#advantages and disadvantages of laser printer
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How Many Types of Ink Are There?
Ink is a significant part of our daily lives — ranging from the printing of documents to the creation of innovative projects and even personalizing clothes. Yet, have you ever stopped and asked yourself how many types of ink exist and which best suits you?

1. Dye-Based Ink Dye ink is among the most popular inks used in inkjet printers. It is a liquid solution of colorants.
Advantages: Rich color reproduction
Low and readily available price
Suitable for photo printing
Disadvantages: It fades with time
Not water-resistant
It smudges when not handled carefully
This ink is best suited for personal printing, school assignments, and color photographs. If you are personalizing items such as posters or personalized t-shirts, especially in collaboration with t shirt manufacturers in Chennai, dye-based ink could be an affordable choice.
2. Pigment-Based Ink Pigment-based ink differs from dye-based ink since it has finely divided particles that rest on the surface of the print instead of being absorbed.
Key Features: More durable prints
Water and fade-proof
Professional documents are preferred
It’s very common in the fine art and publishing business. Companies like t shirt manufacturers in Chennai prefer using pigment inks to achieve durable prints that can resist washing and outdoor weather.
3. Solvent Ink Solvent ink employs chemical solvents to transport color pigments, which is why it’s one of the leading choices when printing on non-porous media such as plastic and vinyl.
Best Suited For: Outdoor signs and banners
Vehicle wraps
Industrial labels
Though solvent inks are durable, they release strong odors and might necessitate proper ventilation during application. Outdoor advertising or custom apparel printing businesses typically use this type due to its resilience and resistance to the elements.
4. UV Ink UV-curable ink cures under ultraviolet light and forms a tough connection with the printed material.
Benefits: Dry instantly
Resistant to scratch and fading
Suitable for application on many types of materials
UV ink is gaining traction for environmentally friendly printing solutions. Several t shirt manufacturers in Chennai have begun using UV technology for intricate, custom designs on both textiles and accessories.
5. Sublimation Ink Sublimation ink is applied to a unique process in which the ink gets evaporated into gas when heated and gets chemically bonded with polyester or polymer-coated materials.
Best Applications: Custom apparel
Promotional items such as mugs and phone cases
Sportswear and team uniforms
This process makes the ink a part of the fabric, which is suitable for soft and breathable customized shirts. If you are looking for means to customize products, approaching t shirt manufacturers in Chennaithrough sublimation printing can be a good place to begin.
6. Toner (Applied in Laser Printers) Technically not a liquid ink, toner happens to be a dry powder utilized in copiers and laser printers.
Pros: High-speed printing
Precise text and lines
Shelf life that is long
Toner is best for office settings and heavy-duty print runs. It’s not good for fabric printing, but with the addition of heat transfer techniques, it can be a part of garment decoration.
7. Water-Based Ink Water-based ink is popular in the screen printing business, particularly on textiles.
Why Use It: Soft feel on fabric
Eco-friendly and non-toxic
Great for light-colored garments
Most environmentally friendly t shirt manufacturers in Chennai are switching to water-based inks for their minimal environmental footprint and gentle, breathable finish on fabrics.
Pro Tip: Ink Type to Your Needs Selecting the appropriate ink is not only about color — it’s about the end use:
Printing at home or in the office? Stay with dye or pigment-based ink.
Outdoor or industrial applications? Opt for solvent or UV inks.
Apparel or merchandise printing? Use water-based or sublimation ink.
As technology in printing continues to advance, so too do opportunities. The world digital print market, a report by Smithers shows, will be worth $225 billion by the year 2032, with demand for sustainability and personalization as the main drivers.
Conclusion: Which Ink Will You Choose? Knowing the various ink types allows you to make more informed, less expensive choices, whether you’re printing portraits, creating clothing designs, or starting a brand. From pigment to sublimation and all that lies between, having the correct ink can be the difference between worlds in terms of quality and longevity.
If you want to plunge into apparel personalization or seek professional advice on the ideal ink for your clothing business, feel free to approach seasoned t shirt manufacturers in Chennai. They tend to have guidance on the ideal means of printing and can assist you in realizing your imaginative vision.
0 notes
Text
What Paper is Used for T-Shirt Printing? Everything You Need to Know
If you’re about to produce special order clothing or venture into a merchandise company, it’s crucial that you know about the material used in t-shirt printing. An important aspect that is usually underappreciated is transfer paper — the vessel transporting your artwork onto the apparel. Selecting the appropriate type of paper guarantees your prints are vivid, long-lasting, and professional-grade.

Why Transfer Paper Is Important Transfer paper is a bridge between your design and fabric. It has a special polymer coating that enables ink or toner to stick to the surface, and it transfers the design when heat and pressure are applied. Depending on the printing process, the paper may be different in terms of its qualities and uses.
If the wrong paper is used, the ink can cause fading, cracking, or peeling of designs. That’s why companies providing custom t shirt printing in chennai spend on superior-quality paper that suits particular print technologies and fabric types.
Types of Transfer Paper for T-Shirt Printing Following is the list of transfer papers most often utilized in the clothing industry:
1. Inkjet Transfer Paper Suitable For: Light cotton, dark cotton.
Printer Needed: Basic inkjet printer.
Pros: Inexpensive, readily available, can be used at home.
Cons: Not as long-lasting when washed repeatedly.
2. Laser Transfer Paper Best For: Cotton or synthetic clothing.
Printer Required: Laser printer.
Pros: Longer lasting than inkjet transfers.
Cons: A bit more costly; needs to be done with a laser printer.
The Indian t shirt printing market is booming, with the demand growing more than 12% every year, particularly in metropolitan cities such as Chennai. That’s why services offering professional Custom t shirt printing in chennai depend on reliable paper types to satisfy rising expectations.
3. Sublimation Transfer Paper Best Suited For: Polyester material and treated items.
Printer Needed: Sublimation printer.
Advantages: Creates bright, long-lasting prints.
Disadvantages: Inapplicable to cotton or dark materials.
4. Heat Transfer Vinyl (HTV) Backing Paper Though not a paper in the classical sense, HTV is on a carrier sheet (frequently paper-based) and remains another favorite method for lettering and basic graphics.
Suitable for one or multi-colored designs and extensively utilized for team shirts, quotes, and logos.
These become regular fixtures in professional custom t shirt printing in chennai processes where conformity and long life are needs to fulfill customer requirements.
Matching Paper to Fabric Type For optimal results, always match the transfer paper to the corresponding fabric:
Fabric Type Recommended Paper 100% Cotton Sublimation Paper or Laser Paper Polyester Sublimation Paper Blended Fabric Depends on the dominant fiber Dark Colors Dark Transfer Paper Light Colors Light Transfer Paper
Getting the right match is particularly crucial in commercial custom t shirt printing in chennai, where the durability of garments and their aesthetics can have a direct relation to customer satisfaction.
Expert Tips for Quality T-Shirt Prints Here are some practical tips to improve your t-shirt printing process:
Use high definition images (at least 300 DPI) for sharp prints.
Pre-wash your garments to avoid any chemicals or shrinkage problem.
Always test print before large-scale production.
Keep paper in a proper storehouse to prevent damage due to humidity.
T-Shirt printing specialist Amit Sharma observes, “The correct paper along with proper heat levels can make the print up to 40% more durable.” This meticulousness is one of the primary reasons that most companies rely on professionals for custom t shirt printing in chennai.
Conclusion:
The Right Paper Makes All the Difference From inkjet and laser to sublimation paper, every choice has its benefit based on your printer, fabric, and design requirements. Having the right knowledge not only enhances the quality of your prints but also the washability and customer satisfaction.
In the booming arena of custom t shirt printing in chennai, having a clue about what paper to use provides you with professional advantage. Whether you print at home or extend your apparel business, begin with the appropriate paper — and you are half way to your dream.
0 notes
Text
More Than Just Models: The Real-World Applications of the Dental 3D Printing Market
Dental 3D Printing Industry Overview
The global Dental 3D Printing Market, estimated at $3.1 billion in 2023, is projected to experience substantial expansion, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 26.4% from 2024 to 2030. The integration of cutting-edge technology with significant potential has firmly established 3D printing in modern dental product manufacturing. Factors such as the design and development of sophisticated products like invisible aligners, advanced fabrication techniques for enhanced aesthetics, and precise delivery positioning are driving increased demand and adoption of dental 3D printers. The user-friendly nature and ease of 3D printing procedures are encouraging the dental industry to produce customized solutions that meet the diverse dental needs of individuals. These printers are expected to boost production output while simultaneously reducing fabrication time. Furthermore, the digitalized workflow promises to minimize procedural discomfort and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
This market is currently experiencing robust growth, with further expansion anticipated in emerging economies. According to the American College of Prosthodontists, approximately 15% of the edentulous population receives dentures annually. Edentulism disproportionately affects vulnerable groups, including economically disadvantaged and aging individuals. In the U.S. alone, around 120 million people are missing at least one tooth, and over 36 million Americans are completely edentulous. These figures are expected to rise in the coming decades, indicating a growing need for tooth replacement solutions among the aging population. Moreover, both partially toothless individuals, regardless of age, are increasingly opting for dental procedures, viewing dental implants as a practical and appealing option.
Detailed Segmentation:
End-use Insights
The dental laboratories segment dominated the market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 55.6% in 2023. The segment is likely to show the highest CAGR of 26.7% over the forecast period. The rising adoption of advanced technologies in laboratories is supplementing the growth of the segment. Moreover, the increasing number of dental laboratories, rising outsourcing of various manufacturing functions to dental laboratories, and increasing demand for fabricated/customized dental framing solutions required for several applications are fueling the demand for dental 3D printing technologies.
Application Insights
The orthodontics segment held the largest revenue share of 39.0% in 2023 and is expected to grow at a significant rate of 26.5% during the forecast period. The growth can be attributed to the rising number of cases of misalignment and gaps in the teeth. Furthermore, it is observed that approximately 3 million Canadian and American teens have braces, with the number of adults beginning orthodontic treatment rising at a steady rate.
Technology Insights
The selective laser sintering segment dominated the market with the largest share of 37.8% in 2023 and is likely to maintain its position throughout the forecast period, owing to its advantages over other technologies such as good chemical resistance, biocompatibility, and excellent surface finishing. The other technological segment is expected to show the highest CAGR of 27.5% during the forecast period, due to the rising investments in R&D related to material jetting, electron beam melting, and binder jetting techniques. The popularity of fused deposition modeling is rising due to the availability of a wide range of strong, biocompatible, and sterilizable thermoplastics. FDM is very cost-effective and is the most widely used technique to produce complicated shapes and designs. This is due to the growing cases of edentulism and tooth decay that are contributing to the growth of the segment.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific is anticipated to witness the most lucrative growth of 27.1% over the forecast period. The growth of the market can be attributed to the rising commercial activities by major industry manufacturers, expanding the number of patients undergoing tooth replacement surgeries, and improving healthcare infrastructure in emerging economies. The rising geriatric population, flourishing dental tourism, growing per capita income, and favorable government policies are some of the factors that are driving the growth of the regional market. India and China are projected to spearhead the growth in the Asia Pacific and market players are looking forward to investing in these countries.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restraints, and growth of the Dental 3D Printing Market
Key Companies & Market Share Insights
Players in the market could face two restrains- a lack of skilled dental professionals and the high cost of dental 3D printers which can hamper their growth pace. The dental 3D printing sector is a highly competitive market with the presence of large and medium-sized organizations. The growing demand for advanced technologies in the field of dentistry is encouraging the manufacturers in the dental 3D printing industry to enhance their existing scope of R&D activities by allocating high funds to incorporate advanced technologies.
These manufacturers also focus on various growth strategies such as mergers & acquisitions and launch of the new products. For instance, In February 2022, 3D Systems and Saremco Dental AG entered into partnership to advance the digital dentistry innovation. Combining 3D Systems' NextDent with Saremco's materials science expertise, the collaboration aims to empower dental laboratories and clinics with enhanced accuracy, repeatability, productivity, and cost-effectiveness across various indications. In February 2023, Stratasys Ltd. has unveiled TrueDent, a groundbreaking full-color 3D printed permanent dentures solution. TrueDent resin allows dental labs to produce natural-looking gums and accurate tooth structure with the desired shade and translucency, all in a single continuous print.
Key Dental 3D Printing Companies:
3D Systems
Stratasys Ltd.
Renishaw
Roland DG
SLM Solutions
EnvisionTec
DentsPly Sirona
Straumann
Form Labs
Prodways
Planmeca
Order a free sample PDF of the Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
0 notes
Text
The Do's and Don'ts of Heat Transfer Printing vs. DTF Techniques
Introduction
When it comes to customizing garments, two popular printing techniques—Heat Transfer Printing and Direct to Film (DTF) Printing—often take center stage. Both methods can produce vibrant designs, but they come with their own sets of advantages and challenges. In this article, we'll explore the do's and don'ts of heat transfer printing vs. DTF techniques, providing you with the insights needed to make informed decisions for your custom printing needs.
The Do's and Don'ts of Heat Transfer Printing vs. DTF Techniques 1. Understanding Heat Transfer Printing
Heat transfer printing is a method where a design is printed onto a special paper using ink and then transferred onto fabric using heat and pressure. This technique is widely used for creating custom apparel, promotional items, and more.
1.1 The Process Explained
To achieve a successful heat transfer print, follow these steps:
Design Creation: Use graphic design software to create your artwork. Printing on Transfer Paper: Print the design onto transfer paper using an inkjet or laser printer. Heat Application: Place the printed transfer paper onto the garment and apply heat using a heat press. Peeling: After cooling slightly, peel away the backing to reveal your design. 1.2 Advantages of Heat Transfer Printing Affordable initial investment Suitable for small runs or one-off designs Good color vibrancy 1.3 Disadvantages of Heat Transfer Printing Limited durability compared to other methods Requires careful handling during washing Not ideal for high-volume production 2. Understanding DTF Printing
Direct to Film Check out here (DTF) printing has emerged as a modern alternative that involves printing designs directly onto a film which can then be transferred onto fabric.

2.1 The Process Explained
The DTF process includes:
Design Creation: Similar to heat transfer, start with graphic software. Printing on Film: Use specialized DTF printers that utilize water-based inks. Powder Adhesive Application: Apply adhesive powder over the wet ink. Curing: Cure the film using heat before transferring it onto fabrics. 2.2 Advantages of DTF Printing Excellent durability and wash resistance Suitable for various fabric types including cotton, polyester, and blends High-quality image reproduction with fine details 2.3 Disadvantages of DTF Printing Higher initial startup costs due to equipment investments Requires specific materials like DTF film and adhesives A learning curve for optimal results 3. Key Differences Between Heat Transfer Printing and DTF Techniques
Understanding the fundamental differences between these two methods can help in selecting the right option DTF Printer for your project.
youtube
| Feature | Heat Transfer Printing | DTF Printing | |----------------------------------|-----------------------------------|-----
0 notes
Text
Ethernet
What is Ethernet?
Definition: Ethernet (pronounced “eether net”) is a computer network technology which is used in different area networks like LAN, MAN, WAN. Ethernet connecting computers together with cable so the computers can share information. Within each main branch of the network, “Ethernet” can connect up to 1,024 personal computers and workstations.
Ethernet provides services on the Physical (Layers 1) and Data Link Layer (Layers 2) of OSI reference model.The Data Link Layer is further divided into two sublayers that are Logical Link Control (LLC) and Media Access Control (MAC),these sublayers can be used to establish the transmission paths and format data before transmiting on the same network segment.
Read More
Systems that use ethernet communication divide their data into packets, which are also known as frames. These frames further contain source and destination address, a mechanism which was used to detect errors in the data and retransmission requests.
History of Ethernet
Ethernet was developed over several years in the early 1970s by group researchers within the company Xerox Palo Alto Research Center (Xerox PARC) including, in particular, Robert Metcalfe (who founded later 3Com company). The goal the research project was to connect networked computers and laser printers. Xerox Corporation filed a patent on this technology late 1977. In 1979, companies Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC), Intel and Xerox combined to improve Ethernet and together published the first standard in 1980: Ethernet Blue Book sometimes called TEN (after the initials of the three companies). Finally, the IEEE this technology became standard in 1983: 802.3 was born … well before the 802.11! A little abuse of language, it is called Ethernet 802.3 standard. The format of DIX Ethernet packets is slightly different from the 802.3 Ethernet packets, but the two can coexist on the same network. The invention of single-chip Ethernet controllers has made Ethernet cards very cheap, and many modern PCs have it built-in on the MOTHERBOARD.
Read More
Wired Ethernet
Initially, ethernet can be designed to run over coaxial cables, twisted pair cables,fiber optic cable.
Wired Ethernet network, devices are connected with the help of a fiber optic cable which connects the devices within a distance of 10km. For this, we have to install a computer network interface card (NIC) in each computer. A unique address is given to each computer that is connected. So, for sharing data and resources like printers, computers, and other machines, Ethernet networking is used as it establishes a communication system.
Ethernet is a shared medium network technology, where all the workstations are connected to the same cable and must connect with one another to send signals over it. The algorithm used to resolve collisions — that is, when two workstations try to speak at the same time — is called CSMA/CD, and works by forcing both workstations to back off for random (and hence probably different) intervals before trying again.
Advantages of using wired Ethernet network
•It is very reliable.
• Ethernet network makes use of firewalls for the security of the data.
Data is transmitted and received at very high speed.
Read More
• It is very easy to use the wired network.
Disadvantages of using wired Ethernet network
• The wired Ethernet network is used only for short distances.
• The mobility is limited.
• Its maintenance is difficult.
• Ethernet cables, hubs, switches, routers increase the cost of installation.
Wireless Ethernet
In this, wireless NICs are used for connecting the computer instead of a cable and these wireless NICs make use of radio waves for communicating between the systems and furthers these NICs are connected with a wireless switch or hub. This technology requires maintenance, but it is more easy to use.
Wired Ethernet network, devices are connected with the help of a fiber optic cable which connects the devices within a distance of 10km. For this, we have to install a computer network interface card (NIC) in each computer. A unique address is given to each computer that is connected. So, for sharing data and resources like printers, computers, and other machines, Ethernet networking is used as it establishes a communication system. Ethernet is a shared medium network technology, where all the workstations are connected to the same cable and must connect with one another to send signals over it. The algorithm used to resolve collisions — that is, when two workstations try to speak at the same time — is called CSMA/CD, and works by forcing both workstations to back off for random (and hence probably different) intervals before trying again.
Read More
Wireless Ethernet
In this, wireless NICs are used for connecting the computer instead of a cable and these wireless NICs make use of radio waves for communicating between the systems and furthers these NICs are connected with a wireless switch or hub. This technology requires maintenance, but it is more easy to use.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
3D Printing Technology

3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a technique for layering a three-dimensional object using a computer-generated design. Subtractive manufacturing procedures, in which a final design is cut from a larger block of material, are the polar opposite of additive manufacturing. As a result, there is less waste from 3D printing. 3D printing is also suitable for rapid prototyping.
Thermoplastics, such as acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), metals (including powders), resins, and ceramics are among the materials used in 3D printing.
Hideo Kodama of the Nagoya Municipal Industrial Research Institute invented the first 3D printing manufacturing equipment when he invented two additive processes for generating 3D models. Hideo Kodama's early work in Laser Cured Resin Rapid Prototyping was finished in 1981, building on Ralf Baker's work in the 1920s for creating decorative objects (patent US423647A). With the launch of stereolithography in 1984, his innovation was further developed over the next three decades. In 1987, 3D Systems' Chuck Hull invented the first 3D printer, which employed the stereolithography method. The development of selective laser sintering and selective laser melting, among other things, followed. Other 3D printing systems were developed in the 1990s and 2000s, but their prices decreased drastically after the patents expired in 2009, allowing more people to access the technology.
3D Printing Technologies
Sintering, melting, and stereolithography are the three main types of 3D printing technique.
• Sintering is a technique for creating high-resolution products in which the material is heated but not to the point of melting. For direct metal laser sintering, metal powder is utilised, while thermoplastic powders are used for selective laser sintering.
• Powder bed fusion, electron beam melting, and direct energy deposition are 3D printing melting processes that use lasers, electric arcs, or electron beams to melt materials together at high temperatures to print objects.
• Photopolymerization is used in stereolithography to manufacture parts. This technology uses the right light source to selectively interact with the material, curing and solidifying a cross section of the product in thin layers.
Types of 3D printing
3D printing can be classified into one of the following categories:
• VAT Polymerization
• Binder Jetting
• Direct Energy Deposition
• Material Extrusion
• Material Jetting
• Powder Bed Fusion
• Sheet Lamination
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of 3D printing include:
• Easy development of unique geometric parts with no extra cost: This technology enables for the easy creation of bespoke geometric components with no further expense. Because 3D printing uses no extra material, it can be cheaper than subtractive manufacturing.
• Cheap start-up costs: Since no moulds are required, these production expenses are low. Material, labour, and post-processing time all contribute to the cost of a part.
• Due to the use of computer-aided designs (CAD), any product modifications are simple and do not affect manufacturing costs.
• Perfect for rapid prototyping as the technology enables small batches and in-house production, it is ideal for rapid prototyping.
• Creates parts with specific properties: While plastics and metals are the most popular materials used in 3D printing, other materials can be used to create parts with specific features. For specialised purposes, parts can be made with increased heat resistance, water resistance, or strength.
The disadvantages of 3D printing include:
• Less strength than traditional manufacturing: While some parts, like metal, have outstanding mechanical qualities, many other 3D printed items are more brittle. Because the parts are created layer by layer, the strength is reduced by 10% to 50%.
• High volume production is more expensive with 3D printing. For quantities above 100 units, 3D printing is estimated to be less cost effective than CNC machining or injection moulding, assuming the parts can be made conventionally.
• Accuracy limitations: It depends on the machine and/or process employed. Because some desktop printers have tighter tolerances than others, the finished pieces may be slightly different. While this can be rectified in post-processing, 3D printed items are not always perfect.
• The majority of 3D printed parts require some type of post-processing to produce a desired finish, removal of support struts, heat treatment to achieve specified material qualities, or final machining.
3D Printing Industries
Due to its versatility, 3D printing is used in many industries, including:
Aerospace
3D printing is utilised in the aerospace (astrospace) industry to make light yet complex parts like blisks. Rather than creating a product from multiple components, 3D printing creates a single component, saving lead times and waste.

Automotive
Its inherent weight and cost reductions have endeared it to the automobile industry. It is a quick prototyping tool for testing or small-scale manufacturing. If a part is no longer available, it can be made as a part of a limited batch, containing spare parts. Alternatives include overnight printing of goods or fixtures for testing before a larger production run.

Medical
3D printing is being used in medicine to create custom implants and gadgets. Hearing aids, for example, may be made swiftly from a digital file matched to a body scan. This reduces costs and production times.

Want to know more about MIT College of Railway Engineering and Research Barshi, MH.
Apply now @ https://bit.ly/2K2tT00
#MITCORER #MITCORERBarshi #TransformIndia #MIT #BTech #RailwayEngineering #railways
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Do's and Don'ts of Heat Transfer Printing vs. DTF Techniques
Introduction
When it comes to customizing garments, two popular printing techniques—Heat Transfer Printing and Direct to Film (DTF) Printing—often take center stage. Both methods can produce vibrant designs, but they come with their own sets of advantages and challenges. In this article, we'll explore the do's and don'ts of heat transfer printing vs. DTF techniques, providing you with the insights needed to make informed decisions for your custom printing needs.
The Do's and Don'ts of Heat Transfer Printing vs. DTF Techniques 1. Understanding Heat Transfer Printing
Heat transfer printing is a method where a design is printed onto a special paper using ink and then transferred onto fabric using heat and pressure. This technique is widely used for creating custom apparel, promotional items, and more.
youtube
1.1 The Process Explained
To achieve a successful heat transfer print, follow these steps:
Design Creation: Use graphic design software to create your artwork. Printing on Transfer Paper: Print the design onto transfer paper using an inkjet or laser printer. Heat Application: Place the printed transfer paper onto the garment and apply heat using a heat press. Peeling: After cooling slightly, peel away the backing to reveal your design. 1.2 Advantages of Heat Transfer Printing Affordable initial investment Suitable for small runs or one-off designs Good color vibrancy 1.3 Disadvantages of Heat Transfer Printing Limited durability compared to other methods Requires careful handling during washing Not ideal for high-volume production 2. Understanding DTF Printing
Direct to Film (DTF) printing has emerged as a modern alternative that involves DTF Printer printing designs directly onto a film which can then be transferred onto fabric.

2.1 The Process Explained
The DTF process includes:
Design Creation: Similar to heat transfer, start with graphic software. Printing on Film: Use specialized DTF printers that utilize water-based inks. Powder Adhesive Application: Apply adhesive powder over the wet ink. Curing: Cure the film using heat before transferring it onto fabrics. 2.2 Advantages of DTF Printing Excellent durability and wash resistance Suitable for various fabric types including cotton, polyester, and blends High-quality image reproduction with fine details 2.3 Disadvantages of DTF Printing Higher initial startup costs due to equipment investments Requires specific materials like DTF film and adhesives A learning curve for optimal results 3. Key Differences Between Heat Transfer Printing and DTF Techniques
Understanding the fundamental differences between these two methods can help in selecting the right option for your project.
| Feature | Heat Transfer Printing | DTF Printing | DTF transfer equipment |----------------------------------|-----------------------------------|-----
0 notes
Text
PART DECORATION FOR PLASTIC INJECTION MOLDING

Many plastic injection molded parts need to have some form of decoration applied to them after being manufactured. Possible reasons for decorating or marking parts include identification, tracking, branding, notices, warnings, instructions, as a product attribute, or otherwise. There are some standard methods of decorating plastic parts, and each has certain advantages and considerations, depending on the part application, the decorating purpose, and the resin being used.
PAD PRINTING
Historically, one of the more popular methods for decorating plastic parts has been with pad printing. There are three different types of pad printing machines: open inkwell, closed ink cup, and rotary gravure, which is used for printing 360 degrees on a part. Machines have a printing plate or a cliché, which commonly are made out of steel for durability. The artwork to be printed onto the parts is etched into the printing plate.
As the name suggests, the machines have transfer pads that come in a few different shapes and that are made out of silicone rubber with various hardness or shore levels. Pad life ranges from 10,000 to 100,000 cycles with an average of about 50,000.
The process consists of the pad picking up ink in the etched image on the cliché and placing it onto the part. Pad printing uses a type of solvent-based ink specifically designed for this purpose. This type of decoration also requires the fabrication of nesting fixtures to hold the parts in place during the printing process.
HEAT TRANSFER
A newer and usually more effective method of part decoration is thermal or heat transfer. With this process, the image is printed on a polyester film, which is coated with an adhesive so the image will stick to the part. Rolls of this film with the digitally printed images are placed on the printing machine’s reels, which index forward to print successive parts. Fixtures to hold parts are used here, as they are in pad printing. Additionally, a silicone decorating head or pad applies heat and pressure to print the transfer image onto the part.
Some advantages of heat transfer include the ability to create an image with four colors plus white in as high as 1200 dpi. In addition, there is no drying or curing time with decorating plastic parts, as there is with pad printing. Further, heat transfer decorations generally are tougher than pad printing and can be dishwasher safe.
HOT STAMP
Another common technique used to decorate plastic injection molded parts is hot stamping. A hot stamp machine transfers an image with pre-dried ink to a part with a die, again using heat and pressure and a fixture to hold the part, as with the previous methods.
One main advantage of hot stamping is the ability to apply a metallic foil or embossing to a plastic part. If you’re reading this article on a desktop computer, chances are the monitor in front of you has a logo that has been hot stamped on it. It also is a relatively clean process, compared to the wet ink used in pad printing.
LASER MARKING
Another method for decorating injection molded parts is by utilizing a laser marking system. This approach includes laser marking, laser engraving, and laser etching. Laser marking (or foaming) changes the color of the part where the text or graphic is, while the surface stays relatively unchanged. Alternatively, laser engraving removes some of the surface material, whereas laser etching melts the surface resin and creates a raised mark.
Of course, laser marking, engraving and etching all require a laser decorating machine. Additionally, fixtures to hold the parts usually are required, as with other decorating methods, although some fixtureless laser decorating systems have been developed. Some advantages of laser decorating include less wear and tear on the decorating equipment, it’s a precise and repeatable process, and it provides the ability to decorate some hard-to-reach part areas. Due to these benefits, industries like medical, automotive and aerospace often utilize the process.
IN-MOLD DECORATION
The method of in-mold decoration involves placing a pre-printed plastic film or appliqué in an injection mold before the part is molded, and the graphic then adheres to the part after it forms in the mold’s cavity. In-mold decoration requires a uniquely designed and built plastic injection mold and a carrier film feeder. The film can be manually placed into the mold between each cycle, but that greatly increases the manufacturing time and labor costs associated with the parts. However, even with a feeder, parts requiring in-mold decoration generally tend to be more expensive than other decorated parts, due to the specialized design, tooling and manufacturing required.
INKJET DECORATION
Inkjet printing on plastics is a relatively newer process, and it involves digitally printing a graphic onto a part. The system essentially is the same as inkjet printers for paper, with which most of us are familiar, although it uses a different type of ink. These machines typically use either conventional or LED lamps, and the process eliminates labels, films, printing plates, clichés or screens, as required with other decorating methods, although they do require a printhead and ink. Historically, this kind of decorating is somewhat slower and more costly than other forms, although advances are being made.
SCREEN PRINTING
Most people are familiar with screen printing in the context of t-shirts, and this also can be referred to as silk screening. Screen printing can be used for parts with flat or cylindrical surfaces but is not recommended for parts with complex curves and shapes. One advantage of screen printing is that it can print metallic graphics onto parts, which some other methods cannot do. Although providing the option of printing with multiple colors, a separate screen is needed for each separate hue, which increases cost and decorating time. The surface to be decorated needs to be prepared prior to printing, too.
PAINTING
When injection molding a part cannot achieve the desired texture, finish or color, painting the parts sometimes is utilized as a secondary operation. This approach can include spray painting and powder coating. As most injection molders do not perform painting as a finishing operation, the parts will need to go to a secondary provider, which often results in increased costs.
PLATING
When looking for a metal finish on an injection molded part, hard chrome plating and electroless nickel plating are two commonly used options. Plating offers a decorative finish, and it provides a certain level of corrosion protection. One item to note is that any surface imperfections on the part can affect the look of the plating, so consideration needs to be given there. Additionally, few molders also perform plating services, so those two suppliers will need to coordinate their work. There also are some design and material considerations that must be taken into account.
CONCLUSION
There are many different methods of decorating a plastic injection molded part, and each has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, depending on the requirements of the project. When developing a new product with components that may need to be decorated in some way, attention should be given to the part design, the polymer being used, the decorating purpose, the part application, the governing regulations, and the cost considerations. If we can answer any questions, don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
--
Ash Brown // VP, Business Development
1 note
·
View note
Text

The Evolution, Advantages, And Potential Future Of 3D Printing Technology
3D printing is a process of creating a physical object from a digital file. It is also known as additive manufacturing, as it creates objects by adding successive layers of material until the final product is complete.
A brief history of 3D printing technology
The concept of 3D printing was first introduced in the 1980s, and it has since evolved into a complex technology with a wide range of applications.
Importance of 3D printing in today’s world
3D printing has revolutionised the way products are designed, prototyped, and manufactured, leading to significant advancements in various industries.
How 3D Printing Works
Overview of the 3D printing process
The 3D printing process involves three main stages: design, slicing, and printing. The design stage involves creating a digital model of the object to be printed. The slicing stage involves breaking down the digital model into individual layers, which are then printed one by one during the printing stage.
Different types of 3D printers and how they work
There are several types of 3D printers, including Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and Digital Light Processing (DLP). Each type of printer uses a different technology to print objects.
Materials used in 3D printing
A wide range of materials can be used in 3D printing, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even food. The material used depends on the application and the desired properties of the final product.
Applications of 3D Printing
Industrial applications
3D printing has revolutionised the manufacturing industry by enabling the production of complex parts with high precision and accuracy. It is widely used in the automotive, aerospace, and medical device industries.
Medical applications
3D printing has transformed the medical industry by allowing the production of customised prosthetics, implants, and even organs. It has also been used to create surgical guides and models for preoperative planning.
Educational applications
3D printing has become an essential tool in the education sector, enabling students to learn about complex concepts in a hands-on and interactive manner. It is widely used in engineering, architecture, and design schools.
Personal use and hobbies
3D printing has also become popular among hobbyists and DIY enthusiasts, who use it to create custom designs, toys, and even musical instruments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing
Advantages of 3D printing technology
The main advantages of 3D printing technology include faster prototyping, reduced waste, lower costs, and the ability to create complex geometries and customised designs.
Disadvantages of 3D printing technology
Despite the numerous advantages of 3D printing technology, there are still some limitations and drawbacks to consider. Here are some of the most common disadvantages of 3D printing:
Limited Materials: Although there is a wide range of materials available for 3D printing, it still lacks some advanced materials used in traditional manufacturing processes, such as metals, ceramics, and glass.
Cost: 3D printing can be an expensive process, especially when it comes to larger and more complex designs. The cost of the printer, software, and materials can add up quickly.
Speed: 3D printing is a relatively slow process compared to traditional manufacturing methods. It can take several hours or even days to print a large and complex object.
Quality: The quality of the final product can be limited by the resolution of the printer, the type of material used, and the complexity of the design. In some cases, post-processing may be required to achieve a higher level of quality.
Intellectual Property: 3D printing makes it easy to replicate existing products without permission, which can lead to copyright and intellectual property issues.
Future of 3D Printing
Despite the limitations of 3D printing, the technology is advancing rapidly, and its future looks bright. Here are some of the potential developments and impacts of 3D printing in the future:
Advancements in 3D Printing Technology
The development of new materials, printing techniques, and software tools will continue to enhance the capabilities of 3D printing technology. Some of the advancements to look out for include:
Faster printing speeds: New technologies such as Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP) and Multi-Jet Fusion (MJF) are pushing the limits of 3D printing speeds.
Higher resolution: Advances in printer resolution and post-processing techniques are allowing for greater detail and complexity in 3D-printed objects.
New materials: Researchers are developing new materials for 3D printing, such as graphene and bioplastics, which offer unique properties and applications.
Advanced software: AI and machine learning algorithms are being developed to optimise 3D printing processes and improve accuracy.
Potential Impact of 3D Printing on Various Industries
As 3D printing technology becomes more advanced and accessible, it has the potential to revolutionise many industries, including:
Manufacturing: 3D printing can significantly reduce production time and costs, allowing for more efficient and customised manufacturing processes.
Healthcare: 3D printing can be used to create personalised medical implants, prosthetics, and surgical tools, among other applications.
Architecture and Construction: 3D printing can be used to create complex and customised building components, reducing waste and improving construction efficiency.
Fashion and Jewellery: 3D printing can be used to create unique and intricate designs in fashion and jewellery, offering a more sustainable and customizable alternative to traditional manufacturing.
Predictions for the Future of 3D Printing
As 3D printing continues to evolve and improve, here are some predictions for its future:
Increased accessibility: As prices come down and technology advances, 3D printing is expected to become more accessible to the general public.
Customization: 3D printing will continue to enable greater customization and personalization in a wide range of products and industries.
On-demand production: 3D printing will allow for more on-demand production, reducing waste and inventory costs.
Integration with other technologies: 3D printing will be integrated with other technologies such as AI and IoT, enabling even more advanced and innovative applications.
In conclusion, 3D printing is a rapidly advancing technology that has revolutionised various industries such as healthcare, aerospace, and automotive. It offers a range of benefits such as customization, cost-effectiveness, and speed that make it an attractive option for many businesses and individuals. However, there are also limitations and challenges associated with 3D printing, such as the high cost of equipment and materials, as well as the limited size and material options.
Despite the current limitations, the future of 3D printing looks promising with ongoing advancements in technology that are expanding its capabilities and making it more accessible to a wider range of industries and applications. From bioprinting to food printing, the possibilities for 3D printing are endless.
0 notes
Text
Advantages & Disadvantages of Inkjet Dyes
Various segments of the business and home market are embracing multi-color inkjet technology. The packaging, publication, and specialty printing industries have a significant and thriving inkjet market. Inkjet Dyes are highly concentrated colorants that are designed to meet the ever-growing needs of today’s inkjet markets.
Many different dyes can be used for Inkjet Inks, including direct, reactive, acid, and pigment dyes. Inkjet dyes come in both powder and liquid forms. To produce inkjet printing, extensive purification and filtration processes are used, and the physicochemical properties of the printing ink have a great impact on the quality.
Dye inks are designed by dissolving the liquid-colored dyes into a fluid carrier which makes the dyes easy to apply. Inkjet dyes are uniformly saturated into the paper, so they reflect light very evenly, as printing is a highly precise process, and dyes need to be more stable and have superior colors with physical properties that are outstanding.
They provide a wide range of colors and possess high-purity dyes that are found to be low in chlorides and designed to address all standard criteria for the inkjet industry segment.
However, Inkjet dyes have some of their pros and cons and if you are curious to know what they are, then the article is for you. Keep reading this further to know more about the advantages & disadvantages of Inkjet Dyes.

Advantages of Inkjet Dyes
The dye-based ink is usually very inexpensive, but the price of the ink varies depending on various factors, such as the manufacturing cost. They are widely used to print better, finest, and smoother details using a higher resolution. Inkjets have the advantage of practically no warm-up time and often lower costs as compared to technologies like thermal wax, dye sublimation, and laser printing.
Inkjet dyes have following several advantages, some of them listed below:
Inkjet dyes are more stable and soluble.
They offer a wide range of colors.
Best suited for providing bright intense colors.
Come up with a wide selection.
Disadvantages of Inkjet Dyes
Unlike most dyes, when dyes are exposed to light or ultraviolet light, the molecules of the dyes get broken and lose their color, which causes the prints to lose their original colors over time. If the ink is set to dry very fast on paper, the drying time of the ink is directly correlated with that of the solvent on the paper (often leading to the untimely nozzle closing).
The following are some of the disadvantages of using inkjet dyes in printers as experienced by users:
It causes more damage to attacks such as sunlight, ozone and ultraviolet rays.
Best suited for low-volume printing.
Low tendency stabilization.
The low thickness of the print.
They are the best fit for high-volume printing
Conclusion
Thus, Inkjet dyes have some of their own advantages and disadvantages, although they are widely used in various industrial applications. Inkjet dyes manufacturers prepare a variety of industrial applications ranging from textiles, 3-D printing, ceramics, and signage to biomedical applications and conductive circuitry.
0 notes
Text
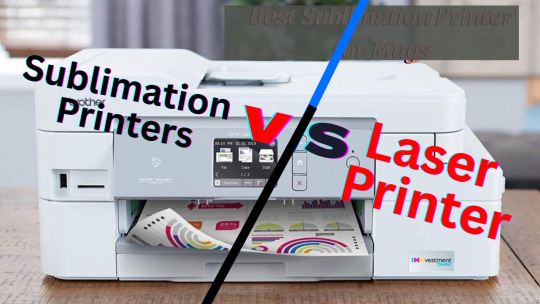
Sublimation VS Laser Printer
Sublimation and laser printers are two very different printers. Each has its own place in the ever-evolving world of garment and substrate decorating each with unique advantages and disadvantages and drawbacks. You will really be impressed with this article because you will never find any difficulty to understand the concept of their comparison. So stay with us and let's go forward to the main idea, Here there are some of the major points to consider. Laser transfer paper can work with a standard laser printer whereas a dye sublimation printer uses a dye sublimation ink and needs a dedicated inkjet printer. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4KHSkplh1QA Realist and Usage of these printers: Laser printers can also sublimate with the sublimate printer used for general office needs and white toner use. Laser toner technology has also come online that allows decorators to deploy toner-based sublimation on the same laser printer for office use, White toner printing, and all other uses. And dye sublimation has a vivid photo-realistic color but must be dedicated to only sublimation cannot be used for regular office printing. Process of these printers: Laser printers can be used in a one-step operation as would be the case when printing white onto dark stationery and also in a two-step operation for heat transfer onto mugs and apparel including dark-colored mugs and apparel dye sublimation always requires a two-step process, where the image first printed on to transfer paper and then transfer it onto a polymer-coated substrate via heat and pressure. Material selection: Laser toner transfer lays on top and hearing to the surface of any color material whereas dye sublimation inks are permanently infused into the chemical structure of the polymer substrate. Sublimation can only attach to white or light-colored polyester or other polymer-coated products. However, it forms a permanent attachment and thus it cannot be washed away. Key differences: Now, we will tell you about some key differences in the comparison of these types of printers in which one is the sublimation printer and the other is the laser printer. By knowing the key differences, you can easily get to understand the comparison between the sublimation printer and the laser printer. So stay with us and let’s go forward, Working process: In the working process of the sublimation printer, the ink is diffused onto the paper. But in the case of a laser printer, it prints through a laser and an electrical charge. The working processes of both of these printers are different. Because the sublimation printers use ink cartridges and the laser printer uses toner cartridges. Cartridges: In the sublimation printer, the ink cartridges are used to produce the color as well as white and black or monochrome printing. But in the case of laser printers, the toner cartridges are used to produce white and black or monochrome printing. So, in this case, both of these printers are different from each other. Ink type: In the sublimation printer, you will see that the ink which is used in this type of printer is in the form of wet or liquid. But on the other hand, the ink which are used in the laser printer is in the form of dry powder. Nozzle: The sublimation printer using the nozzles to spray the ink onto the paper. But on the other hand, the laser printer is not applicable to nozzles to spray the ink onto the paper. So this factor is only used for the sublimation printer, not for the laser printer. Print speed: The printing speed of sublimation printer is lesser than the laser printer. Because in the sublimation printer you can get the high color printing quality with high resolution. So at high resolution, the printing speed of the printer become low than the low printing resolution. On the other hand, the laser printer has high printing speed, because in this case, you print the monochrome printing. And monochrome or white and black printing, the printing speed of any printer become high. The sublimation printer is also used to print white and black or monochrome printing. Print output: The sublimation printer cannot handle the high volume of printing. Because the printing speed of a sublimation printer is less than the printing speed of a laser printer. These printer takes more time to handle the high volume of printing as compared to laser printer. So, the laser printer can handle the high volume of printing. Color print: This is also the main key difference in the comparison of sublimation printers and Laser printers. In the case of a Sublimation printer, you will be able to print out the color printing. But on the other hand, laser printer does not support color printing. By the laser printer, you can only print white and black or monochrome printing. Cost: Generally, sublimation printer are going to be more expensive to operate just because of the ink cartridges and their replacement print heads. But also because they require special sublimation paper. If you want the quality to be good and be more permanent which brings us to the water solubility which is another issue with sublimation printer, but the laser printers use toner which is tiny electrostatically charged particles made of plastic that are then fused to the paper. So you don’t have the water solubility issue with the print in general and color. A laser printer is more permanent. Conclusion: So, in conclusion, if you need to plot better than 12 by 18 then you can get the sublimation printer. If you need more than four colour process CYMK, you need like six or twelve colors to produce original photography by getting a sublimation printer. If you need to print on speciality media like canvas or transfer media then you get a sublimation printer. Otherwise always buy a laser printer, because laser printers are much faster, and much more reliable because you don’t have ink drying out. And laser can use plain paper, so the laser printer is much cheaper to operate. Not because of just the supplies or the longevity of the supplies, but also because you use plain paper, you are not to use expensive special media as you do with the sublimation printer. Now, we will discuss with you the following terms, in which we compares the advantages and disadvantages of the two systems in which one is laser printer and the other is sublimation printer. Advantages of laser printers: Laser transfer advantages are that, - The laser printer can be reused for general office need - It can print white directly onto dark paper - This printer has the ability to print a huge volume of printing - Has the ability to produce fine-quality text documents - It does not need specially coated end products Disadvantages of Laser printers: Laser printers' disadvantages are that, - Applies on top of the target surface - Only print on paper, but its printing has the ability to transfer on different media - It has a shorter wash ability life than the sublimation Advantages of sublimation printer: The advantages of sublimation printers are that, - It infuses with the material and is not just layered on top - It is dishwasher and microwave safe - It provides vivid, photorealistic colors - It maintains the soft feel of garments - It has a long wash ability life Disadvantages of sublimation printer: Disadvantages of sublimation printers are that, - This printer is not usually designed for the high point volume - It is limited to polyester or polytube products - Ink cost by replacement - If they are not using the ink cartridges, then every day they tend to dry up quickly Final verdicts: The sublimation printers come in an advance printers than the laser printers. With the sublimation printer, you can print both monochrome and color printing. But in case of a laser printer, you almost use it for the monochrome or Black and white printing. In the sublimation printer, the ink cartridges are used to print out the color printing on the sublimation paper. But in the laser printer, the toner cartridges are used to print out the printing on the plain paper. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Various Printing Techniques
Do you understand the various advantages and disadvantages that printing has to offer? We will learn about the two most common styles of printing.

Printing Using Offset Lithography Let's begin with one of the most used techniques for printing in huge quantities. In offset printing, your artwork is transferred to metal plates, then moved onto rubber blankets or rollers before being printed on a surface. For media with rough surfaces, including wood and canvas, offset lithography is most frequently utilized. But because of its adaptability, it may also be used for paper and other types of packaging.
Advantages Since offset lithography can be applied to both low- and high-volume print jobs, it is ideal for creating high-quality images. It is adaptable because print media can be printed on any flat surface and any sort of paper. Long-term usability: Because the print media doesn't come into contact with the plates, their life is prolonged. has excellent flexibility. Because rubber rollers and plates are flexible, offset lithography can also be employed on media with uneven surfaces.
Disadvantages Despite the fact that offset lithography excels at creating images of superior quality. There are two primary negatives: It is not cost-effective: Offset printing is not economical for lower quantities due to the time and money needed to set it up. It is often only employed when extremely high print volumes are required. Not environmentally friendly: The only choice when utilizing conventional offset printing techniques is to print in bulk, which may result in additional waste being generated.
Digital Printing Inkjet and laser printing are just two examples of the many modern printing techniques covered under digital printing. It is most frequently used for newsletters, labels, posters, menus, and corrugated boxes. Images are transmitted directly to the printer during the digital printing process utilizing digital files like PDFs. If you are not printing huge numbers, this implies that printing plates are not required, which might save you time and money.
Advantages Digital printing is fantastic for a variety of design applications, including customized packaging. Since personalized packaging is in high demand, the digital printing and inkjet industries will continue to expand rapidly. The use of digital printing techniques has a variety of advantages: Quick turnaround times for digital printing enable businesses to print items as needed. Cost-effectiveness: Digital printing can save money because no plates are required to create prints of comparable quality to those made in larger sizes. Greater adaptability enables you to make frequent adjustments to your printing materials as necessary. Simple customization: You may use digital printing to personalize your package and set it apart from the competition.
Disadvantages Although digital printing has gained a lot of popularity in response to consumer demand for lower volumes and cheaper prices, it still falls short of offset printing in terms of quality. To name a few of digital printing's primary drawbacks: Unable to match color: Traditional offset printers' color quality still cannot be matched by digital printing. As digital printers are not completely absorbed into the paper, cracks may form. When the piece is folded, the color may also fracture. Less variety of materials: While digital printing is catching up to offset printing presses in terms of the types of materials they can print on, it still cannot match offset printing's extensive selection of paper, ink, and finish options.
0 notes
Text
UPS System
We can benefit from UPS systems in cases of power outages or fluctuations. Uninterrupted power supply, or UPS, is the best way to protect your computer hardware and data from power fluctuations. UPS maintains the operation of the audio/video equipment, network equipment, and computer peripherals until standby plans are arranged.
UPS Systems are required.
The energy crisis won't be solved until the most alternative energy sources are used. Power outages, blackouts, and other power variations will continue until that time. In this case, the UPS systems play a crucial role in your professional life. It shields your computer hardware from surges or spikes in the main power supply. Hardware damage, costly downtime, and data corruption are all prevented.
The UPS system makes sure that safe voltage levels are maintained without the need for battery power, and it also makes sure that equipment shuts down properly and unattended when there is a power outage.
Other sectors where UPS is essential
The effective operation of sophisticated medical equipment utilized in a hospital setting depends equally on UPS. Power blackouts or fluctuations can have a negative impact on the operation of expensive and sophisticated MRI/CT scans, and the same is true for commercial applications like CNC machines. The printing industry is the same.
The operation of laser machines is another sector of business where UPS plays a crucial role. The use of online UPS systems is always advised by the laser firm because lasers have become a crucial component of dermatology practice. If there is a power outage or fluctuation during a procedure, the UPS backup ensures its completion.
Because laser printers require a high beginning current, a higher VA rated UPS is required to accomplish the same task.
Types of UPS
As a result, three different types of UPS are available:
Online, interactive lines, and standby
We will talk about the online type of UPS of the aforementioned.
Online UPS System
The On-line UPS systems are the best since they use a double-conversion method to provide more power security. The UPS unit converts incoming AC power to DC first, filters it for surges, sags, or noise, and then converts it back to AC power before it leaves the unit. The inverter receives continuous power, so there is no need to convert to battery mode in the event of a power outage.
Due to the zero transfer time in cases of power failures, it enables immediate correction of power issues. The battery powers the system continuously through the inverter, and line power powers the battery charger.
Making the Best Decision
This system is suitable for any amount of backup power requirements. Additionally, it claims improved reliability and superior power quality. Compared to other types of UPS systems, the size is small. However, the typical energy efficiency ranges from 85% to 92%, which results in more heat being produced, high initial and operating costs, high maintenance costs, and frequent battery replacements—on average every five years. While online UPS systems undoubtedly offer a number of advantages, they also have some disadvantages. Therefore, you must consider both the pros & cons.
Choose the UPS system that best meets your demands because they have changed significantly over time and have made great strides toward being economical and environmentally friendly in modern times.
Your one-stop shop for all your power product needs is Positrix Power Pvt. Ltd. Visit us at https://kbsindia.net/ for more information.
0 notes
Text
Samsung Laser Printers - Advantages to Consider
Samsung laser printers fall inside the lower value scopes of the market, however that doesn't constantly imply that they need as far as quality and highlights. There are a greater number of preferences than hindrances with regards to acquiring from this brand, which demonstrates that you can spare some cash and still get a sturdy printer that conveys astounding, clear prints.
Samsung Advantages: The greatest favorable position to obtaining a Samsung printer is that they are truly moderate. The brand offers numerous models moving admirably under the $500 value point, with a considerable lot of those moving for $200 or less. These models are a blend of essential high contrast printers and multi-working machines with shading capacity.
Multi-work laser printers are to a great degree famous right now since they preserve space in the workplace or home and make working increasingly productive.
Probably the best evaluated Samsung laser printers by buyers are those intended to be minimal, space sparing units. For example, the ML-1630 Monochrome Samsung laser printer has been extremely generally welcomed by purchasers for its appealing, smooth dark appearance and little, convenient casing. It doesn't take up a ton of room and can without much of a stretch be moved around, yet it conveys fresh, clear high contrast prints that turn out in only 15 seconds.
The Monochrome arrangement printers are likewise to a great degree calm, conveying quick prints without the commotion dimension of different printers.
The costs might be lower than what some other name brands move for, however Samsung conveys superb prints and some pleasant model plans.
Samsung Disadvantages: The greatest shopper dissension about Samsung laser printers that move for $200 or less comes down to the nature of the paper feed and other little parts on the machine. The paper feed is noted to cause issues for a few people on models, for example, the CLP-315, however there are numerous different models in a similar essential value extend which don't have those issues.
Another normal protestation from a few clients is that the print cartridges don't print the same number of pages of course before beginning to run low. This can be settled to some degree by buying good cartridges from different brands that hold more ink, yet it must be noticed that numerous models do offer sensible cost per page.
Note that the quality on printers in the most reduced value extend can't be contrasted and the nature of printers moving at greater expenses. Samsung really emerges in the market since they give many ease models f Samsung laser printer that are sturdy enough to keep going for a considerable length of time and which don't experience the ill effects of value issues. However, it must be normal that an exceptionally modest model may not be as tough or solid over the long haul as a progressively costly model.
Keep in mind, certain models are intended for specific highlights and capacities. To figure out which Samsung laserprinter might be best for your home or office, think about what your requirements are regarding quality and highlights. You would then be able to take a gander at what each model is intended for, read customer surveys, and pick the best one for your requirements.
For more information please visit www.ink555.com
1 note
·
View note
Text
3D printing is a revolutionary technology that's likely to have an enormous impact on the world. But what exactly is it? Table of Contents3D Printing-Whatchu Talkin' About?A Brief History of 3D PrintingTypes of 3D Printers3D printerFDM (fused deposition modeling)SLA (stereolithography)Open Source vs. Closed SourceSpeed of the Print ProcessCost of 3D PrintingWhere and How to Find Files to PrintFinal 3D Printing-Whatchu Talkin' About? 3D printing is the process of creating a three-dimensional object from a digital file. It's like printing out a document, except instead of ink being deposited onto paper, plastic or metal powder is laid down layer by layer to create an object with any shape or color you can imagine. 3D printing has been around for decades, but it was only in 2008 that it started to become mainstream. Today, there are more than 1,000 3D printers available for purchase and thousands more in development. A 3D printer essentially reads a digital file and creates a physical object based on that file. That digital file can be created by hand or created using software, such as a CAD (computer-aided design) program. The resulting object is a solid object made of plastic or metal, with the same properties as the materials it was printed from. So you can print an exact copy of something made out of wood or plastic. The idea behind 3D printing is simple: Take an object and convert it into a digital file (usually through CAD software). Then use that file to print out an exact replica of the original object using one of several methods: extrusion (basically squirting out melted plastic), laser sintering (melting together tiny particles of metal) or stereolithography (using lasers to cure liquid resin). A Brief History of 3D Printing Types of 3D Printers When you talk about 3D printing, you may mean one of the following: 3D printer A device that uses a digital blueprint to create a physical object by printing layer upon layer of material. This material can be plastic, metal or even living cells. There are different types of 3D printers, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some can print larger objects than others and some can print in more than one color. FDM (fused deposition modeling) One type of 3D printer that uses a filament spool to extrude plastic material, layer by layer, in order to create an object. FDM is the most common type of 3D printing technology and it's used by several different manufacturers like MakerBot and Stratasys. SLA (stereolithography) Another type of 3D printing technology that uses light shining through a liquid resin to harden it into an object as it's being printed layer by layer. The SLA process is slower than FDM but it produces higher quality parts due to the fact that there are fewer layers involved in the process and that each layer gets cured before adding another layer on top of it . The biggest drawback to the SLA process is that the resin used in it can be expensive and the finished parts are usually more delicate than those produced by FDM. Open Source vs. Closed Source The 3D printing industry is a lot like the Wild West. There are so many different types of printers and materials that it can be difficult to know which one is right for you. To help, we've created a brief guide to some of the most common terms you'll encounter when shopping for 3D printers. The biggest difference between open source 3D printers and closed source ones is that open source ones can be modified and improved by anyone who wants to do so because they use standard parts instead of proprietary ones. A closed source printer would have code that prevents users from being able to modify it in any way, shape or form without breaking copyright laws or licenses if they wanted to use their own parts instead of official ones sold by the manufacturer. The open-source movement has become increasingly popular in recent years, but it's not just software
that benefits from being open source — 3D printing does as well! Open-source printers are made by companies that release their designs and software codes for free, making them available for anyone to download and use at no cost. This allows for faster innovation within the industry, as well as more affordable prices for consumers who want to buy their own printer without having to spend thousands of dollars on proprietary parts or software licenses. Most of our printers fall into this category! Closed-source printers may be less expensive initially, but they're also less customizable and often require costly upgrades if you want to do anything beyond basic printing jobs. There are many reasons why companies choose to use closed source software, but all of them boil down to one thing: money. When you buy a piece of software, it's yours forever — or at least as long as you continue to pay for updates and support. The company that created it has no claim on your product, so if you're unhappy with it in any way, you can just walk away and find something else that works better for you. The same goes for hardware — if someone makes a 3D printer that doesn't work properly for some reason (or worse), then there's nothing stopping you from buying another one from someone else who does their job better than the first one did theirs. Speed of the Print Process The speed of the print process depends on several factors. One of them is the size of the object, which determines how much material needs to be deposited. If you are printing a large object, it will take longer than a small one. Another factor is the level of detail that you want to achieve in your print. The higher the detail, the slower the process becomes because more time is required for each layer to dry and become solid enough for printing to continue on top of it. The speed also depends on your printer manufacturer and model. Some printers have a lower maximum resolution than others, so they cannot achieve high-resolution prints at all speeds or at all layers; some have better hardware than others, allowing them to perform better overall; some have faster print heads (the part that deposits material), etc.. Cost of 3D Printing 3D printers are still a relatively new technology, so it's hard to know what the future will hold for them. However, there are some things we can say about their present. The cost of 3D printing is a big consideration for anyone looking to invest in one. The price of the printer itself can vary greatly depending on what you're looking for and where you buy it from. 3D printers can run from as little as $500 up to $10000 or more. The quality of the print also affects pricing. Some printers are able to produce higher quality prints than others, but this also comes with a higher price tag. 3D printing is a relatively new technology, and it's still evolving. There are many different types of printers available, with different price points and capabilities. There are two main types of 3D printers: FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) and SLA (Stereolithography). FDM printers use plastic filaments that are melted and extruded through a nozzle to create layers of material one on top of another. SLA printers use a UV laser to solidify a liquid resin that is applied one layer at a time. If you want to get started with 3D printing right away, it's best to look at budget options first before investing in more expensive machines with more advanced features and capabilities that may not be necessary at this point. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks: FDM - Cheap and easy to use, but low resolution models can take longer to print than those produced by other methods. SLA - High-quality prints in a short amount of time, but expensive materials cost more per print than FDM models. Where and How to Find Files to Print In order to print anything on your 3D printer, you need a file or template from an object that you want to print. There are several ways to get these files:
If you have access to an office or school computer with internet access and a printer driver installed, you can download files from sites like Thingiverse and MyMiniFactory. These sites have thousands of templates for objects that can be printed on most home 3D printers. If you don't have access to a computer with internet access but still want to print something from Thingiverse or MyMiniFactory, there are some smartphone apps that can help you find what you're looking for by using your camera's built-in scanner. These apps will scan any object that they see through their camera lens and then provide a list of matching options on their website or app store page where they found them . What's great about these mobile apps is that they allow the user more freedom than if they were simply using a computer, as they can scan objects that are not in front of a screen. The downside to these apps is that they require internet access in order to use them, which can be difficult if you don't have access or don't want to pay for data on your phone plan. Final 3D printing technology is going to change the world – so much so that it recently posed a threat to Obama's reelection campaign. It is a revolutionary, evolutionary step forward in technology which guarantees to have a huge impact on our lives. Yet the majority of us still do not know exactly what 3D printing actually is and how we can use it.
0 notes
Text
Understand The Advantages Of Laser Printers
Understand The Advantages Of Laser Printers
Laser printers have many advantages over other types of printers, including higher print quality, lower cost per page, and faster printing speeds. Laser printers also have a number of features that make them more versatile than other types of printers. Disadvantages Of Laser Printer Laser printers have several disadvantages. They’re usually more expensive than inkjet printers, both to buy and…

View On WordPress
0 notes