Text
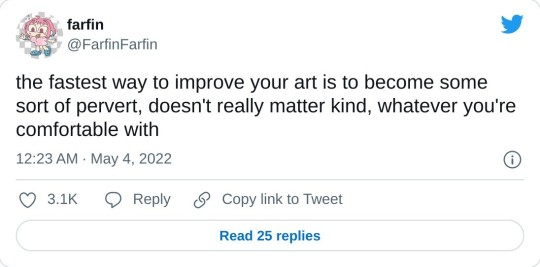
really helpful technique ^ once you know how to divide by halves and thirds it makes drawing evenly spaced things in perspective waaay easier:


113K notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing advice that changed my sentence
When I was a young writer, I was told that I often started my sentences with "there is/there was/there are." I was told to eliminate those as much as possible.
I couldn't believe how often I used them. My first novel was completely littered with them.
I learned to diversify and grow my use of verbs. Instead of the state-of-being verbs, like "is" which isn't very descriptive at all, I started using stronger verbs.
Instead of writing "There were a bunch of trees on the hill" I wrote "A cluster of trees towered over the hill."
"Towered" is a much stronger verb than "Is"
Use the state-of-being words, but if you can, try replacing them with more active verbs. You might be surprised how much your writing improves.
12K notes
·
View notes
Note

I personally know there are multiple types of editing but I've never seen anyone explain it in a way that actually made me understand what the types of editing actually were (yeah cool that you say {}editing is different from []editing but *how*). So if you wanna explain, feel free to.
Your handy-dandy guide to different types of editing
disclaimer: writers, you can literally edit however works for you. these distinction can be useful to your process, or just if you're looking to hire an editor. Not all editors make distinctions in this way; there are various ways of dividing. But no matter what vocabulary you use, it's best practice to start with broad, big-picture stuff and move towards narrower issues. Some editors do all levels of editing, while some specialize.
Developmental Editing (Is it a good story?)
Developmental editing has to do with the content. For a novel, that means working on the bones of the story. The plot. The pacing. The characters. Do their motivations make sense? Can the reader understand why things are happening? Does the story drag in places, or seem to brush past important elements? Do all of the subplots get resolved? etc. etc. (At this stage an editor is mostly going to be offering suggestions, pointing out issues, and throwing out potential solutions. Beta readers can also be very helpful at this stage to get a reader's perspective on the story beats and characters.)
Line Editing (is it well written?)
Sometimes called substantive editing, line editing is zooming in a little bit more to focus on scenes, paragraphs and sentences. Once we've decided that a scene is going to stay, lets look at the mechanics of how it plays out. Does the scene start to early or too late? Does the writing style communicate the emotions we want the reader to feel? Does the dialogue match the characters' voices? do any of the sentences sound awkward or ugly? Is the movement being bogged down by too much purple prose anywhere, or is there not enough detail? (This can get pretty subjective, so it's important that the writer and the editor are on the same page with taste, style goals, etc.)
Copy Editing (is is correct?)
Copy editing is all about the details. Think grammar and punctuation. Do the sentences make sense? are they grammatically correct? Is the dialogue punctuated correctly? Any misspellings? Should this be hyphenated? Should this be capitalized? Should we use a numeral, or write out the number? etc etc. A significant part of copy editing is matching everything to a style manual (like Chicago or AP) a house style guide (individualized preferences from a publisher, for example), and a project's own internal style sheet (are the character's names spelled the same every time? if we used "leaped" in chapter 4, we shouldn't use "leapt" in chapter 7) Copy editing is still subjective, but less so than the earlier levels, so a copyeditor will be more likely to just go in and make a bunch of (tracked!) changes without consulting the author for everything.
Bonus: Proofreading (did the copyeditor catch everything? are there typos? formatting issues? have any errors been introduced?)
Lots of people say editing when they really mean proofreading. Proofreading is the absolute last thing to get done. It's the one last pass just before something is published. It's important, but as you can see, there's a whole lot more to editing than just checking for typos.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text


some anatomy tips for drawing cat legs - works for big cats too
38K notes
·
View notes
Text
Pro Tip: The Way You End a Sentence Matters
Here is a quick and dirty writing tip that will strengthen your writing.
In English, the word at the end of a sentence carries more weight or emphasis than the rest of the sentence. You can use that to your advantage in modifying tone.
Consider:
In the end, what you said didn't matter.
It didn't matter what you said in the end.
In the end, it didn't matter what you said.
Do you pick up the subtle differences in meaning between these three sentences?
The first one feels a little angry, doesn't it? And the third one feels a little softer? There's a gulf of meaning between "what you said didn't matter" (it's not important!) and "it didn't matter what you said" (the end result would've never changed).
Let's try it again:
When her mother died, she couldn't even cry.
She couldn't even cry when her mother died.
That first example seems to kind of side with her, right? Whereas the second example seems to hold a little bit of judgment or accusation? The first phrase kind of seems to suggest that she was so sad she couldn't cry, whereas the second kind of seems to suggest that she's not sad and that's the problem.
The effect is super subtle and very hard to put into words, but you'll feel it when you're reading something. Changing up the order of your sentences to shift the focus can have a huge effect on tone even when the exact same words are used.
In linguistics, this is referred to as "end focus," and it's a nightmare for ESL students because it's so subtle and hard to explain. But a lot goes into it, and it's a tool worth keeping in your pocket if you're a creative writer or someone otherwise trying to create a specific effect with your words :)
33K notes
·
View notes
Text
One of the best tips for writing descriptions of pain is actually a snippet I remember from a story where a character is given a host of colored pencils and asked to draw an egg.
The character says that there’s no white pencil. But you don’t need a white pencil to draw a white egg. We already know the egg is white. What we need to draw is the luminance of the yellow lamp and the reflection of the blue cloth and the shadows and the shading.
We know a broken bone hurts. We know a knife wound hurts. We know grief hurts. Show us what else it does.
You don’t need to describe the character in pain. You need to describe how the pain affects the character - how they’re unable to move, how they’re sweating, how they’re cold, how their muscles ache and their fingers tremble and their eyes prickle.
Draw around the egg. Write around the pain. And we will all be able to see the finished product.
84K notes
·
View notes
Text
Apparently a lot of people get dialogue punctuation wrong despite having an otherwise solid grasp of grammar, possibly because they’re used to writing essays rather than prose. I don’t wanna be the asshole who complains about writing errors and then doesn’t offer to help, so here are the basics summarized as simply as I could manage on my phone (“dialogue tag” just refers to phrases like “he said,” “she whispered,” “they asked”):
“For most dialogue, use a comma after the sentence and don’t capitalize the next word after the quotation mark,” she said.
“But what if you’re using a question mark rather than a period?” they asked.
“When using a dialogue tag, you never capitalize the word after the quotation mark unless it’s a proper noun!” she snapped.
“When breaking up a single sentence with a dialogue tag,” she said, “use commas.”
“This is a single sentence,” she said. “Now, this is a second stand-alone sentence, so there’s no comma after ‘she said.’”
“There’s no dialogue tag after this sentence, so end it with a period rather than a comma.” She frowned, suddenly concerned that the entire post was as unasked for as it was sanctimonious.
104K notes
·
View notes
Photo

File this under “super obvious yet I always seem to forget it.”
119K notes
·
View notes
Photo
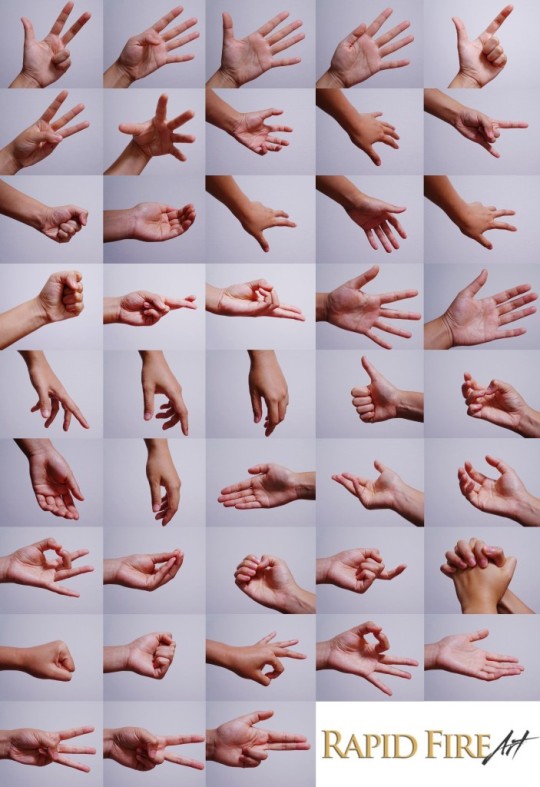
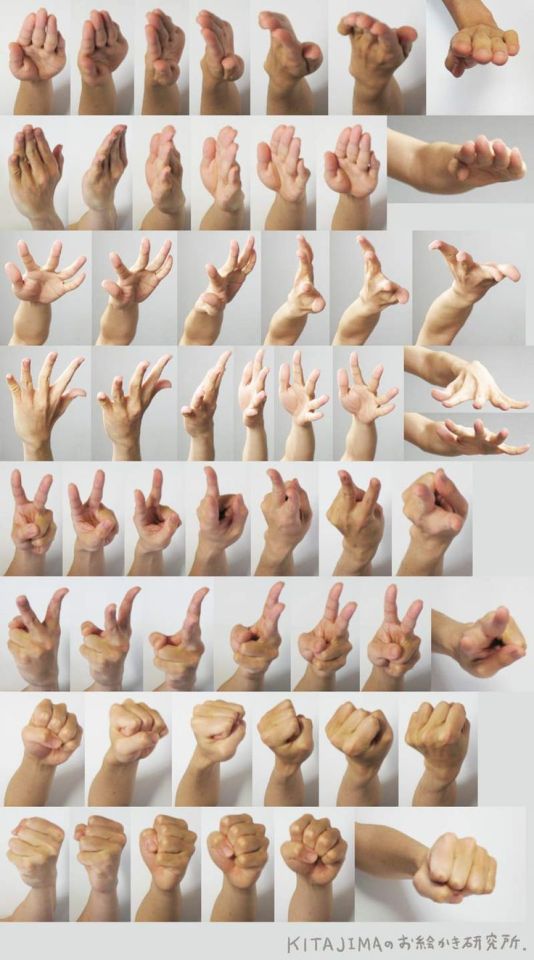
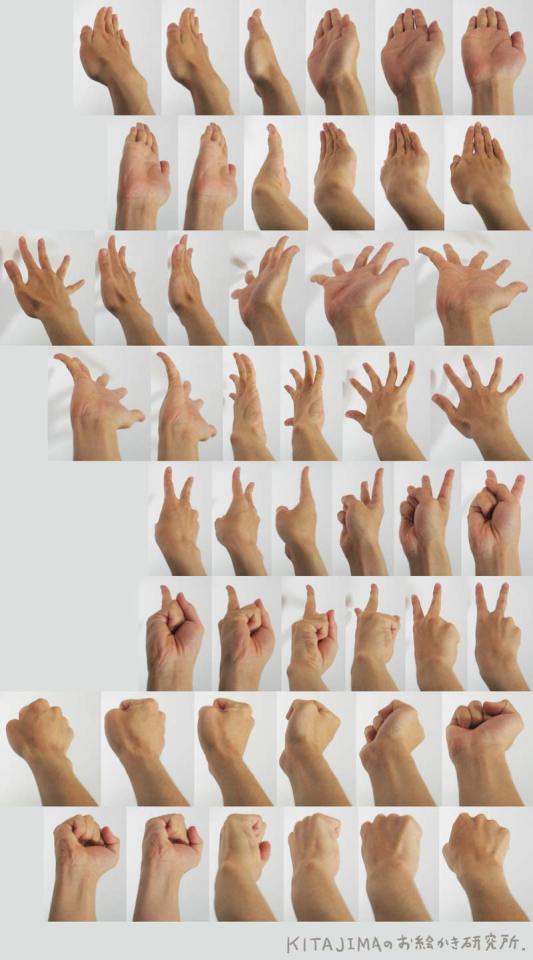
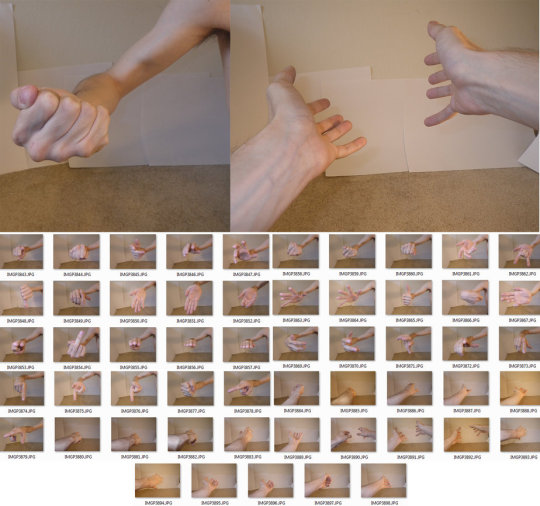
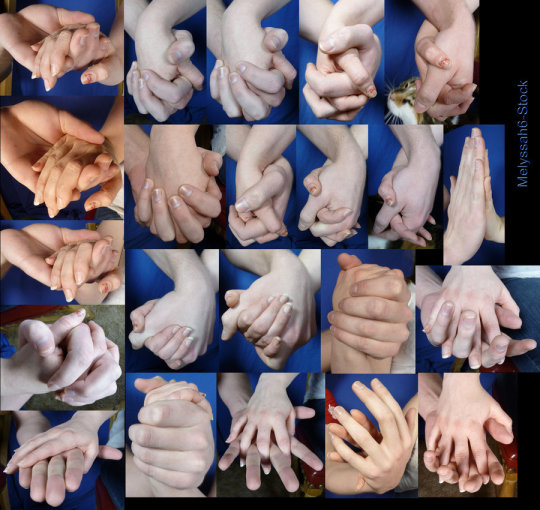
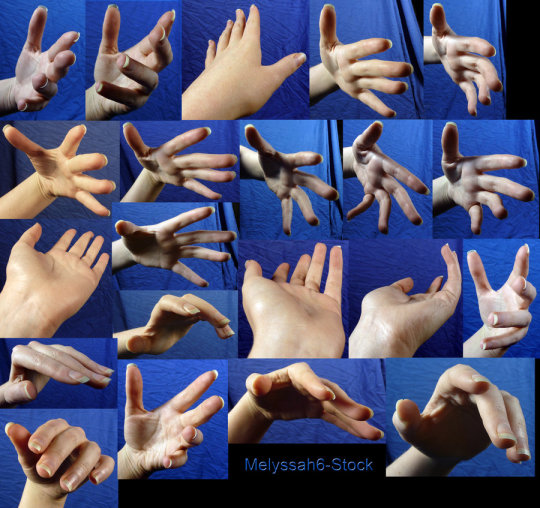




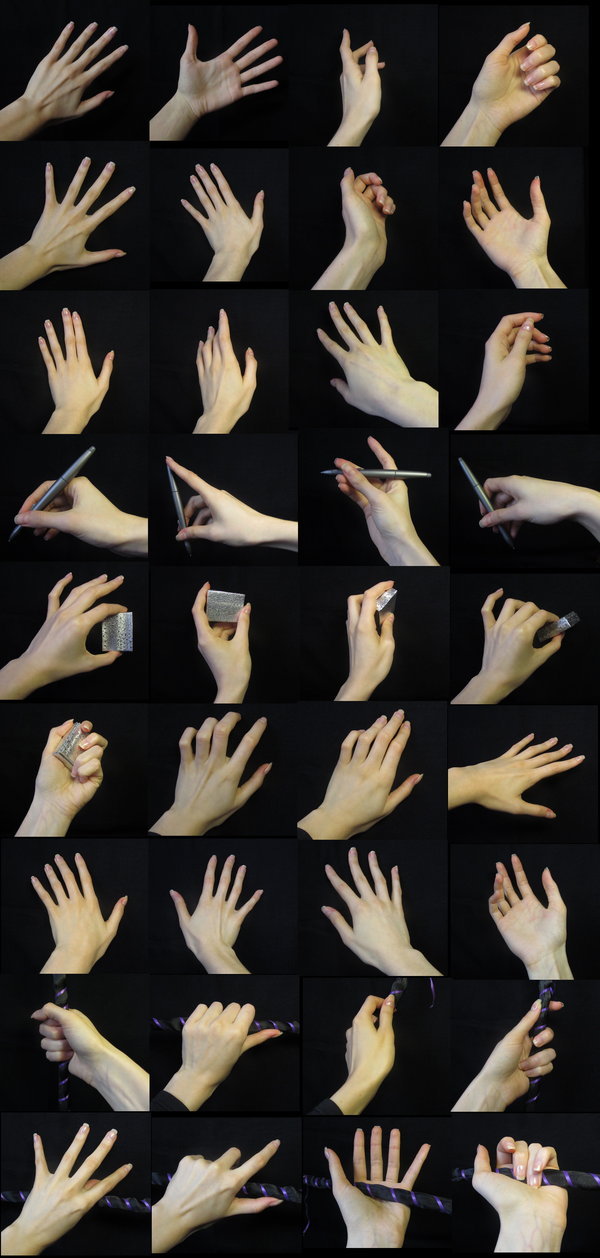
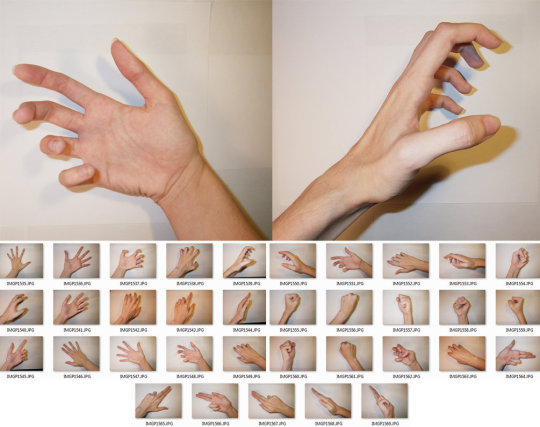
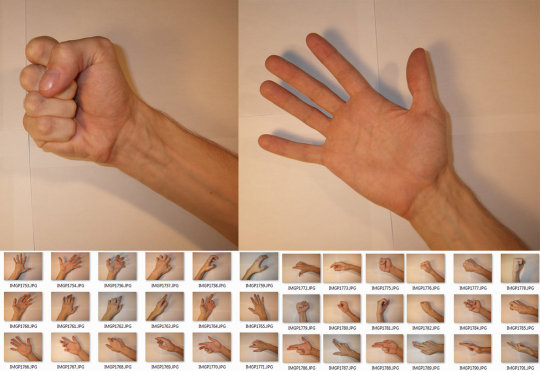



Hands
Row 1 & 2
Row 3
Row 4
Row 5 & 6
Row 7
193K notes
·
View notes
Text
Whgskl. Okay.
PSA to all you fantasy writers because I have just had a truly frustrating twenty minutes talking to someone about this: it’s okay to put mobility aids in your novel and have them just be ordinary.
Like. Super okay.
I don’t give a shit if it’s high fantasy, low fantasy or somewhere between the lovechild of Tolkein meets My Immortal. It’s okay to use mobility devices in your narrative. It’s okay to use the word “wheelchair”. You don’t have to remake the fucking wheel. It’s already been done for you.
And no, it doesn’t detract from the “realism” of your fictional universe in which you get to set the standard for realism. Please don’t try to use that as a reason for not using these things.
There is no reason to lock the disabled people in your narrative into towers because “that’s the way it was”, least of all in your novel about dragons and mermaids and other made up creatures. There is no historical realism here. You are in charge. You get to decide what that means.
Also:

“Depiction of Chinese philosopher Confucius in a wheelchair, dating to ca. 1680. The artist may have been thinking of methods of transport common in his own day.”
“The earliest records of wheeled furniture are an inscription found on a stone slate in China and a child’s bed depicted in a frieze on a Greek vase, both dating between the 6th and 5th century BCE.[2][3][4][5]The first records of wheeled seats being used for transporting disabled people date to three centuries later in China; the Chinese used early wheelbarrows to move people as well as heavy objects. A distinction between the two functions was not made for another several hundred years, around 525 CE, when images of wheeled chairs made specifically to carry people begin to occur in Chinese art.[5]”
“In 1655, Stephan Farffler, a 22 year old paraplegic watchmaker, built the world’s first self-propelling chair on a three-wheel chassis using a system of cranks and cogwheels.[6][3] However, the device had an appearance of a hand bike more than a wheelchair since the design included hand cranks mounted at the front wheel.[2]
The invalid carriage or Bath chair brought the technology into more common use from around 1760.[7]
In 1887, wheelchairs (“rolling chairs”) were introduced to Atlantic City so invalid tourists could rent them to enjoy the Boardwalk. Soon, many healthy tourists also rented the decorated “rolling chairs” and servants to push them as a show of decadence and treatment they could never experience at home.[8]
In 1933 Harry C. Jennings, Sr. and his disabled friend Herbert Everest, both mechanical engineers, invented the first lightweight, steel, folding, portable wheelchair.[9] Everest had previously broken his back in a mining accident. Everest and Jennings saw the business potential of the invention and went on to become the first mass-market manufacturers of wheelchairs. Their “X-brace” design is still in common use, albeit with updated materials and other improvements. The X-brace idea came to Harry from the men’s folding “camp chairs / stools”, rotated 90 degrees, that Harry and Herbert used in the outdoors and at the mines.[citation needed]
“But Joy, how do I describe this contraption in a fantasy setting that wont make it seem out of place?”
“It was a chair on wheels, which Prince FancyPants McElferson propelled forwards using his arms to direct the motion of the chair.”
“It was a chair on wheels, which Prince EvenFancierPants McElferson used to get about, pushed along by one of his companions or one of his many attending servants.”
“But it’s a high realm magical fantas—”
“It was a floating chair, the hum of magical energy keeping it off the ground casting a faint glow against the cobblestones as {CHARACTER} guided it round with expert ease, gliding back and forth.”
“But it’s a stempunk nov—”
“Unlike other wheelchairs he’d seen before, this one appeared to be self propelling, powered by the gasket of steam at the back, and directed by the use of a rudder like toggle in the front.”
Give. Disabled. Characters. In. Fantasy. Novels. Mobility. Aids.
If you can spend 60 pages telling me the history of your world in innate detail down to the formation of how magical rocks were formed, you can god damn write three lines in passing about a wheelchair.
Signed, your editor who doesn’t have time for this ableist fantasy realm shit.
67K notes
·
View notes
Text
I do not want my fantasy media to be realistic. I want my fantasy media to be convincing.
174K notes
·
View notes
Text
I firmly believe that how feminist a book is is better demonstrated by its background characters rather than its mains
47K notes
·
View notes
Text
Unreliable narrators need to add something to the story. They aren’t an excuse for poor storytelling and inconsistencies.
44K notes
·
View notes
Text
Fantasy Guide to Ships, Boats and Nautical Lingo

Of all the ways to travel in fantasy and historical novels, there are two favoured ones: horses and ships. But I covered the horses already so here we have some ship terminology and kinds of ships.
Common Boat Terms
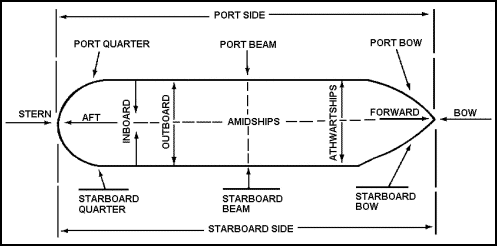
Aft/Stern - The back of a ship.
Bow - The bow is the front part of the ship, the pointy part or the place where Kate Winslet stood on in Titanic.
Port - The left side of the ship
Starboard - The right side of the ship
Windward - The wind the direction is blowing.
Hull- outside of the ship
Leeward - Or sometimes called the lee. This is the opposite direction of the wind is blowing
Boom - A horizontal pole extending from the base of the main mast. It adjusted toward the wind direction in order to harness the wind for the sails.
Rudder - The rudder is a flat piece of wood below the ship, used to steer the ship. It is connected to the wheel of the ship.
Tacking - A common sailing maneuver that involves turning the bow through the wind, to change the wind direction from one side of the ship to the other, making the boom move.
Underway- This is when the ship is moving
Astern- The ship is moving backwards
Amidships- Middle of the boat
Topside- when you move from the lower decks to the upper deck
Compartments of the ship
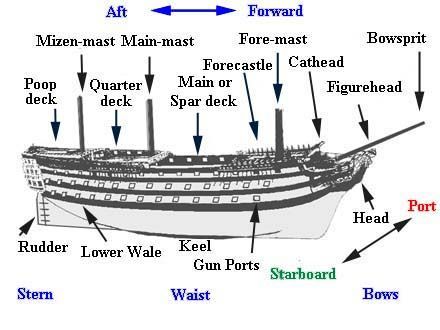
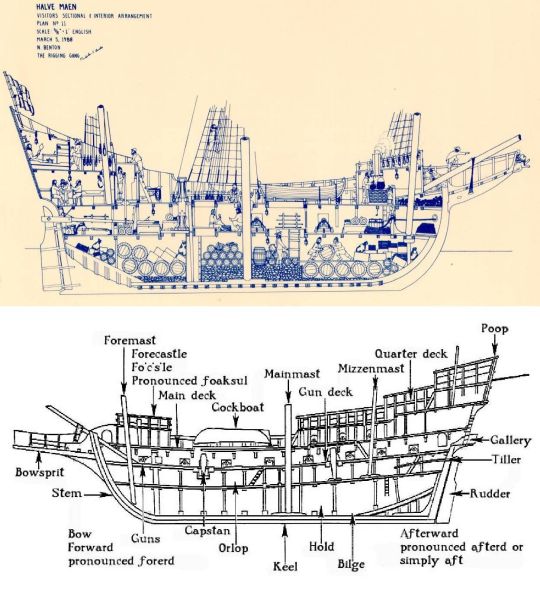
Most ships would have compartments inside the hull and underneath the deck.
Cabins- most war ships and merchant ships would only have one or two main cabin occupied by the captain and higher crew.
Galley- The kitchen on board the ship. The galley would be fitted with tables and cabinets. Galleys were built in such a way that they were more resistant to the heaving of the ship. Most galleys were built with special stoves to stop people from colliding with them and things from spilling out of pots and pans.
Wardroom- some ships are built with a common room for the crew. The wardroom acted as a common room as well as a dining room. It would usually be conjoined with the galley.
Sick Bay- is the compartment of the ship that is given over to the injured and sick. The sick bay would hold the medicines and medical devices and would often be under lock and key.
Hold- This will be the largest compartment in the ship were the cargo or the ship's weapons.
Crew and Positions aboard the Ship

Captain
When we think of captains we imagine them as blackhearted slave drivers (something akin to managers in the customer service industry) but on further research you will find that is not true. There are two kinds of Captains you find in history. Pirate captains and Legitimate Captains. Pirate captains were elected by their merit in battle and dedication to the crew. They were considered equal to the crew, only taking full charge during raids and battles. In the Navy or any legal-bound ship, captains were selected by rank and wealth. There was no equality between captain and crew as in pirate ships. Legal ships were Capitalists and the Pirates were Democratic.
First Mate
First Mate is the captain's deputy. They act as captain when the captain cannot. This was mainly seen in Navies and merchant ships as Pirates usually placed their quartermaster as their deputies.
Quartermaster
The Quartermaster was in charge of ensuring that the ship ran smoothly, rather like the ship's HR manager. The Quartermaster was in charge of supplies and had certain powers such as being able to punish the crew for minor infractions.
Sailing Master
These were officers in charge of piloting the ship. They would have to be educated enough to read a map and was a much desired position because it was a fair paying job. Pirates usually kidnapped sailing masters from ships they attacked to use aboard their own ships.
Gunner
Gunners were the overseers of any many qualified to load and fire guns. They were in charge of aiming cannons and making sure the crew were safely using guns. Most the guns were loaded by young boys called powder monkeys.
Boatswain
Boatswains or junior officers would act as supervisors, watching over the crew as they did their duties. If things were not going well they reported to the captain or quartermaster to punish the crew.
Surgeons
Surgeons handled any diseases and wounds. Since being at sea limited the amount of medicine available. Most ship's surgeons were forced to cut off limbs to avoid infection pike gangrene. Surgeons may not always be found on ships. Cooks or carpenters were often pressed to do amputations: meat was meat and cutting was cutting.
Cooks
All ships needed somebody to cook. Navies and merchant ships would often have trained cooks while on pirate ships it was just a crewmember who was handy in the kitchen.
Kinds of Ship

(Not a complete list, may post more later.)
Brig- A brig is the ship that one most thinks of when you think of a ship. The brig is a large vessel, set with a pair of square-rigged masts. Brigs were fast ships and highly maneuverable. They were used as merchant ships and warships.
Galley- The galley is propelled via oars. The hull is long and slender and most of them featured larger sails. Galleys often were rowed by slaves and used in war.
Galleon- Galleons were large ships, built with multiple decks, carrying three or more masts with square raised stern. The Galleon was usually rigged with square sails on the fore-mast and main-masts.
Caravel- The caravel was a small ship with triangular sails, famed for its manoeuvrability and speed.
Longship- The longships were the ships of the Vikings. They were slender ships, narrow. They were able to keep afloat in shallow waters as well as the deep sea. Longships were able to reverse quickly, a very important skill. The longship was a warship, a raider's ship propelled by oars.
Carrack- the carrack was a large ship, often built with mass cargo holds making the most popular ship to go on long voyages on. The carrack had three or four masts.
Cog- This ship was a large vessel, the hull wide and large. The ship is propelled by a great single sail flown from a tall mast.
Junk- The junk or Chinese junk was a kind of coastal or river ship used as merchant ships, pleasure ships and sometimes houseboats. They are small ships and made with battened sails rather resembling wings.
Trireme- the trireme was a slender ship set with three banks of oars pulled by one man each. The trireme had a concave hull and usually had an underwater ram at the prow of the ship.
For @viola-cola
21K notes
·
View notes