Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Link
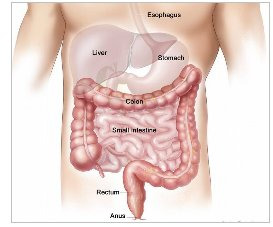
The colon is the large intestine; it is the lower part of digestive tract. The intestine is a long, tubular organ consisting of the small intestine, the colon (large intestine) and the rectum, which is the last part of the colon. After food is swallowed, it begins to be digested in the stomach and then empties into the small intestine, where the nutritional part of the food is absorbed. The remaining waste moves through the colon to the rectum and is expelled from the body. The colon and rectum absorb water and hold the waste until you are ready to expel it.
Symptoms
Although laparoscopic colon resection has many benefits, it may not be appropriate for some patients. Colon stricture due to tuberculosis, Crohns disease and early stage cancer of colon are usually treated with laparoscopic surgery. Our health care team with discuss with you in detail and you are encourage for active discussion regarding appropriate procedure for you.
Diagnosis
Most diseases of the colon are diagnosed with one of two tests: a colonoscopy or barium enema. A colonoscope is a soft, bendable tube about the thickness of the index finger which is inserted into the anus and then advanced through the entire large intestine. A barium enema is a special X-ray where a white milk-shake fluid is flushed into the rectum and by using mild pressure is pushed throughout the entire large intestine. These tests allow the surgeon to look inside of the colon. In case of malignancy, CT scan of abdomen is required to know about local spread of disease.
Laparoscopic Colon Surgery
Laparoscopic colon surgery is performed through small incisions for various indications.
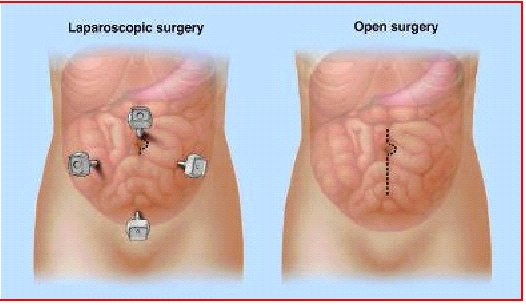
A cannula (hollow tube) is placed into the abdomen and your abdomen will be inflated with carbon dioxide gas to create a space to operate. A laparoscope (a tiny telescope connected to a video camera) is put through one of the cannulas which projects a video picture of the internal organs and spleen on a television monitor. Several cannulas are placed in different locations on your abdomen to allow your surgeon to place instruments inside your belly to work and remove your colon. After the colon is cut from all that it is connected to, it is placed inside a special bag. The bag with the colon inside is pulled up into one of the small, but largest incisions on your abdomen and colon within the special bag is removed for body.
Common advantages of laparoscopic colon surgery are: Less postoperative pain, shorten hospital stay, quicker return to bowel function, quicker return to normal activity & better cosmetic results.
0 notes
Link
WHAT IS GALLBLADDER?
Gall-bladder is a pear shaped small organ lies just below liver on right upper abdomen. It’s attached to right side of liver and with bile-duct via cystic duct.
The size of gallbladder in adult is approximately 7 to 10 centimetres (2.8 to 3.9 inches) in length and 4 centimetres (1.6 in) in diameter when fully distended.
Bile is made in Liver, not in Gallbladder and its pass through bileduct to gallbladder.
FUNCTION OF GALLBLADDER

Gall-bladder stores bile (juice formed by liver) and help in digestion of fatty meals. Gallbladder release the bile for digestion when food reaches to duodenum and gallbladder contract to push bile to travel through bile duct to reach into duondenum.
Development of stones in gall-bladder indicates malfunction of gall-bladder and surgical removal of gall-bladder is easily tolerated by the body thus person can live normal life after gallbladder removal.
0 notes
Link
Mini Gastric Bypass
In this operation, stapling creates a larger size of pouch. Remaining part of stomach remains inside the body.
This new pouch of larger size is joined with small intestine, thus bypassing calorie absorption. Small intestine is not divided unlike R Y Gastric bypass.
Efficacy
Mini-Gastric-bypass is simple & nearly equally effective for its results.
Risks & Side effect
In “Mini-Gastric-bypass”, large length of small intestine is bypassed that may lead to more vitamins & minerals deficiencies.
“Mini-Gastric-bypass”, may lead to higher rates of bile-reflux gastritis which may be difficult to treat & potentially increases stomach cancer risk.
#Mini Gastric Bypass Surgery Cost#Mini Gastric Bypass Surgery#Mini Gastric Bypass Surgeon in Ahmedabad
0 notes
Link
The stomach is a hollow organ in the upper abdomen, under the ribs.
It's part of the digestive system. Food moves from the mouth through the esophagus to the stomach. In the stomach, the food becomes liquid. Muscles in the stomach wall push the liquid into the small intestine.
The wall of the stomach has five layers:
Inner layer or lining (mucosa): Juices made by glands in the inner layer help digest food. Most stomach cancers begin in this layer.
Submucosa: This is the support tissue for the inner layer.
Muscle layer: Muscles in this layer contract to mix and mash the food.
Subserosa: This is the support tissue for the outer layer.
Outer layer (serosa): The outer layer covers the stomach. It holds the stomach in place.
Cancer Cells
Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the stomach and other organs of the body.
Normal cells grow and divide to form new cells as the body needs them. When normal cells grow old or get damaged, they die, and new cells take their place.
Sometimes, this process goes wrong. New cells form when the body doesn't need them, and old or damaged cells don't die as they should. The buildup of extra cells often forms a mass of tissue called a growth, polyp, or tumor.
Tumors in the stomach can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer). Benign tumors are not as harmful as malignant tumors:
Benign tumors:
are rarely a threat to life
can be removed and usually don't grow back
don't invade the tissues around them
don't spread to other parts of the body
Malignant tumors:
may be a threat to life
often can be removed but sometimes grow back
can invade and damage nearby organs and tissues
can spread to other parts of the body
Stomach cancer usually begins in cells in the inner layer of the stomach. Over time, the cancer may invade more deeply into the stomach wall. A stomach tumor can grow through the stomach's outer layer into nearby organs, such as the liver, pancreas, esophagus, or intestine.
Stomach cancer cells can spread by breaking away from the original tumor. They enter blood vessels or lymph vessels, which branch into all the tissues of the body. The cancer cells may be found in lymph nodes near the stomach. The cancer cells may attach to other tissues and grow to form new tumors that may damage those tissues.
The spread of cancer is called metastasis.
0 notes
Link
DR. AVINASH TANK
BEST GASTROENTEROLOGIST IN AHMEDABAD
Dr AvinashTank, is a super-specialist (MCh) Laparoscopic Gastro-intestinal Surgeon, who has in-depth knowledge of disease of digestive organ and their treatment. He has been trained at most prestigious centre of country (SGPGIMS) & Abroad (Japan & South Korea) that makes him one of the best gastroenterologist in Ahmedabad. He is the recipient of many awards as Gastrologist Doctor at various prestigious international and national conferences.

GASTROLOGIST DOCTOR IN AHMEDABAD
Dr Avinash Tank having experience of more than a decade as best gastroenterologist in Ahmedabad & more than thousand surgeries to treat all surgical disease (like Obesity, Stone & Cancer) of Liver, Gall-bladdder, & Gastro-intestinal organs by laparoscopic approach (Key Hole Surgery) & open approach. Being Gastrologist doctor, He is an active member of Prestigious International Surgical Societies, he remains update on advances in treatment and had delivered international quality results for his patients at home.
0 notes
Link
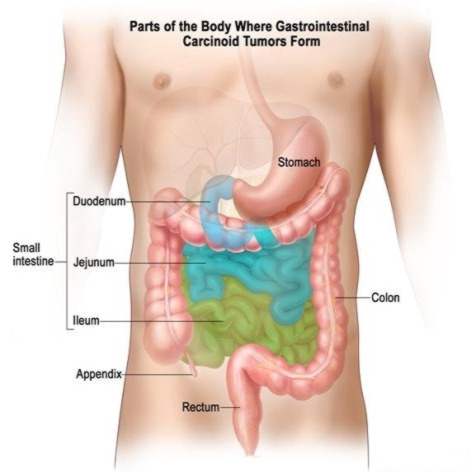
A gastrointestinal carcinoid tumor is cancer that forms in the lining of the gastrointestinal tract.
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is part of the body's digestive system. It helps to digest food, takesnutrients (vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and water) from food to be used by the body and helps pass waste material out of the body. The GI tract is made up of these and otherorgans:
Stomach.
Small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, and ileum).
Colon.
Rectum.
Gastrointestinal carcinoid tumors form in the lining of the gastrointestinal tract, most often in the appendix, small intestine, or rectum.
Gastrointestinal carcinoid tumors form from a certain type of neuroendocrine cell (a type of cell that is like a nerve cell and a hormone -making cell). These cells are scattered throughout the chest andabdomen but most are found in the GI tract. Neuroendocrine cells make hormones that help control digestive juices and the muscles used in moving food through the stomach and intestines. A GI carcinoid tumor may also make hormones and release them into the body.
GI carcinoid tumors are rare and most grow very slowly. Most of them occur in the appendix, small intestine, and rectum. Sometimes more than one tumor will form.
The three ways that cancer spreads in the body are:
Through tissue. Cancer invades the surrounding normal tissue.
Through the lymph system. Cancer invades the lymph system and travels through the lymph vessels to other places in the body.
Through the blood. Cancer invades the veins and capillaries and travels through the blood to other places in the body.
When cancer cells break away from the primary (original) tumor and travel through the lymph or blood to other places in the body, another (secondary) tumor may form. This process is called metastasis. The secondary (metastatic) tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, ifbreast cancer spreads to the bones, the cancer cells in the bones are actually breast cancer cells. The disease is metastatic breast cancer, not bone cancer.
0 notes
Link
Extrahepatic bile duct cancer is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the ducts that are outside the liver. The extrahepatic bile duct is made up of two parts:
Common hepatic duct, which is also called the perihilar part of the extrahepatic duct.
Common bile duct, which is also called the distal part of the extrahepatic duct.
The extrahepatic bile duct is part of a network of ducts (tubes) that connect the liver, gallbladder, andsmall intestine. This network begins in the liver where many small ducts collect bile (a fluid made by the liver to break down fats during digestion). The small ducts come together to form the right and lefthepatic ducts, which lead out of the liver. The two ducts join outside the liver and form the common hepatic duct. Bile from the liver passes through the hepatic ducts, common hepatic duct and cystic ductand is stored in the gallbladder.
When food is being digested, bile stored in the gallbladder is released and passes through the cystic duct to the common bile duct and into the small intestine.
Anatomy of the extrahepatic bile duct. The extrahepatic bile duct is made up of the common hepatic duct and the common bile duct. Bile is made in the liver and flows through the extrahepatic bile duct to the gallbladder where it is stored
Risk Factor
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn't mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk. Risk factors include having any of the following disorders:
Primary sclerosing cholangitis.
Chronic ulcerative colitis.
Choledochal cysts.
Infection with a Chinese liver fluke parasite.
0 notes
Link
LIVER BILE DUCT SURGERIES
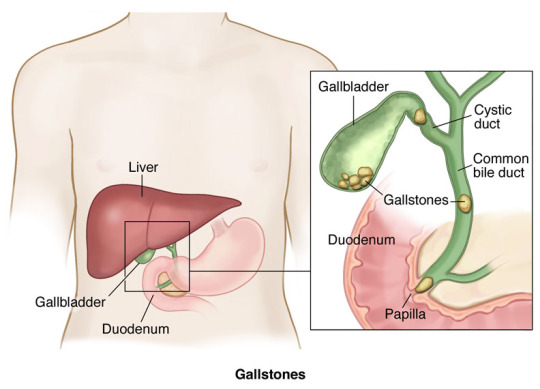
BILE DUCT STONES
Common bile duct stones or gallstones in the bile duct is the presence of a gallstone in the common bile duct. Gallstones usually form in your gallbladder. The bile duct is the small tube that carries bile from the liver to the intestine. The gallbladder joins the bileduct and thus stones from gallbladder may pass with bile into common bileduct and ultimately goes into intestine.
CHOLEDOCHAL CYST
Choledochal Cyst is a congenital (present at birth) defect where the bile ducts (tubes that carry bile from liver to intestines) are dilated and wider than usual. These cysts may be intra-hepatic (bile ducts inside the liver) or extra-hepatic (outside the liver). Based upon there location and size, there are classified in 5 types.
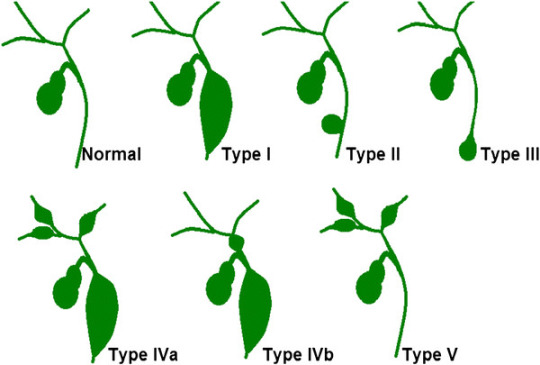
GALL-BLADDER CANCER
Gall Bladder cancer is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the tissues of thegallbladder. The gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ that lies just under the liver in the upper abdomen. The gallbladder stores bile, a fluid made by the liver to digest fat. When food is being broken down in the stomach and intestines, bile is released from the gallbladder through a tube called the common bile duct, which connects the gallbladder and liver to the first part of the small intestine.
Anatomy of the gallbladder. The gallbladder is just below the liver. Bile is stored in the gallbladder and flows through the cystic duct and the common bile duct into the small intestine when food is being digested.
0 notes
Link
Laparoscopic colon surgery is performed through small incisions for various indications.
A cannula (hollow tube) is placed into the abdomen and your abdomen will be inflated with carbon dioxide gas to create a space to operate. A laparoscope (a tiny telescope connected to a video camera) is put through one of the cannulas which projects a video picture of the internal organs and spleen on a television monitor. Several cannulas are placed in different locations on your abdomen to allow your surgeon to place instruments inside your belly to work and remove your colon. After the colon is cut from all that it is connected to, it is placed inside a special bag. The bag with the colon inside is pulled up into one of the small, but largest incisions on your abdomen and colon within the special bag is removed for body.
Common advantages of laparoscopic colon surgery are: Less postoperative pain, shorten hospital stay, quicker return to bowel function, quicker return to normal activity & better cosmetic results.
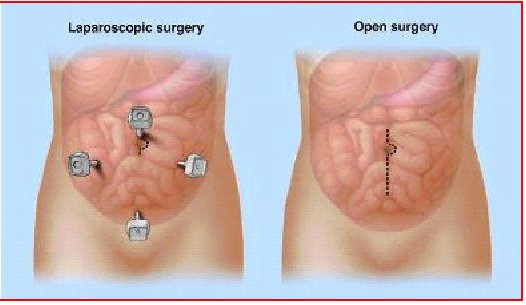
Recovery from Surgery
Pain
You may feel pain at the site of surgery. We aim to keep you pain free after surgery with the help of latest and most effective technique or analgesic (pain relieving medicine).
Eating and Drinking
You will be allowed orally liquids once you recover from effect of anaesthesia medicine and you don't have nausea or vomiting. Gradually you can add soft to normal diet.
Activity
Our health care team will try to have you move around as soon as possible after surgery. You are encouraged to get out of bed and walk the same day. While this may be hard at first, it helps speed your recovery. It also helps your circulation and helps prevent blood clots from forming in your legs.
Going home
Once you are eating and walking, and then you are ready to go home, in most case in next day following surgery. Before leaving for home our health care team shall give you detailed guidance regarding diet, activities, medications & further plan of treatment
0 notes
Link
Appendix is a vestigial organ in human being, attached to right colon.
The appendix produces a bacteria destroying protein called immunoglobulins which help fight infection in the body. Its function, however, is not essential. People who have had appendectomies do not have an increased risk toward infection. Other organs in the body take over this function once the appendix has been removed.
Appendicitis ( infection of appendix) occurs when the appendix becomes blocked, often by stool or as a result of infection in body, since the appendix swells in response to any infection in the body. In elderly person, it may be blocked by tumor, thus requiring proper evaluation before going for surgery.
Appendix Surgery Treatment
The treatment for appendicitis usually is antibiotics and appendectomy (surgery to remove the appendix).
If appendicitis is even suspected, its better to err on the side of safety and quickly remove the appendix to avoid its rupture. If the appendix has formed an abscess, it may need two procedures: one to drain the abscess of pus and fluid, and a later one to remove the appendix.
0 notes
Link
Appendix is a vestigial organ in human being, attached to right colon.
The appendix produces a bacteria destroying protein called immunoglobulins which help fight infection in the body. Its function, however, is not essential. People who have had appendectomies do not have an increased risk toward infection. Other organs in the body take over this function once the appendix has been removed.
Appendicitis ( infection of appendix) occurs when the appendix becomes blocked, often by stool or as a result of infection in body, since the appendix swells in response to any infection in the body. In elderly person, it may be blocked by tumor, thus requiring proper evaluation before going for surgery.
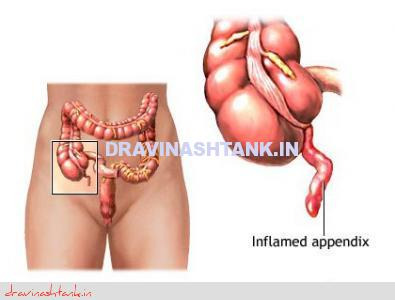
Symptoms
Pain around naval that later moves to the lower right abdomen. This is usually the first sign. This may be associated with nausea and/or vomiting and fever.
Diagnosis
Appendicitis is usually diagnosed by clinical & rectal examination and supported with blood, urine and USG/CT scan.
Laparoscopic Appendix Surgery
A cannula (hollow tube) is placed into the abdomen and abdomen will be inflated with carbon dioxide gas to create a space to operate. A laparoscope (a tiny telescope connected to a video camera) is put through one of the cannula which projects a video picture of the internal organs and appendix on a television monitor. Three cannulas are placed in different locations on your abdomen to allow surgeon to place instruments inside your belly to work and remove your appendix. After appendix is cut from all that it is connected to, it is placed inside a special bag & is pulled up into one of the incision and taken out.
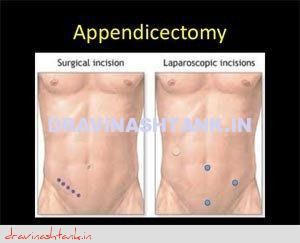
Common advantages of laparoscopic appendectomy are: Less postoperative pain, shorten hospital stay, quicker return to bowel function, quicker return to normal activity & better cosmetic results
0 notes
Link
While these operations also reduce the size of the stomach, the stomach pouch created is much larger than with other procedures. The goal is to restrict the amount of food consumed and alter the normal digestive process, but to a much greater degree. The anatomy of the small intestine is changed to divert the bile and pancreatic juices so they meet the ingested food closer to the middle or the end of the small intestine.
Biliopancreatic Diversion with "Duodenal Switch"
This procedure is a variation of BPD in which stomach removal is restricted to the outer margin, leaving a sleeve of stomach with the pylorus and the beginning of the duodenum at its end. The duodenum, the first portion of the small intestine, is divided so that pancreatic and bile drainage is bypassed.
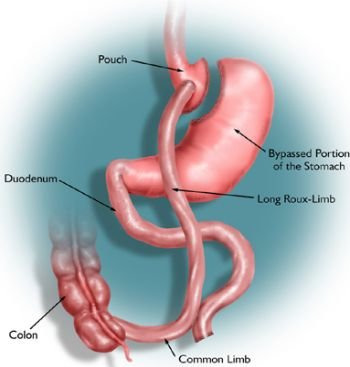
Advantages Biliopancreatic Diversion Surgery
More rapid and effective weight loss
More effective resolution of medical co-morbidities
More malnutrition than Gastric Bypass & Sleeve gastrectomy
Efficacy
In BPD, excess weight loss of 74% at one year, 78% at two years, 81% at three years, 84% at four years, and 91% at five years was achieved.
Risks & Side effect
Staple line leak/bleed
Intestinal Obstruction
Higher degree of mal-nutrition compared to sleeve gastrectomy, Gastric bypass
Risk to Life: 1.1 %
0 notes
Link
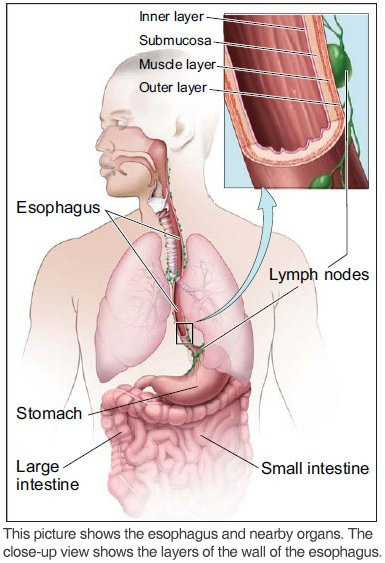
The esophagus is a muscular tube in the chest. It's about 10 inches (25 centimeters) long.
This organ is part of the digestive tract. Food moves from the mouth through the esophagus to the stomach.
The wall of the esophagus has several layers:
Inner layer or lining: The lining (mucosa) of the esophagus is wet, which helps food to pass to the stomach.
Submucosa: Glands in the submucosa layer make mucus, which helps keep the lining of the esophagus wet.
Muscle layer: The muscles push food down to the stomach.
Outer layer: The outer layer covers the esophagus.
Cancer Cells
Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up all tissues and organs of the body, including the esophagus.
Normal cells in the esophagus and other parts of the body grow and divide to form new cells as they are needed. When normal cells grow old or get damaged, they die, and new cells take their place.
Sometimes, this process goes wrong. New cells form when the body doesn't need them, and old or damaged cells don't die as they should. The buildup of extra cells often forms a mass of tissue called a growth or tumor.
A tumor in the esophagus can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer):
Benign tumors:
Are rarely a threat to life
Don't invade the tissues around them
Don't spread to other parts of the body
Can be removed and don't usually grow back
Malignant tumors (cancer of the esophagus):
May be a threat to life
Can invade and damage nearby organs and tissues
Can spread to other parts of the body
Sometimes can be removed but may grow back
Esophageal cancer cells can spread by breaking away from an esophageal tumor. They can travel through blood vessels or lymph vessels to reach other parts of the body. After spreading, cancer cells may attach to other tissues and grow to form new tumors that may damage those tissues.
When esophageal cancer spreads from its original place to another part of the body, the new tumor has the same kind of abnormal cells and the same name as the original tumor. For example, if esophageal cancer spreads to the liver, the cancer cells in the liver are actually esophageal cancer cells. The disease is metastatic esophageal cancer, not liver cancer. For that reason, it is treated as cancer of the esophagus, not liver cancer.
0 notes
Link
GASTRO-INTESTINAL SURGERY
Dr Avinash Tank is the best gastro doctor in Ahmedabad, being trained at most prestigious centre of country (SGPGIMS) & Abroad (Japan & South Korea).
He has presented many research papers at prestigious international and national conferences and recipient of many international awards.
He has been invited at many reputed regional & national scientific meetings to deliver lectures and to chair sessions.
He is having experience of more than a decade and has been known as the best gastro surgeon in Ahmedabad to treat all surgical disease (like Stone, Cancer & Obesity) of Liver, Gall-bladder, & Gastro-intestinal organs by laparoscopic technique and also performing complex surgery by open approach. Hence patient gets uncompromised complete treatment for his disease at same time.
#Best Gastro Doctor in Ahmedabad#Gastro Doctor in Ahmedabad#Gastro Surgery in Ahmedabad#Gastro Surgeon
0 notes
Link
The spleen is a blood filled organ located in the upper left abdominal cavity. It is a storage organ for red blood cells and contains many specialized white blood cells called macrophages (disease fighting cells) which act to filter blood. The spleen is part of the immune system and also removes old and damaged blood particles from your system. The spleen helps the body identify and kill bacteria. The spleen can affect the platelet count, the red blood cell count and even the white blood count.
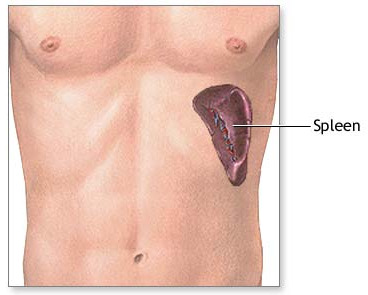
There are several reasons why a spleen might need to be removed, and the following list, though not all inclusive, includes the most common reasons:
The most common reason is a condition called idiopathic (unknown cause) thrombocytopenia (low platelets) purpura (ITP). Platelets are blood cells which aid is blood clotting.
Hemolytic anemia (a condition that breaks down red blood cells) requires a spleen removal to prevent or decrease the need for transfusion.
Also, hereditary (genetic) conditions that affect the shape of red blood cells, conditions known as spherocystosis, sickle cell disease or thalassemia, may require splenectomy.
Often patients with cancers of the cells which fight infection, known as lymphoma or certain types of leukemia, require spleen removal.
When the spleen gets enlarged, it sometimes removes too many platelets from your blood and has to be removed.
Sometimes the blood supply to the spleen becomes blocked (infarct) or the artery abnormally expands (aneurysm) and the spleen needs to be removed.
A cannula (hollow tube) is placed into the abdomen by your surgeon and your abdomen will be inflated with carbon dioxide gas to create a space to operate. A laparoscope (a tiny telescope connected to a video camera) is put through one of the cannulas which projects a video picture of the internal organs and spleen on a television monitor. Several cannulas are placed in different locations on your abdomen to allow your surgeon to place instruments inside your belly to work and remove your spleen.
A search for accessory (additional) spleens and then removal of these extra spleens will be done since 15% of people have small, extra spleens. After the spleen is cut from all that it is connected to, it is placed inside a special bag. The bag with the spleen inside is pulled up into one of the small, but largest incisions on your abdomen. The spleen is broken up into small pieces (morcelated) within the special bag and completely removed.
0 notes
Link
Mini Gastric Bypass Sergery
In this operation, stapling creates a larger size of pouch. Remaining part of stomach remains inside the body.
This new pouch of larger size is joined with small intestine, thus bypassing calorie absorption. Small intestine is not divided unlike R Y Gastric bypass .
Efficacy
Mini-Gastric-bypass Sergery is simple & nearly equally effective for its results.
Risks & Side effect
In “Mini-Gastric-bypass”, large length of small intestine is bypassed that may lead to more vitamins & minerals deficiencies.
“Mini-Gastric-bypass”, may lead to higher rates of bile-reflux gastritis which may be difficult to treat & potentially increases stomach cancer risk.
0 notes
Link
Gastric Bypass Operation
In this procedure, stapling creates a small (15 to 20cc) stomach pouch. The remainder of the stomach is not removed, but is completely stapled shut and divided from the stomach pouch. The outlet from this newly formed pouch empties directly into the lower portion of the jejunum, thus bypassing calorie absorption. This is done by dividing the small intestine just beyond the duodenum for the purpose of bringing it up and constructing a connection with newly formed stomach pouch.
Efficacy
One year after surgery, weight loss can average 77% of excess body weight.
After 10 to 14 years, 50-60% of excess body weight loss has been maintained by some patients
Upto 96% of certain associated health conditions improve or resolve
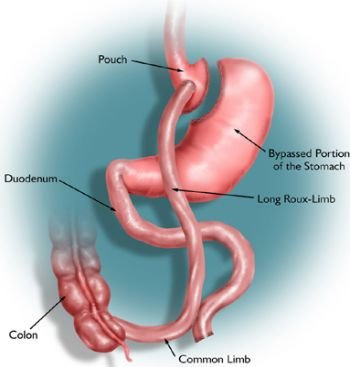
Risks & Side effect
Staple line leak/bleed/ intestinal obstruction
Deficiency of iron and calcium, Vit B 12. All of the deficiencies mentioned above, however, can be managed through proper diet and vitamin supplements.
A condition known as "dumping syndrome" can occur as the result of rapid emptying of stomach contents into the small intestine. This is sometimes triggered when too much sugar or large amounts of food are consumed. While generally not considered to be a serious risk to your health, the results can be extremely unpleasant and can include nausea, weakness, sweating, faintness and, on occasion, diarrhea after eating. So its advised to eat only small portion, chew well and eat slowly, never eat & drink at same time.
Risk to life: 0-0.5%
#Gastric Bypass Surgeon in Ahmedabad#est Gastric Bypass Surgery in Ahmedabad#Best Gastric Bypass Surgery
0 notes