Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Assessment Task 8
Placing different file types in to an After Effects composition.

Taking 1 image from the original 9, and editing the values. Altering colour and opacity to create an interesting composition.

0 notes
Text
Assessment Task 7
Graphic file format types
1. JPEG - Joint photographic experts group
Possibly the most common file type you run across the web. You can use JPEGs for projects on the web, in Microsoft Office documents, or for projects that require printing at a high resolution. Paying attention to the resolution and file size with JPEGs is essential in order to produce a nice looking project.
2. PNG - portable network graphics
Useful for interactive documents such as web pages, but are not suitable to print. The reason PNGs are used in most web projects is that you can save your image with more colours on a transparent background. This makes for a much sharper, web-quality image.
3. GIF - graphics interchange format
Most common in their animated form. In their more basic form, GIFs are formed from up to 256 colours in the RGB colour space. Due to the limited number of colours, the file size is drastically reduced. They are a common file type for web projects where an image needs to load very quickly, as opposed to one that has to retain a high level of quality.
4. TIFF - tagged image file
Despite TIFF images' ability to recover their quality after manipulation, you should avoid using this file type on the web, it can take forever to load. TIFF files are also commonly used when saving photographs for print.
5. PDS - photoshop document
PSDs are files that are created and saved in Adobe Photoshop, the most popular graphics editing software ever. This type of file contains "layers" that make modifying the image much easier to handle. This is also the program that generates the raster file types mentioned above. The largest disadvantage to PSDs is that Photoshop works with raster images as opposed to vector images.
6. PDF - portable document format
If a designer saves your vector logo in PDF format, you can view it without any design editing software (as long as you have downloaded the free Acrobat Reader software), and they have the ability to use this file to make further manipulations. This is by far the best universal tool for sharing graphics.
7. RAW - raw image format
RAW images are valuable because they capture every element of a photo without processing and losing small visual details. Eventually, however, you'll want to package them into a raster or vector file type so they can be transferred and resized for various purposes.
8. AI - adobe illustrator document
Adobe Illustrator is the industry standard for creating artwork from scratch and therefore more than likely the program in which your logo was originally rendered. Illustrator produces vector artwork, the easiest type of file to manipulate.
Lossy/Lossless File Compression
Lossless and lossy compression are characterisations which are used to explicate the distinction between two file compression formats. One (lossless) allows for all of the original data to be recovered whenever the file is uncompressed again. The other (lossy) works differently since it ends up eliminating all the “unnecessary” bits and pieces of information in the original file to make it smaller when compressed.
While lossy file compression are mostly associated with image files, it can also be used for audio files. Files such as MP3s, MP4s, and AAC files, or images such as JPEGs, are usually compressed in the lossy format. Whenever you choose to compress a file using the lossy format, many of the redundant information in the files, are eliminated. Because of that, lossy compression tends to be used whenever people are reducing the size of a bitmap images, or other files.
Unlike lossy file compression, using the lossless format can end up reducing a file’s size without any loss of the original quality. With new compression algorithms available now, lossless compressed files are preserved better than ever before. Using lossless compression to compress a file, will rewrite the data in the same manner as that of the original file.
Metadata and Meta Files
Metadata is data that describes other data. A Metafile is a file format that can store multiple types of data such as graphics file formats. These graphics files can contain raster, vector, and type data.
Meta is a prefix that in most information technology usages means "an underlying definition or description.”
Metadata summarises basic information about data, which can make finding and working with particular instances of data easier. For example, author, date created and date modified and file size are examples of very basic document metadata. Having the ability to filter through that metadata makes it much easier for someone to locate a specific document. Metadata can be created manually, or by automated information processing. Manual creation tends to be more accurate, allowing the user to input any information they feel is relevant or needed to help describe the file.
File Naming Conventions
Naming records consistently, logically and in a predictable way will distinguish similar records from one another at a glance, and by doing so will facilitate the storage and retrieval of records, which will enable users to browse file names more effectively and efficiently.
Following a few simple rules such as these below will greatly improve your file management.
Keep file names, but meaningful
Avoid unnecessary repetition and redundancy in file names
Using capital letters to delimit words, not spaces or underscores
If using a date in the name of the file, always state the date backwards such as YYYYMMDD
Avoid using common words at the start of the file names, unless doing so will make it easier to retrieve the record
Importance of File Management
Having files spread out around on your hard drive in different directories will add time to your day as you have to search for them. Choose or create one folder as a central place to store files, preferably backed up daily. Storing files all over your hard drive also has the added problem of slowing down your computer and if there is a technical malfunction may mean that you lose essential files and information. Create a hierarchy rather than putting everything in one single folder makes it much easier to find the exact information you are looking for. It is easiest if it follows a logical progression.
i.e Animation ‘Year 1 > Block 3 > Technologies > Assessment Task 3’
0 notes
Text
Assessment Task 6
After effects
Opacity Fade
vimeo
Animating Along a Path
vimeo
Keyframe Fill Colours
vimeo
0 notes
Text
Assessment Task 5
Raster Files and Pixel Grids
In computer graphics, a raster graphics or bitmap image is a dot matrix data structure that represents a generally rectangular grid of pixels (points of colour), viewable via a monitor, paper, or other display medium. Raster iimages are stored in image files with varying formats.
However, because raster images are pixel-based, they suffer a malady called image degradation. Just like photographic images that get blurry and imprecise when blown up, a raster image gets jagged and rough. Why? Ultimately, when you look close enough, you can begin to see the individual pixels that comprise the image. Hence, your raster-based logo, magnified to 1000, becomes bitmapped before you know it. Although raster images can be scaled down more easily, smaller versions often appear less crisp or “softer” than the original.
To maximise the quality of a raster image, you must keep in mind that the raster format is resolution-specific — meaning that raster images are defined and displayed at one specific resolution. Better resolution, however, comes at a price. Just as raster files are significantly larger than comparable vector files, high resolution raster files are significantly larger than low resolution raster files.

Bit Depth
Bit depth refers to the colour information stored in an image. The higher the bit depth of an image, the more colours it can store. The simplest image, a 1 bit image, can only show two colours, black and white. That is because the 1 bit can only store one of two values, 0 (white) and 1 (black). An 8 bit image can store 256 possible colours, while a 24 bit image can display over 16 million colours. As the bit depth increases, the file size of the image also increases because more colour information has to be stored for each pixel in the image. When you save (or export) an image as a GIF or a PNG, you can select the bit depth of the resulting file. With certain types of images that naturally have few colours such as logos or simple designs, you may be able to drastically reduce the size of the image file without degrading the quality of the image. With other images (especially those with gradients) reducing the number of colours in an image will severely degrade the image quality.
Resolution
In computers, resolution is the number of pixels (individual points of colour) contained on a display monitor, expressed in terms of the number of pixels on the horizontal axis and the number on the vertical axis. The sharpness of the image on a display depends on the resolution and the size of the monitor. The same pixel resolution will be sharper on a smaller monitor and gradually lose sharpness on larger monitors because the same number of pixels are being spread out over a larger number of inches. Resolution in raster graphics is measured in dpi, or dots per inch. The higher the dpi, the better the resolution.
Vector Files
Unlike pixel-based raster images, vector graphics are based on mathematical formulas that define geometric primitives such as polygons, lines, curves, circles and rectangles. Because vector graphics are composed of true geometric primitives, they are best used to represent more structured images, like line art graphics with flat, uniform colours. Most created images (as opposed to natural images) meet these specifications, including logos, letterhead, and fonts.
Inherently, vector-based graphics are more malleable than raster images — thus, they are much more versatile, flexible and easy to use. The most obvious advantage of vector images over raster graphics is that vector images are quickly and perfectly scalable. There is no upper or lower limit for sizing vector images. Just as the rules of mathematics apply identically to computations involving two-digit numbers or two-hundred-digit numbers, the formulas that govern the rendering of vector images apply identically to graphics of any size.
Further, unlike raster graphics, vector images are not resolution-dependent. Vector images have no fixed intrinsic resolution, rather they display at the resolution capability of whatever output device (monitor, printer) is rendering them. Also, because vector graphics need not memorise the contents of millions of tiny pixels, these files tend to be considerably smaller than their raster counterparts. Overall, vector graphics are more efficient and versatile. Common vector formats include AI, EPS, SVG, and sometimes PDF.

Anti-alias
Aliasing is the visual stair-stepping of edges that occurs in an image when the resolution is too low. You can smooth the hard edges of a selection by anti-aliasing or feathering. Anti-aliasing smoothes the jagged edges of a selection by softening the colour transition between edge pixels and background pixels. Because only the edge pixels change, no detail is lost. Anti-aliasing is useful when cutting, copying, and pasting selections to create composite images.

Aspect-ratio
The aspect ratio of an image describes the proportional relationship between it’s width and it’s height. It is most commonly expressed as two numbers separated by a colon ie 16:9. The width and height are always measured using the same units of length. In a group of images one image might be 8 inches wide and 10 inches high, another 8 centimetres wide and 10 centimetres high and another might be 8 yards wide by 5 yards high. Thus the aspect ratio concerns the relationship of the width and height and not the actual size of the image itself

0 notes
Text
Assessment Task 4
Greyscale

Range of hues

Hexadecimal Colour


By typing a set number in to the # box you can locate specific colours.
Hues

Hue (H) value is 291, as each number stands for a particular colour.

This next column has a different colour, and so a different value. This one is 155.

Likewise this one is 213.
Saturation

Here the saturation (S) value is at 20, in comparison to the top circle, this one appears much paler and more ‘saturated’.

As the level of saturation changes, the small marker on the colour picker moves in a straight line either left or right depending on the value you have set. This changes the appearance of the colour from 100% saturation (full colour) down to 0% which shows as white.
Brightness

The brightness (B) value is at 0%, so the colour appears black due to the complete absence of white in it.

At 50% brightness the colour has lightened.

With 100% brightness the colour has the highest amount of white in it.
0 notes
Text
Assessment Task 3
Colour Modes
There are a number of different ways you can influence how the colours in your image are presented to your audience. Changing the colour “mode” will alter the way an image editing software program saves the colour information. A Raster image file can be in bitmap (1-bit) Greyscale (8-bit), Index (8-bit), RGB (24-bit), or CMYK (32-bit) colour.
RGB
RGB refers to Red(R), Green(G) and Blue(B) - also known as the primary colours. An RGB image contains three channels made up of red, green and blue colour data. It is used by all monitors and is also recommended by Adobe for editing colour images. Scanning is almost exclusively done in RGB, and photos are transferred in this mode as well.
RGB is a standard colour model, the exact range of colours represented can vary, depending on the application or display device. RGB images use three colours, or channels, to reproduce colours on-screen. The three channels translate to 24 (8 bits x 3 channels) bits of colour information per pixel. With 24-bit images, up to 16.7 million colours can be reproduced. If you move up to 48-bit images you can produce even more.
CMYK
CMYK refers to Cyan(C), Magenta(M), Yellow(Y) and Black(K) which are also known as secondary colours. These are formed by mixing the primary colours. The CYMK colour scheme or mode is another very well known colour scheme in Photoshop.
CMYK is a standard colour model, the exact range of colours represented can vary, depending on the press and printing conditions. The CYMK colour scheme is generally used when the image or the graphic created is to be printed on paper - not for use on graphics intended for the Web. This scheme is based on the light absorbing quality on paper. CYMK images comprises of colours produced from the combination of 4 colours of cyan, magenta, yellow and black. Like the RGB mode, the user has to enter values for each colour to get the desired colour.

Hexadecimal
A colour hex code is a way of specifying colour using hexadecimal values. The code itself is a hex triplet, which represents three separate values that specify the levels of the component colours. The code starts with a # and is followed by six hex values or three hex value pairs (for example, #AFD645). The code is generally associated with HTML and websites viewed on a screen. As one hex digit represents 4 bits , two hex digits together make 8 bits (1 byte ). The values for each colour run between 00 and FF. Designers and developers use HEX colours in web design. The use of these codes makes it simple to identify and ensure you are using the correct colour for your project.

HSB
The HSB (standing for Hue, Saturation and Brightness) colour model defines a colour space in terms of three constituent components. This colour model is also known as HSV, standing for Hue, Saturation and Value. According to this model, any colour is represented by 3 numbers.
The first number represents Hue and its value ranges from 0 to 360 degrees, with each degree representing a distinct colour (such as red, blue or yellow)
Second number represents Saturation and it’s value ranges from 0 to 100. It represents the amount of colour where 0 will show no colour and 100 shows the full colour.
The third number represents Brightness. You enhance the brightness by adding white or reduce it by adding black. It’s value ranges from 0 to 100 where 0 represents the white colour and 100 represents the black. The closer to 100 the value, the darker a colour will appear.
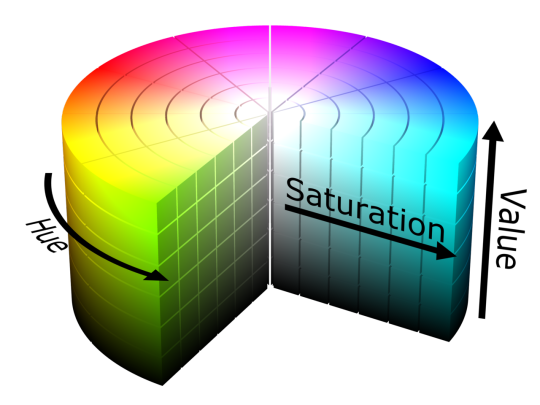
Greyscale
Grayscale is a colour mode, made up of 256 shades of grey. These 256 colours include absolute black, absolute white and 254 shades of grey in-between. Images in grayscale mode have 8-bits of information in them. Black and white photographic images are the most common examples of the grayscale colour mode. We call them black and white photographs but the photo is actually made up of lots of different shades of grey. You can convert both Bitmap-mode and colour images to greyscale. To convert a colour image to a high-quality grayscale image, Photoshop discards all colour information in the original image. The grey levels (shades) of the converted pixels represent the luminosity of the original pixels.

Histograms
In image processing and photography, a colour histogram is a representation of the tonal range, or distribution, of colour in an image. For digital images, a colour histogram represents the number of pixels that have colour in each of a fixed list of colour ranges by graphing the number of pixels at each of the 256 brightness levels in an image. In a histogram, the higher the line from the axis, the greater the number of pixels at that brightness level.
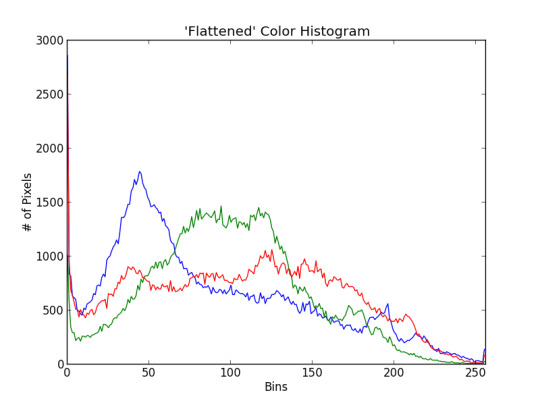
Transparency and Alpha Channels
In digital imagine, the alpha channel controls the transparency or opacity of a colour. It’s value can be represented by a real value, a percentage, and integer: fully transparent is 0.0, 0% or 0, whereas full opacity is 1.0, 100% or 255 respectively.
When a colour (source) is blended with another colour (background), e.g. when an image is overlaid onto another image, the alpha value of the source colour is used to determine the resulting colour. If the alpha value is opaque, the source colour overwrites the destination colour; if transparent, the source colour is invisible, allowing the background colour to show through.
If the value is in between, the resulting colour has a varying degree of transparency/opacity, which creates a translucent effect

0 notes
Text
Assessment Task 2
Network Technologies
In this digital age there are countless new methods available for producing, publishing, promoting and communicating art and design work. It has never been easier to share your creativity with the world and gain recognition for your work. Below are some of the main technologies in use today.
Online Galleries and Image Sharing
Online galleries allow photographers and individuals to share their most precious photos to as many people as they like with the simple click of a button. Instead of expensive and cumbersome photo albums and hard copies, images are stored online and shared via links and emails.
Most people do not go through the trouble and expense of buying and building their own website. Most people find an image host and build their gallery on that platform.
The way the galleries look vary from site to site, which is great because you can compare the available options and choose the host that you like the most. Uploading to online galleries is usually a very easy process. If you can add an attachment to an email, you can upload a photo to an online gallery.
Some of the biggest players in online photo galleries are Google+ Photos, Flickr, and Imgur.
Other sites such as Instagram, Pinterest, DeviantArt offer a mix of photo sharing and social media aspects, creatives can post pictures of their work/art and gather a ‘following’ of people who enjoy what they do.
Video File Sharing
Video Hosting Platforms which allow users to upload, share or live stream their own videos to the Internet. These can either be for the general public to watch, or particular users on a shared network. The largest and most well known being YouTube, which boasts the most extensive collection of online video. These sites enable users to easily upload their own creations in to a shareable format and get instant feedback through the comments sections. Videos can be ‘liked’ which promotes them on main pages of some of these sites, increasing chances of further growth and opportunity. You can even monetise videos on certain sites, allowing creatives to earn for their work the more it is watched and shared throughout the online community.
Other notable examples include sites such as Vimeo, Dailymotion and Twitch.
Forums
An Internet forum, or message board, is an online discussion site where people can hold conversations in the form of posted messages. They differ from chat rooms in that messages are often longer than one line of text, and are at least temporarily archived.
Started in the 1980s, Internet forums are community websites dedicated to the online exchange of information about virtually any subject you can imagine. It provides a venue where people with similar interests can discuss and debate various topics. The most notable and significant Internet forum communities have converged around topics ranging from medicine to technology, and vocations and hobbies.
Eg: Flickr, Digital Spy, Craigslist, Newgrounds, Quora, Reddit, The Student Room, Wattpad…etc.
Blogging
Blog posts are the fundamental aspect of a blog. They are normally public - the whole world can see it. The entries in a blog usually come from a single author. The entries in a blog are usually stream-of-consciousness, ‘diary-entry’ style posts. It can be personal, a project collaboration tool, a guide, or any means of communicating and publishing your creations and designs on the web.
Blogging is a great way to help market or promote yourself or your business, product, or service. This means you can sell something online through your blog or you can use it merely for informative purposes, to let people know what you’re about and what your offering. They usually come with comment sections under each post so readers/customers can offer feedback and start a dialogue with the author.
Examples of popular online blogs: WordPress, Tumblr, Squarespace, Wix, Blogger…etc
Social Media
Thanks to the popularity of the Internet, individuals use social media tools to connect with each other online. Social media can help to improve an individual's sense of connectedness with real or online communities, and can be an effective tool for corporations and entrepreneurs. Creative businesses can use these tools to market their designs and products to connect with existing and potential customers.
This is in contrast to traditional which operates under a ‘mono-logic’ transmission model (one source to many receivers), such as a newspaper which is delivered to many subscribers, or a radio station which broadcasts the same programs to an entire city.
Some of the most popular social media websites, with over 100 million registered users, include Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, QQ, Line…etc
With a small amount of teaching/self-teaching and practice, all of these online technologies can be used with ease. They are designed in a way to make communication and sharing simpler and more succinct than ever before - opening up a whole new avenue of creative expression that was unavailable to us before.
1 note
·
View note