#Mesothelioma malignant
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Why Is Mesothelioma Incurable in 2024? | Behind the Reason
Introduction Mesothelioma, a rare and aggressive form of cancer, remains challenging to cure despite advances in medical research. Its unique characteristics and the way it develops make it difficult to treat effectively. This article explores why mesothelioma is incurable and what options are available for patients.
Contact Us Now For a Free Consultation
1. What Makes Mesothelioma Different from Other Cancers? Mesothelioma originates in the mesothelial cells that line organs like the lungs and abdomen.
Aggressive nature: It spreads quickly to nearby tissues.
Late diagnosis: Symptoms often appear decades after asbestos exposure.
2. Why Is Mesothelioma Difficult to Diagnose Early? The latency period of mesothelioma, combined with non-specific symptoms, leads to delayed detection.
Latency period: Can be 20-50 years from asbestos exposure to symptom onset.
Similar symptoms: Mimics conditions like pneumonia or bronchitis.
3. How Does Mesothelioma Spread in the Body? Mesothelioma tends to spread to nearby organs and tissues, complicating treatment.
Localized spread: Often extends to the lungs, diaphragm, or heart.
Metastasis: Advanced stages may spread to distant parts of the body.
4. What Treatment Options Are Available for Mesothelioma? While there is no cure, treatments can help manage symptoms and prolong life.
Surgery: Removes tumors but is not always possible due to spread.
Chemotherapy: Helps to shrink tumors and manage growth.
Radiation therapy: Used to target cancer cells and reduce pain.
5. Are There Any Emerging Treatments for Mesothelioma? New therapies aim to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Immunotherapy: Boosts the body's immune response to target cancer cells.
Gene therapy: Investigates altering cell behavior to combat the disease.
Clinical trials: Offer access to cutting-edge treatments.
6. What Is the Focus of Current Mesothelioma Research? Research continues to explore better detection methods and new treatments.
Early detection: Developing blood tests and biomarkers for earlier diagnosis.
Targeted therapy: Aims to attack specific cancer cells without harming healthy cells.
Conclusion The incurability of mesothelioma is largely due to its aggressive nature, late diagnosis, and the complexity of its spread. Despite these challenges, advancements in research provide hope for better management and improved quality of life for those affected.
FAQs
Why does mesothelioma take so long to develop? The asbestos fibers cause chronic irritation that eventually leads to cancer after many years.
Can mesothelioma be detected before symptoms appear? Currently, it is difficult, but researchers are working on early detection methods.
Is palliative care common for mesothelioma patients? Yes, palliative care is often used to manage pain and improve comfort.
Why can't surgery cure mesothelioma? Surgery cannot always remove all cancer cells due to their spread to surrounding tissues.
Are mesothelioma survival rates improving? New treatments have improved some outcomes, but survival rates remain low.
What is the most promising new treatment for mesothelioma? Immunotherapy has shown promise in extending survival in some patients.
#mesothelioma#mesothelioma science#mesothelioma and lung cancer#causes of mesothelioma#mesothelioma research#mesothelioma (nci term)#mesothelioma experts#incurable#international symposium on malignant mesothelioma#curable#regulatory challenges in healthcare#house md season 5#out of the apocalypse#dr. jason fung#abandoned vehicles#serling and abramson#pleural disease symptoms#asbestos health precautions#livingwell cancer resource center
0 notes
Link
#what#risk factors#the risk factors#DEVELOPING MALIGNANT MYXOID#DEVELOPING MALIGNANT#MALIGNANT MYXOID#mesothelioma#MALIGNANT MYXOID MESOTHELIOMA
0 notes
Text
Mesothelioma | Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
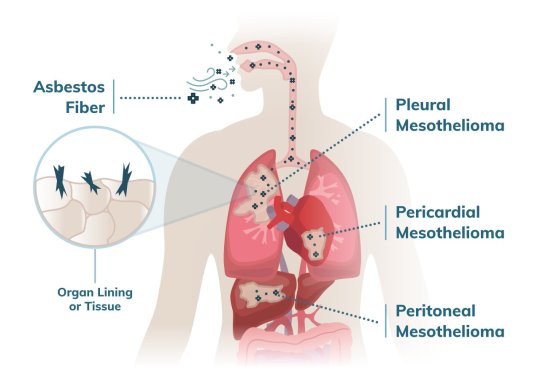
Mesothelioma is a rare and deadly cancer that originates from mesothelial cells of the pleura or serosal surfaces such as the peritoneum, pericardium, and tunica vaginalis.
It is most commonly observed in the pleura (65-70%), followed by the peritoneum (30%), pericardium, and tunica vaginalis (1-2%).
This type of tumor, which is associated with somatic and germline mutations, envelops and compresses organs and body cavities.
Asbestos exposure is the single most common cause (over 90% of mesotheliomas).
Common symptoms of malignant pleural mesothelioma include chest pain and dyspnea.
Dyspnea indicates the presence of pleural effusion.
There may also be general symptoms like unintentional weight loss, loss of appetite, cough, fatigue, and chest wall mass.
The only type of mesothelioma that can be staged is malignant pleural mesothelioma.
Early diagnosis is very difficult due to its silent progression and the long latent period.
A thorough history of occupational and environmental asbestos exposure is required for proper diagnosis.
CXR (or CT) shows:
Pleural effusion
Pleural mass or thickening ± free fluid.
Concomitant pleural plaques or pulmonary fibrosis (minority).
Local invasion of the chest wall, heart, or mediastinum.
Death is unavoidable within 4 to 6 months. Some patients may survive for 15 to 18 months with treatment.
Treatment depends on the stage of the tumor, with Stage III-IV malignant pleural mesothelioma being regarded as incurable and not susceptible to surgical resection.
The most common treatment options are surgical resection, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy.
Read more at: Mesothelioma | Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
0 notes
Text

asked by @ghost-in-a-player-piano: Which body part is the biggest problem for using the badwrong instructions that can make cancer? Is it the liver? Since the liver can regrow itself as part of everyday normal business, I bet it's up there. extension of this thread.
oh! fantastic observation; with respect to liver cancers, this is a big area of discussion. you're right: tissue regeneration, by default, can predispose it to regenerating just a little too well. cancer emerging from hepatocytes (hepatocellular carcinoma), which make up most of the liver, is indeed one of the most common forms of adult cancer.
(note: it's up there, but not the furthest up! more on that later.)
i want to be a bit careful though: the liver's ability to regrow has the potential to influence cancer development, but that's one player among many.
we should consider what makes the liver a potential breeding ground for tumours beyond its powerful ability to regrow itself by asking why it's regrowing so much at all. existing liver tissue likely sustained some damage. this could be through a lot of means, such as excess alcohol consumption or hepatitis. damage means inflammation: tissue becomes swollen, and the affected tissue experiences something called oxidative stress.
you can think of oxidative stress as the production of very hostile molecules that carry oxygen atoms with the potential to mess up DNA. these reactive oxygen species are always present in the cells of the body, because oxygen is key to our ability to get the most energy possible out of sugar (glucose, specifically). they just exist at levels the body can handle. in cases like long-term inflammation, however, there's a fair chance they'll reach overwhelming levels.
the liver's efforts to regenerate are, ironically, an effort to resolve this inflammation—that's the organ trying to heal! however, when cells get ready to divide, they make copies of their DNA, and pass on new mistakes to their descendants. the source of the mistakes might come from the copying process itself, or it might come from our nasty reactive oxygen species hitting our DNA repeatedly until critical instructions get tampered with. following liver damage, both of these things are happening... so things might go awry.
so! chronic inflammation sounds like a big fucking deal, and it is. when it comes to body parts that are the "biggest problem for using the badwrong instructions," a noticeable pattern emerges: several are organs highly susceptible to inflammation. more common than liver cancer are lung cancer and colorectal cancer, to name two.
to showcase the phenomenon that is chronic inflammation in more concrete examples:
tobacco users are more susceptible to lung cancer; cigarette smoke irritates the lungs. that is, it induces inflammation.
asbestos is an extremely infamous cancer-causing substance. this is because asbestos, at the microscopic level, is made up of extremely small, sharp fibers. they quite literally can embed into lung cells and cause long-term inflammation. most often, it causes a form of cancer called malignant mesothelioma.
you'll never guess what inflammatory bowel disease can do. people affected tend to be prescribed anti-inflammatory medications, which both lowers the risk of colorectal cancer while reducing pain.
inflammation and growth capacity are, again, two among many things that can set a healthy cell down the path of evil, but they are extremely common culprits in the world of cancer.
thank you! i hope this was informative. hearts and love and all those nice things
#again posting separately to avoid a massive frankenpost lol#scitag#<- new tag. because i am insane.#cancer mention
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Which Body Parts Are Affected by Mesothelioma in 2024? | Reveal
Introduction Mesothelioma is known for affecting specific parts of the body, particularly the lining of organs. Understanding which areas are most commonly impacted can aid in early detection and treatment. This article explores the various body parts that mesothelioma can affect and the symptoms associated with each type.
Contact Us Now For a Free Consultation
1. What Are the Main Types of Mesothelioma? Mesothelioma is categorized based on the location of the affected tissue. The primary types include:
Pleural mesothelioma: Affects the lining of the lungs.
Peritoneal mesothelioma: Occurs in the lining of the abdomen.
Pericardial mesothelioma: Impacts the lining around the heart.
Testicular mesothelioma: Rarely affects the lining of the testes.
2. How Does Mesothelioma Affect the Lungs? Pleural mesothelioma is the most common form, affecting the lung lining.
Symptoms: Persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath.
Diagnosis: Involves imaging tests and lung biopsies.
3. What Is Peritoneal Mesothelioma? Peritoneal mesothelioma develops in the abdominal lining and is the second most common type.
Symptoms: Abdominal pain, swelling, nausea, weight loss.
Risk factors: Often linked to swallowing asbestos fibers.
4. Can Mesothelioma Affect the Heart? Pericardial mesothelioma is rare and affects the lining surrounding the heart.
Symptoms: Chest pain, irregular heartbeats, breathing difficulties.
Challenges: Difficult to diagnose due to overlap with other cardiac conditions.
5. What Is Testicular Mesothelioma? This extremely rare form affects the lining of the testes and is often discovered during surgery for other conditions.
Symptoms: Testicular lumps, pain or swelling.
Prognosis: Generally better than other forms due to early detection.
6. How Does Mesothelioma Spread to Other Body Parts? In advanced stages, mesothelioma can spread to nearby tissues and organs.
Metastasis: Commonly spreads to the chest wall, liver, and lymph nodes.
Impact on treatment: Limits options and affects prognosis.
Conclusion Mesothelioma can affect various parts of the body, primarily the lungs and abdomen. Awareness of its manifestations in different regions can help individuals recognize symptoms early and seek appropriate medical care.
FAQs
Is pleural mesothelioma more common than peritoneal mesothelioma? Yes, pleural mesothelioma accounts for about 75% of cases.
Can mesothelioma spread to the brain? While rare, mesothelioma can metastasize to the brain in advanced stages.
How is pericardial mesothelioma diagnosed? It typically requires echocardiograms, CT scans, and biopsies.
Is peritoneal mesothelioma linked to asbestos exposure? Yes, it is often associated with swallowing or ingesting asbestos fibers.
Can mesothelioma affect both lungs? Yes, pleural mesothelioma can impact the lining of both lungs.
What is the prognosis for testicular mesothelioma? It tends to have a better prognosis due to its localized nature and potential for early detection.
#mesothelioma#mesothelioma treatment#peritoneal mesothelioma#mesothelioma lawyer#mesothelioma law firm#pleural mesothelioma#mesothelioma symptoms#mesothelioma lawsuit#mesothelioma cancer#mesothelioma stages#mesothelioma lung#mesothelioma claim#malignant mesothelioma#mesothelioma usa#mesothelioma case#mesothelioma attorney#testicular mesothelioma#mesothelioma settlement#pericardial mesothelioma#how do you detect mesothelioma#mesothelioma causes
0 notes
Link
#survival#malignant mesothelioma#PULMONARY MALIGNANT#PULMONARY MALIGNANT MESOTHELIOMA#survival rates
0 notes
Text
What Is Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma in 2024? | Learn More
Introduction Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is one of the three main types of mesothelioma, known for its aggressive nature and poor prognosis. It differs significantly from other types of mesothelioma due to its cell structure, making it more challenging to diagnose and treat. This article delves into sarcomatoid mesothelioma, its characteristics, symptoms, and treatment options.
Contact Us Now For a Free Consultation
1. What Is Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma? Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is a rare subtype that occurs in the mesothelial cells lining organs, especially the lungs.
Cell structure: Spindle-shaped cells that grow more rapidly than other mesothelioma types.
Prevalence: Accounts for about 10-20% of mesothelioma cases.
2. How Does It Differ from Epithelioid Mesothelioma? Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is more aggressive and harder to treat than epithelioid mesothelioma.
Epithelioid mesothelioma: Has a better response to treatment and a more structured cell arrangement.
Sarcomatoid: Cells are disorganized, leading to a faster spread.
3. What Are the Symptoms of Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma? Symptoms are similar to other mesothelioma types but tend to progress more rapidly.
Common symptoms: Shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue.
Advanced signs: Weight loss, difficulty swallowing, fluid buildup.
4. How Is Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma Diagnosed? Diagnosing sarcomatoid mesothelioma can be difficult due to its resemblance to other cancers.
Imaging tests: CT scans, MRIs to detect tumor location.
Biopsies: Essential for confirming cell type through microscopic examination.
5. What Are the Treatment Options for Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma? Treatment focuses on slowing the disease’s progression and managing symptoms.
Common approaches: Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, palliative care.
Surgery: Rarely an option due to the spread and structure of sarcomatoid cells.
6. Why Is the Prognosis for Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma Poor? Its aggressive nature and resistance to treatment contribute to a challenging prognosis.
Median survival time: Ranges from 6 to 12 months post-diagnosis.
Research focus: New therapies and clinical trials aim to improve outcomes.
Conclusion Sarcomatoid mesothelioma presents significant challenges due to its aggressive cell structure and rapid progression. Understanding its characteristics and pursuing early diagnosis can help in managing symptoms and exploring treatment options.
FAQs
Is sarcomatoid mesothelioma more aggressive than other types? Yes, it tends to grow and spread faster than other mesothelioma types, making it harder to treat.
Can sarcomatoid mesothelioma be misdiagnosed? Yes, its cell structure can resemble other types of cancers, leading to potential misdiagnosis.
What is the best treatment for sarcomatoid mesothelioma? There is no definitive best treatment, but a combination of chemotherapy and radiation is commonly used.
Is sarcomatoid mesothelioma linked to asbestos exposure? Yes, like other mesothelioma types, asbestos exposure is the primary risk factor.
Can sarcomatoid mesothelioma occur outside of the lungs? It primarily affects the lungs but can also occur in the lining of the abdomen or heart.
Are there any new treatments for sarcomatoid mesothelioma? Immunotherapy and clinical trials are being explored for more effective treatment options.
#sarcomatoid mesothelioma#best treatment#Sarcomatoid#mesothelioma#mesothelioma treatment#peritoneal mesothelioma#sarcomatoid#peritoneal mesothelioma treatment#sarcomatoid carcinoma mesothelioma#sarcomatoid mesothelioma uk#mesothelioma sarcomatoid type#sarcomatoid mesothelioma causes#sarcomatoid mesothelioma stage 4#sarcomatoid mesothelioma symptoms#sarcomatoid mesothelioma immunotherapy#sarcomatoid malignant mesothelioma#sarcomatoid mesothelioma prognosis
0 notes