#and a C02 set up!!!! SO THESE PLANTS CAN BE RED!!!
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
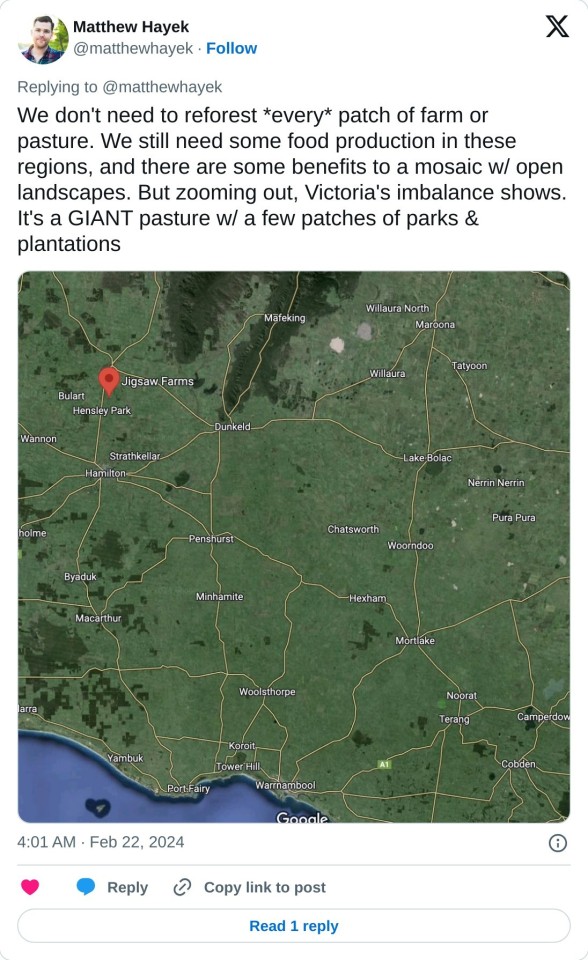
Mark Wootton and his wife, Eve Kantor, were the carbon-neutral pioneers of Australia’s red meat industry.
Years before the Paris agreement to keep global heating below 1.5C, and a decade before the Australian government committed to reaching net zero emissions, their family farm in south-western Victoria was declared carbon-neutral.
“In the early 2010s we were pretty cocky that we had conquered this thing,” Wootton says. “We thought we’d cracked the formula.”
Jigsaw Farms, a mosaic of lush pastures, eucalypt plantations, wildlife corridors and wetlands about 250km west of Melbourne, near the town of Hamilton, was the envy of the industry. It was lionised by the media, a favoured photo opportunity by politicians and held up by the red meat sector as a vision of the future.
The farm’s carbon-rich soils, 20% of which were forested, sequestered enough CO2 to offset its annual emissions from wool, lamb and beef production.
Or at least it did. The latest report tracking Jigsaw’s emissions, which is now undergoing peer review, confirmed that since about 2017 – the same year the industry body Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA) announced a target of net zero emissions by 2030 – Jigsaw Farms has been emitting more greenhouse gases than it could sequester.
“Cows and sheep are still there producing the same amount of methane [every year], but the trees grow up and carbon sequestration slows down,” says the report author, Prof Richard Eckard.
Eckard is an agricultural economist and the director of the school of agriculture, food and ecosystem sciences at the University of Melbourne. He became involved in measuring Jigsaw’s emissions a decade ago.
The 3,378-hectare farm spans six titles, bought by Wootton and Kantor between 1996 and 2003. Hardwood timber plantations cover 295 hectares, 24 hectares is remnant forest and a further 268 hectares are set aside for biodiversity. It hosts a fine wool merino operation with about 20,000 ewes, and 550 head of cattle.
Initially, the hundreds and thousands of trees they planted, combined with a switch to perennial grasses, significantly increased the amount of carbon sequestered on the property.
But those trees have now matured and passed peak sequestration, meaning they absorb less C02 year-on-year, and the soil is so carbon rich it can’t sequester any additional C02 from the atmosphere.
“Ten years later it all slows down because carbon saturation,” Eckard says. “It’s just the law of diminishing returns.”
The latest Jigsaw study estimated that in 2021, the farm sequestered 70.3% to 83.2% of its annual emissions. By 2031, as the farm’s forests grow older, models predict it will absorb just over half of what it did when carbon sequestration peaked in 2012.
The dilemma Jigsaw now faces reflects the broader challenge of decarbonising Australia’s red meat industry, Eckard says.
The industry claims it has reduced its emissions by 65% compared with 2005 levels, but this reduction relies on recorded decreases in deforestation and increases in forest regrowth, which some analysis suggests is overstated.
“Carbon sequestration through forestry is a short-term buy out of trouble,” Eckard says. “You can plant your way out of trouble and, like Jigsaw, get seven years of net zero, but ultimately, unless you do something about the methane, you’re not going to stay net zero.”
Climate neutrality v the ‘seaweed solution’
Other efforts to reduce the industry’s carbon footprint have focused on attempting to reduce the amount of methane expelled from the rumen, which accounts for 80% of the sector’s emissions. MLA has put more than $180m towards the problem, with no solution forthcoming. The results from the longest running commercial trial of a seaweed cow-feed, which aimed to cut methane by more than 80%, were lacklustre.
Selective breeding and dietary changes can help, says Eckard, but it’s slow going.
“It took the animal 50m years to evolve to produce meat and eat grass the way it does,” he says. “That can’t be overcome in three-year funding rounds.”
But he says that if producers adopt current best practices that will reduce their emissions intensity per kilogram of meat produced while research finds the “seaweed solution”.
On Jigsaw Farms, high reproductive rates, fast-growing livestock due to genetic selection and ample feed, and grazing stock at double the density of other farms in the district helps reduce the emissions that go into producing each animal.
“If that lamb or calf grows faster, so it gets to market quicker, so it grows faster, so, to be brutal, it can die and be eaten – your carbon intensity is dropping,” Wootton says.
This allows Jigsaw to sell its wool, lamb and beef at a premium in a market that is increasingly looking for farmers who can demonstrate strong environmental credentials.
This is particularly important for the export-focused Australian market, Eckard says. Seventy per cent of Australian-grown beef is sold into global supply chains ruled by international corporations, all of whom have net zero targets.
That’s the impetus behind the MLA’s “world leading” net zero target. This month Guardian Australia reported that the industry body described the target as “aligning the industry” towards improvement and said it did not need to be met, though it remains committed to the goal. Environmental scientists say reporting on the goal is based on unreliable land clearing data.
David Jochinke, the president of the National Farmers Federation, says the target is about the “aspiration” towards decarbonisation.
“We’ve always said at the NFF, we’re not going to reduce production in an attempt to get to net zero,” he says. “Will we make it? I’m not really sure, but we are going to give it a red hot go.”
A 2023 CSIRO report found the industry would fall short of the net zero goal and recommended a “climate-neutral” target be adopted instead, which would theoretically be achieved by reaching a point where the sector no longer causes any additional warming to the planet.
Australia’s peak cattle body, Cattle Australia, has also called for a shift to climate neutrality. But both Eckard and Wootton say the industry shouldn’t change course.
“I fear that if the industry fiddled with the metric what they would be effectively saying is ‘methane is no longer an issue so we don’t have to worry about it’,” Eckard says.
The director of the Australian National University Institute for Climate, Energy and Disaster Solutions, Mark Howden, says that unachievable or “false [climate] targets” are ineffective and can alienate both industries and the public.
He says the red meat sector’s goal is “in a sense the wrong target���. “We do need to go net zero in terms of C02, but in the case of methane we need to reduce it by about two-thirds in the long term to effectively meet the Paris agreement,” he says.
Wootton says the benefits of their regenerative approach to farming persist even if the farm’s carbon accounts are now in the red.
They did not initially set out to be carbon-neutral. The timber plantations were established on Jigsaw Farms to offer an alternative source of income. They planted permanent native vegetation to encourage biodiversity and shelter belts to protect livestock, and dug deep dams so they would always have a secure water supply.
A bird survey in 1996 found 46 bird species on the land. Today, there are 174. The land is healthier – that is, ironically, why carbon sequestration has stabilised.
“People come to us and go, shit, if they can’t go carbon-neutral, what does that mean for us,” Wootton says.
“It means you’ll have to do some of what we’ve done, do things differently from what we’ve done, and do some other things that we don’t even know we can do yet.
“There’s no silver bullet here, but there’s some silver buckshot, hopefully.”






10 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey! I just found your blog and i think its great
I'm working on a 20 long native Virginia biotope for a while now and was wondering if you had any recommendations for plants or snails I could try, right now I have hornwort and ludwigia repens along with some type of local moss I was able to grow aquatically :) for fish im either thinking fiery red or saffron shiner or bluespotted sunfish
Oh! A person after my own heart. Lots of options depending on what sort of set up you have and how much energy you want to put in.
Let's start with plants. If you have low lights and no C02 set up, then I would most highly recommend our native bladderworts. They grow quickly, require very little fuss, and are pretty interesting. Some of our local potamogeton pondweeds will work as well - we have a number of species so it's all about what you can find. I've had hit or miss luck with vallisneria in low light tanks but have had fantastic luck with good LEDs and do-it-yourself C02. In those kind of tanks, I find anacharis and hydrilla also do great.
As for snails, I think it's worth trying whatever you can find. I've had great luck with Planorbis and Physa species, and okay luck with Bithynia. I really only recommend against Chinese Mystery Snails, which are very destructive towards plants. But even those could be fun in the right hardscape.
We have a lot of smaller fish that would be great choices. I can personally vouch for Tesselated Darters, Banded Killifish, Mummichogs, Eastern Mudminnows, and Bluespotted Sunfish. All are fun, hardy, and peaceful - though a few of those can be shy. I feel like Eastern Mosquitofish get a bad reputation... I've had mine in a 55 for 2 years with no aggression at all. Banded Sunfish are another great choice, but avoid the locally imperiled Black Banded Sunfish. I'm undecided about any of our local minnow species here as they are all either too big or too active to be truly happy in a 20 gallon I think.
If you wanted to try a brackish biotope, we have a few cool Gobiosoma spp. Gobies that I'm tempted to try. Mummichogs, Eastern Mosquitofish, some gobies, and a handful of glass shrimp would be a very fun tank! Rainwater Killifish would also be fun if you can find them. We have some local blennies I don't know much about but could also be fun to investigate.
6 notes
·
View notes
Link

New Zealand schools have introduced a climate change resource that suggests children “eat less meat and dairy”, even though teachers will not know how much meat or dairy any child in their care has eaten. Opinion pieces in the papers have called for the reduction of meat and dairy in hospital menus, not usually generous sources of such foods, despite the well-known risks of undernutrition, especially of protein, in the frail and elderly. Globally, the influential and once-objective medical journal the Lancet has hosted Eat Lancet, a coalition of vegan and vegetarian technocrats backed by processed food manufacturers, and promoted their agenda. The Guardian newspaper accepted an £626783 grant from the backers of Impossible Foods to run a series of articles against animal agriculture.
These initiatives, aimed at remodelling our food supply in a way that favours the multinational food processing and seed-and-chemical corporations, whose control of many aspects of farming and diet is already problematic, have run far ahead of the scientific community’s efforts to understand the health effects of such dietary change.

Our hunter-gatherer past
The Neolithic Revolution was the first alteration in human affairs that is generally considered worthy of the term Revolution. In Marx’s terms, it saw a change in the means of production sufficient to form new classes aware of their identities, and thus a change in the relations between people. Early humans had fed themselves in an opportunistic, hunter-gatherer fashion that tended to favour a diet of animals supplemented with plants where and when these were available. Large animals made the best meals but gathering activities could collect many smaller ones, as well as eggs, grubs etc.
The people of the Mesolithic era discovered that some animals could be herded and some plants grown in gardens (not usually by the same community, because one activity favours nomadism and the other favours a sedentary habit) but these activities, which greatly improved food security after the decline of the prehistoric mega-fauna due to hunting and climate pressures, tended to occur at the communal level and probably did not create major class differences between the people involved.

The invention of farming
The Neolithic Revolution, which unleashed the human potential for war, creativity, and social division, resulted from the identification of the germs of plants (specifically grains and legumes) as durable sources of energy. If grains were grown (I will use grains in the wider sense of “cereals”, after Braudel, including other dried germs such as peas) and there was a surplus, this surplus would still be edible over the next year, a year when drought or pests or diseases might wipe out the other food sources that hunter-gatherers depended on. This advantage was offset by the nutritional poverty of grain-based diets, so that tuberculosis probably became an endemic disease during this period,[1] but the existence of a less-perishable surplus allowed the diversion of part of the population away from food gathering for large parts of the year, and saw the creation of armies and other workforces.
In Europe, the Neolithic Revolution is dated at around 10,000 BC and its arrangements are a matter of prehistory, but in China this change occurred later and the written record around Bi-gu or grain avoidance includes folk-memories of conflict between grain eating and grain avoiding peoples.
The history of colonisation is the history of the conquest of lactose-intolerant peoples by lactose-tolerant populations, and of non-grain eaters by grain-eaters. In the Indian sub-continent, a combination of dairy herding and a cereal diet high in legumes uniquely allowed the survival of a substantially vegetarian population, and saw the conservation of genes favouring reproduction on such a diet, including genetic polymorphisms still rare in European populations (adaptive mutations only predominate where many individuals without them have failed to survive or reproduce).[2] That the Indian social system became more aggressively class-based than any other is probably no co-incidence; prejudice against meat-eating is still used as a tool of social control against minorities, while meat-eating is one way young Indians today identify as modern and egalitarian. However there were some important exceptions to the trend – the Aztecs were a hunter-gather people who conquered and dominated the Mesolithic agriculturalists of Mexico, and the Mongols were nomadic herders and hunters whose greater stamina and independence allowed them to defeat the rice-fed armies of the Chinese Emperors (after conquering this breadbasket, the successive Mongol Khans seem to have eaten and drunk themselves to death).
Early vegetarian ideology
In the European and Asian cereal-based societies the poorest classes went without meat, supplementing cereals when possible with buttermilk or blood pudding which were more economic replacements. The rich ate as much meat as they could. The idea that an entire society might avoid meat is a recent one with its roots in religious practice, and, insofar as it has any political basis, this flows in two distinct streams – the eco-fascist, in which meat avoidance is a sign of “purity”, most humans are a burden on the Earth, and the Indian vegetarians are of course Aryans. This is something like the vegetarian vision that Adolf Hitler picked up while studying anti-Semitism with Wagner’s heirs at Bayreuth.
And then there is a Marxist-Anarchist, and latterly Intersectional, version, founded on a valuation of animal rights as inseparable from, and a logical extension of, human rights. Vegetarianism was a frequent obsession of the early British Socialists; G.B. Shaw, who derived most of his energy from dairy fat and lived to the age of 94, made himself into a well-known example, and the idea was sufficiently entrenched among the British Socialists and their milieu that H.G. Wells preserved its internal contradictions for posterity in The Time Machine. In his far-future vision, humanity has evolved into two separate species. The Morlocks are descendants of working-class meat-eaters, the Eloi of leisure-class vegetarians – all Wells’ loathing is reserved for the Morlocks, yet it is obvious they are (still) the engineering brains keeping their world running and the Eloi fed. The Eloi are useless for anything but enjoying the sunshine and feeding the Morlocks, and the discordance in Wells’ progressive values as he describes both species is as shocking as anything else in the story.
The first large-scale experiment in plant-based protein was attempted by the Bolsheviks. As usual, it’s hard to separate the roles played by idealism and cynicism in the story, but the bare bones are that the Soviets found their initial attempts to remodel the countryside rebuffed, blamed this on the recaltricance of the kulak class, and set out to destroy them. The problem being that the kulaks, owning most of the cattle and sheep across the Russian Republics, helped to feed the people. Beginning in the 1920s, soy experts from the USA (then the Western world’s leading soy producer) were among the many foreign technicians imported into Russia, and soy processing plants were built and soy production increased to 283,000 tonnes in 1931, the year Stalin unleashed enforced collectivisation and the terror against the kulaks (and also the Kazakhs, a herding people who suffered the largest proportionate loss of life during this period). This led to the loss of millions of animals, either killed by their dispossessed owners or mismanaged by their inexperienced new owners. The soy project was hardly able to prevent the massive famines that followed, and by 1935 soy production had dropped to 54,000 tonnes. Though soy milk would later prove useful during the siege of Leningrad, by the 1930s soy had probably only served one purpose, as a statistic needed aforehand to quell the objections of pragmatic delegates to the destruction of the kulaks and their livestock.
Today we face the revival of this idea, of plant protein that will create a world with no need for animal protein, and the remodelling of life in the countryside, with the new impetus of climate change as its driver. Livestock cycles natural carbon, meaning there is no net addition of C02 to the atmosphere – and its contribution to the shorter-lived methane precursor has not changed since 2000 (methane rises have been due to fracking, methane itself AKA “natural gas”, landfill, and rice production; methane-emitting animals have always existed on Earth in substantial numbers, and have not created a novel situation in the sense that the discovery of coal, oil and gas did). We have recently seen how much global disruption is required to reduce fossil fuel CO2 emissions to 2006 levels, levels which will still warm the planet if they continue. It could be still be worth reducing agricultural cycling of CO2 through methane, which is more warming than CO2 if this is cost-free, but is it?

Why humans evolved as meat eaters
Animal foods, and especially red meat, supply a constellation of nutrients not found together (if they are found at all) in any plant food. Nutrients are those chemicals essential for the functioning of the human organism, and plants, but not livestock, can survive well without nutrients such as amino acids, fatty acids, vitamins and minerals that are essential to humans. Surviving as a vegetarian or vegan is possible for some (perhaps assuming the genetic variants referred to earlier are present) but to thrive requires knowledge of these nutrients, where to find them, how to process the foods that supply them, or how to supplement them. Thriving as an omnivore or even a complete carnivore does not – nutritional sufficiency is the reason we evolved eating meat and other animal foods long before we learned there were such things as essential nutrients.
The reasons for avoiding meat or all animal foods can have a class basis – veganism may be taken up by educated middle-class adults, more likely to be exposed to “health food” ideas and aware of the need to supplement, some of whom then commercialise their habits as social media “influencers”. Meat avoidance is also being adopted increasingly by educated middle-class children for identity or compassionate reasons, but the poor may also avoid meat because of its cost when a loaf of bread or a packet of flavoured noodles can be bought for a dollar; these two motivations sometimes coincide when students in temporary poverty make a virtue of what they perceive to be a necessity.
Does the meat-avoiding behaviour of young people have unintended costs? Several observational studies have looked at the characteristics of meat-avoiding populations and found alarming increases in depression, anxiety and self-harm.
“The majority of studies, and especially the higher quality studies, showed that those who avoided meat consumption had significantly higher rates or risk of depression, anxiety, and/or self-harm behaviors. There was mixed evidence for temporal relations, but study designs and a lack of rigor precluded inferences of causal relations. Our study does not support meat avoidance as a strategy to benefit psychological health.”[3]
How can we explain these correlations? Why should we assume that they are causal?There are several lines of evidence to support a causal link: 1) several nutrients found in meat and animal foods are important factors in mood and cognition; vitamin B12, iron, carnitine, DHA, choline and tryptophan are some examples.[4] 2) the fatty acid mix in dairy and red meat has a similar composition to that of amniotic fluid and breast milk which has anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effects in young animals.[5] 3) soy is a convenient and cheap replacement for animal protein; soy processing in Western diets results in a 10-fold higher level of the estrogenic contaminant isoflavone than that found in Asian diets.[6] Soy isoflavone causes anxiety behaviour in young female animals, and there is evidence supporting psychotropic and hormonal effects in humans.[7,8,9.10] Interestingly, while right-wing critiques of soy eating focus on effects it can have on young men, the scientific evidence for adverse effects in younger females, converting to HRT-like benefits after menopause, is stronger.[11] 4) other toxins found in plants, such as salicylates and oxalates, as well as problematic proteins such as gliadin/gluten and zein, may be present at higher levels in meat-free diets (but are not unique to them). A vegan mince sold in Countdown supermarkets is simply a coloured blend of soy protein and gluten, a protein linked to the risk of schizophrenia.[12] In the New Zealand context it would be relatively easy to confirm or dispute some of these associations. Everyone admitted to hospital for longer than a day supplies their dietary preferences. The dietetic preference data from psychiatric admissions could be both linked to outcomes over time and compared with the population average distribution, or the distribution in a ward where diet is least likely to play a role in admissions.
Iron deficiency in women
Young women in New Zealand are the most likely to report being vegan or vegetarian in surveys, as elsewhere in the world. Vegans in the Gender Studies field generate papers linking meat to masculinity, with the implication that this masculinity is toxic and might be improved by a plant-based diet.[13] The corollary of this belief – that women may therefore be weakened by meat-avoidance – is never considered. In a 1980 essay by Gloria Steinem called The Politics of Food (in the collection Outrageous Acts and Everyday Rebellions) she describes some of the cultural constructs by which women are deprived of the good nutrition which men use to stay dominant. The belief that men need to eat red meat more often than women may have been valid when the average man was more likely to have to survive an attack by a wild bear than the average woman, but today it is mainly women who suffer from serious iron deficiency. The rate – and the cost to the health system – is increasing in New Zealand as more women give up meat. Iron deficiency anaemia in early pregnancy is associated with neurodevelopmental disorders in children, not an outcome that will increase the mother’s autonomy.[14]
In Georg Büchner’s 19th century “working class tragedy” Woyzeck, filmed by Werner Herzog with Klaus Kinski in the leading role and the subject of an opera by Alban Berg, the title character, a soldier, is subject to experimentation by a sadistic army doctor. The experiment involves Woyzeck living on nothing but peas. Peas may supply a complete protein, but Woyzeck goes insane; the deprivation being the final straw in his alienation. James Cameron, the film-maker responsible for Avatar and Titanic, is investing heavily in pea protein as if this were his gift to New Zealand. I am not sure whether he has watched Woyzeck – one would think he has.
Plant-based vs meat-based
Again, we have the specificity of plant germs as commodity; their low cost of production, long storage life and versatility of processing outcomes makes them an ideal investment and a robust one, as poverty and adversity increases their consumption, as we saw during the 2020 Lockdown Event. However, a plant-based burger is nutritionally greatly inferior to a meat burger, and that burger is often the most nutritious single food item many will people eat in the course of their day. The current push to eat a plant-based diet for “planetary health” is something that all the multinational food processors have signed up and provided funding for, and why not – Coca Cola, Unilever, Nestlé have always sold us plant-based foods. We notice that while iron-deficiency anaemia increases in New Zealand with the reason in plain sight, Nestlé scientists here in NZ are developing a more potent form of supplemental iron to add value to their products as their parent company backs the push to reduce meat. (As usual, it’s hard to separate the roles played by idealism and cynicism in the story). But, you may well ask, isn’t eating meat linked to an increased risk of cancer and heart disease? These associations are small to begin with, but they are also intensely confounded by social class and educational status. Supposing a factory that makes a carcinogenic chemical is hiring. Who is more likely to apply for that job – a meat eater (who will likely have a bigger family to support, among other considerations) or a vegan? Who, so to speak, eats all the pies, and needs food that is filling and nutritious without having to give it much thought? Who is more likely to work two jobs and be exposed to the disruptive metabolic effect of shift work? Carcinogen exposure and shift work are just two of the confounding variables ignored in diet epidemiology. (That meat-eating in Western populations may symbolise or associate with labour itself – as it did for H.G. Wells when he wrote The Time Machine – is not a consideration I have found discussed in the epidemiological literature.)
Certainly one can think of mechanisms that might link meat to disease, as one can with any food, but one can also think of protective mechanisms; several of the nutrients found mainly or only in animal foods are required for various antioxidant and immune defensive enzymes, and some like carnitine and EPA even have a place in the management of heart disease. The argument against meat-eating should not be confused with the argument for sometimes rationing a valuable food that is in short supply. The wartime rationing of meat in the UK is thought to have improved the health of the poorest by guaranteeing a greater supply than they had had previously, at a more affordable price. In Europe, the peasants who supplied the cities with meat, dairy and luxury foods such as oysters were sometimes forced by network disruptions to consume these foods – which many of them had never tasted before – with benefit to their own health.
The plant-based agenda can scarcely be expected to recognise these benefits, or understand the argument summarised by Williams and Dunbar (with regard to the vitamin nicotinamide and amino acid tryptophan in their tuberculosis paper), that if better data collection and analysis resulted in us ”…returning to our egalitarian past and redistributing meat or its components that supply NAD (avoiding both the highs and the lows between individuals and over individual lifetimes) [this] may be more effective than subsidizing corn grain (while the increased prosperity from unlocking human potential should pay for the intervention).”[1] Progress – which includes unlocking human potential from the chains of preventable mental and physical disease – depends on good data, and we do not yet seem to collate the data required to know whether or for whom plant-based diets are safe in New Zealand.
George Henderson works as a researcher for Professor Grant Schofield and the team behind the What The Fat books and the social enterprise PreKure, which has been running free lifestyle and health programs through the lockdown. He is the author or co-author of several scientific articles and letters published by the BMJ, Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology, the JAMA, and other journals, including an influential review of low carbohydrate diets in diabetes management for the New Zealand Medical Journal. A musician, songwriter and amateur musicologist, he has recently presented a series of podcasts on 20th century women composers for Karyn Hay’s Lately show on RNZ.
References:
[1] Williams AC, Dunbar RI. Big brains, meat, tuberculosis, and the nicotinamide switches: co-evolutionary relationships with modern repercussions?. Int J Tryptophan Res. 2013;6:73‐88. Published 2013 Oct 15. doi:10.4137/IJTR.S12838 [2] Kothapalli KS, Ye K, Gadgil MS, et al. Positive Selection on a Regulatory Insertion-Deletion Polymorphism in FADS2 Influences Apparent Endogenous Synthesis of Arachidonic Acid. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33(7):1726‐1739. doi:10.1093/molbev/msw049
[3] Urska Dobersek, Gabrielle Wy, Joshua Adkins, Sydney Altmeyer, Kaitlin Krout, Carl J. Lavie & Edward Archer (2020) Meat and mental health: a systematic review of meat abstention and depression, anxiety, and related phenomena, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, DOI: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1741505 [4] Frédéric Leroy & Nathan Cofnas (2019) Should dietary guidelines recommend low red meat intake?, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, DOI: 10.1080/10408398.2019.1657063 [5] Contreras CM, Rodríguez-Landa JF, García-Ríos RI, Cueto-Escobedo J, Guillen-Ruiz G, Bernal-Morales B. Myristic acid produces anxiolytic-like effects in Wistar rats in the elevated plus maze. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:492141. doi:10.1155/2014/492141 [6] Fernandez-Lopez A, Lamothe V, Delample M, Denayrolles M, Bennetau-Pelissero C. Removing isoflavones from modern soyfood: Why and how?. Food Chem. 2016;210:286‐294. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.04.126 [7] Hicks KD, Sullivan AW, Cao J, Sluzas E, Rebuli M, Patisaul HB. Interaction of bisphenol A (BPA) and soy phytoestrogens on sexually dimorphic sociosexual behaviors in male and female rats. Horm Behav. 2016;84:121‐126. doi:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2016.06.010 [8] Tillett T. Full of beans? Early soy exposure associated with less feminine play in girls [published correction appears in Environ Health Perspect. 2012 Jan;120(1):A17]. Environ Health Perspect. 2011;119(12):A525. doi:10.1289/ehp.119-a525b [9] Adgent MA, Daniels JL, Rogan WJ, et al. Early-life soy exposure and age at menarche. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2012;26(2):163‐175. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3016.2011.01244.x [10] Hibbeln, J.R., SanGiovanni, J.P., Golding, J., Emmett, P.M., Northstone, K., Davis, J.M., Schuckit, M. and Heron, J. (2017), Meat Consumption During Pregnancy and Substance Misuse Among Adolescent Offspring: Stratification of TCN2 Genetic Variants. Alcohol Clin Exp Res, 41: 1928-1937. doi:10.1111/acer.13494 [11] Patisaul HB, Jefferson W. The pros and cons of phytoestrogens. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2010;31(4):400‐419. doi:10.1016/j.yfrne.2010.03.003 [12] Čiháková D, Eaton WW, Talor MV, et al. Gliadin-related antibodies in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2018;195:585‐586. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2017.08.051 [13] Jessica Greenebaum & Brandon Dexter (2018) Vegan men and hybrid masculinity, Journal of Gender Studies, 27:6, 637-648, DOI: 10.1080/09589236.2017.1287064 [14] Wiegersma AM, Dalman C, Lee BK, Karlsson H, Gardner RM. Association of Prenatal Maternal Anemia With Neurodevelopmental Disorders. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(12):1294–1304. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.2309
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Guidelines For Rearing Crystal Red Shrimp
By Elizabeth Bennett
If you are thinking of an entertaining way to bring your living space back to life, an aquarium would be the best feature to add. With an aquarium, you can keep all sorts of sea animals, but if you are looking for bright colors, you should keep crystal red shrimp. Their bright colors make them beloved, but a lot of dedication and preparation is required if you are to rear them effectively. Before you go to an aquarium shop to buy them, it is essential to know how to set up the perfect environment. If you are a beginner, it is wise to start with a small aquarium that houses a small number to let you monitor them easily. If you are a veteran, a bigger aquarium should suit your breeding needs. As you set up the ambiance in the pool, keep in mind the fragile nature of the creatures. They are easily swept by strong water currents, meaning you should try as much as possible to avoid adding current boosters. Also, as much as the aquarium needs a filter to keep the water and air clean, buying an overly powerful filter might suck them in and even kill them. When setting up the aquarium, include a variety of aquatic plants and mosses, which will provide a lot of food. The vegetation gives them places to play and hide. This breed of shrimp do not like getting exposed to the open water, so you should add features like stones and driftwood, which algae also grows on to provide food. Shrimps need particular water requirements to survive, and changing the atmosphere immediately is dangerous for them. Instead of dumping them straight into the aquarium from the bag, put them first in a container and wait for about half an hour. Then slowly, pour them into the aquarium and keep watching to see how they behave to the change. When it comes to feeding, the planted vegetation acts as a significant source of food and nutrients. Additionally, you can give all sorts of food since they are omnivores in nature. It is also advisable to introduce them to specialized foods, especially when they are young as the specialized foods give them a healthy boost. Just make sure to clean the water after feeding to avoid clogging air circulation and buildup of toxins. Besides regularly cleaning the tank and cleaning the water, the other factor you must always keep in check in the amount of C02 in that water. The vegetation keeps the levels in check during the day, but at night it is recommendable to use artificial C02 machines. Keeping the levels right ensures the water does not become acidic to the extent of harming the inhabitants. There are different grades of shrimps, but they all require the same care and attention if you are to keep them successfully. With everything done right, soon you will see the female lay eggs, which hatch after a month. Dedicated people have turned from keeping this type of shrimp from a hobby to money generating avenue.
About the Author:
Discover the best place to shop for crystal red shrimp by touring our web pages now. To check out our clearance items or to read our FAQs, click the links at http://bit.ly/2D3Cxc2 today.
Guidelines For Rearing Crystal Red Shrimp from netdz http://bit.ly/2BjHoV4
0 notes
Text
Tips To Help You Keep Crystal Red Shrimp
By Elizabeth Bennett
If you are thinking of an entertaining way to bring your living space back to life, an aquarium would be the best feature to add. With an aquarium, you can keep all sorts of sea animals, but if you are looking for bright colors, you should keep crystal red shrimp. Their bright colors make them beloved, but a lot of dedication and preparation is required if you are to rear them effectively. Before you go to an aquarium shop to buy them, it is essential to know how to set up the perfect environment. If you are a beginner, it is wise to start with a small aquarium that houses a small number to let you monitor them easily. If you are a veteran, a bigger aquarium should suit your breeding needs. Due to their fragile nature, it is not recommendable to introduce any current boosters in your aquarium. The natural current of the water is sufficient for them, and increasing it exposes them to great danger. The water filter you get should also be of the right size to avoid sucking them up as they swim around. If the filter is not naturally small enough, you can cover it with a sponge. Always add a variety of water plants to an aquarium as you set it up. The plants and moss act as a source of food as well as hiding places. You can also introduce stones, wood, and any other items that may act as hiding places. Bigger fish usually prey on the shrimps, so if you have to add other species in the aquarium, make sure they do not pose as a threat. They need specific water conditions to thrive. Therefore, even after you get them from the store and the aquarium water is perfect, avoid transferring them in immediately. Instead, first keep them in an open bowl and let them get used to the water. Afterward, you can slowly introduce them to the aquarium, after which you should still observe them for any problems. Feeding them is another essential factor for successfully rearing them. They are naturally omnivorous, feeding on anything they come along. It is, however, advisable to feed them a balanced diet of flakes, pellets, and other special foods. After a feeding session, clear the tank off excess food to maintain required water standards. Always keep the C02 levels in your aquarium in check at night. During the day, the plants will use the C02 for photosynthesis, but the levels might increase at night. Excess C02 also causes acidic buildup in the water, which harms and potentially kills your creatures. Always be wary of the C02 changes in the water by using measuring equipment. If you follow the steps above and keep the water conditions, your female shrimp will soon be full of eggs, ready to give you a new colony. If you choose the rear the babies in the same aquarium, be sure to remove any larger fish that might eat them. With time, you become an expert, and you can start making some money from selling your home bred red shrimps.
About the Author:
Discover the best place to shop for crystal red shrimp by touring our web pages now. To check out our clearance items or to read our FAQs, click the links at http://bit.ly/2D3Cxc2 today.
Tips To Help You Keep Crystal Red Shrimp via zoologist01 http://bit.ly/2S14Il4
0 notes