an art historian trying to figure out wtf to do with her degree
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text

Portrait of a Lady in allegorical guise, holding a dish of pearls (detail)
Pierre Mignard (French, 1612-1695)
3K notes
·
View notes
Photo

Oranges Wrapped by John Frederick Peto (American, 1854–1907)
4K notes
·
View notes
Text

Peder Severin Krøyer (Danish, 1851-1909)
Loggia i Ravello
58 notes
·
View notes
Text






Pictures by ArtZoneStuff of The Cologne Cathedral
The Cologne Cathedral, also known as Kölner Dom, is a masterpiece of Gothic architecture and one of the largest cathedrals in Europe. It is located in the heart of Cologne, Germany, near the Rhine River. The cathedral's construction spanned over 600 years, starting in 1248 and experiencing several halts and resumptions before its completion in 1880. This protracted construction timeline allowed for a blend of architectural styles, though the Gothic influence remains predominant.
#history#famous artists#art exhibition#gothic#goth aesthetic#gothcore#goth#gothic art#cathedral#medieval#cologne#my post#art history#architecture#great artist#architectdesign#architechture#church#catholiscism#catholic
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
actually i think graduates of a university should have access to the library databases forever and ever amen
102K notes
·
View notes
Text
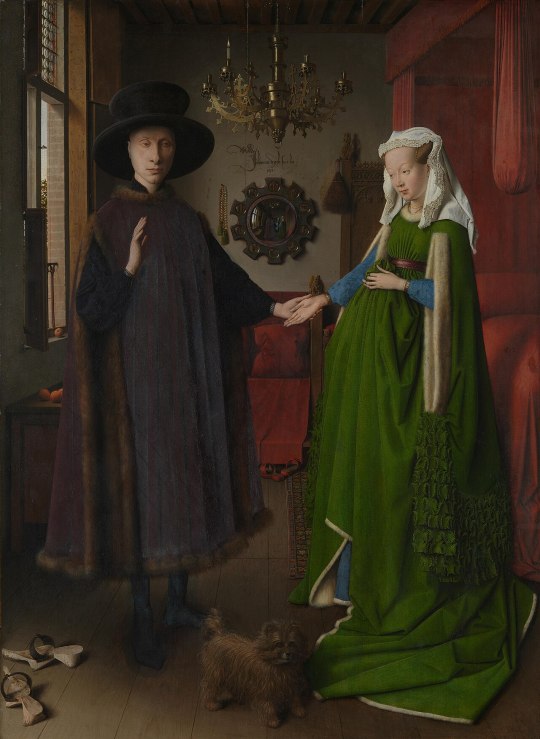
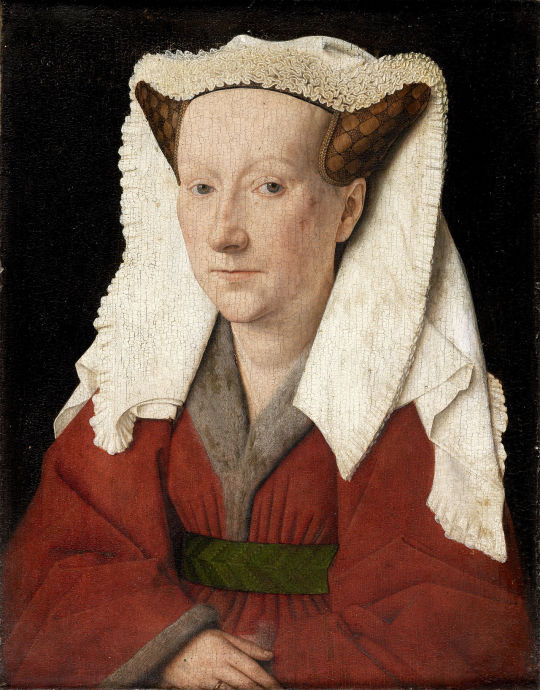




Differences Between the Southern and Northern Renaissance: A Study Through Jan van Eyck's "Portrait of a Man" (self portrait?)"
Written by ArtZoneStuff, 2024
The Renaissance, a period of cultural rebirth and revival of classical learning, manifested differently in the southern and northern regions of Europe. While both regions shared a common interest in humanism, art, and science, the way these ideas were expressed varied significantly due to differing cultural, social, and economic contexts.
The Southern Renaissance, centered in Italy, emphasized classical antiquity, proportion, perspective, and human anatomy. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519), Michelangelo (1475-1564), and Raphael (1483-1520) focused on idealized beauty, harmony, and balanced compositions.
In contrast, the Northern Renaissance, which flourished in regions such as the Netherlands, Germany, and Flanders, focused more on meticulous detail, naturalism, and domestic interiors. Northern artists like Jan van Eyck (1390-1441), Albrecht Dürer (1471-1528), and Hieronymus Bosch (?-1516) were known for their detailed and realistic depictions of nature, landscapes, and everyday life. Their work often contained rich symbolism and a focus on surface textures and fine details.
Jan Van Eyck's self portrait
Jan van Eyck's "Portrait of a Man" (Appendix 1), also known as his Self-Portrait from 1433, is a small-scale Dutch portrait measuring 25.9 x 33.1 cm (Google Arts and Culture, n.d.). The man in the painting emerges from a dark background, with his body depicted in three-quarter view. On his head, he wears a red chaperon, often mistaken for a turban, styled upward rather than hanging down (Nash, 2008, p.154). His dark fur-lined garment resembles the attire in "The Arnolfini Portrait" (Appendix 2), indicative of wealth during an era when textiles were extremely costly (ArtUK, 2019). His detailed face features a faint stubble, white highlights in his eyes and on his cheekbones, non-idealized features such as wrinkles and veins on his forehead, showcasing the Northern realism (Hall, 2014, p.44).
As described by the English art historian James Hall, the painting appears almost fleeting and alive - with the gaze seeming to capture the viewer before the face, and just like that, the penetrating stare turns away, perhaps followed by the light streaming from the right (Hall, 2014, p.43). The portrait conveys that the artist scrutinizes everything closely, including himself, without losing sight of the bigger picture (Hall, 2014, p.43). All these naturalistic details clearly indicate a Flemish painting.
The work is considered a self-portrait due to the frame. Jan van Eyck often used frames he designed and painted to enhance understanding and add meaning to his works (Hall, 2014, p.43; The National Gallery, 2021, 4:45-5.15). The gilded original frame of "Portrait of a Man" is crucial for interpreting the piece. Inscribed at the top of the frame is Jan van Eyck’s motto: "Als Ich can," translated to English: "As I can." At the bottom is his signature, and the date in Roman numerals: October 21, and in Arabic numerals, the year 1433. This results in the inscription: "Jan van Eyck made me on October 21, 1433" (Hall, 2014, p.43). He capitalizes the "I" in "Ich," playing on the pun Ich/Eyck. The motto can be interpreted as either boastful, "As I can," or modest, "As best as I can" (Hall, 2014, p.43).
The inscription highlights the relationship between words and image, indicating his awareness of his talent. His skill in painting surpasses that of a craftsman, which painters in this period was considered as. "As I can" suggests he is the only one capable of achieving such stylistic naturalism which cannot be imitated (The National Gallery, 2021, 5:10-5:58). "Jan van Eyck made me" also reflects a high degree of self-awareness, as he claims a painting of this quality, emphasizing that he created it and is conscious of his own abilities (The National Gallery, 2021, 5:10-5:58). All of this, along with his signing of his works as one of the first artists to do so, demonstrates a desire not to remain an anonymous craftsman (Hall, 2014, p.43; Farmer, 1968, p.159; Blunt, 1962).
The motto "Als Ich can" appears on several of his works, but the self-portrait is the only one where it is so prominent and clear. Additionally, the motto is placed at the top of the frame, where he would usually write the model’s name, thus, the motto can be seen as the model's identity (The National Gallery, 2021, 5:15-6:25). This, along with his direct gaze at the viewer, suggesting it was painted from a mirror, are the strongest indicators that the portrait is a self-portrait (Hall, 2014, p.43).
However, this can be taken with some skepticism, as other portraits by him, such as "Portrait of Margaret van Eyck" (Appendix 3) and "Portrait of Jan De Leeuw" (Appendix 4), share the same penetrating gaze (Pächt, 1994, p.107). This might instead indicate his realism, where the painter’s position does not function as an observer but rather takes an active role. The model’s direct gaze towards the viewer shows that the model has looked at Jan Van Eyck. This shows Jan Van Eyck possessing an active role, which was very different from painters in this period, and by doing so, creating a new respect for the painter as an artist, again showcasing his self-awareness of his position and talent (Pächt, 1994, pp.106-108).
Literature
Books and Journals:
Hall, James (2014). The self-portrait, a cultural history. London: Thames & Hudson Ltd
Nash, Susie (2008). Northeren Renaissance Art. New York: Oxford University Press.
Blunt, Anthony (1962). The Social Position of the Artist. Artistic Theory in Italy, 1450-1600. Oxford & New York: Oxford University Press
Farmer, David (1968). Reflections on a Van Eyck Self-Portrait. Oud Holland. S. 159
Online
Google Arts and Culture (n.d.): Portrait of a Man in a Red Turban (selfportrait). Found at: https://artsandculture.google.com/asset/portrait-of-a-man-in-a-red-turban-selfportrait/SAFcS1U8kYssmg?hl=en
ArtUK: Butchart, Amber (2019). Fashion reconstructed: the dress in Van Eyck's Arnolfini portrait. Found at: https://artuk.org/discover/stories/fashion-reconstructed-the-dress-in-van-eycks-arnolfini-portrait
The National Gallery (2021). Jan van Eyck's self portrait in 10 minutes or less | National Gallery. Found at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VMJK1EDG2X8&t=1s&ab_channel=TheNationalGallery
#my post#history#famous artists#art exhibition#jan van eyck#renaissance#northern renaissance#netherlands#flanders#germany#painting#oil painting#art history#artwork#art#histoire#literature#portrait#raphael#leonardo da vinci#arnolfinis wedding#art historian#research#analysis#art analysis#art anatomy#self portrait#self portrature#self portrayal#portraiture
24 notes
·
View notes
Text

Oswald Achenbach (German, 1827-1905)
Venedig, Blick auf die Piazzetta mit der Biblioteca Marciana, Santa Maria della Salute und der Dogana
70 notes
·
View notes
Text




The Knight of the Flowers (1894)
— by Georges Rochegrosse
72K notes
·
View notes
Text

Johannes Vermeer - The Astronomer, 1668 (detail), oil on canvas
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

Leda and the Swan by Jean-Baptiste Paul Lazerges (1879)
1K notes
·
View notes