinge of criminality. Though it doesn’t have the same exact connotations as “keep it real”, I think it’s about as ideal of a fit as we’ll get because it’s equally evocative of more below the surface. I also chose “tsu blaybn vitish”, which is “to stay vitish”, as opposed to something like “to make it vitish” to keep the slight ambiguity of time that “keep it real” has – keeping it real does< I think, imply that there is a pre-existing “real” to which one can adhere, so I wanted to imply the same.
The rest is straight-forward. “Shtup” is one of a few words the Comprehensive English-Yiddish Dictionary (CEYD) gives for “fuck”, and I think it has a nice sound.
Ok, now Russian
женой твой дом наполнен финтифлюшками
чтоб не блудить с пути, ебемся на полу
zhenoy tvoy dom napolnin fintiflyushkami.
shtob ne bludit’ s puti’, yebyomsya na polu
In order to preserve, more or less, the iambic meter, I made a few more changes here – since Russian, unlike Yiddish, is not a Germanic language, it’s harder to keep the same structure + word order while also maintaining the rhythm. I would translate this back to English as:
“Your house is filled with trifles by your wife. To not stray off the path, we’re fucking on the floor”
So a few notes before we get into the choice of words for “chintz” and “keep it real”. To preserve the iamb, I changed “his” to “your”. This changes the lines from a narration of events to some outside party to a conversation between the two men at the center. Russian also has both formal and informal you (formal you is also the plural form, as is the case in a number of other languages). I went with informal you because I wanted to preserve the fact that his wife has filled his house not their house, as someone pointed out in the original chain (though I don’t think that differentiation is nearly as striking in the 2nd person) and because it’s unlikely you’d be on formal you with someone you’re fucking (unless it’s, like, a kink thing). I honestly didn’t even consider making it formal, but that would actually raise a lot of interesting implications about the relationship between the speaker and the husband, as well as with what that means about the “realness” of the situation. Is, in fact, the narrator only creating a mirage of a more real, more meaningful encounter, while the actual truth – that there is a woman the husband has made promises to that he’s betraying – is obscured? that this intimacy is just a facade? Is there perhaps some sort of power differential that the narrator wishes to point out? Or perhaps is the way that the narrator is keeping it real by pointing out the distance between the two of them? there is no pretense of intimacy, the narrator is calling this what it is – an encounter without deeper significance?
Much to think about, but I actually think the two men do have history – i think the narrator remembers the house back when it was actually only “his house” and was as yet unfilled with chintz. We also don’t know what they were calling each other prior to this moment. This could be the first time they switched to the informal you.
Ok moving on, I originally translated it as “твой дом наполнен финтифлюшками жены”. Honestly, this sounds more elegant than what I have now, but I ultimately though removing the wife from either a subject or agent position (grammatically, I mean) was too big a betrayal of the original. The original judges the wife. She took an active role in filling the house. If she were made passive, that read is certainly a possible one – perhaps even the dominant one – but it could also read more like “we are doing this in a space filled with reminders of his wife and the life they share” – the action of filling is no longer what’s being focused on. Why do I say the current translation is inelegant? I feel you stumble over it a little, because it’s almost a garden path sentence. This is also an assset though. “Zhenoy tvoy dom napolnen” is a fully grammatical sentence on its own, and it means “Your house is filled by your wife” – as in English, the primary read is that the wife is what the house is full of. If the sentence makes you stumble, perhaps that’s even good – we focus, for good reason, on the relationship between the two men, but in a translation, the wife is able to draw more attention to herself.
Ok, chintz: I chose the word “финтифлюшки” (fintiflyushki), meaning trifle/bobble/tchotchke, because it, allegedly, comes from the german phrase finten und flausen, meaning illusions and vanity/nonsense. Once again, I like that the word has a journey, specifically a cross-linguistic one.
Keep it real: this one, frankly, fails to capture the impact of the original, in my opinion, but allow me to explain the reasoning. “Stray off the path” implies, again, that there is some sort of path that both the narrator and the husband were on before the wife and the chintz – and one they intend to continue taking, one that this act is a maintenance of. It brings in a little irony, since the husband very much is straying from the path of his marriage. “Bludit’“ can also mean to be unfaithful in a marriage (as, in fact, can “stray”). The proto-slavic word it comes from can mean to delude or debauch – they want to do the latter but not the former.
As for register – “shtob” is a bit informal. I would write the full version (shto by) in an email, for example. The word for fuck, yebyomsa, is from one of the “mat” words, the extra special top tier of russian swears, definitely not to be said in polite company (and, if you are a man of a certain generation or background, not in front of women; it’s not that the use of mat automatically invokes a male-only environment, but if we’re already thinking that deeply about it. But while we’re on the topic, i will say that in my circles in the US, women use mat much more actively than men (at least in front of me, who was, up until recently, a woman and also a child).)
Ok i think that’s all the comments i have!
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
Translation thoughts on the greatest poem of our time, “His wife has filled his house with chintz. To keep it real I fuck him on the floor”
It’s actually quite tricky to translate. Because it’s so short, each word and grammatical construction is carrying a lot of weight. It also, as people have noted, plays with registers. “Chintz” is a word with its own set of associations. Chintz is a type of fabric with its origins in India. The disparaging connotation is from chintz’s eventual commonality. Chintz was actually banned from England and France because the local textile mills couldn’t compete.
Keep it real” is tremendously difficult to translate – it’s a bit difficult to even define. It means to be authentic and genuine, but it also has connotations of staying true to one’s roots. Like many English slang words, it comes first from AAVE. From this article on the phrase:
“[K]eeping it real meant performing an individual’s experience of being Black in the United States. As such, it became a form of resistance. Insisting on a different reality, one that wasn’t recognized by the dominant culture, empowered Black people to ‘forge a parallel system of meaning,’ according to cultural critic Mich Nyawalo…The phrase’s roots in racialized resistance, however, were erased when it was adopted by the mostly-White film world of the 1970s and ’80s….Keeping it real in this context indicated a performance done so well that audiences could forget it was a performance.This version of keeping it real wasn’t about testifying to personal experience; it was about inventing it.”
One has to imagine that jjbang8 did not have the origins of these phrases in mind when composing the poem, but even if by coincidence, the etymological and cultural journeys of these two central lexemes perfectly reflect the themes of the poem. The two words have themselves traveled away from the authenticity they once represented, and, in a new context, have taken on new meanings – the hero of our poem, the unnamed “him”, is, presumably, in quite a similar situation.
Setting aside the question of register, of the phonology, prosody, and meter of the original, of the information that is transmitted through bits of grammar that don’t necessarily exist in other languages – a gifted translator might be able to account for all of these – how do you translate the journey of the words themselves?
In my translations, I decided to go for the most evocative words, even if they don’t evoke the exact same things as in the original. The strength of these two lines is that they imply that there’s more than just what you see, whether that’s the details of the story – what’s happening in the marriage? how do the narrator and the husband know each other? – or the cultural background of the very words themselves. I wanted to try and replicate this effect.
Yiddish first:
זייַן ווייַב האָט אָנגעפֿילט זייַן הויז מיט הבלים
צו בלייַבן וויטיש, איך שטוף אים אופֿן דיל. zayn vayb hot ongefilt zayn hoyz mit havolim.
tsu blaybn vitish, ikh shtup im afn dil
This translation is pretty direct. There is a word for chintz in Yiddish – tsits – but, as far as I can tell, it refers only to the fabric; it doesn’t have the same derogatory connotation as in English. I chose, instead, havolim, a loshn-koydesh word that means “vanity, nothingness, nonsense, trifles”. In Hebrew, it can also mean breath or vapor. I chose this over the other competitors because it, too, is a word with a journey and with a secondary meaning. Rather than imagining the bright prints of chintz, we might imagine a more olfactory implication – his wife has filled his house with perfumes or cleaning fluids. It can carry the implication that something is being masked as well as the associations with vanity and gaudiness.
Vitish – Okay, this is a good one. Keep in mind, of course, that I’ve never heard or seen it used before today, so my understanding of its nuances is very limited, but I’ll explain to you exactly how I am sourcing its meaning. The Comprehensive Yiddish-English Dictionary (CYED) gives this as “gone astray (esp. woman); slang correct, honest”. I used the Yiddish Book Center’s optical character recognition software, which allows you to search for strings in their corpus, to confirm that both usages are, in fact, attested. It’s a pretty rare word in text, though, as the CYED implies, it might have been more common in spoken speech. It appears in a glossary in “Bay unds yuden” (Among Us Jews) as a thieves cant word, where it’s definted as נאַריש, שרעקעוודיק, אונבעהאלפ. אויך נישט גנביש. אין דער דייַטשער גאַונער-שפראַך – witsch – נאַריש, or “foolish, terrible, clumsy/pathetic. not of the thieves world. in the German thieves cant witsch means foolish”. A vitishe nekeyve (vitishe woman) is either a slacker or a prostitute. I can’t prove this for sure, but my sense is that it might come from the same root as vitz, joke (it’s used a couple of times in the corpus to mention laughing at a vitish remark – which makes it seem kind of similar to witty). I assume the German thieve’s cant that’s being referred to is Rotwelsch, which has its own fascinating history and, in fact, incorporates a lot of Yiddish. In fact, for this reason, some of the first Yiddish linguists were actually criminologists! What an excellent set of associations, no? It has the slangy sense of straightforward of honest; it has a sense of sexual non-normativity (we might use it to read into the relationship between the narrator and the husband) – and a feminized one at that; it was used by an underground subculture, and, again, the meaning there was quite different – like the “real” in “keeping it real” it was used to indicate whether or not someone was “in” on the life (tho “real” is used to mean that the person is in, while “vitish” is used to mean they’re not). It’s variety of meanings are more ambiguous than “keep it real”, which can pretty much only be read positively, and it also brings in a tinge of criminality. Though it doesn’t have the same exact connotations as “keep it real”, I think it’s about as ideal of a fit as we’ll get because it’s equally evocative of more below the surface. I also chose “tsu blaybn vitish”, which is “to stay vitish”, as opposed to something like “to make it vitish” to keep the slight ambiguity of time that “keep it real” has – keeping it real does< I think, imply that there is a pre-existing “real” to which one can adhere, so I wanted to imply the same.
The rest is straight-forward. “Shtup” is one of a few words the Comprehensive English-Yiddish Dictionary (CEYD) gives for “fuck”, and I think it has a nice sound.
Ok, now Russian
женой твой дом наполнен финтифлюшками
чтоб не блудить с пути, ебемся на полу
zhenoy tvoy dom napolnin fintiflyushkami.
shtob ne bludit’ s puti’, yebyomsya na polu
In order to preserve, more or less, the iambic meter, I made a few more changes here – since Russian, unlike Yiddish, is not a Germanic language, it’s harder to keep the same structure + word order while also maintaining the rhythm. I would translate this back to English as:
“Your house is filled with trifles by your wife. To not stray off the path, we’re fucking on the floor”
So a few notes before we get into the choice of words for “chintz” and “keep it real”. To preserve the iamb, I changed “his” to “your”. This changes the lines from a narration of events to some outside party to a conversation between the two men at the center. Russian also has both formal and informal you (formal you is also the plural form, as is the case in a number of other languages). I went with informal you because I wanted to preserve the fact that his wife has filled his house not their house, as someone pointed out in the original chain (though I don’t think that differentiation is nearly as striking in the 2nd person) and because it’s unlikely you’d be on formal you with someone you’re fucking (unless it’s, like, a kink thing). I honestly didn’t even consider making it formal, but that would actually raise a lot of interesting implications about the relationship between the speaker and the husband, as well as with what that means about the “realness” of the situation. Is, in fact, the narrator only creating a mirage of a more real, more meaningful encounter, while the actual truth – that there is a woman the husband has made promises to that he’s betraying – is obscured? that this intimacy is just a facade? Is there perhaps some sort of power differential that the narrator wishes to point out? Or perhaps is the way that the narrator is keeping it real by pointing out the distance between the two of them? there is no pretense of intimacy, the narrator is calling this what it is – an encounter without deeper significance?
Much to think about, but I actually think the two men do have history – i think the narrator remembers the house back when it was actually only “his house” and was as yet unfilled with chintz. We also don’t know what they were calling each other prior to this moment. This could be the first time they switched to the informal you.
Ok moving on, I originally translated it as “твой дом наполнен финтифлюшками жены”. Honestly, this sounds more elegant than what I have now, but I ultimately though removing the wife from either a subject or agent position (grammatically, I mean) was too big a betrayal of the original. The original judges the wife. She took an active role in filling the house. If she were made passive, that read is certainly a possible one – perhaps even the dominant one – but it could also read more like “we are doing this in a space filled with reminders of his wife and the life they share” – the action of filling is no longer what’s being focused on. Why do I say the current translation is inelegant? I feel you stumble over it a little, because it’s almost a garden path sentence. This is also an assset though. “Zhenoy tvoy dom napolnen” is a fully grammatical sentence on its own, and it means “Your house is filled by your wife” – as in English, the primary read is that the wife is what the house is full of. If the sentence makes you stumble, perhaps that’s even good – we focus, for good reason, on the relationship between the two men, but in a translation, the wife is able to draw more attention to herself.
Ok, chintz: I chose the word “финтифлюшки” (fintiflyushki), meaning trifle/bobble/tchotchke, because it, allegedly, comes from the german phrase finten und flausen, meaning illusions and vanity/nonsense. Once again, I like that the word has a journey, specifically a cross-linguistic one.
Keep it real: this one, frankly, fails to capture the impact of the original, in my opinion, but allow me to explain the reasoning. “Stray off the path” implies, again, that there is some sort of path that both the narrator and the husband were on before the wife and the chintz – and one they intend to continue taking, one that this act is a maintenance of. It brings in a little irony, since the husband very much is straying from the path of his marriage. “Bludit’“ can also mean to be unfaithful in a marriage (as, in fact, can “stray”). The proto-slavic word it comes from can mean to delude or debauch – they want to do the latter but not the former.
As for register – “shtob” is a bit informal. I would write the full version (shto by) in an email, for example. The word for fuck, yebyomsa, is from one of the “mat” words, the extra special top tier of russian swears, definitely not to be said in polite company (and, if you are a man of a certain generation or background, not in front of women; it’s not that the use of mat automatically invokes a male-only environment, but if we’re already thinking that deeply about it. But while we’re on the topic, i will say that in my circles in the US, women use mat much more actively than men (at least in front of me, who was, up until recently, a woman and also a child).)
Ok i think that’s all the comments i have!
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
120,000 armenians are currently being driven from nagorno-karabakh, which they've called home for 2,000 years, by azerbaijan. they are going to armenia, a small, poor country without international backing. please donate to the armenian food bank, a non-profit operating in yerevan that is providing incoming displaced persons with food, clothes, and hygienic goods. i personally know people involved and i can tell you that your money will be put to good use
18K notes
·
View notes
Photo

Rosh Hashanah greeting, attributed to Happy Jack (born Angokwazhuk) (Inupiaq, b. Alaska, c. 1870-1918), Nome, Alaska, United States, 1910, engraved walrus tus and gold inset
With the arrival of whalers in the 19th century, Inuit carvers expanded their repertoires as they exchanged techniques and materials. The complexity and diversity of Inuit subjects increased as more sophisticated interpretations displaced schematic figures and linear ornamentation. The most innovative and influential of the carvers was the Alaskan Inuit Angokwazhuk, known as “Happy Jack.” He is credited with the introduction, after 1892, of the art of engraving walrus tusks with a very fine needle, which resulted in an almost perfect imitation of newspaper halftones and fabric textures.
On this tusk, he ably recorded the faces and attire of a religiously observant Jewish couple, believed to have run a store in Nome. The woman seems to be wearing a wig and is dressed in typical turn-of-the-century style. The man’s beard is neatly trimmed; his top hat suggests a holiday or formal occasion. The Hebrew inscription delivers the traditional Jewish New Year greeting: “May you be inscribed for a good year, 5671 [1910].” In English is added: “Nome, Alaska.”
348 notes
·
View notes
Text


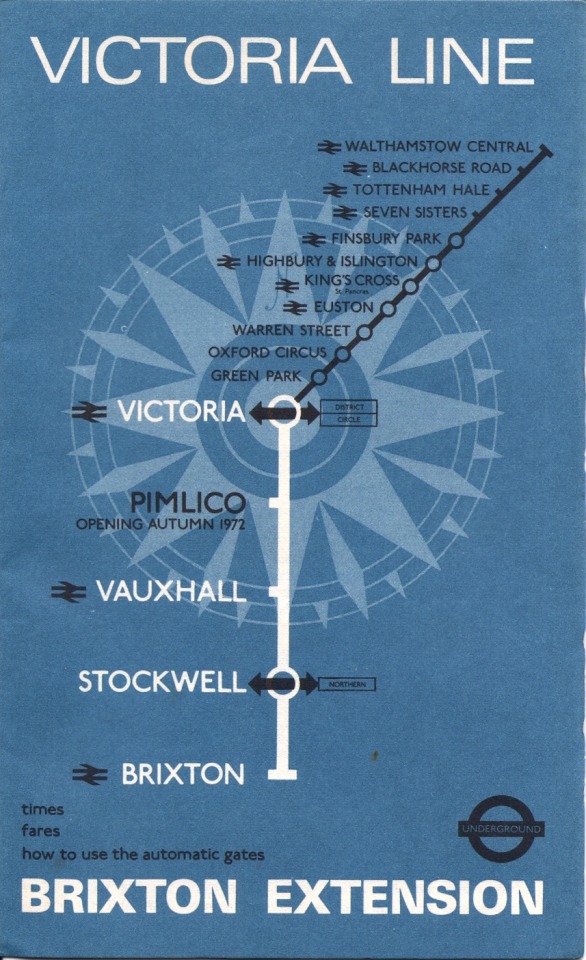

Posters created to advertise the opening and extensions of the Victoria Line 1968-1971 by Tom Eckersley, Denys Nicholls and others
IMages from London Transport Musuem and VADS
Route C: the Victoria Line Opening September 1968
405 notes
·
View notes
Text


Assume you have not forgotten all descriptive words in your moment of need, and that you can speak this language. Regrettably, circumstances do not permit you to spend more than a paragraph scrupulously describing the effect of highlights, and the audience is not necessarily interested in the tiny specific variations of hair color in white people. WHAT COLOR. PICK ONE. GO.
#babygirl in what world is this brunette?????#disclosure of bias: i am a Russian jew and so my and my mothers and many of our family's hair is entirely black#so perhaps in our family we DO divide hair colors into 'dark' (our color) 'light' (mid brown to dark brown)#and 'blond' (light brown to blonde)#BUT even so. this is straight up blond come on#AND also. what the hell kind of bread?? is this color????
9K notes
·
View notes
Note
If you're invested enough, I'd recommend investing in both the online Comprehensive Yiddish-English dictionary (verterbukh.org) and the online Comprehensive English-Yiddish dictionary (englishyiddishdictionary.com) As far as I know, the latter has been updated more recently -- in 2021, they updated it with about 1,000 new words, many of which are hasidisms and yiddishist neologisms. The two dictionaries have pretty substantial overlap, though, and the lexicographic principles are similar. The main reason to get both is that the CYED dictionary is very useful when translating FROM Yiddish and the CEYD is very useful when translating TO Yiddish. If you expect to be doing both of these things a lot, I think it's worth it to get both. You pay for CYED by word and for CEYD by time, and there are generous student discounts available for both -- Harry Bochner runs both websites, so you p much only have to email your student id once :)
If you only want one, think about whether your main goal is to understand Yiddish (CYED) or produce Yiddish (CEYD). I started with verterbukh and got the CEYD only after about a year when I was doing a lot of Yiddish writing and wanted to be easily able to find Yiddish options for the English word I had in mind.
For the vast majority of words, these two will be enough. Come across a Yiddish word neither dictionary recognizes? Do you want to see if a specific expression or word appears frequently? Check THIS shit out:
https://ocr.yiddishbookcenter.org/accounts/login/
This is an ongoing project, but it's already in very usable shape, and I actually use it every more than I expected to. There are currently 11,000 of the Yiddish Book Center's digitized books that have been put through optical character recognition and are now available for digital text search!!!! There's a good number of dictionaries in there too, so sometimes you'll come across a straight-up definition of the word you're looking for. You have to make an account, but the account is free!
Good luck with your Yiddish studies, anon :))
שלום-עליכם!
I’m a relatively new Yiddish learner and I was wondering what you think the best online Yiddish-English dictionary is. Thanks in advance!
Aleichem sholem!
I actually have no opinion on this currently because I made the mistake of buying an absolutely horrible paperback Yiddish-German dictionary I'm now stuck with.
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
Translation thoughts on the greatest poem of our time, “His wife has filled his house with chintz. To keep it real I fuck him on the floor”
It’s actually quite tricky to translate. Because it’s so short, each word and grammatical construction is carrying a lot of weight. It also, as people have noted, plays with registers. “Chintz” is a word with its own set of associations. Chintz is a type of fabric with its origins in India. The disparaging connotation is from chintz’s eventual commonality. Chintz was actually banned from England and France because the local textile mills couldn’t compete.
Keep it real” is tremendously difficult to translate – it’s a bit difficult to even define. It means to be authentic and genuine, but it also has connotations of staying true to one’s roots. Like many English slang words, it comes first from AAVE. From this article on the phrase:
“[K]eeping it real meant performing an individual’s experience of being Black in the United States. As such, it became a form of resistance. Insisting on a different reality, one that wasn’t recognized by the dominant culture, empowered Black people to ‘forge a parallel system of meaning,’ according to cultural critic Mich Nyawalo…The phrase’s roots in racialized resistance, however, were erased when it was adopted by the mostly-White film world of the 1970s and ’80s….Keeping it real in this context indicated a performance done so well that audiences could forget it was a performance.This version of keeping it real wasn’t about testifying to personal experience; it was about inventing it.”
One has to imagine that jjbang8 did not have the origins of these phrases in mind when composing the poem, but even if by coincidence, the etymological and cultural journeys of these two central lexemes perfectly reflect the themes of the poem. The two words have themselves traveled away from the authenticity they once represented, and, in a new context, have taken on new meanings – the hero of our poem, the unnamed “him”, is, presumably, in quite a similar situation.
Setting aside the question of register, of the phonology, prosody, and meter of the original, of the information that is transmitted through bits of grammar that don’t necessarily exist in other languages – a gifted translator might be able to account for all of these – how do you translate the journey of the words themselves?
In my translations, I decided to go for the most evocative words, even if they don’t evoke the exact same things as in the original. The strength of these two lines is that they imply that there’s more than just what you see, whether that’s the details of the story – what’s happening in the marriage? how do the narrator and the husband know each other? – or the cultural background of the very words themselves. I wanted to try and replicate this effect.
Yiddish first:
זייַן ווייַב האָט אָנגעפֿילט זייַן הויז מיט הבלים
צו בלייַבן וויטיש, איך שטוף אים אופֿן דיל. zayn vayb hot ongefilt zayn hoyz mit havolim.
tsu blaybn vitish, ikh shtup im afn dil
This translation is pretty direct. There is a word for chintz in Yiddish – tsits – but, as far as I can tell, it refers only to the fabric; it doesn’t have the same derogatory connotation as in English. I chose, instead, havolim, a loshn-koydesh word that means “vanity, nothingness, nonsense, trifles”. In Hebrew, it can also mean breath or vapor. I chose this over the other competitors because it, too, is a word with a journey and with a secondary meaning. Rather than imagining the bright prints of chintz, we might imagine a more olfactory implication – his wife has filled his house with perfumes or cleaning fluids. It can carry the implication that something is being masked as well as the associations with vanity and gaudiness.
Vitish – Okay, this is a good one. Keep in mind, of course, that I’ve never heard or seen it used before today, so my understanding of its nuances is very limited, but I’ll explain to you exactly how I am sourcing its meaning. The Comprehensive Yiddish-English Dictionary (CYED) gives this as “gone astray (esp. woman); slang correct, honest”. I used the Yiddish Book Center’s optical character recognition software, which allows you to search for strings in their corpus, to confirm that both usages are, in fact, attested. It’s a pretty rare word in text, though, as the CYED implies, it might have been more common in spoken speech. It appears in a glossary in “Bay unds yuden” (Among Us Jews) as a thieves cant word, where it’s definted as נאַריש, שרעקעוודיק, אונבעהאלפ. אויך נישט גנביש. אין דער דייַטשער גאַונער-שפראַך – witsch – נאַריש, or “foolish, terrible, clumsy/pathetic. not of the thieves world. in the German thieves cant witsch means foolish”. A vitishe nekeyve (vitishe woman) is either a slacker or a prostitute. I can’t prove this for sure, but my sense is that it might come from the same root as vitz, joke (it’s used a couple of times in the corpus to mention laughing at a vitish remark – which makes it seem kind of similar to witty). I assume the German thieve’s cant that’s being referred to is Rotwelsch, which has its own fascinating history and, in fact, incorporates a lot of Yiddish. In fact, for this reason, some of the first Yiddish linguists were actually criminologists! What an excellent set of associations, no? It has the slangy sense of straightforward of honest; it has a sense of sexual non-normativity (we might use it to read into the relationship between the narrator and the husband) – and a feminized one at that; it was used by an underground subculture, and, again, the meaning there was quite different – like the “real” in “keeping it real” it was used to indicate whether or not someone was “in” on the life (tho “real” is used to mean that the person is in, while “vitish” is used to mean they’re not). It’s variety of meanings are more ambiguous than “keep it real”, which can pretty much only be read positively, and it also brings in a tinge of criminality. Though it doesn’t have the same exact connotations as “keep it real”, I think it’s about as ideal of a fit as we’ll get because it’s equally evocative of more below the surface. I also chose “tsu blaybn vitish”, which is “to stay vitish”, as opposed to something like “to make it vitish” to keep the slight ambiguity of time that “keep it real” has – keeping it real does< I think, imply that there is a pre-existing “real” to which one can adhere, so I wanted to imply the same.
The rest is straight-forward. “Shtup” is one of a few words the Comprehensive English-Yiddish Dictionary (CEYD) gives for “fuck”, and I think it has a nice sound.
Ok, now Russian
женой твой дом наполнен финтифлюшками
чтоб не блудить с пути, ебемся на полу
zhenoy tvoy dom napolnin fintiflyushkami.
shtob ne bludit’ s puti’, yebyomsya na polu
In order to preserve, more or less, the iambic meter, I made a few more changes here – since Russian, unlike Yiddish, is not a Germanic language, it’s harder to keep the same structure + word order while also maintaining the rhythm. I would translate this back to English as:
“Your house is filled with trifles by your wife. To not stray off the path, we’re fucking on the floor”
So a few notes before we get into the choice of words for “chintz” and “keep it real”. To preserve the iamb, I changed “his” to “your”. This changes the lines from a narration of events to some outside party to a conversation between the two men at the center. Russian also has both formal and informal you (formal you is also the plural form, as is the case in a number of other languages). I went with informal you because I wanted to preserve the fact that his wife has filled his house not their house, as someone pointed out in the original chain (though I don’t think that differentiation is nearly as striking in the 2nd person) and because it’s unlikely you’d be on formal you with someone you’re fucking (unless it’s, like, a kink thing). I honestly didn’t even consider making it formal, but that would actually raise a lot of interesting implications about the relationship between the speaker and the husband, as well as with what that means about the “realness” of the situation. Is, in fact, the narrator only creating a mirage of a more real, more meaningful encounter, while the actual truth – that there is a woman the husband has made promises to that he’s betraying – is obscured? that this intimacy is just a facade? Is there perhaps some sort of power differential that the narrator wishes to point out? Or perhaps is the way that the narrator is keeping it real by pointing out the distance between the two of them? there is no pretense of intimacy, the narrator is calling this what it is – an encounter without deeper significance?
Much to think about, but I actually think the two men do have history – i think the narrator remembers the house back when it was actually only “his house” and was as yet unfilled with chintz. We also don’t know what they were calling each other prior to this moment. This could be the first time they switched to the informal you.
Ok moving on, I originally translated it as “твой дом наполнен финтифлюшками жены”. Honestly, this sounds more elegant than what I have now, but I ultimately though removing the wife from either a subject or agent position (grammatically, I mean) was too big a betrayal of the original. The original judges the wife. She took an active role in filling the house. If she were made passive, that read is certainly a possible one – perhaps even the dominant one – but it could also read more like “we are doing this in a space filled with reminders of his wife and the life they share” – the action of filling is no longer what’s being focused on. Why do I say the current translation is inelegant? I feel you stumble over it a little, because it’s almost a garden path sentence. This is also an assset though. “Zhenoy tvoy dom napolnen” is a fully grammatical sentence on its own, and it means “Your house is filled by your wife” – as in English, the primary read is that the wife is what the house is full of. If the sentence makes you stumble, perhaps that’s even good – we focus, for good reason, on the relationship between the two men, but in a translation, the wife is able to draw more attention to herself.
Ok, chintz: I chose the word “финтифлюшки” (fintiflyushki), meaning trifle/bobble/tchotchke, because it, allegedly, comes from the german phrase finten und flausen, meaning illusions and vanity/nonsense. Once again, I like that the word has a journey, specifically a cross-linguistic one.
Keep it real: this one, frankly, fails to capture the impact of the original, in my opinion, but allow me to explain the reasoning. “Stray off the path” implies, again, that there is some sort of path that both the narrator and the husband were on before the wife and the chintz – and one they intend to continue taking, one that this act is a maintenance of. It brings in a little irony, since the husband very much is straying from the path of his marriage. “Bludit’“ can also mean to be unfaithful in a marriage (as, in fact, can “stray”). The proto-slavic word it comes from can mean to delude or debauch – they want to do the latter but not the former.
As for register – “shtob” is a bit informal. I would write the full version (shto by) in an email, for example. The word for fuck, yebyomsa, is from one of the “mat” words, the extra special top tier of russian swears, definitely not to be said in polite company (and, if you are a man of a certain generation or background, not in front of women; it’s not that the use of mat automatically invokes a male-only environment, but if we’re already thinking that deeply about it. But while we’re on the topic, i will say that in my circles in the US, women use mat much more actively than men (at least in front of me, who was, up until recently, a woman and also a child).)
Ok i think that’s all the comments i have!
#hello??#longpost#chintzhouse translations#this post is a collection of essays at this point#does jjbang8 know of their power
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
Translation thoughts on the greatest poem of our time, “His wife has filled his house with chintz. To keep it real I fuck him on the floor”
It’s actually quite tricky to translate. Because it’s so short, each word and grammatical construction is carrying a lot of weight. It also, as people have noted, plays with registers. “Chintz” is a word with its own set of associations. Chintz is a type of fabric with its origins in India. The disparaging connotation is from chintz’s eventual commonality. Chintz was actually banned from England and France because the local textile mills couldn’t compete.
Keep it real” is tremendously difficult to translate – it’s a bit difficult to even define. It means to be authentic and genuine, but it also has connotations of staying true to one’s roots. Like many English slang words, it comes first from AAVE. From this article on the phrase:
“[K]eeping it real meant performing an individual’s experience of being Black in the United States. As such, it became a form of resistance. Insisting on a different reality, one that wasn’t recognized by the dominant culture, empowered Black people to ‘forge a parallel system of meaning,’ according to cultural critic Mich Nyawalo…The phrase’s roots in racialized resistance, however, were erased when it was adopted by the mostly-White film world of the 1970s and ’80s….Keeping it real in this context indicated a performance done so well that audiences could forget it was a performance.This version of keeping it real wasn’t about testifying to personal experience; it was about inventing it.”
One has to imagine that jjbang8 did not have the origins of these phrases in mind when composing the poem, but even if by coincidence, the etymological and cultural journeys of these two central lexemes perfectly reflect the themes of the poem. The two words have themselves traveled away from the authenticity they once represented, and, in a new context, have taken on new meanings – the hero of our poem, the unnamed “him”, is, presumably, in quite a similar situation.
Setting aside the question of register, of the phonology, prosody, and meter of the original, of the information that is transmitted through bits of grammar that don’t necessarily exist in other languages – a gifted translator might be able to account for all of these – how do you translate the journey of the words themselves?
In my translations, I decided to go for the most evocative words, even if they don’t evoke the exact same things as in the original. The strength of these two lines is that they imply that there’s more than just what you see, whether that’s the details of the story – what’s happening in the marriage? how do the narrator and the husband know each other? – or the cultural background of the very words themselves. I wanted to try and replicate this effect.
Yiddish first:
זייַן ווייַב האָט אָנגעפֿילט זייַן הויז מיט הבלים
צו בלייַבן וויטיש, איך שטוף אים אופֿן דיל. zayn vayb hot ongefilt zayn hoyz mit havolim.
tsu blaybn vitish, ikh shtup im afn dil
This translation is pretty direct. There is a word for chintz in Yiddish – tsits – but, as far as I can tell, it refers only to the fabric; it doesn’t have the same derogatory connotation as in English. I chose, instead, havolim, a loshn-koydesh word that means “vanity, nothingness, nonsense, trifles”. In Hebrew, it can also mean breath or vapor. I chose this over the other competitors because it, too, is a word with a journey and with a secondary meaning. Rather than imagining the bright prints of chintz, we might imagine a more olfactory implication – his wife has filled his house with perfumes or cleaning fluids. It can carry the implication that something is being masked as well as the associations with vanity and gaudiness.
Vitish – Okay, this is a good one. Keep in mind, of course, that I’ve never heard or seen it used before today, so my understanding of its nuances is very limited, but I’ll explain to you exactly how I am sourcing its meaning. The Comprehensive Yiddish-English Dictionary (CYED) gives this as “gone astray (esp. woman); slang correct, honest”. I used the Yiddish Book Center’s optical character recognition software, which allows you to search for strings in their corpus, to confirm that both usages are, in fact, attested. It’s a pretty rare word in text, though, as the CYED implies, it might have been more common in spoken speech. It appears in a glossary in “Bay unds yuden” (Among Us Jews) as a thieves cant word, where it’s definted as נאַריש, שרעקעוודיק, אונבעהאלפ. אויך נישט גנביש. אין דער דייַטשער גאַונער-שפראַך – witsch – נאַריש, or “foolish, terrible, clumsy/pathetic. not of the thieves world. in the German thieves cant witsch means foolish”. A vitishe nekeyve (vitishe woman) is either a slacker or a prostitute. I can’t prove this for sure, but my sense is that it might come from the same root as vitz, joke (it’s used a couple of times in the corpus to mention laughing at a vitish remark – which makes it seem kind of similar to witty). I assume the German thieve’s cant that’s being referred to is Rotwelsch, which has its own fascinating history and, in fact, incorporates a lot of Yiddish. In fact, for this reason, some of the first Yiddish linguists were actually criminologists! What an excellent set of associations, no? It has the slangy sense of straightforward of honest; it has a sense of sexual non-normativity (we might use it to read into the relationship between the narrator and the husband) – and a feminized one at that; it was used by an underground subculture, and, again, the meaning there was quite different – like the “real” in “keeping it real” it was used to indicate whether or not someone was “in” on the life (tho “real” is used to mean that the person is in, while “vitish” is used to mean they’re not). It’s variety of meanings are more ambiguous than “keep it real”, which can pretty much only be read positively, and it also brings in a tinge of criminality. Though it doesn’t have the same exact connotations as “keep it real”, I think it’s about as ideal of a fit as we’ll get because it’s equally evocative of more below the surface. I also chose “tsu blaybn vitish”, which is “to stay vitish”, as opposed to something like “to make it vitish” to keep the slight ambiguity of time that “keep it real” has – keeping it real does< I think, imply that there is a pre-existing “real” to which one can adhere, so I wanted to imply the same.
The rest is straight-forward. “Shtup” is one of a few words the Comprehensive English-Yiddish Dictionary (CEYD) gives for “fuck”, and I think it has a nice sound.
Ok, now Russian
женой твой дом наполнен финтифлюшками
чтоб не блудить с пути, ебемся на полу
zhenoy tvoy dom napolnin fintiflyushkami.
shtob ne bludit’ s puti’, yebyomsya na polu
In order to preserve, more or less, the iambic meter, I made a few more changes here – since Russian, unlike Yiddish, is not a Germanic language, it’s harder to keep the same structure + word order while also maintaining the rhythm. I would translate this back to English as:
“Your house is filled with trifles by your wife. To not stray off the path, we’re fucking on the floor”
So a few notes before we get into the choice of words for “chintz” and “keep it real”. To preserve the iamb, I changed “his” to “your”. This changes the lines from a narration of events to some outside party to a conversation between the two men at the center. Russian also has both formal and informal you (formal you is also the plural form, as is the case in a number of other languages). I went with informal you because I wanted to preserve the fact that his wife has filled his house not their house, as someone pointed out in the original chain (though I don’t think that differentiation is nearly as striking in the 2nd person) and because it’s unlikely you’d be on formal you with someone you’re fucking (unless it’s, like, a kink thing). I honestly didn’t even consider making it formal, but that would actually raise a lot of interesting implications about the relationship between the speaker and the husband, as well as with what that means about the “realness” of the situation. Is, in fact, the narrator only creating a mirage of a more real, more meaningful encounter, while the actual truth – that there is a woman the husband has made promises to that he’s betraying – is obscured? that this intimacy is just a facade? Is there perhaps some sort of power differential that the narrator wishes to point out? Or perhaps is the way that the narrator is keeping it real by pointing out the distance between the two of them? there is no pretense of intimacy, the narrator is calling this what it is – an encounter without deeper significance?
Much to think about, but I actually think the two men do have history – i think the narrator remembers the house back when it was actually only “his house” and was as yet unfilled with chintz. We also don’t know what they were calling each other prior to this moment. This could be the first time they switched to the informal you.
Ok moving on, I originally translated it as “твой дом наполнен финтифлюшками жены”. Honestly, this sounds more elegant than what I have now, but I ultimately though removing the wife from either a subject or agent position (grammatically, I mean) was too big a betrayal of the original. The original judges the wife. She took an active role in filling the house. If she were made passive, that read is certainly a possible one – perhaps even the dominant one – but it could also read more like “we are doing this in a space filled with reminders of his wife and the life they share” – the action of filling is no longer what’s being focused on. Why do I say the current translation is inelegant? I feel you stumble over it a little, because it’s almost a garden path sentence. This is also an assset though. “Zhenoy tvoy dom napolnen” is a fully grammatical sentence on its own, and it means “Your house is filled by your wife” – as in English, the primary read is that the wife is what the house is full of. If the sentence makes you stumble, perhaps that’s even good – we focus, for good reason, on the relationship between the two men, but in a translation, the wife is able to draw more attention to herself.
Ok, chintz: I chose the word “финтифлюшки” (fintiflyushki), meaning trifle/bobble/tchotchke, because it, allegedly, comes from the german phrase finten und flausen, meaning illusions and vanity/nonsense. Once again, I like that the word has a journey, specifically a cross-linguistic one.
Keep it real: this one, frankly, fails to capture the impact of the original, in my opinion, but allow me to explain the reasoning. “Stray off the path” implies, again, that there is some sort of path that both the narrator and the husband were on before the wife and the chintz – and one they intend to continue taking, one that this act is a maintenance of. It brings in a little irony, since the husband very much is straying from the path of his marriage. “Bludit’“ can also mean to be unfaithful in a marriage (as, in fact, can “stray”). The proto-slavic word it comes from can mean to delude or debauch – they want to do the latter but not the former.
As for register – “shtob” is a bit informal. I would write the full version (shto by) in an email, for example. The word for fuck, yebyomsa, is from one of the “mat” words, the extra special top tier of russian swears, definitely not to be said in polite company (and, if you are a man of a certain generation or background, not in front of women; it’s not that the use of mat automatically invokes a male-only environment, but if we’re already thinking that deeply about it. But while we’re on the topic, i will say that in my circles in the US, women use mat much more actively than men (at least in front of me, who was, up until recently, a woman and also a child).)
Ok i think that’s all the comments i have!
#oho!!!!!!!!#i have many thoughts#i love the forcefulness of мишурная дрянь. pulls no punches#i also love the focus on taste in both translations#e.g. when you think of it in the context of camp or other really ostentatious gay subcultures#it's a bit of a role reversal -- the wife is the ostentatious and fake one while the lover is privy to true taste#'to be decent' i really like. the implication that the wife is so gaudy that even a torrid affair in her own home is more tasteful than#whatever her decor situation is#i actually think these translations place more of a focus on the relationship between the wife and the narrator#it almost seems like his affair is a reaction to her as much as to the husband#like he walked into her house and was like 'good lord. ok i have to fuck her husband now#also ty for the info on trenen!#back to the idea of ostentatious/hiding/truth#it's also impossible not to think of it in the context of DL men#is fucking in the house an act of special daring and openness? or is it just another layer to hide behind#is the chintz just as necessary for the men as it is for the wife?
6K notes
·
View notes
Text

I love the use of frauchen and also the tidbit about meter in the tags....that is so interesting and adds a whole extra dimension to the gender dynamics
Translation thoughts on the greatest poem of our time, “His wife has filled his house with chintz. To keep it real I fuck him on the floor”
It’s actually quite tricky to translate. Because it’s so short, each word and grammatical construction is carrying a lot of weight. It also, as people have noted, plays with registers. “Chintz” is a word with its own set of associations. Chintz is a type of fabric with its origins in India. The disparaging connotation is from chintz’s eventual commonality. Chintz was actually banned from England and France because the local textile mills couldn’t compete.
Keep it real” is tremendously difficult to translate – it’s a bit difficult to even define. It means to be authentic and genuine, but it also has connotations of staying true to one’s roots. Like many English slang words, it comes first from AAVE. From this article on the phrase:
“[K]eeping it real meant performing an individual’s experience of being Black in the United States. As such, it became a form of resistance. Insisting on a different reality, one that wasn’t recognized by the dominant culture, empowered Black people to ‘forge a parallel system of meaning,’ according to cultural critic Mich Nyawalo…The phrase’s roots in racialized resistance, however, were erased when it was adopted by the mostly-White film world of the 1970s and ’80s….Keeping it real in this context indicated a performance done so well that audiences could forget it was a performance.This version of keeping it real wasn’t about testifying to personal experience; it was about inventing it.”
One has to imagine that jjbang8 did not have the origins of these phrases in mind when composing the poem, but even if by coincidence, the etymological and cultural journeys of these two central lexemes perfectly reflect the themes of the poem. The two words have themselves traveled away from the authenticity they once represented, and, in a new context, have taken on new meanings – the hero of our poem, the unnamed “him”, is, presumably, in quite a similar situation.
Setting aside the question of register, of the phonology, prosody, and meter of the original, of the information that is transmitted through bits of grammar that don’t necessarily exist in other languages – a gifted translator might be able to account for all of these – how do you translate the journey of the words themselves?
In my translations, I decided to go for the most evocative words, even if they don’t evoke the exact same things as in the original. The strength of these two lines is that they imply that there’s more than just what you see, whether that’s the details of the story – what’s happening in the marriage? how do the narrator and the husband know each other? – or the cultural background of the very words themselves. I wanted to try and replicate this effect.
Yiddish first:
זייַן ווייַב האָט אָנגעפֿילט זייַן הויז מיט הבלים
צו בלייַבן וויטיש, איך שטוף אים אופֿן דיל. zayn vayb hot ongefilt zayn hoyz mit havolim.
tsu blaybn vitish, ikh shtup im afn dil
This translation is pretty direct. There is a word for chintz in Yiddish – tsits – but, as far as I can tell, it refers only to the fabric; it doesn’t have the same derogatory connotation as in English. I chose, instead, havolim, a loshn-koydesh word that means “vanity, nothingness, nonsense, trifles”. In Hebrew, it can also mean breath or vapor. I chose this over the other competitors because it, too, is a word with a journey and with a secondary meaning. Rather than imagining the bright prints of chintz, we might imagine a more olfactory implication – his wife has filled his house with perfumes or cleaning fluids. It can carry the implication that something is being masked as well as the associations with vanity and gaudiness.
Vitish – Okay, this is a good one. Keep in mind, of course, that I’ve never heard or seen it used before today, so my understanding of its nuances is very limited, but I’ll explain to you exactly how I am sourcing its meaning. The Comprehensive Yiddish-English Dictionary (CYED) gives this as “gone astray (esp. woman); slang correct, honest”. I used the Yiddish Book Center’s optical character recognition software, which allows you to search for strings in their corpus, to confirm that both usages are, in fact, attested. It’s a pretty rare word in text, though, as the CYED implies, it might have been more common in spoken speech. It appears in a glossary in “Bay unds yuden” (Among Us Jews) as a thieves cant word, where it’s definted as נאַריש, שרעקעוודיק, אונבעהאלפ. אויך נישט גנביש. אין דער דייַטשער גאַונער-שפראַך – witsch – נאַריש, or “foolish, terrible, clumsy/pathetic. not of the thieves world. in the German thieves cant witsch means foolish”. A vitishe nekeyve (vitishe woman) is either a slacker or a prostitute. I can’t prove this for sure, but my sense is that it might come from the same root as vitz, joke (it’s used a couple of times in the corpus to mention laughing at a vitish remark – which makes it seem kind of similar to witty). I assume the German thieve’s cant that’s being referred to is Rotwelsch, which has its own fascinating history and, in fact, incorporates a lot of Yiddish. In fact, for this reason, some of the first Yiddish linguists were actually criminologists! What an excellent set of associations, no? It has the slangy sense of straightforward of honest; it has a sense of sexual non-normativity (we might use it to read into the relationship between the narrator and the husband) – and a feminized one at that; it was used by an underground subculture, and, again, the meaning there was quite different – like the “real” in “keeping it real” it was used to indicate whether or not someone was “in” on the life (tho “real” is used to mean that the person is in, while “vitish” is used to mean they’re not). It’s variety of meanings are more ambiguous than “keep it real”, which can pretty much only be read positively, and it also brings in a tinge of criminality. Though it doesn’t have the same exact connotations as “keep it real”, I think it’s about as ideal of a fit as we’ll get because it’s equally evocative of more below the surface. I also chose “tsu blaybn vitish”, which is “to stay vitish”, as opposed to something like “to make it vitish” to keep the slight ambiguity of time that “keep it real” has – keeping it real does< I think, imply that there is a pre-existing “real” to which one can adhere, so I wanted to imply the same.
The rest is straight-forward. “Shtup” is one of a few words the Comprehensive English-Yiddish Dictionary (CEYD) gives for “fuck”, and I think it has a nice sound.
Ok, now Russian
женой твой дом наполнен финтифлюшками
чтоб не блудить с пути, ебемся на полу
zhenoy tvoy dom napolnin fintiflyushkami.
shtob ne bludit’ s puti’, yebyomsya na polu
In order to preserve, more or less, the iambic meter, I made a few more changes here – since Russian, unlike Yiddish, is not a Germanic language, it’s harder to keep the same structure + word order while also maintaining the rhythm. I would translate this back to English as:
“Your house is filled with trifles by your wife. To not stray off the path, we’re fucking on the floor”
So a few notes before we get into the choice of words for “chintz” and “keep it real”. To preserve the iamb, I changed “his” to “your”. This changes the lines from a narration of events to some outside party to a conversation between the two men at the center. Russian also has both formal and informal you (formal you is also the plural form, as is the case in a number of other languages). I went with informal you because I wanted to preserve the fact that his wife has filled his house not their house, as someone pointed out in the original chain (though I don’t think that differentiation is nearly as striking in the 2nd person) and because it’s unlikely you’d be on formal you with someone you’re fucking (unless it’s, like, a kink thing). I honestly didn’t even consider making it formal, but that would actually raise a lot of interesting implications about the relationship between the speaker and the husband, as well as with what that means about the “realness” of the situation. Is, in fact, the narrator only creating a mirage of a more real, more meaningful encounter, while the actual truth – that there is a woman the husband has made promises to that he’s betraying – is obscured? that this intimacy is just a facade? Is there perhaps some sort of power differential that the narrator wishes to point out? Or perhaps is the way that the narrator is keeping it real by pointing out the distance between the two of them? there is no pretense of intimacy, the narrator is calling this what it is – an encounter without deeper significance?
Much to think about, but I actually think the two men do have history – i think the narrator remembers the house back when it was actually only “his house” and was as yet unfilled with chintz. We also don’t know what they were calling each other prior to this moment. This could be the first time they switched to the informal you.
Ok moving on, I originally translated it as “твой дом наполнен финтифлюшками жены”. Honestly, this sounds more elegant than what I have now, but I ultimately though removing the wife from either a subject or agent position (grammatically, I mean) was too big a betrayal of the original. The original judges the wife. She took an active role in filling the house. If she were made passive, that read is certainly a possible one – perhaps even the dominant one – but it could also read more like “we are doing this in a space filled with reminders of his wife and the life they share” – the action of filling is no longer what’s being focused on. Why do I say the current translation is inelegant? I feel you stumble over it a little, because it’s almost a garden path sentence. This is also an assset though. “Zhenoy tvoy dom napolnen” is a fully grammatical sentence on its own, and it means “Your house is filled by your wife” – as in English, the primary read is that the wife is what the house is full of. If the sentence makes you stumble, perhaps that’s even good – we focus, for good reason, on the relationship between the two men, but in a translation, the wife is able to draw more attention to herself.
Ok, chintz: I chose the word “финтифлюшки” (fintiflyushki), meaning trifle/bobble/tchotchke, because it, allegedly, comes from the german phrase finten und flausen, meaning illusions and vanity/nonsense. Once again, I like that the word has a journey, specifically a cross-linguistic one.
Keep it real: this one, frankly, fails to capture the impact of the original, in my opinion, but allow me to explain the reasoning. “Stray off the path” implies, again, that there is some sort of path that both the narrator and the husband were on before the wife and the chintz – and one they intend to continue taking, one that this act is a maintenance of. It brings in a little irony, since the husband very much is straying from the path of his marriage. “Bludit’“ can also mean to be unfaithful in a marriage (as, in fact, can “stray”). The proto-slavic word it comes from can mean to delude or debauch – they want to do the latter but not the former.
As for register – “shtob” is a bit informal. I would write the full version (shto by) in an email, for example. The word for fuck, yebyomsa, is from one of the “mat” words, the extra special top tier of russian swears, definitely not to be said in polite company (and, if you are a man of a certain generation or background, not in front of women; it’s not that the use of mat automatically invokes a male-only environment, but if we’re already thinking that deeply about it. But while we’re on the topic, i will say that in my circles in the US, women use mat much more actively than men (at least in front of me, who was, up until recently, a woman and also a child).)
Ok i think that’s all the comments i have!
#chintzhouse translations#someone told me i should have put this under a read more and yes i see the error of my ways lmao#long post
6K notes
·
View notes