Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Differencebetween.com website makes you understand the differences between similar terms. We like to know about the differences since high school. We have a huge collection of differences between the two similar terms. everything in this world will differ from different perspectives, whether it's place, animals, people, anything in this world will differ, so learn from our website about the differences.
0 notes
Text

Differencebetween.com website makes you understand the differences between similar terms. We like to know about the differences since high school. We have a huge collection of differences between the two similar terms. everything in this world will differ from different perspectives, whether it's place, animals, people, anything in this world will differ, so learn from our website about the differences.
0 notes
Text
Understanding The Differences Between PDD-NOS and Autism
In developmental disorders, terms like PDD-NOS and autism are often used interchangeably. However, they represent distinct diagnoses on the broad autism spectrum. Let's explore the differences and similarities between these two terms to shed light on these often misunderstood conditions.
What is Autism?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a complex neuro-developmental disorder characterized by various challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. ASD encompasses a wide spectrum of symptoms and severity levels, making it a highly heterogeneous condition. Key features of autism include difficulties in understanding and responding to social cues, limited interests, and repetitive behaviors.
ASD is typically diagnosed based on specific criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). These criteria help clinicians determine whether an individual meets the diagnostic threshold for autism. Importantly, the diagnosis of ASD is further classified into three levels of severity based on the individual's level of impairment:
Level 1: Requiring support
Level 2: Requiring substantial support
Level 3: Requiring very substantial support

What are the Specifics of PDD-NOS?
PDD-NOS (Pervasive Developmental Disorder-Not Otherwise Specified), on the other hand, is a term previously used in the DSM-IV to describe individuals who displayed some features of autism but did not meet the full criteria for an autism diagnosis. It was often referred to as "atypical autism." However, with the release of the DSM-5 in 2013, the term PDD-NOS was retired and incorporated into the broader category of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
The primary reason for this change was to eliminate confusion and create a more unified diagnostic framework. By doing so, individuals who would have previously received a PDD-NOS diagnosis are now evaluated using the criteria for ASD. This shift ensures that individuals who exhibit behaviors and challenges associated with autism can access the appropriate support and services.
The Difference:
Understanding the difference between two similar terms highlights the evolving nature of autism diagnosis and classification. Autism is now recognized as a spectrum encompassing a wide range of symptoms and levels of severity. This acknowledgment better reflects the diverse experiences and needs of individuals with autism.
In essence, PDD-NOS served as a diagnostic label under the umbrella of autism, and its retirement has led to a more comprehensive approach to evaluating and supporting individuals on the autism spectrum. By focusing on the core features of autism and their impact on an individual's daily life, clinicians can provide tailored interventions and assistance to help individuals thrive.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, while PDD-NOS and autism were once distinct terms, they now share a common home under the umbrella of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). This shift promotes a more inclusive and accurate understanding of the wide-ranging experiences of individuals on the spectrum, allowing for better-informed diagnoses and support systems to meet their unique needs.
0 notes
Text
The French Oven vs. Dutch Oven
Unlocking The Culinary Mysteries!
In the world of culinary delights, two heavyweights often grace our kitchens with their presence—the French oven and the Dutch oven. These cast-iron cookware champions may seem similar at first glance, but subtle differences can greatly impact your cooking experience.
Let's explore the delicious difference between these two kitchen powerhouses.
The French Oven:
When you think of the French, elegance, and refinement come to mind, and the French oven lives up to this reputation. Also known as a "cocotte," it boasts a few key characteristics that set it apart:
Material:French ovens are typically made of enameled cast iron, providing exceptional heat retention and an array of delightful colors. The enamel coating prevents rust and makes them easy to clean.
Shape:They often have a wider base and lower sides than their Dutch cousins. This design promotes even heat distribution, making them ideal for slow-cooked stews, braised dishes, and soups.
Style and Aesthetics:French ovens are known for their aesthetic appeal. They seamlessly transition from stovetop to oven to table, doubling as elegant serving dishes. Their vibrant colors add a touch of sophistication to your dining experience.
Delicate Touch:While they excel in even heating and stylish presentation, French ovens are generally considered more delicate due to their enamel coating. They are sensitive to high temperatures and can chip or crack if mishandled.

The Dutch Oven:
Contrary to its dainty French counterpart, the Dutch oven exudes sturdiness and reliability. Let's uncover the defining features of this kitchen workhorse:
Material:Dutch ovens are typically made of seasoned cast iron. This raw, uncoated surface gives them unmatched durability and resilience. With proper care, a Dutch oven can last for generations.
Shape:Dutch ovens are known for their tall, straight sides and tight-fitting lids. This design is perfect for dishes that require deep frying, baking bread, or anything that needs to be covered for a long, slow cook.
Versatility:They excel in versatility. Dutch ovens can easily go from the stovetop to the oven, making them ideal for searing, simmering, roasting, or baking. They're the ultimate all-in-one kitchen tool.
Heirloom Quality:Dutch ovens are often considered family heirlooms. Their rugged build and ability to withstand high temperatures can be passed down through generations, developing a seasoned, non-stick surface over time.
Which One Should You Choose?
Here was the major difference between French oven and Dutch oven. These are essential tools for any home cook, offering a world of culinary possibilities and the chance to create delicious memories in the heart of your kitchen.
If you lean toward elegance, appreciate aesthetics, and plan to use it mostly for slow-cooked dishes, the French oven might be your best bet. On the other hand, if you're all about durability, versatility, and a timeless piece that can handle anything you throw at it, the Dutch oven is your loyal companion.
0 notes
Text
Peak Flow vs. Spirometry: Unravel the Differences in Respiratory Assessment
Respiratory health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, and medical professionals employ various tools and tests to assess it. Two commonly used terms in this context are peak flow and spirometry. While both are essential for evaluating lung function, they serve different purposes and provide distinct insights into respiratory health.
Peak Flow is The Snapshot of Airflow:
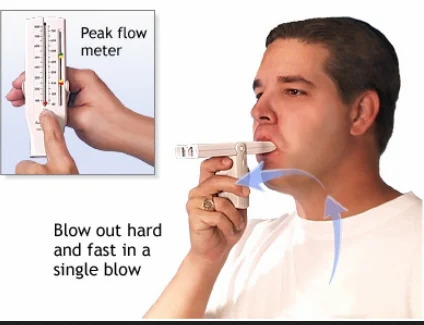
Peak flow is a simple and portable device used to measure the maximum speed at which an individual can blow air out of their lungs. It's often employed in the management of asthma and other respiratory conditions. Here's a closer look at peak flow:
Function:
Peak flow meters are primarily used to monitor airflow limitation and assess the severity of asthma. They help individuals and healthcare providers track changes in lung function over time and make informed decisions about medication and treatment adjustments.
Procedure:
To measure peak flow, an individual takes a deep breath and then blows as hard and fast as possible into the peak flow meter, which records the highest airflow rate achieved. This measurement is usually expressed in liters per minute (L/min).
Use:
Peak flow measurements are often used to establish a baseline for an individual's lung function when they are well. Subsequent measurements can be compared to this baseline to detect changes in airflow, which may indicate worsening asthma or other respiratory conditions.
Portable:
One of the significant advantages of peak flow meters is their portability. Patients can carry them easily and perform measurements at home, making it a valuable tool for self-management.
Spirometry is The Comprehensive Lung Function Test:
Spirometry, on the other hand, is a more comprehensive and detailed lung function test that provides a broader range of data about an individual's respiratory capacity and health. Here's an overview of spirometry:
Function:
Spirometry assesses lung function by measuring various parameters, including forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and the FEV1/FVC ratio. These measurements offer insights into how much air an individual can exhale forcefully and how quickly they can do it.
Procedure:
During a spirometry test, the individual breathes into a spirometer, a device that records the volume and speed of airflow. The test involves a series of forced inhalations and exhalations to generate a detailed lung function profile.
Use:
Spirometry is used for diagnosing and monitoring a wide range of respiratory conditions, including asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and restrictive lung diseases. It provides valuable data for assessing the severity of these conditions and tracking changes over time.
Clinical Setting:
Spirometry is typically performed in a clinical setting, often by a respiratory therapist or healthcare provider. It requires more extensive equipment and expertise compared to peak flow measurements.
Conclusion:
While peak flow and spirometry are vital tools for assessing respiratory health, there is a difference between two similar terms.
Peak flow is a quick and simple test that provides a snapshot of airflow, making it useful for monitoring asthma and detecting changes in lung function over time. Spirometry, on the other hand, offers a comprehensive evaluation of lung function and is employed in diagnosing and managing a broader range of respiratory conditions. The choice between the two depends on the specific needs of the patient and the information required for diagnosis and treatment planning.
1 note
·
View note