Text
33K notes
·
View notes
Text
In a world where a domino mask, or even just taking glasses out, is enough for concealing your identity...
Nobody should be able to recognize Jason post-ressurection.
Like he took 3 feet, 100 pounds of muscles, undergone puberty, magicked a part of his hair white, and his eyes changed colour.
He takes his helmet out in his dramatic reveal, and Batman is like : ... okaaaaay ? I am supposed to know who you are ??
14K notes
·
View notes
Text
28K notes
·
View notes
Text

Observations from both NASA’s James Webb and Hubble space telescopes created this colorful image of galaxy cluster MACS0416. The colors of different galaxies indicate distances, with bluer galaxies being closer and redder galaxies being more distant or dusty. Some galaxies appear as streaks due to gravitational lensing — a warping effect caused by large masses gravitationally bending the space that light travels through.
Like Taylor Swift, Our Universe Has Gone Through Many Different Eras
While Taylor's Eras Tour explores decades of music, our universe’s eras set the stage for life to exist today. By unraveling cosmic history, scientists can investigate how it happened, from the universe’s origin and evolution to its possible fate.
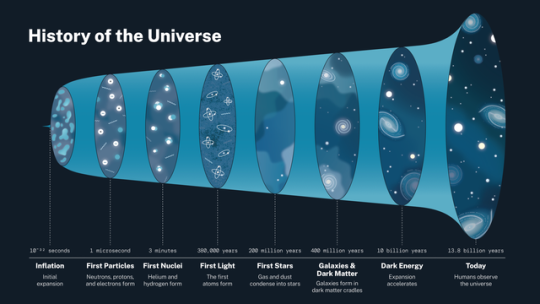
This infographic outlines the history of the universe.
0 SECONDS | In the beginning, the universe debuted extremely small, hot, and dense
Scientists aren’t sure what exactly existed at the very beginning of the universe, but they think there wasn’t any normal matter or physics. Things probably didn’t behave like we expect them to today.

Artist's interpretation of the beginning of the universe, with representations of the early cosmos and its expansion.
10^-32 SECONDS | The universe rapidly, fearless-ly inflated
When the universe debuted, it almost immediately became unstable. Space expanded faster than the speed of light during a very brief period known as inflation. Scientists are still exploring what drove this exponential expansion.
youtube
1 MICROSECOND | Inflation’s end started the story of us: we wouldn’t be here if inflation continued
When inflation ended, the universe continued to expand, but much slower. All the energy that previously drove the rapid expansion went into light and matter — normal stuff! Small subatomic particles — protons, neutrons, and electrons — now floated around, though the universe was too hot for them to combine and form atoms.
The particles gravitated together, especially in clumpy spots. The push and pull between gravity and the particles’ inability to stick together created oscillations, or sound waves.
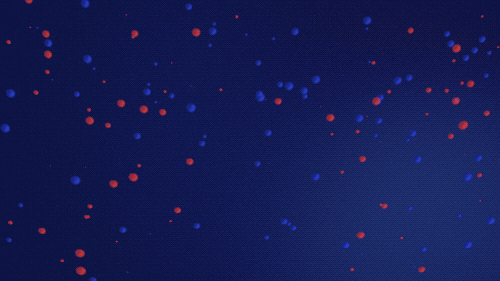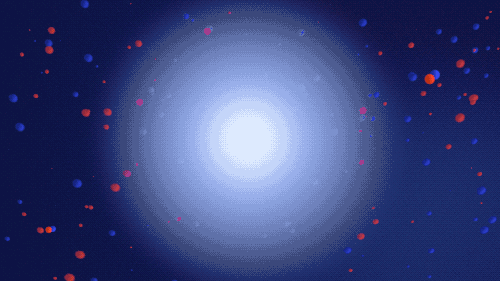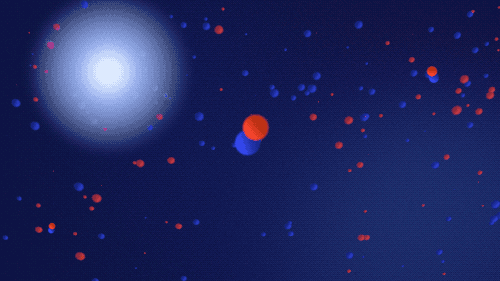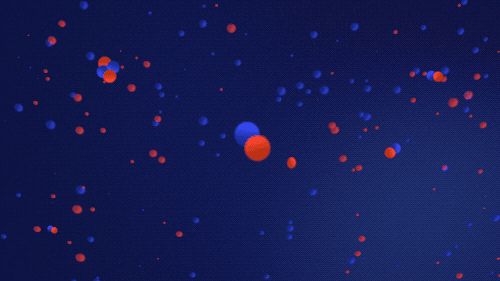
Artist's interpretation of protons and neutrons colliding to form ionized deuterium — a hydrogen isotope with one proton and one neutron — and ionized helium — two protons and two neutrons.
THREE MINUTES | Protons and neutrons combined all too well
After about three minutes, the universe had expanded and cooled enough for protons and neutrons to stick together. This created the very first elements: hydrogen, helium, and very small amounts of lithium and beryllium.
But it was still too hot for electrons to combine with the protons and neutrons. These free electrons floated around in a hot foggy soup that scattered light and made the universe appear dark.
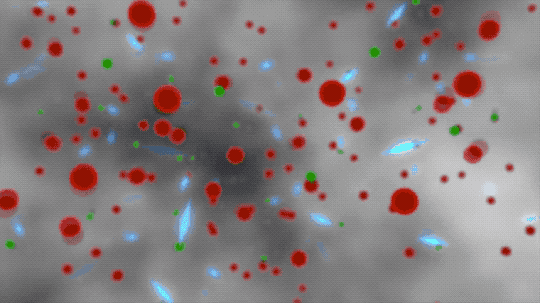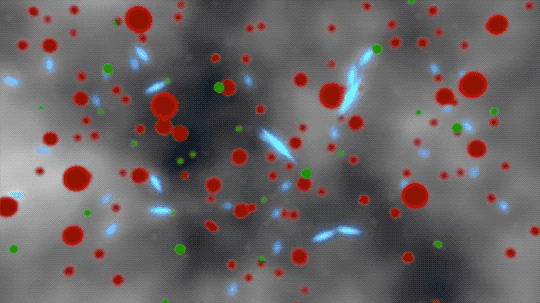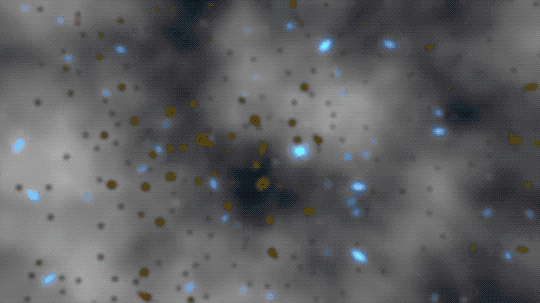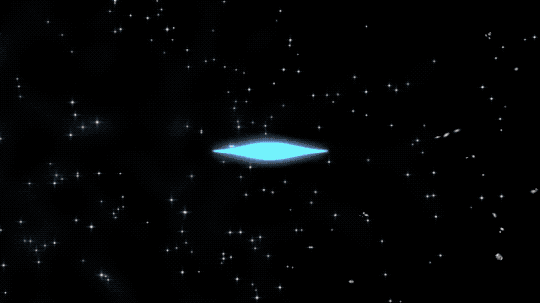
This animated artist’s concept begins by showing ionized atoms (red blobs), free electrons (green blobs), and photons of light (blue flashes). The ionized atoms scattered light until neutral atoms (shown as brown blobs) formed, clearing the way for light to travel farther through space.
380 THOUSAND YEARS | Neutral atoms formed and left a blank space for light
As the universe expanded and cooled further, electrons joined atoms and made them neutral. With the electron plasma out of the way, some light could travel much farther.

An image of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) across the entire sky, taken by ESA's (European Space Agency) Planck space telescope. The CMB is the oldest light we can observe in the universe. Frozen sound waves are visible as miniscule fluctuations in temperature, shown through blue (colder) and red (warmer) coloring.
As neutral atoms formed, the sound waves created by the push and pull between subatomic particles stopped. The waves froze, leaving ripples that were slightly denser than their surroundings. The excess matter attracted even more matter, both normal and “dark.” Dark matter has gravitational influence on its surroundings but is invisible and does not interact with light.

This animation illustrates the absorption of photons — light particles — by neutral hydrogen atoms.
ALSO 380 THOUSAND YEARS | The universe became dark — call it what you want, but scientists call this time period the Dark Ages
Other than the cosmic microwave background, there wasn't much light during this era since stars hadn’t formed yet. And what light there was usually didn't make it very far since neutral hydrogen atoms are really good at absorbing light. This kicked off an era known as the cosmic dark ages.

This animation illustrates the beginning of star formation as gas begins to clump due to gravity. These protostars heat up as material compresses inside them and throw off material at high speeds, creating shockwaves shown here as expanding rings of light.
200 MILLION YEARS | Stars created daylight (that was still blocked by hydrogen atoms)
Over time, denser areas pulled in more and more matter, in some places becoming so heavy it triggered a collapse. When the matter fell inward, it became hot enough for nuclear fusion to start, marking the birth of the first stars!
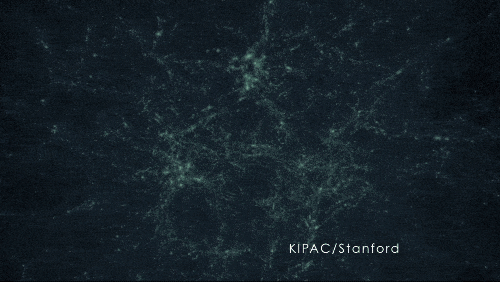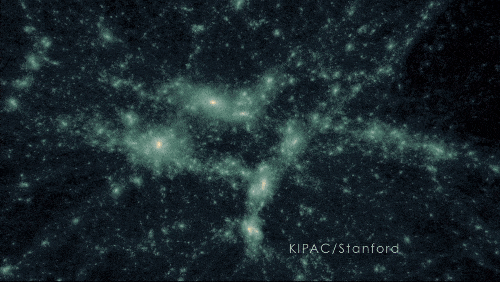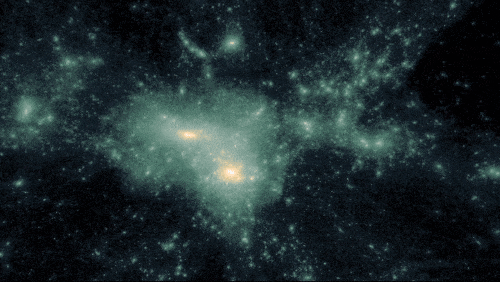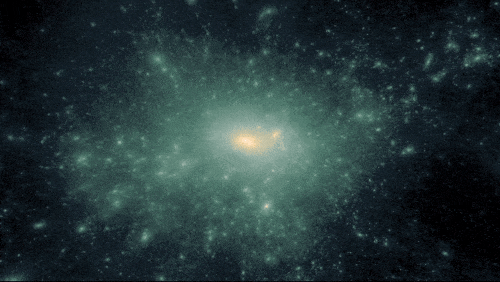
A simulation of dark matter forming structure due to gravity.
400 MILLION YEARS | Dark matter acted like an invisible string tying galaxies together
As the universe expanded, the frozen sound waves created earlier — which now included stars, gas, dust, and more elements produced by stars — stretched and continued attracting more mass. Pulling material together eventually formed the first galaxies, galaxy clusters, and wide-scale, web-like structure.
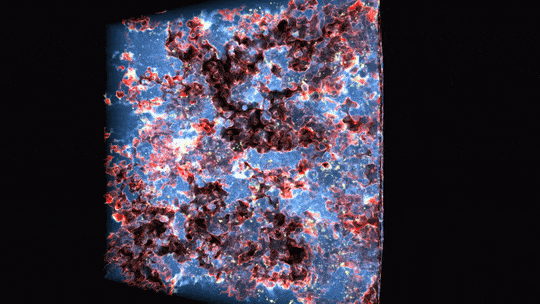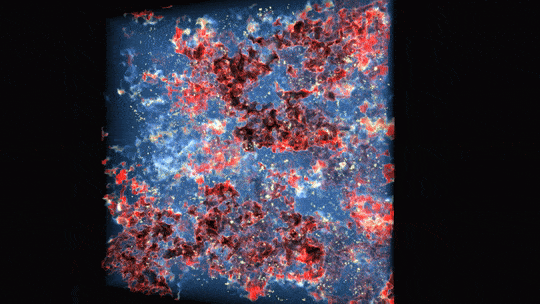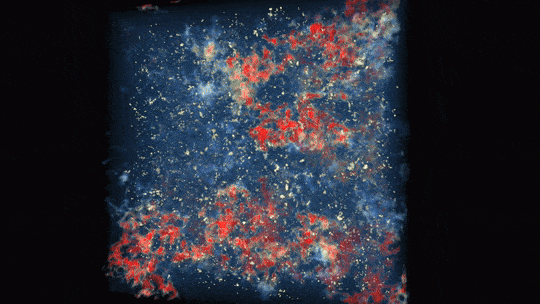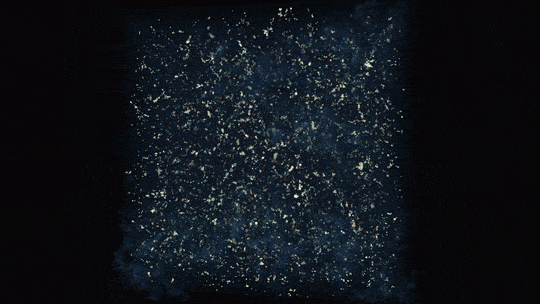
In this animation, ultraviolet light from stars ionizes hydrogen atoms by breaking off their electrons. Regions already ionized are blue and translucent, areas undergoing ionization are red and white, and regions of neutral gas are dark and opaque.
1 BILLION YEARS | Ultraviolet light from stars made the universe transparent for evermore
The first stars were massive and hot, meaning they burned their fuel supplies quickly and lived short lives. However, they gave off energetic ultraviolet light that helped break apart the neutral hydrogen around the stars and allowed light to travel farther.

Animation showing a graph of the universe’s expansion over time. While cosmic expansion slowed following the end of inflation, it began picking up the pace around 5 billion years ago. Scientists still aren't sure why.
SOMETIME AFTER 10 BILLION YEARS | Dark energy became dominant, accelerating cosmic expansion and creating a big question…?
By studying the universe’s expansion rate over time, scientists made the shocking discovery that it’s speeding up. They had thought eventually gravity should cause the matter to attract itself and slow down expansion. Some mysterious pressure, dubbed dark energy, seems to be accelerating cosmic expansion. About 10 billion years into the universe’s story, dark energy – whatever it may be – became dominant over matter.

An image of Earth rising in the Moon’s sky. Nicknamed “Earthrise,” Apollo 8 astronauts saw this sight during the first crewed mission to the Moon.
13.8 BILLION YEARS | The universe as we know it today: 359,785,714,285.7 fortnights from the beginning
We owe our universe today to each of its unique stages. However, scientists still have many questions about these eras.
Our upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will look back in time to explore cosmic mysteries like dark energy and dark matter – two poorly understood aspects of the universe that govern its evolution and ultimate fate.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Athletes Go for the Gold with NASA Spinoffs
NASA technology tends to find its way into the sporting world more often than you’d expect. Fitness is important to the space program because astronauts must undergo the extreme g-forces of getting into space and endure the long-term effects of weightlessness on the human body. The agency’s engineering expertise also means that items like shoes and swimsuits can be improved with NASA know-how.
As the 2024 Olympics are in full swing in Paris, here are some of the many NASA-derived technologies that have helped competitive athletes train for the games and made sure they’re properly equipped to win.
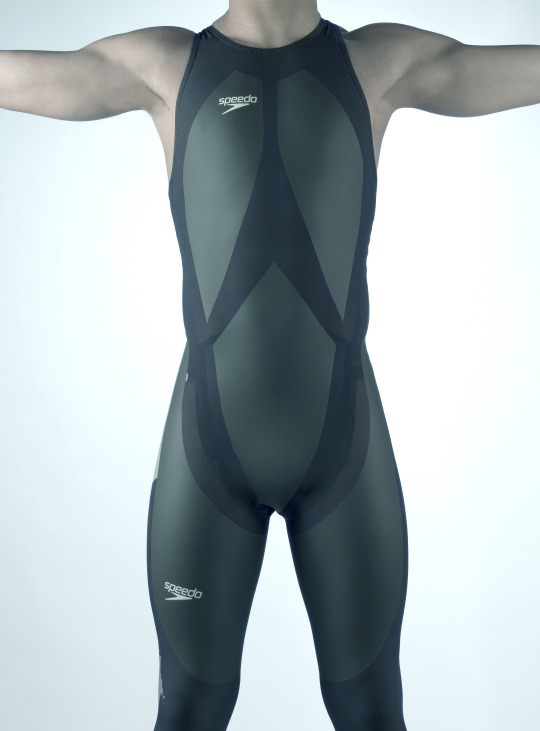

The LZR Racer reduces skin friction drag by covering more skin than traditional swimsuits. Multiple pieces of the water-resistant and extremely lightweight LZR Pulse fabric connect at ultrasonically welded seams and incorporate extremely low-profile zippers to keep viscous drag to a minimum.
Swimsuits That Don’t Drag
When the swimsuit manufacturer Speedo wanted its LZR Racer suit to have as little drag as possible, the company turned to the experts at Langley Research Center to test its materials and design. The end result was that the new suit reduced drag by 24 percent compared to the prior generation of Speedo racing suit and broke 13 world records in 2008. While the original LZR Racer is no longer used in competition due to the advantage it gave wearers, its legacy lives on in derivatives still produced to this day.

Trilion Quality Systems worked with NASA’s Glenn Research Center to adapt existing stereo photogrammetry software to work with high-speed cameras. Now the company sells the package widely, and it is used to analyze stress and strain in everything from knee implants to running shoes and more.
High-Speed Cameras for High-Speed Shoes
After space shuttle Columbia, investigators needed to see how materials reacted during recreation tests with high-speed cameras, which involved working with industry to create a system that could analyze footage filmed at 30,000 frames per second. Engineers at Adidas used this system to analyze the behavior of Olympic marathoners' feet as they hit the ground and adjusted the design of the company’s high-performance footwear based on these observations.

Martial artist Barry French holds an Impax Body Shield while former European middle-weight kickboxing champion Daryl Tyler delivers an explosive jump side kick; the force of the impact is registered precisely and shown on the display panel of the electronic box French is wearing on his belt.
One-Thousandth-of-an-Inch Punch
In the 1980s, Olympic martial artists needed a way to measure the impact of their strikes to improve training for competition. Impulse Technology reached out to Glenn Research Center to create the Impax sensor, an ultra-thin film sensor which creates a small amount of voltage when struck. The more force applied, the more voltage it generates, enabling a computerized display to show how powerful a punch or kick was.
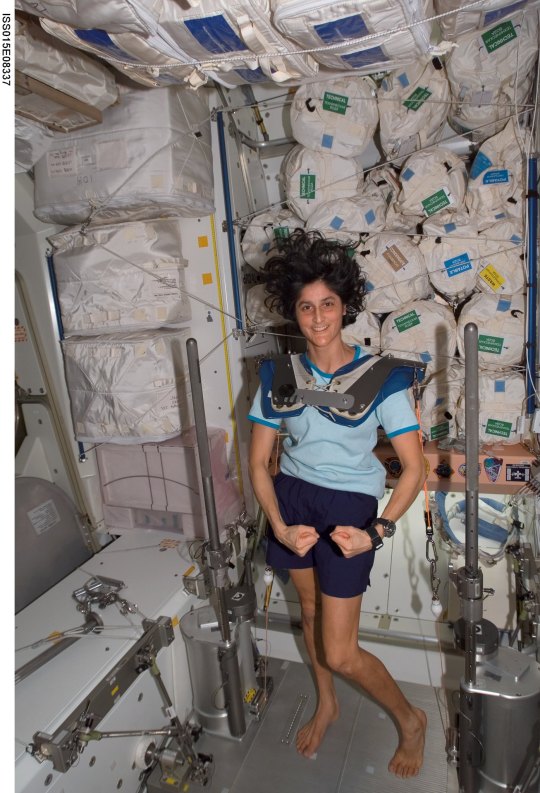

Astronaut Sunita Williams poses while using the Interim Resistive Exercise Device on the ISS. The cylinders at the base of each side house the SpiraFlex FlexPacks that inventor Paul Francis honed under NASA contracts. They would go on to power the Bowflex Revolution and other commercial exercise equipment.
Weight Training Without the Weight
Astronauts spending long periods of time in space needed a way to maintain muscle mass without the effect of gravity, but lifting free weights doesn’t work when you’re practically weightless. An exercise machine that uses elastic resistance to provide the same benefits as weightlifting went to the space station in the year 2000. That resistance technology was commercialized into the Bowflex Revolution home exercise equipment shortly afterwards.
Want to learn more about technologies made for space and used on Earth? Check out NASA Spinoff to find products and services that wouldn’t exist without space exploration.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
2K notes
·
View notes















