Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
How 3 Billion Phishing Emails Can Be Stopped?

When security researchers report on cyber statistics, they ending up being scary rather than informative. A recent statistic about email security was recently published which can have a similar effect: cyber criminals send over 3 billion phishing emails daily from spoofed email addresses. Phishing links are everywhere. Emails that look like they came from a legitimate source, but are in fact a scam. This article explains 3 ways you can stay safe when surfing the internet and avoid getting scammed. Phishing emails have been around since the early days of the internet and spammers have always been keen to get their hands on sensitive information. But with the rapid growth of the internet and the use of computers by more and more people, the problem has become far worse. There are now more than 3 billion emails sent through email every day and more than 500 million of those are destined for spam shelves. But how do you recognize phishing emails?
A Basic Overview of These Phishing Emails
These phishing attempts are carried out by spoofing (disguising) the sender’s email address in the ‘from’ field in messages, and cloaking it under a valid, trusted email address. In this way, hackers get their victims to open fraudulent emails by making them falsely believe they are reading an email from a valid person / organization that they know and trust. Emails are sent in the name of a trusted brand prone to sending newsletters (like Forbes) or sending notifications through email (like Amazon’s delivery system). Hacking is an international problem. Hacking victims come from many countries and nationalities. However, the true number of victims is much larger than reported. According to a report by the cyber security company Symantec, there were over 800 million email accounts hacked in 2016, and that number is expected to grow to 1.8 billion by 2019. Phishing is a form of cyber-attacks that attempt to exploit weaknesses in webmail and other online systems to steal sensitive information.
Hackers can take advantage of these weaknesses to send out spam emails designed to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information. Phishing attacks are very common, and for good reason. They can be used to take control of banking accounts and personal finances if users are not careful. Hackers can also use phishing to spread malware between devices, making it harder to protect against threats. Fortunately, there are ways to combat phishing attacks and generate a false sense of security on your online activity. Below are three tips on how you can increase your safety while protecting yourself from hackers trying to take advantage of you? Phishing scams have become so common that they are almost boring. That's why they have become such successful marketing tactics; convincing individuals that they need to click on a link in an email or download a file when in reality they should be wary.
Social engineers, hackers who obtain private information for financial gain, have been around for years. But in recent years, there has been an increase in the sophistication and efficiency of their scams. Phishing emails come in all shapes and sizes. They can be legitimate, but often they are ruses designed to exploit human emotions. When you open a phishing email, there is a chance you could be taken to a fake website that directs you to an actual website that could steal your sensitive and personal information. If you have ever received an email with a link or attachment that appears to be from a trusted source, but is actually a scam my business pitch or an impersonation of someone trusted, you can imagine how devastating this can be. These phishing emails somehow get you to react emotionally, forgetting all warning bells and cautions. That’s why so many phishing emails still work, even after numerous methods and signatures of phishing attempts get exposed through security blogs and seminars.
According to an email security company, phishing emails consist of 1% of the overall email traffic.
DMARC – Stop Phishing Emails Once and For All
Email spoofing can happen when an email address is used but the domain name (also known as a web hosting provider or web site) is not. Spoofing can also happen when an email address is entered in the address bar and the browser tries to access a web page that isn’t there. This technique can be used to send out mass emails with forged domain names or to steal banking information. It can also be used to obtain personal information from employees of companies and government agencies. If you have ever received an email from someone purporting to be from Google, but it has a different look and feel to an actual Google email, then you can guarantee that it was probably spoofed.
DMARC is an initiative of the Digital Marketing Association (DMA), an industry group made up of more than 90 leading companies in the supply chain. It is implemented at the application, navigation and domain level to stop phishing scams. Phishing scams originate from many sources: government agencies, corporations, hackers. All share one goal: to fraudulently obtain sensitive data from you or your business. While there are many scams out there, most are dependent on the availability of data and connections in order to replicate. By implementing basic email security practices along with minimizing interactions on unknown networks, you can drastically reduce your chances of falling victim to such scams. Domain Management Advanced Trading (DMARC) is a set of enterprise-grade authentication mechanisms designed to fight spam and other spoofing attacks. Although DMARC is primarily designed to help protect corporate networks from malicious actors attempting to spoof email addresses, it can also be used by individual web site owners to prevent phishing scams targeting their site visitors.
Email is the worst form of communication. It is unreliable, it is wasteful of time, and it is easily lead to phishing scams and other security breaches. DMARC, or Domain-based Message Authentication, is a secure alternative to email which uses cryptographic technology to verify the identity of the author of an email message. It requires your cooperation and cooperation alone to establish a secure channel of communication. By implementing this security measure in your DMARC policy, you can stop anyone from spoofing your email address and impersonating you in communications over email, social networks, etc. If you are looking for a security vendor who can help you with DMARC implementation, look no further. Emailauth DMARC Monitor can help make your domain a No Phishing Zone. You can buy DMARC from our online platform.
Source :-https://atozcybersecurity.blogspot.com/2021/09/how-3-billion-phishing-emails-can-be.html
0 notes
Text
Ransomware Protection with DMARC

Ransomware has become a commonplace threat faced by victims of industrial espionage and other cybercrimes. In the simplest terms, a ransomware encrypts all of a user’s data and demands payment in exchange for restoring access. Once the ransom is paid, the information is restored but with barriers raised around the encrypted data. This latter aspect is what makes DMARC such a effective defense mechanism. Unlike other anti-spyware solutions that rely on signatures or other technology to detect and block incoming attacks, DMARC employs a artificial intelligence powered and The inability to access your files and data after an attack makes traditional anti-virus products ineffective. Even the most sophisticated anti-virus programs can fail to detect subtle changes that could take you months to notice. In this post, we'll show you how we prevent data loss due to ransomware and identify the most effective DMARC protection with real-world results.
We'll also provide guidance on how to keep your business data safe even when it's not under the control of an effective anti-virus solution. If you’ve ever been inside of a cyber space, then you know the feeling of helplessness and frustration. You can’t do anything about it, and there isn’t much you can do about it unless you are willing to risk everything. If you are in a position where you could be affected by a cyber-attack, then it is in your best interest to take proactive measures. What that means is implementing measures like detecting when your computer is being used for online activity, and then blocking all access to that computer until it has been properly disinfected. Once that has happened, running the vehicle control software as well as disabling any signals that could help the infection occur can prevent further damage to your computer system and data.
The Role of DMARC in ransomware protection
There are some loitering misconceptions that DMARC is a matter of choice and has to do more with optional email compliance. That it’s fine even if you don’t implement DMARC. While DMARC can validate the standards compliance of emails, it extends way beyond email spam verification to prevent serious domain spoofing attacks and preventing phishing attacks. Email security is so important and DMARC has been working towards improving cyber security standards in the email industry for quite some time now. It's important to remember that DMARC isn't a mechanism for you to opt-in to receive emails containing malware or other potentially unwanted material (like links to scams). You should always be careful when downloading software or opening emails from unknown sources. Also, be sure to change your password immediately after receiving any suspicious emails or visiting unfamiliar websites.
How can DMARC Protect against Ransomware?
A ransomware is a piece of malicious code that encrypts all the files on the infected system, effectively locking a person out of his own system. In return for the decrypting key, the hacker asks for large sums of money. Ransomware is a growing problem in the today’s modern world. Businesses have been hit by these attacks and now are facing a difficult decision: pay the ransom or close down their company.
Here’s how ransomware infection becomes a big problem because of not implementing DMARC:
When DMARC email authentication is not active, hackers can send fraud emails posing as you to your customers, partners, and internal team members.
Fraudulent email messages pass through without getting flagged, effectively delivering ransomware attachments to others. Because the intended victims falsely think the email is from you, they open it, inviting disaster.
Ransomware spreads rapidly. If a ransomware is spread within an organization, all connected systems are endangered. Imagine the panic if your personal data was held hostage. Now think of the scale of disruption when an entire organization faces the same issue.
On the other hand, if the ransomware was delivered to outsiders, say your partners or end-customers, then your reputation gets tarnished. Sometimes, that may hit your business objectives more than the monetary losses of paying the ransom.
Ransomware has become a major threat to digital organizations, and especially to those who generate or store sensitive data. It's the type of cyber attack that affects your business without any reason given, and it's the most profitable attack vector for attackers because it gets access to your secrets and financial info without you even knowing it. The good news is you can still protect yourself and your business from this attack while making a pay-off to the criminals. This post will show you how with DMARC (Data Security Policy and Awareness), and public-key cryptography (PKI), we can achieve complete and total digital security.
How can implementing DMARC prevent ransomware attacks?
Email remains the number one vector for spreading malware like ransomware, through phishing attempts. Phishing, in turn, relies greatly on domain spoofing, a cyber attack in which the hacker sends emails by ‘borrowing’ your valid domain.
When you implement DMARC, however, you can effectively block all emails that don’t originate from your valid channels. This reduces the risk of such borrowed domains being used to deliver emails. Flagged emails will never reach their intended recipients.
Naturally, a good DMARC service won’t just block flagged emails and leave you to guess for yourself how many and when they were triggered. So, along with implementing DMARC, you also need a reporting tool that will provide with useful insights into your email traffic.
A DMARC Monitoring software is useful because it provides:
Frequent and regular monitoring across your email domains.
Easy to digest reports which give you actionable steps along with historic and real-time views of data.
Proper handling of DMARC data, including DMARC records Generate , SPF records, and DKIM configurations.
DMARC really acts as the first line of defense in ransomware protection, by protecting your domain from being spoofed, and also alerting you to heightened spoofing activity. Implementing DMARC with Logic is a guided, 3-month process in which we handhold you to achieve the best DMARC configuration to reject all flagged emails, so as to prevent the spread of ransomware and other dangerous email-borne threats.
0 notes
Text
Top Three Benefits of DMARC

What is DMARC?
DMARC is an email technology that is really cool. It’s essentially an protocol that is Email Authentication designed to give email domain owners the ability to protect their domain from unauthorized use. DMARC email authentication is really valuable to companies because it has three main benefits.
First Benefit of DMARC: Reporting
The first benefit is that you can get a report about every message that your domain sends out – whether it's a spam email or a genuine email from someone seeking your business or attention. What this means is that you can see very quickly who is trying to hack into your domain and what they're trying to do. It also means that if you have suffered a data breach and are working with an organization which has placed strict controls over their networks, then being breached can be prevented by getting a report on all emails sent between you and that organization.
If enough organizations adopt this practice then attackers will be forced to focus on less secure methods of gaining access to customer’s data. Email Marketing is a lucrative business. The top 100 email marketing providers have revenue of over $73 billion dollars. However, the problem with most of these services is they spend a lot of time collecting information and sending the information to third party providers who may then sell it to other companies or just spam your customers. With Dmarc, we’re trying to solve this problem by building an email marketing platform that will enable people to get reports from a single place about the email marketing campaigns that they run—information that they can easily plug into their own campaigns.
It gives you this holistic overview of all the email messages processing on behalf of an organization and their domains. This overview tells you all sorts of great insights like:
What percent of messages are being properly authenticated
Which ones aren’t being authenticated
Where the messages are coming from
Who’s receiving the emails
This data is really valuable and can help organizations and IT departments make better decisions about what they’re doing with email communications.
Second Benefit of DMARC: Control
DMARC improves the experience for everyone when sending email. It makes the message launch more smoothly, allowing recipients to interrupt their schedule to read the message. It blocks spammers and helps build trust on the Internet by enabling domain owners and customers to report abuse without revealing private sensitive information. It makes the whole email system more resistant to attacks by preventing spammers from setting up multiple accounts with the same IP address and pretending to be a real person.
The first benefit of DMARC is it provides organizations with a reporting capability that they wouldn't have had before. Mailbox providers or systems that receive DMARC reports can then use those reports to institute changes and improve their reporting capabilities in a way that would allow them to do things like institute mandatory metrics for reporting and auditing, or create new initiatives for better reporting within their own systems. Secondary benefits of DMARC are that it allows eliminate the guesswork involved in sending DMARC notices to recipients; it reduces the potential for spammers and other forms of unwanted messages; and it gives recipients an incentive to take action. For example, the first benefit of DMARC is it allows domains to be reported even if they do not appear in the Who Is database.
This provides organizations with a powerful new weapon against spammers and other bad actors trying to lurk in the shadows, looking for targets who might not even know they are being spammed.
Third Benefit of DMARC: Security
If you are the type of business owner that sometimes needs to be tech-savvy, send email messages through DMARC. It's easy to set up and it can really save you time by preventing spammers from scanning your address. Send automatically generated email checks with no personal information and you may even find yourself receiving more offers from sponsors that want to reach out to you directly without having to save up for advertising time! Being aware of the risks when setting up email marketing can help provide some perspective when deciding whether a service or product is worth the time and effort if it doesn't provide added value.
DMARC is again driving a ton of value in different aspects of your business.
1) It’s giving you these reporting and analytics insights
2) It’s giving you the ability to set controls and policies about what happens with your email messages
3) And it gives you this value out of trust in security
Getting Started With DMARC
When DMARC was first developed, this was because many of the round-ticket registrars were having significant issues with their receiving infrastructure, and a lot of the email content was being marked as junk by the spam filters. It took us many years to develop and refine a spam detection algorithm that would work across different registrars and DNS providers, and ultimately, worked reliably 99.9% of the time on received messages from valid senders. Email is the best form of communication technology that has ever existed. It also happens to be incredibly useful for communicating with the folks who are in charge of overseeing your network.
DMARC is one of many email technologies that are starting to make an impact on how organizations communicate with each other, but this article isn't about those technologies – it's about getting started with DMARC and how an IT org can apply its benefits to their internal communication and shore up their security posture while saving money too. While DMARC is primarily aimed at protecting internal networks, it can be used by external clients to obtain sensitive information such as employee credentials or financial information. With access to DMARC tokens is free! We’ve made it simple for organizations to gain a foothold in the cloud without having to bear the cost of managing their own CRM or navigating complicated processes through third-party providers. If you’re looking for an experienced and reliable network to help you grow and succeed as an entrepreneur or small business owner we can’t recommend highly enough. Using DMARC in an organization is a great way to help yourself increase your cyber security protection.
Email security alone can be a headache for any organization, so having a system that allows you to automatically send alerts when malicious emails or attachments are opened, across your enterprise, helps to keep threats out and runs faster. By using signals messaging, also known as Signal, all can be connected and flagged as a potential threat for further investigation with less human intervention required.
Learn more about email authentication with Emailauth.
0 notes
Text
How DMARC Advances Email Security
While some identity management protocols such as multi-factor authentication have made modern advancements, others – like email authentication – have remained stuck in the 90s. Yet, email remains one of the most common forms of communication for business and personal use. Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance, or DMARC, is an industry standard created to help protect organizations from data breaches and unwanted emails by integrating behavioral attributes into message and domain verification systems.
It adds an extra layer of security to your email communications. By applying behavioral signals to domain name system (DNS) queries, DMARC allows you to detect if visitors to your site have previously visited a phishing site or if they are attempting to access unauthorized information. Email is considered to be one of the most critical communication tools of the Internet as it enables real-time interaction between organizations and their clients. Email marketing automation can help you to send multiple pieces of important information at the same time to more than one group of recipients. This would be useful for creating an ongoing relationship with your audience. The technique relies on the Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) standard for authenticating and encrypting email messages.
What is it?
In the world of cybersecurity, messages like these are sent out on a daily basis. Spam mail, for example, can be seen as nothing more than irritating spam that will surely slow down your delivery time. However, in this article we are going to find out how Google uses DMARC (Distributed Message Authentication Protocol) in order to provide us valuable information regarding our online transactions. Email authentication protects customers from being impersonated by sending them authentic messages from companies they know and trust. Democratic Member States ensures an optimum level of security for all parties involved in sending emails through DMARC. DMARC is also used by many email marketing platforms as a means of automated email marketing campaigns.
A message from a spoofed email address can trick recipients into revealing sensitive information such as password, credit card number, social security number and other details. It can also trick businesses into revealing login credentials for sensitive systems, making it easier for hackers to steal data. The good news is that many providers have started using DMARC for their email encryption, making it harder for spoofed emails to pass through spam filters. The risk of receiving spam emails has decreased significantly in recent years. Spam filtering typically filters out junk emails, but not all emails are spammed. There are still plenty of people who fall for phishing scams, so using DMARC can help reduce the number of emails you receive from unknown sources. You should always inbox check your junk mail folder and look for messages that look like they may be from a verified source.
How DMARC works
A DMARC policy acts as an additional layer of protection for your email messages, so an SMTP server that receives your email can check to see if the message was actually sent by the person who is said to have sent it. There are various ways a message can be validated: through the domain hosting service, through a DNS record, or even by comparing IP/ DNS information. SMTP relies on these three methods to determine if an email message has been sent from a trusted source. However, there may be other ways as well. DMARC is a system for managing domains that implement an SPF and DKIM record for the domain. When sending email from a domain using DMARC, received emails are marked as not from the sender and are returned without comment.
The domain owner may designate up to three senders as SPF/SPF record holders and three recipients as DKIM users. Any message with insufficient records will be rejected by the system. There is a new tool that will help millions of users to safeguard their inboxes against spam and suspicious emails. It was developed by a team from Symantec, DMARC is an automated email filtering system that consists of a network of applications that periodically scans your Inbox for Organizational emails. If the email is deemed suitable for distribution by one of these applications, it is subsequently delivered to the recipient's inbox without any additional effort on the part of the sender. The recipients can then decide whether to accept or reject the email based on criteria defined by the filtering system.
Cybersecurity benefits of DMARC
Implementing a DMARC policy protects against direct domain spoofing, a common vector for phishing attacks. However, it cannot block all types of phishing, such as cousin domain attacks which use lookalike domains for example or display name abuse. DMARC can also help with:
• Brand protection, by preventing spammers and phishers from using valid organization names
• Increasing deliverability of valid messages
• Visibility, with reports that provide information on unauthorized systems sending email using the organization’s domain
Getting started with DMARC
Organizations should work with their IT security teams to ensure DMARC is properly implemented. This is an important cyber defense practice for preventing phishing and ensuring your organization’s integrity when.
Source :-https://atozcybersecurity.blogspot.com/2021/09/how-dmarc-advances-email-security.html
0 notes
Text
Proactive Measures for Protecting Your Sender Reputati

Financial crimes include identity theft, computer hacking, financial fraud, and money laundering. There are many ways that criminals can steal from you through the mail, including by using fake checks or by sending you fake money orders. The websites below will help you detect if your Online Bank Account has been accessed or if any other suspicious activity has occurred. Coincidentally or not, each of these three sites is listed on Department of Justice (DOJ) lists of fintech activities that help fight financial crime. But consumers who don’t monitor themselves or their surroundings could be exposing themselves to major scams. Someone can make a seemingly innocuous purchase on the Internet and later claim a large amount of money from advertised auctions, instant win games, or other kinds of promotions. Scams can take many forms.
They could take the form of a salesperson telling you they have a special on a product, or a software salesman promising to sell you a package that includes free upgrades when you buy their product. There are many warning signs that someone is being scammed, even when they don't realize it. The best way to prevent getting scammed is to be skeptical about every offer you receive; look for the red flags! And if you have already been scammed, contact the company immediately so they can make it right and Spam may seem like a problem local to your inbox, but it's a global problem affecting billions of devices and apps. In 2016 alone, hackers stole data from over 2015 billion accounts. And that doesn't even begin to consider the costs of lost data or security breaches which can significantly impact on business. In 2018 the Internet Society will host its 25th global conference on cyber security. This year's theme is How to Avoid Being Taken Over by Spam. There are more than a million firewalls in place across the Internet today to protect against spoofing attacks and other attacks designed to steal personal data. This includes everything from your banking information to health records and retail purchases—but also everything else; every bit of information you've transmitted over the Internet in the past three years can be used against you if you're not paying attention. Protecting yourself and your data is vital. It's not about selling stuff or getting famous or anything like that.
This is just about keeping your computer and all the data it has locked down so nobody can steal it from you. It doesn't need to be complicated. It's not about buying expensive hardware products aimed at hacking or tracking you. The solutions are out there, and if you just look hard enough you'll find them. The worst thing is that you may become a victim of cybercrime without even knowing it. This is the email spoofing case – when your website domain or email domain is used by spammers to send spam and phishing emails.
What is Email Spoofing?
Email spoofing is a technique used by spammers to trick email recipients making them think the message came from an organization or person they know. The sender forges the sender’s email address which a recipient sees in the email client. If it’s a name and email address they recognize, they’re more likely to trust it. Spoofing can be carried out by a third party and it is a tool that can be used for sending emails to individuals that have already been identified as spam.
The technique works by tricking your email client into sending a request for an organization or person that doesn’t exist. The trick works because web servers look at the domain name when they’re deciding whether to risk sending an email to that address or not. If you create a completely separate email address, for example, spoofing won’t work because the domain name wouldn’t be included in the DNS records for those mail servers. Spoofing can be performed by ensuring that a single DNS record (a set of domain names and IP addresses) is repeated in an email's From field.
This ensures that the email server returns the same content even if the domain name and IP address have changed. The technique has been around for several years and was first documented by researchers at Symantec in 2014. Since then, many spam groups have begun implementing it extensively, making it increasingly easy to track emails. According to research from Norton Internet Security, around 77% of people have received the spoofed email in the past month. Many businesses use this tactic to extort money from their customers. Some spammers use spoofing to create additional sales by tricking buyers into revealing sensitive information such as their password or banking information.
Spoofing can also be used to help hackers break into computers and take control of their processes, though this is less common. So they open emails, download malware attachments, click malicious links, send personal data, and even wire funds.
How Does Email Spoofing Hurt Sender Reputation?
While some people fall for the bait of phishing emails, others consider them to be spam and send a complaint showing ISP that messages sent from your domain are not wanted and Spam is harmful to the reputation of an ISP and may even lead to fraudulent activity on parts of its network. Spamming can cause numerous problems on the internet infrastructure and may even lead to death or damage to data and systems. All user complaints about spam are important to the ISP, and it has to follow up on all complaints quickly to minimize any further negative impact. Spam emails are sent from different emails addresses and look just like legitimate emails from different companies and organizations.
The trick is that the domain name (the actual name of the website) on the email is different from the domain name on ISP's records. If the domain name on the email has.com and the domain name on ISP records does not have.com plus an underscore, then the email will be deemed spam even if it looks like a genuine request from an actual company or individual. Spam affects the reputation of email service providers, and it can negatively affect both senders and recipients. It's not just annoying — it's harmful. Spam makes it harder to get a real reply and can even cost businesses money by introducing poor customer service. To avoid possible scams, be sure to check your email frequently and follow the guidelines below.
If your email address is posted on a website or advertised in a magazine without your consent, get it changed so that it doesn't show up as Spam or junk mail in the inbox. Email spoofing is designed to trick email address readers into revealing their personal information. It works by tricking recipients into revealing information such as their credit card numbers, addresses, or legal names. More than a billion people rely on email services to receive and reply to messages. Spoofing can lead to identity theft and negative repercussions for business and reputation.
How does email spoofing work?
It works like this: an email service provider creates a website, which looks just like a real email service provider's site. The only difference is the domain name and URL. Anybody who follows the link has his browser automatically redirected to the spoofed site. Email marketing is one of the most vital aspects of a business. But many small businesses fail because they do not realize how vulnerable they are in an email-based market.
They fail because they do not understand how Emails work, or they underestimate the importance of an email marketing strategy. Often, businesses fall prey to spammers who trick legitimate shoppers into revealing sensitive data such as credit card numbers and Social Security Numbers.
How to Protect Your Domain from Spoofing
The good news is that technologies don’t stand still and, at present, domain owners can use email authentication mechanisms to avoid or mitigate damage produced by email spoofing attacks. These mechanisms are:
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) is a web address validation protocol that works in two steps. First, the domain owner adds a TXT record (also called an SPF record, for Simple Payment Failure) to their DNS record for the domain they want to control. This record contains the IP address of anyone who sent an email to that domain within the last hour, based on a histogram generated by a script running on Amazon's CDN service. Second, any recipient who tries to send an email to that domain also has to include the TXT record in their DNS record; if they don't do so, then their email will be ignored by the sending server and will be delivered to anyone with the SPF record configured on their behalf. Again, it's not perfect; as a result of this failure mode, SPF records can be rejected by intermediate servers, and in fact, many senders never bother to configure SPF at all, relying instead on MX records or SPF-base and SPF is a header field in email messages that specifies who should receive emails from a domain.
It can be used to filter out irrelevant or unwanted emails from a mailing list or to perform retargeting efforts. SPF is commonly included in links or form fields that ask users to help identify or help correct the record of a domain name. It can also be included in message body HTML to prevent SPF records from being mistaken for neither SPF nor a legitimate sender’s name.
DKIM (Domain Key Identified Mail) –This method also works by adding a TXT record to DNS. DKIM uses a pair of cryptographic keys to sign an outgoing message and validate an incoming message to make sure that the message wasn’t altered in transit. The weak side of this email authentication method is that the message can be forwarded without breaking the validity of the DKIM signature. This technique is referred to as a “replay attack”.
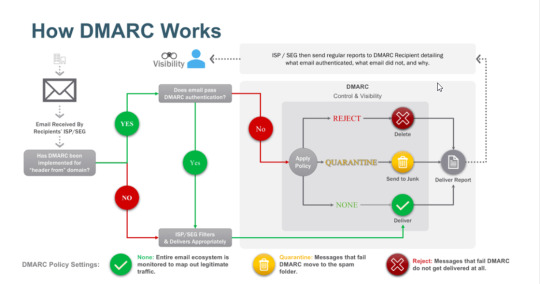
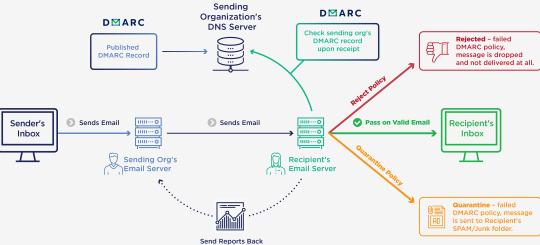
DMARC (Domain-Based Message Authentication)-Reporting, and Conformance). This method ties the two methods mentioned above and gives the highest level of protection when set to enforcement. DMARC is applied by adding a DMARC TXT record to a domain’s DNS. If an email receiver sees that a message passed DMARC authentication, it delivers it to the target recipient. When a message doesn’t pass DMARC authentication, the email receiver looks at the policy in the DMARC record to know what to do with the message.
Benefits of DMARC Authentication
Visibility-Using reports from the Domain Name Server (DNS) history, mail servers, and other resources, you can check for domains that are frequently being used without proper validation. This helps to pinpoint targets of various kinds for additional checks such as SPF and DKIM/SPF fail. Also, it provides the ability to trace phishing emails and other fraudulent activities back to their originating domain owner or service provider. When your website is visited by a robot or a bot, send an email report to the domain registrar that includes the email address and domain name of the visitor. This helps you detect whether a malicious threat was involved in the attack or not. If you are using web-based DMARC services, monitoring your e-mail marketing for signs of compromise is a great way to quickly discover whether an attempted breach went unnoticed or was detected by an informed insider. It can also assist in preventing credential theft by uncovering phishing attempts and other malicious activity.
Control- DMARC gives you the option to instruct the receiver what action to take when an email fails authentication. It’s done by adding the policy (p=) tag to a DMARC record. The p=none policy is normally used for collecting DMARC reports for analysis. The p=quarantine policy tells the email receiver to send the message to the Junk folder, and the p=reject policy tells to block the email at a mailbox gateway. You can also use the percentage tag (pct=) to apply the policy to a part of received messages. For example, pct=50 will tell the receiver to apply the policy to 50% of messages failing DMARC. The 100% reject policy will block all emails sent during a phishing attack and help you avoid user complaints and damaged reputation.
BIMI- The basic concept behind BIMI is simple ‘if I have a brand identifier in my email signature, it should be reflected in the header fields of any messages sent to that recipient. This allows an end-to-end authentication between the sending University and its students. DMARC, on the other hand, is actively being developed as an open standard for message and identity verification across the Internet. It provides guarantees that when you communicate using email services, the information you are sending will be authentic without requiring the sender to maintain a database of usernames and passwords. A BIMI record is used by domain name registrars to associate a series of characteristics with a certain domain name.
These characteristics are defined as keywords or phrases in an email message that are searched for in DNS records kept by various authoritative DNS providers. If the message contains a combination of these keywords or phrases, an email server will respond with a record with that associated value. The DMARC standards mandate that a message be encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS), Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), or some other mechanism before being sent to the recipient. BIMI will allow email senders to show their logo next to their messages in the email clients. BIMI will work for the senders who use the ‘quarantine’ or ‘reject’ DMARC policy. Thus, if the logo appears, the recipient can trust the sender and safely open the message. This adds value for the user and improves the overall user experience through an enhanced sense of security. The main reason domain reputation managers are not using DMARC is because they do not understand why it is important. The potential risk of sending junk data over DMARC is too high for most notifications and reports.
The main reason is many think the risk of getting banned is low enough and don’t care enough to set up their protection systems. A recent study shows less than 1 percent of senders use DMARC correctly. This is a huge failure if you ask me because it allows spam and phishing to continue while leaving consumers without the protection they deserve.
How to Automate Domain Monitoring
The good news is that today there are tools like Emailauth, DMARC Analyzer that do the analysis of DMARC reports for you. The tool creates a DMARC record for your domain that you must add to the domain’s DNS.
Source :-https://atozcybersecurity.blogspot.com/2021/09/proactive-measures-for-protecting-your.html
0 notes
Text
How DMARC Can Protect Employees from COVID-related Email Attacks
As malicious email has multiplied during the COVID pandemic (Google reported on April 16th receiving 18M daily COVID- related malware & phishing attacks), it’s more important than ever for organizations to protect their employees from identity deception. DMARC enforcement adds an identity check to inbound email, but not all organizations with email gateways take advantage of it out of concern for blocking legitimate activity. Researchers identified a list of high-priority domains eligible for DMARC enforcement around which we recommend immediate action.
The tactics hackers use to break into computers and take control of accounts can vary, but one thing they all have in common is access to employee credentials. By implementing a security policy that restricts employees from using personal email accounts for business purposes and requiring employees to maintain their control over their work email addresses, you can help provide critical protection to your organization’s networks while keeping payrolls secure. Included in the analysis of nearly 50 million accounts, DMARC found attackers were increasingly using commercial email addresses with only the domain name and email as part of the email header. Many of these addresses were obtained from social engineering or were spoofing genuine domain names used by legitimate users.
Additionally, attacks that masquerade as internal communication can take advantage of employees' curiosity about how DMARC works. The goal of DMARC is to protect employees from COVID-19, a malicious code injected into target organizations’ internal networks. Since then, hundreds of thousands of organizations have been protected against this emerging threat. Organizations can identify potential carbon copies of valid employee credentials in their network with just a few lines of code. By using an Industrial Rule of the Road (IRT) management application, an insider can be prevented from spoofing administrative access and gaining unauthorized access to company data or sensitive business activities.
Each of the domains on the list is:
1. Eligible for DMARC enforcement
2. Actively being spoofed in malicious, COVID- related campaigns
3. Carries a very low risk of blocking legitimate email
The domains, along with corresponding domain owners, are:
@who.org (World Health Organization)
@cdc.gov (Center for Disease Control and Prevention)
@hhs.gov (Department of Health and Human Services)
@treasury.gov (US Dept. of the Treasury)
@irs.gov (Internal Revenue Service)
DMARC (Domain-based Message Access Protocol) is a solution that can be used to configure email gateways to deny access to unauthorized parties. By implementing DMARC, administrators are able to control who has access to their email inbox and domain. This in turn can help reduce spoofing of legitimate emails, data theft, and other attacks. As organizations continue to struggle with how to clamp down on spoofing and phishing attacks from sources inside and outside their networks, a new approach is needed. With today's malicious intent focused on obtaining personal identifying information from employees, organizations must be able to verify that employees are neither spoofing nor phishing from internal sources. This is precisely why expanded DMARC capabilities are important for organization security.
The most common attack vector being spoofing attack - where an outside party places an impersonating email address into the inbox of an individual who then forwards that email on to the intended recipient. This type of attack can also be prevented if DMARC is properly configured on the upstream email gateway system. The Configuring DMARC for E-mail GATEWAYS (CX) module is used by ISP providers to manage DMARC Registration and Integration on their end-to-end domain policies. The objective of this module is to correctly identify, for each incoming e-mail message, whether it is from a legitimate domain (MX), a spoof domain (SPF), or an Incorrect Domain (ID) challenge. On receiving such an alert, the configured DMARC policy validates the source of the e-mail message and indicates whether it should be handled as a spam or Not Spam message.
0 notes
Text
Tips to Ensure the Prevention of Spoofing, Phishing, and Spam in Google Workspace

With increasing dependency on the web and modernization of the industries moving to the cloud, data security and vulnerability to scams have become a major point of concern. Spoofing, Phishing, Spams are few threats an individual or an entire organization is always prone to in the current scenario.
Now, what do these terms- Spoofing, Phishing, and Spamming mean?
Spoofing- is a criminal activity where a scammer tries to get access to someone's personal information by pretending to be a legitimate business.
Phishing-Phishing attacks are always ensuring you are who you say you are and that any information you provide is genuine. There have been several recent high-profile cyber breaches involving UK government departments. Information that could uncover sources of classified information has been released online, compromising military and diplomatic networks. This has resulted in the necessity for individuals to train themselves how to spot phishing scams in their own inboxes.
The most common source of phishing attacks are emails sent to employees or customers that seem to come from legitimate sources but are loaded with malicious macros or spyware hiding amongst legitimate documents or other material designed to infiltrate computer systems. Aside from trivializing the browsing experience of those who receive them, these tactics also serve as a boon for scammers looking to infiltrate employee or business networks to steal data or infiltrate organizations in hopes of causing financial harm.
Spamming-It is important to understand that there is a difference between spamming and unwanted email. Unwanted email is unwanted because it is bulk and impersonal. Spamming, on the other hand, is personalized and comes from a genuine place. If you want something from someone (an answer to a question, for example), it's important not to fall for the tactics used by spammers. Email marketing has become one of the most potent forms of internet marketing, used to send out hundreds or even thousands of emails to thousands of recipients in an attempt to build a database of potentially interested parties. This forms a huge part of spamming as it will always outnumber genuine emails, which makes it much easier to identify and deal with spam messages.
If you send mass emails without looking for feedback or educational purposes, you run a high risk of spammers finding your address and sending you junk mail. Avoid making purchases from sources that offer free shipping or require you to validate your ID before getting your products. Avoid sending out marketing emails unless you have a good relationship with the senders and can trust them to deliver only legally obtained products or services. It's important to realize that today's social networking is a whole-of-communication platform wherein every message or piece of content is equally available to everybody within a given circle. This creates the urgent need to fight spamming and connect people in a more constructive way. Of late, social networking sites have introduced a feature wherein you can report spamming emails or social media posts to the respective service providers.
Below are a few tips that an Admin of an Organization who has just moved into.
cloud emails with Google Workspace can implement in order to prevent the threats.
Sender policy framework is an email authentication technique that publishes authorized mail servers to send emails for your domain. SPF protects your domain from spoofing and helps to ensure that messages are delivered correctly. It has been designed to improve the overall security of e-mail communication by creating a visible reputation system for sending e-mail messages from an organization. Consequently, SPF also helps avoid spamming. Mail servers verify the origin of emails using the Domain Name System (DNS) records. An SPF record is included in each email message, indicating which mail servers issued the email.
If a domain is registered with multiple mail service providers, then each provider will forward mail to the corresponding mail server. However, since these providers may not keep a consistent record of who owns what domain, SPF falls short of protecting against spoofing and human error. Sender Policy Framework is an email authentication technique that publishes authorized mail servers to send emails for your domain. SPF protects your domain from spoofing and helps to ensure that messages are delivered correctly. SPF prevents spoofing using Gmail accounts by default; however, you can change this behavior and return mail to the sender by including an SPF record in your domain's MX records or adding Spam Warning in your email Header (as well as any other Within Network record).
DomainKey Identified Mail (DKIM) is a protocol that improves email delivery security. It can be used for several purposes, but most importantly it improves message authentication. By ensuring that messages are signed by the actual domain owner, it enables the originator to be verified and protected when sending emails from an address that might not be authorized. The problem with relying solely on email providers to implement domain key-based e-mail protection is that they often implement it in a way that makes it difficult for spammers to hide their identities.
This is why you have to find ways to ensure that your DKIM signed emails aren't automatically deleted by your recipient's mail client or server. You can prevent spammers from sending you spam emails by following best practices for email filtering. By implementing a spam filter, you can also quickly identify when a message is from a known source. Spam filters use DomainKeys Infrastructure (DKI), a public key infrastructure for email domains. When you communicate with an email server using HTTPS, both sides of the communication have a private, randomly generated key a DomainKeys Header. This is used to encrypt the data flow between your computer and the email server. It prevents spoofing of your identity across different servers.
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance or DMARC record is a standardized email authentication method used by organization admins to prevent hackers and other scammers from spoofing their domain. It also helps the admins to request reports that get messages from the company or domain from email servers.
Any changes to your domain will result in the email service using DMARC to send an alert to your at least local domain administrators, including the senior management if there are changes made on the upper-level domain DNS is used to resolve the domain name into an IP address. Without this step, a fake site could still be displayed in your browser because the browser would interpret the domain name as referring to a real server instead of the intended one.
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance or DMARC record is a standardized email authentication method used by organization admins to prevent hackers and other scammers from spoofing their domain. It also helps the admins to request reports that get messages from the company or domain from email servers and It also helps the admins to request reports that get messages from the company or domain from email servers. To help them recognize malicious activity and potential authentication problems for messages sent from their domain, these reports have details.
The 3 major security measures of DKIM, DMARC, and SPF that Google recommends to ensure the prevention of spoofing, phishing, and spam in Google Workspace boosts an organization’s dependency and helps them explore a secure email solution like Google Workspace.
Source :-https://atozcybersecurity.blogspot.com/2021/09/tips-to-ensure-prevention-of-spoofing.html
1 note
·
View note
Text
DMARC is expanding globally in surprising ways

How Does DMARC Help?
DMARC is an email security standard that helps prevent spoofing and spamming of emails. It works by comparing the contents of the email message with a database of known names, addresses, and other attributes. If the attributes match, then the system performs a challenge-response algorithm that verifies the identity of the sender.
DMARC is a privacy protection measure implemented by some of the world’s biggest internet companies to help protect sensitive information, including credential data. It works by encrypting all data between a customer and merchant, protecting it against theft or destruction while still allowing the customer to review their own records. By implementing this privacy protection measure, ecommerce sites and businesses have a better chance of receiving packages from prospective customers that are clearer about their privacy rights. Email is the leading method for personal communication in the world. It is also a crucial method for businesses to communicate with customers, suppliers, and independent research organizations.
DMARC has made it easy for businesses to build trust with consumers by implementing encryption into their mail transmission. This provides businesses with the ability to hold their consumers responsible for the content of their email communications. The goal of DMARC is simple: provide factually accurate information to users when they attempt to access email services from third-party services. The system is designed to prevent fraudulent activity, unauthorized access to private information, and spoofing on merchant accounts.
Today, consumers trust more than ever the security of their email and other online communications services; therefore, email providers must protect themselves against spoofing scams as well as other threats to Information Security. For this article, ISPs are defined as Internet Service Provider that also offers consumer email services and Mailbox Providers (MPs) are companies that provide web-based consumer email services such as Gmail, Outlook.com, etc. Email security has become an increasingly important issue as more and more users are engaging in commercial and intimate networks. DMARC has been included in the Efficient Commerce Platform (ECP) standard since 2008 and is widely deployed by leading companies such as Amazon, eBay, and Paypal; as well as public sector bodies such as the UK's National Health Service, which has mandated ECP as part of its internal email security policy.
DMARC is a global set of voluntary standards for information security and authentication. Over the past 10 years, the standards have been implemented or adopted in 156 countries, under different legal systems, and in environments ranging from private companies to organizations such as universities. In many countries, DMARC has had a huge impact on the marketplace as it lowers costs for consumers, businesses, and governments by providing a single secure method for authenticating multiple identities. Our work highlights that DMARC has opened new doors for innovation in security, while also inspiring new approaches to existing security solutions.
The following are some insights and observations derived from our investigation:
Global DMARC coverage is well past “escape velocity” but its country adoption is uneven.
Countries with large local ISPs tend to have worse DMARC coverage. Conversely, countries with large global MPs generally have much better DMARC coverage.
Japan & Germany are surprisingly far behind in DMARC coverage, but adoption by just 1-2 local ISPs could quickly get them to 70%+ coverage.
Though country coverage is important to track, companies within the same country may see large variances in the coverage of their customers.
DMARC coverage also varies by company
The numbers speak volumes. DMARC is a significant system in the financial world. A successful trait of this system is that it is constantly evolving, constantly improving upon itself. By continually refining its own technology, DMARC continuously improves the level of protection offered by email protection worldwide. The good news is that as more companies start using DMARC systems, the good news for consumers gets even better. We have seen increasing use of the technology over time, particularly among industries that have a high sensitivity to fraud or poor consumer experiences.
A recent study found that DMARC coverage had grown from 19% in 2008 We had an interesting conversation with one customer recently who wanted to know if our company had DMARC coverage on their mailbox. With increasing spam and phishing attacks, contacting companies to report spam or suspicious activities can be a tedious task. Nevertheless, it is vital for individuals who purchase or sell products online to report any suspicious activity immediately. An individual can report possible scams or illegal sales to customer services through “Report Spam” on competitor websites or via spam dot report available on any merchant website. The implication is that each company should perform a quick DMARC coverage test (Emailauth.io) to understand how many of their consumers are covered by DMARC.
Source:-https://atozcybersecurity.blogspot.com/2021/08/dmarc-is-expanding-globally-in.html
1 note
·
View note