#such as knowing the location of a starfish's butthole
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Fun Fact: Starfish get around using a hydraulic system!
I want to start off by saying: you may have heard that starfish have sea water instead of blood! This is not true!
Before I explain, let me point out this little dot that every starfish has (and I SWEAR that this is relevant)

(It’s like they all have lil’ buttons on! 1, 2, 3)
This little spot is known as a madreporite, from Italian madre (”mother”) + Latin poro (”pore”).
What is it? Well, to over-simplify:
The madreporite is basically a pressure valve for the insides of the starfish. It lets water in and out of its water vascular system as needed. In order to prevent debris and sea life and other non-desirables from getting inside the starfish, the madreporite filters the water that it takes in.
this is what the madreporite looks like up close:
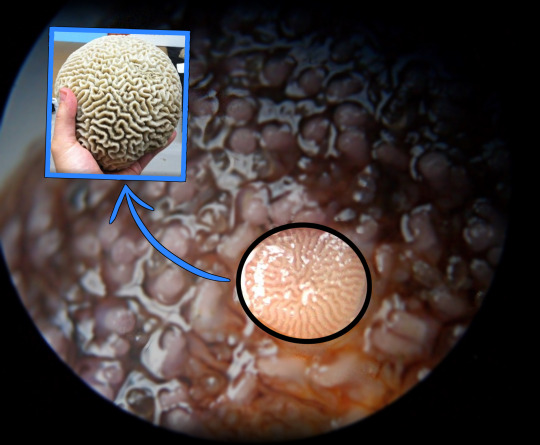
(Name origin: apparently someone saw that and thought “huh, that kind of looks like madrepore coral, but tiny! They... weren’t wrong.)
Now, you may look at the name “water vascular system” and think “hey, I know ‘vascular’! That's related to blood!” This is a reasonable misunderstanding.
While in humans, the circulatory system is part of a vascular system (along with our lymphatic system) in the starfish’s water vascular system, seawater is NOT analogous to blood in a circulatory system. Or, well, it’s complicated, because it does do some things that are similar to a mammalian circulatory system, such as transporting certain types of immune cells, but still (source: Ferguson 1966)
Instead, these seawater-filled tubes are used for things such as the movement of starfish arms (and their little tube feet), which in turn allows them to move around their environment, find and consume food, and stick to surfaces. Mammals generally don’t use their circulatory systems in this way (if I am wrong about this, PLEASE let me know, as that would be absolutely WILD).

(diagram of a starfish’s water-vascular system, revealing the starfish’s final form: some sort of fidget toy, I think)
I admit that “starfish use seawater instead of blood” is a much more attention-grabbing headline, but it’s not true, and it’s also kind of sad, because the water-vascular system is really cool without the misinformation!
(before you ask, yes, this entire post was prompted by one (1) person saying something that was WRONG, and that person may or may not have been related to me 😤😭😭😭😭😭)
The water-vascular system is, essentially, a hydraulic system. By adding and expelling water, as well as opening and closing internal channels via muscle contractions, starfish can create positive and negative pressure within their bodies. This allows them to “flex” their tube feet in surprisingly complex ways, among other functions.
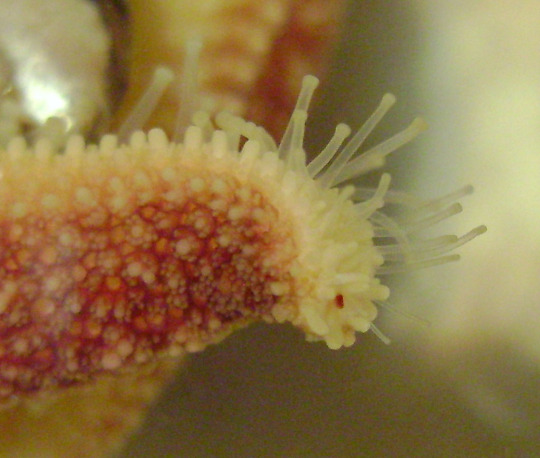

(these^ are a starfish’s “tube feet”. They are little structures with suckers on the ends. If you’ve ever held a starfish in your hands, you probably felt these feet holding onto you. They have a surprising amount of strength!)
You can imagine this sort of like how a whacky inflatable tube man uses air pressure to straighten up and fall down, except with hundreds in one connected, complex system (and also the pressure is more tightly controlled in order to prevent all that flailing, and also to allow fine control required for things like ripping open a mollusc shell).

(I always imagine this when looking at starfish tube feet. And now, maybe you will too! join me. 1, 2)
The confusion regarding starfish blood being seawater is understandable, but in the end it’s essentially a misunderstanding.
Plus, starfish have coelomic fluid, which is honestly more analogous to blood.
Coelomic fluid is, basically, the fluid that fills the starfish’s body cavity between all of its organs and such, facilitating nutrient transport, gas exchange, and overall being more blood-like than the water-vascular system in general (Andradre et al. 2021).
And ok, technically the liquid part of coelomic fluid comes from seawater, ultimately, but that would be like saying I, a human, use tap water for blood. And, ok, yes, there is water in my blood, and that water came from the tap, but no one would say that I have tap water instead of blood! Except my brother but he also says trigonometry doesn’t exist so we will be ignoring his opinion at this time.
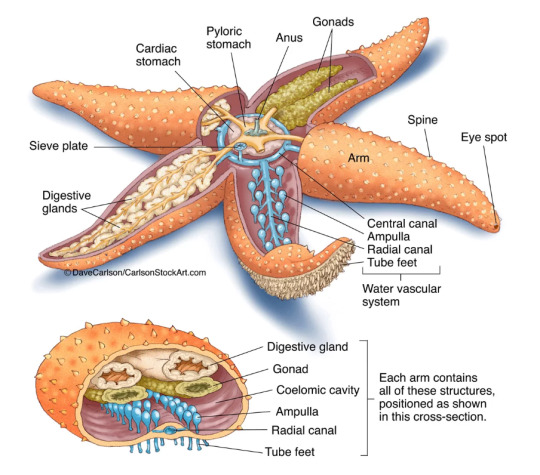
(a more detailed diagram than the one before. The coelomic fluid is found in the coelomic cavity! Also, as a bonus, you now know where a starfish’s anus is! Enjoy this new knowledge next time you look at a starfish! source: x)
Starfish aren’t the only animals with a water vascular system and a madreporite. They can also be spotted in other echinoderms, such as sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers (although in the sea cucumber the madreporite is inside the animal, so you probably won’t see it in the wild).

That said, starfish have my favourite madraporites, because I think they look like little badges. They all win the award of being lil friends (and also keystone species that are essential to many marine ecosystems. So.)
This has been Fun Fact Friday, telling you all about wacky lil friends who have funny little feet and DO NOT HAVE SEAWATER INSTEAD OF BLOOD!
I will do battle with my sibling later, as is tradition
Sources under Read More:
Andrade, C., Oliveira, B., Guatelli, S., Martinez, P., Simões, B., Bispo, C., ... & Coelho, A. V. (2021). Characterization of coelomic fluid cell types in the starfish Marthasterias glacialis using a flow cytometry/imaging combined approach. Frontiers in Immunology, 807.
Ferguson, J. C. (1966). Cell production in the Tiedemann bodies and haemal organs of the starfish, Asterias forbesi. Transactions of the American Microscopical Society, 200-209.
Mao, S., Dong, E., Zhang, S., Xu, M., & Yang, J. (2013, July). A new soft bionic starfish robot with multi-gaits. In 2013 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (pp. 1312-1317). IEEE.
#biology#science#stem#fun fact friday#science side of tumblr#animals#starfish#marine biology#there are many benefits to being a marine biologist#such as knowing the location of a starfish's butthole
1K notes
·
View notes