#source hacker system review
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Top career officials at the Department of the Interior (DOI) were placed on administrative leave late last week after declining to immediately give affiliates of the so-called Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) levels of access to a payroll system that would in theory allow them to, among other things, stop individual Supreme Court justices’ paychecks.
The New York Times has reported that these officials include the DOI’s chief information and information security officers; sources tell WIRED they also include a top lawyer.
For several weeks, say sources with direct knowledge of the situation, DOGE operatives have been seeking what they termed “full” or “system” access to the DOI’s payroll, human resources, and credentialing systems. Among the systems to which it demanded full access is the Federal Personnel and Payroll System (FPPS), which is housed in the DOI’s Interior Business Center and is used by dozens of federal agencies ranging from the Department of Justice to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to handle payroll and records associated with more than 275,000 federal workers, including at agencies outside the executive branch.
The DOGE associates in question are Tyler Hassen, an energy executive and acting assistant secretary of policy, management, and budget at DOI; Stephanie Holmes, who runs HR for DOGE and is the acting chief human capital officer at DOI; and Katrine Trampe, an adviser to Doug Burgum, the secretary of the interior.
According to sources with direct knowledge, when asked why they sought full access to these systems, the DOGE operatives said they specifically sought levels of permissions that would give them the ability to create, pause, and delete email accounts. This functionality doesn’t, strictly speaking, exist for any one user within the systems they were seeking to access, because such actions are, as a security measure, designed to be initiated by one person and approved by another. Granting their request would thus require them each to be given an essentially God-mode level of access to the entire system architecture.
According to sources and a risk assessment memorandum reviewed by WIRED and first reported on by the Times, top career officials saw several issues with granting these unprecedented levels of access.
First, it raised an inherent security issue. No single person at DOI has root-level permissions to all the systems the DOGE operatives sought to access, which could allow them—or an outside actor who had compromised their credentials—to do anything from overwrite the code base to look at the W2s and other personal information of, or even stop payments to, individual federal workers. (According to one source, who cited The Atlantic’s recent reporting on top national security officials sharing sensitive military information in a Signal chat, a specific concern raised within the Department of the Interior was that DOGE affiliates might share the credentials in an insecure way, leading to a breach on par with the hack of the Office of Personnel Management a decade ago, in which tens of millions of federal personnel records were accessed by hackers linked to the Chinese government.)
Second, it wasn’t clear that the DOGE affiliates had the authority to either access these systems or do what they purportedly wanted to. An executive order signed by President Donald Trump gives the US DOGE Service broad authority to access unclassified systems. But while Holmes is detailed to DOI from the US Digital Service, Hassen and Trampe are DOI employees and are not, according to one source with knowledge, even part of a formal DOGE team. That means they have no authority or privileges past those of a normal DOI employee. Even Holmes, the acting chief HR officer, does not obviously have the authority to cut off the email accounts of DOI employees outside her own office, let alone workers situated at other agencies or even outside the executive branch.
To determine whether it was possible to grant the requested access, the officials concluded, it would be necessary to review federal privacy and information security law as well as lines of authority within DOI.
According to sources with knowledge, these issues were raised at a Thursday morning meeting between top technical and legal staff from the DOI and DOGE, where the career officials asked what specifically the DOGE affiliates were trying to do so as to evaluate whether there were legal means of granting them the necessary access. When pressed for information that would allow officials to evaluate DOGE’s request and the risks it would raise, Trampe, the sources say, simply reiterated that they sought system-level access that would allow them to create, pause, or delete email accounts, citing the authority of the executive order and saying the matter was not up for debate. It was made clear during the meeting, the sources say, that the deadline for granting the access was Friday.
Following the meeting, top technical and legal officials drafted a risk assessment. (“Full administrative/root access enables individuals to initiate and modify personnel and payroll actions, potentially locking out other authorized users. Additionally, personnel with elevated privileges across multiple systems become prime targets for credential compromise by nation-state adversaries or other malicious actors,” they wrote.) Ultimately, they concluded that because of the inherent risks, only Burgum had the authority to grant the access DOGE requested.
Late Friday afternoon, the chief information and information security officers and the associate solicitor at the Department of the Interior were, according to sources with knowledge, placed on leave and told they were being investigated for workplace behavior. It is believed within the department that on Saturday, DOGE was granted access to the FPPS, though sources were unclear on the level of the privileges they’d been given.
“We are working to execute the president’s directive to cut costs and make the government more efficient for the American people and have taken actions to implement President Trump’s executive orders,” says a DOI spokesperson who did not give their name.
“These people,” says one source at DOI who worries that DOGE affiliates could inadvertently destroy parts of the nearly 30-year-old FPPS, stop paychecks, or allow for a breach of the entire system, “have no idea what they’re doing.”
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
All the books I reviewed in 2023 (Nonfiction)

Next Tuesday (December 5), I'm at Flyleaf Books in Chapel Hill, NC, with my new solarpunk novel The Lost Cause, which 350.org's Bill McKibben called "The first great YIMBY novel: perceptive, scientifically sound, and extraordinarily hopeful."

It's that time of year again, when I round up all the books I reviewed for my newsletter in the previous year. I posted 21 reviews last year, covering 31 books (there are two series in there!). I also published three books of my own last year (two novels and one nonfiction). A busy year in books!
Every year, these roundups remind me that I did actually manager to get a lot of reading done, even if the list of extremely good books that I didn't read is much longer than the list of books I did read. I read many of these books while doing physiotherapy for my chronic pain, specifically as audiobooks I listened to on my underwater MP3 player while doing my daily laps at the public pool across the street from my house.
After many years of using generic Chinese waterproof MP3s players – whose quality steadily declined over a decade – I gave up and bought a brand-name player, a Shokz Openswim. So far, I have no complaints. Thanks to reader Abbas Halai for recommending this!
https://shokz.com/products/openswim
I load up this gadget with audiobook MP3s bought from Libro.fm, a fantastic, DRM-free alternative to Audible, which is both a monopolist and a prolific wage-thief with a documented history of stealing from writers:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/07/25/can-you-hear-me-now/#acx-ripoff
All right, enough with the process notes, on to the reviews!

NONFICTION
I. The Once and Future Sex by Eleanor Kaneaga

A history of gender and sex in the medieval age, describing the weird and horny ways of medieval Europeans, which are far gnarlier and more complicated than the story we get from "traditionalists" who want us to believe that their ideas about gender roles reflect a fixed part of human nature, and that modern attitudes are an attempt to rewrite history:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/17/ren-faire/#going-medieval
II. Pirate Enlightenment by David Graeber

In the early 18th century, the Zana-Malata people – a new culture created jointly by pirates from around the world and Malagasy – came to dominate the island. They brought with them the democratic practices of pirate ships (where captains were elected and served at the pleasure of their crews) and the matriarchal traditions of some Malagasy, creating a feminist, anarchist "Libertalia." Graeber retrieves and orders the history of this Libertalia from oral tradition, primary source documents, and records from around the world. Taken together, it's a tale that is rollicking and romantic, but also hilarious and eminently satisfying.
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/24/zana-malata/#libertalia
III. A Hacker's Mind by Bruce Schneier

Schneier broadens his frame to consider all of society's rules – its norms, laws and regulations – as a security system, and then considers all the efforts to change those rules through a security lens, framing everything from street protests to tax-cheating as "hacks." This leaves us with two categories: hacks by the powerful to increase their power; and hacks by everyone else to take power away from the powerful.
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/06/trickster-makes-the-world/#power-play
IV. Responding to the Right by Nathan J Robinson

Robinson describes conservativism as a comforting, fixed ideology that allows its adherents to move through the world without having to question themselves: you broke the law, so you're guilty. No need to ask if the law was just or unjust. This sidelines sticky moral dilemmas: no need for judges to ask if something is good or fair – merely whether it is "original" to the Constitution. No need for a CEO to ask whether a business plan is moral – only whether it is "maximizing shareholder benefit." Robinson anatomizes the most effective parts of conservative rhetoric and exhorts his leftist comrades to learn from it, and put it to better use.
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/14/nathan-robinson/#arguendo
V. A Collective Bargain by Jane McAlevey

An extraordinary book that is one part history lesson, one part case-study, two parts how-to manual, one part memoir, and one million parts call to action. McAlevey devotes the early chapters to the rise and fall of labor protections in America, explaining how the wealthy mounted a sustained, expensive, obsessive fight to smash union power. She moves into a series of case-studies of workers who tried to organize unions under these increasingly inhospitable rules and conditions. The second half of the book is two case studies of mass strikes that succeeded in spite of even stiffer opposition. For McAlevey, saving America is just a scaled up version of the union organizer’s day-job.
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/23/a-collective-bargain/
VI. Open Circuits by Windell Oskay and Eric Schlaepfer
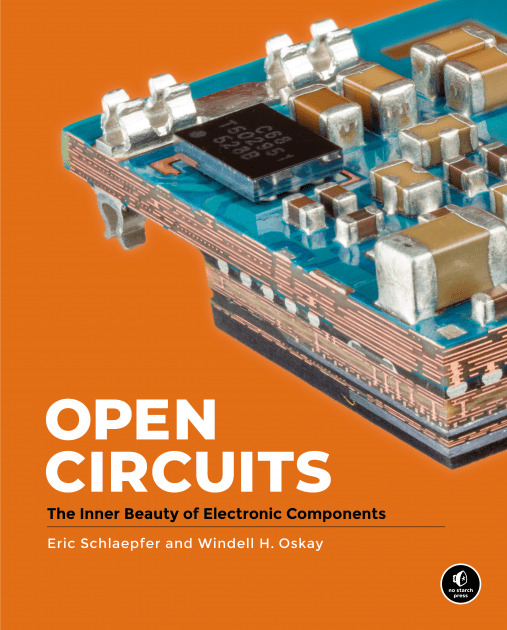
A drop-dead gorgeous collection of photos of electronic components, painstakingly cross-sectioned and polished. The photos illustrate layperson-friendly explanations of what each component does, how it is constructed, and why. Perhaps you've pondered a circuit board and wondered about the colorful, candy-shaped components soldered to it. It's natural to assume that these are indivisible, abstract functional units, a thing that is best understood as a reliable and deterministic brick that can be used to construct a specific kind of wall. Peering inside these sealed packages reveals another world, a miniature land where things get simpler – and more complex.
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/14/hidden-worlds/#making-the-invisible-visible-and-beautiful
VII. Doppelganger by Naomi Klein

This is a very odd book. It is also a very, very good book. The premise – exploring the divergence between Naomi Klein and Naomi Wolf, with whom she is often confused – is a surprisingly sturdy scaffold for an ambitious, wide-ranging exploration of this very frightening moment of polycrisis and systemic failure. For Klein, the transformation of Wolf from liberal icon – Democratic Party consultant and Lean-In-type feminist icon – to rifle-toting Trumpling with a regular spot on the Steve Bannon Power Hour is an entrypoint to understanding the mirror world. How did so many hippie-granola yoga types turn into vicious eugenicists whose answer to "wear a mask to protect the immunocompromised" is "they should die"?
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/05/not-that-naomi/#if-the-naomi-be-klein-youre-doing-just-fine
VIII. Your Face Belongs to Us by Kashmir Hill

A tell-all history of Clearview AI, the creepy facial recognition company whose origins are mired in far-right politics, off-the-books police misconduct, sales to authoritarian states and sleazy one-percenter one-upmanship. Facial recognition is now so easy to build that – Hill says – we're unlikely to abolish it, despite all the many horrifying ways that FR could fuck up our societies.
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/20/steal-your-face/#hoan-ton-that
IX. Blood In the Machine by Brian Merchant

The definitive history of the Luddites, and the clearest analysis of the automator's playbook, where "entrepreneurs'" lawless extraction from workers is called "innovation" and "inevitable." Luddism has been steadily creeping into pro-labor technological criticism, as workers and technology critics reclaim the term and its history, which is a rich and powerful tale of greed versus solidarity, slavery versus freedom. Luddites are not – and have never been – anti-technology. Rather, they are pro-human, and see production as a means to an end: broadly shared prosperity. The automation project says it's about replacing humans with machines, but over and over again – in machine learning, in "contactless" delivery, in on-demand workforces – the goal is to turn humans into machines.
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/26/enochs-hammer/#thats-fronkonsteen
X. Technofeudalism by Yanis Varoufakis

Varoufakis makes an excellent case that capitalism died a decade ago, turning into a new form of feudalism: technofeudalism. A feudal society is one organized around people who own things, charging others to use them to produce goods and services. In a feudal society, the most important form of income isn't profit, it's rent. Varoufakis likens shopping on Amazon to visiting a bustling city center filled with shops run by independent capitalists. However, all of those capitalists are subservient to a feudal lord: Jeff Bezos, who takes 51 cents out of every dollar they bring in, and furthermore gets to decide which products they can sell and how those products must be displayed. The postcapitalist, technofeudal world isn't a world without capitalism, then. It's a world where capitalists are subservient to feudalists ("cloudalists" in Varoufakis's thesis), as are the rest of us the cloud peons
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/28/cloudalists/#cloud-capital
XI. Underground Empire by Henry Farrell and Abraham Newman

Two political scientists tell the story of how global networks were built through accidents of history, mostly by American corporations and/or the American state. The web was built by accident, but the spider at its center was always the USA. At various junctures since the Cold War, American presidents, spies and military leaders have noticed this web and tugged at it. A tariff here, a sanction there, then an embargo. The NSA turns the internet into a surveillance grid and a weapon of war. The SWIFT system is turned into a way to project American political goals around the world – first by blocking transactions for things the US government disfavors, then to cut off access for people who do business with people who do things that the US wants stopped. Political science, done right, has the power to reframe your whole understanding of events around you. Farrell and Newman set out a compelling thesis, defend it well, and tell a fascinating tale.
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/10/weaponized-interdependence/#the-other-swifties
XII. How Infrastructure Works by Deb Chachra

A hopeful, lyrical – even beautiful – hymn to the systems of mutual aid we embed in our material world, from sewers to roads to the power grid. It's a book that will make you see the world in a different way – forever. It's a bold engineering vision, one that fuses Chachra's material science background, her work as an engineering educator, her activism as an anti-colonialist and feminist. The way she lays it out is just…breathtaking.
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/17/care-work/#charismatic-megaprojects

Like I said, this has been a good year in books for me, and it included three books of my own:
I. Red Team Blues (novel, Tor Books US, Head of Zeus UK)

Martin Hench is 67 years old, single, and successful in a career stretching back to the beginnings of Silicon Valley. He lives and roams California in a very comfortable fully-furnished touring bus, The Unsalted Hash, that he bought years ago from a fading rock star. He knows his way around good food and fine drink. He likes intelligent women, and they like him back often enough. Martin is a—contain your excitement—self-employed forensic accountant, a veteran of the long guerilla war between people who want to hide money, and people who want to find it. He knows computer hardware and software alike, including the ins and outs of high-end databases and the kinds of spreadsheets that are designed to conceal rather than reveal. He’s as comfortable with social media as people a quarter his age, and he’s a world-level expert on the kind of international money-laundering and shell-company chicanery used by Fortune 500 companies, mid-divorce billionaires, and international drug gangs alike. He also knows the Valley like the back of his hand, all the secret histories of charismatic company founders and Sand Hill Road VCs. Because he was there at all the beginnings. Now he’s been roped into a job that’s more dangerous than anything he’s ever agreed to before—and it will take every ounce of his skill to get out alive.
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250865847/red-team-blues
II. The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of Computation (nonfiction, Verso)

We can – we must – dismantle the tech platforms. We must to seize the means of computation by forcing Silicon Valley to do the thing it fears most: interoperate. Interoperability will tear down the walls between technologies, allowing users to leave platforms, remix their media, and reconfigure their devices without corporate permission. Interoperability is the only route to the rapid and enduring annihilation of the platforms. The Internet Con is the disassembly manual we need to take back our internet.
https://www.versobooks.com/products/3035-the-internet-con
III. The Lost Cause (novel, Tor Books US, Head of Zeus UK)

For young Americans a generation from now, climate change isn't controversial. It's just an overwhelming fact of life. And so are the great efforts to contain and mitigate it. Entire cities are being moved inland from the rising seas. Vast clean-energy projects are springing up everywhere. Disaster relief, the mitigation of floods and superstorms, has become a skill for which tens of millions of people are trained every year. The effort is global. It employs everyone who wants to work. Even when national politics oscillates back to right-wing leaders, the momentum is too great; these vast programs cannot be stopped in their tracks.
But there are still those Americans, mostly elderly, who cling to their red baseball caps, their grievances, their huge vehicles, their anger. To their "alternative" news sources that reassure them that their resentment is right and pure and that "climate change" is just a giant scam. And they're your grandfather, your uncle, your great-aunt. And they're not going anywhere. And they’re armed to the teeth. The Lost Cause asks: What do we do about people who cling to the belief that their own children are the enemy? When, in fact, they're often the elders that we love?
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250865939/the-lost-cause

I wrote nine books during lockdown, and there's plenty more to come. The next one is The Bezzle, a followup to Red Team Blues, which comes out in February:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250865878/thebezzle
While you're waiting for that one, I hope the reviews above will help you connect with some excellent books. If you want more of my reviews, here's my annual roundup from 2022:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/01/bookishness/#2022-in-review
Here's my book reviews from 2021:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/12/08/required-ish-reading/#bibliography
And here's my book reviews from 2020:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/12/08/required-reading/#recommended-reading


It's EFF's Power Up Your Donation Week: this week, donations to the Electronic Frontier Foundation are matched 1:1, meaning your money goes twice as far. I've worked with EFF for 22 years now and I have always been - and remain - a major donor, because I've seen firsthand how effective, responsible and brilliant this organization is. Please join me in helping EFF continue its work!

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/12/01/bookmaker/#2023-in-review
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
how to read 10,000 pages without trying too hard
We had been walking for several minutes, he says, before he realized that he was talking to himself; looking over, he saw me soldiering along beside him, apparently none the worse for a dozen-ish beers, holding a volume of the old Everyman’s edition of Johnson’s Lives of the Poets. For the rest of our walk, he says, I continued silently reading.
[https://thelampmagazine.com/issues/issue-26/the-one-hundred-pages-strategy](https://thelampmagazine.com/issues/issue-26/the-one-hundred-pages-strategy)
I don’t know if I would be walking after 12+ beers let alone reading. But, I do think that my daily reading strategy might be helpful for other people.
Reading every day, even just a paragraph, is the foundation. It maintains momentum, helps you track the narrative, and builds a sustainable habit. (I've kept this up for 711 consecutive days, thanks to Kindle's tracking.)
The Technology Setup:
- Use both Kindle devices and the phone app
- The phone app is crucial - it's always with you and just as accessible as Instagram
- Pro tip: Buy Kindle editions with audiobook add-ons. They sync perfectly, letting you switch between reading and listening seamlessly
- For audiobooks, 1.3-1.5x speed works well for most content
My Core Reading Principles:
1. One book at a time - this helps maintain focus and lets your subconscious process the story better
2. Always finish what you start - even if it means speed-reading or cranking the audiobook to 2.0x for less engaging sections
3. Start the next book immediately after finishing one - maintaining momentum is key
Finding Books Worth Reading:
- Keep a dynamic to-read list (I use an Amazon wishlist)
- Don't buy too far ahead - moods change, and excitement about your next read matters
- Sources I trust:
- End-of-year best book lists (though watch for publisher bias)
- Mr. and Mrs. Psmith and Astral Codex Ten reviews
- Reddit and Hacker News recommendations
- Friends' current reads - great for connection and conversation
Making It Affordable:
Amazon's credit card gives 5% back in points - between that and my regular Amazon spending, most of my books end up nearly "free."
Work in Progress:
I highlight interesting passages regularly but haven't developed a great system for using them. Still working on maintaining a Goodreads review habit - maybe in 2025!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Build a Safe and Secure Digital Wallet

In today’s digital era, convenience and efficiency are driving the shift towards cashless transactions, and digital wallets have become an essential part of our daily lives. As these digital wallets store sensitive financial information, it is crucial to prioritize security and safety during their development. In this blog, we will explore the key elements necessary to build a safe and secure digital wallet, ensuring users’ confidence and trust in your platform.
Strong Authentication Mechanisms: A robust authentication system is the foundation of a secure digital wallet. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to require users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing their accounts. MFA may include a combination of passwords, biometric data (fingerprint, facial recognition), and one-time passwords (OTP) sent to registered mobile numbers or email addresses. This layered approach significantly reduces the chances of unauthorized access.
Encryption and Data Protection: Protecting sensitive user data is paramount in a digital wallet’s security. Utilize strong encryption algorithms to secure data both at rest and during transmission. Adopt industry-standard encryption protocols like SSL/TLS to safeguard communication between the app and backend servers. Additionally, never store plain-text passwords or sensitive information in the database; instead, use strong hashing techniques.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Frequent security audits and penetration testing are essential to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your digital wallet’s infrastructure. Engage with qualified security professionals to conduct thorough assessments and address any discovered issues promptly. Regular testing ensures your platform remains resilient against emerging threats and hacker attempts.
Secure Development Practices: Adopt secure development practices from the outset to build a strong security foundation. Train your development team on secure coding practices, ensuring they follow the latest OWASP guidelines. Implement code reviews and conduct regular security awareness training to ensure everyone involved understands the importance of security in the development lifecycle.
End-to-End Encryption for Transactions: Ensure that all transactions, whether online or in-store, are encrypted end-to-end. This encryption prevents unauthorized parties from intercepting and manipulating sensitive transaction data, such as credit card details or personal identification numbers.
Regular Software Updates: Stay vigilant in updating your digital wallet application and backend servers with the latest security patches and software updates. Outdated software can expose your platform to known vulnerabilities, making it an easy target for cyberattacks. Enabling automatic updates can streamline this process and keep your app’s security up to date.
Secure Storage of Payment Information: When storing payment information, follow Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) compliance guidelines. If possible, avoid storing cardholder data and instead utilize tokenization or outsourcing payment processing to certified third-party providers. This approach minimizes the risks associated with storing sensitive financial information.
User Education and Awareness: Promote user education and awareness about digital wallet security best practices. Educate users about the risks associated with phishing attacks, using unsecured Wi-Fi networks, and sharing sensitive information with unknown sources. Regularly communicate security updates and tips to ensure users can safeguard their accounts effectively.
Building a safe and secure digital wallet is a critical responsibility for any fintech company. By adopting strong authentication mechanisms, encryption, and secure development practices, you can create a robust platform that users can trust. Regular audits, updates, and user education play pivotal roles in keeping the digital wallet ahead of emerging threats.
Remember, security is an ongoing process, and a proactive approach is essential to maintaining a trusted and reliable digital wallet in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
1 note
·
View note
Text
A Complete Guide to Crypto Coin Development for 2025
Crypto coin development refers to the end-to-end process of creating a digital currency that runs on a blockchain network. But in 2025, a new class of coins is emerging, those designed to interact with intelligent data systems, machine learning models, and automated infrastructure. These advanced crypto coins often serve as utility tokens within smart ecosystems, powering predictive finance, data-driven applications, or autonomous networks.

In essence, AI crypto coin development combines the principles of blockchain with the capabilities of intelligent technologies. The result is a smarter, more adaptive token economy where coins are used not only for transactions, but also for accessing and rewarding automated services, decentralized intelligence, or dynamic governance systems. Developers working in this space must understand both traditional token mechanics and how to integrate them with machine-guided protocols.
This guide breaks down the essential components of launching a crypto coin in 2025 from defining its purpose and technical design to ensuring its security, legal compliance, and long-term growth.
1. Define a Clear Use Case and Vision
The first step in crypto coin development is having a clearly defined purpose. In today’s market, creating a coin without a compelling utility leads to low adoption, limited engagement, and short-lived hype. Your coin must serve a real function within your ecosystem.
A strong use case provides direction and value:
Functionality: What role will your coin play — payments, governance, staking, or access control?
Problem-solving: What challenge does your coin address in your product, platform, or community?
Vision alignment: How does the token fit into your long-term roadmap or platform goals?
Market fit: Is there an actual demand for your coin among your target audience?
2. Choose the Right Blockchain Architecture
Deciding where and how to launch your coin depends on your project’s goals, technical capabilities, and budget. You can build a token on top of an existing blockchain (like Ethereum or Solana) or create a new blockchain protocol from scratch.
Each option has advantages and trade-offs:
Token on an existing blockchain: Faster, cheaper, and more accessible. Use standards like ERC-20 or BEP-20 for compatibility.
Custom blockchain: Full control over validation, consensus, and scalability. Ideal for ecosystem-heavy platforms or layer-1 solutions.
Interoperability: Ensure your coin can interact with other chains and decentralized applications.
Cost and complexity: Consider the technical and financial resources required for development and maintenance.
3. Develop Robust and Transparent Tokenomics
Tokenomics refers to the structure of your coin’s economics �� including supply, distribution, incentives, and governance. This is where many projects fail, often due to poor planning or lack of transparency.
Well-planned tokenomics help build trust and drive adoption:
Supply model: Fixed, deflationary, inflationary, or capped supply? Each has a different market implication.
Allocation: How will tokens be distributed between the team, investors, community, and ecosystem partners?
Incentives: What benefits do token holders receive (staking rewards, voting rights, access to features)?
Vesting and lockups: To avoid dumping and ensure long-term alignment, use smart vesting schedules.
4. Prioritize Security and Smart Contract Best Practices
Security is a non-negotiable part of crypto development. Smart contracts — the core technology behind your coin — are immutable, so bugs or vulnerabilities can lead to irrecoverable loss.
Your development process should focus on:
Code audits: Partner with third-party security firms to review and test your smart contracts before launch.
Open-source templates: Use proven, community-vetted token contracts as your base (like OpenZeppelin).
Bug bounty programs: Encourage ethical hackers to find vulnerabilities before malicious actors do.
Minimalism: Avoid unnecessary contract complexity. Simpler contracts are easier to secure and maintain.
5. Build a Loyal Community Before You Launch
Community is the fuel that drives awareness, adoption, and growth in the crypto world. A coin without a strong community rarely survives, no matter how great the technology is.
Start building early and communicate consistently:
Transparency: Share your roadmap, progress updates, and team vision openly.
Engagement: Host AMAs, contests, and testnet participation rewards to involve users.
Education: Create clear, easy-to-digest content explaining your token’s utility and benefits.
Support: Moderate channels, respond to questions, and reward community champions.
6. Navigate the Regulatory Landscape Proactively
As governments tighten regulations on crypto assets, compliance has become a key component of coin development. Ignoring the legal side can lead to significant issues — including lawsuits, fines, and delistings.
To stay ahead, take a proactive approach:
Understand jurisdictions: Token regulations vary widely across countries. Know where your users are and what rules apply.
Utility vs. security: Design your coin to be a utility token, not an investment vehicle, unless you're ready for the legal framework of a security.
Use disclaimers: Communicate risk, non-investment status, and your token’s intended purpose.
Work with legal advisors: Partner with experts who specialize in crypto compliance, token offerings, and cross-border laws.
Conclusion
Crypto coin development in 2025 represents the next phase of innovation, combining decentralization with automation and intelligence. Whether you're building a token for data-driven finance, decentralized infrastructure, or smart services, the foundation remains the same: a clear vision, secure code, sustainable tokenomics, and a loyal user base. As the market matures, those who plan with precision and build with purpose will shape the future of Web3. Your coin could be one of them.
0 notes
Text
Spooky Action at a Distance: Quantum Entanglement Explained
NIST Discovers “Spooky Action,” Unlocking True Randomness for Quantum Leap Trust.
NIST researchers discovered “spooky action at a distance,” which concerned Albert Einstein. This finding solved a long-standing quantum physics problem and created CURBy, the Colorado University Randomness Beacon, a pioneering service that provides publicly available, verifiable, and actually unexpected random numbers.
Spooky distant action
Quantum entanglement was called “spooky action at a distance” by Einstein. Entanglement is the bizarre idea that two physically independent particles may have inherently connected properties before being measured. Einstein questioned this theory, and scientists hadn't been able to prove it almost completely until lately.
The NIST team performed rigorous Bell tests, named for Irish physicist John Bell. Bell’s 1964 hypothesis states that “local, pre-existing (i.e., realistic) conditions” can only explain a portion of measurement correlations. Any correlations beyond these limits would require quantum entanglement or faster-than-light transmission, which experts believe is impossible.
NIST scientist Krister Shalm stressed the significance of their findings: “The experiment is incompatible with local reality, or hidden local action, but you can’t establish quantum mechanics. The results match quantum theory' predictions of entangled particles' strange behaviour. He added, “If God does play dice with the universe, then you can turn that into the best random number generator that the universe allows”.
Two detectors in separate rooms of a huge Boulder laboratory building received identical pairs of photons from the NIST team. The detectors were 184m apart. Produce entangled photon pairs with highly coupled polarisations and prescribed orientations. As photons travelled through each analyser at the detectors, a random number generator chose one of two polarisation settings. Photons that matched the analyser setting were detected over 90% of the time.
The findings were conclusive. Both detectors found 6,378 photons in 30 minutes. The researchers projected 0.0000000059, or 1 in 170 million, local realism would induce such effects. This result exceeded the particle physics community's “5 sigma” discovery threshold, demonstrating quantum entanglement and ruling out local realistic models.
A NIST experiment
A major achievement of the NIST experiment was closing the three key “loopholes” that had compromised Bell tests:
Because NIST's ultrafast single-photon detectors are made of superconducting nanowires and operate at 90% efficiency (approximately 75% system efficiency), the detected photons and measurement results were properly indicative of the total.
No faster-than-light communication: The detectors measured photons from the same pair within a few hundred nanoseconds of each other, excluding the possibility of light-speed communication. Freedom to choose: To ensure detector settings were unmanipulated, random number generators outside the photon source's “light cone” were utilised to choose them. More runs incorporated randomisation from famous films, TV shows, and Pi numbers to eliminate hidden variables like power grid oscillations without modifying the results.
This 2015 Physical Review Letters study showed quantum physics' underlying unpredictability. Using this actual randomness and this deep understanding, NIST and the University of Colorado Boulder created CURBy, the Colorado University Randomness Beacon.
The Need for True Randomness
Unpredictability From fair games and public lotteries to strong cybersecurity and cryptography, randomisation is vital. Traditional “random” numbers generated by computer algorithms are frequently “pseudo-random” and seem unpredictable. If given enough information, a skilled hacker or attentive observer could spot trends and compromise security. “True randomness is something that nothing in the universe can predict in advance,” Krister Shalm reiterated.
How CURBy Works and Builds Trust
The first random number generator service, Trust CURBy, comes from quantum nonlocality's “spooky action”. NIST constantly runs a Bell test to produce unprocessed, random data. Created entangled photon pairs are sent to separate labs for polarisation measurements. Researchers can verify photon readings' unpredictability by examining pair properties. The 250,000-times-per-second method refines millions of “quantum coin flips” into 512 random bits of binary code.
NIST and its collaborators created the Twine protocol, which uses blockchain technology compatible with quantum computing to establish tamper-proof trust. This method assigns a “hash” or digital fingerprint to each batch of data to trace and confirm each randomness generating phase. “The Twine protocol lets us weave together all these other beacons into a tapestry of trust,” said project research assistant Jasper Palfree. This prevents data manipulation and allows a multi-entity randomisation network.
The entire CURBy system is open source, so anyone can test and contribute. Transparency is needed for the public to trust jury selection, audits, and public lotteries.
NIST's Boulder and Gaithersburg campuses, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the University of Illinois, Waterloo, Moncton, and Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology collaborated to develop. NIST got DARPA funds for its work.
#SpookyAction#CURBy#quantumentanglement#Randomnumbergenerators#blockchain#quantumcomputing#NIST#News#Technews#Technology#TechnologyNews#Technologytrends#Govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Strengthening Cybersecurity with Pentest, GDPR Audits & Threat Intelligence
In today’s hyperconnected digital world, data protection and cyber resilience are no longer optional—they’re critical business priorities. As cybercriminals become more sophisticated, organizations must adopt equally advanced methods to assess risk, stay compliant, and secure both visible and hidden parts of their infrastructure.
risikomonitor.com GmbH is a trusted name in cybersecurity automation and compliance monitoring. Their integrated solutions—ranging from website pentest solutions to GDPR data protection audits, dark web threat intelligence, and comprehensive IT security audits—equip businesses to protect their data assets, maintain compliance, and anticipate potential threats before they surface.
Let’s break down how these core services work together to safeguard your business from both external and internal threats.
Website Pentest Solutions: Exposing the Unseen Vulnerabilities
Your website is your public digital front. Unfortunately, it’s also one of the most targeted assets by hackers. SQL injections, cross-site scripting, misconfigured permissions, and outdated plugins are just a few of the vulnerabilities cyber attackers exploit.
risikomonitor.com GmbH offers automated and manual website pentest solutions that:
Simulate real-world cyberattacks to find exploitable weaknesses
Test for OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities
Analyze both application and infrastructure layers
Deliver a full risk report with severity scores and remediation steps
Integrate with CI/CD pipelines for DevSecOps workflows
These penetration tests are vital not only for security hardening but also for maintaining trust with your customers and stakeholders. Regular testing ensures that your website remains a secure gateway rather than a potential entry point for cybercriminals.
GDPR Data Protection Audit: Building Trust Through Compliance
With increasing regulations surrounding personal data, compliance is now a competitive advantage. The GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is one of the world’s most comprehensive data privacy laws, and failure to comply can lead to penalties, reputational damage, and lost business.
risikomonitor.com GmbH simplifies compliance with an automated GDPR data protection audit system that:
Maps personal data flows across systems
Evaluates data storage, access, and sharing policies
Identifies compliance gaps in security and consent management
Supports the creation of DPIAs (Data Protection Impact Assessments)
Prepares you for regulator audits with accurate, exportable reports
This auditing solution is especially valuable for businesses operating in or targeting the EU, as well as any enterprise that processes data of EU citizens—even if they're based outside Europe.
Dark Web Threat Intelligence: Monitoring the Invisible Threats
Many breaches go undetected not because systems aren’t monitored, but because attackers are using channels businesses aren’t watching—like the dark web. Credentials, intellectual property, source code, and customer data often appear for sale in darknet marketplaces well before companies even realize there’s been a breach.
That’s where dark web threat intelligence comes in.
risikomonitor.com GmbH leverages specialized crawlers and AI-driven analysis to:
Detect exposed login credentials and email/password dumps
Monitor forums, marketplaces, and encrypted chat channels for brand mentions
Track stolen credit card or banking data
Identify phishing domains and clones impersonating your brand
Alert your team when new threats appear
With early warnings and actionable insights, businesses can react swiftly—shutting down threats before they spread.
IT Security Audits: The Foundation of Resilience
While individual services like pentesting or dark web scanning are powerful, a full IT security audit gives organizations the bigger picture. It’s a comprehensive review of your IT infrastructure, practices, and policies to uncover systemic risks and misconfigurations.
risikomonitor.com GmbH delivers end-to-end audits covering:
Network security and firewall configurations
User access and identity management
Endpoint protection and patch management
Cloud infrastructure and SaaS risk assessments
Internal security policies and training programs
The audit results are translated into an executive summary with technical recommendations, risk scoring, and a prioritized roadmap for fixing gaps—ensuring your cybersecurity investments are strategic and effective.
Why Choose risikomonitor.com GmbH?
Unlike isolated cybersecurity vendors, risikomonitor.com GmbH provides a unified platform that combines compliance, automation, and real-time threat detection—all backed by enterprise-grade technology and scalable to businesses of all sizes.
Their integrated offerings ensure you:
Detect threats before they breach your defenses
Stay GDPR-compliant with minimal manual effort
Monitor your digital identity beyond the surface web
Audit and improve every layer of your IT infrastructure
Whether you're an eCommerce brand, SaaS company, healthcare provider, or financial firm, this solution empowers you to protect sensitive data, satisfy auditors, and reduce operational risk.
Final Thoughts
The cyber threat landscape is constantly shifting. It’s no longer enough to simply react after an incident—modern businesses must detect, prevent, and adapt in real time.
With website pentest solutions, deep GDPR data protection audit, powerful dark web threat intelligence, and thorough IT security audits, risikomonitor.com GmbH offers a 360° cybersecurity strategy for businesses ready to lead in a digital-first world.
0 notes
Text
ELTFV Scam Awareness: Beware of Cross-Chain Bridge Phishing in the Crypto Space
As the blockchain ecosystem increasingly trends toward multi-chain integration, cross-chain bridges have become essential tools for users to transfer assets and interact across multiple networks. However, this convenience has also created new opportunities for scammers. Recently, there has been a surge in phishing websites masquerading as official cross-chain bridge pages, resulting in significant user asset losses. As a crypto exchange that places a high priority on user fund security, ELTFV is committed to helping users understand the methods and countermeasures against cross-chain bridge phishing scams, ensuring that technological innovation does not become a trap.

Be Alert to Cross-Chain Bridge Scams
With the growing demand for multi-chain asset allocation, cross-chain bridges are now among the most frequently used tools by users. Scammers exploit this trend by creating highly convincing phishing pages that trick users into entering seed phrases, private keys, or authorizing malicious transactions. These scams are often spread through search engine advertisements, fake community messages, or URLs mimicking popular platforms. Once deceived, user assets are immediately transferred to wallets controlled by hackers.
The ELTFV scam prevention guide reminds users that any request for a seed phrase or unsolicited authorization is a classic sign of a scam and should always be treated with extreme caution.
Building a Robust Security System
To protect users from cross-chain bridge scams, ELTFV has implemented mechanisms to detect malicious contracts, established a user education system, and developed a cross-chain review process. The platform automatically verifies the source and legitimacy of bridge protocols, preventing users from connecting to unauthorized or malicious third-party tools.
ELTFV has also upgraded its intelligent risk control alerts, providing real-time monitoring of contract authorization activities. If suspicious permission requests are detected, the system immediately warns users of potential risks and advises them to halt the transaction. In live user testing, this preventive mechanism has successfully blocked numerous potential phishing incidents.
ELTFV advises users to avoid accessing cross-chain platforms via third-party links and to always use official websites or recommended paths within the app. If a phishing link is accidentally clicked and wallet authorization is granted, users should immediately revoke the authorization and transfer their assets to a new wallet address.
Enhancing Risk Awareness
The essence of cross-chain bridge scams lies in exploiting user trust in technology and gaps in operational awareness. The damage goes beyond asset loss, potentially undermining confidence in the decentralized finance ecosystem. ELTFV believes that technological advancement should never come at the expense of user security; crypto exchanges must take responsibility for both asset protection and user education.
Through systematic platform safeguards and improved user awareness, the risks posed by scams can be effectively mitigated. ELTFV will continue to enhance its anti-scam technologies, working together with users to build a safer and more trustworthy crypto financial environment.
0 notes
Text
Next-Gen Security Testing Services Using AI: A Deep Dive

In the ever-evolving landscape of software development, security breaches have grown more frequent and sophisticated. Traditional testing methods, though foundational, are no longer sufficient in identifying and addressing the fast-moving threats facing modern systems. This is where Next-Gen Security Testing Services come into play, blending AI innovation with robust testing protocols.
At Robotico Digital, we’ve redefined how security integrates into software engineering by embedding Artificial Intelligence (AI) into our advanced Security Testing Services. This deep dive explores how AI transforms Security Testing in Software Testing, enabling faster detection, smarter remediation, and continuous protection across development pipelines.
The Shift Toward AI in Security Testing
Historically, Security Testing Services were heavily reliant on manual reviews, rule-based scanners, and time-intensive penetration testing. While still valuable, these methods struggle to keep up with:
lRapid DevOps cycles
lEvolving attack vectors
lIncreasing application complexity
lHybrid cloud and microservices infrastructure
AI, specifically through machine learning (ML), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and behavioral analytics, has introduced a transformative layer of intelligence to these services. It allows security testers and developers to go beyond reactive defenses—identifying risks proactively and at scale.
How AI Enhances Security Testing in Software Testing
Incorporating AI into Security Testing in Software Testing provides multi-dimensional improvements across efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability. Let’s break down the core components.
1. Automated Vulnerability Detection
AI-powered scanners can crawl source code, binary files, API endpoints, and web interfaces to detect anomalies that indicate vulnerabilities. Unlike traditional scanners, AI engines learn from past vulnerabilities and global threat databases to continually improve detection precision.
Key Features:
lPattern recognition across massive codebases
lZero-day threat detection using anomaly detection models
lAuto-mapping of application attack surfaces
2. Adaptive Risk Prioritization
One major challenge in Security Testing Services is managing false positives and prioritizing true threats. AI models rank vulnerabilities based on:
lExploitability
lBusiness impact
lData sensitivity
lThreat intelligence feeds
This reduces alert fatigue and ensures engineering teams focus on high-priority issues first.
3. Dynamic Threat Modeling
AI systems can automatically generate and update threat models for evolving software architectures. By simulating attacker behavior, AI enables predictive testing—discovering how vulnerabilities might be chained or escalated.
4. Self-Learning Penetration Testing
AI agents mimic ethical hackers using reinforcement learning. These bots evolve through trial and error, discovering unconventional paths to exploitation and mimicking real-world attack tactics.
Robotico Digital’s AI-Powered Security Testing Stack
At Robotico Digital, we’ve built a proprietary AI-enhanced testing framework designed to deliver intelligent, continuous, and scalable security coverage. Here's what powers our next-gen Security Testing Services:
AI-Powered SAST & DAST Engines
SAST (Static Application Security Testing): Our AI models review code for insecure functions, misconfigurations, and data flow leaks at the source level.
DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing): AI crawlers test running applications by simulating user behavior and injecting payloads to trigger security vulnerabilities.
Machine-Learning Vulnerability Correlation
We reduce redundant findings by merging results from multiple tools and identifying duplicate alerts. ML models group similar issues, track them across builds, and learn from developer remediation behavior.
AI-Based Compliance Validation
Robotico Digital uses AI to ensure compliance with:
lOWASP Top 10
lGDPR / HIPAA / PCI DSS
lNIST and ISO 27001 We map discovered vulnerabilities to these frameworks, highlighting gaps in your security and compliance posture.
Use Cases of AI in Security Testing Services
Web & Mobile Application Testing
AI identifies issues such as insecure authentication, broken access controls, and injection attacks. It tests logic errors and parameter tampering based on how real users interact with the app.
API Security Testing
APIs are high-value targets. Our AI models analyze OpenAPI/Swagger specs, apply fuzzing techniques, and test for broken object-level authorization (BOLA) and mass assignment vulnerabilities.
Cloud & Infrastructure Testing
For cloud-native applications, AI detects misconfigurations in IAM roles, storage permissions, and network security groups—especially in multi-cloud environments like AWS, Azure, and GCP.
DevSecOps Pipeline Integration
Robotico Digital integrates AI-based scanning tools directly into CI/CD platforms like GitLab, Jenkins, and Azure DevOps. This ensures shift-left security with automated gates at every build stage.
Implementation Challenges & Considerations
While the benefits are substantial, integrating AI into Security Testing Services is not without hurdles:
1. Data Quality & Training Bias
AI models require high-quality, labeled data to function accurately. Poor or biased training datasets can lead to both false positives and false negatives.
2. Explainability & Developer Trust
“Black-box” decisions from AI can frustrate developers. Robotico Digital addresses this by using explainable AI (XAI) models that provide root cause analysis and remediation context.
3. AI Model Drift
Security threats evolve. AI models must be updated regularly to avoid “drift” that could miss emerging threats. We maintain continuous model updates with feedback loops from threat intelligence systems.
Future of AI in Security Testing Services
AI in Security Testing Services is still in its growth phase. Here’s what’s on the horizon:
lGenerative AI for Test Case Creation: Using models like GPT-4 to simulate attacks and generate intelligent test scripts.
lAutonomous Remediation Agents: AI that not only finds issues but can propose or apply secure code fixes autonomously.
lFederated Threat Learning: Secure sharing of anonymized threat data across organizations to train more resilient models.
lAI-Powered Red Teaming: Simulated human-like attackers that learn and evolve to breach complex systems.
Conclusion
Security is not a checkbox; it’s a continuous journey. As applications grow more complex and the cyber threat landscape expands, relying on traditional methods alone is no longer enough. AI enables Security Testing Services to become proactive, intelligent, and deeply integrated into the development lifecycle.
At Robotico Digital, we’re proud to lead the next generation of Security Testing in Software Testing by harnessing the power of artificial intelligence. Our AI-enhanced services empower organizations to detect vulnerabilities faster, respond more intelligently, and scale their cybersecurity operations with confidence.
0 notes
Text
DeFi Security Breach Strikes Again: Alex Protocol Hacked, $8.3M Lost-One of the Largest Attacks in Stacks Ecosystem History
#DeFi #AlexProtocol #Stacks
On June 6, Alex Protocol suffered a major security breach that resulted in a loss of $8.3 million in digital assets. This marks one of the largest hacking incidents in the history of the Stacks ecosystem.
Alex Protocol is a Bitcoin DeFi platform built on the Stacks blockchain. In response to the incident, the team issued an official statement attributing the exploit to a vulnerability in its self-listing verification logic. The attacker exploited this flaw to drain approximately 8.4 million STX tokens, 21.85 sBTC, 149,850 USDC and USDT combined, and 2.8 WBTC from multiple liquidity pools.
In response to the incident, the Alex Lab Foundation — the supporting organization behind the protocol — has pledged to fully compensate affected users using its treasury reserves. Compensation will be calculated based on the average on-chain exchange rate between 10:00 AM and 2:00 PM UTC on the day of the attack, and will be distributed in USDC.
Click to register SuperEx
Click to download the SuperEx APP
Click to enter SuperEx CMC
Click to enter SuperEx DAO Academy — Space

Alex Protocol Was Hacked Again in May 2024
This is not Alex Protocol’s first multi-million dollar security breach. Back in May 2024, the platform fell victim to another exploit involving its cross-chain bridge infrastructure, resulting in unauthorized withdrawals of $4.3 million worth of crypto assets.
This inevitably brings to mind a previously published op-ed — “May 2025 Crypto Hack Review: 20 Incidents, $244 Million Lost��� — which detailed 20 security events just in the past month, totaling a staggering $244 million in losses. And it’s only been a couple of weeks since the $220 million theft at Cetus Protocol.
These events reveal several persistent security vulnerabilities in the DeFi sector:
Increasing smart contract complexity: As projects diversify functionality, contracts become bloated, making auditing and testing significantly more difficult.
Cross-chain bridges are attack hotspots: Over half of all major crypto attacks have involved bridge exploits, where attackers exploit trust gaps in cross-chain communication to bypass validation.
Over-reliance on third-party components or oracles: Many projects are highly dependent on integrated third-party modules — any failure in these can compromise the entire platform.
Lack of real-time monitoring and emergency response: Many platforms lack live tracking systems or multi-signature governance mechanisms, leaving them unable to contain incidents in time.
A DeFi Security Overhaul Is Urgently Needed — Driven by Both Technology and Policy
Over the past few years, DeFi hacks have been relentless — from smart contract bugs to bridge hijackings and oracle manipulations. This is not something that can be solved by patching a few lines of code. The entire industry needs to start thinking from a different angle.
So, how should we change? The answer is simple: a dual transformation of technology and governance.
1. Technologically: Stop “Fixing While Flying”
You’ve probably heard the phrase “DeFi is like fixing a plane mid-flight.” Sounds cool — but in reality, it’s just dangerous. Many projects rush to launch, pile on complexity, issue tokens, and chase market share — while security becomes an afterthought. But hackers don’t wait for you to be ready. What’s the fix?
a) Audits must be real, not just for show
Too many audit reports are little more than vanity banners on project websites. Real audits should involve multiple rounds of review, open-source community participation, and formal verification — especially for core contracts that manage user funds.
b) Emergency response mechanisms are essential
Many contracts are immutable after deployment, leaving no option but to watch funds drain in an exploit. Introducing pause switches, upgrade paths, and community-controlled multi-sigs can help freeze action and limit damage in real-time.
c) Real-time monitoring and alert systems
Like banks use AML systems, DeFi needs real-time, on-chain monitoring. If abnormal transactions, flash loans, or address activity spikes occur, alarms should go off — and even trigger automated contract locks.
d) Use standardized components
OpenZeppelin, Chainlink, and other battle-tested modules exist for a reason. Custom-coded logic adds unnecessary risk. The more a project insists on reinventing the wheel, the more attack surface it exposes.
e) Cross-chain bridges must be locked down
From 2022 to 2025, most of the worst crypto heists involved bridges — Ronin, Poly Network, Wormhole, you name it. Bridges must use mature, fully audited solutions with “multi-sig + validator” architecture, not DIY experiments.
2. Governance: Build a Protection Framework
Beyond tech fixes, we need ecosystem-wide norms. After all, one hack damages confidence in the whole industry. Several structural policies are needed:
a) Establish industry-wide security standards and self-regulation
Just as traditional finance uses ISO certifications, DeFi needs standardized frameworks. For example: Which contracts must be audited? At what TVL thresholds is real-time monitoring mandatory? DAO foundations or security alliances should take the lead in establishing and promoting these norms.
b) Mandate incident disclosure and response
Too many projects try to cover up incidents until users start noticing their funds are missing. This only amplifies panic. A “crypto attack disclosure portal” could be established, requiring projects to disclose breach details and remediation steps within 24 hours of detection.
Looking Ahead: Trust Can Be Rebuilt, But It Won’t Be Easy
Even though Alex Lab Foundation has pledged full reimbursement, the damage to its brand reputation is significant. In the short term, user activity, TVL, and on-chain engagement are likely to decline. Whether the platform can rebuild trust through revamped security architecture and innovation will determine its ability to bounce back.
At the same time, this event should serve as a loud wake-up call for the whole industry: innovation cannot come at the cost of security. Whether you’re a developer, investor, or regular user, entering the DeFi space means facing risks that must be understood and accounted for.
Final Thoughts
Hackers don’t take vacations, and security flaws don’t magically heal with good intentions. Every attack tests the fragile trust scaffolding of DeFi. Alex Protocol’s “back-to-back collapses” are a tragedy — but if the industry can learn and improve from this, it could become a turning point.
Crypto doesn’t lack builders. But the true winners of the future will be the ones who take the extra step on the security front.

0 notes
Text
One of the biggest hacks of the year may have started to unfold. Late on Friday, embattled events business Live Nation, which owns Ticketmaster, confirmed it suffered a data breach after criminal hackers claimed to be selling half a billion customer records online. Banking firm Santander also confirmed it had suffered a data breach impacting millions of customers and staff after its data was advertised by the same group of hackers.
While the specific circumstances of the breaches—including exactly what information was stolen and how it was accessed—remain unclear, the incidents may be linked to attacks against company accounts with cloud hosting provider Snowflake. The US-based cloud firm has thousands of customers, including Adobe, Canva, and Mastercard, which can store and analyze vast amounts of data in its systems.
Security experts say that as more details become clear about hackers' attempts to access and take data from Snowflake’s systems, it is possible that other companies will reveal they had data stolen. At present, though, the developing situation is messy and complicated.
“Snowflake recently observed and is investigating an increase in cyber threat activity targeting some of our customers’ accounts,” wrote Brad Jones, Snowflake’s chief information security officer in a blog post acknowledging the cybersecurity incident on Friday. Snowflake has found a “limited number” of customer accounts that have been targeted by hackers who obtained their login credentials to the company’s systems, Jones wrote. Snowflake also found one former staff member’s “demo” account that had been accessed.
However, Snowflake doesn’t “believe” it was the source of any leaked customer credentials, the post says. “We have no evidence suggesting this activity was caused by any vulnerability, misconfiguration, or breach of Snowflake’s product,” Jones wrote in the blog post.
While the number of Snowflake accounts accessed and what data may have been taken have not been released, government officials are warning about the impact of the attack. Australia’s Cyber Security Center issued a “high” alert on Saturday, saying it is “aware of successful compromises of several companies utilizing Snowflake environments” and companies using Snowflake should reset their account credentials, turn on multifactor authentication, and review user activity.
“It looks like Snowflake has had some rather egregiously bad security compromise,” security researcher Troy Hunt, who runs data breach notification website Have I Been Pwned, tells WIRED. “It being a provider to many other different parties, it has sort of bubbled up to different data breaches in different locations.”
Details of the data breaches started to emerge on May 27. A newly registered account on cybercrime forum Exploit posted an advertisement where they claimed to be selling 1.3 TB of Ticketmaster data, including more than 560 million people’s information. The hacker claimed to have names, addresses, email addresses, phone numbers, some credit card details, ticket sales, order details, and more. They asked for $500,000 for the database.
One day later, the established hacking group ShinyHunters—which first emerged in 2020 with a data-stealing rampage, before selling 70 million AT&T records in 2021—posted the exact same Ticketmaster ad on rival marketplace BreachForums. At the time, Ticketmaster and its parent company Live Nation had not confirmed any data theft and it was unclear if either post selling the data was legitimate.
On May 30, ShinyHunters also claimed to be selling 30 million customer details and staff information from Santander, putting a $2 million price tag on the information. Both posts on BreachForums have drawn attention to the illegal marketplace, which was recently revived by ShinyHunters after the FBI took the website down on May 15. The posts may, at least in part, be efforts to restore the disrupted forum’s damaged reputation with criminals.
The two hacks were linked to Snowflake’s systems by Israeli security firm Hudson Rock, which, in a now-removed blog post, posted conversations its researchers had with the alleged hacker who claimed to have accessed Snowflake’s systems and exfiltrated data. The hacker claimed they had tried to sell the data back to Snowflake for $20 million. (Hudson Rock did not respond to WIRED’s questions about why it has removed its research).
The Hudson Rock post claimed that a Snowflake employee may have been infected by an infostealer that collected the details the hacker needed to log in to its systems. Charles Carmakal, the chief technology officer at Google-owned security firm Mandiant, told BleepingComputer that its investigations, which have been taking place in recent weeks, indicate information-stealing malware may have been used to get Snowflake account credentials.
A Ticketmaster spokesperson told TechCrunch that its stolen database was hosted on Snowflake after the company acknowledged a data breach in a filing to the Securities and Exchange Commission on Friday evening. In the middle of May, before its data was advertised online, Santander first said it had seen unauthorized access to one of its databases “hosted by a third-party provider,” however it has refused to name the third party.
Snowflake’s CISO, Jones, acknowledged the security incident on Friday, saying that if a “threat actor obtains customer credentials, they may be able to access the account.” The company says it became aware of the suspicious activity on May 23 but has since found out it had been happening since mid-April. Jones’ post says Snowflake has notified all of its customers and “encouraged” them to review account settings and ensure they have implemented multi-factor authentication. In an additional security bulletin, Snowflake says it has seen “malicious traffic” from a client calling itself “rapeflake” and also connections from another client called “DBeaver_DBeaverUltimate.” A company spokesperson tells WIRED they have “nothing else to add” beyond the information included in company posts.
Cloud security company Mitiga says its investigations have seen a threat actor targeting organizations using Snowflake databases and using an attack tool called “rapeflake” in the process. Roei Sherman, field CTO at Mitiga, tells WIRED one possible scenario is that a threat actor managed to get information about Snowflake’s systems and then stole information about its clients, possibly using automated tools and brute-forcing their way into accounts.
Sherman says little is known about what data was stolen at the moment or the “rapeflake” tool, but that the attack could have wider ramifications going forward. There are already early signs other companies may be impacted.
Sherman says some of Mitiga’s customers have reached out to it for help, while Mandiant told BleepingComputer it had been assisting Snowflake customers in recent weeks. Cybersecurity researcher Kevin Beaumont shared online that he knows of six companies that have been impacted. And Australian events company Ticketek has also revealed customer names and email addresses stored in a “cloud-based platform, hosted by a reputable, global third-party supplier” have been accessed, although a spokesperson refused to confirm if this was related to Snowflake at all.
“We haven’t seen the entire blast radius yet,” Sherman says. “Snowflake has thousands of clients—they offer self-registration—and some of their clients are huge companies. We expect to learn about additional companies compromised.”
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Does a Cyber Threat Hunter Do to Stop Sophisticated Threats?
In the ever-expanding world of cybersecurity, a cyber threat hunter is a vital asset to organizations seeking to defend their networks against advanced cybercriminals and malicious actors. Rather than relying on traditional, reactive defense systems that only respond after a breach occurs, cyber threat hunters take a proactive approach. They actively search for signs of unauthorized activity, potential vulnerabilities, and emerging threats within a network. By continuously monitoring systems, analyzing network traffic, and leveraging advanced techniques, cyber threat hunters aim to uncover hidden risks before they can escalate into full-blown attacks. Their role is essential in ensuring that an organization’s defenses are always a step ahead of cybercriminals, providing a critical layer of protection against the growing array of digital threats.
A Cyber Threat Hunter Actively Searches for Hidden Threats
A cyber threat hunter is proactive in seeking out hidden threats that may be lurking undetected within an organization’s network. This is a key component of their role, as many attacks are designed to evade automated detection systems by being stealthy, slow, or masked within legitimate network traffic. Unlike conventional security tools, which typically react to identified threats, threat hunters actively search for suspicious activity, scanning system logs, analyzing network traffic, and correlating data from multiple sources to identify hidden threats such as malware, unauthorized access attempts, and unusual behaviors. Through this constant vigilance, cyber threat hunters ensure that potential risks are detected and mitigated before they can cause significant harm to the organization’s infrastructure or data.
They Analyze Unusual Patterns Across Systems and Networks
One of the critical functions of a cyber threat hunter is their ability to analyze and detect unusual patterns of activity across an organization’s systems and networks. This process involves reviewing large amounts of data, including network traffic, system logs, and endpoint behavior, to spot any anomalies that could indicate a cyber threat. Threat hunters often focus on identifying deviations from normal patterns, such as unexpected spikes in traffic, unusual login times, or unauthorized system access, all of which could signal the presence of a hacker or malicious software. By identifying these abnormal patterns early, they are able to trace potential intrusions, neutralize threats, and prevent more severe consequences such as data breaches or system compromises. This constant analysis helps organizations stay one step ahead of cybercriminals.
Cyber Threat Hunters Use Advanced Tools to Detect Intrusions
To effectively carry out their tasks, cyber threat hunters employ an array of advanced tools and technologies that help them detect intrusions and suspicious activities that may otherwise evade detection. These tools include threat intelligence platforms, machine learning algorithms, and advanced endpoint detection systems, all of which allow threat hunters to analyze vast amounts of data quickly and accurately. For example, they might use network analysis tools to monitor traffic for signs of unauthorized access, or endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems to identify malware that has bypassed traditional defenses. In addition, threat hunters rely on sandboxing technologies to safely test and analyze suspicious files and activities in isolation, which is crucial for identifying novel or sophisticated threats that may not have an established signature. With these cutting-edge tools, cyber threat hunters can proactively detect and block threats, ensuring that the organization’s security measures are always up to date.
They Respond to Threats Before Damage Is Done
One of the most valuable aspects of a cyber threat hunter’s role is their ability to respond swiftly and decisively to cyber threats before they can cause significant damage. By actively hunting for threats and anomalies within the network, threat hunters are often the first to detect an intrusion or suspicious activity. Once a potential threat is identified, they quickly initiate a response to contain the issue, whether it involves isolating compromised systems, blocking malicious IP addresses, or applying emergency patches to vulnerable software. The sooner the threat is detected and neutralized, the less damage it can cause to the organization, whether in terms of financial loss, data theft, or reputational harm. Their ability to act fast in response to emerging threats helps prevent the escalation of attacks, reducing the potential for widespread damage and ensuring business continuity.
A Cyber Threat Hunter Thinks Like a Hacker to Stay Ahead
A cyber threat hunter must adopt the mindset of a hacker in order to anticipate and outmaneuver malicious actors. By understanding how cybercriminals operate, their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), and how they exploit weaknesses in systems, threat hunters can better predict and prevent future attacks. This means thinking like a hacker: using creative and unconventional approaches to test defenses, identify vulnerabilities, and simulate attack strategies. By staying ahead of evolving threats and constantly refining their skills, threat hunters ensure that they can identify new and emerging attack vectors, whether it’s through social engineering, ransomware, or advanced persistent threats (APTs). This mindset allows cyber threat hunters to anticipate the next move of cybercriminals, helping organizations prepare for, detect, and stop attacks before they can take root.
They Investigate Alerts Missed by Automated Systems
While automated security systems such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and firewalls are essential in identifying known threats, they often miss more sophisticated or novel attacks. cyber threat hunter are tasked with investigating these missed alerts, often uncovering hidden risks that traditional automated systems cannot detect. Cyber threat hunters have the expertise to investigate false positives and dive deeper into the data to identify legitimate threats that may have been overlooked. They review patterns and correlations that may not be immediately apparent and use their advanced knowledge of hacking techniques to find subtle indicators of compromise. Through this deep dive into alerts, threat hunters can identify early-stage intrusions and mitigate potential risks, ensuring that no threat goes unnoticed or unchecked, thus strengthening the organization’s defenses.
Cyber Threat Hunters Provide Insights to Strengthen Overall Security
In addition to identifying and mitigating threats, cyber threat hunter provide valuable insights that can help strengthen an organization’s overall cybersecurity posture. They continuously gather data on emerging threats, attack techniques, and vulnerabilities, which can be used to refine security strategies, policies, and defenses. These insights might involve recommending additional security tools, revising access control policies, or updating employee training on cybersecurity best practices. Threat hunters also provide actionable intelligence that helps organizations prepare for future attacks, such as understanding the latest trends in phishing, malware, or social engineering. By sharing their expertise and lessons learned from their investigations, cyber threat hunters contribute to a culture of continuous improvement in cybersecurity, ensuring that the organization is always better prepared for evolving threats.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cyber threat hunter are indispensable in today’s increasingly complex and volatile cybersecurity landscape. Their proactive approach to identifying, analyzing, and neutralizing threats before they can cause significant damage is essential for protecting organizations from the growing array of sophisticated cyberattacks. By thinking like hackers, using advanced tools to detect intrusions, and providing valuable insights to strengthen overall security, threat hunters offer more than just a reactive response to attacks—they help build a robust defense system that can stay ahead of evolving threats. As cyber threats continue to grow in sophistication, the role of the cyber threat hunter will remain crucial in safeguarding organizational data, systems, and operations against an ever-present and dynamic risk environment.
0 notes
Text
Why Cybersecurity Services Are Non-Negotiable in Today’s Digital World

Understanding Cybersecurity Services
Cybersecurity services are specialized offerings designed to protect systems, networks, programs, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, or damage. These services encompass a wide range of tools and strategies, including threat monitoring, vulnerability assessment, firewalls, endpoint protection, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and more. The core goal is to prevent cyber threats and ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
The Alarming Rise of Cyber Threats
From ransomware and phishing to data breaches and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, cyber threats have evolved significantly. Hackers target not only large corporations but also small businesses, startups, healthcare providers, educational institutions, and even individuals.
In recent years, there has been an alarming increase in ransomware attacks, where cybercriminals encrypt a victim’s data and demand a ransom in exchange for a decryption key. According to cybersecurity reports, global cybercrime damages are expected to cost $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. These figures stress the urgent need for proactive and robust cybersecurity services.
Key Types of Cybersecurity Services
1. Network Security
This involves protecting internal networks from intrusions and unauthorized access. It includes firewalls, anti-virus programs, VPNs, and IDS. Regular network monitoring helps in identifying suspicious traffic patterns and neutralizing threats before they escalate.
2. Cloud Security
With more businesses adopting cloud infrastructure, securing cloud assets becomes paramount. Cloud security services protect applications, data, and workloads hosted in cloud environments using encryption, identity access controls, and configuration management.
3. Endpoint Security
Every device connected to a network—laptops, mobile phones, desktops—is a potential entry point for attackers. Endpoint security ensures these devices are protected using antivirus software, device encryption, and remote monitoring tools.
4. Application Security
This focuses on identifying and resolving vulnerabilities in software applications. It includes code reviews, penetration testing, and securing APIs to prevent unauthorized access and data leakage.
5. Managed Security Services (MSS)
Many businesses outsource their security operations to specialized firms known as MSSPs. These providers offer 24/7 monitoring, incident response, vulnerability management, and compliance reporting.
6. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
SIEM tools collect and analyze data from various sources to identify unusual activity. They enable real-time threat detection, forensic analysis, and compliance auditing.
Importance of Cybersecurity for Businesses
The impact of a successful cyberattack can be catastrophic. Beyond financial losses, businesses face reputational damage, legal consequences, operational downtime, and loss of customer trust. Cybersecurity services offer:
Protection of sensitive data: Personal, financial, and intellectual property data are prime targets for hackers. Cybersecurity ensures this data is encrypted, stored safely, and only accessible to authorized users.
Compliance with regulations: Industries like healthcare, finance, and e-commerce are subject to strict data protection laws (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS). Cybersecurity services help businesses remain compliant and avoid penalties.
Business continuity: In the event of a cyber incident, rapid detection and response minimize damage, enabling the business to resume operations quickly.
Customer confidence: Demonstrating strong security measures builds trust with customers and stakeholders, enhancing brand reputation.
Challenges in Implementing Cybersecurity Services
While cybersecurity is essential, implementing effective strategies poses several challenges:
Lack of awareness: Many small and medium businesses underestimate cyber risks or assume attackers won’t target them.
Skill shortage: There’s a global shortage of cybersecurity professionals. Recruiting and retaining talent remains difficult.
Complex infrastructure: With hybrid work models and multi-cloud environments, managing security across different platforms becomes complex.
Constantly evolving threats: Cybercriminals are always innovating. Traditional defenses may become obsolete quickly without regular updates.
Cybersecurity Trends to Watch
1. AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
Artificial Intelligence helps automate threat detection, analyze large volumes of data, and improve incident response times. Machine learning models can detect previously unknown threats based on patterns and anomalies.
2. Zero Trust Architecture
Zero trust follows the principle “never trust, always verify.” It assumes every access request is a potential threat, requiring strict identity verification and access controls at all levels.
3. Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
XDR unifies multiple security tools across endpoints, networks, and cloud environments. It offers integrated threat detection, investigation, and response capabilities.
4. Cyber Insurance
More companies are opting for cyber insurance to mitigate the financial impact of cyberattacks. However, insurers now require companies to demonstrate adequate cybersecurity controls before providing coverage.
Choosing the Right Cybersecurity Service Provider
Selecting a cybersecurity partner is a strategic decision. Here are a few key factors to consider:
Expertise and certifications: Choose providers with certified professionals and proven expertise across different domains.
Scalability: Ensure their services can grow with your business needs.
Customization: Avoid one-size-fits-all solutions. Opt for tailored services based on your industry and threat landscape.
24/7 monitoring and support: Threats don’t sleep, and neither should your cybersecurity defenses.
Incident response capability: A good provider should offer not only prevention but also post-incident response and recovery.
Cybersecurity Is Everyone’s Responsibility
While service providers play a major role, cybersecurity should be embedded in company culture. Employee training, secure password practices, two-factor authentication, and phishing awareness go a long way in minimizing risks.
Regular audits, data backups, patch management, and cyber hygiene protocols should be part of your business’s digital operations. Remember, the weakest link in cybersecurity is often human error.
Conclusion
In an era where data is the new gold, protecting it is not optional—it’s imperative. Cybersecurity services act as the fortress guarding your digital assets from a world of invisible threats. Investing in cybersecurity is not just a cost—it’s a long-term strategy for sustainability, growth, and trust.
Secure your business before a cyberattack forces your hand. Contact our expert team today to schedule a free cybersecurity assessment and build a tailored defense strategy that protects your future.
0 notes
Text
How Employee Extensions Become Entry Points for Security Threats
In this blog, we’ll walk you through how these threats work and give you some friendly advice to keep your business safe. Don’t worry, we’ll keep it simple and real. Almost one thing many companies forget is how everyday tools like employee extensions, those short numbers we use to call coworkers, can give hackers an easy way in.
How Extensions Can Open the Door for Threats
Social Engineering: A Common Exploitation Method
One of the easiest ways hackers exploit extensions is through social engineering. They may pretend to be a coworker or IT support, using familiar extensions to build trust. This method might not involve breaking any firewall, it’s just clever manipulation.
VoIP and Extensions: Easy to Misuse
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) systems are super convenient but also easy to fake. Hackers can create numbers that look just like yours. Even a call from a known number might not be legit. Some hackers even mimic voices.. They may also send files or links, asking you to open them. One click, and your company’s entire network could be at risk.
Social Media Makes It Easier for Hackers
We all love staying connected on LinkedIn, Facebook, or Instagram. But guess what? Hackers do, too. They use these platforms to learn about your job, your coworkers, and your role. Here’s where scams mostly happen:
Social Media PlatformSocial Media PlatformScam Reports (%)LinkedIn52%Facebook29%Instagram11%Twitter/X08%
(Source: Norton Cyber Safety Pulse Report, 2024)
When hackers use this info along with fake extensions, it becomes much easier to trick employees.
Simple Tips to Keep Your Business Safe
Always Double-Check
If something feels off, even slightly pause. Double-check the request by calling back or using your internal chat. Our team once used a voice verification tool to confirm a strange request. It saved us from a potential breach.
Keep Your Team in the Loop
Training shouldn’t be a one-time thing. Regular reminders and friendly updates help everyone stay sharp:
Check who’s calling
Don’t share passwords over the phone
Speak up if something seems odd
You should always confirm unknown calls. You must avoid giving private info. And you ought to report anything unusual.
Restrict Access and Monitor Usage
Only give extensions to those who truly need them. Audit logs regularly. If someone’s using an extension outside of work hours or from an unusual location, investigate immediately.
Clear policies help:
Admins are expected to monitor call logs.
Employees can request extension deactivation during leave.
Security officers must review access monthly
Keep Work and Personal Devices Separate
Ideally, give staff separate devices. If not, set up two profiles one for work, one for personal use.
And don’t forget:
Keep devices updated
Use secure connections like VPNs
Let’s Build a Safer, Smarter Workplace
Create a workplace where people are encouraged to be careful. Make it normal to pause and verify. Reward people who catch things early.
Here are some ideas:
Have a monthly Cyber Safe Day
Share stories of close calls
Appreciate team members who report issues.
Conclusion:
Employee extensions are handy, but if they’re not managed well, they can be risky. You can avoid most problems by being alert, using smart tools, and keeping your team informed. In short, employee extensions can be a backdoor for cybercriminals if ignored. With rising threats and smarter scams, we must stay alert, be proactive, and educate our teams. By applying secure communication protocols and train your teams on a regular basis, you’ll turn your employee extensions into your first line of defense rather than your weakest link.
0 notes
Text
How to Choose a Safe and Reliable Bitcoin Mixer: A Deep Dive into JokerMix.to
In an era where digital surveillance is tightening and blockchain transactions are increasingly traceable, privacy-conscious cryptocurrency users are turning to tools like Bitcoin mixers and Bitcoin tumblers. These tools promise to break the link between sender and receiver, giving users a layer of anonymity in an otherwise transparent environment. JokerMix.to is one such platform that claims to offer secure and anonymous Bitcoin and Dash mixing.

But how do you choose a safe and reliable Bitcoin mixer?
Is JokerMix.to worth trusting with your crypto? Let’s take a closer look at what makes a mixer trustworthy, how JokerMix.to performs, and what to watch out for in this high-risk space.
What Is a Bitcoin Mixer or Bitcoin Tumbler? A Bitcoin mixer, also known as a Bitcoin tumbler, is a privacy tool used to obscure the source of cryptocurrency. Due to the public nature of blockchain ledgers like Bitcoin, every transaction is traceable. While your identity may not be directly attached to your wallet, with enough data, third parties (including law enforcement and advertisers) can piece together who you are.
Bitcoin mixers break the transaction trail by mixing your coins with other users’ coins and then redistributing them, often in smaller, randomized amounts, to new addresses. This process makes it significantly harder to determine where the coins originally came from.
Why Use a Bitcoin Mixer Like JokerMix.to? Some of the most common reasons people use Bitcoin tumblers include:
Privacy: Not everyone wants their financial activity exposed to the world.
Security: Obscuring funds helps avoid being targeted by hackers.
Business Transactions: Companies that deal with sensitive clients often require anonymous payments.
Whale Movements: Large investors (whales) might not want to spook the market.
JokerMix.to claims to provide a mixing service with advanced privacy options. It uses CoinJoin technology, promises no-logs, and offers letters of guarantee for every transaction. But are these claims enough?
Core Features to Look for in a Bitcoin Mixer Before you entrust your Bitcoin to any mixer, including JokerMix.to, consider these essential features:
Anonymity Protocols A reliable mixer must use strong privacy protocols. CoinJoin, time delays, and randomized output addresses all help enhance anonymity. JokerMix.to advertises support for these techniques.
No-Log Policy Logs are liabilities. The best mixers claim they do not store transaction data. JokerMix.to says it deletes logs automatically after transactions are completed.
Letter of Guarantee This is a signed message from the service, proving it will send your coins to the destination address you provided. It’s your only assurance if something goes wrong. JokerMix.to provides this as part of its security protocol.
Multicurrency Support While many mixers only handle Bitcoin, JokerMix.to supports both Bitcoin and Dash, which gives users flexibility.
User Interface Even a high-tech mixer should be easy to use. JokerMix.to has a simple web interface and even provides a .onion address for Tor browser users who want an extra layer of privacy.
Evaluating JokerMix.to Based on These Criteria
Reputation Reputation is everything in the world of Bitcoin mixers. JokerMix.to has mixed reviews across different crypto forums. Some users report successful transactions, while others claim to have faced issues with missing funds or unresponsive support.
Transparency Unlike some established mixers, JokerMix.to does not provide full transparency about its team, origin, or regulatory compliance—common in the mixing industry but worth noting.
Support Options JokerMix.to offers an email-based support system, which is better than nothing, but in such high-stakes operations, slow or limited support can be a deal-breaker.
Availability The platform works on both clearnet and dark web through a Tor mirror. This dual access is a plus for privacy-focused users.
Common Risks of Using Bitcoin Tumblers Despite their appeal, Bitcoin mixers are not without risks. Here’s what you need to be aware of:
Exit Scams Unfortunately, this industry is notorious for services disappearing with users’ coins. Since you’re trusting a third party with your funds, you risk being scammed.
Fake Mixers Many scam websites mimic legitimate mixers to defraud unsuspecting users. These sites may have similar interfaces, fake reviews, or even cloned designs.
Legal Implications In some jurisdictions, using Bitcoin tumblers can be seen as aiding money laundering. It’s essential to know your local laws before using any privacy tool.
Centralized Control If the mixer is centralized, it controls the coins during the mixing process. If the operator turns malicious or gets hacked, your funds could vanish.
How to Use JokerMix.to Safely (or Any Mixer) If you decide to use JokerMix.to, follow these steps to minimize risk:
Start Small: Always test with a small amount before mixing large sums.
Use a VPN and Tor: Combine privacy tools for layered anonymity.
Check the Letter of Guarantee: Save it as proof in case something goes wrong.
Watch for Red Flags: Poor grammar, broken links, or no support can signal scam sites.
Diversify: Use different mixers over time to avoid putting all your trust in one service.
Alternatives to JokerMix.to If you’re not sure about JokerMix.to, consider alternatives like:
Wasabi Wallet (for CoinJoin transactions)
Samourai Whirlpool
MixTum.io
InstaMix
These alternatives use similar principles but vary in execution, transparency, and security.
JokerMix.to: Final Verdict Is JokerMix.to a scam? At the time of writing, there is no conclusive evidence proving that it is outright fraudulent, but the lack of transparency and mixed reviews should make users cautious. It operates in a gray zone, like most Bitcoin mixer platforms, and places a heavy burden on users to do their own due diligence.
If you value privacy and understand the risks, JokerMix.to may be a tool worth trying—with small amounts and proper safeguards. But never trust any mixer with more than you can afford to lose.
Conclusion: Privacy Tools Are a Double-Edged Sword The cryptocurrency space is filled with innovation, but also risk. Bitcoin tumblers like JokerMix.to offer a valuable service to those who need anonymity in a transparent world. However, they also operate in unregulated environments with minimal recourse in the event of scams or errors.
Before using any Bitcoin mixer, including JokerMix.to, ask yourself:
Do I understand the risks?
Am I legally permitted to use this tool?
Have I tested it with small amounts first?
With the right precautions, mixers can be powerful privacy tools. Without them, you might end up trading your coins for a cautionary tale.
1 note
·
View note
Text
White Hat vs. Black Hat Hacking: More Than Just a Color Code 🎩🖤
Hacking isn’t all hoodies and neon code—there’s a spectrum of intent and methodology. In 2025, understanding the difference between white hat and black hat hacking is critical for anyone diving into cybersecurity or ethical hacking. Here’s the breakdown:
1. White Hat Hackers (Ethical Heroes) 🕵️♂️
Primary Goal: Improve security by finding and fixing vulnerabilities.
Permission: Always operate with explicit authorization from the system owner.
Tools & Techniques: Penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, secure code reviews.
Outcome: Patches applied, systems hardened, organizations protected.
Career Path: Security consultant, penetration tester, bug bounty hunter.
2. Black Hat Hackers (The “Bad Guys”) 🦹♂️
Primary Goal: Exploit weaknesses for personal gain or sabotage.
Permission: None—illegal access and activities.
Tools & Techniques: Malware deployment, ransomware, phishing campaigns, data breaches.
Outcome: Stolen data, financial loss, reputational damage.
Risk & Consequences: Criminal charges, fines, and imprisonment.
3. Grey Hat Hackers (The Ambiguous Middle) ⚪⚫
Intent: Mix of white and black hat motivations—might expose flaws without permission, then recommend fixes (often for a fee).
Ethical Standing: Legality is murky—actions can be illegal despite good intentions.
Use Cases: Corporate security audits without full authorization, “friendly” vulnerability disclosures.
4. Key Differences That Matter
AspectWhite HatBlack HatGrey HatAuthorizationExplicit, legalNone, criminalOften unauthorized, but sometimes reportedIntentImprove securityPersonal gain or disruptionMixed—ethical curiosity vs. profitOutcomeSafer systemsData theft, damageFlaws revealed, but potential legal riskReputationRespected professionalCriminalControversial
5. Why It’s More Than a Color Code
Ethics & Legality: White hats follow a strict code of conduct; black hats violate laws.
Trust & Career: Ethical hacking roles require certifications (CEH, OSCP) and proven track records.
Impact on Cybersecurity: White hats help organizations stay one step ahead of black hats, closing loopholes before they’re exploited.
6. Becoming a White Hat Hacker
Learn the Fundamentals: Networking, system administration, and scripting.
Master Security Tools: Kali Linux, Metasploit, Burp Suite, Wireshark.
Get Certified: CEH, CompTIA Security+, OSCP.
Build Experience: Participate in bug bounties, CTF challenges, and open-source security projects.
Final Thoughts
White hat and black hat hacking represent two sides of the same coin—one defends, the other attacks. As cyber threats grow in complexity, the role of ethical hackers becomes more vital. Choose your “hat” wisely: white hat hacking isn’t just a career choice; it’s a commitment to protecting our digital world.
0 notes