Text
Something I find incredibly cool is that they’ve found neandertal bone tools made from polished rib bones, and they couldn’t figure out what they were for for the life of them.
Until, of course, they showed it to a traditional leatherworker and she took one look at it and said “Oh yeah sure that’s a leather burnisher, you use it to close the pores of leather and work oil into the hide to make it waterproof. Mine looks just the same.”
“Wait you’re still using the exact same fucking thing 50,000 years later???”
“Well, yeah. We’ve tried other things. Metal scratches up and damages the hide. Wood splinters and wears out. Bone lasts forever and gives the best polish. There are new, cheaper plastic ones, but they crack and break after a couple years. A bone polisher is nearly indestructible, and only gets better with age. The more you use a bone polisher the better it works.”
It’s just.
50,000 years. 50,000. And over that huge arc of time, we’ve been quietly using the exact same thing, unchanged, because we simply haven’t found anything better to do the job.
381K notes
·
View notes
Photo



Sorting some files. This was an internal work-related document that I made for a design job in 2016. I was working with this company to design science lessons in VR, and I was the Biology expert, the concept artist, and also the lesson writer/designer. It was a small team. Snyway, we had all these activities on arctic animals, and I made this for the product management team to explain seal reproduction. I never really had a job title at this job, but I was the person they called in to explain weird stuff like seal reproduction and deep sea fish to corporate types.
Other places to see my posts: INSTAGRAM / FACEBOOK / ETSY / KICKSTARTER
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
etymology is so funny. canary yellow means “the color of a bird that comes from some islands that were named due to having a lot of dogs there”
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
It's always so weird to come down from the biology heavens to see what the average person believes about animals, plants, ecosystems, just the world around them. I don't even mean things that one simply doesn't know because they've never been told or things that are confusing, I'm talking about people who genuinely do not see insects as animals. What are you saying. Every time I see a crawling or fluttering little guy I know that little guy has motivations and drive to fulfill those motivations. There are gears turning in their head! They are perceiving this world and they are drawing conclusions, they are conscious. And yet it's still a whole thing if various bugs of the world feel pain or if they are simply Instinct Machines that are Not Truly Aware of Anything At All????? Help!!!!!! How can you look at a little guy and think he is just the macroscopic animal version of a virus
14K notes
·
View notes
Text
Oh have y’all heard of the river dolphin piss thing?
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Why aren’t there more people constantly talking about flatfishes. This is an animal that lives its whole adult life on its side so it has to move one of its eyeballs around to the other side. Are there people who don’t even know this or is it one of those things everybody just takes for granted so they never stop and think about how completely nuts that is.

I bet people don’t even know that some of them are pretty


That some are so specialized they practically evolved into flatworms
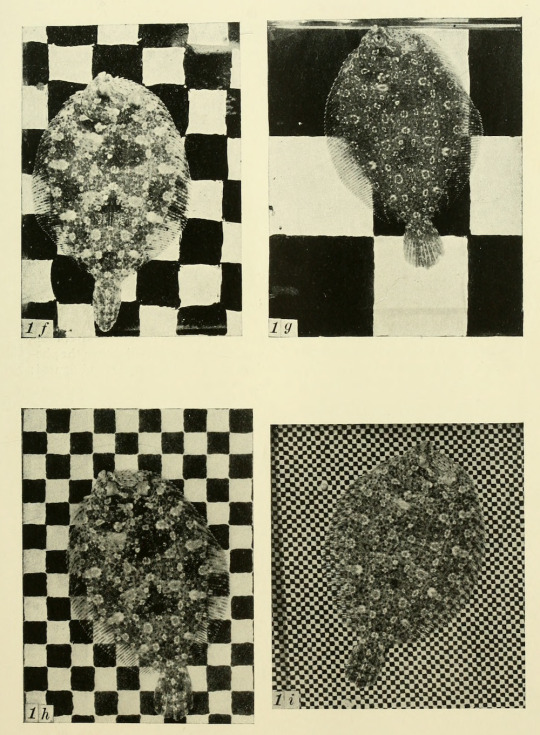
Or that some can change their color patterns to try and match their surroundings
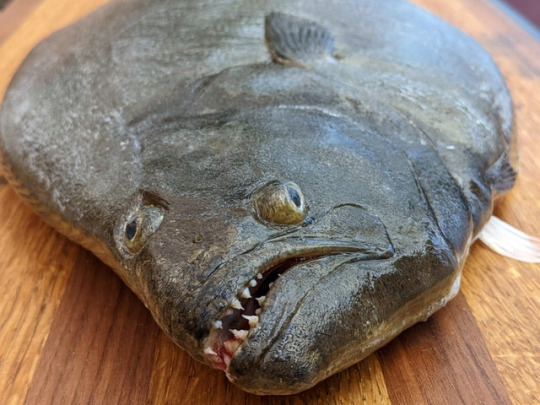

Or that all of them are predators

Or that some of them, like the many popularly eaten species of halibut, get big enough that if they really wanted to, they could probably eat you too!!

This is a good shot of a big one swimming, presumably before photographer Audun H Rikardsen disappeared mysteriously
10K notes
·
View notes
Text
Lake Mendota in Wisconsin is transformed by the changing seasons – covered by ice in winter, and by algae in summer – and a new study shows how these cyclical shifts are putting the lake's bacteria into evolutionary loops. Led by researchers from the University of Texas at Austin, the team behind the study analyzed 471 lake microbe samples collected across 20 years, looking at genetic variations within and between species through time. The data showed thousands of bacteria species evolving through the generations, then evolving back to a virtually identical state as the seasons shifted. As microbes live just a few days, we're talking about genetic evolution crossing thousands of generations within the span of one year.
Continue Reading.
631 notes
·
View notes
Text
Yeast, Algae, and Bacterial Staples
Yeast and algae are the two major staples of spacer human diets in Runaway to the Stars, providing energy efficient sources of protein, lipids, and carbohydrates.
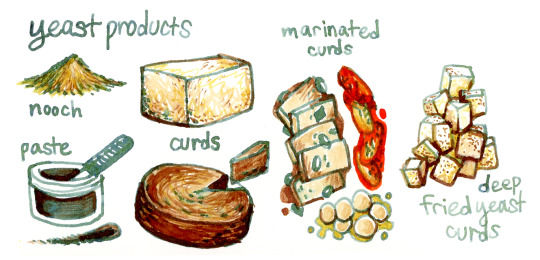
Yeast is never eaten raw but is found in a variety of processed forms, the most common of which are powders, pastes, and curds. Powders and pastes tend to be most strongly flavored. Some are given flavored additives, or salt-fermented for an even stronger taste. The powder forms (often called nooch) tend to taste cheesy, and the pastes most commonly resemble yeast extracts like Vegemite or Marmite in flavor. Yeast curd is a tofu-like substance with a faint mushroom flavor and high protein content. It’s most popular marinated or fried, and comes in a variety of firmnesses from silken to jerky. “Trained” yeast is genetically modified to produce a specific desired biological compound or set of compounds, and is widely used in the manufacture of synthetic flavors, dairy products, proteins, enzymes, and more.
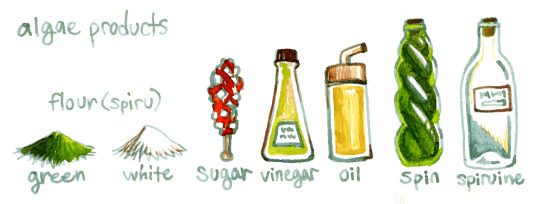
Algae eaten by spacers is mostly genetically modified chlorophytes such as Botryococcus braunii and the Chlorella genus, and the most commonly cultivated cyanobacteria is Arthrospira platensis (spirulina). These are used to produce a wide variety of refined food products, including flour, sugar, agar, oil, and vitamins. When fermented by yeast, vinegar and spirits can be produced from algae products as well. Algae flour (sometimes called spira) comes in two main forms, green and white. Green flour is unrefined algae powder and can have a very strong grassy taste. White flour is refined to remove most of the compounds in the powder that aren’t starch, and it can be used to make dough. Some white algae flour has synthetic gluten added to give it an elasticity similar to wheat flour, but it is more rare than agar being added as a stabilizing agent. Leavened dough with agar tends to have a more brittle, crumbly structure than glutenous dough.

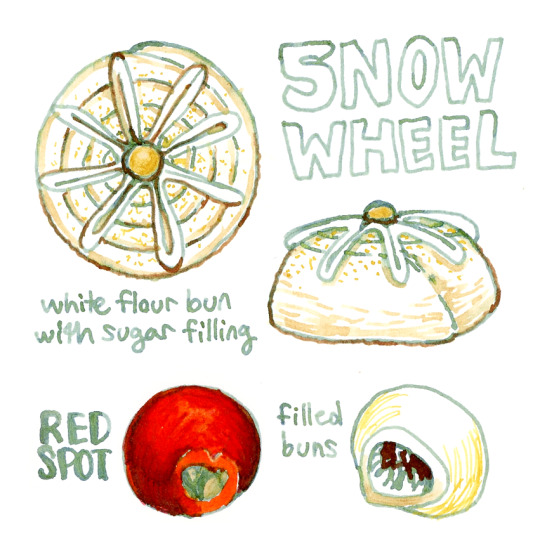
Fried, baked, or steamed spira dough dumplings with yeast paste and other fillings inside are an iconic spacer food with many regional variations. Jovia’s variation are a steamed rolled bun that uses enough green spira to make the dough green, and has yeast paste painted on the rolled side. Slices of curd are sometimes laid on top with a yellow cherry tomato or egg yolk in the center to make the bun resemble a wheel, or a cross section of a habitat cylinder. These are known as Jovian wheels and they are commonly eaten on Jovian Independence Day.
Spin is a kind of spirulina-based hard liquor produced on Mars, known for its bright green color and strong, controversial flavor. It is traditionally not sweet, but sweetened versions and cocktails are more commonly enjoyed by those less used to the stuff. Clear, relatively flavorless hard-proof liquor produced from algae is generally called spiruine. On Earth, yeast products have been gaining popularity but algal farming remains relatively rare. Soil farming is the cheaper option when air and light are free.
Read more about human food in RttS here.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text



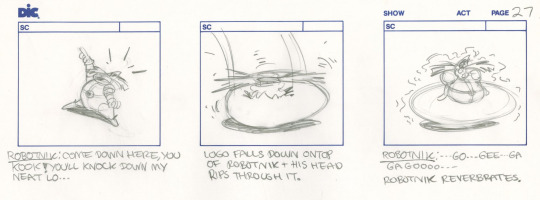

Storyboards of a deleted scene from Adventures of Sonic The Hedgehog, Episode 1 ("Super Special Sonic Search & Smash Squad").

Drawn by Milton Knight; found on Van Eaton Galleries.
237 notes
·
View notes
Photo

In a world where giant monsters are a fact of life, would there be toys of them? Would it be ethical to profit off of what are essentially walking natural disasters? If the profits went to charity, yeah sure. Also if they’re educational. I assume many are like Papo/Schleich dinosaur toys and get sold at craft supply stores and museum gift shops.
Keep reading
265 notes
·
View notes
Text

Silly bird gets a fish.
Pursuant to my last post about using photoscan terrain instead of homemaking all my background assets; this Qurupeco scene I did right after took half the time for a substantially better looking result; I was able to just focus my time on sculpting and painting the actual monster and I'm reasonably happy with this one.
The original in-game model is extremely ambiguous on which purple parts are scales and which are feathers, a thing literally no piece of official art can agree on either. More scales was easier, so I did that.
189 notes
·
View notes
Text
Have you seen this post?

You probably have. It currently has over 120,000 notes, largely because of this addition.
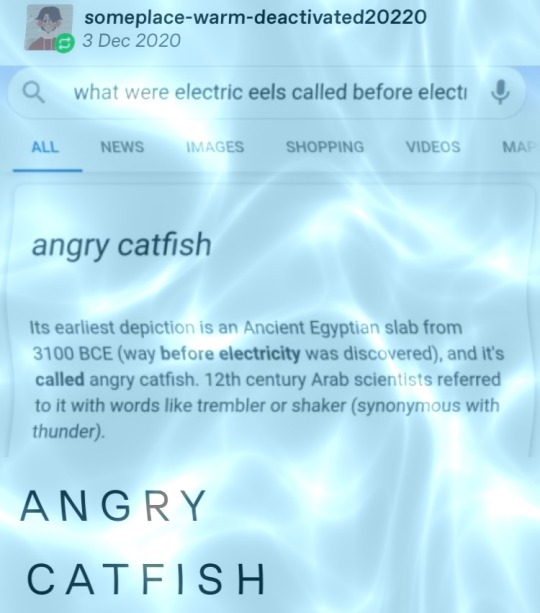
Of course it's going to get reblogged, this kind of unsourced factoid does numbers on here. But something about it wasn't quite right.
A bit of searching turned up the origin of the "fact".
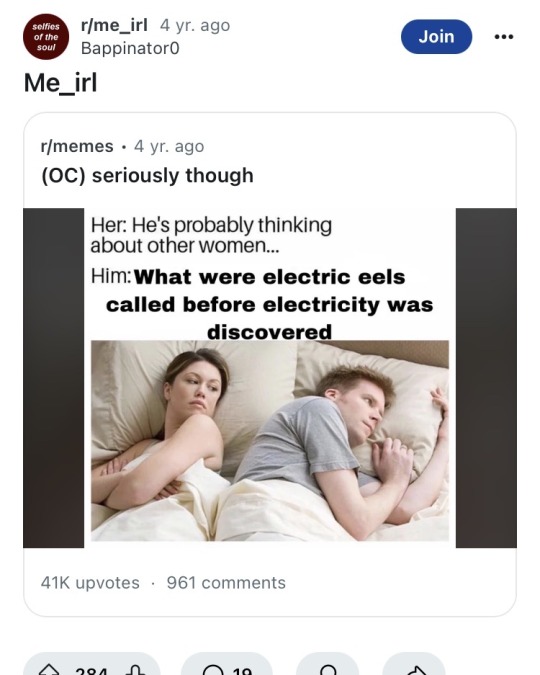
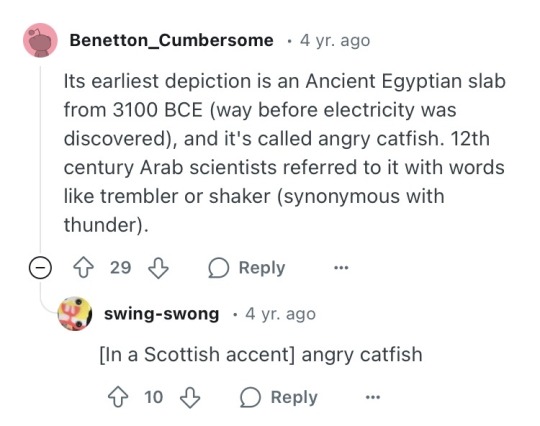
Alright, so it's someone who posted this on reddit 4 years ago and somehow ended up in the search hits. And the post confuses the electric eel (from South America) with the electric catfish (from the Nile, which the Egyptians would have known about).
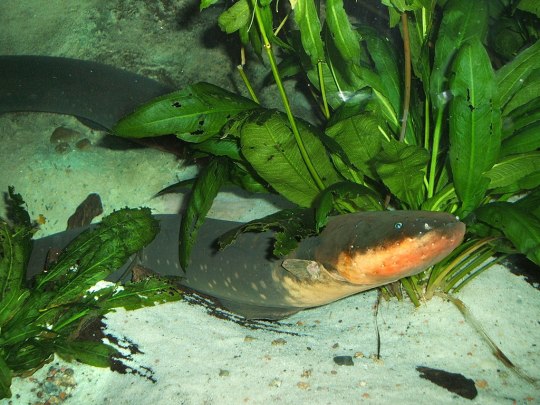

Reminder: this is an electric eel (Electrophorus electricus). It is from South America. (image from Wikipedia)

And this is an electric catfish (Malapterurus electricus). It is from the Nile and would have been familiar to the ancient Egyptians. (image from Wikipedia)
And then of course people were speculating in the notes to that post about trade routes between South America and Egypt. Excellent scholarship everyone.
At this point I was ready to call it another made-up internet fact that gets reified by people repeating it. But something was still bothering me.
An ancient Egyptian slab from 3100 BC. What could that be...
Oh.

The Narmer palette. It's the goddamn Narmer palette. (image, once again, from Wikipedia)
So where is this "angry catfish"?
It's not the Egyptian name for the electric catfish.
It's... Narmer. It's Narmer himself.

Narmer's name is written as above (detail of top middle of the palette), using the catfish (n`r) and the chisel (mr), giving N'r-mr. The chisel is associated with pain, so this reads as "painful catfish", "striking catfish", or, yes, "angry catfish" or other similar variants, although some authors have suggested that it means "Beloved of [the catfish god] Nar".
So.
Where does this leave us?
It would appear that this redditor not only confused electric eels with electric catfish, but also confused a Pharaoh's name with the name of a fish. And then it got pushed to the top search hits by a crappy search engine and shared uncritically on tumblr.
In short, "the electric eel is called angry catfish" factoid actually literacy error. Angry Catfish, who ruled upper Egypt and smote his enemies, is an outlier adn should not have been counted.
Also the Arabic name for the electric catfish is raad (thunder) or raada (thunderer).
References
Afsaruddin, A., & Zahniser, A. H. M. (1997). Humanism, culture, and language in the Near East: studies in honor of Georg Krotkoff. Eisenbrauns.
Clayton, P. A. (2001). Chronicle of the Pharaohs. Thames & Hudson.
Godron, G. (1949). A propos du nom royal. Annales du Service des antiquités de l'Egypte, 49, 217-221.
Sperveslage, G., & Heagy, T. C. (2023). A tail's tale: Narmer, the catfish, and bovine symbolism. The Journal of Egyptian Archaeology, 109(1), 3-319.
45K notes
·
View notes
Photo

It’s fascinating to me how a pincer “works” anatomically though, like in cartoons and stuff we’re kinda trained to think of the whole claw as like the “hand” at the end of the leg but this is how the joints of a “leg” and “claw” match up in a crab.
It’s more like the “forearm” sticks out past the “hand” to serve as sort of an opposable thumb
496 notes
·
View notes
Text

apparently we're calling them "sand strikers" now, which is a lot better, or is that actually older? To this day I have no idea who started calling them bobbit worms. One day they were just suddenly being called that and nobody knew what I was talking about unless I also called them that instead of Eunice aphroditis. I know what it's a reference to, which also means it was recent, and it had to have started on the internet right?
239 notes
·
View notes


