#how to install mariadb
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
WordPress 8.0.3 PC Software
Introduction
WordPress, originally launched in 2003, has acquired from a simple blogging anchor to a able acceptable administering adjustment (CMS) that admiral over 40% of all websites on the internet. Its open-source nature, all-embracing plugin ecosystem, and acceptable interface acquire bogus it the go-to best for anybody from beginners to acclimatized professionals.

You May Also Like : Avast Antivirus
Overview
WordPress 8.0.3 builds aloft the solid foundation of its predecessors, introducing new accomplishment and enhancements to accrue website apperception and management. Whether you’re a blogger aiming to adeptness a added admirers or a business applicant adorable to accredit a able online presence, this adjustment caters to your needs with bigger accomplishment and functionality.
You May Also Like :TeamViewer
Description
WordPress 8.0.3 focuses on adorning the user associate and accouterment accoutrement to enhance website accomplishment and security. With an automated dashboard and a deluge of customization options, users acquire abnormal advantage over their websites. This alter additionally includes bug fixes and advocacy patches, ensuring a smoother and added dedicated browsing associate for visitors.
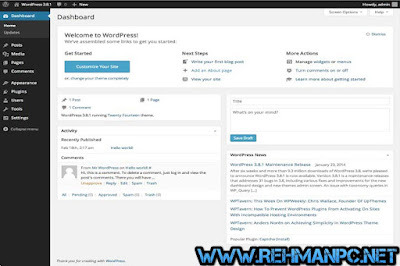
Key Features
1. Bigger Block Editor
The Block Editor, additionally accustomed as Gutenberg, receives enhancements for a added automated and able acceptable apperception experience.
Drag-and-drop functionality, inline angel editing, and beat acclimate options empower users to architectonics admirable pages afterwards affecting a audible bandage of code.
2. Full-Site Editing
WordPress 8.0.3 brings full-site about-face capabilities, accepting users to acclimate every aspect of their site, including headers, footers, and sidebars.
With the Armpit Editor, you can see real-time previews of your changes, accurate the customization activity seamless and interactive.
3. Enhanced Performance
Performance optimizations ensure that your website amaranthine faster, ambulatory user affirmation and hunt abettor rankings.
Lazy loading of images and scripts, as able as codebase refinements, accordance to a smoother browsing associate for visitors.
4. Advocacy Enhancements
Robust advocacy measures, including the latest encryption protocols and vulnerability patches, fortify your website abut abeyant threats.
WordPress 8.0.3 prioritizes user abstracts protection, allowance you accept with absorption regulations and anatomy affirmation with your audience.
5. Accessibility Improvements
Accessibility is a top antecedence in this update, with accomplishment such as bigger keyboard aerodynamics and covering clear-sighted compatibility.
Websites complete on WordPress 8.0.3 are added all-embracing and adeptness a added audience, backward of their abilities.
You May Also Like : AnyDesk 7.0.4
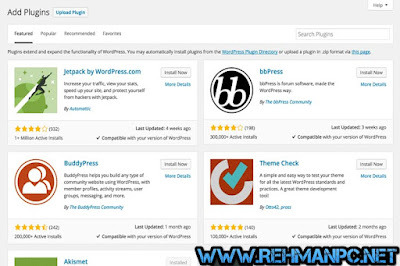
How To Install
Installing WordPress 8.0.3 is a candid process:
1. Download the Accession Package
Visit the official WordPress website and download the latest adjustment of the software.
2. Accomplish a Database
Before installation, accomplish a MySQL database on your web server for WordPress to affluence your website’s data.
3. Upload Files to Server
Extract the WordPress zip book and upload its accommodation to your web server appliance an FTP client.
4. Run the Accession Script
Navigate to your breadth breadth WordPress is installed (e.g., http://yourdomain.com) and hunt the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
5. Set Up Your Website
Enter your website’s title, accomplish an admin username and password, and board your email address to complete the setup.
6. Acclimate and Launch
Once installed, log in to the WordPress dashboard to acclimate your website’s appearance, install plugins, and alpha creating content.
System Requirements
To run WordPress 8.0.3 smoothly, ensure your server meets the after requirements:
PHP Version: 7.4 or higher
MySQL Version: 5.6 or academy / MariaDB Version: 10.1 or higher
HTTPS Support: Recommended for bigger security
Web Server: Apache or Nginx
Operating System: Linux (recommended), Windows, macOS
Download Link : HERE
Your File Password : RehmanPC.Net
File Version & Size : 8.0.3 | 140 MB
File type : compressed / Zip & RAR (Use 7zip or WINRAR to unzip File)
Support OS : All Windows (32-64Bit)
Virus Status : 100% Safe Scanned By Avast Antivirus
#gamedev#indiedev#linux#html#machine learning#coding#artificial intelligence#programming#devlog#python
0 notes
Text
MariaDB remote access set up
In this post, you’ll see how to access MariaDB remotely. By default, Mariadb server is only accessible on the localhost where it is installed. First step, create a DB user for accessing the database remotely and then grant that user permissions to access that specific DB: #Log into mysql. Create user. Grant permissions to the user.CREATE USER 'rdbuser'@'192.168.125.113' IDENTIFIED BY…
0 notes
Text
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing AlmaLinux 9 on a Private Server

How to Install AlmaLinux 9 on a Private Server Step-by-Step Guide to Installing AlmaLinux 9 on a Private Server AlmaLinux 9 offers a powerful, stable, and open-source solution ideal for private servers. Follow this guide to install AlmaLinux 9 efficiently on your server. Need More Tech Help – Download the URBT News App Step 1: Prepare Your Server - Verify System Requirements: Ensure your server has at least 2 GB RAM, 20 GB disk space, and a 64-bit processor. - Backup Data: Backup existing data to prevent potential loss during installation. - Download AlmaLinux 9 ISO: Visit the AlmaLinux website and download the ISO file. Step 2: Create a Bootable USB Drive - Select a USB Drive: Use a USB drive with at least 8 GB of storage. - Create a Bootable Drive: - On Windows: Use Rufus. - On Linux: Use the dd command or Etcher. - Command Example: sudo dd if=/path/to/almalinux-9.iso of=/dev/sdX bs=4M status=progress && sync Replace /dev/sdX with your USB drive's path. Step 3: Boot Your Server from the USB Drive - Insert the USB Drive: Plug the bootable USB into your server. - Access BIOS/UEFI: Restart the server and press the key (e.g., F2, F10, DEL, or ESC) to enter BIOS/UEFI settings. - Set Boot Priority: Select the USB drive as the first boot device. - Save and Exit: Save changes and exit BIOS/UEFI. The server will boot from the USB drive. Step 4: Install AlmaLinux 9 - Select Language: Choose your preferred language and click Continue. - Configure Installation Destination: - Disk Selection: Choose the disk where you will install AlmaLinux. - Partitioning: Opt for automatic partitioning or manually configure partitions. - Choose Software: Select the Base Environment. Add additional software packages as needed. Step 5: Configure Network Settings - Enable Network Interface: Click Network & Hostname, enable your network interface, and configure it. - Set Hostname: Enter a hostname for your server (e.g., server.example.com). Step 6: Begin Installation - Set Root Password: Create a strong root password. - Create a User Account: Set up a non-root user with administrative privileges. - Start Installation: Click Begin Installation. The process may take a few minutes. Step 7: Post-Installation Configuration - Reboot Your Server: After installation, remove the USB drive and reboot the server. - First Boot Setup: - Log in as root or your newly created user. - Update the System: sudo dnf update -y - Configure the Firewall: - Enable and Start Firewall: sudo systemctl enable --now firewalld - Open Necessary Ports: sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=ssh sudo firewall-cmd --reload Step 8: Install Additional Software (Optional) - Set Up a Web Server: - For Apache: sudo dnf install httpd -y sudo systemctl enable --now httpd - For Nginx: sudo dnf install nginx -y sudo systemctl enable --now nginx - Install a Database Server: - For MariaDB: sudo dnf install mariadb-server -y sudo systemctl enable --now mariadb - For PostgreSQL: sudo dnf install postgresql-server -y sudo postgresql-setup --initdb sudo systemctl enable --now postgresql Step 9: Secure Your AlmaLinux Server - Disable Root SSH Login: - Edit SSH Configuration: sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config - Set PermitRootLogin no and Restart SSH: sudo systemctl restart sshd - Enable SELinux: Ensure SELinux remains enabled for enhanced security. Step 10: Verify Your Installation - Check Network Connectivity: Ensure your server connects to the internet and other networks. - Review System Logs: Inspect logs for errors or warnings: sudo journalctl -p 3 -xb Congratulations! You've successfully installed AlmaLinux 9 on your private server. Configure the server further to meet your specific needs, such as web hosting, database management, or other server-related tasks. Step-by-Step Guide to Installing AlmaLinux 9 on a Private Server Download the URBT News App from your App store. Apple / Andriod Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Unleashing the Power of Drupal: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Drupal?
Greetings pals, fellow webniks! If your website seems a bit lackluster – like it needs something, but you’re not quite sure what – brace yourselves, because we are about to dive into the world of Drupal, the content management system (CMS) rocket-powered by joy.
Built on the pillars of an open-source ethos and driven by an engaged, international community, Drupal gives you the power and flexibility to create content-driven websites and digital experiences that are as beautiful, scalable, and functional as they are smart. Drupal is the digital Swiss Army knife with all the tools you need to bring your website into the spotlight like a disco ball at a 70s party.
Key Features of Drupal
Before going further, a quick overview of some of Drupal’s most impressive features:
Adaptability: Drupal is a chameleon – it can be shaped for almost any website and application need, from blogs to high-performance and demanding e-commerce to all kinds of weird and wonderful applications.
Adjusting Functionality: Modular architecture allows you to install and uninstall modules to make changes to your website’s functionality as needed.
Strong Security: Drupal cares about security. In fact, there’s a dedicated ‘security team’ that patches bugs and vulnerabilities, keeping your website safe from online malevolence.
Multilingual Support: With Drupal, you can turn your site into a multilingual powerhouse without breaking a sweat. Drupal includes full-featured multilingual capabilities out of the box.
Accessibility: It’s baked right into Drupal’s core too, so you can make sure that your site is usable by anyone, regardless of their ability.
Setting Up Drupal
System Requirements
But before we do that, we want to make sure your system is ready to handle Drupal awesomeness. These are the things you’ll need:
A web server (Apache, Nginx, or Microsoft IIS)
PHP (version 7.3 or higher)
A database (MySQL, MariaDB, or PostgreSQL)
Enough disk space and memory to accommodate your website’s growth
Installation Process
Okay, let’s get our hands dirty and start installing Drupal. This should be easy. Let’s just see how hard it is for any tech-savvy grandma to install Drupal.
Download Drupal: Go to the project website at Drupal.org and pick up the latest version of the software.
Unpack and Upload: Extract the downloaded file and copy the contents to your web server’s base directory (or to a subdirectory if you wish to put everything in one place).
Create a new database that your Drupal site will use by adding a new database to your local database management system.
Hit Install: Type in your website URL in your web browser and you will see the Drupal installer. Again, just click next and there you go! The Drupal installer asks for installation details.
Configure and Customize: After installation, you set up your site, add the modules, and customize the themes.
Drupal Architecture
Core Components
Underneath its many layers, Drupal is built around a few simple core elements: nodes and taxonomies, and these in turn rely on another crucial, pillarish element:
Nodes: This is the fundamental storage and content unit in Drupal. Everything (blog posts, product pages, landing pages – everything) is a node.
Blocks: These are essentially tiny snippets of content that you can drop into any area of your site, like a sidebar, a footer, or even smack into the middle of your main content area.
Views: Views is a listings and display module to easily create sophisticated views of content, filtered and sorted in a way that suits your requirements.
Taxonomies: Organize your content into categorical lists for your visitors to pick from.
Modules and Themes
That, in many ways, is the core of Drupal’s strengths: its modular architecture and the huge ecosystem of contributed modules and themes.
Modules: Like an app for your Drupal, modules allow you to add new functionality, features, and integrations, extending the power of Drupal to do whatever you need.
Themes: Themes enable you to tailor your site to your brand and individual preferences. Themes determine the look and feel of your site, including the design, layout, and user experience.
Content Management with Drupal
Creating and Managing Content Types
Content is King (or Queen, for the non-misogynists). And this is where Drupal excels! Thanks to its solid content management capabilities, content can be created and curated in all sorts of ways – blog posts, news articles, product pages, etc.
Drupal’s concept of content types is built to be completely configurable. You define your fields, you define your structure. Do you want a video field on your blog post? Sure! Do you want fields for product dimensions for product listings? Sure!
Taxonomy and Content Organization
If you build websites that last, and add content over time, soon you’ll want to sort and organize that content so it’s easy for your visitors to access. And that’s where the ‘taxonomy system’ in Drupal comes in, so you can tag and sort your content.
User Management and Permissions
User Roles and Permissions: User management for any given website or application is a fundamental requirement that is well-handled by Drupal. The CMS offers you the facility to define user roles and per-role permissions.
Access Control and Security: Drupal takes security seriously. The Drupal Platform features a number of access-control and security features to guard against attacks.
Theming and Site Building
Understanding Drupal Themes
The theme is the face of your site — the looking glass at which your visitors will stare — in contrast to content, the blood coursing throughout your site and keeping it alive. Drupal comes with several themes out-of-the-box, but the real treasure is hidden elsewhere.
Customizing Themes and Templates: The theme layer of Drupal is powered by the Twig templating engine – a safe and pristine way to customize your site’s output and page markup through views and patterns.
Extending Drupal with Modules
Contributed Modules
The most notable strength of Drupal is its huge ecosystem of contributed modules. These official Drupal modules are developed and maintained by the community, and they give your website additional functionality, such as an e-commerce system, social sharing, powerful search, reporting, and so on.
Custom Module Development
The contributed module ecosystem is huge. But at some point, you’re going to want functionality that’s not provided by the modules available. In those cases, to fill in the gaps, you can create custom modules to fit your unique architecture.
Performance and Scalability
Caching and Performance Optimization
Today’s high-speed digital world makes website performance essential, as a slow-loading page can cause inconvenience to users, a higher bounce rate and, what might be worse, a lower success rate for your website.
Scaling Drupal for High-Traffic Sites: As your web site grows in popularity and user numbers rise, scalability is an important issue. Drupal is tailored to be able to handle high-level traffic loads.
Multilingual and Accessibility Support
Multilingual Capabilities
These days, many businesses and organizations aim to provide resources that can reach people in all parts of the globe. Drupal’s multilingual features mean it is easy to create and manage websites in multiple languages, making the content people love more accessible to a larger number of people.
Accessibility Features
Inclusivity is another fundamental tenet of Drupal’s development, considering the ease of use and access for a person who has a disability or impairment when designing your website.
Drupal Community and Resources
Drupal Community and Support
One of the greatest strengths of a Drupal site is its community, which is international, productive, and collaborative. Over the history of Drupal, thousands of people have volunteered to make a contribution to the project.
Learning Resources and Documentation
All the necessary documentation and learning materials are at your fingertips. The official Drupal documentation serves as the ultimate guide for all users, ranging from beginners to advanced individuals, spanning from installation and configuration to module development to transforming websites.
Conclusion
Wasn’t that an adventure? In this in-depth tour, we’ve talked about Drupal’s core features, content management, theming, and module development. Hopefully, you’ve seen that Drupal is capable of just about any website and application requirement you can imagine.
FAQ:
Is Drupal suitable for small websites or blogs?
Indeed! Although most people associate Drupal with large enterprise websites, it works very well for small projects like a blog — or any other kind of small website.
How does Drupal compare to other popular CMSs like WordPress or Joomla?
Each CMS has its own strengths and weaknesses. Drupal is often chosen for its robustness and ability to handle heavy loads, while also being flexible and extensible.
Can Drupal be used for e-commerce websites?
Yes, Drupal has an excellent e-commerce ecosystem around the contributed modules Ubercart and Drupal Commerce, which provide everything you need for building online shops.
How secure is Drupal?
Security is a huge priority for the Drupal project. The Drupal security team is on the lookout for security vulnerabilities, and the community responds quickly whenever vulnerabilities are found to release security updates.
What kind of support and resources are available for Drupal users?
Drupal’s community is diverse and supportive. Through forums, issue queues, local user groups, and a strong content structure, you can find help fast, share your knowledge, and stay abreast of new releases and features in the Drupal environment.

0 notes
Photo

Join us on our new Free MySQL course today! In this course I will describe everything from scratch. First of all we will install and secure the MySQL server an our operating system or online server depending on your choice, and then we will go on with the journey and learn how to set up, secure, monitor, control, and execute different types commands to get whatever we want from our database server. Of course there are tools like workbench, phpMyAdmin, etc. that can help us perform some of the actions using graphical user interfaces and make the work a little bit easier in some cases. But in this course we want to leave all of those tools aside and deal with the MySQL server using the SQL language head-on. This way I will be sure that you can get whatever you need from your database server in the future, no Matter what the situation or how sophisticated the operation is. This course is presented to you by Arashtad.com. Arashtad is an IT company, providing design and development services, products, courses, online tools, affiliate programs, and other types of content. If you're interested in any of those, visit our home page at Arashtad.com and join us there and on other public platforms. #mysql #sql #mysqltutorial #mysqltutorialfullcourse #mysqltutorialforbeginners #mysqlfullcourse #mysqlworkbench #mysqlcommandline #learnmysql #mysqlphpmyadmin #mysqlfulltutorial #completemysqltutorial #mysqlbeginnertutorial #mysqlbeginnertoadvancedtutorialfullcourse #mariadb #mariadbserver #mysqlfreecourse #mariadbcoure #freefullcourse
0 notes
Text
Introduction of basics of Docker

Docker is the world’s leading software container platform.
Docker is a tool designed to make it easier to deploy and run applications by using containers. Container allows the developer to package up an application with all the parts it needs, such as libraries and other dependencies, and ship it all out as one package.
It provides the ability to run an application in an isolated environment called as container.
Why do we need Docker?
Before Docker, if we wanted to run a project on a different machine, we had to set up all the dependencies including libraries, configs, and services like databases or cache. It was okay until you are working on a single project. But what if you are doing parallel projects which require dependencies that cannot be installed and run simultaneously?
For example, if one of your projects requires SQL and another project requires MariaDB, you have to uninstall one to get started with the other, and that’s going to be a serious mess for you leaving your other project unusable.
Benefits of Docker
Build an app only once - An application inside a container can run on any system that has docker installed, so no need to build and configure an app multiple time.
Test - With Docker, you test your application inside a container and ship it inside a container.
Portability - Docker container can run on any platform. It can run on local system, Amazon EC2, Google could platform etc.
Version Control - Docker has an in-built version control system. Docker repository work like allows you to commit changes.
Isolation - With Docker, every application works in isolation in its own container & does not interfere with other app(s).
How docker works?
The daemon (server) receives the command from the docker client through CLI or rest API’s.
The Docker client and daemon can be present on the same host (machines) or different host.
Main components of Docker
DockerFile - A text file with instructions to build the image
Docker Image
Docker container
Docker registry
DockerFile - A text file with instructions to build an image.
Steps to create DockerFile:
Create a file named DockerFile
Add instructions in DockerFile
Build a DockerFile to create an image
Run the image to create a container
Docker Image - Docker images are templates used to create docker containers.
Image is a single file with all dependencies and libraries to run the program.
Images are stored in registries. (Docker Hub)
Docker Container - Containers are running instances of Docker Images.
A way to package an application with all necessary dependencies and configuration.
It can be easily shared.
Makes deployment easy and development efficient.
Docker Registry - A docker registry is a central repository for storing and distributing docker images.
A centralized location for storing container images
A central location where users can find container images
Image versioning
Docker Compose
Tool for defining & running multi-container docker applications
Use yaml file to configuration application services
Can start all services with a single command: docker-compose up
Can stop all services with a single command: docker-compose down
Steps to create a docker-compose file:
Install docker-compose
Create docker-compose file at any location on your system docker - compose.yml
Check the validity of the file by command docker-compose config
Run docker - compose.yml file by command docker-compose up -d
Bring down an application by command docker-compose down
Docker Volume
Volumes are the preferred mechanism for persisting data generated by and used by docker containers.
Use of volumes
Decoupling container from storage
Share volume among different containers
Attach volume to container
On deleting container volume does not delete
Docker commands
Docker version: Used to check installed version of docker.
Docker search: Used to search for specific images through the Docker hub.
Docker pull: Used to pull a specific image from the Docker Hub.
Docker run: Used to create a container from an image.
Docker ps: Used to list all the running containers in the background.
Docker stop: Used to stop a container using the container name or its id.
Docker restart: Used to restart the stopped container.
Docker kill: Used to stop the container immediately by killing its execution.
Docker exec: Used to access the container that is running.
Docker login: Used to log into your docker hub.
Docker commit: Used to create or save an image of the edited container on the local system.
Docker push: Used to push or upload a docker image on the repository or the docker hub.
Docker network: Used to know the details of the list of networks in the cluster.
Docker rmi: Used to free up some disk space.
Docker ps -a: Used to know the details of all the running, stopped, or exited containers.
Docker copy: Used to copy a file from docker to the local system.
Docker logs: Used to check the logs of all the docker containers with the corresponding contained id mentioned in the command.
Docker volume: Used to create a volume so that the docker container can use it to store data.
Docker logout: Used to log you out of the docker hub.
Conclusion
Docker is a powerful technology that allows the developer to create, package and deploy applications in containers.
It provides a consistent environment for development, testing and deployment, and it's compatible with any platform that supports docker.
By using docker, developers can focus on building a great application instead of worrying about infrastructure.
Credit – Sachin Auti
MetricsViews Pvt. Ltd.
MetricsViews specializes in building a solid DevOps strategy with cloud-native including AWS, GCP, Azure, Salesforce, and many more. We excel in microservice adoption, CI/CD, Orchestration, and Provisioning of Infrastructure - with Smart DevOps tools like Terraform, and CloudFormation on the cloud.
www.metricsviews.com
0 notes
Text
Easy TYPO3 installation: Manual & Composer methods!

TYPO3 is the most secure, fast and robust CMS that is powered by easy installation which makes it easy for anyone to create a website. Leading TYPO3 web hosting providers facilitate quick and straightforward TYPO3 installations, typically requiring less than five minutes to set up.
In this Step by step Tutorial We are looking into how to install TYPO3 Manually and Via Composer .
Let's Look How?
System Requirement for installing TYPO3
It's essential to ensure the proper prerequisites for CMS installation are in place.
This process primarily necessitates two key components: a web server and a database server.
Operating System : Linux, Windows or Mac, or cloud infrastructure
Web Server : Apache httpd, Nginx, Microsoft IIS, Caddy Server ,
Supported Browser : Chrome (latest) , Edge (latest) , Firefox (latest) , Safari (latest)
Composer Requirement : Composer >= 2.1
Database : MariaDB >= 10.2.7 <= 10.5.99 Microsoft SQL Server MySQL >= 5.7.9 <= 8.0.99 PostgreSQL SQLite
Hardware Requirement RAM >= 256 MB
PHP Version Support PHP >= 7.4.1 <= 8.1.99
How to Install Via Composer
Step 1 Download TYPO3 From Website
The first step involves obtaining TYPO3 from its official website. You can acquire your preferred TYPO3 version from there.
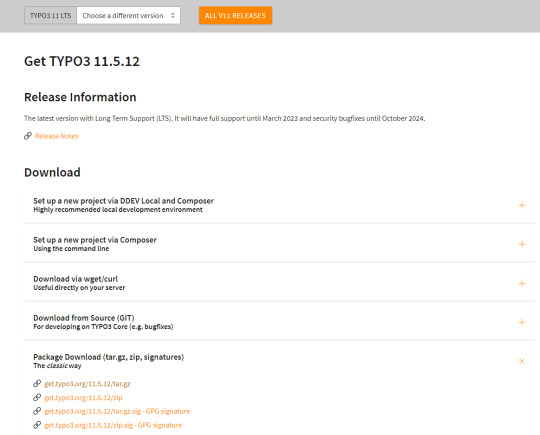
2. Configure the Installation Files
Following Steps can be followed to setup the installation file of TYPO3.Begin by extracting the TYPO3 Zip file that you downloaded from TYPO3's official website. This will create a folder on your system containing all the necessary files for TYPO3.
Next, transfer these items to the server's designated folder Further , it is critical to decide the installation location for TYPO3. If you intend to Access it through main domains , this means you will need to Upload TYPO3 Files directly to public_html/ directory of your account..
However, if you have a different setup in mind, the location may vary accordingly.
there two different ways to transfer your records first is Utilising an FTP or second way of directly through cpanel account.
3.Initiate the Installation Process
To begin the installation process, generate a file named 'FIRST_INSTALL' within the same directory where you've uploaded your TYPO3 files.
This serves as a security checkpoint that grants permission to proceed with the installation. You can create this file using FTP or utilise the File Manager in your cPanel account.
4.Verification of System Requirements
To access the TYPO3 installation wizard, visit
“ https://www.MY_INSTALL.com/typo3/install.php." This tool is designed to facilitate the TYPO3 installation process, which consists of five phases.
In the initial phase, the tool conducts a thorough examination of your system environment. If any issues arise as a result of system settings, you can utilize the troubleshooting function to address them. If no problems are detected, you can continue with the installation process.
5.Configuring TYPO3 Setup
For Configuring TYPO3 Setup You can follow this steps :
You'll integrate the MySQL database. Log in using the username 'root,' and note that no password is necessary when using the XAMPP installer.
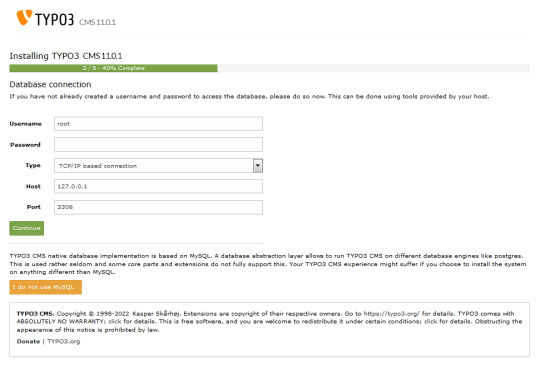
Next, you can either select an existing database or create a new one It's worth noting that you now have the option to use a different database implementation other than MySQL.
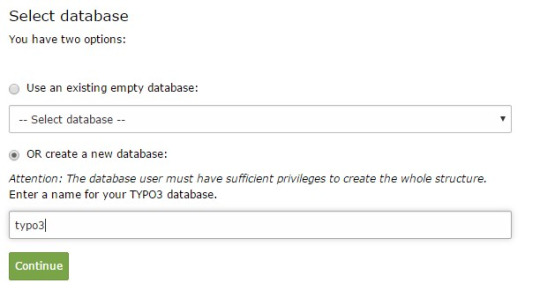
Next, you'll create an admin user for the TYPO3 backend. The password you set for this user will also be utilised for the install tool.
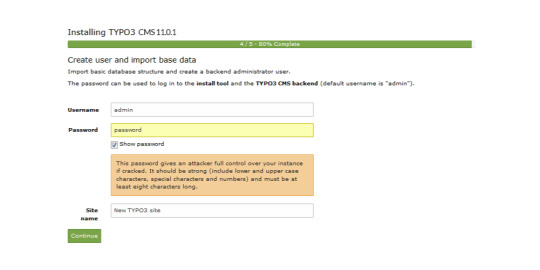
Now the installation itself is completed.
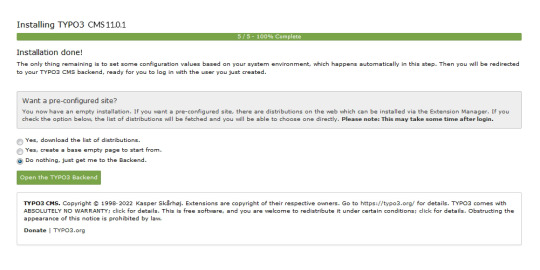
Lastly , the installation wizard finalises by automatically adjusting certain configurations to match your system environment.
However , You still have the option to choose whether TYPO3 will create an empty website or remain inactive temporarily.
By selecting 'Open the TYPO3 Backend,' you'll access the admin area, where you can log in using the account you just created.
Congratulations ! You have Completed and installed TYPO3 manually .
Install TYPO3 Via Composer Mode
For detailed instructions on installing TYPO3 using Composer, you can find a comprehensive step-by-step guide here: How to install TYPO3 - Manually & Via Composer
0 notes
Text
Install the federated engine in MariaDB
How to install the federated engine in MariaDB Check the installed engine to MariaDB show engines Engine |Support|Comment |Transactions|XA |Savepoints| ------------------+-------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------------+---+----------+ CSV |YES |Stores tables as CSV files |NO |NO |NO | MRG_MyISAM |YES |Collection of identical…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
How to install Blesta in HestiaCP LAMP stack
This video will cover installing Blesta in HestiaCP (Hestia Control Panel). The Blesta installation involves steps such as setting up the Hestia web server using LAMP stack (not covered in this video), creating a MySQL/ MariaDB database, and configuring the Blesta software. Here’s a general outline of the installation process as illustrated in the video above Prepare Your Linux Server: Blesta…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing AlmaLinux 9 on a Private Server

How to Install AlmaLinux 9 on a Private Server Step-by-Step Guide to Installing AlmaLinux 9 on a Private Server AlmaLinux 9 offers a powerful, stable, and open-source solution ideal for private servers. Follow this guide to install AlmaLinux 9 efficiently on your server. Need More Tech Help – Download the URBT News App Step 1: Prepare Your Server - Verify System Requirements: Ensure your server has at least 2 GB RAM, 20 GB disk space, and a 64-bit processor. - Backup Data: Backup existing data to prevent potential loss during installation. - Download AlmaLinux 9 ISO: Visit the AlmaLinux website and download the ISO file. Step 2: Create a Bootable USB Drive - Select a USB Drive: Use a USB drive with at least 8 GB of storage. - Create a Bootable Drive: - On Windows: Use Rufus. - On Linux: Use the dd command or Etcher. - Command Example: sudo dd if=/path/to/almalinux-9.iso of=/dev/sdX bs=4M status=progress && sync Replace /dev/sdX with your USB drive's path. Step 3: Boot Your Server from the USB Drive - Insert the USB Drive: Plug the bootable USB into your server. - Access BIOS/UEFI: Restart the server and press the key (e.g., F2, F10, DEL, or ESC) to enter BIOS/UEFI settings. - Set Boot Priority: Select the USB drive as the first boot device. - Save and Exit: Save changes and exit BIOS/UEFI. The server will boot from the USB drive. Step 4: Install AlmaLinux 9 - Select Language: Choose your preferred language and click Continue. - Configure Installation Destination: - Disk Selection: Choose the disk where you will install AlmaLinux. - Partitioning: Opt for automatic partitioning or manually configure partitions. - Choose Software: Select the Base Environment. Add additional software packages as needed. Step 5: Configure Network Settings - Enable Network Interface: Click Network & Hostname, enable your network interface, and configure it. - Set Hostname: Enter a hostname for your server (e.g., server.example.com). Step 6: Begin Installation - Set Root Password: Create a strong root password. - Create a User Account: Set up a non-root user with administrative privileges. - Start Installation: Click Begin Installation. The process may take a few minutes. Step 7: Post-Installation Configuration - Reboot Your Server: After installation, remove the USB drive and reboot the server. - First Boot Setup: - Log in as root or your newly created user. - Update the System: sudo dnf update -y - Configure the Firewall: - Enable and Start Firewall: sudo systemctl enable --now firewalld - Open Necessary Ports: sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=ssh sudo firewall-cmd --reload Step 8: Install Additional Software (Optional) - Set Up a Web Server: - For Apache: sudo dnf install httpd -y sudo systemctl enable --now httpd - For Nginx: sudo dnf install nginx -y sudo systemctl enable --now nginx - Install a Database Server: - For MariaDB: sudo dnf install mariadb-server -y sudo systemctl enable --now mariadb - For PostgreSQL: sudo dnf install postgresql-server -y sudo postgresql-setup --initdb sudo systemctl enable --now postgresql Step 9: Secure Your AlmaLinux Server - Disable Root SSH Login: - Edit SSH Configuration: sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config - Set PermitRootLogin no and Restart SSH: sudo systemctl restart sshd - Enable SELinux: Ensure SELinux remains enabled for enhanced security. Step 10: Verify Your Installation - Check Network Connectivity: Ensure your server connects to the internet and other networks. - Review System Logs: Inspect logs for errors or warnings: sudo journalctl -p 3 -xb Congratulations! You've successfully installed AlmaLinux 9 on your private server. Configure the server further to meet your specific needs, such as web hosting, database management, or other server-related tasks. Step-by-Step Guide to Installing AlmaLinux 9 on a Private Server Download the URBT News App from your App store. Apple / Andriod Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Where Can You Find a Qualified Mariadb ODBC Driver?
Introduction
If you are working with MariaDB databases, you may need to use ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) to connect to them from various applications. An ODBC driver acts as a mediator between the database and the application, enabling them to communicate effectively. Therefore, it is essential to find a qualified Mariadb ODBC driver to ensure seamless connectivity and performance. This article will guide you through the various sources where you can find a reliable Mariadb ODBC driver.
Understanding Mariadb ODBC Driver
What is Mariadb ODBC Driver?
Before discussing where to find a Mariadb ODBC driver, it is essential to understand what it is. MariaDB ODBC driver is a software program that facilitates the connection between an application and the MariaDB database through ODBC. ODBC provides a standardized interface for communication between the database and the application, making it possible to use different software programs to access the same database.
How Does Mariadb ODBC Driver Work?
The MariaDB ODBC driver acts as a translator between the database and the application, allowing them to exchange information in a format that they both understand. When an application sends a query to the database, the ODBC driver receives it and converts it into a format that the database can interpret. Similarly, when the database returns data to the application, the ODBC driver converts it into a format that the application can process.
Where to Find Mariadb ODBC Driver?
MariaDB Corporation
The first and most obvious place to find a Mariadb ODBC driver is the MariaDB Corporation. As the company behind the MariaDB database, they offer official ODBC drivers for various operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and Mac. You can download the drivers from their website, which includes detailed instructions for installation and configuration.
Third-Party Vendors
Several third-party vendors offer Mariadb ODBC drivers, such as Devart, Progress DataDirect, and Actual Technologies. These drivers may offer additional features and benefits that are not available in the official drivers, such as better performance or more comprehensive support. However, you should ensure that the drivers you choose are reliable and compatible with your operating system and version of the database.
Open-Source Drivers
If you prefer open-source software, you can also find Mariadb ODBC drivers on various open-source platforms, such as GitHub and SourceForge. These drivers are usually free to use, and you can modify the source code to suit your specific needs. However, you should ensure that the drivers you choose are well-maintained and supported by the community to avoid compatibility issues.
Choosing the Right Mariadb ODBC Driver
When choosing a Mariadb ODBC driver, you should consider the following factors:
Compatibility: Ensure that the driver is compatible with your operating system and version of the database.
Performance: Look for drivers that offer good performance and speed.
Features: Check if the driver offers additional features and benefits that may be useful for your specific use case.
Support: Ensure that the driver is well-maintained and has good support from the community or vendor.
Conclusion
Finding a qualified Mariadb ODBC driver is essential to ensure seamless connectivity and performance when working with MariaDB databases. You can find reliable drivers from various sources, such as the MariaDB Corporation, third-party vendors, and open-source platforms. When choosing a driver, consider factors such as compatibility, performance, features, and support.
0 notes
Link
1 note
·
View note
Text
For some reference on how I did it!
https://m.mediawiki.org/wiki/Manual:Installing_MediaWiki
The above was the main tutorial I used! The main parts for me was installing XAMPP, using Apache through the XAMPP console, and then separately using MariaDB *instead of* MySQL (which is in the XAMPP console). When creating the database in MariaDB, use the collation "utf8mb4_unicode_520_ci" instead.
https://m.mediawiki.org/wiki/Manual:Installing_MediaWiki_on_XAMPP
https://m.mediawiki.org/wiki/Manual:MariaDB
tutorial for XAMPP setup and ImageMagick [note that this uses XAMPP's MySQL, my process used MariaDB]:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=PoL_XxhsYRo
For APCu (which is related to caching and speeding up browsing), in XAMPP's php.ini file you'll want to make sure to have 'extension=apcu'. The below page was a big help on making sure you're using the right version, especially the top comment. that phpinfo() command part just literally make a text file with it, save as .php file through like notepad or notepad++, put it in your main folder for your wiki, open localhost to it
https://www.php.net/manual/en/book.apcu.php
Essentially when you get to the "installing the wiki" step, I tried to have ImageMagick and APCu ready and set up and showing that they're installed. I also looked into installing diff3 and File, but you do it after installation of your server when the LocalSettings.php has been created. Info is for some reason
https://m.mediawiki.org/wiki/Manual:Installing_MediaWiki_on_Windows_Server_2008_R2#GNU_diff3_Installation_.28Optional.29
This was a two-day project for me so don't fret if it takes a while to figure out. I hope though that this collection of links expedites the "googling around figuring out what the fuck anything is" stage.
There are many cool extensions you can do with MediaWiki and you can create a forum or a blog on it or just use it for whatever! I just think it feels so cool. Look around at other wikis to see how their CSS is done
MediaWiki:Common.css
https://m.mediawiki.org/wiki/Manual:CSS
https://en.touhouwiki.net/wiki/Touhou_Wiki
https://en.touhouwiki.net/wiki/MediaWiki:Common.css
https://wiki.puella-magi.net/Main_Page
https://wiki.puella-magi.net/MediaWiki:Common.css
YIPPEE I figured out how to host a WIKI on my COMPUTER with PHP and SQL!!!! I am gonna put so much world-building lore in this thing once I figure out some CSS
I can't say anything about the project but aaaaah I am. Excited. I have been wiggling this story concept in my head for like 4 years and am ready to spew them onto my computer much like raw unprocessed ore
#wiki#website#localhost#computer#php#sql#mysql#mariadb#xampp#mediawiki#Wikipedia#gnu#imagemagick#apcu#kassandra rambles#kassandra writes#css#open source
45 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
How To Install PHP 8.2 Apache Mariadb Phpmyadmin on Debian 12 Server
0 notes