#Quantitative MRI
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Preserved in our archive
A research letter from 2022 highlighting the effects of even "mild" covid on the brain.
Dear Editor,
A recent study published in Nature by Douaud and colleagues1 shows that SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with longitudinal effects, particularly on brain structures linked to the olfactory cortex, modestly accelerated reduction in global brain volume, and enhanced cognitive decline. Thus, even mild COVID-19 can be associated with long-lasting deleterious effects on brain structure and function.
Loss of smell and taste are amongst the earliest and most common effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection. In addition, headaches, memory problems, confusion, or loss of speech and motility occur in some individuals.2 While important progress has been made in understanding SARS-CoV-2-associated neurological manifestations, the underlying mechanisms are under debate and most knowledge stems from analyses of hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19.2 Most infected individuals, however, develop mild to moderate disease and recover without hospitalization. Whether or not mild COVID-19 is associated with long-term neurological manifestations and structural changes indicative of brain damage remained largely unknown.
Douaud and co-workers examined 785 participants of the UK Biobank (www.ukbiobank.ac.uk) who underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) twice with an average inter-scan interval of 3.2 years, and 401 individuals testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection between MRI acquisitions (Fig. 1a). Strengths of the study are the large number of samples, the availability of scans obtained before and after infection, and the multi-parametric quantitative analyses of serial MRI acquisitions.1 These comprehensive and automated analyses with a non-infected control group allowed the authors to dissect consistent brain changes caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection from pre-existing conditions. Altogether, the MRI scan processing pipeline used extracted more than 2,000 features, named imaging-derived phenotypes (IDPs), from each participant’s imaging data. Initially, the authors focused on IDPs involved in the olfactory system. In agreement with the frequent impairment of smell and taste in COVID-19, they found greater atrophy and indicators of increased tissue damage in the anterior cingulate cortex, orbitofrontal cortex and insula, as well as in the ventral striatum, amygdala, hippocampus and para-hippocampal gyrus, which are connected to the primary olfactory cortex (Fig. 1b). Taking advantage of computational models allowing to differentiate changes related to SARS-CoV-2 infection from physiological age-related brain changes (e.g. decreases of brain volume with aging),3 they also explored IDPs covering the entire brain. Although most individuals experienced only mild symptoms of COVID-19, the authors detected an accelerated reduction in whole-brain volume and more pronounced cognitive declines associated with increased atrophy of a cognitive lobule of the cerebellum (crus II) in individuals with SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to the control group. These differences remained significant when 15 people who required hospitalization were excluded. Most brain changes for IDPs were moderate (average differences between the two groups of 0.2–2.0%, largest for volume of parahippocampal gyrus and entorhinal cortex) and accelerated brain volume loss was “only” observed in 56–62% of infected participants. Nonetheless, these results strongly suggest that even clinically mild COVID-19 might induce long-term structural alterations of the brain and cognitive impairment.
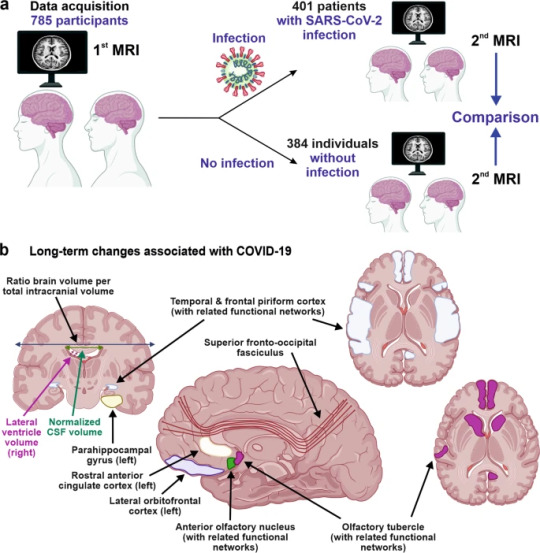
The study provides unique insights into COVID-19-associated changes in brain structure. The authors took great care in appropriately matching the case and control groups, making it unlikely that observed differences are due to confounding factors, although this possibility can never be entirely excluded. The mechanisms underlying these infection-associated changes, however, remain to be clarified. Viral neurotropism and direct infection of cells of the olfactory system, neuroinflammation and lack of sensory input have been suggested as reasons for the degenerative events in olfactory-related brain structures and neurological complications.4 These mechanisms are not mutually exclusive and may synergize in causing neurodegenerative disorders as consequence of COVID-19.
The study participants became infected between March 2020 and April 2021, before the emergence of the Omicron variant of concern (VOC) that currently dominates the COVID-19 pandemic. During that time period, the Alpha and Beta VOCs dominated in the UK and all results were obtained from individuals between 51 and 81 years of age. It will be of great interest to clarify whether Omicron, that seems to be less pathogenic than other SARS-CoV-2 variants, also causes long-term brain damage. The vaccination status of the participants was not available in the study1 and it will be important to clarify whether long-term changes in brain structure also occur in vaccinated and/or younger individuals. Other important questions are whether these structural changes are reversible or permanent and may even enhance the frequency for neurodegenerative diseases that are usually age-related, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or Huntington’s disease. Previous findings suggest that cognitive disorders improve over time after severe COVID-19;5 yet it remains to be determined whether the described brain changes will translate into symptoms later in life such as dementia. Douaud and colleagues report that none of top 10 IDPs correlated significantly with the time interval between SARS-CoV-2 infection and the 2nd MRI acquisition, suggesting that the observed abnormalities might be very long-lasting.
Currently, many restrictions and protective measures are relaxed because Omicron is highly transmissible but usually causes mild to moderate acute disease. This raises hope that SARS-CoV-2 may evolve towards reduced pathogenicity and become similar to circulating coronaviruses causing mild respiratory infections. More work needs to be done to clarify whether the current Omicron and future variants of SARS-CoV-2 may also cause lasting brain abnormalities and whether these can be prevented by vaccination or therapy. However, the finding by Douaud and colleagues1 that SARS-CoV-2 causes structural changes in the brain that may be permanent and could relate to neurological decline is of concern and illustrates that the pathogenesis of this virus is markedly different from that of circulating human coronaviruses. Further studies, to elucidate the mechanisms underlying COVID-19-associated neurological abnormalities and how to prevent or reverse them are urgently needed.
REFERENCES (Follow link)
#public health#wear a mask#covid 19#pandemic#covid#wear a respirator#mask up#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2#long covid#covid conscious#covid is airborne
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Addiction
A/N: Hi friends! This is my first time posting anything related to Bones, but I’ve binged 12 seasons in less than a month and it has to come out somewhere, so here it is!
Read on AO3
--
A character study of Seeley Booth that ties in the Pilot and The Parts in the Sum of the Whole.
--
He’s an addict.
Addiction was etched in his genes, grown from the tang of bourbon that stained his father’s breath. His father was addicted to dark liquor, to swinging his hand against his mother’s cheek, to the crunch of his and Jared’s ribs underneath his knuckles. Bones talks relentlessly about statistics and certainties, of predicted outcomes based on probabilities.
“Statistics allows you to validate claims based on quantitative evidence, Booth. It’s a crucial process in scientific expansion!”
The evidence of his life would all predict the same outcome - all the numbers and equations leading to the same conclusion. The remodeled fractures on his ribs that Bones had pointed out on his x-rays, the few and far between moments from his childhood that weren’t stained by a well-hidden bottle of whiskey and his father’s shadow looming behind him. The tally he keeps - 48, 49, 50 notches scratched on the back of a leather pocket notebook he carried in his gun case throughout his tours in Iraq and Afghanistan. The other tally of 19 names, all brothers, and their next of kin’s contact information. The remnants of a sharp, burning pain as the butt of a rifle smashed each of his toes individually, tones of the Tehrani accent heavy on his captor’s tongue.
Blood drenched his fatigues, both of his comrades and his enemies. If Bones ever successfully convinced him to do an MRI, she would find traces of the bullets that inscribed his bones. She would point out where shrapnel entered his lower back in Shindhad after he shielded the green private whose lower legs were blown off by an IED during a routine patrol. The bullet that wedged itself too close to his lungs in Mosul after an explosives raid went sideways by an ambush. Many more injuries that he brushed off as flesh wounds, his pain always ebbed away by the adrenaline that flooded into his veins with every close brush with death.
A laundry list of scars and traumas - he drowns in nightmares and holy water, hoping that God will eventually grant him mercy from the panic and pain that the war had woven into him. The beads of his rosary leave imprints on his palms, his knees cracking from the hours spent on them, praying for the safe passage of fallen soldiers and avoiding thoughts of the Sixth Commandment.
But the nightmares follow him, as do the screams, and he just wants it to stop.
Booth tries to avoid the bottle - always limiting himself to two whiskey doubles or no more than four beers. He drinks to dull, not to forget, not like his father. Not like Jared, who’s been bound to the bottle since he took a swig from the whiskey wedged between empty boxes of laundry soap in their garage at the age of 13. He tries not to be resilient, tries not to drink except on certain days, but it quickly becomes too much. He wants to feel something, anything, that wasn’t the guilt, the shame, the sorrow.
He placed his first bet in Iraq while his unit was on patrol. The burning desert sun beating on his back as enthusiasm for their next hot meal had grown into a bet on what food was being served at the mess that night. Booth had seen what shipments had come in two days before and was confident that the shipment of ground beef and tomato sauce would result in chili. Phillips, three years his senior and had a gnarly hook that caught him on the chin during training last week, slipped him a fistful of twenties and tens after dinner that night.
He stuffed the cash in his foot locker and joined betting pools for other things - fifty bucks to the person who could disassemble and reassemble their firearm the fastest, twenty to whoever could guess what time the visiting Sergeant snuck into their Corporal’s private quarters. There were a group of specialists who were Rangers fans and he egged them on to bet 50 each on the Flyers winning 3-1.
Booth racked in $800 that night. More money than he’d ever earned in a week. His pay was shit, not nearly enough to take off the edge of all the hits he’s taken. Rebecca had called him earlier that day, tears thick in her voice when she said pregnant and father. He had just started his third tour. His deployment was 12 months and he was only three months in. She was alone in DC and he was in Baghdad. If he keeps winning, he can provide for her, for them.
It has nothing to do with the feeling of winning, of the elation that God had twisted the tides in his favor.
He gets an honorable discharge after he gets captured - he can’t keep up with the long distances, his once broken toes unable to stand being in his combat boots for hours. But he’s good with a gun and someone had taken notice. Some sargeant from the Rangers shows up at the hospital, telling him that with his abilities he could be a sniper. He could keep serving his country and didn’t need to end his career. There’s something about going back into war that makes his stomach curl and he says he’ll think about it. He gets sent back to the States and watches his son enter the world, loud yet so tiny and fragile and swears to protect him, to make the world a better place for him.
Parker is three months old when he’s called in - one of the Ranger squads had lost someone and they needed help. National security, they said. For your country. He tells Rebecca that they should marry before he goes, that he wants Parker to have a complete family.
“I’m so sorry, Seeley. I love you, I do, but I can’t do it.”
They ask more from him. From surveillance to assassinating a member of the Shura council. His hand is steady when he flexes his finger over the trigger, delivering a clean bullet right between the eyes. A piercing wail fills the air. They chant his name, both a plea and a prayer. His stomach turns and he’s almost sick on his shoes, but he did it for Parker, for his country. They tell him he is a hero, the potential destruction that could have happened, but all he dreams of is the chant of a dead man’s name.
But there are more members, more high ranking officers who are threats to their democracy, their freedom. Soon, he perfects it. The most accurate shot in their entire base, a moniker Booth wears with honor. To him, shooting is as easy as breathing, his rifle simply an extension of him. He adapts to the sweltering air, the arid climate, and learns how to ignore the sweat that beads on his eyebrow and drips onto his scope.
He feels that same rush, the flood of adrenaline, every time he hits a shot. Booth is good at what he does. He’s meticulous - he shifts his barrel based on the slope of the terrain beneath them, listens to the wind and does a rough estimate of his bullet’s trajectory as he aims downsight. He can read the differences in rooms full of high-ranking officials and rooms full of insurgents with AK-47s slung across their backs. He makes observations and adjusts accordingly, takes smart shots, misses only a handful.
He counts his shots and tallies the lives he takes. By the 20th life, he feels something shift. By the 30th, he’s two years into being a Ranger and six months being a sergeant. He leads his own men, his own unit. By the 50th life, he’s lost too many men, too much blood is dripping from his fatigues and he can’t stand it anymore. He goes to the chapel when he can, whispers scared confessions into Aldo’s ear, and he’s not surprised when Aldo tells him one afternoon that God is a bastard.
Suddenly, the sweltering desert air starts to suffocate him. There’s too much death, too much destruction around him and he feels like he’s losing himself. He’s trained not to sleep, to keep your guard up at every second of every day, but soon his nightmares start to chase away the little sleep he could have. At the end of his fourth tour, he doesn’t renew his contract. He flies back to DC, starts taking Parker on the weekends, and spends every moment between his time with his son trying to keep his demons at bay.
In the idleness between his visits with Parker, the war comes back to haunt him. Nightmares of men he’s lost, brothers and friends, every life he’s seized before their time, every person he couldn’t save. Booth thinks of all the things he’s lost and wonders why God wouldn’t grant him a win.
On a random Tuesday after three nights of recurring nightmares, he ends up on a Greyhound headed to Atlantic City. He bets $100 on a blackjack table and wins $2,300 in return when a King of Hearts is flipped up over his Ace. He takes it as a sign that God was finally making up for the shit hand he’s been dealt, and bets another $300.
He’s only left with $500 at the end of the night, but it was still more than the $100 he had started with. He’s finally winning, gaining something instead of losing it.
It quickly slips out of control. He keeps chasing it, keeps going for little tastes of victory among the hundreds of losses, and soon he can’t pay for rent. He owes so much money to his bookie after someone at the casino had told him about sports betting and the Flyers were having a shit season. Rebecca never asks for child support but Parker gets sick with pneumonia and needs to go to the hospital after he contracts a secondary infection. He tells Pops that he needs help because Parker is sick and his old man gives him $500 in old bills that he had put aside for Parker’s college fund.
The money gets sucked into horses because he read in the paper that Stardust hadn’t lost five races in a row and they could use a little more money. Stardust breaks a leg on the track, and he burns with shame when he tells Rebecca that he doesn’t have anything . Luckily, Parker improves, and Rebecca’s new lawyer boyfriend offers to help with the bills. He almost gets evicted because he’s two months late on rent, subsisting on feeble meals of boxed mac and cheese and grilled sandwiches, when God gives him grace.
An old army buddy had told him that they were looking for agents at the FBI; it was a few months of training, but it was a steady paycheck. He throws himself into training at the Academy, has less time to gamble but when his evaluation to be a Special Agent comes around, he’s flagged during a background check.
“Addicts will do anything to get their fix. It’s a breeding ground for corruption. We cannot have such individuals representing the Agency, Mr. Booth.”
The psychologist assigned to him had told him that if he managed to get his gambling addiction under control, that he would be an excellent addition to the FBI. The elderly man pushed up his wire frame glasses up his liver-spotted nose as he gave Booth some resources on help for veterans and told him of the Gamblers Anonymous meetings that happened on Mondays and Thursdays in the basement of the Catholic church up the street.
He attends his meetings and gets a sponsor. He talks in group therapy about the things he’s seen and he feels a little less alone when a few veterans in his group speak up. He acknowledges that he has a problem, that he’s an addict like his father. He pinches pennies and apologizes to the landlord for the late rent, trying to pay him at least once a week to make up for the last two months. Soon, his re-evaluation comes and he passes with flying colors.
He slips once in a while - bets $50 on an upcoming Flyers game, bets $40 that he can beat a biker at pool, but he doesn’t let it run his life anymore. He focuses on being a good agent and a good father. Two years into being a Special Agent, Jocelyn Arrington comes calling, pleading for help. She reminds him of a mother of one of his men lost in a rescue mission gone south named Paul Adams. She had collapsed into his arms, much like Jocelyn did, when they released Paul’s remains to her after he was executed by insurgents. Another bereaved mother pleads for help and he’s not about to deny her the closure so few people got.
But the case is bare bones, only a few scraps of evidence and split jurisdictions led only to dead end after dead end. He confides in Camille, the now Chief Coroner of New York that he had gotten into a friends with benefits type of relationship during his first few cases as a special agent, and she suggests that he looks at Gemma Arrington from a different perspective.
She tells him of a forensic anthropologist, one of the best, that had solved a 400 year old murder. He’s skeptical of the use of forensics because knowing your suspect is more important but the only leads he had led him nowhere. He figures that it’s worth a shot.
Camille had said that a Dr. Temperance Brennan was teaching An Alternative Approach to Traditional Bone Cleaning Methods for Forensic Practice in a series of lectures this week at American University. Booth imagines a stuffy old academic, dressed in clothes mostly made of wool and smelled of old books. He imagines someone in their early 50s to late 60s at most, to garner the high regard that the Chief Coroner of New York held for the scientist.
Instead, he walks into the lecture hall and is met with a woman who is probably a few years his junior, commanding the room with such rapport and attention. She speaks with certainty, as if dictating pre-written information from an invisible book in front of her, and every single person has their attention solely on her.
He’s not surprised when she steals his attention, too. There’s something in her blue eyes that he’s drawn to, like there was a story between them that’s waiting to be written. He wants to know if she feels it too.
“Do you believe in fate?” He asks her.
“Absolutely not. Ludicrous.”
She doesn’t believe in fate, but he can’t help but think that this is what it feels like.
She says that she’s the best, but he needs his own evidence, his own proof. He never goes into a situation without reading it himself - a skill that’s kept him alive for years while serving overseas, won him many bluffs on a poker table.
That, and old habits are hard to break. He felt like taking a risk on her.
He realizes that she is, in fact, the best when she lists out Gemma Arrington’s life with the same certainty she had at her lecture. She knows of the move from Alabama, the car wreck that killed her father in 1996, that she sang without even knowing the existence of the tape loaded in the briefing room. She was arrogant with her intelligence, often using words that had Booth wishing he still had his old dictionary from his hot English teacher.
The arrogance was well-deserved. She slots evidence into a timeline, identifies the murder weapon and a potential exit path. He thought he knew what smart people looked like, what they sounded and thought like, but Bones was in a whole different league.
Temperance Brennan was brilliant.
Blindingly, absolutely brilliant. She has a brilliant idea, something about showing individuality and he thinks about the drawer of socks he can’t wear at the FBI. She asks him a brilliant question; why shouldn’t they be allowed to go on a date? He almost lies to her, wants to sidestep that rule about fraternizing with other agencies, but he plays the good agent and her response is as brilliant as she was:
“That’s too bad.”
She was exceptional - had an exceptional left hook that she used to sock a federal judge. It’s awesome and hot and exceptional like she is. He tells her as much and can’t stop the smile that curves his lips at the color that floods her cheeks.
She has an exceptional tolerance for alcohol when he takes her drinking because he wants to soften to blow when he tells her she can’t work the case anymore. They drink, and they drink some more, and soon a soft, steady haze of alcohol blankets him. He can’t stop staring, can’t believe that a woman like her can drink shitty tequila like a sailor. She has an exceptional idea, that they should have sex because they’re not working together and Booth wonders if he’s ever going to stop being blown away by her.
He feels his adrenaline surge when she slaps a few crumpled bills on the table and tugs on his sleeve towards the door. Booth stops her, wants to tell her his deepest darkest secret because he has a feeling that they were barrelling towards something he did not want to screw up.
He knew it would be as brilliant, as exceptional, as amazing as she was.
And he was right. It might have been the tequila, but he swears he gets more drunk on her. The soft warmth of her lips, the slide of her tongue against him, makes him dizzy. He feels something inside him slide into place and feels empty when she pulls away and tells him that they won’t be sleeping together. Booth wants to chase that feeling, those 15 seconds when her lips are on his. He wants to have it over, and over, and over again.
He’ll never get enough.
---
It all falls apart, too soon after. The judge is bulletproof and Bones doesn’t understand that powerful people get away with terrible things all the time. They fight and he is on the receiving end of only a taste of what she gave to the judge and he grows resentful of her - her fancy words, her seemingly endless knowledge of everything.
She’s brilliant and he’s not.
Temperance Brennan walks out of his life and is determined to keep him out of hers. In the year between Gemma Arrington and Clio Eller, he thinks of that moment in front of the poolhouse more times than he’ll ever admit. He can smell the supple scent of antiseptic mixed with fresh rain. He can feel the warm hand that anchors on the back of his neck pushing him closer to her in the same urgency he felt.
He thinks of the slender angle of her jaw, the waft of warm breath and tequila, of brilliant blue eyes, and feels an itch, an urge.
Then reaches for his phone, wondering if his buddy in the TSA was willing to do him a small favor.
---
They slowly become friends, partners. They dance on this fine line, between friends and something more than friends. Maybe he’s a little too protective of her, following her around on crime scenes and always urging her to stay back, to stand behind him even if he’s seen her take down suspects bigger and burlier than she was. Maybe she’s a little too attached to him, wandering hands that catch on his elbows, his forearm, his knee. She tells him things he suspects she’s never told anyone before, her well-earned trust handed to him in a file folder that contained the details of her parents’ disappearance.
They still argue and bicker, one of them always insisting that their viewpoint was the superior one when more often than not they found their answer in compromise. Bones lived by the laws governed by science and logic, while he relied on faith and feeling to guide him.
She teaches him how to be more rational, to take the facts before him and use it to their advantage. He teaches her to trust in him, in other people - that she could be vulnerable and understand the human portion of her that she tries to bury under anthropological facts and history.
They share bottles of beer and glasses of whiskey, barely dodge bullets, bombs, and close brushes with their death. He hops on the first plane to Louisiana when she wakes up bruised and battered with no recollection of the last 24 hours. He threatens, holds guns to people who would dare and try to hurt her. He holds her when her mother’s bones turn up, when she tells him that she doesn’t know who she is anymore.
But he knows who she is.
She was the one who always hovered in his periphery, the slant of her smile and the furrow of her brow something he could draw from memory, if he ever learned how to draw. He knew her Thai takeout order, the kind of whiskey she enjoyed, the burden of rationality she carries around in every aspect of her life. He knew that she was scared of being left behind again, so he always tells her that he’s not leaving, that she could always count on him.
She was his partner.
She was the unspoken reason as to why all his relationships were just meaningless reruns of women it never worked out with. She was the standard he held them all to, even if he would never admit it, especially to the new psychologist who looks like he’s barely out of high school.
He knows who she is.
--
He chases her, through war and ghosts and snakes and serial killers.
He chases those 15 seconds she gave him in front of the poolhouse almost five years ago now, chasing it in the subtle upturn of her lips when he presents her with Jasper for the first time. He chases the way her eyes sparkle when she sings on the stage they set up for her, chases the feeling of her hand in his when the world starts to fade as a bullet he takes for her lodges into his chest. He chases the flip of his stomach when he finds her on the sidelines of his hockey game, a red beanie pulled tightly over her ears when she waves at him.
Booth can’t stop himself, can’t stop the itch, the urge, that overwhelms him when she’s not near. An itch that had almost torn up his insides when she mentions that Sully wanted to take her away from him for an entire year and the relief of it when she decides to stay, to be rational, to keep doing their jobs because they’re amazing partners. He can’t stop the urge to shove the barrel of his gun down the mouth of any person who threatens her, or the urge to never give up on her because she wouldn’t give up on him.
He can’t stop himself when Sweets tells him to use his addiction, his problem, to break the stalemate. He’s thought about it over the years, made and replayed scenarios in his head on what it would be like to finally cross that fine line they’ve been dancing on all these years. But he’s a good agent, one who follows the rules, and they always said that there would be no fraternizing with consultants or other agencies. He decides to screw it all because they were on the brink of something, of the unwritten story he saw in her eyes when they first met.
It was going to be brilliant, exceptional, and amazing.
He tells her that he’s a gambler, unashamed in the fact that he’s an addict. He wants to take a chance on this, on her, on them .
But she pushes him away, tells him that he needs protecting. He hands her his heart and she crumbles it into little pieces in front of him. She doesn’t know how to make them work, doesn’t know how to risk the status quo for the potential. She didn't know how to take the less-traveled route, to bet on something out of her control.
“I’m a scientist. I can’t change. I don’t know how.”
Booth had forgotten that gambling always came with risks. He forgot that you came down from the adrenaline you get when you place a bet, that reality always had the odds tilted against him.
“Can we still work together?” She asks, after breaking the heart he’s offered to her. He glances at her, watching the tears that carve pathways into her cheeks and doesn’t fight the urge when he says yes.
He’s an addict.
And now, she is his only vice.
--
#bones#bones and booth#booth and bones#booth x brennan#brennan x booth#temperence brennan#seeley booth#thank god this is done i've been DREAMING about bones and it all needed to come out somewhere#also i haven't written in a while and this was a joy and delight#maybe i write more#maybe i don't
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Yes? Perhaps?
But also, in our case, we are quantitatively and objectively plural.
That's a neurotype, and as you've described it exists largely because of how atypical our behavior and experiences are from what society considers to be typical.
However, we have a precise number of separate consciousnesses and streams of long term memory in our brain, and the fact that we do is detectable with an active MRI. And, as such, it is a materially different state than that of having one single consciousness.
In our case, it's like you've said, "'three' is not an ontological status."
Like, what you're saying is important for understanding ableism and systems of justice constructed to deconstruct ableism.
But it's also just fucking wrong, from an actual material analysis of our existence.
the neurotypical invents the neurodivergent. neuro(non)normativity is a constant negotiation of social conditions + relation to capital + carceral frameworks of legal, educational, medical systems. “neurotype” is not an ontological status. it is a mirror held to the world in which it exists.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Clinical Trial Imaging Market In-depth Analysis and Forecast Report, 2030
The global clinical trial imaging market size is expected to reach USD 1.91 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 7.8% from 2025 to 2030, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. Increasing research and development spending to discover new drugs and therapies to treat chronic diseases is propelling the industry growth. Images obtained from the internal examination of the body are used to determine drug activity. Clinical trial imaging provides rapid, detailed, and accurate screening. The need for clinical trial imaging is rapidly increasing in all phases of trials. Medical imaging in clinical trials is used as a primary, quantitative, and surrogate biomarker.
The clinical trial design includes selecting patient population, stratification based on biomarkers, different methods for allocation treatments, choosing efficient and reliable endpoints and validation of surrogate endpoints, calculating sample size, trial simulations, adaptive trial set-up, statistical and interim analysis, and assisting clients to deal with regulatory authorities such as EMA and FDA to discuss study design or defend study results.
Market players provide analytical testing services, pharmacokinetic, reading, and pharmacodynamics services for enhanced clinical development. IXICO offers advanced technologies for catalyzing clinical trials in neuroscience. Imaging biomarkers by the company help in measuring the safety and effectiveness of therapies used for neuro-imaging. Imaging biomarkers are effective in radiological reads. This provides the reading of MRI scans for central neuro to enhance the assessment of ongoing monitoring of drug safety and subject eligibility
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Global Clinical Trial Imaging Market
Clinical Trial Imaging Market Report Highlights
The reading and analytical services segment held the largest market share at 30.95% in 2024 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.4% from 2025 to 2030, highlighting its critical role in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of imaging data in clinical research.
The biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies segment accounted for the largest share of 28.7% in 2024. The factor attributing to the dominance of this segment is the need to develop new drugs and therapies to cure chronic diseases.
Oncology segment held the largest market share of 23.63% in 2024. High prevalence of cancer cases and the constant need for new and innovative therapies to treat various types of cancer are expected to fuel the market growth.
The contract research organizations (CROs) segment is expected to grow significantly with a CAGR of 8.5% over the forecast period, owing to its essential role in developing new drugs and therapies for chronic diseases.
North America dominated the market with a revenue share of 47.93% in 2024 due to the increasing geriatric population, along with chronic diseases and growing demand for treatment options.
Browse through Grand View Research's Medical Devices Industry Research Reports.
Ophthalmic Drug Delivery Systems Market: The global ophthalmic drug delivery systems market size was estimated at USD 15.76 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.6% from 2025 to 2030.
Endoluminal Suturing Devices Market: The global endoluminal suturing devices market size was valued at USD 73.6 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.1% from 2025 to 2030.
Clinical Trial Imaging Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the global clinical trial imaging market based on modality, therapeutic area, services, end use and region:
Clinical Trial Imaging Modality Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Computed Tomography Scan
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
X-Ray
Ultrasound
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Other Modalities
Clinical Trial Imaging Therapeutic Area Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Neurovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular Diseases
Orthopedics & MSK Disorders
Oncology
Ophthalmology
Nephrology
Other Therapeutic Areas
Clinical Trial Imaging Services Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Clinical Trial Design and Consultation Services
Reading and Analytical Services
Operational Imaging Services
System and Technology Support Services
Project and Data Management
Clinical Trial Imaging End Use Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Companies
Medical Devices Manufacturers
Academic and Government Research Institutes
Contract Research Organizations (CROs)
Other End Users
Clinical Trial Imaging Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
North America
Europe
Asia Pacific
Latin America
Middle East & Africa
Order a free sample PDF of the Clinical Trial Imaging Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
0 notes
Text
Clinical Trial Imaging Industry Demand, Trend & Top Key Players Update By 2030
The global clinical trial imaging market size is expected to reach USD 1.91 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 7.8% from 2025 to 2030, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. Increasing research and development spending to discover new drugs and therapies to treat chronic diseases is propelling the industry growth. Images obtained from the internal examination of the body are used to determine drug activity. Clinical trial imaging provides rapid, detailed, and accurate screening. The need for clinical trial imaging is rapidly increasing in all phases of trials. Medical imaging in clinical trials is used as a primary, quantitative, and surrogate biomarker.
The clinical trial design includes selecting patient population, stratification based on biomarkers, different methods for allocation treatments, choosing efficient and reliable endpoints and validation of surrogate endpoints, calculating sample size, trial simulations, adaptive trial set-up, statistical and interim analysis, and assisting clients to deal with regulatory authorities such as EMA and FDA to discuss study design or defend study results.
Market players provide analytical testing services, pharmacokinetic, reading, and pharmacodynamics services for enhanced clinical development. IXICO offers advanced technologies for catalyzing clinical trials in neuroscience. Imaging biomarkers by the company help in measuring the safety and effectiveness of therapies used for neuro-imaging. Imaging biomarkers are effective in radiological reads. This provides the reading of MRI scans for central neuro to enhance the assessment of ongoing monitoring of drug safety and subject eligibility
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Global Clinical Trial Imaging Market
Clinical Trial Imaging Market Report Highlights
The reading and analytical services segment held the largest market share at 30.95% in 2024 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.4% from 2025 to 2030, highlighting its critical role in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of imaging data in clinical research.
The biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies segment accounted for the largest share of 28.7% in 2024. The factor attributing to the dominance of this segment is the need to develop new drugs and therapies to cure chronic diseases.
Oncology segment held the largest market share of 23.63% in 2024. High prevalence of cancer cases and the constant need for new and innovative therapies to treat various types of cancer are expected to fuel the market growth.
The contract research organizations (CROs) segment is expected to grow significantly with a CAGR of 8.5% over the forecast period, owing to its essential role in developing new drugs and therapies for chronic diseases.
North America dominated the market with a revenue share of 47.93% in 2024 due to the increasing geriatric population, along with chronic diseases and growing demand for treatment options.
Browse through Grand View Research's Medical Devices Industry Research Reports.
Ophthalmic Drug Delivery Systems Market: The global ophthalmic drug delivery systems market size was estimated at USD 15.76 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.6% from 2025 to 2030.
Endoluminal Suturing Devices Market: The global endoluminal suturing devices market size was valued at USD 73.6 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.1% from 2025 to 2030.
Clinical Trial Imaging Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the global clinical trial imaging market based on modality, therapeutic area, services, end use and region:
Clinical Trial Imaging Modality Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Computed Tomography Scan
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
X-Ray
Ultrasound
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Other Modalities
Clinical Trial Imaging Therapeutic Area Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Neurovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular Diseases
Orthopedics & MSK Disorders
Oncology
Ophthalmology
Nephrology
Other Therapeutic Areas
Clinical Trial Imaging Services Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Clinical Trial Design and Consultation Services
Reading and Analytical Services
Operational Imaging Services
System and Technology Support Services
Project and Data Management
Clinical Trial Imaging End Use Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Companies
Medical Devices Manufacturers
Academic and Government Research Institutes
Contract Research Organizations (CROs)
Other End Users
Clinical Trial Imaging Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
North America
Europe
Asia Pacific
Latin America
Middle East & Africa
Order a free sample PDF of the Clinical Trial Imaging Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
0 notes
Text
2024 Clinical Trial Imaging Market Outlook: Future Trends and Insights

Clinical Trial Imaging Market Outlook, Scope & Overview:
Industry reports indicate that the global clinical trial imaging market was valued at USD 1.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 2.14 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 7.5% over the forecast period 2024-2031.
Technological Advancements to Drive Growth of Global Clinical Trial Imaging Market
The adoption of advanced imaging technologies in clinical trials will continue to influence global market revenues. Pharmaceutical companies, contract research organizations (CROs), and academic institutions are increasingly utilizing imaging solutions to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of clinical trial data.
As a product segment, imaging services currently hold a significant share of the global clinical trial imaging market. This segment is anticipated to grow at a year-over-year rate of 7.5% in 2024 over 2023 and reach USD 2.14 billion in revenues by 2031. The increasing demand for precise and quantitative imaging in drug development and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases are expected to drive market growth.
Clinical Trial Imaging Solutions – Market Dynamics
Drivers:
Clinical trial imaging solutions are witnessing significant growth in the global market due to their ability to provide detailed and quantifiable data, which is crucial for assessing the efficacy and safety of new therapies. The growing emphasis on personalized medicine, the rising number of clinical trials, and advancements in imaging modalities, such as MRI, CT, and PET, are key factors driving the adoption of imaging solutions in clinical trials. Additionally, regulatory requirements for more rigorous and comprehensive data are further propelling market growth.
Restraints:
Despite the growth potential, challenges such as high costs associated with imaging equipment and services, the complexity of image analysis, and concerns about patient privacy and data security are hindering the widespread adoption of clinical trial imaging solutions. Moreover, the need for specialized training and expertise to operate imaging systems and interpret data poses additional challenges to market expansion.
Clinical Trial Imaging Solutions – Market Outlook
The proven benefits of clinical trial imaging solutions in enhancing trial accuracy, reducing trial duration, and improving data quality have contributed to the market's growth. Clinical trial imaging solutions are expected to witness increased adoption across major markets, including North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific, driven by technological advancements and the growing focus on precision medicine and oncology trials.
Global Clinical Trial Imaging Market
The rise in demand for clinical trial imaging solutions in developed and emerging markets is expected to drive market growth over the forecast period. North America currently holds a significant market share in the global clinical trial imaging market, with the US being a key contributor to market revenues. Europe and Asia Pacific regions are also experiencing rapid adoption of clinical trial imaging solutions, supported by increasing healthcare investments and the growing number of clinical research activities.
Key Players in the Clinical Trial Imaging Solutions Market
Leading companies in the clinical trial imaging solutions market include BioClinica, Parexel International Corporation, ICON plc, and Radiant Sage LLC. These companies are at the forefront of developing and commercializing advanced imaging technologies for various clinical trial applications, including drug development, biomarker identification, and patient monitoring.
In conclusion, the global clinical trial imaging market is poised for substantial growth over the forecast period, driven by technological advancements, increasing clinical trial activities, and the expanding adoption of imaging solutions in drug development and regulatory processes.
Other Trending Reports
Antiepileptic Drugs Market Share by Company
Mental Health Treatment Market Share by Company
eHealth Market Share by Company
Electronic Medical Record (EMR) Systems Market Share by Company
0 notes
Text
Data Science for Medical Imaging: Bridging Technology and Healthcare
In recent years, the intersection of data science and medical imaging has sparked revolutionary advancements in healthcare. This convergence leverages the power of data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to enhance diagnostic accuracy, streamline processes, and ultimately improve patient outcomes. Medical imaging, encompassing techniques such as MRI, CT scans, and X-rays, generates vast amounts of data that hold the key to more precise diagnostics and personalized treatment plans.
The Role of Data Science in Medical Imaging
Data science in medical imaging involves the extraction of valuable insights from complex datasets generated by various imaging modalities. Traditional methods of interpreting medical images rely heavily on the expertise of radiologists and clinicians. However, with the advent of data science techniques, these interpretations can be augmented and validated with quantitative analysis.
Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms play a pivotal role in analyzing medical images. By training models on large datasets, these algorithms can learn to detect patterns that are imperceptible to the human eye, leading to early detection of diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and neurological disorders. Techniques like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have shown remarkable success in segmenting tumors, identifying abnormalities, and even predicting disease progression based on imaging data.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) further enhances the capabilities of data science in medical imaging by enabling predictive analytics and real-time decision support systems. AI models can continuously learn from new data, improving their accuracy and reliability over time. This iterative learning process is particularly beneficial in dynamic medical environments where treatment protocols evolve based on the latest research and patient outcomes.
Applications and Benefits
Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
One of the primary benefits of data science in medical imaging is its ability to enhance diagnostic accuracy. By analyzing subtle patterns and variations in medical images, algorithms can assist radiologists in making more informed diagnoses. This not only reduces the likelihood of misdiagnosis but also ensures that patients receive timely and appropriate treatment.
Personalized Medicine
Data science enables the concept of personalized medicine, where treatment plans are tailored to individual patient profiles. By integrating imaging data with other clinical data sources, such as genomics and patient history, healthcare providers can deliver targeted therapies that optimize efficacy and minimize side effects.
Operational Efficiency
Beyond clinical applications, data science certification improves operational efficiency within healthcare institutions. Automated image analysis and workflow optimization tools streamline processes, allowing radiologists to focus more on complex cases and patient care. This efficiency translates into shorter wait times for diagnoses and faster treatment initiation.
What is Covariance
youtube
Challenges and Considerations
Data Quality and Standardization
One of the primary challenges in leveraging data science training for medical imaging is ensuring data quality and standardization. Medical images vary in resolution, quality, and format, making it challenging to integrate data from different sources. Establishing robust protocols for data collection, storage, and sharing is essential to ensure the reliability and accuracy of AI models.
Interpretability and Validation
The interpretability of AI-driven insights remains a significant concern in medical imaging. While algorithms can detect patterns with high accuracy, understanding the rationale behind their decisions is crucial for clinical acceptance. Validation studies that compare algorithmic predictions with clinical outcomes are necessary to build trust among healthcare professionals and regulatory bodies.
Future Directions
Advancements in Technology
The future of data science course in medical imaging holds promise for further technological advancements. Continued research in AI, machine learning, and deep learning will lead to more sophisticated algorithms capable of detecting subtle biomarkers and predicting disease progression with greater precision.
Integration with Healthcare Systems
Integrating data science solutions into existing healthcare systems remains a priority. This includes developing user-friendly interfaces for clinicians, ensuring seamless interoperability with electronic health records, and addressing cybersecurity concerns associated with sensitive medical data.
Data science course has revolutionized medical imaging by unlocking insights from complex datasets and transforming how healthcare professionals diagnose and treat patients. The synergy between data science and medical imaging represents a paradigm shift towards precision medicine and personalized care. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of data-driven approaches in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of healthcare. Embracing these innovations requires ongoing collaboration between data scientists, clinicians, and healthcare stakeholders to harness the full potential of data science in transforming the future of medical imaging.
What is Cross Entropy
youtube
0 notes
Text
Understanding the Global MRI Market: Size and Growth Trends

The Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Market was valued at USD 6.6 Bn in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 11 Bn by 2031 and grow at a CAGR of 6.6% during the forecasted period 2024-2031.The Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) market has evolved into a cornerstone of modern medical diagnostics, revolutionizing the way clinicians visualize and understand the human body. With its non-invasive approach and unparalleled detail, MRI technology continues to expand its applications across various medical specialties, from neurology to oncology and orthopedics.
The study contains in-depth information on new market trends, market drivers, development opportunities, and market restraints that may have an impact on the industry's market dynamics. It examines the product, applications, and competitive landscape in the market segments in depth. Strategy analysis, trend and scenario analysis for micro and macro markets, price analysis, and a full review of the market position for the projected period are all included in the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Market research report. This research includes primary and secondary drivers, market share, crucial areas, and geographical analysis. It is a comprehensive and professional report.
Get Sample of This Report @ https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/2906
Market Segmentation
By Architecture outlook
Open System
Closed System
By Field Strength Outlook
Low Field Strength
Mid Field Strength
High Field Strength
By Application Outlook
Cardiac
Abdominal
Vascular
Brain and Neurological
Other
By End Use
Hospitals
Imaging centres
Ambulatory surgical centres
Others
Regional Overview
The Magnetic Resonance Imaging Market is classified into five primary geographical regions, according to the regional study: North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Middle East and Africa. The report delves deeply into each region's production and consumption ratios, market size and share, import and export, and infrastructure development.
Research Methodology
The report's results were corroborated by primary research with industry professionals and opinion leaders from throughout the world. To compile and validate the data, various market estimation and data validation methodologies are employed. We also employ a proprietary data forecasting methodology to anticipate market growth. Using both primary and secondary research approaches, we analyzed the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Market from every viewpoint. This helped us grasp current market dynamics like supply-demand imbalances, pricing trends, product preferences, and customer behavior patterns, among other things.
Key Reasons to Purchase Magnetic Resonance Imaging Market Report
The study contains crucial information such as market dynamics and forecast period prospects.
Regional, sub-regional, and country statistics cover market influence, demand, and supply dynamics.
Comprehensive product companies, key financial data, current events, SWOT analysis, and top players' strategies
Quantitative, qualitative, value, and volume statistics are among the segments and sub-segments.
The competitive environment includes a wide range of key players, new developments, and strategies.
About Us
SNS Insider is a market research and insights firm that has won several awards and earned a solid reputation for service and strategy. We are a strategic partner who can assist you in reframing issues and generating answers to the trickiest business difficulties. For greater consumer insight and client experiences, we leverage the power of experience and people.
When you employ our services, you will collaborate with qualified and experienced staff. We believe it is crucial to collaborate with our clients to ensure that each project is customized to meet their demands. Nobody knows your customers or community better than you do. Therefore, our team needs to ask the correct questions that appeal to your audience in order to collect the best information.
Related Reports
Protein Engineering Market Share
AI in Cancer Diagnosis Market Share
Blood Group Typing Market Share
Immunomodulators Market Share
Lymphoma Treatment Market Share
0 notes
Text
Reference archived on our website (follow the link to see more than 1,000 open-access covid studies! daily updates!)
This study is currently being misquoted by a lot of science reporters who are claiming it's the cause of all long covid symptoms: this shows inflammation and lasting damage in the brainstem following a covid infection is responsible for many *neurological* symptoms of Long covid such as heart palpitations and loss of sensation.
Abstract
Post-mortem studies have shown that patients dying from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection frequently have pathological changes in their CNS, particularly in the brainstem. Many of these changes are proposed to result from para-infectious and/or post-infection immune responses. Clinical symptoms such as fatigue, breathlessness, and chest pain are frequently reported in post-hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients. We propose that these symptoms are in part due to damage to key neuromodulatory brainstem nuclei. While brainstem involvement has been demonstrated in the acute phase of the illness, the evidence of long-term brainstem change on MRI is inconclusive. We therefore used ultra-high field (7 T) quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) to test the hypothesis that brainstem abnormalities persist in post-COVID patients and that these are associated with persistence of key symptoms.
We used 7 T QSM data from 30 patients, scanned 93–548 days after hospital admission for COVID-19 and compared them to 51 age-matched controls without prior history of COVID-19 infection. We correlated the patients’ QSM signals with disease severity (duration of hospital admission and COVID-19 severity scale), inflammatory response during the acute illness (C-reactive protein, D-dimer and platelet levels), functional recovery (modified Rankin scale), depression (Patient Health Questionnaire-9) and anxiety (Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7).
In COVID-19 survivors, the MR susceptibility increased in the medulla, pons and midbrain regions of the brainstem. Specifically, there was increased susceptibility in the inferior medullary reticular formation and the raphe pallidus and obscurus. In these regions, patients with higher tissue susceptibility had worse acute disease severity, higher acute inflammatory markers, and significantly worse functional recovery.
This study contributes to understanding the long-term effects of COVID-19 and recovery. Using non-invasive ultra-high field 7 T MRI, we show evidence of brainstem pathophysiological changes associated with inflammatory processes in post-hospitalized COVID-19 survivors.
#mask up#long covid#covid conscious#covid#covid 19#pandemic#wear a mask#public health#coronavirus#sars cov 2#still coviding#wear a respirator#covid is not over
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Breakthrough in 0.05 Tesla MRI reported by HKU Engineering team in Science Journal
HONG KONG SAR – Media OutReach Newswire – 25 June 2024 – Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has revolutionised healthcare with its non-ionising, non-invasive, multi-contrast and quantitative capabilities. It also presents a promising platform for future artificial intelligence-driven medical diagnoses. However, limited accessibility, especially in low and middle-income countries, is a challenge due…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Cardiovascular Imaging: Comprehensive Insights from Dr. Richard Zelman
Cardiovascular imaging is an essential tool in the diagnosis, management, and treatment of heart diseases. Advanced imaging techniques provide detailed views of the heart and blood vessels, aiding in early detection and precise intervention. Dr. Richard Zelman, a leading expert in cardiology, offers a comprehensive overview of cardiovascular imaging modalities, their applications, and advancements.
Types of Cardiovascular Imaging
1. Echocardiography
Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE):
Description: A non-invasive test that uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart.
Applications: Assesses heart size, structure, and function; evaluates valve diseases, cardiomyopathies, and pericardial diseases.
Advancements: 3D echocardiography provides more detailed and accurate images.
Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE):
Description: An invasive test where a probe is inserted into the esophagus to obtain clearer images of the heart, especially the back structures.
Applications: Used when detailed images are needed, such as in the assessment of prosthetic valves, endocarditis, and atrial septal defects.
2. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Description:
**Non-invasive technique using magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the heart and blood vessels.
Applications:
Cardiac Anatomy and Function: Provides precise information about heart muscle viability, volumes, and ejection fraction.
Myocardial Diseases: Diagnoses conditions like myocarditis, cardiomyopathies, and fibrosis.
Congenital Heart Disease: Offers comprehensive anatomical details crucial for surgical planning.
Advancements:
T1 and T2 Mapping: Enhanced tissue characterization allows better diagnosis of myocardial diseases.
4D Flow MRI: Provides detailed information about blood flow dynamics.
3. Computed Tomography (CT)
Coronary CT Angiography (CCTA):
Description: A non-invasive imaging method that uses X-rays to visualize coronary arteries.
Applications: Detects coronary artery disease, evaluates chest pain, and plans interventions.
Advancements: High-resolution CT scanners reduce radiation exposure and improve image quality.
Cardiac CT for Structural Heart Disease:
Applications: Assesses aortic aneurysms, congenital heart defects, and helps in planning procedures like transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
4. Nuclear Cardiology
Myocardial Perfusion Imaging (MPI):
Description: Uses radioactive tracers to assess blood flow to the heart muscle.
Applications: Diagnoses coronary artery disease, evaluates myocardial viability, and determines the effectiveness of treatments.
Advancements: PET imaging offers higher resolution and quantitative assessment compared to SPECT.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET):
Applications: Evaluates myocardial metabolism, perfusion, and detects inflammatory and infiltrative diseases.
5. Invasive Imaging Techniques
Coronary Angiography:
Description: An invasive procedure where contrast dye is injected into coronary arteries to visualize blockages.
Applications: Gold standard for diagnosing coronary artery disease and guiding percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI).
Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) and Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT):
Description: Catheter-based imaging techniques providing detailed views of the artery walls.
Applications: Assess plaque characteristics, guide stent placement, and evaluate stent results.
Applications and Benefits
1. Early Diagnosis and Intervention:
Benefit: Early detection of cardiovascular diseases allows timely intervention, reducing morbidity and mortality.
2. Risk Stratification:
Benefit: Imaging helps stratify patients based on their risk, guiding appropriate management strategies.
3. Treatment Planning and Monitoring:
Benefit: Detailed anatomical and functional information aids in planning surgical and interventional procedures and monitoring treatment efficacy.
4. Non-Invasive and Minimally Invasive Options:
Benefit: Many imaging techniques are non-invasive or minimally invasive, reducing patient discomfort and recovery time.
Emerging Trends and Future Directions
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Description: AI algorithms enhance image analysis, improve diagnostic accuracy, and predict outcomes.
Applications: Automated interpretation of imaging studies, risk assessment, and personalized treatment planning.
2. Molecular Imaging:
Description: Combines imaging with molecular biology to visualize biological processes at the cellular and molecular levels.
Applications: Early detection of atherosclerosis, monitoring therapeutic responses, and evaluating new treatments.
3. Hybrid Imaging:
Description: Combines different imaging modalities (e.g., PET/CT, PET/MRI) to provide comprehensive information.
Applications: Improves diagnostic accuracy and provides detailed anatomical and functional data.
Conclusion
Cardiovascular imaging has revolutionized the field of cardiology, enabling precise diagnosis and effective management of heart diseases. Richard Zelman MD expertise highlights the importance of using advanced imaging techniques to improve patient outcomes. With ongoing advancements in technology and the integration of AI, the future of cardiovascular imaging promises even greater accuracy and innovation in diagnosing and treating cardiovascular conditions.
0 notes
Text
Diagnostic Imaging Services Market Worldwide Industry Analysis, Future Demand and Forecast till 2032

Diagnostic Imaging Services Market size is expected to grow from USD 611.3 Billion in 2023 to USD 1041.58 Billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 6.1% during the forecast period (2024-2032).
Diagnostic Imaging Services is a medical procedure using advanced technologies to visualize the internal structures of the body, aiding in disease detection and diagnosis. Techniques like X-ray, CT scan, MRI, ultrasound, and nuclear medicine are employed to create detailed images of organs and tissues. These services play a crucial role in identifying and assessing various medical conditions, enabling healthcare professionals to formulate accurate treatment plans.
Advancements in imaging technologies services provide healthcare professionals with essential insights for early detection and effective treatment planning, leading to improved patient outcomes. It can be performed in hospitals, and diagnostic imaging services contribute to early detection, monitoring, and management of diseases, enhancing patient care. Rapid advancements in technology continue to refine these services, promoting precision and efficiency in medical diagnostics.
Get Full PDF Sample Copy of Report: (Including Full TOC, List of Tables & Figures, Chart) @
https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/request/9887
Updated Version 2024 is available our Sample Report May Includes the:
Scope For 2024
Brief Introduction to the research report.
Table of Contents (Scope covered as a part of the study)
Top players in the market
Research framework (structure of the report)
Research methodology adopted by Worldwide Market Reports
Leading players involved in the Diagnostic Imaging Services Market include:
Center for Diagnostic Imaging (U.S), Novant Health (US), RadNet (U.S), Dignity Health (US), Alliance Medical (UK), Medica Group (UK), Global Diagnostics (UK), Concord Medical Services Holdings Limited (China), Healthcare Imaging Services Pty Ltd. (Australia), Sonic Healthcare (Australia), and Other Major Players
Moreover, the report includes significant chapters such as Patent Analysis, Regulatory Framework, Technology Roadmap, BCG Matrix, Heat Map Analysis, Price Trend Analysis, and Investment Analysis which help to understand the market direction and movement in the current and upcoming years.
If You Have Any Query Diagnostic Imaging Services Market Report, Visit:
https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/inquiry/9887
Segmentation of Diagnostic Imaging Services Market:
By Imaging Modality
X-ray
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Ultrasound
Computed Tomography (CT)
Nuclear Imaging
By Application
Cardiology
Gynecology
Oncology
Orthopedics & Musculoskeletal
Neurology & Spine
General Imaging
By End-User
Hospitals
Diagnostic Centers
Ambulatory Surgical Centers
An in-depth study of the Diagnostic Imaging Services industry for the years 2024–2032 is provided in the latest research. North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, the Middle East, and Africa are only some of the regions included in the report's segmented and regional analyses. The research also includes key insights including market trends and potential opportunities based on these major insights. All these quantitative data, such as market size and revenue forecasts, and qualitative data, such as customers' values, needs, and buying inclinations, are integral parts of any thorough market analysis.
Market Segment by Regions: -
North America (US, Canada, Mexico)
Eastern Europe (Bulgaria, The Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Rest of Eastern Europe)
Western Europe (Germany, UK, France, Netherlands, Italy, Russia, Spain, Rest of Western Europe)
Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, The Philippines, Australia, New Zealand, Rest of APAC)
Middle East & Africa (Turkey, Bahrain, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, UAE, Israel, South Africa)
South America (Brazil, Argentina, Rest of SA)
Key Benefits of Diagnostic Imaging Services Market Research:
Research Report covers the Industry drivers, restraints, opportunities and challenges
Competitive landscape & strategies of leading key players
Potential & niche segments and regional analysis exhibiting promising growth covered in the study
Recent industry trends and market developments
Research provides historical, current, and projected market size & share, in terms of value
Market intelligence to enable effective decision making
Growth opportunities and trend analysis
Covid-19 Impact analysis and analysis to Diagnostic Imaging Services market
If you require any specific information that is not covered currently within the scope of the report, we will provide the same as a part of the customization.
Acquire This Reports: -
https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/checkout/?user=1&_sid=9887
About us:
Introspective Market Research (introspectivemarketresearch.com) is a visionary research consulting firm dedicated to assist our clients grow and have a successful impact on the market. Our team at IMR is ready to assist our clients flourish their business by offering strategies to gain success and monopoly in their respective fields. We are a global market research company, specialized in using big data and advanced analytics to show the bigger picture of the market trends. We help our clients to think differently and build better tomorrow for all of us. We are a technology-driven research company, we analyze extremely large sets of data to discover deeper insights and provide conclusive consulting. We not only provide intelligence solutions, but we help our clients in how they can achieve their goals.
Contact us:
Introspective Market Research
3001 S King Drive,
Chicago, Illinois
60616 USA
Ph no: +1 773 382 1049
Email: [email protected]
#Diagnostic Imaging Services#Diagnostic Imaging Services Market#Diagnostic Imaging Services Market Size#Diagnostic Imaging Services Market Share#Diagnostic Imaging Services Market Growth#Diagnostic Imaging Services Market Trend#Diagnostic Imaging Services Market segment#Diagnostic Imaging Services Market Opportunity#Diagnostic Imaging Services Market Analysis 2024
0 notes
Text
UNLOCKING THE POTENTIAL: ADVANCEMENTS IN ULTRASOUND IMAGING
In the realm of medical diagnostics, ultrasound imaging stands as a cornerstone technology, providing invaluable insights into the human body without the need for invasive procedures. From monitoring fetal development to diagnosing internal injuries, ultrasound has continually evolved, unlocking new potentials and revolutionizing medical practices. Today, we delve into the latest advancements in ultrasound imaging, exploring how technology is reshaping healthcare and improving patient outcomes.
Traditionally, ultrasound imaging has been synonymous with obstetrics, offering expecting parents the first glimpse of their unborn child. However, its utility extends far beyond pregnancy monitoring. With advancements in transducer technology, image processing algorithms, and data visualization techniques, modern ultrasound systems can capture detailed images of various anatomical structures with unprecedented clarity and precision.
One of the most significant breakthroughs in ultrasound imaging is the development of 3D and 4D ultrasound. Unlike traditional 2D scans, these techniques provide volumetric images, offering clinicians a comprehensive view of the target area. This spatial awareness enhances diagnostic accuracy, particularly in complex cases such as fetal abnormalities or cardiac anomalies. Moreover, real-time 4D imaging allows for dynamic visualization, enabling clinicians to observe moving structures like the beating heart or fetal movements, aiding in early detection and intervention.
Another area of advancement lies in contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS), which involves the administration of microbubble contrast agents to improve image quality. These microbubbles resonate in response to ultrasound waves, enhancing the reflection and allowing for better delineation of blood flow patterns and tissue perfusion. CEUS has emerged as a valuable tool in assessing vascular conditions, detecting liver lesions, and guiding interventional procedures, offering a safer alternative to contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms has propelled ultrasound imaging to new heights of efficiency and accuracy. Machine learning algorithms trained on vast datasets can analyze ultrasound images in real-time, assisting clinicians in image interpretation, lesion detection, and quantitative analysis. AI-driven automation streamlines workflow, reduces human error, and optimizes resource utilization, ultimately leading to faster diagnoses and improved patient outcomes.
Advancements in transducer technology have also expanded the clinical applications of ultrasound imaging. High-frequency transducers can now penetrate deeper into tissues while maintaining excellent resolution, enabling the visualization of small structures and subtle abnormalities. Additionally, the miniaturization of ultrasound probes has facilitated point-of-care imaging, allowing clinicians to perform bedside ultrasound examinations in diverse clinical settings, from emergency departments to rural healthcare facilities.
Beyond diagnostic imaging, therapeutic ultrasound has emerged as a promising modality for targeted drug delivery, tissue ablation, and non-invasive surgery. High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) utilizes focused ultrasound waves to generate localized heat, effectively destroying diseased tissue while minimizing damage to surrounding structures. HIFU has been successfully employed in the treatment of uterine fibroids, prostate cancer, and essential tremor, offering patients a non-invasive alternative to traditional surgery.
Looking ahead, the future of ultrasound imaging holds even greater promise. Emerging technologies such as photoacoustic imaging, elastography, and molecular imaging are poised to further enhance the capabilities of ultrasound systems, allowing for deeper tissue penetration, quantitative tissue characterization, and molecular-level diagnostics. Moreover, advancements in portable and wearable ultrasound devices are democratizing access to medical imaging, empowering healthcare providers in resource-limited settings and enabling remote monitoring of patients in the comfort of their homes.
In conclusion, the landscape of ultrasound imaging is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by technological innovation and interdisciplinary collaboration. From improved image quality and diagnostic accuracy to novel therapeutic applications, the advancements in ultrasound imaging are revolutionizing healthcare delivery and transforming patient care. As we continue to unlock the full potential of this versatile modality, the future of medical imaging appears brighter than ever before.
Orignal Source: https://av-imaging.com/unlocking-the-potential-advancements-in-ultrasound-imaging.html
0 notes
Text
Superconductors Market SWOT Analysis Of Top Key Player And Forecast 2024-2033
A superconductor is a material that can conduct electricity with zero resistance. This means that when a current is applied to a superconductor, it will flow forever without losing any energy. Superconductors are made from materials that have been cooled to extremely low temperatures, typically near absolute zero. The first superconductor was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes.
Key Trends
Some of the key trends in superconductors technology include the development of high-temperature superconductors, the use of superconductors in energy storage, and the use of superconductors in transportation.
To Know More@ https://www.globalinsightservices.com/reports/superconductors-market/?utm_id=Pranalip
High-temperature superconductors (HTS) are a type of superconductor that can operate at temperatures above the traditional limit of around 20 Kelvin. HTS materials are typically made from copper oxide or iron-based compounds. HTS superconductors are used in a variety of applications, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and high-speed electrical power transmission.
The use of superconductors in energy storage is a relatively new development. Superconductors can be used to store large amounts of energy in a small space. This energy can then be released quickly when needed. Superconductors could potentially be used in a variety of energy storage applications, including grid-scale energy storage and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems.
The use of superconductors in transportation is also a relatively new development. Superconducting magnets can be used to levitate trains or other vehicles, which would allow for frictionless travel. This technology is already being used in prototype high-speed trains. In the future, superconductors could be used in a variety of other transportation applications, including electric vehicles and maglev trains.
Key Drivers
The key drivers of the superconductors market are the increasing demand for energy-efficient products, the need for miniaturization of electronic devices, and the growing adoption of superconductors in the healthcare sector.
The increasing demand for energy-efficient products is one of the major drivers of the superconductors market. Superconductors are highly efficient in carrying electrical current with zero resistance, which helps in reducing energy losses. This is expected to fuel the demand for superconductors from the power sector.
The need for miniaturization of electronic devices is another driver of the superconductors market. Superconductors can be used to create smaller and more efficient electronic devices. This is expected to fuel the demand for superconductors from the consumer electronics sector.
Request Sample@ https://www.globalinsightservices.com/request-sample/GIS24407/?utm_id=Pranalip
The growing adoption of superconductors in the healthcare sector is another driver of the market. Superconductors are used in various medical applications such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and cancer treatment. This is expected to fuel the demand for superconductors from the healthcare sector.
Research Objectives
Estimates and forecast the overall market size for the total market, across product, service type, type, end-user, and region
Detailed information and key takeaways on qualitative and quantitative trends, dynamics, business framework, competitive landscape, and company profiling
Identify factors influencing market growth and challenges, opportunities, drivers and restraints
Identify factors that could limit company participation in identified international markets to help properly calibrate market share expectations and growth rates
Trace and evaluate key development strategies like acquisitions, product launches, mergers, collaborations, business expansions, agreements, partnerships, and R&D activities
Thoroughly analyze smaller market segments strategically, focusing on their potential, individual patterns of growth, and impact on the overall market
To thoroughly outline the competitive landscape within the market, including an assessment of business and corporate strategies, aimed at monitoring and dissecting competitive advancements.
Identify the primary market participants, based on their business objectives, regional footprint, product offerings, and strategic initiatives
Request Customization@ https://www.globalinsightservices.com/request-customization/GIS24407/?utm_id=Pranalip
Market Segments
The superconductors market report is bifurcated on the basis of type, product, application, and region. On the basis of type, it is segmented into low temperature superconductors and high temperature superconductors. Based on product, it is analyzed across magnets, cables, transformers, and others. By application, it is categorized into energy, electronics, medical, and others. Region-wise, it is studied across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and rest of the World.
Key Player
The superconductors market report includes players such as ABB Ltd., Advanced Magnet Lab Inc., Alstom, American Magnetics Inc., ASG Superconductors Spa, Babcock Noell GmbH, Cryoelectra GmbH, Cryomagnetics Inc., Cryoton Ltd., and D-Wave Systems Inc.
Buy your copy here@ https://www.globalinsightservices.com/checkout/single_user/GIS24407/?utm_id=Pranalip
Research Scope
Scope – Highlights, Trends, Insights. Attractiveness, Forecast
Market Sizing – Product Type, End User, Offering Type, Technology, Region, Country, Others
Market Dynamics – Market Segmentation, Demand and Supply, Bargaining Power of Buyers and Sellers, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Threat Analysis, Impact Analysis, Porters 5 Forces, Ansoff Analysis, Supply Chain
Business Framework – Case Studies, Regulatory Landscape, Pricing, Policies and Regulations, New Product Launches. M&As, Recent Developments
Competitive Landscape – Market Share Analysis, Market Leaders, Emerging Players, Vendor Benchmarking, Developmental Strategy Benchmarking, PESTLE Analysis, Value Chain Analysis
Company Profiles – Overview, Business Segments, Business Performance, Product Offering, Key Developmental Strategies, SWOT Analysis.
With Global Insight Services, you receive:
10-year forecast to help you make strategic decisions
In-depth segmentation which can be customized as per your requirements
Free consultation with lead analyst of the report
Infographic excel data pack, easy to analyze big data
Robust and transparent research methodology
Unmatched data quality and after sales service
Contact Us:
Global Insight Services LLC 16192, Coastal Highway, Lewes DE 19958 E-mail: [email protected] Phone: +1-833-761-1700 Website: https://www.globalinsightservices.com/
About Global Insight Services:
Global Insight Services (GIS) is a leading multi-industry market research firm headquartered in Delaware, US. We are committed to providing our clients with highest quality data, analysis, and tools to meet all their market research needs. With GIS, you can be assured of the quality of the deliverables, robust & transparent research methodology, and superior service.
0 notes
Text
Picture Archiving & Communications Systems (PACS) Market to Witness Significant Incremental Opportunity Through 2033
Market Definition
Picture Archiving & Communications Systems (PACS) is a medical imaging technology that stores, retrieves, distributes, and displays digital medical images. It is used in the healthcare industry to store, manage, and share medical images such as X-rays, CT scans, and ultrasounds. The PACS system is designed to provide a secure, centralized repository for medical images, which can be accessed from any authorized workstation.
Download Free Sample of Report – https://www.globalinsightservices.com/request-sample/GIS25016/
Market Outlook
PACS consists of three basic components: a storage server, a workstation, and a network. The storage server is a computer system that stores the digital images and provides access to authorized users. The workstation is a computer system used to view, manipulate, and store the images. The network is the communication link that connects the storage server and workstations.
PACS is used to improve workflow in healthcare settings by allowing physicians to access images quickly and conveniently. It also reduces the amount of time and resources required for physical storage, retrieval, and distribution of medical images. Additionally, PACS can provide secure access to images from any location, allowing for remote consultations and collaboration.
PACS is also used to improve medical image quality and accuracy. By providing a centralized repository for images, PACS ensures that all images are consistent and up-to-date. Additionally, PACS can be used to automate tasks such as image formatting and manipulation, allowing for faster image processing.
Overall, Picture Archiving and Communications Systems (PACS) is an important technology in the healthcare industry. It provides a secure, centralized repository for medical images, which can be accessed from any authorized workstation. It also improves workflow by allowing physicians to access images quickly and conveniently. Additionally, PACS can improve medical image quality and accuracy by providing a centralized repository for images and automating tasks such as image formatting and manipulation.
Research Objectives
Estimates and forecast the overall market size for the total market, across product, service type, type, end-user, and region
Detailed information and key takeaways on qualitative and quantitative trends, dynamics, business framework, competitive landscape, and company profiling
Identify factors influencing market growth and challenges, opportunities, drivers and restraints
Identify factors that could limit company participation in identified international markets to help properly calibrate market share expectations and growth rates
Trace and evaluate key development strategies like acquisitions, product launches, mergers, collaborations, business expansions, agreements, partnerships, and R&D activities
Thoroughly analyze smaller market segments strategically, focusing on their potential, individual patterns of growth, and impact on the overall market
To thoroughly outline the competitive landscape within the market, including an assessment of business and corporate strategies, aimed at monitoring and dissecting competitive advancements.
Identify the primary market participants, based on their business objectives, regional footprint, product offerings, and strategic initiatives
Report Overview- https://www.globalinsightservices.com/reports/picture-archiving-communications-systems-pacs-market
Picture Archiving & Communications Systems (PACS) technology is a digital imaging system that stores, manages, and distributes medical images. This technology is used in the medical field to enable the storage, retrieval, and sharing of medical images such as x-rays, CT scans, ultrasounds, and MRIs. As PACS technology continues to evolve, there are several key trends that have emerged in recent years.
The first key trend in PACS technology is the move towards cloud-based solutions. Cloud-based PACS solutions offer a number of advantages, including cost savings, scalability, and the ability to access images from anywhere. With cloud-based solutions, images can be securely stored in the cloud and accessed from any device with an internet connection. This allows for greater collaboration between healthcare providers, as well as improved patient care.
The second key trend in PACS technology is the development of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms. AI algorithms can be used to analyze medical images and provide diagnoses with greater accuracy and speed. AI-based PACS systems can detect anomalies in medical images and alert the healthcare provider, which can help to improve patient outcomes.
The third key trend in PACS technology is the use of mobile applications. Mobile applications allow healthcare providers to access patient images from any device, such as a smartphone or tablet, which can be used to make diagnoses or provide patient education. Furthermore, mobile applications can be used to securely transfer images between healthcare providers, eliminating the need for physical media.
Get a customized scope to match your need, ask an expert – https://www.globalinsightservices.com/request-customization/GIS25016
The fourth key trend in PACS technology is the move towards integrated solutions. Integrated PACS solutions allow for the integration of medical images with other data sources, such as electronic health records (EHRs). This allows healthcare providers to access a patient’s medical history and images in one place, providing a more comprehensive view of the patient’s health.
The fifth key trend in PACS technology is the use of voice recognition software. Voice recognition software can be used to transcribe medical images into text, which can then be used to make diagnoses or to provide patient education. This technology is becoming increasingly popular as it eliminates the need for manual transcription, saving time and improving accuracy.
In conclusion, Picture Archiving & Communications Systems (PACS) technology is evolving rapidly, and there are several key trends that have emerged in recent years. These trends include the move towards cloud-based solutions, the development of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, the use of mobile applications, the move towards integrated solutions, and the use of voice recognition software. These trends are enabling healthcare providers to access and share medical images more quickly and accurately, leading to improved patient outcomes.
Picture Archiving & Communications Systems (PACS) is a technology that enables healthcare professionals to access, store, and manage medical images such as X-rays, CT scans, Ultrasounds, and MRIs. The technology is used to improve the efficiency and accuracy of diagnoses, and to reduce the costs associated with medical imaging. The PACS market is expected to reach US$4.5 billion by 2024, driven by the increasing demand for cost-effective and efficient healthcare solutions, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and the growing need for better patient care.
The key drivers of the PACS market are the increasing demand for cost-effective and efficient healthcare solutions, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and the growing need for better patient care.
First, the increasing demand for cost-effective and efficient healthcare solutions is propelling the growth of the PACS market. The use of PACS technology helps to reduce the costs associated with medical imaging, such as the cost of film and chemicals for processing. Moreover, it helps to improve the efficiency of diagnosis, as images can be quickly accessed and shared. This helps to reduce the time taken for diagnosis, thus saving time and money.
Second, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases is also driving the growth of the PACS market. Chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases require frequent medical imaging for diagnosis and treatment. The use of PACS technology helps to improve the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosis, as images can be quickly accessed and shared. This helps to reduce the time taken for diagnosis, thus improving the quality of patient care.
Third, the growing need for better patient care is another key driver of the PACS market. The use of PACS technology helps to improve the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosis, as images can be quickly accessed and shared. This helps to reduce the time taken for diagnosis, thus improving the quality of patient care. Moreover, PACS technology helps to reduce the risks associated with medical imaging, as it eliminates the need for physical films. This helps to reduce the chances of errors, thus improving patient safety.
Overall, the key drivers of the PACS market are the increasing demand for cost-effective and efficient healthcare solutions, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and the growing need for better patient care. These drivers are expected to continue to drive the growth of the PACS market in the coming years.
Market Segmentation:
Picture Archiving & Communications Systems Market is segmented into business mode, components, end-users and region. Based on business mode the market is categorized into Enterprise and Departmental. On the basis of components, it is further segmented into Imaging Modalities, Secured Network and Workstations and Archives. Based on end-users it is segmented into Hospitals, Clinic Imaging, Dental Practices, Diagnostic Centers and Others. Whereas based on region it is divided into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Rest of the World.
Buy Now – https://www.globalinsightservices.com/inquiry-before-buying/GIS25016
Research Scope
Scope – Highlights, Trends, Insights. Attractiveness, Forecast
Market Sizing – Product Type, End User, Offering Type, Technology, Region, Country, Others
Market Dynamics – Market Segmentation, Demand and Supply, Bargaining Power of Buyers and Sellers, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Threat Analysis, Impact Analysis, Porters 5 Forces, Ansoff Analysis, Supply Chain
Business Framework – Case Studies, Regulatory Landscape, Pricing, Policies and Regulations, New Product Launches. M&As, Recent Developments
Competitive Landscape – Market Share Analysis, Market Leaders, Emerging Players, Vendor Benchmarking, Developmental Strategy Benchmarking, PESTLE Analysis, Value Chain Analysis
Company Profiles – Overview, Business Segments, Business Performance, Product Offering, Key Developmental Strategies, SWOT Analysis
Key Players:
The Picture Archiving & Communications Systems Market Report includes players such as Agfa-Gevaert Group (Belgium), Fujifilm Holdings Corporation (Japan), Carestream Health, Inc. (U.S), Siemens Healthineers AG (Germany), GE Healthcare (U.S), Koninklijke Philips N.V. (Netherlands), Sectra AB (Sweden), INFINITT Healthcare Co., Ltd. (South Korea), Novarad Corporation (U.S) and Hyland Software, Inc. (U.S), among others.
With Global Insight Services, you receive:
10-year forecast to help you make strategic decisions
In-depth segmentation which can be customized as per your requirements
Free consultation with lead analyst of the report
Excel data pack included with all report purchases
Robust and transparent research methodology
About Global Insight Services:
Global Insight Services (GIS) is a leading multi-industry market research firm headquartered in Delaware, US. We are committed to providing our clients with highest quality data, analysis, and tools to meet all their market research needs. With GIS, you can be assured of the quality of the deliverables, robust & transparent research methodology, and superior service.
0 notes
Text
How MRI Technology Improves Dental Implant Performance

Introduction:
Nowadays in the dynamic dental world where new innovations that take form, treatment protocols are always enhanced affecting better clinical results and patients satisfaction. The MRI imaging technique does not use any ionizing radiation and can be used without fear of interfering with the implant. In this thorough guide, we take a look at the awesome power of MRI technology in the field of improving Dental Implant in Mohali performance in the old and modern times.
Come along with us for a tour through MRI technology in dental implant, unravelling its benefits, applications, and influence, unveiling how clinics are like Deep Dental Clinic and OPG Centre are putting this beloved advance to good clinical practice and providing the best care available.
The Evolution of Dental Implant in Mohali:
Mohali, being renowned for progressive healthcare infrastructure and commitment to innovation, has seen quite some changes in the way we approach today to dental implant services being one of the most remarkable advancements. As the leading dental care provider in India, there are several dental clinics and centers in Mohali run by experts providing the latest technology in dental implants to patients who are looking for a replacement of their smiles or restoring their oral functions.
Dental implants, usually referred to the elite among tooth replacement options, have gained a remarkable popularity among individuals trying to help their eating process by putting the missing tooth back. Whether they are trying to regain self-esteem in the form of their teeth or for better chewing, Dental Implant in Mohali are becoming a widely accepted solution as they are long lasting and reliable options for tooth replacement.
The Role of MRI Technology in Dental Implant Procedures:
An MRI technology, which has been developed as an indispensable instrument in dentistry for various applications is the game changer in the field of dental implant, as it renders quantitative and accurate information and boosts the precision of the implant procedure. Here’s how MRI technology improves dental implant performance
Comprehensive Preoperative Assessment:

An MRI scan is capable of providing very precise images of the jawbone area, the surrounding tissues, and anatomic structures which will be useful in a complete preoperative assessment. In Mohali, clinics employ MRI technology that depicts the bone density, the condition of the soft tissues surrounding the bone and identifies any impending obstacles or structural abnormality that may occasion removal of the bone or displace the implantation.
Precise Treatment Planning:
The use of MRI scans by Dental Implant in Mohali on the other hand helps in developing of individualized treatment programs, which are based on the characteristics of each patient and include the specific dental health problems. This exact-fit precise implant placement, and perfect implant positioning yield higher rates of patient success and a better overall outcome after dental implant procedures.
Real-Time Guidance during Surgery:
MRI-guided hones provide the dentist professionals in Mohali the ability to conduct implants operations with unrivalled precision and accuracy. Due to the anatomical transparency created by overlaying MRI images onto real-time surgical views, dentists can precisely identify the relationship between the implants and all surrounding structures and thus they can be confident about optimal placement that is stable.
Postoperative Evaluation and Monitoring:
MR imaging can be done after the dental implant surgery to evaluate and assess the integration of the implants with the bone surrounding the implantation sites. Frequent MRI scans offer a versatile tool in the hands of the dentists of Mohali to check the progress of healing, identify any problem signs or complications at the initial stage. They can then take appropriate measures quickly to achieve desirable long-term results.
Applications of MRI Technology in Dental Implant in Mohali:
In Mohali, a number of dental clinics and centers utilize various MRI techniques throughout the dental implant process in preoperative planning, as well as in postoperative evaluation.
Preoperative Assessment: X-ray formation of MRIs is used to conduct bone quality, quantity, and shape assessment and are also used to examine the health of the surrounding soft tissues.
Treatment Planning: Coordinated with MRI certain measurement of implant size, shape, and position find the right destination that maximize chances for the successful treatment of a patient who undergoes dental implants.
Surgical Navigation: There are MRI-navigated operated systems that aim to aid dentist through their operation during implant surgery, allowing for more exact implant placing and reducing complications possibility.
Postoperative Monitoring: Using of MRI allows dentists to track the progress of healing, examine eventual stability of implant and detect any problems or complications that might occur after the surgery.
Deep Dental Clinic and OPG Center is well-established in Mohali and has received the accolade of delivering excelled practice. The facility is known for its team of highly-skilled professionals who dedicate themselves to caring for patients, employing advanced treatment methods and technologies. Using advanced MRI scanning machines and guided by a group of experienced medical doctors, Deep Dental Clinic is recognized among the leading facilities that perform the MRI-guided dental implant in Mohali.
FAQs:
Dental implants are safe if they are aided by MRI. Is the technology robust and secure?
Yes, MRI technology is considered safe for patients who have dental implants as they do not get hurt by the magnetic fields. The latter is a harmless method, and radiation is not involved, like in X-ray and some other methods. Thus, it constitutes minimal risk to patients. Besides, there are some individuals with specific medical conditions or with metallic implants who should collaborate with their healthcare providers before imaging with an MRI Scanner.
What is MRI technology advantage in terms of improving exactness of brain implant processes?
MRI technology simply scans the jaw bone and the surrounding tissues and structures featuring incredible details. This radiological technique enables dental practitioners to assess the density of bone, evaluate the health status of soft tissues, and identify any impediments or abnormalities which may negatively affect the placement of the implants. The exactness of that knowledge, hence, plays a critical role in treatment planning, thereby ensuring the same is optimally done for the success of the implants in the long run.
Will this MRI technology be capable of catching any problems or complexities with the dental implant following the surgery?
Absolutely, MRI procedure can be applied to tracking the successful results of dental implants and the moreover it is possible to discover any complications and issues over the beginning of the recovery. Computed tomography (MRI) of the implant helps dentists to predict the stability of the implant, diagnose the problems related with its adjacent bone integration, infection and inflammation and also to stop the occurrence of any implant failure early interventions to obtain the best results.
Are MRI-guided dental implant procedures more expensive than off-line implemented dental implant procedures?
The MRI-guided reconstruction cost may change from clinic to clinic, country to country and various personal patient needs. Although MRI-guided implantation may involve higher costs than the general implant technique, many patients can readily argue that the benefits of improved accuracy, better fitting and long-term consequences are worth the extra cost of protecting their oral health and good condition.
Conclusion:
Howbeit, MRI technology has grown to become the life-opening tool that changes the game of performance and success of dental implant procedures in the region of the city around Mohali. MRI technology empowers dentist professionals with verified anatomic information, effective treatment planning, and in- surgery-navigation that liberates them from other surgical procedures hindrances, providing patients optimal outcomes of dental implant treatments.
To put it simply, Mohali is on a roadmap with a pathway of Deep Dental Clinic and OPG Centre as leaders who pave the way and innovate in MRI-guided dental implant. It means that there is no reason for patients in Mohali to worry that they are not receiving the highest quality care and creativity in getting dental implants.
As MRI technology goes on evolving and becomes more and more accessible, the future of dental implant in Mohali will be rosier than ever, without a doubt, with ultra-precision, accuracy, and patient satisfaction to lead the way in the development area of oral health care.
0 notes