Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
UX Checklist Series: Form Design
From lead generation to online purchases, forms are everywhere. Unfortunately, nobody ever really wants to fill out a form, despite them being such a basic part of our online experience.
A well-designed form helps to reduce the friction that stands between the user and what they want.
…
The post UX Checklist Series: Form Design appeared first on Seer Interactive.
https://ift.tt/2IMtscz
0 notes
Text
Google Ads’ Average Position Metric is Going Away
Earlier this week, Google announced they plan to sunset the average position metric. While this change won’t take place until September 2019, it’s still a major announcement that has a lot of search marketers worried. After all, average position is one of the main metrics that advertisers look at when making manual bid adjustments and assessing visibility and position on the SERP.…
The post Google Ads’ Average Position Metric is Going Away appeared first on Seer Interactive.
https://ift.tt/2GRF1NB
0 notes
Text
Domain Properties Update Now Available on Google Search Console
Last updated on February 28, 2019 at 05:46 pm
Google Search Console has received a number of updates over the past few months, with these updates giving the tool more functionality and introducing a new interface that is more user-friendly and organized. While an AMP crawl bug hampered the tool for a short time, Google Search Console in 2019 remains an essential SEO tool that works efficiently.
Speaking of updates, Search Console has received another update in the form of Domain Properties. Here’s what you need to know about this new update, and how it makes using Search Console much more efficient.
Domain Properties
One of the best features of Google Search Console is the ability to track and verify every version of your website, which comes in handy when identifying individual page performance and issues that need to be optimized. Despite having this feature, one of the issues was how the domains were organized and presented.
Listings were separate, which makes it challenging to navigate and track domains. Going around each domain can mean using the Search Property feature frequently just to find what you need. With the new Domain Properties update, your domain listings are now more organized than before.
Each domain property within the same set of domains would be organized under one set in your list, making sure that each website that you own or handle would be accounted for. The best part is that Google Search Console will be able to automatically create new domain properties once you have DNS verification.
This allows you to segment your domain to specific sections, which is much easier to view and navigate. You also have the option to filter and change which domains would be tracked based on your preferences.
A Complete View
This update offers users with a complete view of their website data, whether it be from mobile domains, sites that have yet to migrate to HTTPS, and subdomains. This comes in handy when it comes to analyzing and reporting your data, as you no longer have to go through the long process of tracking manually.
Our Google Search Console contains a high number of domains that we track on a regular basis, making it an essential tool in our arsenal. Before the update, tracking individual subdomains and properties tend to be a real issue, as sending reports mean tracking specific parts of data that our clientele wishes to see.
Thanks to the Domain Properties update, this process is much more efficient, allowing us to save even more time to perform more SEO tasks. The process is also easy to perform, as you only need to add a domain and have it verified.
Filtering can be done by going to Performance and add page filters that would prevent or allow the tracking of data you would need.
With this being a new update, user feedback from our end would help bring in more improvements for this feature and help make Search Console an even more effective tracking tool. Efficiency is the key to SEO success, and features like these are a welcoming sigh of relief that helps us make what we do that much better.
Key Takeaway
Domain Properties is a handy feature that makes Google Search Console more accessible and provides ways to maximize its functionality. Like many Google tools and platforms, Search Console will continue to receive a fair share of updates in the upcoming months, helping it become an even more effective SEO tool.
If you have questions and inquiries about Google Search Console or SEO in General, leave a comment below and let’s talk.
https://ift.tt/2TrdGYQ
0 notes
Text
Link building for bloggers
As your blog grows, the situations you’re dealing with seem to become harder. Whoever says blogging is for the lazy, has not dealt with optimization for search engines, the ever-changing algorithms of Facebook and Instagram, the best practices of Pinterest or the ever dreaded link building.
What is link building?
Link building means, in short, that you’re getting links from other websites to your own blog. It helps your posts to rank. Link building is not an easy task, as you are depending on third parties to link to your website. And not only that, you don’t want a link from every website. Spammy websites or websites that have little to do with your niche, are not valuable at all. I’ve tried link building, the holistic SEO way, and will share my experiences here. If you want to learn more about this, read this article Marieke wrote about link building from a holistic SEO perspective.
Asking for relevant links
To get relevant backlinks, you should know the websites you would like to get a backlink from. Send them a polite email requesting to place a link to your content, if it’s relevant to their audience as well. Please note that often, you will not get a reply at all. To improve your chances of getting a link to your website, your content should really be unique. Trying to get a link for a blogpost that is extremely basic and could’ve been written by anyone, is less likely to succeed than when you provide some very good content: content people can only find on your website. If you, for example, are a planner guru or the nation’s funniest mom blogger, it’s way easier to get a link to your website than if you just started out.
Facebook Groups
Do your hands get sweaty by the idea of having to email your fellow bloggers to ask for links? Fear not! Luckily, there are a lot of Facebook Groups, where bloggers post they might be working on a blog post that, for example, collects the best recipes for Easter, the best bullet journal tips or something different. You can often drop your link in the comments if you’ve written about the topic requested and with a little bit of luck, you’ll be featured in a blog post. It depends on your country which Facebook groups could be suitable, so ask your fellow bloggers or look around on Facebook.
Guest blogging
Another option to get links to your website, is through guest blogging for other blogs. Often, blogs are looking for input from fellow bloggers and in return will let you link to your own content. You’ll not only get a link to your website from a relevant website, you’ll get attention from the readers of that particular blog as well. Visit your favorite blogs and check to see if they accept guest submissions. They’ll usually mention this on their contact page or their collaboration page. Please note that a website could have certain guidelines before they accept your guest blog. It has to be unique content, but it also has to be in line with that website.
Do your thing
Link building for bloggers can be hard. I’ve said it before and I’ll say it again. When you’re already working on optimizing your posts, finding your voice and creating original blog posts, you might not want to add another massive project to your list. Because that is what link building is: it is not something you do just once. That’s why I’ve decided to quit my attempts at link building. I find it removes the focus from my blog entirely and turns into a popularity contest, at least in my mind. Not only that, I am not someone who finds it easy to reach out to other bloggers to request links in their content.
Instead, I’ve decided to focus on my own website and on helping others. I’ve found that I’ve received backlinks whenever I give a talk at a conference or after I helped someone with their website. This is not something that I take for granted, but when it happens, I realize why I’ve spent a few hours helping a blogger out with a bug on her website. For me, this means that I stay true to my own beliefs without having to focus on an entire strategy that is not my thing. And I found out that this is a link building strategy in itself: it helps my reputation as a blogger in the Dutch community. Find whatever works for you. And if you are actively building links, could you tell me your strategy?
The post Link building for bloggers appeared first on Yoast.
https://ift.tt/2XsGHT5
0 notes
Text
Forecasting Marketing Data At Scale
Written By Annmarie Stockinger & Lindsay Stecklein
What if we told you that you can make informed decisions using forecasts for the most common business predicaments? And what if we sweetened the deal by saying you could have the answers to these questions constantly at your beck and call?…
The post Forecasting Marketing Data At Scale appeared first on Seer Interactive.
https://ift.tt/2GPnOES
0 notes
Text
Yoast SEO 9.7: Fixes and enhancements
Do you know what’s inching closer? The release of Yoast SEO 10.0, featuring a new and improved SEO analysis! If you’ve participated in our beta test, you know what to expect. If you haven’t, please stay tuned! It’s only a couple of weeks away. In the meantime, we’re keeping up with our two-week release schedule, so now it’s time to present Yoast SEO 9.7. This release mostly concerns bug fixes and enhancements.
Enhancements
There’s a lot happening behind the scenes at Yoast HQ — we’re hard at work at all kinds of cool stuff. Before we present some of that work, we’re going to do some more cleaning up. So let’s go through some of the improvements in Yoast SEO 9.7.
First, something new for Yoast SEO Premium users. If you fill in your related keyphrases for your article, Yoast SEO can now highlight those keyphrases in the text — just click the eye icon. This makes it easier to discover how you use your related words and concepts inside your articles.
In both versions, we’re now providing better feedback for the cornerstone assessment that checks the length of your most important articles. In our never-ending quest for a product that’s accessible for everyone, we’ve improved the accessibility and focus management for the How-To and FAQ structured data blocks. We’ve also improved the headers for the Internal Links feature on the post overview to allow for better translations and accessibility.
Turns out we were using inch marks around the search term in the breadcrumbs, we’ve now replaced these with smart quotes. We’ve also added a description of the SEO and Readability score to the posts and taxonomies overview in mobile view.
Bug fixes in Yoast SEO 9.7
In this release, we’ve fixed some specific bugs. For one, there was a bug where a Flesch Reading Ease score of exactly ninety would trigger incorrect feedback, so we fixed that. Here are some of the other bugs we fixed — you can find all changes in the changelog.
There were instances where the taxonomy sitemap provider would not handle private taxonomies as expected, which meant that sitemaps would not be accessible in specific situations. We fixed that. There were also bugs related to empty Twitter descriptions, and an ‘undefined index’ warning when saving a Facebook image. Also, some people reported the Recalibration Beta not loading on specific server configurations. All fixed!
Coming up soon: Yoast SEO 10.0!
As you can see, this is a regular bug fix release with nothing too spectacular. We’re saving the spectacular stuff for our next release. As I said, Yoast SEO 10.0 is around the corner. You can expect to hear about that real soon. We’re very excited!
The post Yoast SEO 9.7: Fixes and enhancements appeared first on Yoast.
https://ift.tt/2U4E47L
0 notes
Text
Introducing Google Merchant Center and Google Manufacturer Center
Last updated on February 26, 2019 at 05:44 pm
Google has become a solid business and marketing platform over the years, with numerous updates to tools such as Google My Business helping businesses establish their online presence. This has allowed us to optimize local SEO and help promote their brand and products accordingly.
Having an updated business profile appearing on search provides users with accurate information appearing on search snippets, thus driving more traffic altogether. Along with business information, products are another way to drive both traffic and sales, with an increasing number of users conducting transactions online. With the emergence of numerous e-commerce platforms and websites, the landscape has become increasingly competitive.
With more businesses aiming to promote their products and connect with their customers, Google has introduced two new platforms that allow you to do just that. These two platforms are Google Merchant Center and Google Manufacturer Center, and here’s what we know so far about these newly-introduced platforms, and how they can impact your SEO strategy.
What’s the difference?
Google Merchant Center and Google Manufacturer are two different platforms that both aim to enhance the e-commerce experience and connect users to products. However, knowing which one of your business needs is crucial when it comes to maximizing these platforms.
Google Merchant Center is a platform that allows businesses to manage their website and be able to upload their product information in an efficient manner. The options that Google Merchant Center offers include Adwords and Analytics Support, product reviews, more accurate listings on Google Shopping, direct website listings, and local search support.
When it comes to promoting your products and uploading them into Google Shopping listings, the Merchant Center is the platform you should be using. Another benefit included is the ability to create shopping campaigns that can help promote specific products to the right audience, which is definitely a feature that will surely be highly utilized soon.
On the other hand, Google Manufacturer Center is a platform that allows companies to provide detailed product information to Google. Information quality and accuracy have become one of the most important concerns by Google over the past few years, with numerous websites experiencing ranking fluctuations due to low-quality content.
Manufacturer center allows you to input information such as Product description and name, measurements and statistics, and even production and legal codes. These pieces of information allow Google and users to know that you are providing them with trustworthy information that they can use to make a purchasing decision. The information will also be shown on other Google platforms, such as Google Shopping.
While these two platforms may be similar at a glance, both of them allow businesses to provide accurate information about their products and listings, which is not only a big plus for Google but also establish customer trust.
How it can help your SEO
As we have stated before, quality content is a big factor that drives in organic traffic to a well-optimized website. Google Merchant Center and Google Manufacturer Center both provide you with the platform to optimize your product listings, which not only show up in search results but also contain quality content. If Google My Business ensures that your business information and location is accurate and updated, Merchant Center and Manufacturer Center make sure that your products contain the right information and is presented well when searched.
These factors allow your business to be more searchable, allowing more organic traffic flowing into your website. Showing up on other Google platforms is also very beneficial, as it expands your online presence significantly. Overall, the main purpose of these platforms is to make sure that your products are presented in an organized manner, making it easier to search, providing users with the key elements that want to know about. The ability to create campaigns is also a definite plus, as it helps target the right audience, and gives you a promotion platform that is cost-effective.
Integration with other Google platforms also makes it very user-friendly and seamless when it comes to optimization. This ensures that you would be less likely to experience any compatibility issues, along with being able to monitor traffic and other activities.
Key Takeaway
While these two Google platforms are relatively new, both of them have the potential to help your business have a significant online presence through optimizing your product listings. This also helps level the playing field and allow smaller businesses to be able to promote and create campaigns that would help generate sales and meaningful connections. Brand loyalty and trust can also be improved, as you are sure that people looking at your products are receiving correct information that is beneficial for their decision as a buyer. When it comes to establishing your business online, utilizing these platforms will surely boost your SEO.
If you have questions and inquiries about business SEO and SEO in general, leave a comment below and let’s talk.
https://ift.tt/2GMk1Ii
0 notes
Text
What is storytelling and why should you use it?
Once upon a time, there was a young girl. She was 9 years old and her name was Wende. Wende was incredibly intelligent, yet she had a hard time learning things by heart. No matter how hard she tried, she just could not memorize the planets of the solar system. It just did not stick in her head. One day her teacher told her a story about all the planets. A story about how the sun was lonely and Mercury was his first friend. How Mercury fell madly in love with Venus and how Planet Earth got jealous. After telling her the story, Wende was able to remember all of the planets in the right order. Why? Because of the magic of storytelling. Wende could remember the story and with that, she could remember the planets.
In this blogpost, I will tell you what storytelling is and why it is an important tool to use in the texts on your website. This post will be the first of a series of blog posts about storytelling.
What is storytelling?
The word storytelling pretty much speaks for itself. Storytelling is about telling stories. It is about using stories to engage your audience, or to make something more clear. Photos, pictures and film of course really help to tell a good story too.
Stories have always been a way to communicate. Before people learnt how to write, they would tell each other stories. Stories are much easier to remember than simple facts. That’s why Wende from the story remembered the planets. Also, stories are enjoyable, they stimulate your imagination. That’s why parents tell their children stories. That’s why we like to see movies and read books. People love stories, people are addicted to stories.
Some examples of (great) storytelling
In 2017 I visited a conference and I saw David JP Phillips on stage. He talked about the magical science of storytelling. I was blown away. His tolk was such an inspiration for me. Two weeks later, I had to speak at a WordCamp and I was so very inspired by David’s talk, that I did some storytelling of my own.
Next to using storytelling in presentations, you can use it in writing. Lots of travelblogs, personal blogs or momblogs use storytelling throughout all of their posts. Geraldine de Ruyter has a really funny blog about travel and many other things. Every post is a little story on her blog. But even informational blogs could use storytelling by adding an anekdote or an example. In my post about site structure and why it is important I used the exact same story as in my presentation at the WordCamp.

Why use storytelling?
Using storytelling in your blog post will – if you do it the right way – make your post a more engaging one. Your blog post will become something people want to read. Stories increase the attention of your audience.
If you use stories the right way, stories will help you to make your message more clear. Stories can help you to provide proof for your argumentation. They can add clarity. My story about Alice (screenshot above) is written in order to help people understand the importance of a clean site structure. This is a rather difficult subject to grasp. A story adds clarity.
Most importantly, people will remember your story, and with that, they’ll remember the message of your post or even your brand. If you use stories in a good way, you could even inspire people to take action. Maybe you’ll inspire people to clean up their website or to get started with storytelling in their blog posts and presentations.
Up next in this series
If you Google ‘storytelling’ you’ll see amazing things. Lots of online storytelling is about brand storytelling. Perhaps I’ll write a blogpost about that in the future. For this series, I’ll be focussing on using storytelling in your writing. And, I will also focus on the topic of storytelling and SEO.
In the next post in this series about storytelling, I want to focus on how to use storytelling in a blogpost. I want to start off by discussing the elements that are necessary for a good story. Also, I will share some practical tips and examples of how to start using storytelling in your blogposts.
If you have nice examples of your own use of storytelling, I would love to see those! Maybe I can even share a few of your examples in one of my next posts!
Read more: Blogging: the ultimate guide »
The post What is storytelling and why should you use it? appeared first on Yoast.
https://ift.tt/2IG4XOj
0 notes
Text
How to Optimize Keyword Research by Understanding User Intent
Last updated on February 21, 2019 at 06:02 pm
SEO has become increasingly competitive as the years go by, with new techniques, algorithm updates, and tools that help give you an edge over the competition. There are many ways to craft your own winning strategy with the right combination of tools and techniques, and this certainly rings true for keyword research.
Keyword research will always be the most crucial element in the success of your SEO efforts, especially at a time where search has become more versatile than before. With voice search gaining a more significant presence, the traditional practice of finding keywords that have high search volume is at times not as effective as before. The factors that we have to consider when looking for the right keywords have increased, with user intent becoming one element that makes a difference in your success in search rankings.
When it comes to user intent, there are a number of factors to consider when implementing the right strategy. Here are ways you can optimize your keyword research with user intent in mind.
What is User Intent?
User Intent is the reason, motive, or intention for conducting a search query. User intent looks into why and how users conduct search queries and use this understanding to formulate the appropriate keywords. User intent can be classified into at least 4 types depending on where you look, along with being the most popular queries, and they are as follows:
Commercial – This refers to search terms with the intent of browsing through a variety of brands, products, and websites without conducting a purchase. This type of intent is from users who want to research about the products that they might purchase in the future, and find the best results.
Transactional – Related to Commercial Intent, Transactional Intent refers to users who conduct search queries, with the goal of finding e-commerce websites, and purchasing a product online. This and Commercial Intent tend to be used to search for business and commerce websites.
Navigational – This refers to the intent of searching for a specific website by directly entering their names. This tends to be effective in generating traffic once you have garnered a significant online presence for your brand.
Informational – Informational refers to search queries whose goal is to provide users with information. This information varies from the news, facts, tips, lists, and other related queries. Content such as blog articles and infographics tend to be the target of these keywords.
Understanding User Intent
By understanding how, what, and why people search, you would be able to find the best keywords that would drive organic traffic to any website. There are many ways to help you understand user intent for your keyword research, and some of them are handy tools that you might have used before as well. Here are some of these tools:
Google Trends – One of the more effective keyword and content research tools around, Google Trends allows you to see keywords and topics the generate the most buzz in a specific region. You have the option of tracking their statistics over certain time periods, and even compare each topic or keyword side by side.
Quora – One of the most popular Q&A websites around, Quora is a great place to see user-generated questions that you can use to generate keywords. Quora is a platform that has been used by numerous SEO professionals to generate traffic for their content, and now, its questions can now be used to formulate keywords.
Ahrefs – One of the most effective keyword research tools in the market, Ahrefs is also a great place to find a wide variety of related search terms that you can utilize to formulate terms that would help you generate traffic.
Answer the Public – Another top location that would help you find quality search terms and analyze search intent is by using Answer the Public. You have the option of going through numerous types of queries and question types that users would most likely try out.
Online Forums – Sites like Reddit offer a lot of content related to inquiries as well, making it another great platform to analyze user intent. Going around other online forums is also another solid approach, as these have been the best places to ask around the internet for years, providing you with a massive archive of queries waiting to be utilized.
Tinkering with Google or even Facebook Search might also help you find interesting results that allow you to see how people look around on the internet. This makes crowdsourcing for information another viable method of finding unique and genuine results that come from actual users.
Moving away from the traditional
While traditional keyword research is still able to help you find keywords that generate a significant amount of traffic, the arrival of voice search was a signal to a lot of SEOs that this might no longer be an effective method in the near future. This means that we have to diversify our strategies and use fresh methods that would help us find what we are looking for.
While this may lead to bumps along the way, the ultimate reward of experimentation makes it all worth it after a good number of tries. One of the traditional keyword research metrics that is used as a measurement of keyword success is the search volume. While search volumes tend to give you a good assessment of keyword performance, there are times that they might be inaccurate, especially on more specific search terms that might be more helpful for your rankings.
While completely moving away from tried and tested methods is still not advisable, finding new ways to generate keywords that understand user intent allows you to get out of your SEO comfort zone, and create your own unique approach to keyword research.
Create a list or chart of your keywords
Once you have done your research, it is time to categorize each search query and put them in a list or chart, depending on your preference. This allows you to identify each search query accordingly, and even connect each of them to formulate more queries.
It is best to start with single root words and branch out from there. From there, you can add elements such as brand names, key prefixes or suffixes, categories, geotagging, adjectives, and even common phrases used when asking. With a plethora of information mostly consisting of unique search terms, there is no doubt that you might have an overwhelmingly long test after doing this. This is why filtering your list is the most crucial step towards finding the best search queries that would fit your needs.
Key Takeaway
User Intent adds another dimension to keyword research, as it provides us with a fresh approach to generating the best search queries that would how users across the internet perform their search. Along with these important tips, you can also take a look at our previous posts about long-tail keywords and exact search terms, which helps give you a deeper look into how keyword research is changing.
If you have questions and inquiries about Keyword Research and SEO in general, leave a comment below and let’s talk.
https://ift.tt/2ElMPoA
0 notes
Text
Sell Clean
In July of 2006, I first learned of Humpy Wheeler, one of the foremost promotors of NASCAR. He was a guest on NPR’s news quiz show, “Wait Wait! Don’t Tell Me!” And what he did thrilled me. Sell Clean
Humpy talked about running the motor speedway about 12 miles away from the theater where the episode was being filmed. He asked, “You want to come? I’ve got tickets in my pocket.”
The post Sell Clean appeared first on chrisbrogan.com.
https://ift.tt/2T4avpK
0 notes
Text
How Named Anchor Links Optimize Your Search Snippets
Last updated on February 19, 2019 at 05:56 pm
As a student of SEO, I’ve learned so many things that can affect your online presence over the years, from algorithm updates to various strategies borne out of experimentation. All of these are done just for our websites to show up on the first page of Google’s search results, along with expanding your presence and brand and generate revenue in the ever-expanding digital landscape.
Google’s search snippet has gone through a multitude of changes over the past few years, with the introduction of featured snippets and knowledge graphs providing instant information containing more detailed results. Along with these two features, regular search snippets have also become more versatile as well with the introduction of Named Anchor Links. Here’s what you need to know about Named Anchor Links, how to apply them, and how they can impact your search.
What are Named Anchor Links?
Named Anchor Links are links that can be viewed below the search snippet in Google. These links can direct you to various pages in your website, or a specific section on the webpage itself.
This feature allows users to quickly navigate to places they want on a website, providing more opportunities for more webpages to generate traffic. Most search queries have become increasingly specific, especially with the emergence of voice and visual search, and named anchors surely make it even more so than before.
The user experience is crucial when it comes to search results and being more direct can lead to more positive results that can generate more opportunities for conversions and discovering content.
How to apply named anchors
Named anchors appearing on search snippets is possible through content optimization, as Google tends to generate these results based on how they viewed your content. The best way to ensure that names anchors would be present is by making each section of your page clear and well-defined.
This means applying the right H2 and H3 tags on the page, which allows you to see links to different pages on your search snippet, which we were able to do in our website. Content optimization is key to making this work and applying this to your home page and landing pages allow for better navigation. The title tags for these sections must also describe what the user would access upon clicking on them. This means that direct title tags such as “Frequently Asked Questions” or “Best SEO Strategies” are good examples of title tags that are straight to the point and can be read by Google as distinct sections.
Quick navigation, table of contents, and related content sections also work well when it comes to appearing on search snippets. These quick links allow users to be able to view additional content, which can be found in the search snippet, allowing users to click and access multiple web pages. The Fetch as Googlebot option also works as well, which is one of the most effective ways to ensure that your webpage would contain named anchors after some content optimization. The applied changes
Impacting your search
Named anchors not only make navigation and content discovery much more convenient but also benefit traffic as well. Users not only have access to one webpage but also has access to others that they might be interested in taking a look. If you have content that might need an extra traffic boost, having it show up in your quick navigation or related content section would help give it more visibility.
If featured snippets and knowledge graphs provide quick information that lessens the need to click more, named anchors to allow more content to be discovered within your website, providing in-depth information that fits Google’s E-A-T standards.
Key Takeaway
Named anchors may have been a feature that has been around for a long time, it is still a very efficient way of providing more content to the users, along with increasing the visibility of related content. While knowledge graphs and featured snippets are being prioritized by numerous websites, making use of Named Anchor Links is another way of providing information, while improving your search traffic.
If you have questions or inquiries about SEO, leave a comment below and let’s talk.
http://bit.ly/2DWuPzJ
0 notes
Text
How Fraggles Optimize Your Search Snippets
Last updated on February 19, 2019 at 03:50 pm
As a student of SEO, I’ve learned so many things that can affect your online presence over the years, from algorithm updates to various strategies borne out of experimentation. All of these are done just for our websites to show up on the first page of Google’s search results, along with expanding your presence and brand and generate revenue in the ever-expanding digital landscape.
Google’s search snippet has gone through a multitude of changes over the past few years, with the introduction of featured snippets and knowledge graphs providing instant information containing more detailed results. Along with these two features, regular search snippets have also become more versatile as well with the introduction of Fraggles, also known as named anchors. Here’s what you need to know about Fraggles, how to apply them, and how they can impact your search.
What are “Fraggles”?
Named anchors, or Fraggles, are links that can be viewed below the search snippet in Google. These links can direct you to various pages in your website, or a specific section on the webpage itself.
This feature allows users to quickly navigate to places they want on a website, providing more opportunities for more webpages to generate traffic. Most search queries have become increasingly specific, especially with the emergence of voice and visual search, and named anchors surely make it even more so than before.
The user experience is crucial when it comes to search results and being more direct can lead to more positive results that can generate more opportunities for conversions and discovering content.
How to apply named anchors
Named anchors appearing on search snippets is possible through content optimization, as Google tends to generate these results based on how they viewed your content. The best way to ensure that names anchors would be present is by making each section of your page clear and well-defined.
This means applying the right H2 and H3 tags on the page, which allows you to see links to different pages on your search snippet, which we were able to do in our website. Content optimization is key to making this work and applying this to your home page and landing pages allow for better navigation. The title tags for these sections must also describe what the user would access upon clicking on them. This means that direct title tags such as “Frequently Asked Questions” or “Best SEO Strategies” are good examples of title tags that are straight to the point and can be read by Google.
Quick navigation, table of contents, and related content sections also work well when it comes to appearing on search snippets. These quick links allow users to be able to view additional content, which can be found in the search snippet, allowing users to click and access multiple web pages. The Fetch as Googlebot option also works as well, which is one of the most effective ways to ensure that your webpage would contain named anchors after some content optimization.
Impacting your search
Named anchors not only make navigation and content discovery much more convenient but also benefit traffic as well. Users not only have access to one webpage but also has access to others that they might be interested in taking a look. If you have content that might need an extra traffic boost, having it show up in your quick navigation or related content section would help give it more visibility.
If featured snippets and knowledge graphs provide quick information that lessens the need to click more, named anchors to allow more content to be discovered within your website, providing in-depth information that fits Google’s E-A-T standards.
Key Takeaway
Named anchors may have been a feature that has been around for a long time, it is still a very efficient way of providing more content to the users, along with increasing the visibility of related content. While knowledge graphs and featured snippets are being prioritized by numerous websites, making use of Fraggles is another way of providing information, while improving your search traffic.
If you have questions or inquiries about SEO, leave a comment below and let’s talk.
http://bit.ly/2V7aSx6
0 notes
Text
Context Clusters in Search Query Suggestions
unsplash-logoSaketh Garuda
Context Clusters and Query Suggestions at Google
A new patent application from Google tells us about how the search engine may use context to find query suggestions before a searcher has completed typing in a full query. After seeing this patent, I’ve been thinking about previous patents I’ve seen from Google that have similarities.
It’s not the first time I’ve written about a Google Patent involving query suggestions. I’ve written about a couple of other patents that were very informative, in the past:
6/10/2016 – Google Entity Search Suggestions Patent (Associating an entity with a search query)
5/26/2010How a Search Engine Might Identify Possible Query Suggestions (Generating query suggestions using contextual information)
In both of those, the inclusion of entities in a query impacted the suggestions that were returned. This patent takes a slightly different approach, by also looking at context.
Context Clusters in Query Suggestions
We’ve been seeing the word Context spring up in Google patents recently. Context terms from knowledge bases appearing on pages that focus on the same query term with different meanings, and we have also seen pages that are about specific people using a disambiguation approach. While these were recent, I did blog about a paper in 2007, which talks about query context with an author from Yahoo. The paper was Using Query Contexts in Information Retrieval. The abstract from the paper provides a good glimpse into what it covers:
User query is an element that specifies an information need, but it is not the only one. Studies in literature have found many contextual factors that strongly influence the interpretation of a query. Recent studies have tried to consider the user’s interests by creating a user profile. However, a single profile for a user may not be sufficient for a variety of queries of the user. In this study, we propose to use query-specific contexts instead of user-centric ones, including context around query and context within query. The former specifies the environment of a query such as the domain of interest, while the latter refers to context words within the query, which is particularly useful for the selection of relevant term relations. In this paper, both types of context are integrated in an IR model based on language modeling. Our experiments on several TREC collections show that each of the context factors brings significant improvements in retrieval effectiveness.
The Google patent doesn’t take a user-based approach ether, but does look at some user contexts and interests. It sounds like searchers might be offered a chance to select a context cluster before showing query suggestions:
In some implementations, a set of queries (e.g., movie times, movie trailers) related to a particular topic (e.g., movies) may be grouped into context clusters. Given a context of a user device for a user, one or more context clusters may be presented to the user when the user is initiating a search operation, but prior to the user inputting one or more characters of the search query. For example, based on a user’s context (e.g., location, date and time, indicated user preferences and interests), when a user event occurs indicating the user is initiating a process of providing a search query (e.g., opening a web page associated with a search engine), one or more context clusters (e.g., “movies”) may be presented to the user for selection input prior to the user entering any query input. The user may select one of the context clusters that are presented and then a list of queries grouped into the context cluster may be presented as options for a query input selection.
I often look up the inventors of patents to get a sense of what else they may have written, and worked upon. I looked up Jakob D. Uszkoreit in LinkedIn, and his profile doesn’t surprise me. He tells us there of his experience at Google:
Previously I started and led a research team in Google Machine Intelligence, working on large-scale deep learning for natural language understanding, with applications in the Google Assistant and other products.
This passage reminded me of the search results being shown to me by the Google Assistant, which are based upon interests that I have shared with Google over time, and that Google allows me to update from time to time. If the inventor of this patent worked on Google Assistant, that doesn’t surprise me. I haven’t been offered context clusters yet (and wouldn’t know what those might look like if Google did offer them. I suspect if Google does start offering them, I will realize that I have found them at the time they are offered to me.)
Like many patents do, this one tells us what is “innovative” about it. It looks at:
…query data indicating query inputs received from user devices of a plurality of users, the query data also indicating an input context that describes, for each query input, an input context of the query input that is different from content described by the query input; grouping, by the data processing apparatus, the query inputs into context clusters based, in part, on the input context for each of the query inputs and the content described by each query input; determining, by the data processing apparatus, for each of the context clusters, a context cluster probability based on respective probabilities of entry of the query inputs that belong to the context cluster, the context cluster probability being indicative of a probability that at least one query input that belongs to the context cluster and provided for an input context of the context cluster will be selected by the user; and storing, in a data storage system accessible by the data processing apparatus, data describing the context clusters and the context cluster probabilities.
It also tells us that it will calculate probabilities that certain context clusters might be requested by a searcher. So how does Google know what to suggest as context clusters?
Each context cluster includes a group of one or more queries, the grouping being based on the input context (e.g., location, date and time, indicated user preferences and interests) for each of the query inputs, when the query input was provided, and the content described by each query input. One or more context clusters may be presented to the user for input selection based on a context cluster probability, which is based on the context of the user device and respective probabilities of entry of the query inputs that belong to the context cluster. The context cluster probability is indicative of a probability that at least one query input that belongs to the context cluster will be selected by the user. Upon selection of one of the context clusters that is presented to the user, a list of queries grouped into the context cluster may be presented as options for a query input selection. This advantageously results in individual query suggestions for query inputs that belong to the context cluster but that alone would not otherwise be provided due to their respectively low individual selection probabilities. Accordingly, users’ informational needs are more likely to be satisfied.
The Patent in this patent application is:
(US20190050450) Query Composition System Publication Number: 20190050450 Publication Date: February 14, 2019 Applicants: Google LLC Inventors: Jakob D. Uszkoreit Abstract:
Methods, systems, and apparatus for generating data describing context clusters and context cluster probabilities, wherein each context cluster includes query inputs based on the input context for each of the query inputs and the content described by each query input, and each context cluster probability indicates a probability that at a query input that belongs to the context cluster will be selected by the user, receiving, from a user device, an indication of a user event that includes data indicating a context of the user device, selecting as a selected context cluster, based on the context cluster probabilities for each of the context clusters and the context of the user device, a context cluster for selection input by the user device, and providing, to the user device, data that causes the user device to display a context cluster selection input that indicates the selected context cluster for user selection.
What are Context Clusters as Query Suggestions?
The patent tells us that context clusters might be triggered when someone is starting a query on a web browser. I tried it out, starting a search for “movies” and got a number of suggestions that were combinations of queries, or what seem to be context clusters:
The patent says that context clusters would appear before someone began typing, based upon topics and user information such as location. So, if I were at a shopping mall that had a movie theatre, I might see Search suggestions for movies like the ones shown here:
One of those clusters involved “Movies about Business”, which I selected, and it showed me a carousel, and buttons with subcategories to also choose from. This seems to be a context cluster:
This seems to be a pretty new idea, and may be something that Google would announce as an availble option when it becomes available, if it does become available, much like they did with the Google Assistant. I usually check through the news from my Google Assistant at least once a day. If it starts offering search suggestions based upon things like my location, it could potentially be very interesting.
User Query Histories
The patent tells us that context clusters selected to be shown to a searcher might be based upon previous queries from a searcher, and provides the following example:
Further, a user query history may be provided by the user device (or stored in the log data) that includes queries and contexts previously provided by the user, and this information may also factor into the probability that a user may provide a particular query or a query within a particular context cluster. For example, if the user that initiates the user event provides a query for “movie show times” many Friday afternoons between 4 PM-6 PM, then when the user initiates the user event on a Friday afternoon in the future between these times, the probability associated with the user inputting “movie show times” may be boosted for that user. Consequentially, based on this example, the corresponding context cluster probability of the context cluster to which the query belongs may likewise be boosted with respect to that user.
It’s not easy to tell whether the examples I provided about movies above are related to this patent or if it is tied more closely to the search results that appear in Google Assistant results. It’s worth reading through and thinking about potential experimental searches to see if they might influence the results that you may see. It is interesting that Google may attempt to anticipate what is suggests to show to us as query suggestions, after showing us search results based upon what it believes are our interests based upon searches that we have performed or interests that we have identified for Google Assistant.
The contex cluster may be related to the location and time that someone accesses the search engine. The patent provides an example of what might be seen by the searcher like this:
In the current example, the user may be in the location of MegaPlex, which includes a department store, restaurants, and a movie theater. Additionally, the user context may indicate that the user event was initiated on a Friday evening at 6 PM. Upon the user initiating the user event, the search system and/or context cluster system may access the content cluster data 214 to determine whether one or more context clusters is to be provided to the user device as an input selection based at least in part on the context of the user. Based on the context of the user, the context cluster system and/or search system may determine, for each query in each context cluster, a probability that the user will provide that query and aggregate the probability for the context cluster to obtain a context cluster probability.
In the current example, there may be four queries grouped into the “Movies” cluster, four queries grouped into the “Restaurants” cluster, and three queries grouped into the “Dept. Store” cluster. Based on the analysis of the content cluster data, the context cluster system may determine that the aggregate probability of the queries in each of the “Movies” cluster, “Restaurant” cluster, and “Dept. Store” cluster have a high enough likelihood (e.g., meet a threshold probability) to be input by the user, based on the user context, that the context clusters are to be presented to the user for selection input in the search engine web site.
I could see running such a search at a shopping mall, to learn more about the location I was at, and what I could find there, from dining places to movies being shown. That sounds like it could be the start of an interesting adventure.
Copyright © 2019 SEO by the Sea ⚓. This Feed is for personal non-commercial use only. If you are not reading this material in your news aggregator, the site you are looking at may be guilty of copyright infringement. Please contact SEO by the Sea, so we can take appropriate action immediately. Plugin by Taragana
The post Context Clusters in Search Query Suggestions appeared first on SEO by the Sea ⚓.
http://bit.ly/2Ne7Y6P
0 notes
Text
WordPress 5.1 is incoming, Gutenberg Phase 2 updates, and bonus links!
We have a big week ahead of us! WordPress 5.1 will be released this week and with it comes a lot of improvements for the Block Editor as well as a whole bunch of other improvements. I’m also updating you on Gutenberg phase 2. And of course, there are some bonus links as well. Let’s dive in!
WordPress 5.1 slated for this week
It’s only been a little over two months since WordPress 5.0 was released, but the next release, WordPress 5.1, has been progressing very nicely. So well, in fact, that it’s slated for the February 21st. That’s this week!
WordPress 5.1 will add a nice set of improvements such as Site Health notices, version 4.8 of the Gutenberg plugin which comes with a lot of improvements to the Block Editor. But, wait, there’s more! It will also have Multisite Support for Site Metadata, Cron improvements, a new JavaScript build process, and updated styles and text strings. Additionally, there are a lot of under the hood improvements. All of which you can find in the WordPress 5.1 Field Guide, published on Make WordPress Core.
As soon as WordPress 5.1 is released, we’ll see continued work happening on features for WordPress 5.2. This will include things like Gutenberg performance and UX improvements, Core Widgets converted to blocks (Gutenberg Phase 2), PHP Fatal Recovery (WSOD), and a further improved version of the Site Health Check.
Gutenberg Phase 2 progress
Gutenberg Phase 2 is well underway with converting Core Widgets into Gutenberg blocks. Phase 2 also includes converting the current Navigation menu into a Navigation block solution. The Navigation block is currently being discussed and there are mockups in GitHub that would benefit from your feedback. Go check them out and let your voice be heard.
Gutenberg 5.0 introduced additional blocks such as an RSS block and a Kindle block. It also introduced some improvements to existing blocks such as the possibility to define a custom focal point for the cover block’s background. Read more about all the other improvements now part of the Gutenberg plugin in the Gutenberg 5.0 release post.
Sharing is caring
Here’s list of a few interesting things I came across this past week:
Customizing Gutenberg Blocks
Customizing Gutenberg blocks is a relatively complicated thing to do, but there’s actually a simple way to start customizing Gutenberg blocks. You can do this by utilizing block styles. They take only a few minutes to pick up, and mostly just require you to know CSS. You can learn more about it over at the ThemeShaper blog.
Query Monitor 3.3
One of my favorite debugging tools has been updated. Query Monitor 3.3 now has new features that introduce related hooks section for each panel, allows for debugging of wp_die() calls, support for debugging JavaScript translation files. And my personal favorite, we now have the ability to move the panel to the side of your window.
Gutenberg Blocks Design Library plugin
Gutenberg Blocks Design Library is a new plugin that provides pre-built page designs using only the default core blocks that come with WordPress. There’s a free version that comes with 50 different designs that users can import from the growing library.
The post WordPress 5.1 is incoming, Gutenberg Phase 2 updates, and bonus links! appeared first on Yoast.
http://bit.ly/2GNIJHq
0 notes
Text
Visual search: The future is now
We are a visually oriented species. Humans can understand pictures in the blink of an eye. In comparison, we read terribly slow and understand the text even slower. What’s more, a percentage of the world’s population consists of visual thinkers — people who also think in pictures. Considering this, it is not strange to see search move towards a more visual way. You might just start your next search by opening the camera app on your smartphone. Meet visual search.
What is visual search?
Visual search consists of every search that uses real-world images like photos or screenshots as a starting point. Every time you point your Google Lens camera at a piece of clothing, you are performing a visual search. Whenever you use Pinterest to do a style match, you are doing a visual search. Visual search answers questions like: “Show me stuff that’s kinda like that but different”, or “I don’t know what I want, but I’ll know it when I see it”.
It’s not just style matching that awesome outfit you saw or finding out what type of chair is in that hipster interior, it going much farther than that and still we’re only at the beginning. Photo apps can read text in images and translate it. Computer vision can recognize tons of entities, from celebrities to logos and from landmarks to handwriting. At the moment, visual search is making waves in the fashion and home decor sectors, with big brands like Amazon, Macy’s, ASOS and Wayfair leading the way.
Research shows consumers are very interested in using visual search as part of their shopping experience. What’s more, a recent Sparktoro article uncovered that Google Images is the second largest player in the search engine market with 21% of searches starting there. Images are here to stay.

Many US internet users would consider visual search a great addition to regular site search channels:
Today, people are taking pictures of everything, not just beautiful sceneries or mementos of their adventures, but stuff they need to remember or tasks they need to do. Visual search will increasingly help turn those images into actual tasks. Take a photo of a business card and automatically add the contact details to my address book. Or take a photo of my written shopping list and add the items to the shopping cart of my favorite supermarket. Everything is possible.
Visual search differs from image search
Visual search is part of something called sensory search, which consists searching via text, voice and vision. In the past, nearly every search started with someone typing in a couple of words in a text field. Today, increasingly, searches start by voice or by pointing a camera app at something. You’ll see these different types of searches converge more and more as visual search is a great addition to text and voice search.
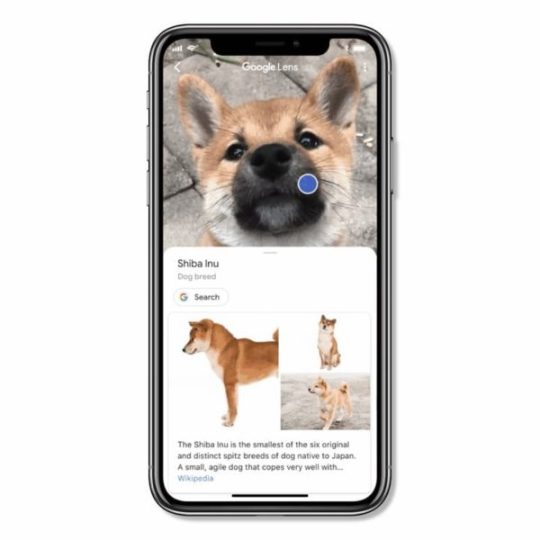
Google Lens immediatly recognizes this cute dog as a Shiba Inu
While visual search uses visuals as a starting point, image search is different. Image search has been around forever. A classic image search starts with a typed search prompt in a search field and leads to a SERP that shows a number of images that match that specific search. These images can be narrowed down by selecting smart filters from the menu bar.
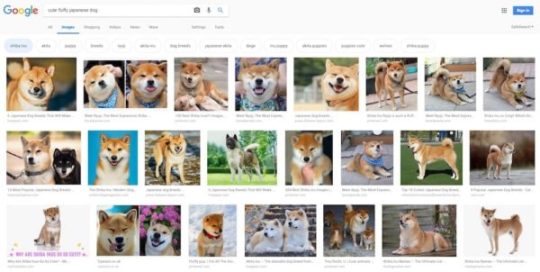
Google Image search gives great suggestions and lets you easily filter the results How does visual search work?
People have been talking about visual search for a long time, but over the past couple of years it has really come into its own. Very powerful smartphones, increasingly smart artificial intelligence and consumer interest drive the growth of this exciting development. But how does visual search work?
Visual search is powered by computer vision and trained by machine learning. Computer vision can be described as the technology that lets computers see. Not only that, it makes computers understand what they see and to make them do something useful with that knowledge. In a sense, computer vision tries to get machines to understand the world we as humans see.
Computer vision has been around for ages, but thanks to hardware developments and vast new discoveries in the field of machine learning it is improving with leaps and bounds. Machine learning provides much of the input needed for an algorithm to make sense of images. To a machine, an image is just a bunch of random numbers — it needs context to get even the slightest understanding of what’s on it. Machine learning can provide that context.
Teaching a computer to see
Using machine learning, you can literally teach a computer what something is with a training set — starting small and then scaling up quickly. Feed it enough data and it can tell the differences between slight variations as well. To increase the knowledge of these machines, Google cross-references its finding with its knowledge graph. This way, it is becoming much easier for machines to connect the pieces of the puzzle to find out what’s in a particular image and how that image fits within the bigger picture — pun intended. Many providers also give their computer vision models OCR capabilities, meaning they understand text as well.
There are many third-party providers of this kind of technology if you want to add integrate computer vision into your software. In addition to all the third-party providers, platforms like Google’s Cloud Vision and Bing’s Visual Search Developer Platform give you various ways of incorperating visual search into your sites and apps.
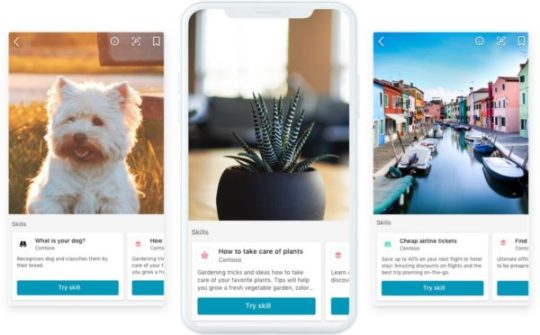
Bing visual search matches intent to skills Uses of visual search
You might be mistaken to think visual search is of not much use to the average site owner. Or maybe you think it doesn’t mean much for SEO. That would be wrong. Big brands are out there testing this and condition their consumers to use visual search. If you’re in commerce, you have to keep an eye on this development. We’ll see many more players enter the visual search ecommerce space, or quickly build their presence and power, like Pinterest with their new automated Shop The Look pins. There’s a lot happening, but visual search is still only at the beginning of its lifecycle.
Currently, the focus is on making sense of images and doing something useful with it. Soon, we’ll also see visual search come into contact with augmented reality and maybe even virtual reality? While AR and VR have been hyped to death by now, the killer application of these technological developments still has to be found. Maybe augmenting the real-world onto visual search results might be just that?
Visual search can be used for a lot of things, like helping you discover landmarks in a strange city, helping you increase productivity or find the beautiful pair of shoes that fits perfectly with that new dress you bought. It can also help you identify stuff like plants and animals and teach you how to do a particular chore. Who knows what else?
Some visual search applications
When we think of visual search there are a couple of players that immediately come to mind. It’s not so weird that almost every big brand is experimenting with visual search or doing research into what computer vision can bring for their platform.
Facebook, for instance, works on building an AI powered version of their Marketplace. They even purchased a visual search technology start up called GrokStyle that could drive that development. Apple also bought several companies active in the visual search space, mostly to improve their photo apps, while their ARKit developer program has very interesting options for working with visuals. Both Snapchat and Instagram let you buy stuff on Amazon by pointing your camera at an object.
Here are some of the most used visual search tool of this moment:
Pinterest Lens
Visual search has been around for some time, but there’s one platform that brought it into the limelight: Pinterest. Pinterest is the OG, so to say. It is an inherently visual platform as it lets users collect images in boards and helps them get inspired by looking at other peoples boards. While helpful and interesting, it was a fairly static product.
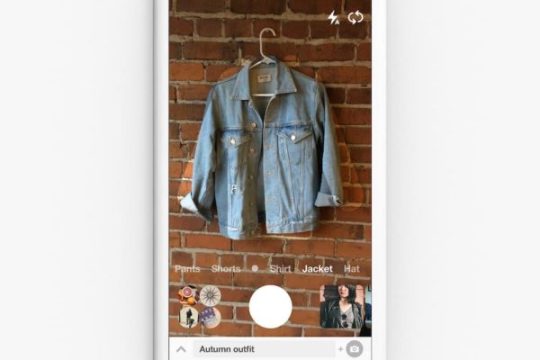
A couple of years ago, the company started investing loads in computer vision, AI and machine learning that eventually led to an app called Lens. Ongoing development brought things like Shop the Look, which was the first visual shopping tool of its kind. Things really took off for Pinterest. In 2018, a year after the release of Lens people did more than 600 million visual searches every month. That’s a 140 percent increase year over year. That suggests a meteoric rise, but its platform dependency makes it too ‘closed’ to reach critical mass. Plus, the competition is picking up speed.
Shop the Look lets you discover similar items Google Lens
Google Lens wants to turn your phone into a visual search engine. Hit the tiny Lens icon, point your camera at an item and voila! Google is pushing Lens pretty hard. You can find it everywhere: the Photos app, Google Search app and Google Assistant. That last one is interesting, as you can use Assistant to do something with the images you capture. Take a picture of a recipe and ask Assistant to add it to your recipe book. Or use Google Translate to translate the foreign text on that sign — live, if you want.
Google Lens works in real time and recognizes over a billion products. At the end of last year, Google announced that Lens was also available for regular Image searches. The US only for now, but it is expected to be rolled out worldwide later this year.
youtube
Bing Visual Search
Bing is very active in the visual search space. Microsoft has been doing a lot of research and making lots of knowledge freely available. Not only do they have integrated their visual search in a really cool mobile app for the large platforms, but they also have a dedicated web platform. This website demonstrates the power of Bing visual search and it works very well. Just upload an image and see what Bing makes of it. Or use one of the example images to get a quick idea of how good it works.
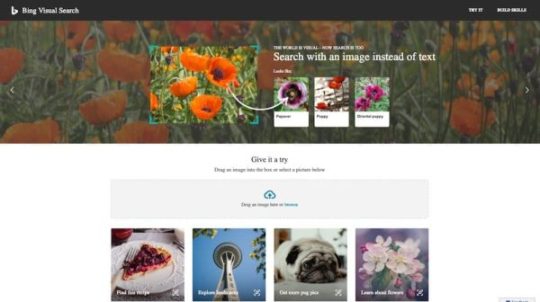
While Bing mobile does much of the same stuff the other visual search providers do — point your camera at something and have it figure out what it is —, they have a big differentiator: skills. Developers can harness the power of visual search to append a skill to a matched image. So, if you have loads of products that Bing recognizes, you can define what a searcher should be able to do once your image has been analyzed. For this, the visual search identifies the intent of the search and requests different skills based on that intent. After that, Bing combines the skills and sends them to the app. If you have a home decor store, a search like this might not only yield a buy skill, but also a DIY skill. You can build these skills yourself. Try it on the Bing Visual Search Development Platform.
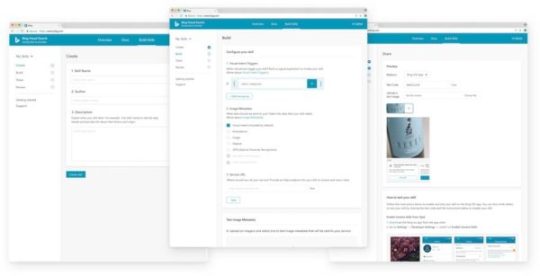
You can visual develop a skill for Bing Visual search Amazon
Amazon is using their visual search technology mostly to provide other platforms a way of visually shopping for stuff. I’ve already mentioned they are working with Snapchat and Instagram to let shop via their camera app. For Amazon, visual search is important as it gives them a new way to have users shop. Now, if you see something in a store you can take a picture of it with the Camera Search functionality inside the Amazon app. It shows you all the relevant products that are available on Amazon and you can refine your search via visual attributes if you want.
Apparently, Amazon was working on an AI-powered shopping platform called Scout. Last month, however, Amazon announced a new delivery robot with the name Scout. As of now, it’s unclear what happened to the old Scout product. The old Scout let users build up a sort of taste database by liking or disliking products and product variants. This would eventually help them narrow down the number and uncover new products that would fit their taste.
Another interesting thing Amazon is working on, is combining visual and voice search. Products like the Echo Show and Echo Spot bring a smart voice assistant into your home, that supports the search results with visuals. Amazon also offers a lot of insights into how visual search works and how you can build your own integration on AWS.
But how does Google Image search tie into this?
Reading all this, you might think that good old image search is on its way out. Well, you’re wrong. A large part of searches happen in image search. Visual search is a kind of add-on for image search. You use it in different circumstances. The results are different as well. If you know what you need, you’ll go find an image in image search. If you see something interesting on an image, but you’re not quite sure what it is, hit that image and let visual search do its job.
Google Image search had a makeover this year. Almost every month, Google changed something or added new features. I’ve already mentioned the availability of Lens inside the image search results on mobile. Simply tap an image and see if Lens can see what it is. Image search now also has related concepts filters that let you drill down into your topic or uncover related items you never thought of. There are now badges to identify if something is a product you can buy directly. This is only a small sampling of the changes Image search underwent. O, did I mention that you can just type [fluffy Japanese dog] to come up with the search result of those cute Shina Ibu dogs you saw earlier in this post? Yay entities, yay knowledge graph!
Image SEO: More important than ever
As we are using images more and more to search for stuff, we need to take better care of our image SEO. Image SEO has always been something of an afterthought for many people, but please don’t be like that. You can win a lot if you just high-quality, relevant images and optimize these thoroughly. Google sees the massive potential and is putting even more weight into it. Here’s Googles Gary Illyes in a recent AMA on Reddit:
“We simply know that media search is way too ignored for what it’s capable doing for publishers so we’re throwing more engineers at it as well as more outreach.”
Gary Illyes
Last year, Google’s latest algorithmic change for Image search focussed on:
ranking results based on both great images and content
authority
relevance
freshness
location
context
It’s not hard to get your images ready for image search. We have an all-encompassing post on image SEO if you need to learn more. In short:
Use structured data where relevant: mark up your images
Use alt attributes to describe the images
Find unique images — not stock photos
Make them high quality if you want AI to figure out what’s on it
Add them in a relevant place, where they provide context to the text
Use descriptive filenames, not IMG168393.jpg
Add captions where necessary
Use the right sized images
Always compress them!
Our world is visual: now you can search with visuals
Over the past year, we truly see sensory search come to light. Everyone was all about voice search, but visual search is providing a helpful new dimension. Lots of the time, a visual search just makes much more sense than a spoken one. And sometimes, it’s the other way around. That’s why voice and visual will never be the default search experience: they build on the others strength and weaknesses. Combined with good-old text search, you have every possibility to search the way you want!
Now… where’s that mindreader?
The post Visual search: The future is now appeared first on Yoast.
http://bit.ly/2SExPuU
0 notes
Text
How to Boost Your Business Using Facebook Local Search
Last updated on February 14, 2019 at 09:56 pm
Ever since Facebook came into the fold during the 2000s, social media sites have become the most widely used internet platforms across the world. Boasting a user base of billions, this is also one of the best places for digital marketers to promote their brands.
In the past few articles, we have emphasized the need to optimize your local SEO strategies to boost your traffic and rankings. While Facebook search is no Google, it has gradually developed into a more capable search platform that works best when looking for local businesses near your area. This adds another layer to your social media marketing strategy that you can take advantage of to give your brand that much-needed boost. Here are some strategies that will help you do exactly just that.
Keep your business updated
In the same way as making sure that your Google My Business listing information is accurate, updating the information in your Facebook page ensures that users would be receiving the correct and latest information about your brand. Too often I see business pages on Facebook that contain information that is outdated, which includes unchanged business addresses, incorrect phone numbers, and even old photos that do not reflect hot their business currently looks like.
This will cause your page to stagnate and damage your brand as a whole. It is best to keep your Facebook page updated as regularly as possible, from the primary information to your posts. Active pages on Facebook show up on people’s timelines more often, and you would need that organic reach to establish your presence. While sponsoring posts boosts your traffic significantly in a shorter period of time, growing your organic traffic would be able to give you a more solid user base that you would be interacting with on a regular basis.
Keywords and hashtags
Using Facebook search for the first time might seem confusing at first but becoming familiar with how to find posts and pages is relatively easy. Facebook allows you to search for public posts, photos, videos, and pages near the area you have listed, with the option of searching further as well. Using keywords is similar to other search engines, as it would track every related content that contains the keyword.
The versatility of Facebook’s search allows you to access so much content, which is why it would help boost your business. Like other search engines, your results would be based on the area that you’re located. Upon checking a few search results, I can see similarities with Google, in a way that local business search results allow me to see maps, photos, and other pieces of content that I might find useful.
For hashtags, Facebook incorporates another system that can be found in other social media platforms, as you can track related hashtags upon clicking on them. This allows users to find content in two different ways, which further expands the opportunities for searchability. Using keywords on your posts allow more users to see your content, while hashtags work best for social media campaigns. While tracking keywords and hashtags on Facebook is still not as refined as Google, making use of them allows you to let your organic reach grow.
Make use of reviews and events
Reviews are a great indicator of quality and allow users to see what people think about the quality of your service. Social media provides a great degree of interaction, as it allows you to provide quick replies through comments and messages. Reviews can be seen publicly, which is why having a negative review can cause your reach to drop if not dealt with properly.
Creating events is also another great way to generate more organic reach on Facebook, as users are notified of all the events that would be happening within the month on the pages that they follow. Events are searchable as well, which is another way for users to reach your page. Events help generate buzz about your business, which in turn makes more people interact and inquire, providing more reach that keeps your page present in timelines.
Search works in groups too
Groups on Facebook also have a search function that allows you to view posts within the group. Sharing your page posts helps generate a significant amount of organic traffic depending on the group size, making it another great place to promote your brand. There are numerous groups on Facebook dedicated to connecting people to a business that they want to find and making use of hashtags and the right keywords would make joining these groups beneficial in boosting your brand.
Key Takeaway
Facebook has gradually developed their search to become more versatile and effective for their users, and for SEO professionals and social media marketers, this provides a great opportunity to establish your online presence even further. Facebook is the largest social media network around, and optimizing your brand would mean being able to reach the most people possible.
If you have questions about social media marketing and SEO in general, leave a comment below and let’s talk.
http://bit.ly/2IcI04T
0 notes
Text
We Don’t Want to Fit In. We Want to Belong
There has been a big shift in how people interact with brands. In the old days, a product or service would show up on the scene, and we’d evaluate whether the product was something we could use. Sure, there were some products and brands where we felt like we wanted to belong (you are either a Coke or Pepsi person, for instance). But most times, when something new came out, the question was whether you could fit yourself into the right category to make that product useful.
This has all reversed. People are tired of fitting in. They want to go where they belong.
The post We Don’t Want to Fit In. We Want to Belong appeared first on chrisbrogan.com.
http://bit.ly/2V1vAyt
0 notes