#RFID hospital
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

RFID Hospital Tracking
RFID hospital tracking revolutionizes patient care and inventory management. By utilizing Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, hospitals can efficiently track equipment, medications, and patient movement, enhancing operational efficiency and safety. This innovative approach leads to improved patient outcomes and streamlined hospital workflows, making it an essential tool in modern healthcare.
0 notes
Text
RFID Technology for Healthcare: The Smart Choice for Healthcare Cards
In the modern healthcare environment, patient identification and medical data management are crucial for ensuring efficient operations and patient safety. Traditional healthcare card systems face issues such as misidentification of patients, inefficient manual management, and security vulnerabilities. These problems not only affect the quality of healthcare services but can also lead to medical errors and data breaches. That’s why an increasing number of healthcare institutions are turning to RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology. RFID healthcare cards offer more accurate, rapid, and secure identity verification while seamlessly integrating into existing medical management systems. Whether it’s for patient admission, ward management, or tracking medications and medical equipment, RFID technology is propelling the healthcare industry towards a smarter and more efficient future.

1. What is RFID Technology?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a wireless communication technology that uses radio frequency signals to identify and track objects without the need for direct contact or line-of-sight. Compared to traditional magnetic stripe cards or barcode technology, RFID can transmit information over long distances and at high speeds, giving it a distinct advantage in identity verification and asset management.
How Does RFID Work? A complete RFID system typically consists of the following three primary components:
RFID Tags: Also known as RFID chips, these are embedded in cards, wristbands, or other mediums, storing unique identification information.
RFID Readers: These devices are responsible for sending radio frequency signals and receiving data from RFID tags.
Backend Database (Software System): The reader transmits the collected information to the Hospital Management System (HMS) or Electronic Health Record (EHR) system for identity verification and data processing.
Patients only need to tap their RFID healthcare cards lightly for the system to quickly identify them, retrieve medical records, and verify insurance information, significantly reducing manual processing time and enhancing the efficiency of patient admission and treatment processes.
In the healthcare sector, most RFID healthcare cards utilize high-frequency (HF) passive RFID tags. Passive tags do not require a battery; their energy is supplied by the radio frequency signals from the reader, making them cost-effective and long-lasting, particularly well-suited for large-scale patient management, asset tracking, and access control.
2. RFID Healthcare Cards: A Smarter Solution
RFID healthcare cards are being widely adopted in medical institutions around the world, providing more efficient solutions for patient identification, data management, and hospital operations.
Enhanced Patient Identification and Safety
Identification errors can lead to misdiagnoses, medication errors, and even medical accidents. RFID healthcare cards utilize unique electronic tags to ensure that patient information is accurate and reliable. During patient admission, medication dispensing, surgeries, or nursing care, healthcare personnel can quickly scan the RFID card to access critical information such as name, medical history, allergy information, and treatment plans, effectively reducing the risk of errors.
Fast and Efficient Data Access
RFID healthcare cards automate and expedite patient registration and information retrieval, reducing wait times and increasing hospital efficiency:
Patient Admission: Patients can complete identity verification and medical record retrieval with a simple card swipe.
Medication Management: Scanning the RFID card provides immediate access to prescription information, ensuring safe medication use.
Emergency Care: Physicians can rapidly access a patient's medical history, enabling accurate decision-making in critical situations.
Integration with Existing Systems
RFID healthcare cards seamlessly integrate with various medical systems such as Electronic Health Records (EHR), Hospital Information Systems (HIS), Laboratory Information Systems (LIS), and Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS), facilitating data sharing and automated management:
One-Click Medical Record Access: Reduces the time doctors spend searching for information.
Smart Surgery Management: Ensures synchronized surgical information, reducing operational risks.
Patient Flow Monitoring: Optimizes resource allocation and enhances service efficiency.
3. Benefits of Using RFID Cards in the Healthcare Industry
The application of RFID healthcare cards not only enhances patient safety but also significantly optimizes hospital management efficiency. Here are the key advantages it brings to healthcare institutions:
Improved Patient Safety and Care Quality
Medical accidents often result from identification errors or medication mistakes, but RFID cards effectively mitigate these issues:
Accurate Identity Verification: RFID healthcare cards ensure that each patient's identity matches their medical records, preventing misdiagnoses and erroneous treatments.
Safe Medication Management: Scanning the RFID card allows verification of the patient's prescriptions, reducing the chances of dispensing the wrong medication or incorrect dosages.
Fraud Risk Reduction: RFID technology can help prevent healthcare insurance fraud, ensuring transparency and security in medical services.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
RFID healthcare cards automate multiple processes, making hospital operations smoother:
Rapid Patient Registration: A simple card swipe completes identity verification, shortening wait times.
Efficient Billing Management: Automatically records the costs of medical services, reducing manual entry errors.
Intelligent Asset Management: Used to track medical equipment, ensuring that critical resources are always available.
Cost Savings
In the long run, RFID healthcare cards can significantly reduce operational costs:
Reduction of Human Errors: Minimizes the likelihood of medical accidents that can lead to legal and compensation expenses.
Optimized Human Resources: Decreases the need for paper records and manual data entry.
Less Material Waste: Real-time tracking of medications and equipment reduces inventory backlog.
Real-Time Monitoring and Data Tracking
RFID cards provide real-time data, enhancing the transparency and efficiency of hospital management:
Patient Flow Monitoring: Tracks patient movements within the facility, optimizing bed and departmental allocation.
Medication and Equipment Tracking: Ensures availability of critical medical supplies, reducing losses or misuse.
Emergency Response: In urgent situations, RFID can assist healthcare staff in quickly locating patients or equipment, improving care delivery efficiency.
As the healthcare industry evolves towards smarter solutions, RFID healthcare cards have become a key tool for enhancing safety, efficiency, and cost control, providing a win-win solution for both hospitals and patients.
Security and Compliance
In the healthcare industry, data security and privacy protection are paramount. RFID healthcare cards can aid hospitals in adhering to various regulations:
Compliance with International Standards like HIPAA: RFID cards can store encrypted data, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring patient information security.
Prevention of Identity Theft and Fraud: Unique electronic tags ensure that medical services are reserved for designated patients, averting insurance fraud or identity misuse.
Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: Compared to traditional magnetic stripes or barcodes, RFID technology is more difficult to copy, enhancing the reliability of identity verification.

5. How to Choose the Right RFID Card Solution for Your Healthcare Institution
Selecting the right RFID healthcare card is crucial for enhancing management efficiency, ensuring patient safety, and protecting data. Here are some key considerations:
✅ Durability: Choose materials that are waterproof, scratch-resistant, and chemically resistant, such as PVC or eco-friendly materials like BioPoly™ Stone, to withstand frequent use and the need for disinfection.
✅ Security: Opt for encrypted chips (such as MIFARE DESFire or ICODE) and implement two-factor authentication (like PIN codes or biometrics) to prevent data breaches.
✅ System Compatibility: Ensure that the RFID card supports EHR/HIS systems and complies with standards like ISO 14443 and ISO 15693, allowing seamless integration with existing medical devices.
RFIDCard.com: Your One-Stop Shop for High-Quality RFID Healthcare Card Solutions
With over a decade of card production experience in the RFID industry, RFIDCard.com specializes in providing high-quality, customized RFID healthcare cards tailored to meet the diverse needs of hospitals:
✅ Variety of Eco-Friendly Materials: Options available that combine sustainability with durability.
✅ Highly Customizable Design: Ability to add elements such as hospital logos, color coding, and photos for personalization.
✅ Multiple Chip Configurations: Supports various performance chips ranging from Low Frequency (LF) to High Frequency (HF) to meet different hospital application requirements.
✅ Seamless System Integration: Ensures that the RFID healthcare cards integrate effortlessly with your existing medical systems, enhancing operational efficiency and security.
Whether you’re looking to optimize patient management, improve data security, or drive smart hospital operations, RFIDCard.com can provide you with the most suitable RFID healthcare card solutions.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Surgical Instrument Tracking: Revolutionizing Modern Surgery The Indispensable Role of Minimally Invasive Techniques
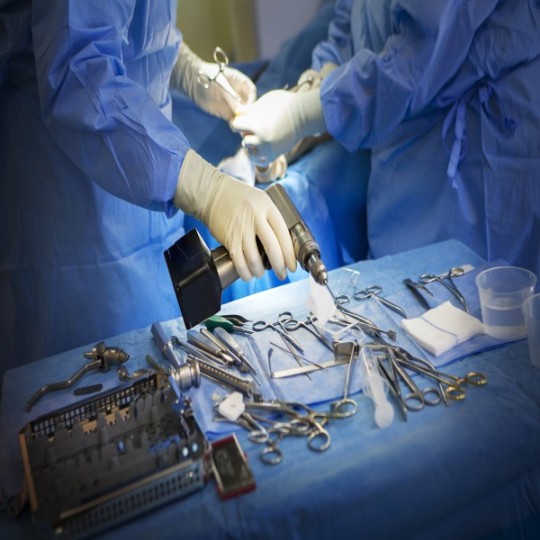
The Importance of Instrument Tracking in Surgery Surgery is an intricate and complex medical procedure that requires precision from medical professionals. From the first incision to the final stitch, countless surgical instruments are used inside the sterile operating field. With so many tools being passed between surgeons and nurses, it’s easy for an instrument to get misplaced or left inside the patient unintentionally. This presents serious risks to patient health and safety. To mitigate these risks, hospitals have increasingly adopted surgical instrument tracking systems. Surgical sponges and other small items left inside patients after surgery, known as retained surgical items or “gossips”, remain a serious problem. Studies show retained items occur in about 1 in every 5,500 to 18,000 surgeries performed. While rare, when they do happen the consequences can be life-threatening or disfiguring for the patient. Not only that, but unintentionally retained items also expose hospitals to legal liability and malpractice claims amounting to millions of dollars each year. Comprehensive surgical instrument tracking helps prevent such incidents from occurring in the first place. How Instrument Tracking Systems Work Modern Surgical Instrument Tracking systems use advanced radio-frequency identification (RFID) or barcode scanning technology to account for each instrument used during a procedure. Small RFID or barcode tags are attached to individual instruments. As instruments are brought into and out of the operating room, they are scanned into a dedicated tracking computer or software system. Before closing the surgical incision, staff perform a final instrument and sponge count using the tracking system. Any discrepancies between what was scanned into the room versus what is accounted for after surgery trigger an alert. This final count helps provide a clear audit trail confirming all items were properly removed from the patient’s body before stitching up the incision. The Benefits of Instrument Tracking Implementing a comprehensive instrument tracking solution yields several important benefits for hospitals: Patient Safety - As mentioned, accurate accounting for all items used during surgery helps prevent life-threatening retained surgical items. Instrument tracking adds an extra layer of safety for patients. Reduced Risk of Liability - Clearly documenting the use and removal of all items helps protect hospitals legally if questions ever arise about whether something was unintentionally left inside a patient. Increased Revenue - Fewer medical malpractice lawsuits related to retained items means less payouts and legal expenses for hospitals over time. Less time is also spent managing liability issues. Process Efficiencies - Automatic identification and counting of instruments streamlines perioperative workflows. Less time is spent manually counting items, searching for missing objects, or filling out paperwork. Staff can instead focus on direct patient care tasks. Asset Management - Tracking technologies provide real-time visibility into instrument locations and usage. This information helps with equipment maintenance planning, usage reports, and inventory management across the hospital system. Overall, a well-designed surgical instrument solution should save hospitals money in the long run through reduced risk and greater process efficiencies, while more importantly enhancing patient care and safety. When implemented and utilized comprehensively, these systems have been shown in studies to virtually eliminate unintended retained surgical items.
Get more insights on Surgical Instrument Tracking
For Deeper Insights, Find the Report in the Language that You want.
French
German
Italian
Russian
Japanese
Chinese
Korean
Portuguese
About Author:
Ravina Pandya, Content Writer, has a strong foothold in the market research industry. She specializes in writing well-researched articles from different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/ravina-pandya-1a3984191)
#Surgical Instrument Tracking#Medical Device Tracking#Surgical Tool Management#Instrument Traceability#Hospital Inventory#RFID Tracking#Surgical Asset Management#Barcode Tracking
0 notes
Text
Comparison of Top ID Card Printers for 2024

As the demand for secure and professional identification solutions continues to grow across industries, ID card printers have become essential tools for businesses, schools, and organizations. In 2024, several manufacturers have introduced cutting-edge models that offer high-quality printing, enhanced security features, and greater efficiency. If you’re in the market for an ID card printer, understanding the differences between the latest models can help you make an informed purchasing decision. This article compares the top ID card printers from brands like Datacard, HID Fargo, Magicard, and Zebra, focusing on their features, print quality, and pricing.
1. Datacard SD360: High-Security Features for Advanced Card Printing
The Datacard SD360 is one of the most advanced ID card printers on the market in 2024, offering premium features that make it ideal for organizations needing secure and durable cards.
Key Features:
Superior speed and productivity: Print more cards in less time. SD Series printers are much faster than other desktop card printers in their class. TruePick™ anti-jam card handling accurately picks cards, both standard and thin, with no need for adjustments.
Superb image quality for high-impact IDs: New TrueMatch™ printing technology ensures consistent, high-quality printing results from the first card to the last, with colors closely matching those on your screen.
Easy operation that anyone can master: The soft-touch control panel and LCD screen are seamlessly guided by intuitive icons. Loading cards and supplies is a breeze, thanks to the user-friendly design. Plus, the ergonomically designed ribbon cartridge includes a convenient drop-in cleaning roller.
All the right connections for easy setup: The SD Series printers can be easily integrated into any application or IT environment using the standard USB/Ethernet ports and the browser-based Printer Manager.
Print Quality:
The Datacard SD360 offers crisp text and vibrant images, using dye-sublimation technology to produce high-resolution cards. Its edge-to-edge printing capability ensures no unprinted margins, giving a clean and professional look to every card.
Pricing:
Priced between 55,000 and 60,000, the Datacard SD360 is a high-end solution, primarily suited for businesses requiring advanced security features, such as businesses, schools, hospitals, fitness clubs
2. HID Fargo DTC4500e: Robust and Flexible for Large Organizations
The HID Fargo DTC4500e is another top contender in 2024, known for its versatility and ability to handle high-volume card issuance.
Key Features:
Modular design: The printer’s modular design allows businesses to add optional modules for dual-sided printing, lamination, or encoding as needed.
Secure printing: Like the Datacard SD360, the DTC4500e offers security features such as password protection and data encryption during the printing process.
High-volume printing: Its input hopper holds up to 200 cards, making it ideal for large batches.
Optional lamination: While lamination is optional, adding this feature increases the longevity of printed cards and reduces wear and tear.
Print Quality:
The HID Fargo DTC4500e offers reliable, high-quality printing using dye-sublimation technology. It delivers full-color prints with precise details and vibrant colors, suitable for high-profile use cases such as corporate IDs or government credentials.
Pricing:
The HID Fargo DTC4500e is priced between 1,50000 and 1,80000, depending on the modules added. This makes it a flexible option for growing businesses that may want to upgrade their printer's capabilities over time.
3. Magicard Ultima: Premium Features with Built-in Security
Magicard is known for producing some of the best secure ID card printers on the market, and the Magicard Ultima is no exception in 2024. This model is designed for organizations that require both high-quality prints and integrated security.
Key Features:
Retransfer technology: The Ultima uses retransfer printing, which produces higher-quality images compared to traditional direct-to-card (DTC) printers. It also allows edge-to-edge printing on various card materials, including those with embedded technology.
Customizable security features: One of its key advantages is the ability to print customized security features, such as watermarks or holographic overlays, directly onto the card during the printing process.
Dual-sided printing: It supports dual-sided printing out of the box, saving time and reducing manual card flipping.
Print Quality:
The retransfer printing technology of the Magicard Ultima allows for exceptional color saturation and crisp image quality. It's ideal for businesses that need their cards to make a strong visual impact, such as universities or loyalty programs.
Pricing:
The Magicard Ultima is priced at the higher end of the spectrum, around 60,000 to 80,000 due to its premium security features and superior print quality. It’s a worthy investment for organizations where security and aesthetics are critical.
4. Zebra ZC350: Fast and Efficient for High-Volume Use
The Zebra ZC350 is a popular choice for businesses seeking fast, high-volume printing without sacrificing quality. Zebra’s reputation for durable, reliable printers shines through in the ZC350.
Key Features:
User-friendly interface: The ZC350 features an intuitive design with an easy-to-use LCD interface, making it accessible for operators with varying skill levels.
High-speed printing: With a print speed of up to 225 color cards per hour (single-sided), this model is ideal for businesses or institutions with a high card issuance volume.
Flexible encoding options: The ZC350 supports a wide range of encoding options, from magnetic stripes to RFID Technology, making it suitable for industries requiring smart card issuance.
Print Quality:
The Zebra ZC350 delivers sharp, vibrant cards with its dye-sublimation printing method. Its fast print speeds don’t compromise on quality, making it a favorite among businesses with high-volume printing needs.
Pricing:
The ZC350 is priced between 3,00000 and 3,50000 making it an affordable option for businesses that need high-quality prints in large quantities. It's a practical choice for universities, large corporations, and event organizers.
Which Printer Is Best for ID Card Printing?
Choosing the best printer depends on your specific needs. Here’s a quick breakdown:
Best for Small to Mid-Size Businesses: The Datacard SD360 offers a balance of affordability, dual-sided printing, and user-friendliness.
Best for High-Speed Printing: The HID Fargo DTC1250e provides fast printing speeds, making it ideal for businesses needing quick card issuance at an affordable price.
Best for High Security: The Magicard 300 is the top choice for businesses needing enhanced security features like custom watermarks.
Best for Large-Scale Operations: The Zebra ZC350 is perfect for large businesses or institutions that need to print a high volume of cards quickly and efficiently.
Conclusion
The ID card printer market in 2024 offers a variety of models suited for different needs, from high-security environments to large-scale operations requiring high-speed printing. Printers like the Datacard SD360, HID Fargo DTC4500e, Magicard Ultima, and Zebra ZC350 provide a range of features, print quality, and price points, ensuring that businesses can find a solution tailored to their specific requirements.
For organizations looking to invest in ID card printing technology, understanding these differences through detailed comparisons can make all the difference in selecting the right tool. As product comparison articles continue to attract significant search traffic, they also serve as valuable resources for potential buyers navigating this competitive market.
#id cards#id card printers#PVC Cards#pvc card printers#ID card printing technology#RFID Technology#Smart Cards#businesses#schools#hospitals
0 notes
Text

Exclusive Interview with Ljudmila Vetrova- Inside Billionaire Nathaniel Thorne's Latest Venture
CLARA: I'm here with my friend Ljudmila Vetrova to talk about the newest venture of reclusive billionaire Nathaniel Thorne- GAMA. Ljudmila, could you let the readers in on the secret- what exactly is this mysterious project about?
LJUDMILA: Sure, Clara! As part of White City's regeneration programme, Nathaniel has teamed up with the Carlise Group to create a cutting-edge medical clinic like no other. Introducing GAMA– a private sanctuary for the discerning, offering not just top-notch medical care and luxurious amenities, but also treatments so innovative they push the envelope of medical science.
CLARA: Wow! Ljudmila, it sounds like GAMA is really taking a proactive approach to healthcare. But can you tell us a bit more about the cutting-edge technology behind this new clinic?
LJUDMILA: Of course! Now, GAMA is not just run by human professionals, it's also aided by an advanced AI system known as KAI – Kronstadt Artificial Intelligence. KAI is the guiding force behind every intricate detail of GAMA, handling everything from calling patients over the PA system to performing complex surgical procedures. Even the doors have a touch of ingenuity, with no keys required- as KAI simply detects the presence of an RFID chip embedded in the clothing of both patients and staff, allowing swift and secure access to the premises. With KAI at the helm, patients and staff alike benefit from streamlined care.
CLARA: A medical AI? That's incredible! I've heard much of the medical technology at GAMA was developed by Kronstadt Industries and the Ether Biotech Corporation, as a cross-disciplinary partnership to create life-saving technology. Is that true?
LJUDMILA: It sure is, Clara! During the COVID-19 pandemic, GAMA even had several departments dedicated to researching the virus, assisting in creating a vaccine with multiple companies. From doctors to nurses and administrative personnel, the team at GAMA is comprised of skilled individuals who are committed to providing the best care possible. All of the GAMA staff are highly educated with advanced degrees and have specialized training in their respective fields.
CLARA: Stunning! Speaking of the GAMA staff, rumors surrounding the hiring of doctors Pavel Frydel and Akane Akenawa have made headlines, with claims that they supposedly transplanted a liver infected with EHV, leading to the unfortunate demise of the patient shortly after. Such allegations might raise questions about the hospital's staff selection process and adherence to medical guidelines and ethical standards. Do you have any comment on these accusations, Ljudmila?
LJUDMILA: Er- well, Clara, the management of GAMA Hospital has vehemently denied all allegations of unethical practices and maintains that they uphold the highest standards of care for all patients. They state that they conduct thorough background checks on all staff members, including doctors, and that any individuals found to be involved in unethical practices are immediately removed from their position. The hospital has a strict code of ethics that all staff must adhere to, and any violations are taken very seriously. In response to the specific claims about the transplant procedure, GAMA states that they are investigating the matter in cooperation with the relevant authorities.
CLARA: Wonderful! I'm afraid that's all we have time for at the moment- lovely chatting with you again, Ljudmila!
@therealharrywatson @artofdeductionbysholmes @johnhwatsonblog
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Scan the online brochures of companies who sell workplace monitoring tech and you’d think the average American worker was a renegade poised to take their employer down at the next opportunity. “Nearly half of US employees admit to time theft!” “Biometric readers for enhanced accuracy!” “Offer staff benefits in a controlled way with Vending Machine Access!”
A new wave of return-to-office mandates has arrived since the New Year, including at JP Morgan Chase, leading advertising agency WPP, and Amazon—not to mention President Trump’s late January directive to the heads of federal agencies to “terminate remote work arrangements and require employees to return to work in-person … on a full-time basis.” Five years on from the pandemic, when the world showed how effectively many roles could be performed remotely or flexibly, what’s caused the sudden change of heart?
“There’s two things happening,” says global industry analyst Josh Bersin, who is based in California. “The economy is actually slowing down, so companies are hiring less. So there is a trend toward productivity in general, and then AI has forced virtually every company to reallocate resources toward AI projects.
“The expectation amongst CEOs is that’s going to eliminate a lot of jobs. A lot of these back-to-work mandates are due to frustration that both of those initiatives are hard to measure or hard to do when we don’t know what people are doing at home.”
The question is, what exactly are we returning to?
Take any consumer tech buzzword of the 21st century and chances are it’s already being widely used across the US to monitor time, attendance and, in some cases, the productivity of workers, in sectors such as manufacturing, retail, and fast food chains: RFID badges, GPS time clock apps, NFC apps, QR code clocking-in, Apple Watch badges, and palm, face, eye, voice, and finger scanners. Biometric scanners have long been sold to companies as a way to avoid hourly workers “buddy punching” for each other at the start and end of shifts—so-called “time theft.” A return-to-office mandate and its enforcement opens the door for similar scenarios for salaried staff.
Track and Trace
The latest, deluxe end point of these time and attendance tchotchkes and apps is something like Austin-headquartered HID’s OmniKey platform. Designed for factories, hospitals, universities and offices, this is essentially an all-encompassing RFID log-in and security system for employees, via smart cards, smartphone wallets, and wearables. These will not only monitor turnstile entrances, exits, and floor access by way of elevators but also parking, the use of meeting rooms, the cafeteria, printers, lockers, and yes, vending machine access.
These technologies, and more sophisticated worker location- and behavior-tracking systems, are expanding from blue-collar jobs to pink-collar industries and even white-collar office settings. Depending on the survey, approximately 70 to 80 percent of large US employers now use some form of employee monitoring, and the likes of PwC have explicitly told workers that managers will be tracking their location to enforce a three-day office week policy.
“Several of these earlier technologies, like RFID sensors and low-tech barcode scanners, have been used in manufacturing, in warehouses, or in other settings for some time,” says Wolfie Christl, a researcher of workplace surveillance for Cracked Labs, a nonprofit based in Vienna, Austria. “We’re moving toward the use of all kinds of sensor data, and this kind of technology is certainly now moving into the offices. However, I think for many of these, it’s questionable whether they really make sense there.”
What’s new, at least to the recent pandemic age of hybrid working, is the extent to which workers can now be tracked inside office buildings. Cracked Labs published a frankly terrifying 25-page case study report in November 2024 showing how systems of wireless networking, motion sensors, and Bluetooth beacons, whether intentionally or as a byproduct of their capabilities, can provide “behavioral monitoring and profiling” in office settings.
The project breaks the tech down into two categories: The first is technology that tracks desk presence and room occupancy, and the second monitors the indoor location, movement, and behavior of the people working inside the building.
To start with desk and room occupancy, Spacewell offers a mix of motion sensors installed under desks, in ceilings, and at doorways in “office spaces” and heat sensors and low-resolution visual sensors to show which desks and rooms are being used. Both real-time and trend data are available to managers via its “live data floorplan,” and the sensors also capture temperature, environmental, light intensity, and humidity data.
The Swiss-headquartered Locatee, meanwhile, uses existing badge and device data via Wi-Fi and LAN to continuously monitor clocking in and clocking out, time spent by workers at desks and on specific floors, and the number of hours and days spent by employees at the office per week. While the software displays aggregate rather than individual personal employee data to company executives, the Cracked Labs report points out that Locatee offers a segmented team analytics report which “reveals data on small groups.”
As more companies return to the office, the interest in this idea of “optimized” working spaces is growing fast. According to S&S Insider’s early 2025 analysis, the connected office was worth $43 billion in 2023 and will grow to $122.5 billion by 2032. Alongside this, IndustryARC predicts there will be a $4.5 billion employee-monitoring-technology market, mostly in North America, by 2026—the only issue being that the crossover between the two is blurry at best.
At the end of January, Logitech showed off its millimeter-wave radar Spot sensors, which are designed to allow employers to monitor whether rooms are being used and which rooms in the building are used the most. A Logitech rep told The Verge that the peel-and-stick devices, which also monitor VOCs, temperature, and humidity, could theoretically estimate the general placement of people in a meeting room.
As Christl explains, because of the functionality that these types of sensor-based systems offer, there is the very real possibility of a creep from legitimate applications, such as managing energy use, worker health and safety, and ensuring sufficient office resources into more intrusive purposes.
“For me, the main issue is that if companies use highly sensitive data like tracking the location of employees’ devices and smartphones indoors or even use motion detectors indoors,” he says, “then there must be totally reliable safeguards that this data is not being used for any other purposes.”
Big Brother Is Watching
This warning becomes even more pressing where workers’ indoor location, movement, and behavior are concerned. Cisco’s Spaces cloud platform has digitized 11 billion square feet of enterprise locations, producing 24.7 trillion location data points. The Spaces system is used by more than 8,800 businesses worldwide and is deployed by the likes of InterContinental Hotels Group, WeWork, the NHS Foundation, and San Jose State University, according to Cisco’s website.
While it has applications for retailers, restaurants, hotels, and event venues, many of its features are designed to function in office environments, including meeting room management and occupancy monitoring. Spaces is designed as a comprehensive, all-seeing eye into how employees (and customers and visitors, depending on the setting) and their connected devices, equipment, or “assets” move through physical spaces.
Cisco has achieved this by using its existing wireless infrastructure and combining data from Wi-Fi access points with Bluetooth tracking. Spaces offers employers both real-time views and historical data dashboards. The use cases? Everything from meeting-room scheduling and optimizing cleaning schedules to more invasive dashboards on employees’ entry and exit times, the duration of staff workdays, visit durations by floor, and other “behavior metrics.” This includes those related to performance, a feature pitched at manufacturing sites.
Some of these analytics use aggregate data, but Cracked Labs details how Spaces goes beyond this into personal data, with device usernames and identifiers that make it possible to single out individuals. While the ability to protect privacy by using MAC randomization is there, Cisco emphasizes that this makes indoor movement analytics “unreliable” and other applications impossible—leaving companies to make that decision themselves.
Management even has the ability to send employees nudge-style alerts based on their location in the building. An IBM application, based on Cisco’s underlying technology, offers to spot anomalies in occupancy patterns and send notifications to workers or their managers based on what it finds. Cisco’s Spaces can also incorporate video footage from Cisco security cameras and WebEx video conferencing hardware into the overall system of indoor movement monitoring; another example of function creep from security to employee tracking in the workplace.
“Cisco is simply everywhere. As soon as employers start to repurpose data that is being collected from networking or IT infrastructure, this quickly becomes very dangerous, from my perspective.” says Christl. “With this kind of indoor location tracking technology based on its Wi-Fi networks, I think that a vendor as major as Cisco has a responsibility to ensure it doesn’t suggest or market solutions that are really irresponsible to employers.
“I would consider any productivity and performance tracking very problematic when based on this kind of intrusive behavioral data.” WIRED approached Cisco for comment but didn’t receive a response before publication.
Cisco isn't alone in this, though. Similar to Spaces, Juniper’s Mist offers an indoor tracking system that uses both Wi-Fi networks and Bluetooth beacons to locate people, connected devices, and Bluetooth tagged badges on a real-time map, with the option of up to 13 months of historical data on worker behavior.
Juniper’s offering, for workplaces including offices, hospitals, manufacturing sites, and retailers, is so precise that it is able to provide records of employees’ device names, together with the exact enter and exit times and duration of visits between “zones” in offices—including one labeled “break area/kitchen” in a demo. Yikes.
For each of these systems, a range of different applications is functionally possible, and some which raise labor-law concerns. “A worst-case scenario would be that management wants to fire someone and then starts looking into historical records trying to find some misconduct,” says Christl. "If it’s necessary to investigate employees, then there should be a procedure where, for example, a worker representative is looking into the fine-grained behavioral data together with management. This would be another safeguard to prevent misuse.”
Above and Beyond?
If warehouse-style tracking has the potential for management overkill in office settings, it makes even less sense in service and health care jobs, and American unions are now pushing for more access to data and quotas used in disciplinary action. Elizabeth Anderson, professor of public philosophy at the University of Michigan and the author of Private Government: How Employers Rule Our Lives, describes how black-box algorithm-driven management and monitoring affects not just the day-to-day of nursing staff but also their sense of work and value.
“Surveillance and this idea of time theft, it’s all connected to this idea of wasting time,” she explains. “Essentially all relational work is considered inefficient. In a memory care unit, for example, the system will say how long to give a patient breakfast, how many minutes to get them dressed, and so forth.
“Maybe an Alzheimer’s patient is frightened, so a nurse has to spend some time calming them down, or perhaps they have lost some ability overnight. That’s not one of the discrete physical tasks that can be measured. Most of the job is helping that person cope with declining faculties; it takes time for that, for people to read your emotions and respond appropriately. What you get is massive moral injury with this notion of efficiency.”
This kind of monitoring extends to service workers, including servers in restaurants and cleaning staff, according to a 2023 Cracked Labs’ report into retail and hospitality. Software developed by Oracle is used to, among other applications, rate and rank servers based on speed, sales, timekeeping around breaks, and how many tips they receive. Similar Oracle software that monitors mobile workers such as housekeepers and cleaners in hotels uses a timer for app-based micromanagement—for instance, “you have two minutes for this room, and there are four tasks.”
As Christl explains, this simply doesn’t work in practice. “People have to struggle to combine what they really do with this kind of rigid, digital system. And it’s not easy to standardize work like talking to patients and other kinds of affective work, like how friendly you are as a waiter. This is a major problem. These systems cannot represent the work that is being done accurately.”
But can knowledge work done in offices ever be effectively measured and assessed either? In an episode of his podcast in January, host Ezra Klein battled his own feelings about having many of his best creative ideas at a café down the street from where he lives rather than in The New York Times’ Manhattan offices. Anderson agrees that creativity often has to find its own path.
“Say there’s a webcam tracking your eyes to make sure you’re looking at the screen,” she says. “We know that daydreaming a little can actually help people come up with creative ideas. Just letting your mind wander is incredibly useful for productivity overall, but that requires some time looking around or out the window. The software connected to your camera is saying you’re off-duty—that you’re wasting time. Nobody’s mind can keep concentrated for the whole work day, but you don’t even want that from a productivity point of view.”
Even for roles where it might make more methodological sense to track discrete physical tasks, there can be negative consequences of nonstop monitoring. Anderson points to a scene in Erik Gandini’s 2023 documentary After Work that shows an Amazon delivery driver who is monitored, via camera, for their driving, delivery quotas, and even getting dinged for using Spotify in the van.
“It’s very tightly regulated and super, super intrusive, and it’s all based on distrust as the starting point,” she says. “What these tech bros don’t understand is that if you install surveillance technology, which is all about distrusting the workers, there is a deep feature of human psychology that is reciprocity. If you don’t trust me, I’m not going to trust you. You think an employee who doesn’t trust the boss is going to be working with the same enthusiasm? I don’t think so.”
Trust Issues
The fixes, then, might be in the leadership itself, not more data dashboards. “Our research shows that excessive monitoring in the workplace can damage trust, have a negative impact on morale, and cause stress and anxiety,” says Hayfa Mohdzaini, senior policy and practice adviser for technology at the CIPD, the UK’s professional body for HR, learning, and development. “Employers might achieve better productivity by investing in line manager training and ensuring employees feel supported with reasonable expectations around office attendance and manageable workloads.”
A 2023 Pew Research study found that 56 percent of US workers were opposed to the use of AI to keep track of when employees were at their desks, and 61 percent were against tracking employees’ movements while they work.
This dropped to just 51 percent of workers who were opposed to recording work done on company computers, through the use of a kind of corporate “spyware” often accepted by staff in the private sector. As Josh Bersin puts it, “Yes, the company can read your emails” with platforms such as Teramind, even including “sentiment analysis” of employee messages.
Snooping on files, emails, and digital chats takes on new significance when it comes to government workers, though. New reporting from WIRED, based on conversations with employees at 13 federal agencies, reveals the extent to Elon Musk’s DOGE team’s surveillance: software including Google’s Gemini AI chatbot, a Dynatrace extension, and security tool Splunk have been added to government computers in recent weeks, and some people have felt they can’t speak freely on recorded and transcribed Microsoft Teams calls. Various agencies already use Everfox software and Dtex’s Intercept system, which generates individual risk scores for workers based on websites and files accessed.
Alongside mass layoffs and furloughs over the past four weeks, the so-called Department of Government Efficiency has also, according to CBS News and NPR reports, gone into multiple agencies in February with the theater and bombast of full X-ray security screenings replacing entry badges at Washington, DC, headquarters. That’s alongside managers telling staff that their logging in and out of devices, swiping in and out of workspaces, and all of their digital work chats will be “closely monitored” going forward.
“Maybe they’re trying to make a big deal out of it to scare people right now,” says Bersin. “The federal government is using back-to-work as an excuse to lay off a bunch of people.”
DOGE staff have reportedly even added keylogger software to government computers to track everything employees type, with staff concerned that anyone using keywords related to progressive thinking or "disloyalty” to Trump could be targeted—not to mention the security risks it introduces for those working on sensitive projects. As one worker told NPR, it feels “Soviet-style” and “Orwellian” with “nonstop monitoring.” Anderson describes the overall DOGE playbook as a series of “deeply intrusive invasions of privacy.”
Alternate Realities
But what protections are out there for employees? Certain states, such as New York and Illinois, do offer strong privacy protections against, for example, unnecessary biometric tracking in the private sector, and California’s Consumer Privacy Act covers workers as well as consumers. Overall, though, the lack of federal-level labor law in this area makes the US something of an alternate reality to what is legal in the UK and Europe.
The Electronic Communications Privacy Act in the US allows employee monitoring for legitimate business reasons and with the worker’s consent. In Europe, Algorithm Watch has made country analyses for workplace surveillance in the UK, Italy, Sweden, and Poland. To take one high-profile example of the stark difference: In early 2024, Serco was ordered by the UK's privacy watchdog, the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO), to stop using face recognition and fingerprint scanning systems, designed by Shopworks, to track the time and attendance of 2,000 staff across 38 leisure centers around the country. This new guidance led to more companies reviewing or cutting the technology altogether, including Virgin Active, which pulled similar biometric employee monitoring systems from 30-plus sites.
Despite a lack of comprehensive privacy rights in the US, though, worker protest, union organizing, and media coverage can provide a firewall against some office surveillance schemes. Unions such as the Service Employees International Union are pushing for laws to protect workers from black-box algorithms dictating the pace of output.
In December, Boeing scrapped a pilot of employee monitoring at offices in Missouri and Washington, which was based on a system of infrared motion sensors and VuSensor cameras installed in ceilings, made by Ohio-based Avuity. The U-turn came after a Boeing employee leaked an internal PowerPoint presentation on the occupancy- and headcount-tracking technology to The Seattle Times. In a matter of weeks, Boeing confirmed that managers would remove all the sensors that had been installed to date.
Under-desk sensors, in particular, have received high-profile backlash, perhaps because they are such an obvious piece of surveillance hardware rather than simply software designed to record work done on company machines. In the fall of 2022, students at Northeastern University hacked and removed under-desk sensors produced by EnOcean, offering “presence detection” and “people counting,” that had been installed in the school’s Interdisciplinary Science & Engineering Complex. The university provost eventually informed students that the department had planned to use the sensors with the Spaceti platform to optimize desk usage.
OccupEye (now owned by FM: Systems), another type of under-desk heat and motion sensor, received a similar reaction from staff at Barclays Bank and The Telegraph newspaper in London, with employees protesting and, in some cases, physically removing the devices that tracked the time they spent away from their desks.
Despite the fallout, Barclays later faced a $1.1 billion fine from the ICO when it was found to have deployed Sapience’s employee monitoring software in its offices, with the ability to single out and track individual employees. Perhaps unsurprisingly in the current climate, that same software company now offers “lightweight device-level technology” to monitor return-to-office policy compliance, with a dashboard breaking employee location down by office versus remote for specific departments and teams.
According to Elizabeth Anderson’s latest book Hijacked, while workplace surveillance culture and the obsession with measuring employee efficiency might feel relatively new, it can actually be traced back to the invention of the “work ethic” by the Puritans in the 16th and 17th centuries.
“They thought you should be working super hard; you shouldn’t be idling around when you should be in work,” she says. “You can see some elements there that can be developed into a pretty hostile stance toward workers. The Puritans were obsessed with not wasting time. It was about gaining assurance of salvation through your behavior. With the Industrial Revolution, the ‘no wasting time’ became a profit-maximizing strategy. Now you’re at work 24/7 because they can get you on email.”
Some key components of the original work ethic, though, have been skewed or lost over time. The Puritans also had strict constraints on what duties employers had toward their workers: paying a living wage and providing safe and healthy working conditions.
“You couldn’t just rule them tyrannically, or so they said. You had to treat them as your fellow Christians, with dignity and respect. In many ways the original work ethic was an ethic which uplifted workers.”
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
ZKTeco F19 Fingerprint Reader Access Control - Trimatrik Multimedia
What is Zkteco?
ZKTeco is a Chinese company that specializes in the development and manufacturing of biometric access control systems. The company was founded in 1998 and is headquartered in Shenzhen, China. ZKTeco has over 2,000 employees and operates in over 100 countries around the world.
ZKTeco offers a wide range of biometric access control products, including fingerprint readers, facial recognition devices, and RFID readers. The company also offers a variety of software solutions for managing access control systems. ZKTeco's products are used by a wide range of customers, including businesses, government agencies, and educational institutions.
ZKTeco is a leading provider of biometric access control solutions. The company's products are known for their high quality, reliability, and affordability. ZKTeco is committed to providing innovative and cutting-edge biometric access control solutions to its customers.
Here are some of the products and solutions offered by ZKTeco:
Fingerprint readers, Facial recognition devices, RFID readers, Access control software, Time and attendance systems, Video surveillance systems, Turnstiles, Barricades, Door controllers, Locks, Keys
ZKTeco's products and solutions are used in a variety of industries, including:
Healthcare, Education, Government, Manufacturing, Retail, Logistics
Transportation, Hospitality, Financial Services, Technology
ZKTeco is a global leader in the biometric access control market. The company is committed to providing innovative and cutting-edge solutions to its customers.
ZKTeco a good brand?
Yes, ZKTeco is a good brand. It is a Chinese company that manufactures biometric devices, such as fingerprint readers, facial recognition systems, and access control systems. ZKTeco products are known for their high quality and competitive prices. They are also used by a wide range of customers, including businesses, schools, and government agencies.
ZKTeco has been in business for over 20 years and has a strong track record of innovation. The company is constantly developing new products and technologies to meet the needs of its customers. ZKTeco is also committed to providing excellent customer service. Its products come with a one-year warranty and the company offers 24/7 technical support.
If you are looking for a reliable and affordable biometric device, ZKTeco is a good option. The company has a wide range of products to choose from and its products are backed by a strong warranty and excellent customer service.
Here are some of the pros and cons of ZKTeco:
High-quality products
Competitive prices
Wide range of products to choose from
Excellent customer service
Consultation:
Some products may be more expensive than other brands
Some products may not be as user-friendly as other brands
Overall, ZKTeco is a good brand that offers a wide range of high-quality biometric devices at competitive prices. The company is committed to providing excellent customer service and its products come with a one-year warranty.
Which company Zkteco biometric is best?
ZKTeco is a Chinese company that specializes in biometrics. They offer a wide range of products, including fingerprint scanners, facial recognition systems, and access control devices.
ZKTeco is a well-respected company in the biometrics industry. They have a long history of innovation and have developed some of the most advanced biometric technologies on the market.
Some of the best ZKTeco biometric products include:
ZKBioSecurity Fingerprint Time Attendance Terminal: This device is a great option for businesses that need a reliable and affordable biometric time and attendance system.
ZKAccess 3.0 Biometric Access Control System: This system is a powerful and versatile access control solution that can be used to secure a wide range of facilities.
ZKFaceX Facial Recognition Terminal: This terminal is a great option for businesses that need a high-accuracy facial recognition system.
ZKTeco biometric products are available in a variety of price points, so you can find a solution that fits your budget. They also offer a variety of features, so you can choose a product that meets your specific needs.
If you are looking for a reliable and affordable biometric solution, ZKTeco is a great option. They offer a wide range of products with a variety of features, so you can find a solution that fits your needs.
What is the Zkteco best attendance device?
The ZKTeco best attendance device is the ZKBio Security Fingerprint Time Attendance Terminal. It is a reliable and affordable biometric time and attendance system that is easy to use and has a variety of features.
The ZKBioSecurity Fingerprint Time Attendance Terminal features a high-speed fingerprint scanner that can accurately identify employees in less than a second. It also has a built-in camera that can take pictures of employees when they clock in or out. This information can be used to create reports that track employee attendance and productivity.
The ZKBioSecurity Fingerprint Time Attendance Terminal is also easy to use. Employees can simply swipe their fingerprint or enter their PIN to clock in or out. The system also supports multiple users and shifts, so it can be used by businesses of all sizes.
The ZKBioSecurity Fingerprint Time Attendance Terminal is a great option for businesses that are looking for a reliable and affordable biometric time and attendance system. It is easy to use, has a variety of features, and is accurate and secure.
Here are some of the key features of the ZKBioSecurity Fingerprint Time Attendance Terminal:
High-speed fingerprint scanner
Built-in camera
Multiple users and shifts supported
Easy to use
Affordable
Accurate and secure
If you are looking for a reliable and affordable biometric time and attendance system, the ZKBioSecurity Fingerprint Time Attendance Terminal is a great option.
Trimatrik Multimedia offer by Fingerprint Time Attendance Terminal Zkteco
Trimatrik Multimedia offers a variety of fingerprint time attendance terminals from ZKTeco. These terminals are designed to help businesses track employee attendance and productivity. They are also used to control access to facilities and resources.
ZKTeco fingerprint time attendance terminals are available in a variety of models to meet the needs of businesses of all sizes. Some of the features that are available on these terminals include:
Fingerprint recognition
RFID card reader
Password entry
Built-in camera
Display screen
Ethernet port
USB port
Wiegand output
ZKTeco fingerprint time attendance terminals are easy to use and can be configured to meet the specific needs of businesses. They are also reliable and secure, making them a good choice for businesses that are looking for a way to improve their attendance and security.
Here are some of the benefits of using Zkteco fingerprint time attendance terminals:
Improved attendance tracking: Zkteco fingerprint time attendance terminals can help businesses to improve their attendance tracking by providing accurate and reliable data on employee attendance. This data can be used to identify areas where attendance is low and to take corrective action.
Increased productivity: Zkteco fingerprint time attendance terminals can help businesses to increase productivity by reducing the time that employees spend clocking in and out. This frees up employees to focus on their work and can lead to increased productivity.
Improved security: Zkteco fingerprint time attendance terminals can help businesses to improve security by controlling access to facilities and resources. This can help to prevent unauthorized access and can protect assets from theft.
If you are looking for a reliable and secure way to track employee attendance and improve security, then Zkteco fingerprint time attendance terminals are a good option.
Which biometrics is the most expensive?
The most expensive biometrics are those that are the most accurate and secure. These include:
Iris scanning: Iris scanning is the most accurate biometric technology available. It can identify individuals with a high degree of accuracy, even if they are wearing glasses or contact lenses. Iris scanning is also very secure, as it is difficult to spoof an iris.
Retina scanning: Retina scanning is also very accurate and secure. It works by scanning the blood vessels in the retina, which are unique to each individual. Retina scanning is more expensive than iris scanning, but it is also more secure.
Facial recognition: Facial recognition is becoming more accurate and secure, but it is still not as accurate or secure as iris scanning or retina scanning. Facial recognition is also more susceptible to spoofing, as it can be fooled by masks or makeup.
Voice recognition: Voice recognition is the least accurate and secure biometric technology. It can be fooled by impersonators, and it is not as reliable as other biometric technologies.
The cost of biometrics varies depending on the technology, the accuracy, and the security. Iris scanning and retina scanning are the most expensive biometric technologies, while facial recognition and voice recognition are the least expensive.
The cost of biometrics is also affected by the size of the system. Larger systems with more features are more expensive than smaller systems with fewer features.
If you are looking for the most accurate and secure biometric technology, then iris scanning or retina scanning are the best options. However, these technologies are also the most expensive. If you are looking for a less expensive option, then facial recognition or voice recognition may be a better choice.
What is the most commonly used biometrics?
The most commonly used biometrics are fingerprint recognition and facial recognition. These two biometrics are used in a variety of applications, including:
Access control: Fingerprint recognition and facial recognition are used to control access to facilities and resources. For example, they can be used to unlock doors, start cars, and access computers.
Time and attendance: Fingerprint recognition and facial recognition are used to track employee attendance and productivity. For example, they can be used to clock in and out of work, and to track breaks and overtime.
Payment: Fingerprint recognition and facial recognition are used to make payments. For example, they can be used to pay for goods and services with a mobile phone or a wearable device.
Security: Fingerprint recognition and facial recognition are used to improve security. For example, they can be used to identify criminals and to prevent fraud.
Fingerprint recognition and facial recognition are the most commonly used biometrics because they are accurate, reliable, and secure. They are also relatively inexpensive to implement.
How do I choose a biometric system?
Here are some things to consider when choosing a biometric system:
Purpose: What do you need the biometric system for? Are you looking for a system to control access to a facility, track employee attendance, or make payments?
Accuracy: How accurate does the system need to be? If you are using the system to control access to a secure facility, you will need a system with a high degree of accuracy. If you are using the system to track employee attendance, you may not need as high a degree of accuracy.
Security: How secure does the system need to be? If you are using the system to control access to a sensitive facility, you will need a system that is very secure. If you are using the system to track employee attendance, you may not need as high a level of security.
Cost: How much are you willing to spend on a biometric system? Biometric systems can range in price from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars.
Ease of use: How easy is the system to use? If you are using the system with employees, you will need a system that is easy to use. If you are using the system with customers, you will also need a system that is easy to use.
Features: What features are important to you? Some biometric systems have features such as the ability to store multiple fingerprints or the ability to integrate with other systems.
Once you have considered these factors, you can start to narrow down your choices and choose the best biometric system for your needs.
Here are some additional tips for choosing a biometric system:
Read reviews: Read online reviews of different biometric systems to get feedback from other users.
Talk to other businesses: Talk to other businesses that use biometric systems to get their recommendations.
Get a demo: Ask the manufacturer or distributor of a biometric system to give you a demo so that you can see how it works.
By following these tips, you can choose the best biometric system for your needs and ensure that your system meets your requirements.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
EAS & RTLS Solutions – AIDC India for Retail & Warehousing

In an age where inventory loss, asset misplacement, and operational delays directly impact business performance, EAS (Electronic Article Surveillance) and RTLS (Real-Time Locating Systems) offer the smart edge businesses need. Whether you're running a retail outlet or a warehouse facility, AIDC India delivers cutting-edge security and tracking solutions that boost visibility, reduce shrinkage, and enhance efficiency.
What is an EAS System?
Electronic Article Surveillance (EAS) is an anti-theft technology designed to prevent shoplifting or unauthorized removal of goods from a store or storage facility.
Core Components:
Tags or Labels: Attached to merchandise and deactivated at checkout.
Detection Antennas: Placed at exit points to sense active tags.
Detachers or Deactivators: Remove or disable tags after payment.
EAS is widely used in retail environments to alert staff if items are taken without being paid for.
Benefits of EAS:
Acts as a visible theft deterrent.
Reduces inventory loss due to shoplifting.
Allows staff to focus more on customer service.
Can be tailored for high-value or small-size items.
What is RTLS?
Real-Time Locating Systems (RTLS) use RFID, infrared, or Bluetooth technology to track the real-time location of assets, people, or inventory inside a facility.
Key Features:
Constant location tracking through tags and readers.
Interactive dashboards showing movement history.
Alerts for unauthorized movement or misplaced assets.
RTLS is ideal for warehouses, logistics hubs, hospitals, and large retail stores where physical asset movement is constant and must be monitored precisely.
Benefits of RTLS:
Full visibility of assets and inventory.
Streamlined picking, packing, and dispatch operations.
Real-time alerts reduce errors and losses.
Enables audit trails for compliance and reporting.
AIDC India’s End-to-End Solutions
For EAS Systems:
Technology Options: Choose from RF, AM, or EM-based systems.
Installation: Optimized placement for maximum tag detection.
Tags & Accessories: Hard tags, soft labels, detachers, and deactivators.
Integration: Seamless setup with POS and inventory systems.
For RTLS Solutions:
Infrastructure Setup: Readers, antennas, and sensors placed across key zones.
Tag Management: RFID tags for products, pallets, or personnel.
Software Dashboard: Real-time tracking and movement history.
Custom Alerts: Set rules for unauthorized movement or delays.
Industries We Serve
Retail
Prevent shrinkage with EAS.
Improve floor visibility and customer flow using RTLS.
Warehousing & Logistics
Track movement of goods from inbound to outbound.
Automate stock counting and asset tracking.
Healthcare
Monitor medical equipment, patient files, or even staff location in large facilities.
Manufacturing
Ensure real-time visibility of tools, parts, and safety equipment across the floor.
Why Choose AIDC India?
Over 10 years of experience in security and asset-tracking technologies.
Custom deployment plans tailored to your business layout and industry.
Ongoing training, support, and software updates.
Solutions designed to scale with your growth.
Smarter Security and Tracking with AIDC India
As businesses scale, so does the complexity of managing physical inventory, assets, and security. With EAS and RTLS technologies, AIDC India empowers you to stay ahead—preventing loss, optimizing workflows, and ensuring full operational transparency.
Contact Us
Get in touch with AIDC India to discuss customized EAS and RTLS solutions for your business. Let’s build a smarter, more secure operation together.
#real time tracking#asset management#aidc technologies india#qr code#rfid solutions#electronic devices#barcode#technology#aidc#barcode printers
0 notes
Text

Why effective laundry record keeping is the cornerstone of a successful operation
Let’s start with a question: Does your team spend hours searching for missing linen, reconciling inventory, or prepping for compliance audits? This situation, unfortunately, is all too frequent in many commercial laundries—but this is entirely avoidable with good laundry record keeping.
In the hustle of commercial laundry operations, record-keeping often gets overlooked. But here’s the thing: Without solid records, your operation is flying blind. Lost linen, missed deadlines, and compliance nightmares aren’t just inconveniences—they’re profit killers.
Effective laundry record-keeping isn’t just about ticking boxes. It’s about creating a foundation for efficiency, accountability, and growth. Let’s break it down.
Why laundry record keeping matters
Commercial laundries handle thousands of items daily, from hospital gowns to hotel towels. Each item follows a lifecycle: soiled, washed, stored, and delivered. Without meticulous tracking, this lifecycle becomes a tangled web of inefficiencies.
Consider the stakes:
● Inventory control ensures you know exactly what you have, where it is, and when to reorder.
● Compliance demands precise logs for sterilisation, sustainability, or safety audits.
● Client trust hinges on transparency—proving linens were handled correctly and delivered on time.
The hidden costs of neglecting records
When record-keeping falls short, the consequences ripple through every part of a laundry operation. Facilities might turn inventory annually due to poor tracking, translating to thousands of expensive replacement costs. Staff waste hours reconciling manual logs instead of focusing on tasks that boost revenue, like improving customer service or optimising delivery routes.
Compliance risks add another layer of pressure. Hospitals require sterilisation records for surgical linens; hotels need proof of eco-friendly practices. Missing these details can lead to failed audits, fines, or even lost contracts. Without data, decision-making becomes guesswork—like scheduling staff or predicting inventory needs without knowing historical trends.
Building a record-keeping system that works
Effective record-keeping starts with intentionality. Here’s how to create a system that stands the test of time:
1. Start with clarity
Define what needs tracking: inventory levels, wash cycles, delivery times, and client-specific requirements. While spreadsheets can work temporarily, dedicated software like laundry asset management systems offers scalability and real-time insights.
2. Embrace automation
Manual processes are prone to human error. Modern tools like RFID systems automate data entry, logging items the moment they enter or exit your facility. AI-powered alerts can flag low stock levels or delayed shipments, while cloud storage ensures records are secure and accessible from anywhere. Automation isn’t about replacing staff—it’s about freeing them to focus on higher-value work.
3. Standardise and simplify
Consistency is key. Train your team to log data uniformly—whether it’s documenting wash cycles or reporting damaged linens. Create templates for common tasks, like wash logs or delivery manifests, and hold quarterly reviews to refine workflows. A Midwest hospital laundry slashed audit prep time from 20 hours to 2 by standardising sterilisation logs across shifts.
4. Prioritise compliance
Different industries have unique needs. Healthcare clients require meticulous sterilisation records, while hotels may demand sustainability certifications. Build compliance into your daily routines—for example, by automatically logging wash temperatures or chemical usage. Secure, cloud-based systems ensure records are audit-ready at a moment’s notice.
5. Invest in training
Even the best system fails without user buy-in. Regular workshops keep skills sharp, and sharing success stories—like how RFID tracking saved a Florida resort $45k annually—builds enthusiasm. Encourage feedback to identify pain points; sometimes, a small tweak can resolve a major bottleneck.
The cumulative power of small wins
Laundry record keeping isn’t about overnight transformation. It’s about incremental progress—the daily act of logging a wash cycle, scanning a delivery, or updating a digital dashboard. Over time, these small steps compound into fewer losses, smoother audits, and stronger client relationships.
In an industry where margins are tight and trust is paramount, the quiet discipline of good record-keeping isn’t just a best practice. It’s the foundation of resilience, efficiency, and long-term success. Start small, stay consistent, and let the data guide your way.
0 notes
Text
RFID in Linen tracking
Implementing RFID in linen tracking enhances efficiency and accuracy in managing laundry processes. This technology reduces losses, ensures timely inventory replenishment, and streamlines operations in healthcare and hospitality industries.
1 note
·
View note
Text
What is the mechanism behind RFID hotel key cards?
In the modern hospitality industry, enhancing guest experience and operational efficiency is a core goal for every hotel manager. With advancements in technology, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) has become an essential tool in hotel management. Particularly in the application of hotel key cards, RFID technology has brought unprecedented transformations. RFID hotel key cards not only simplify the check-in and check-out processes but also provide enhanced security, significantly improving guest convenience and overall satisfaction. How does RFID technology make all this possible? What is its working principle? This is a common curiosity among hotel managers, and today, we will explore this topic.

1. The Working Principle of RFID Hotel Key Cards
Before delving into how RFID hotel key cards work, let’s briefly introduce what RFID technology is.
What is RFID Technology?
RFID technology facilitates the exchange of information between objects through radio waves. It employs a tag and a reader for contactless data transmission, eliminating the need for physical contact. Users can simply bring an RFID card close to the reading device, and data will automatically transfer to complete authorization, authentication, or operations.
RFID hotel key cards are a type of RFID tag that connects with the hotel lock system via an RFID reader installed on the door lock, enabling contactless identity authentication and unlocking functions. Each card contains a tiny embedded chip that can store encrypted data such as the guest's room number, validity period, and access permissions. When a guest approaches the door lock with their card, the RFID reader communicates with the card via electromagnetic waves, retrieves the stored information, and decides whether to unlock the door based on pre-set security rules.
How RFID Cards Interact with Hotel Lock Systems
The interaction between RFID cards and hotel lock systems is grounded in simple, efficient wireless communication. In this process, the embedded chip within the RFID card contains a unique ID number, which is decoded by the RFID reader upon receiving a signal. Here’s a breakdown of the specific workflow:
Signal Emission: When the RFID card nears the lock system, the RFID reader within the lock emits an electromagnetic signal, activating the chip in the card.
Data Transmission: The chip in the card transmits its stored ID information to the reader, which then compares this information against the hotel management system.
Authentication and Authorization: If the card information matches the records in the system and the access validation is successful, the door lock will unlock, granting the guest entrance to their room.
The contactless feature of RFID technology makes the hotel check-in process smoother and more convenient, as guests don’t have to insert the card or physically manipulate a key, significantly enhancing the overall fluidity and experience of entering the hotel room.
Additionally, RFID cards offer heightened security. Compared to traditional magnetic stripe cards, the data transmission of RFID cards employs more complex encryption algorithms, making it harder to copy or tamper with information, thus providing greater security for hotels.
Through this series of simple and efficient operations, RFID hotel key cards not only ensure guest convenience but also significantly enhance hotel operational efficiency and security.
2. Advantages of RFID Hotel Key Cards
The introduction of RFID hotel key cards offers significant advantages to hotels, enhancing not only security but also customer experience and operational efficiency.
Enhanced Security
RFID cards utilize encrypted data transmission and unique chip designs to prevent card information from being copied or hacked. They can also be configured with specific validity periods and access permissions, ensuring that rooms can only be accessed within authorized times, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorized entry. Many five-star hotels have effectively improved room security and protected customer privacy through such solutions.
Improved Customer Experience
RFID cards streamline the check-in and check-out processes, allowing guests to simply hold the card near their room door to unlock it automatically. This contactless operation not only enhances convenience but also reduces the risk of contact transmission, increasing guests' peace of mind.
Cost Savings in Operations
RFID technology aids hotels in automating management tasks related to rooms and keys, minimizing human errors and wasted time. The system can monitor card usage in real time, alerting staff to lost or unauthorized use of cards promptly, which improves management efficiency and lowers operational costs.
Increased Management Flexibility and Scalability
RFID technology can seamlessly integrate with other management systems, enabling hotels to expand functionality on demand, such as automated climate control or lock management. This flexibility allows hotels to respond quickly to changing demands and easily upgrade their systems.
Enhanced Brand Image and Customer Loyalty
The use of RFID cards boosts the technological appeal of the hotel, enhancing its brand image. Additionally, through RFID cards, hotels can offer personalized services, which helps increase customer loyalty.
In summary, RFID hotel key cards provide a range of advantages that contribute to a safer, more efficient, and more enjoyable experience for both guests and hotel staff. This technology is not just a trend but a valuable asset in modern hotel management.
3. Future Development of RFID Hotel Key Cards
As technology continues to advance, the application of RFID technology in the hotel industry is expected to become more widespread and intelligent.
Smarter Integrated Systems
Future RFID systems will be more tightly integrated with other intelligent systems within hotels, such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices, smart room controls, and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems. Through this integration, hotels can offer more personalized services, such as automatically adjusting room temperature, lighting, and other amenities based on guest preferences, thereby enhancing the customer experience and reducing energy consumption.
Enhanced Security and Encryption Technologies
As security requirements continue to grow, future RFID hotel key cards will employ more advanced encryption technologies to ensure the safety of guests' personal information and room security. With dynamic encryption and multi-factor authentication mechanisms, RFID cards will effectively defend against various cyber attacks and forgery attempts, further strengthening the security of hotel management.
Data Analytics and Personalized Services
RFID systems will evolve beyond being simple door lock management tools. In the future, they will integrate with data analytics tools to help hotels analyze guest behavior and preferences, thereby enabling more personalized services. For example, hotels could automatically push tailored offers and services based on guests’ check-in history and spending habits, enhancing customer engagement and loyalty.
In summary, the future of RFID hotel key cards promises to be more intelligent, secure, and personalized, transforming the hospitality experience and paving the way for a new era in hotel management. As these technologies develop, they will not only improve operational efficiency but also create a more satisfying experience for guests.
4. RFID Hotel Key Cards: The Key to Enhanced Hotel Management Efficiency and Customer Experience
Through contactless, efficient, and secure solutions, RFID hotel key cards not only provide guests with a more convenient and safe check-in experience but also enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs for hotels.
As technology continues to advance, RFID systems will become increasingly intelligent and integrated, with a stronger focus on security and data analytics functions. Whether through integration with smart room control systems or the fusion of mobile devices with RFID cards, future RFID technology will bring even more innovative opportunities to the hospitality industry.
However, to ensure the successful deployment of RFID systems and maximize business value, choosing an appropriate RFID vendor is crucial. With over a decade of deep experience in RFID technology, many hotel managers have achieved intelligent upgrades and heightened management efficiency through our customized RFID solutions, providing guests with an unparalleled stay.
If you are interested in the RFID hotel key card system or want to know more about solutions for improving hotel management efficiency, please feel free to contact us. Our RFIDCard.com professional team is ready to provide you with free consultation and testing services to ensure you select the RFID products and systems that best meet your needs. Take action now, and let us help you offer your guests a safer, more convenient check-in experience while driving your hotel towards future success!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Surgical Instrument Tracking System is Poised to Register Strong Growth due to Increasing Need

The surgical instrument tracking system market has witnessed significant growth in recent years. Surgical instrument tracking systems provide real-time tracking and assists in maintaining inventory of surgical instruments in healthcare settings. Tracking systems help identify instrument location, usage history and shelf life. They facilitate improved inventory management, streamline sterile processing workflows and help reduce overall operational costs for healthcare facilities.
The global surgical instrument trackingmarket was valued at US$ 301.5 Mn in 2022 and is forecast to reach a value of US$ 1,206.5 Mn by 2030 at a CAGR of 19.0% between 2023 and 2030.
Key Takeaways Key players operating in the surgical instrument tracking market are 3M, E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company, Aculon Inc., BASF SE, P2i, ABRISA TECHNOLOGIES, NEI Corporation, DRYWIRED, ACCUCOAT INC., OerlikonMetco (US) Inc, and NANEX COMPANY. The Surgical Instrument Tracking Market Size offers significant opportunities in terms of innovation and technology integration. Adoption of RFID, barcode and GPS based tracking systems allows for real-time location monitoring and automated instrument count workflows. Integration of IoT and cloud computing enables centralized monitoring and data analysis. Globally, the surgical instrument tracking market is expected to witness strong growth in North America, Europe and Asia Pacific. Increasing healthcare expenditure, rising surgical volumes and focus on reducing operating costs are driving demand for tracking systems across major countries. Ongoing technological advancements also allow for expansion into new applications such as endoscopy and dental equipment tracking. Market drivers The major driver for the surgical instrument tracking market is the increasing need for improved inventory management and asset utilization in healthcare facilities. Manual tracking systems are tedious and prone to errors. Automated tracking solutions help identify missing instruments quicker, reduce miscounts and optimize staff allocation. This helps reduce product wastage and improves sterilization turnaround times. The growing regulatory requirements regarding instrument recalls and traceability also boost the demand for advanced tracking solutions.
PEST Analysis Political: Regulations regarding tracking of surgical instruments are becoming stricter to ensure patient safety. This is driving demand for effective tracking systems. Economic: Rising healthcare costs are pushing hospitals to optimize operations and reduce expenses like instrument replacement. Tracking systems help achieve these goals. Social: Growing awareness about risks of expired or misplaced instruments is making surgeons and patients more careful. This boosts adoption of tracking technologies. Technological: Advanced RFID and barcode technologies enable real-time location of instruments through the surgical workflow from sterilization to usage and disposal. Some solutions also offer instrument condition monitoring. Geographical Regions with High Market Concentration North America accounts for the largest share of the surgical instrument tracking market due to stringent regulations and protocols regarding instrument tracking and management in this region. High healthcare spending in countries like the US and Canada also contributes to market growth. Hospitals are more willing to invest in new technologies for optimized operations and improved patient outcomes. Fastest Growing Regional Market The Asia Pacific region is expected to grow at the fastest rate during the forecast period. This is attributed to improving healthcare infrastructure, rising medical tourism, and growing focus on reducing surgical site infections in major countries like India, China and Japan. With increasing awareness, more hospitals are implementing instrument tracking systems for better regulatory compliance and cost-effectiveness.
Get more insights on Surgical Instrument Tracking Market
About Author:
Ravina Pandya, Content Writer, has a strong foothold in the market research industry. She specializes in writing well-researched articles from different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/ravina-pandya-1a3984191)
#Coherent Market Insights#Surgical Instrument Tracking Market#Surgical Instrument Tracking#Healthcare Technology#Medical Devices#Asset Management#Surgery#Sterilization#Patient Safety#Hospital Logistics#Instrument Inventory#RFID Technology
0 notes
Text
🛡️ Sterilization Container Systems Are Trending Up — $5.8B by 2034
Sterilization container systems play a critical role in healthcare facilities, hospitals, and surgical centers by providing a secure and contamination-free environment for surgical instruments. These rigid containers are designed to protect instruments from bacteria, dust, and moisture while allowing effective sterilization through steam, ethylene oxide (EO), hydrogen peroxide, and gamma radiation. Unlike traditional wrap-based sterilization methods, container systems offer superior durability, reusability, and cost-effectiveness. Their microbial barrier properties, high-grade aluminum or stainless-steel construction, and advanced filtration systems ensure that sterilized instruments remain safe until use.
To Request Sample Report : https://www.globalinsightservices.com/request-sample/?id=GIS10359 &utm_source=SnehaPatil&utm_medium=Article
Benefits of Sterilization Containers: ✅ Extended Sterility Maintenance — Provides a sealed environment to keep instruments sterile for long periods. ✅ Eco-Friendly & Cost-Effective — Reduces waste from disposable sterilization wraps. ✅ Enhanced Protection — Prevents instrument damage during transportation and storage. ✅ Efficient Workflow — Standardized designs improve handling and reduce preparation time.
With advancements in sterilization technology, modern sterilization containers now feature color-coded filters, RFID tracking, tamper-evident locks, and customizable compartments, ensuring compliance with infection control protocols and healthcare regulations.
As infection prevention remains a top priority in medical settings, investing in high-quality sterilization container systems enhances patient safety, operational efficiency, and sustainability. Upgrade your sterile processing department (SPD) with the latest in sterilization technology!
🛑🔬🏥 #sterilizationcontainers #infectioncontrol #medicalsterilization #surgicalinstruments #sterileprocessing #hospitalhygiene #medicalpackaging #sterilecontainer #autoclavesterilization #medicaldevices #healthcareinnovation #instrumentcare #sterileprocessingdepartment #patientprotection #sterilityassurance #hospitalinfectioncontrol #surgicalsafety #medicalequipment #medicaltechnology #infectionprevention #sterilebarriersystem #sterilesupplies #hospitalstandards #surgicalinstrumentcare #sterilizationtech #sterileprocessingtech #healthcaresafety #medicalgrade #medicalsafety #surgicalprocedures #autoclave #hospitalstandards #sterilizationprocess #hospitalsupplies #healthtech #sterilizationmethods #sterileprocessingunit #biotechsolutions #futureofhealthcare #packagingengineering #medicalsolutions #surgerytools #hospitalsafety #qualityassurance #medtech #germfree
🔬 Protecting patients, one sterilized instrument at a time!
Research Scope:
· Estimates and forecast the overall market size for the total market, across type, application, and region
· Detailed information and key takeaways on qualitative and quantitative trends, dynamics, business framework, competitive landscape, and company profiling
· Identify factors influencing market growth and challenges, opportunities, drivers, and restraints
· Identify factors that could limit company participation in identified international markets to help properly calibrate market share expectations and growth rates
· Trace and evaluate key development strategies like acquisitions, product launches, mergers, collaborations, business expansions, agreements, partnerships, and R&D activities
About Us:
Global Insight Services (GIS) is a leading multi-industry market research firm headquartered in Delaware, US. We are committed to providing our clients with highest quality data, analysis, and tools to meet all their market research needs. With GIS, you can be assured of the quality of the deliverables, robust & transparent research methodology, and superior service.
Contact Us:
Global Insight Services LLC 16192, Coastal Highway, Lewes DE 19958 E-mail: [email protected] Phone: +1–833–761–1700 Website: https://www.globalinsightservices.com/
0 notes
Text
Workwear Dispensing
Clothes dispenser, uniform dispenser, clothes vending machine. Automatic clothes dispensing machines. rfid hospitals. traceability
Workwear Dispensing
Acerca de la compañía :-La Fábrica de Software es una empresa de ingeniería especializada en el desarrollo de sistemas informáticos integrados con nuestros equipos y máquinas, para la gestión automatizada y control textil en hospitales, fábricas, lavanderías industriales, tintorerías, etc.Contamos con personal cualificado dedicado a la investigación y desarrollo de soluciones innovadoras orientadas a atender las necesidades específicas de cada uno de nuestros clientes. Somos creadores del Lavander 4, un sistema informático diseñado para ofrecer, desde cualquier dispositivo, el control real e inmediato de albaranes, facturas, stocks, producción y rentabilidad de una planta, entre otras muchas funcionalidades.Ofrecemos sistemas de última generación para el control de vestuario profesional, entre lo que destacamos nuestros dispensadores automáticos de ropa laboral, máquinas de retorno de unformidad y sistemas de taquillas inteligentes.
Haga clic aquí para más información. :- https://lafabricadesoftware.es/en/dispensadora-de-ropa/
0 notes
Text
North America RTLS for Healthcare Market Trends, Size, Segment and Growth by Forecast to 2030
North America RTLS for Healthcare Market: Growth and Competitive Landscape
The North American RTLS (Real-Time Location System) market for healthcare was valued at US$ 689.83 million in 2018 and is projected to reach US$ 3,090.08 million by 2027, expanding at a CAGR of 18.9% during the forecast period. 𝐃𝐨𝐰𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐝 𝐏𝐃𝐅 𝐁𝐫𝐨𝐜𝐡𝐮𝐫𝐞 - https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/sample/TIPRE00006837
Key Growth Drivers
The market's rapid growth is driven by the advantages of RTLS systems and the increasing competitiveness brought by emerging startups.
Rising Competition and Innovation
The RTLS market has seen a surge in new entrants, leading to heightened competition and the development of innovative and customized solutions across various sectors. Between 2014 and 2017, six startups globally emerged to provide RTLS solutions.
Pozyx Labs (Founded in 2015, Belgium) – Specializes in ultra-wideband (UWB) RTLS hardware and software, delivering high-precision positioning with 10 cm accuracy.
Sewio Networks (Founded in 2014, Czech Republic) – Offers RTLS hardware and software solutions designed for data accuracy, productivity, cost-efficiency, and safety.
Proxicon Limited (Founded in 2015, UK) – Provides customized RTLS solutions for various industries.
North America RTLS for Healthcare Strategic Insights
Strategic insights for the North America RTLS for Healthcare provides data-driven analysis of the industry landscape, including current trends, key players, and regional nuances. These insights offer actionable recommendations, enabling readers to differentiate themselves from competitors by identifying untapped segments or developing unique value propositions. Leveraging data analytics, these insights help industry players anticipate the market shifts, whether investors, manufacturers, or other stakeholders. A future-oriented perspective is essential, helping stakeholders anticipate market shifts and position themselves for long-term success in this dynamic region. Ultimately, effective strategic insights empower readers to make informed decisions that drive profitability and achieve their business objectives within the market.
North America RTLS for Healthcare Report Scope
Attribute
Details
Market Size (2018)
US$ 689.83 Million
Market Size (2027)
US$ 3,090.08 Million
Global CAGR (2018-2027)
18.9%
Historical Data
2016-2017
Forecast Period
2019-2027
Segments Covered
By Technology: RFID, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, GPS, UWB By Facility Type: Hospitals & Healthcare, Senior Living By Application: Inventory Tracking, Patient Tracking, Security, Monitoring, Supply Chain, Automation
Regions Covered
North America (US, Canada, Mexico)
Market Leaders
CenTrak, Impinj, Intelligent InSites, Aruba, Midmark, Sanitag, Sonitor, STANLEY Healthcare, Teletracking, Zebra Technologies
North America RTLS for Healthcare Regional Insights
The geographic scope of the North America RTLS for Healthcare refers to the specific areas in which a business operates and competes. Understanding local distinctions, such as diverse consumer preferences (e.g., demand for specific plug types or battery backup durations), varying economic conditions, and regulatory environments, is crucial for tailoring strategies to specific markets. Businesses can expand their reach by identifying underserved areas or adapting their offerings to meet local demands. A clear market focus allows for more effective resource allocation, targeted marketing campaigns, and better positioning against local competitors, ultimately driving growth in those targeted areas. Company Profiles
CenTrak
Impinj, Inc.
Intelligent InSites
Aruba (Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP)
Midmark Corporation
Sanitag
Sonitor Technologies
STANLEY Healthcare
Teletracking Technologies, Inc.
Zebra Technologies Corp.
About Us: Business Market Insights is a market research platform that provides subscription service for industry and company reports. Our research team has extensive professional expertise in domains such as Electronics & Semiconductor; Aerospace & Défense; Automotive & Transportation; Energy & Power; Healthcare; Manufacturing & Construction; Food & Beverages; Chemicals & Materials; and Technology, Media, & Telecommunications Author’s Bio Akshay Senior Market Research Expert at Business Market Insights
0 notes
Text
¶ … Healthcare: How Technology Has Changed Medicine OBJECITVE The objective of this work is to examine how technology has effectively changed the practice of medicine. (1) Electronic health record (EHR): Originally, the EHRs were viewed as electronic file cabinets to hold patient data from various sources however, they are now viewed as a part of an automated order-entry and patient-tracking system providing real-time access to patient data, as well as a continuous longitudinal record of their care. (2) Computerized provider order entry (CPOE): CPOE in its basic form is typically a medication ordering and fulfillment system. More advanced CPOE will also include lab orders, radiology studies, procedures, discharges, transfers, and referrals. (3) Clinical decision support system (CDSS): CDSS provides physicians and nurses with real-time diagnostic and treatment recommendations. The term covers a variety of technologies ranging from simple alerts and prescription drug interaction warnings to full clinical pathways and protocols. CDSS may be used as part of CPOE and EHR. (4) Picture archiving and communications system (PACS): This technology captures and integrates diagnostic and radiological images from various devices (e.g., x-ray, MRI, computed tomography scan), stores them, and disseminates them to a medical record, a clinical data repository, or other points of care. (5) Bar coding: Bar coding in a health care environment is similar to bar-code scanning in other environments: An optical scanner is used to electronically capture information encoded on a product. Initially, it will be used for medication (for example, matching drugs to patients by using bar codes on both the medications and patients' arm bracelets), but other applications may be pursued, such as medical devices, lab, and radiology. (6) Radio frequency identification (RFID): This technology tracks patients throughout the hospital, and links lab and medication tracking through a wireless communications system. It is neither mature nor widely available, but may be an alternative to bar coding. (7) Automated dispensing machines (ADMs): This technology distributes medication doses. (8) Electronic materials management (EMM): Health care organizations use EMM to track and manage inventory of medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, and other materials. This technology is similar to enterprise resource planning systems used outside of health care. (9) Interoperability: This concept refers to electronic communication among organizations so that the data in one IT system can be incorporated into another. Discussions of interoperability focus on development of standards for content and messaging, among other areas, and development of adequate security and privacy safeguards. (Report to Congress, June, 2004, p.160) INTRODUCTION The implementation of information technology in the field of health care has not progressed as smoothly and has not been effectively integrated across domains as it was hoped might be the case. There are still technical and practical issues that must be overcome and as well the design and development process of information technology applications must consider key issues that have previously been appointed less important than other issues in design and development of information technology applications. As well, the implementation of information technology has progressed at a much slower rate than was originally expected however, until the issues identified in this report are addressed this will not be possible. This report will conduct a review of the literature that has been published in the past five years in order to determine what issues must be addressed in order to effectuate the implementation of information technology applications across all health care providers locally, regionally, nationally, and internationally in the future. LITERATURE REVIEW Electronic Medical Records The work of Brookstone (2004) entitled: "Electronic Medical Records: Creating the Environment for Change" states that "as physicians become more advanced users of technology, they are exposed to a wider range of tools and technology-based clinical management systems: software and hardware intended to solve problems they face in clinical practice." (Brookstone, 2004) Brookstone states that the level of change "required to implement these solutions is significant and requires a methodological review of work processes before implementation. Even in the most organized practices, it is unlikely that there has been a clear enough documentation of workflow relating to the management of specific clinical data." (Brookstone, 2004) Electronic Medical Record Systems Providers are enabled through electronic medical record (EMR) system which is fully implemented to "easily share patient information, legibly document patient visit, prescribe medication with built-in decision support in terms of drug-drug and drug-disease interaction warnings and create automated patient-recall programs." (Brookstone, 2004) Brookstone states that the ability "to view laboratory results within the EMR system significantly increases the richness of the clinical environment by allowing clinical decision support as part of chronic disease management." (Brookstone, 2004) It requires adequate preparation for physicians to benefit from the electronic medical record system. The electronic medical record systems are being implemented by physicians with "varying degrees of success." As "some systems have been quite successful while other have been complete disasters." (Brookstone, 2004) Barriers to Implementation of EMR Systems Brookstone (2004) identifies specific barriers to electronic medical record implementation systems to include those as follows: (1) Software immaturity. Software development is not advanced enough, despite extensive pre-implementation evaluation. (2) Training issues. Both physicians and staff vary significantly in terms of computer expertise, ranging from novice to advanced users. (3) Privacy concerns. Difficulties arise over who will be entitled to access confidential patient information, and when EMR software architecture does not allow users to easily restrict access to certain providers. (Brookstone, 2004) Barriers to investment of IT include the "…cost and complexity of IT implementation which often necessitates significant work process and cultural changes." (Report to Congress, June, 2004, p.157) Stated as a major barrier to electronic medical records being adopted on a widespread basis is "the limited ability to access health information from external sources." (Brookstone, 2004) Interfaces are described as "pieces of software that allow different systems to communicate with one another and securely transfer information in one or two directions." (Brookstone, 2004) The electronic medical record, when no interface is present "is restricted in its ability to provide a comprehensive view of patient care. Interfaces are complex and costly to develop." (Brookstone, 2004) Brookstone states that there is a need for "a simplified standards-based approach to creating interfaces." Brookstone states that there is currently an existing 'value-gap' "in terms of where physicians are and where they need to be in order to implement an EMR system. The value-gap can be defined as the difference between the efficiencies gained using the current level of technology in a specific medical practice and the total cost of making the jump to the next level of technology. The total cost must be measured in the time, expense, training needs, systems change, loss of productivity, and pain in implementing a new technology." (Brookstone, 2004) Drivers of Investment in IT In a 2004 Report to Congress entitled "New Approaches in Medicare" it is stated that information technology (IT) has the potential to improve the quality, safety and efficiency of health. Diffusion of IT in health care is generally low but surveys indicate that providers plan to increase their investments." (p.1) Drivers of investment in IT are stated to include: (1) the promise of quality; and (2) efficiency gains. (Report to Congress, June, 2004) Barriers to investment of IT include the "…cost and complexity of IT implementation which often necessitates significant work process and cultural changes." (p.157) Characteristics of the Health Care Market The 2004 Report to Congress states that certain characteristics of the health care market -- including payment policies that reward volume rather than quality, and a fragmented delivery system -- can also pose barriers to IT adoption." (p.157) The provision of new methods for providers and their patients to readily access and use health information, information technology (IT) has the potential to improve the quality, safety, and efficiency of health care." (Report to Congress, June, 2004, p.158) Despite this, very few health care providers have adopted IT fully. Low diffusion is stated to be due in part to the "complexity of IT investment, which goes beyond acquiring technology to changing work processes and cultures, and ensuring that physicians, nurses and other staff use it." (Report to Congress, June, 2004, p.158) It is additionally stated that there is a great deal that remains unknown about the "role of IT in the health care setting." (Report to Congress, June, 2004, p.158) The delivery of quality health care makes a requirement of providers and patients in the integration of complex information from many different sources therefore "increasing the ability of physicians, nurses, clinical technicians and others to readily access and use the right information about their patients should improve care." (Report to Congress, June, 2004, p.159) The ability for patients in obtaining information that allows them to manage their condition better and that would improve communication with the health care system could also result in an improvement of the "efficiency and quality of care." (Report to Congress, June, 2004, p.159) The Report to Congress states that both the private and the public health care sectors have "engaged in numerous efforts for promote use of IT within health care institutions and across delivery care settings." (2004, p.159) Activities have included: (1) Development and promotion of industry-wide standards; (2) Funding of research for investigation of the impact of IT on quality; (3) Provision of incentives that provide encouragement of investment in IT; (4) Giving grants to investors in IT; and (5) Development of strategies to improve the flow of information across providers. (Report to Congress, June, 2004, p.159) Stated additionally in the Report to Congress is that there are multiple functions that must be considered when purchase IT and hundreds of applications that various vendors offer. The various IT applications are stated to be within three categories including those of: (1) Administrative and financial systems that facilitate billing, accounting and other administrative tasks; (2) Clinical systems that facilitate or provide input into the care process; and (3) Infrastructure that supports both the administrative and clinical applications. (Report to Congress, June 2004, p.160) The work published by The Royal Society entitled: "Digital Healthcare: The Impact of Information and Communication Technologies on Health and Healthcare" states: "The single most important factor in realizing the potential of healthcare ICTs is the people who use them. The end users of any new technology must be involved at all stages of the design, development and implementation, taking into account how people work together and how patients, carers and healthcare professionals interact." (2006, p.1) It is additionally stated that it should be recognized by all healthcare professionals that ICTs hold great potential value in the health care workplace. It is important that healthcare managers "ensure sufficient time for healthcare professionals to be involved properly in the design, development and implementation of new technologies. This includes local and national health authorities ensuring that funding and time are allocated for initial training and ongoing support when new systems are introduced." (The Royal Society, 2006, p.1) The Royal Society additionally states that higher education institutions and professional bodies "…must ensure that both basic training and continuing professional development include the use and understanding of ICTs as an integral part of healthcare professionals' everyday role." (2006, p.1) The Royal Society states the belief that "Healthcare ICTs will change the roles of patients, carers and healthcare professionals in the delivery of healthcare. For example, more healthcare-related material is available now for patients via the worldwide web, leading to a new role for healthcare professionals in guiding patients through the various information sources. Continued research into the socio-cultural impact of healthcare ICTs is required." (2006, p.1) The Royal Society states that data access is both a complex as well as a controversial issue since it is "…technically possible to establish systems that allow different levels of access to an individual's electronic health records. However, it is not clear what a sensible access policy would be because there is an unresolved conflict between privacy and sharing healthcare data for both individual and public benefit." (2006, p.2) In order that a resolution be found to this conflict "…there needs to be further engagement with patients, carers and the wider public to determine where a workable balance lies between privacy issues and data sharing." (The Royal Society, 2006, p.2) The health policy of future government is stated to be presented with a need to "…be informed by the findings of this engagement." (The Royal Society, 2006, p.2) The Royal Society states that it advocates strongly for "an incremental and iterative approach to the design, implementation and evaluation of healthcare ICTs. This involves engaging the end users at all appropriate stages from determining the specifications through to training and ongoing support once the system is introduced." (2006, p.2) Stated to be a major part of this approach is the design and development since this includes good or bad elements of systems. Particular attention should be paid to the "impact of the speed and scale of the different programs and the varying levels of user-engagement." (The Royal Society, 2006, p.3) The criteria for evaluating the technical and financial performance should be establishing in the beginning of the development process as should user satisfaction. There is a requirement that "…local, regional, national and international systems must be able to operate together and share information, which requires national and international standards. We encourage the Government to build on its ongoing work to achieve connectivity as quickly as possible between the different national and international standards being developed. It will not be possible to establish fully interoperable systems until these standards are agreed." (The Royal Society, 2006, p.3) The following figure lists examples of health information technology for hospitals and physicians. Figure 1 Examples of Health Information and Technology for Hospitals and Physicians Source: Report to Congress (June, 2004) SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION This work has identified the primary barriers and drivers of information technology in the health care environment and as well has noted the various challenges that are presented in implementation of electronic medical record systems and other information technology applications in the health care workplace. Barriers have been noted to include the immaturity of software and training issues accompanied by concerns over privacy. Cost and complexity have also been noted in this study to present specific challenges to implementation of IT. Interfaces are noted in this study as a particular problem in electronic medical record system implementation. That which serves to drive information technology investment are two factors: (1) the promise of quality and (2) gains in efficiency. The effort should be specifically driven by management in the health care sector and by higher educational institutions and professional bodies through making sure that basic training as well as ongoing professional development are inclusive of the understanding of the use of the information technology as being integral in the role of the healthcare professional daily. Concerns of patients over privacy will have to be effectively addressed as well as issues relating to integration of systems on local, regional, national and international levels. While information technology implementation in health care has not progressed at the expected rate, it is likely that as health care professionals become more attuned to and informed of the capacity and potential of information technology applications in the health care workplace that information technology will be implemented widely across the health care sector. BIBLIOGRAPHY BC Medical Association. Getting IT Right: Patient Centered Information Technology . Vancouver: BCMA. 2004:39-40. Blum E. Paperless medical record not all it's cracked up to be AMNews; 17 February 2003. Online available Brookstone A, Braziller C. Engaging physicians in the use of electronic medical records. Electronic Healthcare 2003;2:23-27. Brookstone, Alan. 2004. Electronic Medical Records: Creating the Environment for Change. BCMJ, Vol. 46, No. 5 June 2004. Online available at: http://www.bcmj.org/electronic-medical-records-creating-environment-change Center for Information Technology Leadership. 2003. The value of computerized provider order entry in ambulatory settings. Boston, MA: CITL. Chin, T. 2004. Financing high-tech: You can afford it after all. American Medical News (March 8). http://www.amaassn.org/amednews. Darves, B. 2004. CPOE: The promise and the pitfalls. HealthLeaders (February 5). http://www.healthleaders.com. De La Garza, P. 2004. VA vows to retrain Bay Pines staffers. St. Petersburg Times. March 23. Devers, K.J., and G. Liu. 2004. Leapfrog patient-safety standards are a stretch for most hospitals. Issue brief no. 77. Washington, DC: Center for Studying Health System Change. Digital Healthcare: The Impact of Information and Communication Technologies on Health and Healthcare. (2006) The Royal Society. The Clyvedon Press Ltd., Cardiff CF15 9QR, UK. Dodge, J. 2004. Exclusive: A conversation at HIMSS with Richard Granger. Health-IT World (March 29). http://www.bioitworld.com/archive/retort/.February. First Consulting Group. 2003. Computerized physician order entry: Costs, benefits and challenges, a case study approach. Prepared for American Hospital Association and Federation of American Hospitals. January. Food and Drug Administration. 2004. Bar code label requirements for human drug products and biological products. Final rule. Federal Register 69, no. 38 (February 26): 9119 -- 9171. iHealthBeat. 2003. Report: Health care IT spending growth continues. iHealthBeat. November 20. http://www.ihealthbeat.org. Information Technology in Health Care (2004) Report to Congress: New Approaches in Medicare. June 2004. MEDPAC. Institute of Medicine. 2000. To err is human: Building a safer health system. ed. L. Kohn, J. Corrigan, and M. Donaldson. Washington, DC: National Academy Press Institute of Medicine. 2001. Crossing the quality chasm: A new health system for the 21st century. Washington, DC: National Academy Press. Institute of Medicine. 2002. Leadership by example: Coordinating government roles in improving health care quality, ed. J. Corrigan, J. Eden, and B. Smith. Washington, DC: National Academy Press. Institute of Medicine. 2003. Read the full article
0 notes