#Mobiles Launches in December 2021
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Leaked documents show Pavel Durov secretly visited Russia dozens of times after moving away
Pavel Durov, the Russian tech mogul arrested in Paris on Saturday, has traveled to Russia more than 50 times since moving away from the country a decade ago, iStories reported on Tuesday, citing leaked border crossing data from Russia’s Federal Security Service (FSB).
In 2014, Durov sold his stake in the social media service he founded, VKontakte, and moved out of Russia, writing: “There’s no going back. Especially after I publicly refused to cooperate with the authorities.” He also published a manifesto titled “Seven Reasons Not to Return to Russia” in which he criticized the country’s system of government.
The next year, however, Durov traveled to St. Petersburg — and he made at least 41 more trips to Russia over the two years that followed. These visits continued after Moscow passed the “Yarovaya law,” which requires companies to let the FSB access user messaging data, and even after the Kremlin launched a propaganda campaign against Durov’s app Telegram following its refusal to comply with the law. His last visit for several years came in December 2017, after the messenger had been fined the equivalent of about $14,000 for ignoring an FSB request. The Russian authorities banned Telegram in April 2018 but were unable to block users from accessing it.
Durov next returned to Russia in the summer of 2020, soon after a U.S. court blocked Telegram from launching a cryptocurrency called Gram. On June 4, Durov wrote on his channel that he would welcome a removal of the Kremlin’s block on the app and that its administrators had begun removing “extremist propaganda” (Moscow’s stated reason for banning the service) more actively. He vowed to support the Russian authorities if they wanted to fight terrorism without violating citizens’ right to secrecy of correspondence.
On June 18, 2020, Russia’s federal censorship agency announced that it was “unblocking” Telegram in light of Durov’s “stated willingness to counteract terrorism and extremism.” That evening, the billionaire flew out of Russia from St. Petersburg. Over the next year and a half, he visited Russia multiple times, with his last visit in October 2021. During this period, iStories notes, Telegram blocked Alexey Navalny’s Smart Voting bot (designed to help Russians mobilize against ruling party candidates), and other opposition tools ahead of the September 2021 State Duma elections.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The History of Three Houses Saturation: An Impromptu Heroes Retrospective
I've been poking through the Heroes archives some more. There's been a predictable amount of wank over Engage's sales numbers, and its supposed poor performance is sometimes propped up by the fact that so far FE17 has only gotten a single Heroes banner. Ignoring of course that IS must plan out these banners months in advance, I wanted to take a look back and see just what the mobile game was putting out around the time that Three Houses launched.
In 2019, FEH released the following for Three Houses:
July: New Heroes banner, with both Byleths and the house leaders as well as Mythic Sothis
August: New Heroes banner, with Hubert, Petra, Mercedes, and Hilda, also Kronya as the GHB unit linked to the July banner and the Death Knight as the GHB unit linked to this month's
December: Seasonal winter banner including Sothis
And...that's it, actually. FE16 wouldn't get any more new units until March 2020. The units added in 2019 make a lot of sense considering that Three Houses is much more frontloaded in terms of its playable roster; counting all routes, the player has access to 25 of its 40 characters by Chapter 1, and Sothis, Kronya, and the DK are all revealed fairly early (Kronya less so, but the two large reasons that she was the game's first GHB unit go without saying). The two banners combined account for whales who chose any of the three houses, with the leader and a wide-appeal(?) waifu option available for each of them.
It's tough to compare because FEH was less structured the first year of its launch, but this is in fact more restrained than how hard IS pushed Echoes in 2017 which got four banners within the first two months of its release. Looking at that, it's little wonder that Valentia doesn't have enough for even one more new heroes banner at this point.
Now, as for 2020:
March: New Heroes banner, with Ferdinand, Bernadetta, Annette, and Lysithea, also the Flame Emperor as the GHB unit
April: Legendary Edelgard
July: Seasonal summer banner, with Duo f!Byleth/Rhea, Dorothea, Sylvain, Ingrid, and Lorenz as the TT unit
August: Brave banner with CYL 4 winners which was swept by Three Houses: the house leaders plus Lysithea
October: New Heroes banner, with Seteth, Flayn, Catherine, and Shamir, also Nemesis as the GHB unit as well as Legendary Dimitri
December: Seasonal winter banner including Bernadetta and Hilda with Felix as the TT unit
That's twenty-four new units from a single game in a year. It's easy to understand why Three Houses fatigue would be setting in, especially when combined with the pandemic and this being more or less when the discourse got infamously bad. But the oversaturation got even worse in 2021:
January: Seasonal desert banner including Harmonic Dorothea/Lene and Raphael, also Mythic Seiros
February: Legendary Claude
March: New Heroes banner, with Linhardt, Dedue, Ingrid, and Marianne, also Solon as the GHB unit
May: New Heroes Fallen banner including Edelgard and Dimitri
June: Seasonal summer banner, with Duo Hilda/Marianne, Caspar, Ashe, Mercedes, and Leonie as the TT unit, also Legendary m!Byleth
August: Brave banner with CYL 5 winners including Marianne and the Gatekeeper
September: New Heroes banner, with Yuri, Constance, and Hapi sharing a banner with a Heroes OC, also Balthus added to the standard summon pool and Aelfric as the GHB unit
October: Seasonal Halloween banner including Duo Sothis/m!Byleth and Rhea
November: Seasonal ninja banner including Shamir as the TT unit
December: Seasonal winter banner including Harmonic Lysithea/Lute, Manuela, and Ignatz as the TT unit, also Legendary f!Byleth
That's thirty-one units, with only two months out of the year not getting any new Three Houses content. One of those was also the notoriously meta-centralizing Fallen Edelgard, plus I think this was the first year to have a bunch of Reddit drama related to her alts with A Hero Rises? That's not really what I'm looking at here.
I've looked into this this far - might as well finish it up with how 2022 fared. This was the year that Hopes released, so there was some new-ish Fódlan content to pull from at last. I'll go ahead and throw what we've gotten so far of 2023 in here too:
May: New Heroes Fallen banner including Rhea
June: Seasonal summer banner including Harmonic Edelgard/Altina, Dimitri, and Claude
August: New heroes banner with CYL 6 winners including f!Byleth, also Jeralt as the GHB unit
September: New heroes banner with Ascended Hilda (uses her Hopes design), m!Shez, and Monica, also f!Shez added to the standard summon pool and Holst as the GHB unit
October: Mythic Arval
December: Seasonal winter banner including Dorothea and Annette using their Hopes designs, also Legendary f!Shez
January 2023: Seasonal desert banner including m!Byleth
March 2023: Seasonal spring banner including Bernadetta and Ashe, also Legendary Yuri
April 2023: New Heroes banner with Rearmed Ingrid (uses her Hopes design), Felix, Sylvain, and Rhea, also Cornelia as the GHB unit
May 2023: New Heroes Fallen banner including f!Byleth (based on Hopes)
A mere fifteen units in 2022, and ten so far in 2023. This gives Houses/Hopes 93 units so far - more than any other individual game aside from Awakening (which is only slightly higher at 97) and Fates (a hefty 129). Both those games have larger playable rosters and were pushed hard in FEH's early years to the point that people also complained about it, so FE16's oversaturation is impossible to ignore.
I very much doubt that it will get another New Heroes banner this year...not because there still aren't candidates but because there's exactly one Agarthan with a unique portrait (Thales) they haven't used as a GHB unit at this point. Seasonals are always a tossup, although I'm wondering if Fódlan can carry a summer banner for the fourth(!) year in a row when the only remaining high-value waifu IS has left to stick in a swimsuit is...um...Petra, I guess? Unless they go with church units - and Rhea's already been put in a bikini - or the Wolves, all the rest are the type to go for more innocence fanservice appeal, like Bernadetta and Lysithea. We can safely say at least that IS has been treating Hopes like an expansion pack after its single banner, using it out only for some seasonals, a limited selection of Legendaries (m!Shez incoming at some point, probably), Mythics (...this one's pretty much just Arval), and Fallen units (I fully expect Fallen m!Shez next year) and for easy Ascended/Rearmed designs, in the same way that the post-timeskip Houses designs seem to be reserved for Legendary and Brave units.
How much does any of this reflect on Engage? Probably not much, really. It's nowhere near as frontloaded in terms of units so IS can't dive too far into the roster for characters like the Brodians and Elusians without getting into spoiler writing territory, whereas both FE15 and FE16 had multiple starting groups to pull from for early banners. As I mentioned re: Valentia, they may have also learned that adding a bunch of new units in quick succession is an easy way to struggle to fill out new banners in the future and draw the ire of some of the fanbase at the same time. I do expect another Engage banner in 2023, although it'll probably be in the second half of the year. Maybe they'll be used more in seasonals? The Awakening-and-Fates-esque vibe of FE17 better lends itself to goofiness like the summer and Halloween banners, and if they do thieves again in August that'd be a sure way to slip in fan favorite Yunaka before she's scheduled for a regular banner.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Is social media useful in spreading information on Covid-19 in Malaysia?

Covid-19 is claimed to have originated in Wuhan, China, in late December 2019 and ultimately expanded to 200 nations globally (Salman, 2021). Social media, with over billion users, is vital for Malaysia’s government to spread Covid-19 awareness timely and educate the public on precautionary conduct. Social media enables people to generate and share information while socializing, enabling the flow of opinions, notions, and insights in online communities (Hussin et al., 2021). Governmental initiatives to enhance public health via social media have sprouted in the last several years (Dawi et al., 2021).
Navigating the Pandemic Wave: How Social Media Amplified COVID-19 Response in Malaysia
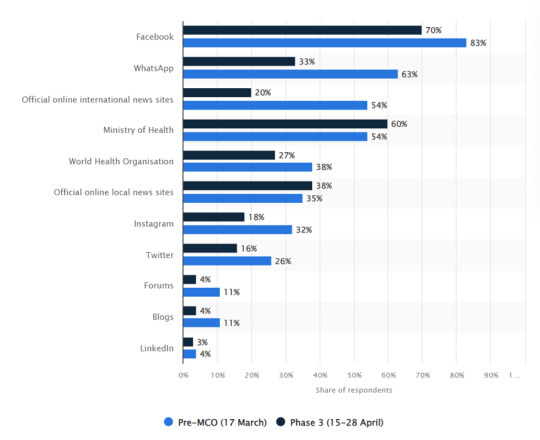
Malaysian citizens have access to Covid-19 updates through social media, including the official Facebook page, YouTube channel, and Twitter account of the Ministry of Health Malaysia, known as “Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM)”. Besides, the Director-General of Health live-streams Covid-19 information on Facebook (Hussin et al., 2021). Notably, the Malaysian Ministry of Health and National Security Council reported Covid-19 cases on Facebook, WhatsApp, Telegram, and Twitter when Covid-19 initially affected Malaysia. This move was made because social media can approach individuals quickly with crucial information and updates.


Twitter represents one of the social media channels that the Malaysian government has selected in providing updates on the Covid-19 situation to alert people about maintaining good hygiene practices to prevent the spread of the virus and to share dos and don'ts during the outbreak (Hussin et al., 2021). It was overwhelming when users gave input, participated in online conversations, commented on status or live video broadcasting, tweeted the news, and shared within communities. Public questions, complaints, and misunderstandings can be published on government official pages for speedy replies. Social media content can change people's behavior and reduce the efficacy of government remedies. The Malaysian Ministry of Health (MOH) tweeted Covid-19 information, covering daily cases, deaths, new patients, discharges, hospitalization, and verified cases to caution the citizens (Hussin et al., 2021). Roughly 20 posts on SOP reminded Twitter users of SOPs such as business operations, purchasing processes, or social events daily. Additionally, MOH published 164 Covid-19 instructions and precautions. For instance, postings mentioned the red zone, where numerous cases were found, and special precautions. Notably, hashtags are frequently included to prioritize Covid-19 information from reliable organizations to make it easy for individuals for browsing later.

Empowering Malaysia’s COVID-19 Response: MySejahtera
In April 2020, the government launched the MySejahtera mobile application to assist individuals in tracking their health status and registering their locations, allowing authorities to collect timely information in fighting Covid-19 which had a positive impact on people's inclination to be involved in protective behaviours (Dawi et al., 2021). Public health guidelines were more probable to be followed when citizens realized the scenario and government response. The COVID-19 epidemic is updated daily by MySejahtera. For instance, this includes the cumulative confirmed cases and the daily new cases.

Dangers of Social Media Reliance during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Dissemination of False Information
Social media during the Covid-19 epidemic has enabled a rapid dissemination of unverified content, potentially deceiving and perplexing a considerable segment of the public. This encompasses misinformation about drinking warm salts or lemon water and taking hydroxychloroquine for curation (Balakrishnan, 2022). In Malaysia, a notable occurrence was the rise in the dissemination of false information pertaining to the lockdown measures and Covid-19-related information. This surge prompted Malaysian government to establish the Rapid Response Troop as a means to combat the proliferation of fake news, namely sebanarnya.my. Several instances of false information being spread in the country can be observed, such as the circulation of a compilation of locations within the Klang Valley that purportedly have a significant concentration of Covid-19 cases (Balakrishnan, 2022). Relying extensively on social media might increase dread, dissatisfaction, anxiety, and paranoia. Disinformation was spread in Malaysia by locals using fake or anonymous accounts (Salman, 2021). Many people detect deceptive information poorly, particularly on social media. Following the MCO's adoption, people panic-purchase and buy vast amounts of items and non-essentials at supermarkets (Ngadiron et al., 2021).
Disseminating false information is akin to spreading the Covid-19 virus. The battle against fake information persists, and the community requires daily education via diverse platforms. Social media platforms have a significant impact on fostering societal awareness and enhancing interpersonal connections within Malaysian communities. However, individuals should be cautious, as the proliferation of fabricated information on these platforms is intended to captivate netizens and generate sensationalized or trending discussions.

In my opinion, social media is useful in spreading essential COVID-19 information in Malaysia. It enables the government to swiftly provide updates, guidance, and safeguards to Malaysians. The MySejahtera mobile app, Facebook, and Twitter have allowed direct interaction with individuals, encouraging safety and behavioural alterations. Nevertheless, fighting disinformation is vital. Overall, social media is useful, but it demands careful scrutiny to guarantee information authentication.
List of References
Balakrishnan, V. (2022). COVID-19 and fake news dissemination among Malaysians – motives and its sociodemographic correlates. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 73, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2022.102900
Dawi, N. M., Namazi, H., Hwang, H. J., Ismail, S., Maresova, P., & Krejcar, O. (2021). Attitude toward protective behavior engagement during COVID-19 pandemic in Malaysia: The role of e-government and social media. Frontiers in Public Health, 9, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.609716
Hussin, R., Rahman, S. H. A., & Azudin, N. (2021). Social media approach to crisis communication during COVID-19 pandemic: An analysis from Malaysian perspective. Ulum Islamiyyah, 33(S5), 77–88. https://doi.org/10.33102/uij.vol33nos5.404
Ngadiron, S., Aziz, A. A., & Mohamed, S. S. (2021). The spread of COVID-19 fake news on social media and its impact among Malaysians. International Journal of Law, Government and Communication, 6(22), 253–260. https://doi.org/10.35631/ijlgc.6220024
Salman, A. (2021). Knowledge, curiosity, communication channels and panic during COVID-19 movement control order. International Journal of Media and Communication Research (IJMCR), 2(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.25299/ijmcr.v2i1.6205
Statista. (2022). Distribution of main news sources during MCO COVID-19 Malaysia 2020. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1118979/malaysia-main-news-sources-during-covid-19/
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Public Health Campaigns & Communities
What is public health?
Public health, as a multidisciplinary field, is dedicated to enhancing the health and overall well-being of communities (Lee, 2023). It strives to create safe environments for people to live, learn, work, and enjoy their lives. Many people mistakenly believe that public health is the same as healthcare. However, it is important to distinguish between the two, as public health focuses on entire populations with the objective of preventing illnesses and injuries, while the healthcare industry concentrates on treating individual patients who are already sick (APHA, 2023).
For example, public health is responsible for the following:

"Public health is the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private communities, and individuals." — Winslow, 1920
The 10 Essential Public Health Services
The 10 Essential Public Health Services (EPHS), first created in 1994 by a federal working group, serves as the description of the activities that public health systems should undertake in all communities. EPHS is organised around the three core functions of public health: assessment, policy development and assurance. Health departments and community partners collaborators across the nation structure their work around the EPHS model, while educational institutions and public health programs also incorporate it into their teachings (CDC, 2023).

In 2020, a revised version of the 10 EPHS was unveiled during a virtual launch event. The revised EPHS centres around equity and promotes policies that enable optimal health for all and seek to remove systemic and structural barriers such as poverty, racism, gender discrimination and others, that have resulted in health inequities (CDC, 2023).
“The revised 10 EPHS not only centres equity but acknowledges the importance of community voice and the different roles public health plays.” — Jessica Fisher, Vice President of Strategic Initiatives at Public Health National Center for Innovations (PHNCI).
COVID-19 and Public Health
COVID-19, caused by an infection of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, was initially detected in December 2019 in Wuhan, a city in China's Hubei province. The COVID-19 pandemic has posed a substantial threat to nations across the world, and it is regarded as the biggest public health crisis the world has confronted in over a century (Miyah, 2022). In late 2020, the World Health Organisation (WHO) declared the COVID-19 outbreak as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern in which countries with vulnerable healthcare facilities may be at an excessive hazard (Tabari, 2020).
In response to this crisis, many countries have enacted travel restrictions, including flight suspensions and measures to limit incoming travellers. Others have introduced social distancing and quarantine policies as well as encouraging the reduction of social interactions, postponing events, locking down schools, and isolating suspected cases. Furthermore, some regions have utilized telemedicine for remote consultations and monitoring during the outbreak (Tabari, 2020).

MySejahtera is a mobile app developed by the Malaysian government to support various aspects of public health throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. This app enables citizens to conduct self-health assessments, track their health status, and communicate information with the Ministry of Health (MOH), so that necessary actions could be implemented.
Here are its primary functions:
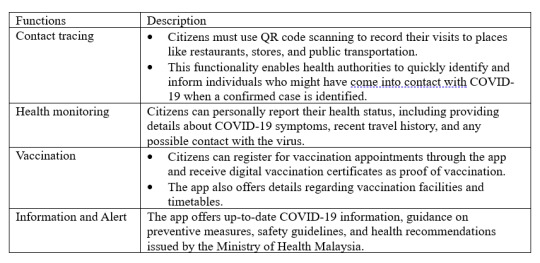
Explore https://www.maaedicare.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/MySejahtera_compressed.pdf for detailed function and process of using MySejahtera.
Mental Health Problem Attribute to Social Media
Last but not least, mental health is a crucial aspect of public health, and the well-being of individuals, particularly those in the 16-24 age group, is a matter of significant concern. A survey conducted in Malaysia in May 2022 revealed that a considerable portion of young respondents in this age range reported experiencing heightened levels of stress and anxiety over the past year (Statista Research Department, 2023). Furthermore, this research suggests that social media plays a substantial role in contributing to this mental health problem.
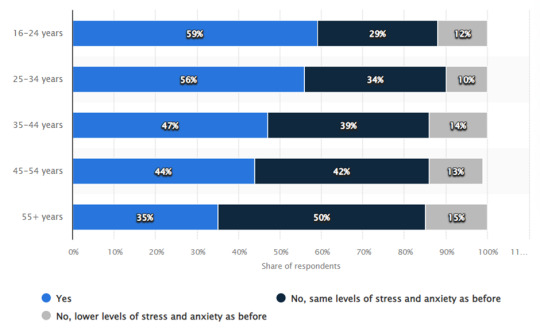
Source: Statista Research Department, 2023
Multiple studies have demonstrated a strong connection between heavy use of social media and the risk for mental health issues (Robinson, 2023). Social media platforms can be hotspots for the dissemination of hurtful rumours, lies and online harassment. About 10 percent of teens report being bullied on social media and many other users are subjected to offensive comments (Robinson, 2023). Additionally, fear of missing out (FOMO) can compel someone to pick up their phone every few minutes to check for updates, or compulsively respond to every alert. When individuals prioritize online interactions over in-person relationships, they become more vulnerable to mood disorders, such as anxiety and depression.

These findings highlight the importance of recognizing the influence of social media on mental health, especially among young adults. In summary, striking a balance between the advantages of digital connectivity and the preservation of mental well-being is crucial to ensure that social media serves as a positive and constructive tool in the lives of young individuals.
References:
American Public Health Association. (n.d.). What is public health. https://www.apha.org/what-is-public-health
CDC. (2021). Public health system and the 10 essential public health services. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/publichealthgateway/publichealthservices/essentialhealthservices.html
C.-E. A. Winslow, The Untilled Fields of Public Health.Science51,23-33(1920).DOI:10.1126/science.51.1306.23
Lee, D., Chen, K., & Kruger, J. S. (2023, January 1). Chapter 93 - Public health (A. E. M. Eltorai, J. A. Bakal, P. C. Newell, & A. J. Osband, Eds.). ScienceDirect; Academic Press. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780323903004000616
Malaysia: stress levels by age group 2022. (2023, August 25). Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1322323/malaysia-share-of-people-feeling-more-stressed-or-anxious-by-gender/#:~:text=According%20to%20a%20survey%20on
Miyah, Y., Benjelloun, M., Lairini, S., & Lahrichi, A. (2022). COVID-19 Impact on Public Health, Environment, Human Psychology, Global Socioeconomy, and Education. TheScientificWorldJournal, 2022, 5578284. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5578284
Robinson, L., & Smith, M. (2020, September). Social Media and Mental Health - HelpGuide.org. Https://Www.helpguide.org. https://www.helpguide.org/articles/mental-health/social-media-and-mental-health.htm#:~:text=Since%20it
Tabari, P., Amini, M., Moghadami, M., & Moosavi, M. (2020). International Public Health Responses to COVID-19 Outbreak: A Rapid Review. Iranian journal of medical sciences, 45(3), 157–169. https://doi.org/10.30476/ijms.2020.85810.1537
World Health Organization (WHO). (2022, June 17). Mental Health. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-health-strengthening-our-response
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
[ad_1] Launch of the Portl UltraGym, an advanced portable strength training system Expansion into Qatar, UAE, and Saudi Arabia: Driving International Growth. Partnerships with Taj, Accor, and many more luxury hotels establish Portl as a Leader in Hospitality Wellness Solutions Targeting 100% Growth : Ambitious Plans to Double User Base Within 12 Months Portl, a leading innovator in home fitness technology, has announced the launch of the Portl UltraGym, an all-in-one portable strength training system designed to make strength training more accessible at home. This marks a significant milestone in Portl’s growth journey as it expands its product offerings across India. As part of its broader strategy, Portl is also focusing on strengthening its presence in international markets, particularly the Middle East, while deepening partnerships with key hospitality brands. UltraGym The Portl UltraGym sets a new benchmark for home fitness with its innovative digital weights technology, offering professional-grade workouts in a compact design that requires just 2.4 square feet of space. Combining convenience and efficiency, it eliminates the need for bulky traditional equipment like dumbbells and squat racks, making it ideal for users at any fitness level. With a launch price of Rs.59,990/- , the UltraGym delivers world-class trainingwhile being both versatile and portable. It will be available starting 19th December, 2024 on Portl’s official website (https://portl.co) Since its inception in 2021, Portl has established itself as a disruptor in the fitness tech sector, serving users across India and international markets, collectively completing over 20,000 hours of workouts. With strong customer engagement, Portl aims to double its user base in the next 12 months, driven by innovation and strategic market expansion. Advanced Features of the Portl UltraGym The Portl UltraGym seamlessly integrates its proprietary Hydraulic and Electromagnetic Resistance (H.E.R.S) Technology with unparalleled ease of use. Designed to cater to diverse fitness needs, it offers revolutionary adjustable digital weights, starting from as little as 0.5 kg and scaling up to 70 kg, making it ideal for users across all fitness levels. With multiple training modes-including standard, eccentric, isokinetic, elastic, and rowing-it provides a versatile workout experience that adapts to individual goals. The UltraGym also pairs with its companion mobile app, which enhances the overall experience by enabling effortless control of the device. Users can explore guided workout plans, create personalized routines, and monitor their progress with detailed metrics, ensuring a highly customized fitness journey. “The launch of the UltraGym marks a pivotal moment in our journey to redefine fitness and wellness. By combining unparalleled versatility, compact design, and affordability, the UltraGym makes professional-grade strength training accessible to everyone, regardless of their fitness level or space constraints. This launch is also a testament to our commitment to innovation, as we continue to invest in cutting-edge hardware, AI, computer vision, and imaging technologies to deliver personalized, data-driven fitness experiences. As we expand our footprint across India and key international markets, we remain focused on empowering individuals worldwide to achieve their fitness goals with greater efficiency, convenience, and impact,” Indraneel Gupta, Founder and CEO of Portl. Strategic Partnerships and Market Expansion Portl is actively strengthening its footprint in India while gearing up for expansion into the Middle East, targeting markets such as Qatar, UAE, and Saudi Arabia over the next 12 to 18 months. The company has already forged collaborations with renowned hospitality brands, including the Taj Group of Hotels (IHCL), Accor Group, positioning itself as a reliable provider of on-demand wellness solutions for premium travelers.
To support its global growth ambitions, Portl has aligned with strategic partners who will help introduce its cutting-edge products and services to new audiences across different regions, making fitness and wellness more accessible worldwide. R&D and Technological Innovation Portl remains deeply committed to investing in research and development to stay ahead in the fitness technology space. By harnessing advancements in artificial intelligence, computer vision, and imaging, the company continues to innovate and aims to bring more products to market. These innovations include non-invasive health tracking, real-time feedback on exercise form, and hyper-personalized fitness programs. This dedication to technological progress will ensure that Portl delivers an engaging and effective experience for users at every stage of their fitness journey. About Portl Portl is a technology company specializing in fitness, health, and wellness based out of Hyderabad. Founded in 2021, Portl leverages cutting-edge AI and personalization technology to deliver accessible, highly-tailored fitness experiences directly into people’s homes. Portl’s mission is to empower individuals to achieve their wellness goals with products that adapt to their unique needs and preferences. With a steadfast commitment to innovation and quality, Portl aspires to become the leading Fitness & Wellness ecosystem of the world, For more information Visit to www.portl.co. !function(f,b,e,v,n,t,s) if(f.fbq)return;n=f.fbq=function()n.callMethod? n.callMethod.apply(n,arguments):n.queue.push(arguments); if(!f._fbq)f._fbq=n;n.push=n;n.loaded=!0;n.version='2.0'; n.queue=[];t=b.createElement(e);t.async=!0; t.src=v;s=b.getElementsByTagName(e)[0]; s.parentNode.insertBefore(t,s)(window,document,'script', 'https://connect.facebook.net/en_US/fbevents.js'); fbq('init', '311356416665414'); fbq('track', 'PageView'); [ad_2] Source link
0 notes
Text
[ad_1] Launch of the Portl UltraGym, an advanced portable strength training system Expansion into Qatar, UAE, and Saudi Arabia: Driving International Growth. Partnerships with Taj, Accor, and many more luxury hotels establish Portl as a Leader in Hospitality Wellness Solutions Targeting 100% Growth : Ambitious Plans to Double User Base Within 12 Months Portl, a leading innovator in home fitness technology, has announced the launch of the Portl UltraGym, an all-in-one portable strength training system designed to make strength training more accessible at home. This marks a significant milestone in Portl’s growth journey as it expands its product offerings across India. As part of its broader strategy, Portl is also focusing on strengthening its presence in international markets, particularly the Middle East, while deepening partnerships with key hospitality brands. UltraGym The Portl UltraGym sets a new benchmark for home fitness with its innovative digital weights technology, offering professional-grade workouts in a compact design that requires just 2.4 square feet of space. Combining convenience and efficiency, it eliminates the need for bulky traditional equipment like dumbbells and squat racks, making it ideal for users at any fitness level. With a launch price of Rs.59,990/- , the UltraGym delivers world-class trainingwhile being both versatile and portable. It will be available starting 19th December, 2024 on Portl’s official website (https://portl.co) Since its inception in 2021, Portl has established itself as a disruptor in the fitness tech sector, serving users across India and international markets, collectively completing over 20,000 hours of workouts. With strong customer engagement, Portl aims to double its user base in the next 12 months, driven by innovation and strategic market expansion. Advanced Features of the Portl UltraGym The Portl UltraGym seamlessly integrates its proprietary Hydraulic and Electromagnetic Resistance (H.E.R.S) Technology with unparalleled ease of use. Designed to cater to diverse fitness needs, it offers revolutionary adjustable digital weights, starting from as little as 0.5 kg and scaling up to 70 kg, making it ideal for users across all fitness levels. With multiple training modes-including standard, eccentric, isokinetic, elastic, and rowing-it provides a versatile workout experience that adapts to individual goals. The UltraGym also pairs with its companion mobile app, which enhances the overall experience by enabling effortless control of the device. Users can explore guided workout plans, create personalized routines, and monitor their progress with detailed metrics, ensuring a highly customized fitness journey. “The launch of the UltraGym marks a pivotal moment in our journey to redefine fitness and wellness. By combining unparalleled versatility, compact design, and affordability, the UltraGym makes professional-grade strength training accessible to everyone, regardless of their fitness level or space constraints. This launch is also a testament to our commitment to innovation, as we continue to invest in cutting-edge hardware, AI, computer vision, and imaging technologies to deliver personalized, data-driven fitness experiences. As we expand our footprint across India and key international markets, we remain focused on empowering individuals worldwide to achieve their fitness goals with greater efficiency, convenience, and impact,” Indraneel Gupta, Founder and CEO of Portl. Strategic Partnerships and Market Expansion Portl is actively strengthening its footprint in India while gearing up for expansion into the Middle East, targeting markets such as Qatar, UAE, and Saudi Arabia over the next 12 to 18 months. The company has already forged collaborations with renowned hospitality brands, including the Taj Group of Hotels (IHCL), Accor Group, positioning itself as a reliable provider of on-demand wellness solutions for premium travelers.
To support its global growth ambitions, Portl has aligned with strategic partners who will help introduce its cutting-edge products and services to new audiences across different regions, making fitness and wellness more accessible worldwide. R&D and Technological Innovation Portl remains deeply committed to investing in research and development to stay ahead in the fitness technology space. By harnessing advancements in artificial intelligence, computer vision, and imaging, the company continues to innovate and aims to bring more products to market. These innovations include non-invasive health tracking, real-time feedback on exercise form, and hyper-personalized fitness programs. This dedication to technological progress will ensure that Portl delivers an engaging and effective experience for users at every stage of their fitness journey. About Portl Portl is a technology company specializing in fitness, health, and wellness based out of Hyderabad. Founded in 2021, Portl leverages cutting-edge AI and personalization technology to deliver accessible, highly-tailored fitness experiences directly into people’s homes. Portl’s mission is to empower individuals to achieve their wellness goals with products that adapt to their unique needs and preferences. With a steadfast commitment to innovation and quality, Portl aspires to become the leading Fitness & Wellness ecosystem of the world, For more information Visit to www.portl.co. !function(f,b,e,v,n,t,s) if(f.fbq)return;n=f.fbq=function()n.callMethod? n.callMethod.apply(n,arguments):n.queue.push(arguments); if(!f._fbq)f._fbq=n;n.push=n;n.loaded=!0;n.version='2.0'; n.queue=[];t=b.createElement(e);t.async=!0; t.src=v;s=b.getElementsByTagName(e)[0]; s.parentNode.insertBefore(t,s)(window,document,'script', 'https://connect.facebook.net/en_US/fbevents.js'); fbq('init', '311356416665414'); fbq('track', 'PageView'); [ad_2] Source link
0 notes
Text
👉 FREE Eatventure UNLIMITED Gems / Diamonds & Money generator 👈
Eatventure, developed by the indie studio Lessmore, debuted in December 2021 and quickly established itself as a significant player in the mobile gaming market. The game is a hybrid casual title that blends elements of idle simulation and restaurant management, allowing players to start from a humble lemonade stand and work their way up to managing upscale dining establishments. This journey reflects a broader trend in mobile gaming where players engage in incremental progress and management mechanics, appealing to a wide audience looking for accessible yet engaging gameplay. Development Background Lessmore, founded in 2021, is composed of a team with extensive experience from major mobile gaming companies such as Kolibri Games and Rovio. This background played a crucial role in the development of Eatventure, as the team's expertise allowed them to create a polished product that resonated with players.
The game's design philosophy emphasizes simplicity and intuitiveness, making it easy for new players to dive into the experience without feeling overwhelmed by complex mechanics or lengthy tutorials. According to Sophie Brügmann, one of the founders, the goal was to create a game that tells its story visually rather than through text, which helps to broaden its appeal across different demographics and regions35. Gameplay Mechanics Eatventure's gameplay revolves around managing various food stations, hiring staff, and upgrading facilities to maximize profits. Players begin with basic operations and gradually expand their business by introducing new food items and enhancing their service capabilities. The game incorporates a core loop that encourages continuous engagement through item collection and limited-time events that refresh weekly.
This design not only keeps the gameplay dynamic but also fosters a sense of achievement as players progress through different levels14. The game features approximately 60 distinct locations that players can unlock as they advance, each representing a different city around the world. This geographical diversity adds an element of exploration to the game, as players can experience various culinary cultures while striving to build their restaurant empire2. The aesthetic of Eatventure is characterized by low-poly graphics that enhance its charm without compromising performance, making it suitable for a wide range of mobile devices. Market Reception and Success Upon its release, Eatventure experienced rapid growth in popularity, achieving nearly 1.5 million downloads on Google Play by July 2022.
This surge can be attributed to effective marketing strategies and the game's engaging gameplay loop. The success of Eatventure has also led to the emergence of several copycat games attempting to replicate its formula; however, many have struggled to capture the same level of player engagement15. The game's revenue trajectory has remained positive since its launch, indicating strong player retention and monetization strategies. By integrating in-app purchases seamlessly into the gameplay experience—without disrupting the flow—Lessmore has managed to create a sustainable business model that supports ongoing development and updates35. Challenges Faced by Indie Developers Despite its success, Lessmore faces typical challenges encountered by indie developers, including financial management and market competition. The team's ability to iterate quickly on feedback has been vital in maintaining relevance in a crowded market. They prioritize rapid prototyping and testing new ideas based on player input, which allows them to stay ahead of trends and adapt their offerings accordingly.
0 notes
Text
Events 11.30 (after 1960)
1962 – Eastern Air Lines Flight 512 crashes at Idlewild Airport, killing 25 people. 1966 – Decolonization: Barbados becomes independent from the United Kingdom. 1967 – Decolonization: South Yemen becomes independent from the United Kingdom. 1967 – The Pakistan Peoples Party is founded by Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, who becomes its first chairman. 1967 – Pro-Soviet communists in the Philippines establish Malayang Pagkakaisa ng Kabataan Pilipino as its new youth wing. 1971 – Iran seizes the Greater and Lesser Tunbs from the Emirates of Sharjah and Ras Al Khaimah. 1972 – Vietnam War: White House Press Secretary Ron Ziegler tells the press that there will be no more public announcements concerning American troop withdrawals from Vietnam because troop levels are now down to 27,000. 1981 – Cold War: In Geneva, representatives from the United States and the Soviet Union begin to negotiate intermediate-range nuclear weapon reductions in Europe. (The meetings end inconclusively on December 17.) 1995 – Official end of Operation Desert Storm. 1995 – U.S. President Bill Clinton visits Northern Ireland and speaks in favor of the "Northern Ireland peace process" to a huge rally at Belfast City Hall; he calls IRA fighters "yesterday's men". 1999 – Exxon and Mobil sign a US$73.7 billion agreement to merge, thus creating ExxonMobil, the world's largest company. 1999 – In Seattle, United States, demonstrations against a World Trade Organization meeting by anti-globalization protesters catch police unprepared and force the cancellation of opening ceremonies. 1999 – British Aerospace and Marconi Electronic Systems merge to form BAE Systems, Europe's largest defense contractor and the fourth largest aerospace firm in the world. 2000 – NASA launches STS-97, the 101st Space Shuttle mission. 2004 – A McDonnell Douglas MD-82, operating as Lion Air Flight 538, overran the runway and crashed, killing 25 people. 2005 – John Sentamu becomes the first black archbishop in the Church of England with his enthronement as the 97th Archbishop of York. 2018 – A magnitude 7.1 earthquake with its epicenter only 24 km from Anchorage, Alaska causes significant property damage but no deaths. 2021 – Barbados becomes a republic. 2021 – A 15-year-old gunman murders four students and injures seven people, including a teacher, in a mass shooting at Oxford High School in Oxford Township, Michigan. 2022 – The AI chatbot ChatGPT is launched by OpenAI.
0 notes
Text
Smart Cities Market 2030 Future Scope, Size Estimation, Regional Outlook
The global smart cities market was valued at approximately USD 748.7 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.8% from 2023 to 2030. Several factors are driving this growth, including rapid urbanization, the need for efficient management of resources, heightened public safety concerns, and the demand for energy-efficient environments. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic underscored the importance of urban resilience and public healthcare, revealing the dependency of global economies on urban infrastructure and emphasizing the potential role of smart cities in safeguarding public health.
As a result, many organizations are turning to emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to address urban challenges. These technologies enable city infrastructure to become more interconnected and responsive, offering real-time solutions for traffic, energy, and healthcare, among other sectors. As urban populations grow, the need for sustainable infrastructure becomes increasingly critical, driving governments to implement smart city initiatives across key areas, including mobility, utility management, public safety, and urban administration.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Smart Cities Market
Local governments play a significant role in driving these initiatives, often fostering organizational and institutional transformations that attract investments and promote collaboration across industries. In this landscape, a new model of public-private partnerships has emerged, facilitating cooperation between governments and private businesses to develop and maintain smart city infrastructure. Additionally, innovative financing and governance models are key in scaling infrastructure projects, supporting ongoing growth in the smart cities market.
The growth of smart cities is also fueled by the adoption of advanced technologies, including nanotechnology, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), cloud computing, IoT, cognitive computing, big data analytics, and open data platforms. Emerging business models, such as Build-Own-Operate (BOO), Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT), Original Brand Manufacturer (OBM), and Bill of Material (BOM), are increasingly applied to smart city projects, enhancing their implementation and operational success. In Asia, countries are aggressively promoting digital technologies for smart city applications while addressing consumer data privacy concerns, and governments worldwide are initiating various programs to accelerate market growth further.
Application Segmentation Insights:
The smart utility segment led the market with a share exceeding 28% in 2022. This segment is central to city infrastructure, encompassing areas such as water treatment, energy distribution, consolidated data management, and civil distribution infrastructure management. The rise of smart grids, which use advanced data analytics and cloud technology, is a major factor driving the adoption of smart utilities. With the surge in global energy demand, companies and governments are prioritizing strategies to increase the share of renewable energy in the overall energy mix, which supports the growth of the smart utility segment.
Meanwhile, the environmental solutions segment is projected to grow at a remarkable CAGR of 28.8% through the forecast period. This expansion is driven by increasing government initiatives aimed at reducing pollution, optimizing renewable energy use, and creating a sustainable ecosystem. Industry players are also focusing on expanding their environmental solutions portfolios, as these solutions contribute to brand identity and increase revenue potential. For instance, in December 2021, SENSORO, an IoT and AI solutions company, launched the Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) brand SENSORO Solution, offering climate monitoring, garbage classification, and ecological protection services. Such developments highlight the growing market potential for environmental solutions within smart cities as governments and corporations alike prioritize sustainability.
Order a free sample PDF of the Smart Cities Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
#Smart Cities Market Share#Smart Cities Market Trends#Smart Cities Market Growth#Smart Cities Industry
0 notes
Text
Smart Cities Market Key Players, Supply and Consumption Demand Analysis to 2030
The global smart cities market was valued at approximately USD 748.7 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.8% from 2023 to 2030. Several factors are driving this growth, including rapid urbanization, the need for efficient management of resources, heightened public safety concerns, and the demand for energy-efficient environments. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic underscored the importance of urban resilience and public healthcare, revealing the dependency of global economies on urban infrastructure and emphasizing the potential role of smart cities in safeguarding public health.
As a result, many organizations are turning to emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to address urban challenges. These technologies enable city infrastructure to become more interconnected and responsive, offering real-time solutions for traffic, energy, and healthcare, among other sectors. As urban populations grow, the need for sustainable infrastructure becomes increasingly critical, driving governments to implement smart city initiatives across key areas, including mobility, utility management, public safety, and urban administration.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Smart Cities Market
Local governments play a significant role in driving these initiatives, often fostering organizational and institutional transformations that attract investments and promote collaboration across industries. In this landscape, a new model of public-private partnerships has emerged, facilitating cooperation between governments and private businesses to develop and maintain smart city infrastructure. Additionally, innovative financing and governance models are key in scaling infrastructure projects, supporting ongoing growth in the smart cities market.
The growth of smart cities is also fueled by the adoption of advanced technologies, including nanotechnology, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), cloud computing, IoT, cognitive computing, big data analytics, and open data platforms. Emerging business models, such as Build-Own-Operate (BOO), Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT), Original Brand Manufacturer (OBM), and Bill of Material (BOM), are increasingly applied to smart city projects, enhancing their implementation and operational success. In Asia, countries are aggressively promoting digital technologies for smart city applications while addressing consumer data privacy concerns, and governments worldwide are initiating various programs to accelerate market growth further.
Application Segmentation Insights:
The smart utility segment led the market with a share exceeding 28% in 2022. This segment is central to city infrastructure, encompassing areas such as water treatment, energy distribution, consolidated data management, and civil distribution infrastructure management. The rise of smart grids, which use advanced data analytics and cloud technology, is a major factor driving the adoption of smart utilities. With the surge in global energy demand, companies and governments are prioritizing strategies to increase the share of renewable energy in the overall energy mix, which supports the growth of the smart utility segment.
Meanwhile, the environmental solutions segment is projected to grow at a remarkable CAGR of 28.8% through the forecast period. This expansion is driven by increasing government initiatives aimed at reducing pollution, optimizing renewable energy use, and creating a sustainable ecosystem. Industry players are also focusing on expanding their environmental solutions portfolios, as these solutions contribute to brand identity and increase revenue potential. For instance, in December 2021, SENSORO, an IoT and AI solutions company, launched the Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) brand SENSORO Solution, offering climate monitoring, garbage classification, and ecological protection services. Such developments highlight the growing market potential for environmental solutions within smart cities as governments and corporations alike prioritize sustainability.
Order a free sample PDF of the Smart Cities Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
#Smart Cities Market Share#Smart Cities Market Trends#Smart Cities Market Growth#Smart Cities Industry
0 notes
Text
New Trends of Physical Security Market with Industry Analysis by 2023 – 2030
Physical Security Industry Overview
The global physical security market size was valued at USD 127.01 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. The need to secure the physical environment from activities such as crime, vandalism, potential burglaries, theft, and fire incidences is one of the crucial factors expected to drive the market. Moreover, factors such as increased spending on the security to protect organization’s critical asset, adoption of cloud-based data storages, advanced analytics, as well as technological developments in access control and video surveillance are some of the key trends expected to drive the market growth.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Physical Security Market
In addition, the shifting focus from legacy solutions such as badge readers, alarm systems, and door locks to advanced logical security which encompasses breach detection, threat management, and intrusion prevention, among others, has helped the organization and government agencies to deter crime incidence and breach at a higher success rate.
For instance, in September 2022, Axis Communications launched two multidirectional, dual-sensor cameras. They are designed for 24/7 operation in difficult lighting conditions and provide excellent wide-angle overviews and zoomed-in detailed coverage. These powerful cameras use a deep learning processing unit based on ARTPEC-8 (DLPU), making it possible to collect and analyze more data and improve processing and storage capacities.
This will help securely communicate precise information about the emergency, such as the severity, kind of danger, and position within the affected building, all before the first rescuers arrive. Governments across different countries and regions are taking up smart city initiatives to enhance their infrastructure and are hence deploying improved security systems. Additionally, modernizing the existing infrastructure with robust security measures and strengthening the security of government agencies have been some of the top priorities for governments across developed countries.
Organizations are increasingly concerned about employee safety and are hence setting up systems to prevent unauthorized access; further driving the demand for physical security solutions. The physical security environment continues to evolve globally. During the past few years, numerous sectors and leading industries such as BFSI, residential, government, and transport, among others have witnessed a swift growth in the number of security breaches.
Furthermore, the growing concerns to ensure the safety of resources, people, and vital assets, against physical threats and unique vulnerabilities are anticipated to become major factors driving the need for a robust security environment. Moreover, rising threat incidents have surged the need to strengthen efforts to maintain a highly secured physical infrastructure at residential as well as business premises.
For instance, in August 2022, Uber and ADT teamed up to integrate ADT's mobile safety solutions into the Uber app. ADT is the most reputable name in smart home and small business security. Uber users in the U.S. can now contact ADT professional monitoring specialists by phone or text to receive live assistance. By integrating ADT's 24/7 professional monitoring, Safe by ADT helps secure millions of gig economy employees and customers. It gives them access to assurance and emergency services when they most need them.
Governments across major regions are continuously involved in strengthening their physical security infrastructure to curb the growing threats. For instance, in December 2021, Axis Communications, AB., a Sweden-based company that provides services to private sectors and governments around the world, launched its body-worn camera for the private security of government officials. The body-worn cameras have advantages of multiple benefits for liability protection, personal safety, and operational efficiency.
The advent of technology such as the Internet of Things (IoT) has potentially created vulnerabilities with additional entry points into the data systems through the connectivity of physical objects. However, IoT has also widened the scope of opportunities for the consumer by enabling data protection through the advanced connected networks of the physical security system.
Furthermore, innovations and technological advancement in integrated sensors, video, and access systems for IoT-enabled devices are anticipated to spur the market at a high rate. For instance, in September 2021, Intel Corporation stated that it uses a software-based IoT platform to manage its physical security and virtual device access. Further, this also ensures that only authorized workers have physical access to the devices through keys or access credentials.
Browse through Grand View Research's Electronic Security Industry Research Reports.
• The global IR camera market size was valued at USD 7.79 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% from 2024 to 2030. As concerns about safety and security continue to rise, businesses, government agencies, and homeowners are investing in infrared camera (IR) cameras to enhance their monitoring capabilities.
• The global commercial radars market size was estimated at USD 6.44 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.6% from 2024 to 2030. Commercial radars are a dynamic market encompassing a wide range of applications such as aviation, marine, weather monitoring, automotive, security, etc.
Physical Security Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the global physical security market report based on the component, organization size, end-user, and region:
Physical Security Component Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2017 - 2030) • Systems o Physical Access Control System (PACS) o Video Surveillance System o Perimeter Intrusion Detection And Prevention o Physical Security Information Management (PSIM) o Physical Identity & Access Management (PIAM) o Fire And Life Safety • Services o System Integration o Remote Monitoring o Others
Physical Security Organization Size Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2017 - 2030) • SMEs • Large Enterprises
Physical Security End-user Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2017 - 2030) • Transportation • Government • Banking & Finance • Utility & Energy • Residential • Industrial • Retail • Commercial • Hospitality • Others
Physical Security Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion 2017 - 2030) • North America o U.S. o Canada o Mexico • Europe o U.K. o Germany o France • Asia Pacific o China o India o Japan • South America o Brazil • Middle East & Africa
Order a free sample PDF of the Physical Security Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
Key Companies profiled: • Hangzhou Hikvision Digital Technology Co., Ltd. • Honeywell International, Inc. • Genetec Inc. • Cisco Systems Inc. • Axis Communications AB • Pelco • Robert Bosch GmbH • Johnson Controls • ADT LLC • Siemens
0 notes
Text
History repeating: Nintendo vs. Colplo and Nintendo vs. Poket Pair
History repeating: Nintendo vs. Colplo and Nintendo vs. Poket Pair On December 22, 2017, Nintendo filed a lawsuit against Colopl over six counts of patent infringement. The main talking point in this lawsuit is the use of a joystick-like control scheme known as ぷにコン (Punicon) in the mobile game Shironeko Project. Nintendo argued that the control scheme violated patent #3734820, which was registered back in October 2005 and used in Super Mario 64 DS. The lawsuit ended with a settlement where Colopl agreed to change the control scheme and pay a settlement fee.What doesn’t get talked about much in the West is that Nintendo made amendments twice in 2016 before filing the lawsuit against Colopl. In other words, Nintendo adjusted the patents to specifically target Punicon to increase their chances of winning.Nintendo is doing the same thing against Pocket Pair Inc.To clarify, we do not have confirmation on which patents Nintendo is using against Pocket Pair. Unlike Colopl’s case, neither Nintendo nor Pocket Pair has disclosed the information to the public. What we speculate to be the violated patents are the Pokéball throwing/capturing and Pokémon riding techniques. I will be focusing on these specific patents henceforward.https://ift.tt/Y5zCQ0N patents in question are #7349486 for monster riding and #7398425 for ball throwing/capturing. These patents were applied for back in 2021 and officially registered on September 13, 2023, and December 6, 2023, respectively. Since the launch of Palworld in January, Nintendo has been making adjustments to the patents behind the scenes, presumably to set up the stage for the lawsuit.The technique Nintendo is using this time is known as a Divisional Patent Application (分割出願). While it’s not the same as an amendment, the intention is the same: to adjust the patent’s context to be more specific against the defendant’s product.There are three child patents created since the beginning of this year:7493117 (applied on February 26, registered on May 30)7505854 (applied on February 6, registered on June 17)7528390 (applied on March 5, registered on July 26)This could explain why it took so long for Nintendo to act. Nintendo is waiting for the patents to be approved before pulling the trigger. Personally I wish they can reach a settlement asap. A prolong battle serve gamer no good. However, seeing Colopl case took 4 years, I'm not optimistic about this.As a side note, this is business as usual in Japan. KONAMI’s lawsuit against Cygames for patent infringement over Umamusume also took advantage of Divisional Patent Applications, creating 14 child and grandchild patents before launching the attack. You can see the "patent family tree" in the middle of the article.Other sources:What Exactly was the Issue in the Lawsuit Between Nintendo and ColoplThis Japanese article talks about the amendments in more details for Nintendo vs. Colopl case Submitted September 21, 2024 at 10:14AM by tagle420 https://ift.tt/h9HG8CE via /r/gaming
0 notes
Text
5G C-band on airplanes ?

The C-band network is scheduled to launch in December. On October 5, 2021, the aviation industry and the FAA argued that the C-band signal from aircraft radios, which estimates the distance of aircraft from the ground for landing in bad weather, should be picked up. These altimeters are designed to use the same band as the 5G network (the aircraft frequency is 400 MHz in the network launch of 2022), but some of them are designed not to scan the surrounding frequencies, because these frequencies are not used to power when altimeters. was built. The FAA and air carriers agree on a two-mile "exclusion zone" around most airports where air carriers will not launch c band first. cities like Chicago, Dallas, New York and San Diego that are close to the airport. Our tests showed that Verizon appears to maintain a signal beyond the two-mile limit, at least in New York.
The FAA is also working to review and approve altimeter models with precision filters, although some observers wonder why the agency could not have done so a year ago, when a different model was installed. separate for the sale. No aircraft interference affects frequencies below 3.7 GHz. This means that it does not affect CBRS, or T-Mobile's mid-band, or AT&T's 3.45 GHz. This gives AT&T and T-Mobile a significant advantage over Verizon right now, as they are able to install centralized systems near airports where Verizon is not.
0 notes
Text
Podcasting Market Worth $130.63 Billion By 2030 | CAGR 27.6%
The global podcasting market size is expected to reach USD 130.63 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 27.6% from 2023 to 2030, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. Podcasting is an episodic series of digital media, often audio, that can be listened to or watched over the internet or downloaded on a device. The increasing popularity of audio-on-demand platforms is the primary factor driving the market growth. Other factors contributing to the market growth include minimal entry barriers for the creators and easy accessibility for the users, as they can listen to podcasts while performing tasks such as cleaning, walking, gardening, traveling, or exercising.
The recent evolution of podcasting content, wherein various creators are discussing un debated global scenarios, is bringing about numerous growth opportunities for the market. The subscriber base of podcasts pertaining to racism, patriarchy, and political disputes, among others, is significantly growing, thereby encouraging companies and creators to come up with more content that taps diverse audiences.
For instance, in June 2021, iHeartMedia, Inc. partnered with Celsius, the global industry-leading crypto currency yield–earning platform, to launch a new iHeartRadio original podcast network and reach out to new audiences with crypto currency education in creative and innovative ways.
In addition, in December 2022, Spotify partnered with Inevitable Foundation, a non-profit organization for disabled people, to support and empower podcasters with disabilities. Meanwhile, challenges such as limited mobile phone storage and low internet connectivity are likely to hinder the market growth during the forecast period.
The COVID-19 outbreak has unfolded new opportunities for the podcasting platform, where many creators are offering content with the sole purpose of educating the global population on the hidden long-term effects of the coronavirus. National public health organizations and private healthcare entities are also releasing podcasts to spread awareness among the masses about the prevention of the virus. For instance, the American Hospital Association (AHA) has released a podcast to talk about community health improvement during and after the pandemic.
Request a free sample copy or view report summary: Podcasting Market Report
Podcasting Market Report Highlights
Based on genre, the news and politics segment dominated with a revenue share of more than 27.0% of the overall market in 2022. The increasing need for receiving updated information on global events has resulted in the segmental growth
Based on format, the solo segment is estimated to account for a reasonable share, expanding at a CAGR of above 29.0% from 2023 to 2030. Market entry is the easiest with this format as the host requires only basic equipment and related software to record podcasts
Latin America is expected to record the fastest growth, registering a CAGR of more than 37.0% from 2023 to 2030. This can be attributed to the increasing popularity of digital devices coupled with the accessibility of podcasting content offered in Spanish
Podcasting Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the global podcasting market based on the genre, format, and region:
Podcasting Genre Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
New & Politics
Society & Culture
Comedy
Sports
Others
Podcasting Format Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Interviews
Panels
Solo
Repurposed Content
Conversational
Podcasting Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
North America
U.S.
Canada
Europe
U.K.
Nordic Countries
Asia Pacific
China
South Korea
Australia
Latin America
Brazil
Mexico
Middle East & Africa
List of Key Players in Podcasting Market
Amazon.com, Inc.
Apple, Inc.
iHeartMedia Inc.
Megaphone LLC
Pandora Media, LLC
Audacy, Inc.
Sound Cloud Limited
Spotify AB
Stitcher
Tune In, Inc.
0 notes
Text
5G C-band on airplanes?

The C-band network is scheduled to launch in December. On October 5, 2021, the aviation industry and the FAA argued that the C-band signal from aircraft radios, which estimates the distance of aircraft from the ground for landing in bad weather, should be picked up. These altimeters are designed to use the same band as the 5G network (the aircraft frequency is 400 MHz in the network launch of 2022), but some of them are designed not to scan the surrounding frequencies, because these frequencies are not used to power when altimeters. was built. The FAA and air carriers agree on a two-mile "exclusion zone" around most airports where air carriers will not launch c band first. cities like Chicago, Dallas, New York and San Diego that are close to the airport. Our tests showed that Verizon appears to maintain a signal beyond the two-mile limit, at least in New York.
The FAA is also working to review and approve altimeter models with precision filters, although some observers wonder why the agency could not have done so a year ago, when a different model was installed. separate for the sale. No aircraft interference affects frequencies below 3.7 GHz. This means that it does not affect CBRS, or T-Mobile's mid-band, or AT&T's 3.45 GHz. This gives AT&T and T-Mobile a significant advantage over Verizon right now, as they are able to install centralized systems near airports where Verizon is not.
0 notes
Text
5G C-band on airplanes?

The C-band network is scheduled to launch in December. On October 5, 2021, the aviation industry and the FAA argued that the C-band signal from aircraft radios, which estimates the distance of aircraft from the ground for landing in bad weather, should be picked up. These altimeters are designed to use the same band as the 5G network (the aircraft frequency is 400 MHz in the network launch of 2022), but some of them are designed not to scan the surrounding frequencies, because these frequencies are not used to power when altimeters. was built. The FAA and air carriers agree on a two-mile "exclusion zone" around most airports where air carriers will not launch c band first. cities like Chicago, Dallas, New York and San Diego that are close to the airport. Our tests showed that Verizon appears to maintain a signal beyond the two-mile limit, at least in New York.
The FAA is also working to review and approve altimeter models with precision filters, although some observers wonder why the agency could not have done so a year ago, when a different model was installed. separate for the sale. No aircraft interference affects frequencies below 3.7 GHz. This means that it does not affect CBRS, or T-Mobile's mid-band, or AT&T's 3.45 GHz. This gives AT&T and T-Mobile a significant advantage over Verizon right now, as they are able to install centralized systems near airports where Verizon is not.
0 notes