#aerobic composting
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How does one create a compost pile for their garden?
Composting is an essential practice for any gardener looking to improve soil health and reduce waste. By creating a compost pile, you can turn kitchen scraps, yard waste, and other organic materials into a nutrient-rich soil amendment that will nourish your plants and help them grow. In this article, we will guide you through the steps of creating a compost pile for your garden. Continue reading…

View On WordPress
#aerobic#anaerobic#brown materials#carbon#compost#composting#decomposition#fertilizer#gardening#green materials#heat#microorganisms#moisture#nitrogen#nutrients#organic material#oxygen#soil#sustainability#waste reduction
1 note
·
View note
Photo

Composting toilets are gaining in popularity, especially among eco-conscious consumers. Similar to the process of composting food scraps, composting toilets transform human waste into compost-like material that can then be used as fertilizer (if local laws allow it) to enrich soil and support plant growth. Here's what you should know and consider before buying a composting toilet. How Do Composting Toilets Work? SolStock / Getty Images Composting toilets use a process known as aerobic decomposition—when organic materials decompose in the presence of oxygen—to break down human waste instead of flushing it down the sewer pipe. There are no chemicals or water involved. When you "flush" a composting toilet, a trapdoor opens and drops the waste into a chamber. Some composting toilet models have two chambers: one for solids and one for liquids. After using a composting toilet, you will need to add a carbon-rich material such as sawdust, peat moss, or coconut coir to the chamber. This will help reduce odor and create space for oxygen to get to the waste to break it down. Want more gardening tips? Sign up for our free gardening newsletter for our best growing tips, troubleshooting hacks, and more! Handling the Nitty-Gritty Details Here are a few specifics of how a composting toilet works with urine, feces, and more. Separating urine and feces: Urine and feces include many chemicals that react when combined, resulting in foul odors. Separating waste substantially reduces odors. That's why composting toilets have a solids bucket or chamber for feces and a urine diverter specifically for liquids. How long does it take for feces to decompose: Feces do not decompose inside the toilet's chamber. Feces decompose over months outside the toilet in a compost pile. What happens to diarrhea and vomit: Diarrhea and vomit contain more liquid but it will likely fall to the solids bucket or chamber. Simply clean the toilet out more frequently and keep the exhaust fan running. What happens to toilet paper: Toilet paper can be used in this type of toilet but it is slow to decompose. It's best to use marine or RV toilet paper which is made to decompose faster but it's also thinner and less comfortable. Some people forgo toilet paper and instead use reusable toilet paper made from washable fabric scraps (like the concept of cloth diapers). What stops the smell of urine and feces: Several things can stop the smell of waste and it depends on the model of the toilet. These methods include an exhaust fan system that runs frequently or continuously, a urine separator that contains the liquid, and/or a layer of sawdust (or other material) that traps smelly gases. Where to put urine and feces when cleaning a composting toilet: Most people put feces and urine in a composting pile. Or, the feces that collects in the bowl's bag or removable chamber can go into a heavy-duty trash bag and the urine into a "soaking pit" or a nearby gray water drain. Types of Composting Toilets pastie / Getty Images You'll generally find two types of composting toilets: split systems and self-contained systems. The one you choose will depend on the bathroom space and budget you're working with. Split System Sometimes called central systems, these composting toilets look similar to traditional toilets that hook up to a septic tank. They are split into two sections: a pedestal (above the floor) and a compost tank (below the floor) connected by a waste chute. Split systems usually have a larger capacity and are installed in high-traffic areas, making them great for homes, parks, or clubhouses. They are generally more expensive than self-contained composting toilets. Self-Contained System These all-in-one models have both the pedestal and the composting container in the same unit. Self-contained composting toilets are popular in tiny houses, cabins, RVs, motorhomes, boats, and single-level homes built on a concrete slab. What to Consider Before Purchasing a Composting Toilet If you're looking to be more sustainable at home, a composting toilet may be for you. But before you swap your traditional toilet for a composting toilet, consider these factors. The model you purchase will depend on your situation, needs, and budget. Capacity Composting toilets need to be emptied, and how often you have to do so will depend on its capacity. The larger the unit, the longer you can go between emptying. Regular emptying of your composting toilet is important to keep it clean and functioning properly. In general, if your composting toilet is used regularly at your residence, you will want to remove the compost at least once a month. If your composting toilet is used occasionally—such as on RV road trips—then the compost can be emptied once a season. Cleaning You can't use harsh chemicals to clean a composting toilet. Commercial toilet cleaners and cleaning wipes are designed to kill bacteria—including the good bacteria necessary for composting. Instead, use a homemade toilet cleaner containing vinegar or liquid citric acid, which will effectively clean without disrupting the composting environment. When choosing a composting toilet, consider how easy it will be to clean, as some are easier to wipe down and empty than others. Smell Odor is one of the top concerns people have with composting toilets. However, a properly maintained composting toilet should not smell. If it does, that indicates something is wrong. There are a few main reasons why a composting toilet may emit an odor: The solids chamber may be too wet; the urine diverter may not work correctly.There's too much humidity in the air and the chamber requires more covering material.The ventilation/exhaust fan stopped working.Harsh chemicals were used to clean the toilet but in the process killed composting bacteria.Toilet paper or wipes negatively affected the covering material in the chamber; put toilet paper in a separate disposal container to reduce odors. When used and cared for properly, a composting toilet will not smell. FAQ If the chamber of your composting toilet is lined with a biodegradable bag, simply remove and tie the bag with a knot. If the chamber is not lined, take it out and empty the contents directly into a compost pile. Composting toilets require more upkeep and maintenance than standard toilets to work properly. Poorly maintained composting toilet systems can lead to odors and health hazards. They also require you to manually remove the end product, rather than just being able to flush human waste down the drain. Yes, you have to empty a composting toilet when it gets full since it can't be flushed into the sewer or septic systems like traditional toilets. Source link
1 note
·
View note
Text
Fermentation Compost Turning Machine: The "Magician" in Organic Fertilizer Production Line
In the wonderful world of organic fertilizer production line, the fermentation compost turning machine acts like a skilled magician, transforming seemingly useless organic waste into precious "black gold". How exactly does this amazing machine perform its magic? Let's uncover its crucial role in the fertilizer production line.

The fermentation compost turning machine serves as the heart of organic fertilizer production, accelerating decomposition through aeration and mixing. In the organic fertilizer production process, this equipment performs the critical magic of transforming raw organic waste into stable, nutrient-rich compost. By regularly turning the materials, it maintains optimal temperature and oxygen levels for microbial activity, ensuring efficient breakdown while eliminating pathogens and weed seeds - a vital step before granulation and final processing in the complete fertilizer production line.
1. The Efficient Mixing "Bartender"
Imagine the compost turner as a professional bartender, perfectly blending various organic materials - livestock manure, crop straw, kitchen waste, etc. Through its precise mechanical structure, it ensures an ideal carbon-to-nitrogen ratio, creating the best environment for subsequent fermentation. This uniform mixing not only improves fermentation efficiency but also guarantees consistent quality of the final product.
Data shows that production lines using professional turners can improve material mixing uniformity by over 40%, significantly reducing fermentation dead zones and allowing every inch of material to fully participate in this "organic transformation show".
2. The Oxygen-regulating "Breathing Expert"
Aerobic fermentation is the core of organic fertilizer production, and the turner serves as the "breathing expert" in this process. By regularly turning the compost pile, it delivers fresh oxygen to microorganisms while expelling waste gases like carbon dioxide. This intelligent "breath regulation" function boosts the activity of beneficial microorganisms, increasing organic matter decomposition speed by more than 50%.
3. The Temperature-managing "Physician"
During fermentation, pile temperature is like a patient's body temperature that needs precise monitoring. The turner acts like a careful physician, regulating pile temperature through turning operations to prevent local overheating ("burning") or insufficient temperature causing incomplete fermentation. Modern intelligent turners even come equipped with temperature sensing systems for precise "targeted treatment" regulation.
4. The Moisture-balancing "Gardener"
Moisture is the lifeline of organic fertilizer fermentation. During operation, the turner can both evaporate excess moisture to prevent anaerobic conditions and assist in adding water when necessary to maintain the ideal humidity around 60%. This "gardener-like" careful nurturing ensures microorganisms work in the most comfortable environment.
Compared with traditional static composting, dynamic fermentation systems using turners can reduce production cycles from 3-6 months to just 15-30 days while improving space utilization by 3 times or more, truly achieving "speed and passion" in organic fertilizer production.
5. The Green Production "Environmental Guardian"
In today's increasingly strict environmental requirements, the compost turner also plays the role of "environmental guardian". It effectively controls odor emissions during fermentation, reduces greenhouse gas production like methane, making the organic fertilizer production line truly achieve green recycling of "turning waste into treasure". Some high-end models are even equipped with deodorizing systems, making the production process more friendly.
From mixing to fermentation, temperature control to environmental protection, the fermentation compost turning machineruns through every key link of organic fertilizer production. It is not only the core equipment in the production line but also the unsung hero promoting the development of organic agriculture. Choosing a suitable turner means inviting an all-around "magician" for your organic fertilizer production!
#fertilizer production line#organic fertilizer production process#fermentation compost turning machine
0 notes
Text
Eco-Friendly Options for Portable Toilet Rentals in Hoover
Introduction: Embracing Sustainable Sanitation
In today's ecologically mindful society, the demand for environmentally friendly options has actually surged throughout various sectors. Among these, portable toilet leasings in Hoover are no exception. As events and building projects are plentiful, the requirement for hygienic centers has grown, triggering lots of to look for sustainable options. This post checks out the myriad environment-friendly options offered for portable toilet leasings in Hoover, highlighting their benefits and showcasing reliable services that make green options accessible.
Why Choose Eco-Friendly Portable Toilets?
When thinking about a hoover porta potty rental service, one may wonder about the advantages of going with environment-friendly alternatives. These systems typically use less water, include eco-friendly materials, and promote sustainability without jeopardizing hygiene or convenience. By picking an eco-friendly portable toilet rental service in Hoover AL, you add to reducing your carbon footprint while still meeting important sanitation needs.
youtube
Understanding Eco-Friendly Portable Toilets The Mechanics of Environment-friendly Toilets
Eco-friendly portable toilets operate on principles that reduce environmental impact. Traditional designs typically count on substantial water usage for flushing and waste hoover portable bathroom rental experts management. In contrast, eco-friendly alternatives might employ:
Composting Systems: These toilets break down waste organically without water. Biodegradable Chemicals: Rather of extreme chemicals that can harm the environment, these toilets utilize natural enzymes to handle odor and breakdown waste. Solar-Powered Features: Some models include solar panels to power ventilation systems or lighting. Types of Eco-Friendly Portable Toilets 1. Composting Toilets
Composting toilets are progressively popular for outdoor events and building and construction websites. They transform human waste into compost through aerobic decomposition. This process not only decreases waste but also creates nutrient-rich garden compost that can be utilized securely in landscaping.
2. Vacuum Toilets
Utilizing vacuum innovation significantly minimizes water usage compared to standard flushing systems. Vacuum toilets need less than a quart of water per flush, making porta potty rental company near hoover them an outstanding choice for water-scarce areas.

3. Biodegradable Chemical Toilets
These systems make use of eco-friendly chemicals instead of standard extreme chemicals to handle odors and break down waste efficiently without harming the environment.
Advantages of Selecting Eco-Friendly Options 1. Decreased Water Usage
One of the most significant advantages is decreased water intake. Conventional portable toilets can use up to 3 gallons per flush; eco-friendly models can operate on just a pint and even none at all.
2. Lower Carbon Footprint
By choosing a portable washroom rental near Hoover with sustainable functions, you're taking steps toward minimizing greenhouse gas emissions related to waste management.
3. Much Healthier Waste Management
0 notes
Text
Requirements for the windrow compost turning machine’s working site
The windrow compost turning machine is a core piece of equipment in organic fertilizer production. It’s mainly used for turning compost piles during fermentation to promote oxygen exchange, moisture adjustment, and even decomposition.
For stable operation and efficient production, proper planning of the working site is essential.
1.Basic Site Requirements
Ground Flatness: The turner needs firm, level ground to run on. Uneven surfaces can cause the machine to tilt or damage its tracks.
Ground Load-Bearing Capacity: Since windrow compost turning machines are heavy (usually 5-10 tons), the site must support their weight to prevent ground sinking.
Drainage System: The fermentation area needs good drainage to avoid pooling rainwater or seepage, which can affect composting.

2.Site Size and Layout
Fermentation Trough Width: Turners are typically suited for troughs 3-6 meters wide. The machine’s turning width should match the trough width to ensure full coverage.
Pile Height: Keep material piles between 1.2 and 1.8 meters high. Piles that are too high hinder turning, while piles too low reduce efficiency.
Working Paths: Leave enough space for the machine to turn and move in or out. Tight spaces can make operation difficult.
3.Environment and Supporting Facilities
Ventilation: Good airflow in the fermentation area is crucial for aerobic composting and preventing harmful gas buildup.
Rain Protection: For outdoor sites, installing a rain shelter is recommended. This stops rain from soaking the material and disrupting the fermentation process.
In short, choosing a suitable site is key to letting the windrow compost turning machine bring out its best performance.
0 notes
Text
Compost Turning Machines: The Unsung Heroes of Organic Fertilizer Production
The compost turning process is the critical bridge between organic fertilizer production and compost making. While organic fertilizer production focuses on creating nutrient-rich end products through various processing stages, compost turning specifically enhances the aerobic decomposition at the heart of compost fertilizer making. This essential mechanical process accelerates breakdown of organic materials, improves oxygen circulation, and ensures uniform microbial activity - transforming raw organic waste into stable, nutrient-dense compost that can then be further processed into commercial organic fertilizers. The efficiency of compost turning directly impacts both the quality of compost and the subsequent organic fertilizer production outcomes.
Why Your Fertilizer Plant Needs a Compost Turner
Speed up decomposition: Regular turning introduces oxygen, keeping those beneficial microbes happy and active
Consistent quality: No more hot and cold spots - your compost matures evenly throughout
Labor savings: One machine replaces dozens of workers with pitchforks
Odor control: Proper aeration prevents those nasty anaerobic conditions that cause smells
Pathogen elimination: The heat from regular turning kills harmful bacteria and weed seeds
1. Wheel Compost Turner - The All-Rounder

How it works: Uses rotating wheels with paddles to lift and aerate the compost as it moves along windrows.
Best for: Medium to large operations with long, straight windrows. Excellent for materials like manure and yard waste.
Bonus: Some models can straddle windrows up to 3 meters wide!
2. Chain Compost Turner - The Heavy-Duty Performer

How it works: Features a series of chain-mounted flails that aggressively tear through tough materials.
Best for: Processing fibrous or chunky materials like tree trimmings, municipal green waste, or palm waste.
Bonus: The chains are replaceable, so you don't need a whole new machine when parts wear out.
3. Windrow Compost Turner - The High-Capacity Specialist

How it works: A large rotating drum with paddles moves down pre-formed windrows, turning and aerating as it goes.
Best for: Large-scale commercial operations processing hundreds of tons daily.
Bonus: Some advanced models can add water or inoculants during turning.
0 notes
Text
Organic Fertilizer Production: How to Build an Efficient and Eco-Friendly Process?
The Relationship Between Production Process and Manufacturing Technology

The terms "organic fertilizer production process" and "organic fertilizer manufacturing process" are often used interchangeably in practice, but there are subtle differences. The production process emphasizes the complete chain from raw materials to finished products, while the manufacturing process focuses more on specific technical methods and operational details.
Key Stages of Organic Fertilizer Production
A typical organic fertilizer production line includes these core stages:
Raw Material Pretreatment: Sorting, crushing, moisture adjustment
Fermentation: Aerobic composting or anaerobic fermentation (usually takes 15-30 days)
Secondary Processing: Adding supplements, adjusting nutrient ratios
Granulation: Disc granulation, extrusion granulation or rotary drum granulation
Drying and Cooling: Controlling final moisture content at 10-15%
Screening and Packaging: Grading and final packaging
Five Strategies to Improve Production Line Efficiency
1. Optimize Fermentation Process: Trough fermentation systems can improve efficiency by 40% compared to traditional windrow methods, reducing fermentation period to 7-10 days[1].
2. Automated Control Systems: Install temperature, humidity and oxygen sensors for intelligent monitoring of fermentation process.
3. Modular Equipment Layout: U-shaped production line design reduces material transfer distance, saving 15-20% energy consumption.
4. Heat Energy Recovery: Heat recovery systems in drying section can reduce energy consumption by 30%.
5. Preventive Maintenance Program: Regular inspection of key equipment (like granulator molds, conveyor bearings) reduces unplanned downtime.
Win-Win Solutions for Ecology and Efficiency
Modern organic fertilizer production increasingly focuses on balancing ecology and efficiency:
Adopt enclosed fermentation systems to reduce odor emissions
Install dust removal equipment to control particulate pollution
Utilize solar-assisted drying to reduce carbon footprint
Implement water recycling systems
0 notes
Text
How to build an efficient bio-organic fertilizer production line?
Setting up a scientific and efficient bio-organic fertilizer production line can meet market demand and boost your business’s competitiveness.
1.Raw Material Selection and Prep
Bio-organic fertilizer mainly uses organic waste like livestock manure, crop straw, food waste, and mushroom residue. When starting your line, choose raw materials based on local availability. You’ll also need prep equipment like crushers and screeners.
2.Designing the Fermentation Process
Fermentation is the heart of making bio-organic fertilizer. It’s usually done through aerobic composting. Your line needs a compost turning machine (like a windrow type) and high-efficiency microbial agents to speed up organic matter breakdown.
3.Crushing, Mixing and Granulating
After fermentation, crush the material finely. Then, add functional microbes or trace elements as needed for your product. Mix everything evenly in a blender. For granulated fertilizer, use a granulator (like a disc type) to shape it – this makes it more competitive.

4.Drying, Cooling and Screening
Granules are often too wet, so dry them to ≤30% moisture. Then, cool them down to prevent clumping. Finally, screen them to separate good-sized particles. Anything too big or small can go back for re-granulating, cutting waste.
5.Packaging and Storage
Pack the finished product using an automatic bagging machine. Store it in a dry, well-ventilated warehouse to avoid moisture damage. If your fertilizer includes live microbes, store it at low temperatures to keep them active.
Building a bio-organic fertilizer production line means balancing raw materials, process design, equipment choice, and market needs. Smart planning boosts efficiency while cutting energy use and running costs.
0 notes
Text
Windrow compost turning machine: Key equipment for boosting organic fertilizer fermentation efficiency
The windrow compost turning machine is a core piece of modern organic fertilizer fermentation equipment. Known for being efficient, thorough, and energy-saving, it significantly boosts composting productivity.
1.Speeds up aerobic fermentation
Organic fertilizer fermentation relies on aerobic microbes. The turner mechanically flips the pile, loosening the material to increase oxygen exposure. This boosts microbial activity and shortens the fermentation time.
2.Regulates moisture and temperature
Moisture: While working, the turner can spray water to keep the pile from getting too dry or too wet, maintaining the best moisture level.
Temperature: Even turning prevents hot spots, keeping the pile temperature stable at 55-65°C to speed up decomposition.

3.Breaks up clumps
Its powerful breaking device crushes large chunks, ensuring raw materials (like manure or crop stalks) mix more evenly. This improves the final fertilizer's consistency and nutrient content.
4.Cuts labor costs
Highly automated, the windrow compost turning machine greatly reduces manpower needs. It's especially suited for large fertilizer plants or livestock manure treatment projects.
5.Reduces odor emissions
Regular turning cuts down on harmful gases (like hydrogen sulfide and ammonia) produced in anaerobic pockets, lowering smelly pollution and meeting environmental standards.
In short, the windrow compost turning machine not only improves fertilizer quality but also lowers production costs, driving the sustainable development of organic agriculture.
0 notes
Text
vimeo
[direct link to video, part 1 of 2]
vimeo
[direct link to video, part 2 of 2]
Disaster Sanitation, with Merilee Karr
- Part 1: How does this happen? (2025.06.18) - Part 2: What can you do about it? (2025.06.25)
Resources mentioned during these sessions:
Merilee’s Disaster Sanitation page on her website. Slides, class handouts, and other notes.
DOGAMI report on CSZ impact by city
Emergency Volunteer Corps of Nehalem Bay, especially pages on Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WaSH)
One-bucket hands-free handwashing station
Two-bucket foot-pump handwashing station
Green Concepts Containers
Tippy Tap video
Topographical map of water table depth
Water filter source
Cedar is okay for dry covering material in poo buckets
Question: What’s the risk of methane buildup in stored bags of poo? Could they explode? Answer: In progress, but initial search indicates it takes about a month for human waste to produce methane. Aerobic composting of waste, that is, with air circulation, produces carbon dioxide more than methane. Anaerobic composting, which could occur in a closed plastic bag, produces more methane than carbon dioxide.
0 notes
Text
How a Compressed OWC Machine Works: Process Explained with Benefits

In today's world, where sustainable waste management is a growing priority, understanding how a Compressed OWC machine works: process explained with benefits is essential for industries, institutions, and municipalities. OWC stands for Organic Waste Converter, a revolutionary technology that transforms organic waste into compost efficiently. Let’s dive into the working process of a Compressed OWC machine and discover its key advantages.
What Is a Compressed OWC Machine?
A Compressed OWC machine is a compact, high-efficiency system designed to convert organic waste into nutrient-rich compost. Unlike traditional composting methods, this machine compresses and accelerates the natural decomposition process using controlled aeration, microbial cultures, and mechanical agitation. It is ideal for areas with limited space but a high volume of organic waste, such as residential complexes, hotels, restaurants, and corporate campuses.
Understanding how a Compressed OWC machine works: process explained with benefits not only showcases its technical functionality but also highlights why it’s a vital component of modern waste management systems.
How a Compressed OWC Machine Works: Step-by-Step Process
Here is how a Compressed OWC machine works: process explained with benefits in a detailed, easy-to-follow format:
1. Segregation of Organic Waste
The process begins with the segregation of organic waste at the source. This includes kitchen waste, food scraps, garden waste, and biodegradable materials. Proper segregation ensures better efficiency and compost quality.
2. Feeding the Waste into the Machine
Once segregated, the organic waste is loaded into the input chamber of the Compressed OWC machine. Some machines come with a shredder attachment to reduce the particle size of the waste, which enhances microbial activity.
3. Compression and Mixing
This is the heart of the process. The machine compresses the organic waste using rotating blades or agitators while mixing it with microbial culture or composting inoculants. This step accelerates the breakdown of organic matter by promoting aerobic decomposition.
4. Controlled Aeration and Heating
The machine maintains optimal temperature and moisture levels, which are crucial for microbial action. The built-in blowers supply oxygen, maintaining aerobic conditions to ensure odor-free and hygienic processing.
5. Curing and Maturation
After 24 to 48 hours of processing, the partially decomposed material is moved to the curing tray or chamber. Here, the compost matures naturally over 10 to 15 days, resulting in a nutrient-rich, ready-to-use compost.
Key Benefits of Using a Compressed OWC Machine
When exploring how a Compressed OWC machine works: process explained with benefits, it’s vital to understand the advantages that make it a preferred solution for waste management:
1. Space-Saving Design
Compressed OWC machines are compact and require minimal installation space, making them ideal for urban environments and institutions with limited area.
2. Fast Processing Time
Traditional composting can take weeks or months. A Compressed OWC machine reduces this to a matter of days, providing rapid results with minimal manual intervention.
3. Odor and Pest Control
With a sealed design and controlled aeration, the machine operates without foul odors or attracting pests—ideal for locations near residential or commercial setups.
4. Eco-Friendly Waste Disposal
By converting organic waste into compost, these machines help divert waste from landfills and reduce methane emissions, contributing to a greener planet.
5. Cost-Efficient Solution
Over time, the cost savings in waste disposal, reduced transportation, and free compost make the investment in a Compressed OWC machine economically viable.
Applications Across Sectors
Understanding how a Compressed OWC machine works: process explained with benefits is especially useful for stakeholders in:
Residential Societies – promoting community composting.
Hotels & Restaurants – managing food waste efficiently.
Educational Institutions – incorporating sustainability practices.
Corporate Offices & IT Parks – achieving green certification goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, knowing how a Compressed OWC machine works: process explained with benefits empowers organizations and individuals to adopt a smarter, eco-friendly way of handling organic waste. With the growing emphasis on sustainability, this technology plays a crucial role in achieving zero-waste goals and promoting environmental stewardship.
Biopower is a leading name in delivering innovative waste management solutions. If you’re looking to implement an efficient system and want to know more about how a Compressed OWC machine works: process explained with benefits, Biopower offers industry-grade machines backed by expert service and support. Choose Biopower for a cleaner, greener future.
0 notes
Text
Eco-Friendly Compost Garbage Bins for Sustainable Waste Management in UAE
Crateco offers eco-conscious compost garbage bins that support sustainable waste segregation and composting efforts across the UAE. Ideal for residential communities, farms, food facilities, and municipalities, these bins are made from durable, weather-resistant plastic and feature proper ventilation for aerobic composting. Their user-friendly design supports the breakdown of organic waste while minimizing odor. Whether for small-scale home composting or commercial green waste management, Crateco provides bins in various sizes to meet your needs. With a growing demand for sustainability, compost bins from Crateco help reduce landfill waste and promote greener practices.
0 notes
Text
A Cleaner Future: Transforming Waste Management in Kerala

In recent years, waste management in Kerala has undergone a remarkable transformation. Once burdened with growing landfills and poor waste disposal practices, the state is now a frontrunner in sustainable waste solutions, thanks to a mix of innovative technologies, community participation, and strong policy support.
The Shift Toward Decentralized Waste Management
Kerala has embraced a decentralized waste management model — one that encourages each household, ward, and municipality to manage waste locally. Rather than relying on massive central landfills, small-scale treatment plants and composting units are being established across the state.
Key Initiatives Driving the Change
Aerobic Bins & Organic Composting Urban areas now use aerobic compost bins to process food and garden waste, turning it into valuable compost that supports local agriculture.
Biogas Plants Households, schools, and markets are installing biogas units that convert organic waste into cooking fuel, reducing dependence on LPG and firewood.
Material Recovery Facilities (MRFs) Segregated dry waste is sent to MRFs where it is sorted, recycled, and processed, creating income for local workers and reducing landfill load.
Plastic Waste Control Strict plastic bans and extended producer responsibility (EPR) policies have reduced single-use plastic drastically, encouraging businesses to adopt sustainable packaging.
Community Participation: The Backbone of Kerala’s Waste Policy
What makes waste management in Kerala truly effective is the active role played by citizens. Local residents are encouraged to:
Practice source segregation (separating wet and dry waste at home)
Participate in clean-up drives organized by local bodies
Use kitchen compost bins for daily biodegradable waste
Attend workshops on zero-waste living and eco-friendly alternatives
Tech Meets Clean-Up: Digital Monitoring & Data Tools
Many municipalities have adopted GPS-enabled garbage collection, mobile tracking apps, and real-time data dashboards to monitor progress and ensure transparency in waste collection and processing.
Kerala’s Model Cities & Awards
Cities like Alappuzha, Thiruvananthapuram, and Kochi have been recognized nationally and internationally for their waste management systems. Alappuzha, in particular, was featured by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) as one of the top five clean cities in the world using decentralized solid waste management.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the progress, Kerala still faces challenges like:
Inconsistent segregation practices in rural belts
Limited awareness in tourist-heavy areas
Need for better hazardous waste disposal systems
With continued education and infrastructure upgrades, these gaps can be bridged.
Conclusion
The evolution of waste management in Kerala showcases how a focused, community-driven, and tech-backed approach can lead to cleaner, more livable cities. As Kerala continues to innovate and inspire, it sets a powerful example for the rest of India and beyond — a vision of a zero-waste future grounded in local action and global responsibility.
#biogas in kerala#biogas plant for home#kerala#biogas#incinerator manufacturers in kerala#portable biogas plant for home#incinerators in kerala
0 notes
Text
Eco-Friendly Options: Sustainable Portable Toilet Rentals in Stockton
Introduction
In the bustling city of Stockton, California, outdoor occasions, building jobs, and recreational events require innovative options to sanitation difficulties. As we pursue a more sustainable future, environmentally friendly choices for portable toilets are gaining traction. This article looks into the numerous Eco-Friendly Options: Sustainable Portable Toilet Rentals in Stockton, clarifying the benefits, kinds of services available, and ideas for picking the right vendor.
What Are Eco-Friendly Portable Toilets?
When we think of portable toilets, pictures of confined spaces and unpleasant odors might come to mind. Nevertheless, modern advancements have actually transformed these necessary centers into eco-friendly alternatives that focus on sustainability. These units use eco-friendly products and save water, making them an exceptional option for ecologically conscious consumers.
The Value of Sustainability in Sanitation
As awareness about climate modification grows, the value of sustainable practices across all sectors intensifies. The sanitation market is no exception. By selecting Stockton portable toilet rental services that focus on eco-friendliness, consumers contribute to decreased waste and lower carbon footprints.


Advantages of Eco-Friendly Portable Toilets Reduced Ecological Effect: Conventional portable toilets typically rely on chemicals that can hurt ecosystems. Eco-friendly choices use natural cleaning agents and composting processes. Water Preservation: Many eco-friendly units employ innovative systems that minimize water usage while maintaining hygiene. Enhanced User Experience: Modern designs offer much better ventilation and convenience compared to standard models. Types of Eco-Friendly Portable Toilets Available in Stockton
Choosing the right kind of environment-friendly portable toilet is important for ensuring user complete satisfaction throughout your occasion or project.
Composting Toilets
Composting toilets break down waste luxury porta potty rental stockton ca using aerobic germs. They convert human waste into garden compost without needing water or chemicals. This makes them a perfect option for remote places or long-lasting installations.
Solar-Powered Units
These systems use solar energy to power lights and other functions within the washroom. They are perfect for big events where electricity gain access to may be limited.
Biodegradable Facilities
These toilets are made from eco-friendly materials that break down naturally with time, minimizing their environmental impact after disposal.

How to Pick a Reputable Portable Toilet Rental Company Near Stockton
When it concerns picking a porta potty rental company near Stockton, think about a number of factors:
youtube
Reputation: Look for customer reviews and reviews online. Service Variety: Guarantee they use a series of alternatives tailored to your needs. Customer Service: A responsive group can help resolve any issues you may have. Sustainability Practices: Inquire about their commitment to eco-friendly products and practices. The Process of Renting an Eco-Friendly Portable Toilet
Renting a
1 note
·
View note
Text
Using deodorants in composting processes
During the composting process, odor control is a key factor affecting work efficiency and the surrounding environment. WaveClean deodorant for composting, with highly efficient and active deodorizing bacteria and a variety of plant extracts as core ingredients, is specially designed for fermentation scenarios such as livestock and poultry manure, organic kitchen waste, and agricultural waste composting.
Deodorizing bacteria can rapidly reproduce in an aerobic environment and decompose malodorous gases such as ammonia and hydrogen sulfide released by organic matter; plant extracts achieve a fast and lasting deodorizing effect through adsorption and molecular chain scission. Simply dilute and spray on the surface of the compost in proportion, or spray automatically with an atomization system, and you can effectively reduce the odor concentration and improve air quality within minutes, achieving true odor control and odor remover.
If you are troubled by the odor of compost, please contact WaveClean for free professional advice and sample trials, and start fresh and odorless compost management immediately!
0 notes
Text
Two Major Challenges in Organic Fertilizer: Perfect Solutions for C/N Ratio & Fiber
Optimizing the production of organic fertilizers can be achieved by addressing the challenges of C/N ratio and fibrous materials.In fertilizer production lines, balancing C/N ratio and fiber content is crucial for efficient organic fertilizer manufacturing, ensuring proper decomposition and quality output.
Challenge 1: The C/N Ratio Dilemma
The carbon-to-nitrogen ratio (C/N) is a critical parameter affecting composting efficiency. The ideal range is 25-30:1. Deviation causes:
Too high (>40:1): Microbes lack nitrogen, decomposition slows by 50%+
Too low (<20:1): Significant nitrogen loss (up to 30%) with strong ammonia odor
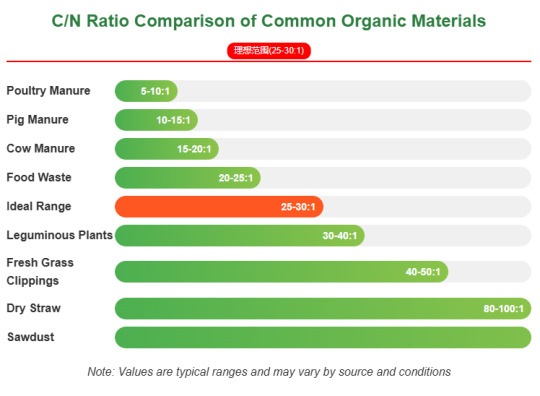
Four Golden Rules for C/N Adjustment
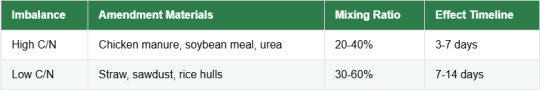
Pro Tip: Use portable C/N testers (±2 accuracy), test every 48 hours for dynamic adjustment. Increase C/N by 5-10% in summer, decrease by 5-10% in winter.
Challenge 2: High Fiber Content
When lignin/cellulose exceeds 35%:
Temperature struggles to reach 55°C+ (pathogen kill rate insufficient)
Composting extends to 60-90 days (normal 30-45 days)
Final product contains 10-20% undigested fibers
Three-Step Advanced Fiber Treatment
Step 1: Mechanical Pretreatment
Shred to 1-3cm particles (invest in 15-30kW straw crusher)
Use fiber disruptors (40% efficiency gain)
Step 2: Biological Enhancement
Inoculate with composite microbes (Trichoderma, etc.), 0.2-0.5% dosage
Add 5-10% mature compost as "starter"
Step 3: Chemical Assistance
Adjust pH to 7.5-8.5 (wood ash or lime)
Add 0.5-1% urea solution for fast nitrogen
Innovation: Try novel cellulase enzymes (e.g. from Trichoderma reesei) - reduces cycle by 30% but increases cost 15-20%.
Benefits of Solving C/N Ratio & Fiber Challenges
Optimizing C/N ratio and fiber content in organic fertilizer production improves decomposition efficiency, enhances product quality, and reduces processing time. This leads to more stable, nutrient-rich fertilizers with better market value.
Connection to Production Process
Proper C/N balance (25-30:1) accelerates composting in the fermentation stage, while fiber adjustment ensures optimal porosity for aerobic digestion. These solutions directly impact critical process parameters like temperature control and maturation time in organic fertilizer production.
References:
[1] "Compost Science & Technology" (3rd Ed.), China Agriculture Press, 2022
[2] FAO Organic Fertilizer Production Guide, 2023 Revision
[3] German Composting Association Technical Report, 2021
0 notes