Writing, psychology, animation, science both fictional and real, assorted goodies
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Hey clover-lawn lovers, may I introduce you to wood sorrel? It looks a lot like clover but has cute yellow flowers and is native to much of the US.

In my experience it’s less likely to get taken over by neighbors turf grass, creeping Charlie or other unwanted additions. As a native there are native insect and mammals who like it. As a bonus- it’s very tasty! Like it has a lemon zest thing going on. (Remember to test your soil for lead tho). And you can get it as a crop seed, which helps is spread faster and cheaper than plugs. It loves sun and is chill about a wide array of wetness conditions. I find it as robust against foot traffic as most lawn grass, and it never gets so tall you have to mow it.
help im trying to relax by looking at gardening posts on pinterest but half of the things they say are wrong
5K notes
·
View notes
Photo

To help meet the need for content related to racism, anti-racism, and Black voices, JSTOR has created free open library as a companion to the Schomburg Center’s Black Reading List.
Explore the list of more than 2k BIPOC+Q-authored resources today.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
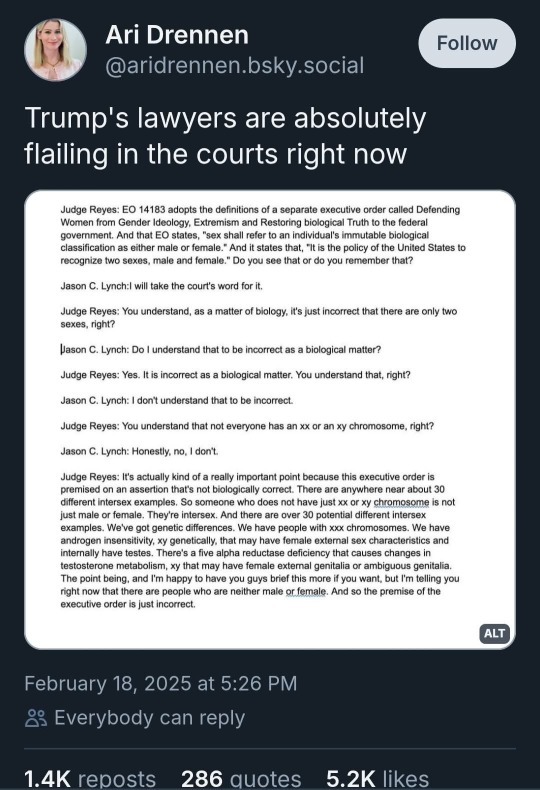
Literally sobbing. A judge, a US judge defended us. A judge brought up intersex people, uaing the term intersex, to *defend* us by not allowing our erasure. I'm having a lot of feelings right now
107K notes
·
View notes
Text
Genuinely think I may never fully outgrow teen romances since I HAD a tropetastic teen romance turned HEA.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
18K notes
·
View notes
Text
"China’s additions of wind and solar capacity once again exceeded forecasts and prior records in 2024, new data releases show.
Another 277GW of solar was installed through the year, 28% more than was added in 2023, according to the National Energy Administration. That brings the country’s total operational solar capacity to 887GW. Wind installations also hit a fresh record of 79GW — a 5% increase from the previous year — taking total capacity to 521GW.
That means China now has 1,408GW of wind and solar capacity — well ahead of the government’s prior target of having 1,200GW in place by 2030....
“The combination of accelerating clean energy growth and moderating power demand growth promises to bend China’s emissions down further from the current plateau,” Myllyvirta said in a post.
That’s despite coal- and gas-fired power capacity additions of 54GW in 2024, a slight decline from the prior year.
Myllyvirta said energy capacity additions tend to accelerate towards the end of each year, which means last year’s new installations will only fully show up in generation statistics from 2025.
“So the record additions in the end of 2024 are highly relevant for the 2025 emission trend,” Myllyvirta said.
Close to half of the experts surveyed by CREA last year said China’s carbon dioxide emissions had probably already peaked, or would do so in 2025, thanks in large part to its unprecedented wind and solar boom.
However, it’s still too soon to call the top. China’s fossil fuel power plants generated 1.5% more electricity in 2024 than the previous year, per the National Bureau of Statistics. This indicates that electricity consumption continued to grow faster than clean energy output.
Meanwhile, 11 million electric vehicles were sold in China in 2024, a 40% increase, according to a tally by research group Rho Motion. One in two new cars sold in the country now has a plug, meaning China is expected to see a steady decline in gasoline demand in the years ahead. The country’s crude oil imports fell 1.9% in 2024, the first annual decline in two decades, barring the Covid-induced slump.
China’s rapid progress in electrifying transport, heavy industry, and heating will help turn the tide on emissions. The eastern province of Zhejiang has reached a world-leading electrification rate of 51%, according to an analysis by US-based research group RMI."
-via The Progress Playbook, January 21, 2025
486 notes
·
View notes
Text

This is performative.
It's unconstitutional.
An executive order is not a law. Republican lawyers know this is a joke, but they let First Felon cosplay.
Context:

3K notes
·
View notes
Text

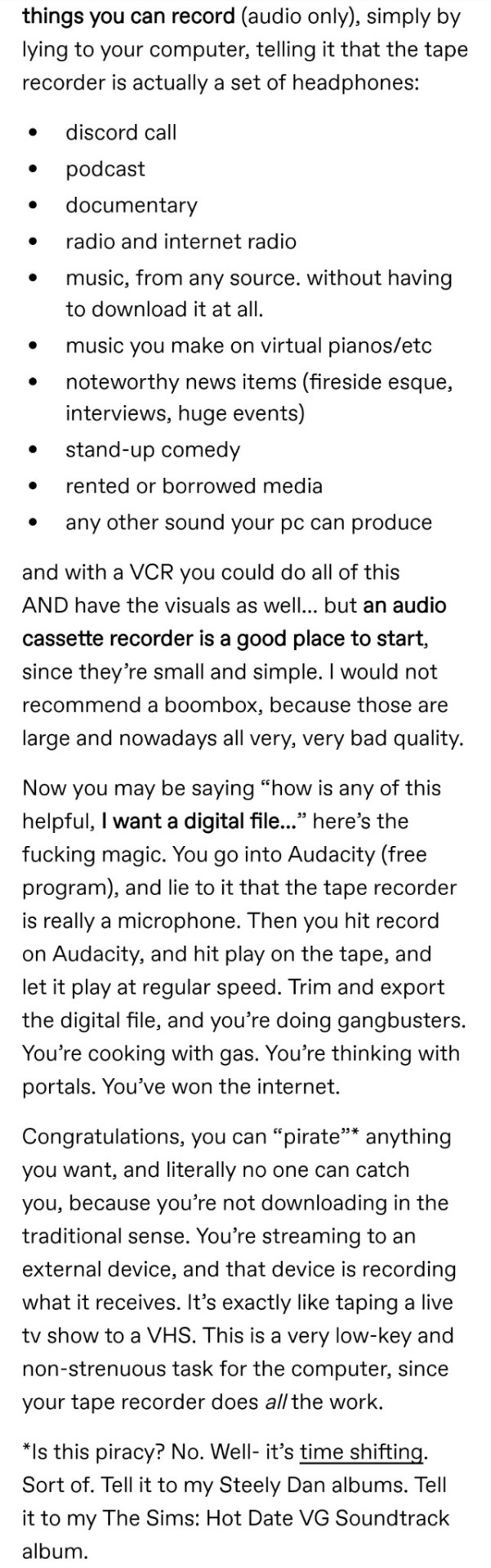
Time shifting
––
I wanted this but the original poster is transphobic
75K notes
·
View notes
Text
Not sure if I've told this story here before, but once upon a time, I didn't really get the point of most protests happening my area because I viewed them as "preaching to your own echo chamber" in a lot of cases. Ex: I saw people do a climate march through a very liberal university campus within a very liberal city, and I was just like "Okay, everyone here agrees with you. This place has crazy aggressive sustainability goals. What is the point of this?"
Then when Roe fell, there were a lot of protests outside the courthouses in cities near me, and though those city courthouses do serve the surrounding rural areas as well, the cities themselves are all rather progressive and left-leaning, so once again I was like "Okay, what is the point of this?" but I went anyway just for the experience. We stood on a street corner with our signs. Most people driving by honked in agreement with us. A few people yelled "abortion is murder" at us out their car windows, and we yelled back "abortion is healthcare!" Cool, okay, still didn't get the point because it's not like we were changing any minds or there in large numbers (we were no threat to any power structures), and the city already largely agreed with us.
But then we got another SUV that pulled up and yelled "abortion is murder!" at us (both husband and wife this time). Looked in the back seat, and they were traveling with their daughter who was maybe 13ish. She locked eyes with me, gave me the most serious look I've ever received, and gave us a thumbs up just above the window ledge so that her family couldn't see.
And that's the day I learned that protests are not always about threatening entrenched power structures but letting people in isolated ideological bubbles know that there are other perspectives and that if they share them, they're not alone.
26K notes
·
View notes
Text
Artists.
You do not need your Twitter.
Twitter is not the boost you think it is anymore.
I have seen at least 6 people I follow on BlueSky saying they have looked into their numbers and compared to Twitter? BSky gives them over double the exposure and follow through for outside links (probably because Twitter kills your tweet if you have links).
Twitter is testing a feature to allow other users to click a button attached to your posts to put your art into their Grok ai and make ai art with it without your permission automatically.
It is marking non-ai art as being made with Grok (probably to promote it).
You do not need Twitter.
Twitter needs you.
Starve the fuckin thing.
13K notes
·
View notes
Text
Just a quick note from your friendly neighborhood bookworm/indie author
if you use kindle for the majority of your library, they will be shutting down the function that allows you to download your files and transfer them via USB on the 26th of February. Which doesn't sound like a huge deal, but this also means that if a book is taken off Amazon for any reason—like it being banned—they can scrape it off your kindle as well. So maybe backup your library?
22K notes
·
View notes
Text
Although dam removals have been happening since 1912, the vast majority have occurred since the mid-2010s, and they have picked up steam since the 2021 Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, which provided funding for such projects. To date, 806 Northeastern dams have come down, with hundreds more in the pipeline. Across the country, 2023 was a watershed year, with a total of 80 dam removals. Says Andrew Fisk, Northeast regional director of the nonprofit American Rivers, “The increasing intensity and frequency of storm events, and the dramatically reduced sizes of our migratory fish populations, are accelerating our efforts.”
Dam removals in the Northeast don’t generate the same media attention as massive takedowns on West Coast rivers, like the Klamath or the Elwha. That’s because most of these structures are comparatively miniscule, built in the 19th century to form ponds and to power grist, textile, paper, saw, and other types of mills as the region developed into an industrial powerhouse.
But as mills became defunct, their dams remained. They may be small to humans, but to the fish that can’t get past them “they’re just as big as a Klamath River dam,” says Maddie Feaster, habitat restoration project manager for the environmental organization Riverkeeper, based in Ossining, New York. From Maryland and Pennsylvania up to Maine, there are 31,213 inventoried dams, more than 4,000 of which sit within the 13,400-square-mile Hudson River watershed alone. For generations they’ve degraded habitat and altered downstream hydrology and sediment flows, creating warm, stagnant, low-oxygen pools that trigger algal blooms and favor invasive species. The dams inhibit fish passage, too, which is why the biologists at the mouth of the Saw Kill transported their glass eels past the first of three Saw Kill dams after counting them...
Jeremy Dietrich, an aquatic ecologist at the New York State Water Resources Institute, monitors dam sites both pre- and post-removal. Environments upstream of an intact dam, he explains, “are dominated by midges, aquatic worms, small crustaceans, organisms you typically might find in a pond.” In 2017 and 2018 assessments of recent Hudson River dam removals, some of which also included riverbank restorations to further enhance habitat for native species, he found improved water quality and more populous communities of beetles, mayflies, and caddisflies, which are “more sensitive to environmental perturbation, and thus used as bioindicators,” he says. “You have this big polarity of ecological conditions, because the barrier has severed the natural connectivity of the system. [After removal], we generally see streams recover to a point where we didn’t even know there was a dam there.”

Pictured: Quassaick Creek flows freely after the removal of the Strooks Felt Dam, Newburgh, New York.
American Rivers estimates that 85 percent of U.S. dams are unnecessary at best and pose risks to public safety at worst, should they collapse and flood downstream communities. The nonprofit has been involved with roughly 1,000 removals across the country, 38 of them since 2018. This effort was boosted by $800 million from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law. But states will likely need to contribute more of their own funding should the Trump administration claw back unspent money, and organizations involved in dam removal are now scrambling to assess the potential impact to their work.
Enthusiasm for such projects is on the upswing among some dam owners — whether states, municipalities, or private landholders. Pennsylvania alone has taken out more than 390 dams since 1912 — 107 of them between 2015 and 2023 — none higher than 16 feet high. “Individual property owners [say] I own a dam, and my insurance company is telling me I have a liability,” says Fisk. Dams in disrepair may release toxic sediments that potentially threaten both human health and wildlife, and low-head dams, over which water flows continuously, churn up recirculating currents that trap and drown 50 people a year in the U.S.
Numerous studies show that dam removals improve aquatic fish passage, water quality, watershed resilience, and habitat for organisms up the food chain, from insects to otters and eagles. But removals aren’t straightforward. Federal grants, from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration or the Fish and Wildlife Service, favor projects that benefit federally listed species and many river miles. But even the smallest, simplest projects range in cost from $100,000 to $3 million. To qualify for a grant, be it federal or state, an application “has to score well,” says Scott Cuppett, who leads the watershed team at the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation’s Hudson River Estuary Program, which collaborates with nonprofits like Riverkeeper to connect dam owners to technical assistance and money...

All this can be overwhelming for dam owners, which is why stakeholders hope additional research will help loosen up some of the requirements. In 2020, Yellen released a study in which he simulated the removal of the 1,702 dams in the lower Hudson watershed, attempting to determine how much sediment might be released if they came down. He found that “the vast majority of dams don’t really trap much sediment,” he says. That’s good news, since it means sediment released into the Hudson will neither permanently worsen water quality nor build up in places that would smother or otherwise harm underwater vegetation. And it shows that “you would not need to invest a huge amount of time or effort into a [costly] sediment management plan,” Yellen says. It’s “a day’s worth of excavator work to remove some concrete and rock, instead of months of trucking away sand and fill.” ...
On a sunny winter afternoon, Feaster, of Riverkeeper, stands in thick mud beside Quassaick Creek in Newburgh, New York. The Strooks Felt Dam, the first of seven municipally owned dams on the lower reaches of this 18-mile tributary, was demolished with state money in 2020. The second dam, called Holden, is slated to come down in late 2025. Feaster is showing a visitor the third, the Walsh Road Dam, whose removal has yet to be funded. “This was built into a floodplain,” she says, “and when it rains the dam overflows to flood a housing complex just around a bend in the creek.” ...
On the Quassaick, improvements are evident since the Strooks dam came out. American eel and juvenile blue crabs have already moved in. In fact, fish returns can sometimes be observed within minutes of opening a passageway. Says Schmidt, “We’ve had dammed rivers where you’ve been removing the project and when the last piece comes out a fish immediately storms past it.”
There is palpable impatience among environmentalists and dam owners to get even more removals going in the Northeast. To that end, collaborators are working to streamline the process. The Fish and Wildlife Service, for example, has formed an interagency fish passage task force with other federal agencies, including NOAA and FEMA, that have their own interests in dam removals. American Rivers is working with regional partners to develop priority lists of dams whose removals would provide the greatest environmental and safety benefits and open up the most river miles to the most important species. “We’re not going to remove all dams,” [Note: mostly for reasons dealing with invasive species management, etc.] says Schmidt. “But we can be really thoughtful and impactful with the ones that we do choose to remove.”
-via Yale Environment 360, February 4, 2025
944 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR) has issued a landmark ruling, declaring that failure to address environmental pollution constitutes a violation of the right to life. The court found that governments must inform citizens living in pollution-affected areas, allowing them to assess risks to their health and well-being.
The case was brought by Italian citizens affected by hazardous emissions and widespread illegal waste dumping and burning in Campania. The pollution crisis has had severe public health consequences, and the court determined that the Italian government’s failure to intervene effectively, despite the pollution being caused by private actors, breached human rights law.
The ruling is expected to set a precedent for environmental cases across Europe, reinforcing government accountability in pollution control.
ClientEarth fundamental rights lawyer Malgorzata Kwiedacz-Palosz hailed the decision as a crucial step in linking environmental protection to human rights.
“This ruling confirms that human rights depend on access to clean air, water, and soil. Governments have an obligation to shield citizens from environmental hazards, no matter their source. The court has now explicitly recognised that pollution can directly threaten the right to life, meaning states will face greater scrutiny and stricter enforcement obligations,” she said.
Leading epidemiologist Dr Fabrizio Bianchi, who submitted expert testimony, stressed the severe health risks linked to pollution in Campania, where nearly three million residents have been exposed to toxic air since the 1980s.
“The health impacts are undeniable—higher rates of cancer, cardiovascular disease, and respiratory illnesses. Authorities must implement immediate clean-up measures and long-term monitoring to protect public health,” he stated.
This ruling strengthens environmental case law within the European Court of Human Rights, setting a binding precedent for future litigation.
In a separate legal challenge in Italy, ClientEarth is supporting a mother’s case advocating for her son’s right to breathe clean air, citing Article 2 of the European Convention on Human Rights —the same provision that underpinned the ECtHR’s latest decision.
Legal experts from Torino Respira, a group supporting the case in Italy, welcomed the ruling: “This judgment reinforces our argument that failing to keep air pollution within legal limits violates a child’s fundamental right to life and health. It sets an authoritative precedent for human rights protections against environmental harm.”
With growing global recognition of environmental degradation as a human rights issue, this ruling is expected to reshape legal approaches to pollution-related cases, compelling governments to act decisively against environmental threats."
-via ESG Post, February 1, 2025
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
And the older you get the more your ghost selves are sitting in ghost buildings that were bulldozed years ago.
kind of weird how parts of your soul are left in various locations without any warning… like yes i’m always at the top of that hill, sitting at the bus stop, in the cool light of the Japanese restaurant, standing at the pier etc etc
33K notes
·
View notes
Text

the white house is now so right wing, the GOP turtle man is by default on "our side." Trump's only response to this so far is to insinuate he's lying about the polio. Classy!
46K notes
·
View notes