#financial loan record
Text

Accounting and Audit
Blockchain's transparent and immutable ledger promises a trans formative shift in accounting practices. With blockchain, financial records become easily accessible for auditing purposes, enhancing compliance and operational efficiency.
Borrowing and Lending
Blockchain significantly enhances credit assessments and mitigates the risk of bad loans. By enabling secure sharing of verified customer data among banks, it streamlines processes like syndicated lending, reducing redundancy and accelerating transactions.
Trade Finance
The digitisation of trade finance through blockchain can replace outdated, paper-based systems. This modernisation enables faster, more secure, and transparent global transactions, fundamentally transforming traditional trade finance methods.
Trading and Settlements
Blockchain's decentralised framework is poised to revolutionise trading and settlements. By removing the need for central clearinghouses, blockchain technology facilitates quicker, more accurate transactions with reduced errors.
Fundraising
Blockchain introduces innovative fundraising options, including Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Security Token Offerings (STOs). These methods offer startups new ways to raise capital, expanding beyond traditional banking avenues.
Adopting blockchain across these banking functions can lead to a more efficient, transparent, and technologically advanced financial ecosystem.
#Accounting and Audit#Blockchain's transparent and immutable ledger promises a trans formative shift in accounting practices. With blockchain#financial records become easily accessible for auditing purposes#enhancing compliance and operational efficiency.#Borrowing and Lending#Blockchain significantly enhances credit assessments and mitigates the risk of bad loans. By enabling secure sharing of verified customer d#it streamlines processes like syndicated lending#reducing redundancy and accelerating transactions.#Trade Finance#The digitisation of trade finance through blockchain can replace outdated#paper-based systems. This modernisation enables faster#more secure#and transparent global transactions#fundamentally transforming traditional trade finance methods.#Trading and Settlements#Blockchain's decentralised framework is poised to revolutionise trading and settlements. By removing the need for central clearinghouses#blockchain technology facilitates quicker#more accurate transactions with reduced errors.#Fundraising#Blockchain introduces innovative fundraising options#including Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Security Token Offerings (STOs). These methods offer startups new ways to raise capital#expanding beyond traditional banking avenues.#Adopting blockchain across these banking functions can lead to a more efficient#transparent#and technologically advanced financial ecosystem.#for more details visit : https://smartncode.com/block-chain-development.html#blockchaintechnology#blockchain#blockchaininbanking#blockchainfinance
0 notes
Note
saw a meme basically going 'which hacker is gonna step up and wipe away all this student loan debt, morgages, etc.' and was curious as I have very little logistical knowledge of both! What stops you from going "hmmmm I think ill go into a banks records today and start going crazy" on a day to day basis?
people say this stuff all the time because somehow hacking is the one skill where it's expected of you that as soon as you know any of it you can do literally everything, when really that response of "why aren't they doing X instead of smaller hack/hack i vaguely disagree with/hack for money (TO SURVIVE)" is basically the same thing as going up to a random protestor on the street and asking them why they haven't taken over the white house yet.
all forms of resistance require patience and while i wish i could just sit down and when i get up from the computer again the world is perfect that just isn't how the world works. hacktivists (and hackers in general) have had massive positjve material impacts over the last decades and just because the specific thing you want them to do hasn't happened yet doesn't mean we don't want to do that.
and as for why loan forgiveness hacks aren't really a thing, financial hacks are extremely hard, at this point it's basically impossible to steal money from a bank you hack without having to hack a whole number of them, and to truly get rid of something like debt which is info there is tons of copies and backups of is a monumental task which requires massive amounts of stealth and access that no one person alone could pull off and is incredibly risky. computer crime alone is already one of the most harshly policed areas to do activism in and financial crimes would only make it worse and basically impossible not to end up in jail forever.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Accountant of Theed
Read on AO3
After all is said and done, someone needs to balance these books, and nobody actually told the accounting department how they paid for this new hyperdrive.
Mimi really hopes it's not a loan from the Hutts.
Disclaimer: I am not an accountant, but I work in an adjacent field (and have been considering getting a certification, but that's neither here nor there). While I did take some courses on it, I asked an Accounting Person to look over the excel sheet before I went forward with the rest of the fic to make sure it's internally consistent. Thank you to @gnomer-denois for confirming my balance on these works!
The reconciliation sheet does NOT follow contemporary guidelines in terms of format etc, but that is because it is:
In space! Standard practice differs from Modern United States or what have you.
Not the primary balance sheet, just the simplified version made to show to Queen Amidala.
If you'd prefer to view the Excel sheet in a more easily navigable form, there is a google drive link available. This is also your best option if using a screen reader.
-----------------------------------------
Theed is safe. They are rebuilding. There is even financial support, aid, from the Republic.
It comes with strings attached. Oversight. Auditors.
Wouldn’t want Naboo to misuse funding after that nasty mistake with the Trade Federation, right? Sure, Naboo wasn’t the one at fault, but one can never be too careful...
Mimi, as an accountant for the government of Naboo, does not in fact want to commit fraud, or enable corruption, but the rolling audits do feel a little like the Republic is punishing them for getting invaded.
“Hey, boss?”
That tone. Mimi does not like that tone. “Please tell me it’s not another unauthorized purchase with a missing receipt. Which account did they pull from this time?”
“Um... we don’t know?”
Mimi gives them a moment. No elaboration is given.
“You don’t know?”
“We don’t know,” the younger employee repeats.
“What do you mean?” Mimi asks. “People charge things to accounts or cards. They forget to submit receipts. We hunt them down for receipts, and make sure nobody is skimming off the top. That’s how it goes. Unless this is a purchase on a personal and we need to reimburse—”
“Um, maybe?”
“In which—what? That’s just... okay. There’s a process for reimbursements. You aren’t following it, which means... what? What do you mean, you don’t know? Did they use cash, or pull from an account?”
The younger employee looks down at their datapad. Looks back up at her. Looks baffled and a little scared. “Um, it’s... we still don’t have a receipt, but we also don’t know where the money for it came from? But nobody’s put in a reimbursement request and I can’t imagine anyone on the mission had those funds on them, not even the Queen herself.”
“The money for what?”
“Um. It sort of just... showed up?”
“So, it’s some kind of gift?” Mimi presses.
“Too big,” the younger mumbles, refusing to meet her eyes. “It would have to be disclosed.”
“I am giving you five seconds—”
“It’s a hyperdrive!” they yelp.
“...Explain.”
“One of the mechanics was looking over the Royal Cruiser, and found that there was unrecorded repair work to the hyperdrive. The ship took enough damage during the escape that he wasn’t surprised, but then he noticed that it was from an earlier run of the part, and when he checked, the serial number was completely wrong. The hyperdrive was completely replaced.”
Mimi closes her eyes and takes a breath. “The mechanic doesn’t know?”
“He said there’s nothing in the records that matches it at all, and it’s a big enough part that there’s no way it would just slip through the cracks, not when it’s that expensive and going on the Royal Cruiser.”
“So,” Mimi says, “we have a part worth almost as much as the rest of the cruiser combined, that just... came out of nowhere, and nobody claiming for reimbursement.”
“Yes, ma’am. That’s what it looks like.”
Mimi has no interest in fraud.
“Find out who was piloting when Queen Amidala escaped, and see if they have any answers,” Mimi tells them. “If we can keep it to just the hangar staff without drawing in the Royal Retinue, it’ll be easier on all of us.”
“Here’s hoping, ma’am.”
(Continue on AO3)
#phoenix files#star wars#the phantom menace#original characters#naboo#accounting#Padme Amidala#Sabe#Tsabin#Anakin Skywalker#Obi-Wan Kenobi#Shmi does not appear but this is like half about her. and Qui-Gon. and Watto.#so#Shmi Skywalker#Qui Gon Jinn#Watto#receipt reconciliation
219 notes
·
View notes
Note
So odd to see people deny that trans mascs experience physical violence?? I have no legal record of how I was homeless because I couldn't go to any shelters. They are sex segregated in my city and I was warned by my social worker and shelter employees (both trying to do me a genuine favor) that I'd be beaten for being trans masc (I'm butch not even a man) and later when I asked a former admin the most she could muster was "...they'd try to protect you. But they wouldn't be able to stop anyone." And this was explicitly because I'm trans masc, butch, and can't pass as a gender conforming woman anymore (medical transition). I was direct about being AFAB and butch with everyone I talked to. I was still warned. (And on the systemic oppression end of things - bc I never went to a shelter I was/am intelligible for rapid rehousing programs, specific benefits programs, social and financial support programs, and student loan benefits. Just spent a few weeks in a car until my situation improved.)
Yeah, this aligns with what I've read about transmasc experiences with sex-segregated shelters. Both men and women's shelters can be unsafe for us to be in (almost like we're trans or something....)
264 notes
·
View notes
Text
America owes its independence to Haym Salomon, a Sephardic Jewish Patriot
youtube
A Jewish American Hero
by Yosef Kaufmann
October 17, 1781. An eerie silence takes hold over the battlefield outside Yorktown, Virginia. After weeks of non-stop artillery shells and rifle fire, the rhythmic pounding of a drum is all that is heard. Through the wispy smoke that floats above the battlefield, a British officer can be seen waving a white flag. General Cornwallis has surrendered Yorktown, ending the last major battle of the American Revolution. The surrender of Yorktown and the nearly 8,000 British troops convinced the British Parliament to start negotiating an end to the war. On September 3, 1783, the treaty of Paris was signed. The war was over.
If not for Haym Salomon, however, the decisive victory at Yorktown never would have happened.
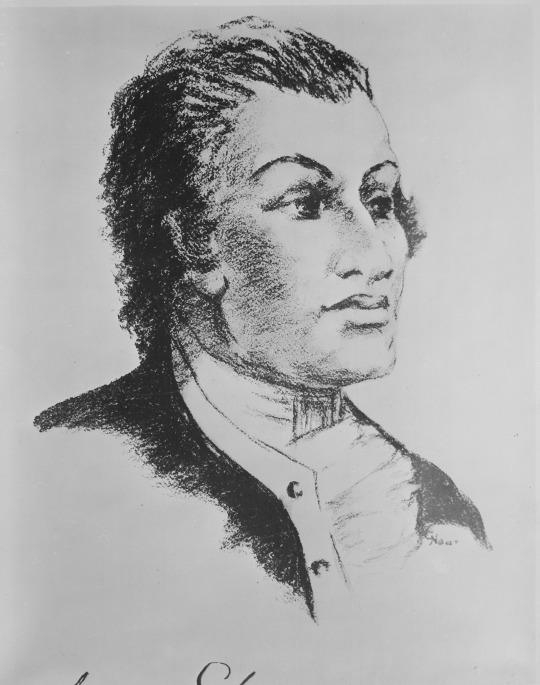

Haym Salomon was born in Leszno, Poland, in 1740. In 1770, he was forced to leave Poland for London as a result of the Partition of Poland. Five years later, he left London for New York City, where he quickly established himself as a broker for international merchants.
Sympathetic to the Patriot cause, Haym joined the New York branch of the Sons of Liberty, a secret society that did what it could to undermine British interests in the colonies. In 1776, he was arrested by the British and charged with being a spy. He was pardoned on condition that he spend 18 months on a British ship serving as a translator for the Hessian mercenaries, as he was fluent in Polish, French, German, Russian, Spanish and Italian. During those 18 months, Haym used his position to help countless American prisoners escape. He also convinced many Hessian soldiers to abandon the British and join the American forces.
In 1778, he was arrested again and sentenced to death for his involvement in a plot to burn the British Royal fleet in the New York Harbour. He was sent to Provost to await execution, but he managed to bribe a guard and escape under the cover of darkness.
He fled New York, which was under the control of the British army, and moved to Philadelphia, the capital of the Revolution.
He borrowed money and started a business as a dealer of bills of exchange. His office was located near a coffee house frequented by the command of the American forces. He also became the agent to the French consul and the paymaster for the French forces in North America. Here he became friendly with Robert Morris, the newly appointed Superintendent of Finance for the 13 colonies. Records show that between 1781 and 1784, through both fundraising and personal loans, he was responsible for financing George Washington over $650,000, today worth approximately over $13 million.
By 1781, the American congress was practically broke. The huge cost of financing the war effort had taken its toll. In September of that year, George Washington decided to march on Yorktown to engage General Cornwallis. A huge French fleet was on its way from the West Indies under the command of Comte De Grasse. The fleet would only be able to stay until late October, so Washington was facing immense pressure to lead an attack on Yorktown before then.
After marching through Pennsylvania, with little in the way of food and supplies, Washington’s troops were on the verge of mutiny. They demanded a full month's pay in coins, not congressional paper money which was virtually worthless, or they would not continue their march. Washington wrote to Robert Morris saying he would need $20,000 to finance the campaign. Morris responded that there was simply no money or even credit left. Washington simply wrote, “Send for Haym Salomon.” Within days, Haym Salomon had raised the $20,000 needed for what proved to be the decisive victory of the Revolution.
Haym’s chessed continued after the war. Whenever he met someone who he felt had sacrificed during the war and needed financial assistance, he didn’t hesitate to do whatever he could to help.
He was also heavily involved in the Jewish community. He was a member of Congregation Mikveh Yisroel in Philadelphia, the fourth oldest synagogue in America, and he was responsible for the majority of the funds used to build the shul’s main building.
He also served as the treasurer to the Society for the Relief of Destitute Strangers, the first Jewish charitable organization in Philadelphia.
On January 8, 1785, Haym died suddenly at the age of 44. Due to the fact the government owed him hundreds of thousands of dollars, his family was left penniless.
His obituary in the Independent Gazetteer read:
Thursday, last, expired, after a lingering illness, Mr. Haym Salomon, an eminent broker of this city, was a native of Poland, and of the Hebrew nation. He was remarkable for his skill and integrity in his profession, and for his generous and humane deportment. His remains were yesterday deposited in the burial ground of the synagogue of this city.
Although there is little proof, many believe that when designing the American Great Seal, George Washington asked Salomon what he wanted as compensation for his generosity during the war. Salomon responded “I want nothing for myself, rather something for my people.” It is for this reason that the 13 stars are arranged in the shape of the Star of David.
#jumblr#haym salomon#where is his musical?#jewish history#4th of july#independence day#american history#american war of independence#american revolution#jewish diaspora in america#Youtube#NOTE: I report and block antisemites. Any antisemites who comment on this post I will report and block you. You have been warned.
155 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Best News of Last Year
1. Belgium approves four-day week and gives employees the right to ignore their bosses after work

Workers in Belgium will soon be able to choose a four-day week under a series of labour market reforms announced on Tuesday.
The reform package agreed by the country's multi-party coalition government will also give workers the right to turn off work devices and ignore work-related messages after hours without fear of reprisal.
"We have experienced two difficult years. With this agreement, we set a beacon for an economy that is more innovative, sustainable and digital. The aim is to be able to make people and businesses stronger," Belgian prime minister Alexander de Croo told a press conference announcing the reform package.
2. Spain makes it a crime for pro-lifers to harass people outside abortion clinics

Spain has criminalized the harassment or intimidation of women going for an abortion under new legislation approved on Wednesday by the Senate. The move, which involved changes to the penal code, means anti-abortion activists who try to convince women not to terminate their pregnancies could face up to a year behind bars.
3. House passes bill to federally decriminalize marijuana

The House has voted with a slim bipartisan majority to federally decriminalize marijuana. The vote was 220 to 204.
The bill, sponsored by Democratic Rep. Jerry Nadler of New York, will prevent federal agencies from denying federal workers security clearances for cannabis use, and will allow the Veterans’ Administration to recommend medical marijuana to veterans living with posttraumatic stress disorder.
The bill also expunges the record of people convicted of non-violent cannabis offenses, which House Majority Leader Steny Hoyer said, “can haunt people of color and impact the trajectory of their lives and career indefinitely.”
4. France makes birth control free for all women under 25

The scheme, which could benefit three million women, covers the pill, IUDs, contraceptive patches and other methods composed of steroid hormones.
Contraception for minors was already free in France. Several European countries, including Belgium, Germany, the Netherlands and Norway, make contraception free for teens.
5. The 1st fully hydrogen-powered passenger train service is now running in Germany. The only emissions are steam & condensed water.

Five of the trains started running in August. Another nine will be added in the coming months to replace 15 diesel trains on the regional route. Alstom says the Coradia iLint has a range of 1,000 kilometers, meaning that it can run all day on the line using a single tank of hydrogen. A hydrogen filling station has been set up on the route between Cuxhaven, Bremerhaven, Bremervörde and Buxtehude.
6. Princeton will cover all tuition costs for most families making under $100,000 a year, after getting rid of student loans

In September, the New Jersey Ivy League school announced it would be expanding its financial aid program to offer free tuition, including room and board, for most families whose annual income is under $100,000 a year. Previously, the same benefit was offered to families making under $65,000 a year. This new income limit will take effect for all undergraduates starting in the fall of 2023.
Princeton was also the first school in the US to eliminate student loans from its financial aid packages.
7. Humpback whales no longer listed as endangered after major recovery

Humpback whales will be removed from Australia's threatened-species list, after the government's independent scientific panel on threatened species deemed the mammals had made a major recovery. Humpback whales will no longer be considered an endangered or vulnerable species.
Climate change and fishing still pose threats to their long-term health.
Some other uplifting news from last year:
A Cancer Trial’s Unexpected Result: Remission in Every Patient
California 100 percent powered by renewables for first time
Israel formally bans LGBTQ conversion therapy
Tokyo Passes Law to Recognize Same-Sex Partnerships
First 100,000 KG Removed From the Great Pacific Garbage Patch
As we ring in the New Year let’s remember to focus on the good news. May this be a year of even more kindness and generosity. Wishing everyone a happy and healthy 2023!
Thank you for following and supporting this g this newsletter
Buy me a coffee ❤️
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Cohost sucks, too (but not for the reasons that one user said)
So, you may recall a person on tumblr saying that Cohost sucks, which accused a transfem on the cohost team of predatory behavior. That was transmisogynistic bullshit, and was blatantly untrue.
But cohost does suck. Just for reasons unrelated to that.
Listing everything loosely in an order of “weird and sort of annoying” to “holy fuck”:
Tag capitalization is determined by how the first person who used the tag capitalized it
You have to personally email support and wait for them to get back to you if you want to delete your account
They call themselves a “not for profit” or “non profit”, despite being registered as a for profit LLC
There is only one moderator for this site of 30k+ users, which means reports aren’t responded to for weeks at a time
Staff and the userbase have a very odd parasocial relationship. The staff chronically overshares, call users their ‘friends’, and have gotten mad at users for reporting too many things on weekends, after hours, or holidays (with the subtext being that you should not expect them to do anything after hours). They even publicly post about how they are worried about paying rent because of the site’s financial situation, which is frankly disgusting. Especially when you see people in the comments barely able to scrape up the $5 USD to give them for the subscription service.
A member of staff publicly bragged about how Cloudflare forgot to bill them for hosting, which is not only wildly unprofessional, but could likely get them sued. (And Cloudflare could, at any time, ask them for the money they owe, for the record.)
Staff say that they want to be transparent with financials, but are incredibly inconsistent about financial updates
The platform is losing $10k-40k USD each month
Meanwhile, staff currently pays themselves $94k USD a year, per person. Sure, that’s not as much as the average person with their job title… but Cohost is losing tens of thousands of dollars each and every month, so that doesn’t really apply.
On top of the previous two points, staff doesn’t accept volunteers, and they’ve consistently implemented features that make no difference to the financials of the company
TL;DR:
The cohost staff are tech people who wanted to do a startup, got a loan from a rich friend, and is doing nothing to make the site sustainable. Meanwhile, they’re paying themselves almost $100k USD a year while still guilt-tripping their dirt-poor, largely queer userbase.
It sucks, because I really believe Cohost could succeed. You know what, no — I know Cohost could succeed. Between the Elon Musk-ification of Twitter (who has deemed Tweeting “I hate trans people” fine, but automatically blocks people from Tweeting “I hate cis people” for hate speech), and the owner of tumblr going mask-off transphobic Zionist… Right now, maybe more than ever, there is a serious niche of ‘social media for queer fandom nerds’, just waiting to be filled! And on the surface, Cohost is perfect!
And I like everything about Cohost… except for how it’s being managed. I want to see it succeed, because it could be amazing, if the people behind it just made better decisions. But, ultimately, I do not trust the people running Cohost to help it realize its potential.
Alas, it seems this isn’t the tumblr alternative we are looking for.
#cohost#tumblr#tumblr alternative#long post#azure does a thing#this one’s been cooking for a lil while#hellsite tag
127 notes
·
View notes
Text

Nobody
* * * *
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
August 2, 2024
Heather Cox Richardson
Aug 03, 2024
Today, Aaron C. Davis and Carol D. Leonnig of the Washington Post reported that there is reason to believe that when Trump’s 2016 campaign was running low on funds, Trump accepted a $10 million injection of cash from Egypt’s authoritarian leader Abdel Fatah al-Sisi. It is against the law to accept direct or indirect financial support from foreign nationals or foreign governments for a political campaign in the United States.
In early 2017, CIA officials told Justice Department officials that a confidential informant had told them of such a cash exchange, and those officials handed the matter off to Robert Mueller, the special counsel who was already looking at the links between the 2016 Trump campaign and Russian operatives. FBI agents noted that on September 16, Trump had met with Sisi when the Egyptian leader was at the U.N. General Assembly in New York City.
After the meeting, Trump broke with U.S. policy to praise Sisi, calling him a “fantastic guy.”
Trump’s campaign had been dogged with a lack of funds, and his advisers had begged him to put some of his own money into it. He refused until October 28, when he loaned the campaign $10 million.
An FBI investigation took years to get records, but Davis and Leonnig reported that in 2019 the FBI learned of a key withdrawal from an Egypt bank. In January 2017, five days before Trump took office, an organization linked to Egypt’s intelligence service asked a manager at a branch of the state-run National Bank of Egypt to “kindly withdraw” $9,998,000 in U.S. currency. The bundles of $100 bills filled two bags and weighed more than 200 pounds.
Once in office, Trump embraced Sisi and, in a reversal of U.S. policy, invited him to be one of his first guests at the White House. “I just want to let everybody know, in case there was any doubt, that we are very much behind President al-Sissi,” Trump said.
Mueller had gotten that far in pursuit of the connection between Trump and Sisi when he was winding down his investigation of Russian interference in the 2016 election. He handed the Egypt investigation off to the U.S. attorney’s office in Washington, D C., where it appears then–attorney general William Barr killed it.
Today, Brian Schwartz of CNBC reported that Elon Musk and other tech executives are putting their money behind a social media ad campaign for Trump and Vance, and are creating targeted ads in swing states by collecting information about voters under false pretenses. According to Schwartz, their America PAC, or political action committee, says it helps viewers register to vote. And, indeed, the ads direct would-be voters in nonswing states to voter registration sites.
But people responding to the ad in swing states are not sent to registration sites. Instead, they are presented with “a highly detailed personal information form [and] prompted to enter their address, cellphone number and age,” handing over “priceless personal data to a political operation” that can then create ads aimed at that person’s demographic and target them personally in door-to-door campaigns. After getting the information, the site simply says, “Thank you,” without directing the viewer toward a registration site.
Forbes estimates Musk’s wealth at more than $235 billion.
In June the Trump Organization announced a $500 million deal with Saudi real estate developer Dar Global to build a Trump International hotel in Oman.
In January 2011, when he was director of the FBI, Robert Mueller gave a speech to the Citizens Crime Commission of New York. He explained that globalization and modern technology had changed the nature of organized crime. Rather than being regional networks with a clear structure, he said, organized crime had become international, fluid, and sophisticated and had multibillion-dollar stakes. Its operators were cross-pollinating across countries, religions, and political affiliations, sharing only their greed. They did not care about ideology; they cared about money. They would do anything for a price.
These criminals “may be former members of nation-state governments, security services, or the military,” he said. “They are capitalists and entrepreneurs. But they are also master criminals who move easily between the licit and illicit worlds. And in some cases, these organizations are as forward-leaning as Fortune 500 companies.”
In order to corner international markets, Mueller explained, these criminal enterprises "may infiltrate our businesses. They may provide logistical support to hostile foreign powers. They may try to manipulate those at the highest levels of government. Indeed, these so-called 'iron triangles' of organized criminals, corrupt government officials, and business leaders pose a significant national security threat."
In a new book called Autocracy, Inc.: The Dictators Who Want to Run the World, journalist Anne Applebaum carries that story forward into the present, examining how today’s autocrats work together to undermine democracy. She says that “the language of the democratic world, meaning rights, laws, rule of law, justice, accountability, [and] transparency…[is] harmful to them,” especially as those are the words that their internal opposition uses. “And so they need to undermine the people who use it and, if they can, discredit it.”
Those people, Applebaum says, “believe they are owed power, they deserve power.” When they lose elections, they “come back in a second term and say, right, this time, I'm not going to make that mistake again, and…then change their electoral system, or…change the constitution, change the judicial system, in order to make sure that they never lose.”
Almost exactly a year ago, on August 1, 2023, a grand jury in Washington, D.C., indicted former president Donald J. Trump for conspiring to defraud the United States, conspiring to disenfranchise voters, and conspiring and attempting to obstruct an official proceeding. The charges stemmed from Trump’s attempt to overturn the results of the 2020 election. A grand jury is made up of 23 ordinary citizens who weigh evidence of criminal activity and produce an indictment if 12 or more of them vote in favor.
The grand jury indicted Trump for “conspiracy to defraud the United States by using dishonesty, fraud, and deceit to impair, obstruct, and defeat the lawful federal government function by which the results of the presidential election are collected, counted, and certified by the government”; “conspiracy to corruptly obstruct and impede the January 6 congressional proceeding at which the collected results of the presidential election are counted and certified”; and “conspiracy against the right to vote and to have one’s vote counted.”
“Each of these conspiracies,” the indictment reads, “targeted a bedrock function of the United States federal government: the nation’s process of collecting, counting, and certifying the results of the presidential election.” “This federal government function…is foundational to the United States’ democratic process, and until 2021, had operated in a peaceful and orderly manner for more than 130 years.”
The case of the United States of America v. Donald J. Trump was randomly assigned to Judge Tanya S. Chutkan, who was appointed by President Obama in 2014 and confirmed 95–0 in the Senate. Trump pleaded not guilty on August 3, after which his lawyers repeatedly delayed their pretrial motions until, on December 7, Trump asked the Washington, D.C., Circuit Court of Appeals to decide whether he was immune from prosecution. Chutkan had to put off her initial trial date of March 4, 2024, and said she would not reschedule until the court decided the question of Trump’s immunity.
In February the appeals court decided he was not immune. Trump appealed to the Supreme Court, which waited until July 1, 2024, to decide that Trump enjoys broad immunity from prosecution for crimes committed as part of his official acts. Today the Washington, D.C., Circuit Court of Appeals sent the case back to Chutkan, almost exactly a year after it was first brought.
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#WAPO#bribery#Letters From An American#Heather Cox Richardson#corrupt SCOTUS#Chutkan#certification of the presidential election#voting rights#disenfranchising voters#organized crime
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
On Wednesday, Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions (HELP) Chair Bernie Sanders (I-Vermont) and Rep. Pramila Jayapal (D-Washington) reintroduced a proposal to make higher education free at public schools for most Americans — and pay for it by taxing Wall Street.
The College for All Act of 2023 would massively change the higher education landscape in the U.S., taking a step toward Sanders’s long-standing goal of making public college free for all. It would make community college and public vocational schools tuition-free for all students, while making any public college and university free for students from single-parent households making less than $125,000 or couples making less than $250,000 — or, the vast majority of families in the U.S.
The bill would increase federal funding to make tuition free for most students at universities that serve non-white groups, such as Historically Black Colleges and Universities (HBCUs). It would also double the maximum award to Pell Grant recipients at public or nonprofit private colleges from $7,395 to $14,790.
If passed, the lawmakers say their bill would be the biggest expansion of access to higher education since 1965, when President Lyndon B. Johnson signed the Higher Education Act, a bill that would massively increase access to college in the ensuing decades. The proposal would not only increase college access, but also help to tackle the student debt crisis.
“Today, this country tells young people to get the best education they can, and then saddles them for decades with crushing student loan debt. To my mind, that does not make any sense whatsoever,” Sanders said. “In the 21st century, a free public education system that goes from kindergarten through high school is no longer good enough. The time is long overdue to make public colleges and universities tuition-free and debt-free for working families.”
Debt activists expressed support for the bill. “This is the only real solution to the student debt crisis: eliminate tuition and debt by fully funding public colleges and universities,” the Debt Collective wrote on Wednesday. “It’s time for your member of Congress to put up or shut up. Solve the root cause and eliminate tuition and debt.”
These initiatives would be paid for by several new taxes on Wall Street, found in a separate bill reintroduced by Sanders and Rep. Barbara Lee (D-California) on Wednesday. The Tax on Wall Street Speculation would enact a 0.5% tax on stock trades, a 0.1% tax on bonds and a 0.005% tax on trades on derivatives and other types of assets.
The tax would primarily affect the most frequent, and often the wealthiest, traders and would be less than a typical fee for pension management for working class investors, the lawmakers say. It would raise up to $220 billion in the first year of enactment, and over $2.4 trillion over a decade. The proposal has the support of dozens of progressive organizations as well as a large swath of economists.
“Let us never forget: Back in 2008, middle class taxpayers bailed out Wall Street speculators whose greed, recklessness and illegal behavior caused millions of Americans to lose their jobs, homes, life savings, and ability to send their kids to college,” said Sanders. “Now that giant financial institutions are back to making record-breaking profits while millions of Americans struggle to pay rent and feed their families, it is Wall Street’s turn to rebuild the middle class by paying a modest financial transactions tax.”
#us politics#news#truthout#sen. bernie sanders#progressives#progressivism#Democrats#senate health education labor and pensions committee#College for All Act of 2023#tax Wall Street#tax the rich#tax the 1%#tax the wealthy#college for all#student debt#student loan debt#tuition-free college#Historically Black Colleges and Universities#pell grants#Higher Education Act#Rep. Barbara Lee#rep. pramila jayapal#2023
466 notes
·
View notes
Text
Watcher's Expenses
I didn't major in accounting: I took three classes and it grinded my brain to a fine powder. However, after graduating with a business admin degree, being a former eager fan of their videos, and from a cursory glance over their socials, there's a lot to consider in their spending behavior that really could start racking up costs. Some of these things we've already noticed, but there are other things I'd like to highlight, and I'll try to break it down into the different categories of accounting expenses (if I get something wrong, let me know. I was more concentrated in marketing 🤷♀️). I'm not going to hypothesize numbers either, as that would take out more time than I'm willing to afford-- you can assume how much everything costs. Anyways, here's my attempt at being a layman forensic accountant:
Note: All of this is assuming they're operating above board and not engaging in any illegal practices such as money laundering, tax evasion, not paying rent, etc.
Operating Expenses
Payroll: 25+ staff salaries and insurance
Overhead Expenses
CEO/founder salaries
Office space leasing or rent (In L.A, one of the most expensive cities in the US)
Utilities (water, electricity, heating, sanitation, etc.)
Insurance
Advertising Costs
Telephone & Internet service
Cloud Storage or mainframe
Office equipment (furniture, computers, printers, etc.)
Office supplies (paper, pens, printer ink, etc.)
Marketing costs (Social media marketing on Instagram, Youtube, SEO for search engines, Twitter, etc. Designing merchandise and posters, art, etc. )
Human Resources (not sure how equipped they are)
Accounting fees
Property taxes
Legal fees
Licensing fees
Website maintenance (For Watchertv.com, Watcherstuff.com, & Watcherentertainment.com)
Expenses regarding merchandising (whoever they contract or outsource for that)
Inventory costs
Potentially maintenance of company vehicles
Subsequent gas mileage for road trips
Depreciation (pertains to tangible assets like buildings and equipment)
Amortization (intangible assets such as patents and trademarks)
Overhead Travel and Entertainment Costs (I think one of the biggest culprits, evident in their videos and posts)
The travel expenses (flights, train trips, rental cars, etc. For main team and scouts)
Hotel expenses for 7-8 people at least, or potentially more
Breakfasts, lunches and dinners with the crew (whether that's fully on their dime or not, I don't know; Ryan stated they like to cover that for the most part)
Recreational activities (vacation destinations, amusement parks, sporting activities etc.)
The location fees
Extraneous Overhead costs (not sure exactly where these fall under, but another culprit, evident in videos and posts)
Paying for guest appearances
Expensive filming & recording equipment (Cameras, sound equipment, editing software subscriptions, etc.)
The overelaborate sets for Ghost files, Mystery Files, Puppet History, Podcasts etc. (Set dressing: Vintage memorabilia, antiquated tech, vintage furniture, props, etc.)
Kitchen & Cooking supplies/equipment
Office food supply; expensive food and drink purchases for videos
Novelty items or miscellaneous purchases (ex. Ghost hunting equipment, outfits, toys, etc.)
Non-Operating Expenses
These are those expenses that cannot be linked back to operating revenue. One of the most common examples of non-operating expenses is interest expense. This is because while interest is the cost of borrowing money from a creditor or a bank, they are not generating any operating income. This makes interest payments a part of non-operating expenses.
Financial Expenses
Potential loan payments, borrowing from creditors or lenders, bank loans, etc.
Variable Expenses
Hiring a large amount of freelancers, overtime expenditure, commissions, etc.
PR consultations (Not sure if they had this before the scandal)
Extraordinary Expenses
Expenses incurred outside your company’s regular business activities and during a large one-time event or transactions. For example, selling land, disposal of a significant asset, laying off of your employees, unexpected machine repairing or replacement, etc.
Accrued Expenses
When your business has incurred an expense but not yet paid for it.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(If there's anything else I'm missing, please feel free to add or correct things)
To a novice or a young entrepreneur, this can be very intimidating if you don't have the education or the support to manage it properly. I know it intimidates the hell out of me and I'm still having to fill in the gaps (again, if I've mislabeled or gotten anything wrong here, please let me know). For the artistic or creative entrepreneur, it can be even harder to reconcile the extent of your creative passions with your ability to operate and scale your business at a sustainable rate. That can lead to irresponsible, selfish, and impulsive decisions that could irreparably harm your brand, which is a whole other beast of its own.
My guess at this point is that their overhead and operation expenses are woefully mismanaged; they've made way too many extraneous purchases, and that they had too much confidence in their audience of formerly 2.93 million to make up for the expenses they failed to cover.
It almost seems as if their internal logic was, "If we make more money, we can keep living the expensive lifestyle that we want and make whatever we want without anyone telling us we can't, and we want to do it NOW, sooner rather than later because we don't want wait and compromise our vision." But as you can see, the reality of fulfilling those ambitions is already compromised by the responsibility of running a business.
And I wrote this in another post here, but I'll state it again: Running a business means you need to be educated on how a business can successfully and efficiently operate. Accounting, marketing, social media marketing, public relations, production, etc; these resources and internet of things is available and at your disposal. If they had invested more time in educating themselves on those aspects and not made this decision based on artistic passion (and/or greed), they would have not gotten the response they got.
Being a graphic designer, I know the creative/passionate side of things but I also got a degree/got educated in business because I wanted to understand how to start a company and run it successfully. If they’re having trouble handling the responsibility of doing that, managing production costs, managing overhead expenses, and especially with compensating their 25+ employees, then they should hire professionals that are sympathetic to their creative interests, but have the education and experience to reign in bad decisions like these.
Anyways, thanks for coming to my TedTalk. What a shitshow this has been.

#watcher#watcher entertainment#ryan bergara#shane madej#steven lim#watcher tv#watchergate#accounting
63 notes
·
View notes
Text



Study of Elite College Admissions Data Suggests Being Very Rich Is Its Own Qualification
By Aatish Bhatia, Claire Cain Miller and Josh Katz July 24, 2023 (full text under the cut)
Elite colleges have long been filled with the children of the richest families: At Ivy League schools, one in six students has parents in the top 1 percent.

A large new study, released Monday, shows that it has not been because these children had more impressive grades on average or took harder classes. They tended to have higher SAT scores and finely honed résumés, and applied at a higher rate — but they were overrepresented even after accounting for those things. For applicants with the same SAT or ACT score, children from families in the top 1 percent were 34 percent more likely to be admitted than the average applicant, and those from the top 0.1 percent were more than twice as likely to get in.
The study — by Opportunity Insights, a group of economists based at Harvard who study inequality — quantifies for the first time the extent to which being very rich is its own qualification in selective college admissions.
The analysis is based on federal records of college attendance and parental income taxes for nearly all college students from 1999 to 2015, and standardized test scores from 2001 to 2015. It focuses on the eight Ivy League universities, as well as Stanford, Duke, M.I.T. and the University of Chicago. It adds an extraordinary new data set: the detailed, anonymized internal admissions assessments of at least three of the 12 colleges, covering half a million applicants. (The researchers did not name the colleges that shared data or specify how many did because they promised them anonymity.)
The new data shows that among students with the same test scores, the colleges gave preference to the children of alumni and to recruited athletes, and gave children from private schools higher nonacademic ratings. The result is the clearest picture yet of how America’s elite colleges perpetuate the intergenerational transfer of wealth and opportunity.
“What I conclude from this study is the Ivy League doesn’t have low-income students because it doesn’t want low-income students,” said Susan Dynarski, an economist at the Harvard Graduate School of Education, who has reviewed the data and was not involved in the study.
In effect, the study shows, these policies amounted to affirmative action for the children of the 1 percent, whose parents earn more than $611,000 a year. It comes as colleges are being forced to rethink their admissions processes after the Supreme Court ruling that race-based affirmative action is unconstitutional.
“Are these highly selective private colleges in America taking kids from very high-income, influential families and basically channeling them to remain at the top in the next generation?” said Raj Chetty, an economist at Harvard who directs Opportunity Insights, and an author of the paper with John N. Friedman of Brown and David J. Deming of Harvard. “Flipping that question on its head, could we potentially diversify who’s in a position of leadership in our society by changing who is admitted?”
Representatives from several of the colleges said that income diversity was an urgent priority, and that they had taken significant steps since 2015, when the data in the study ends, to admit lower-income and first-generation students. These include making tuition free for families earning under a certain amount; giving only grants, not loans, in financial aid; and actively recruiting students from disadvantaged high schools.
“We believe that talent exists in every sector of the American income distribution,” said Christopher L. Eisgruber, the president of Princeton. “I am proud of what we have done to increase socioeconomic diversity at Princeton, but I also believe that we need to do more — and we will do more.”
Affirmative action for the rich
In a concurring opinion in the affirmative action case, Justice Neil Gorsuch addressed the practice of favoring the children of alumni and donors, which is also the subject of a new case. “While race-neutral on their face, too, these preferences undoubtedly benefit white and wealthy applicants the most,” he wrote.
The new paper did not include admissions rates by race because previous research had done so, the researchers said. They found that racial differences were not driving the results. When looking only at applicants of one race, for example, those from the highest-income families still had an advantage. Yet the top 1 percent is overwhelmingly white. Some analysts have proposed diversifying by class as a way to achieve more racial diversity without affirmative action.
The new data showed that other selective private colleges, like Northwestern, N.Y.U. and Notre Dame, had a similarly disproportionate share of children from rich families. Public flagship universities were much more equitable. At places like the University of Texas at Austin and the University of Virginia, applicants with high-income parents were no more likely to be admitted than lower-income applicants with comparable scores.
Less than 1 percent of American college students attend the 12 elite colleges. But the group plays an outsize role in American society: 12 percent of Fortune 500 chief executives and a quarter of U.S. senators attended. So did 13 percent of the top 0.1 percent of earners. The focus on these colleges is warranted, the researchers say, because they provide paths to power and influence — and diversifying who attends has the potential to change who makes decisions in America.
The researchers did a novel analysis to measure whether attending one of these colleges causes success later in life. They compared students who were wait-listed and got in, with those who didn’t and attended another college instead. Consistent with previous research, they found that attending an Ivy instead of one of the top nine public flagships did not meaningfully increase graduates’ income, on average. However, it did increase a student’s predicted chance of earning in the top 1 percent to 19 percent, from 12 percent.
For outcomes other than earnings, the effect was even larger — it nearly doubled the estimated chance of attending a top graduate school, and tripled the estimated chance of working at firms that are considered prestigious, like national news organizations and research hospitals.
“Sure, it’s a tiny slice of schools,” said Professor Dynarski, who has studied college admissions and worked with the University of Michigan on increasing the attendance of low-income students, and has occasionally contributed to The New York Times. “But having representation is important, and this shows how much of a difference the Ivies make: The political elite, the economic elite, the intellectual elite are coming out of these schools.”
The missing middle class
The advantage to rich applicants varied by college, the study found: At Dartmouth, students from the top 0.1 percent were five times as likely to attend as the average applicant with the same test score, while at M.I.T. they were no more likely to attend. (The fact that children from higher-income families tend to have higher standardized test scores and are likelier to receive private coaching suggests that the study may actually underestimate their admissions advantage.)
An applicant with a high test score from a family earning less than $68,000 a year was also likelier than the average applicant to get in, though there were fewer applicants like this.
Children from middle- and upper-middle-class families — including those at public high schools in high-income neighborhoods — applied in large numbers. But they were, on an individual basis, less likely to be admitted than the richest or, to a lesser extent, poorest students with the same test scores. In that sense, the data confirms the feeling among many merely affluent parents that getting their children into elite colleges is increasingly difficult.
“We had these very skewed distributions of a whole lot of Pell kids and a whole lot of no-need kids, and the middle went missing,” said an Ivy League dean of admissions, who has seen the new data and spoke anonymously in order to talk openly about the process. “You’re not going to win a P.R. battle by saying you have X number of families making over $200,000 that qualify for financial aid.”
The researchers could see, for nearly all college students in the United States from 1999 to 2015, where they applied and attended, their SAT or ACT scores and whether they received a Pell grant for low-income students. They could also see their parents’ income tax records, which enabled them to analyze attendance by earnings in more detail than any previous research. They conducted the analysis using anonymized data.
For the several elite colleges that also shared internal admissions data, they could see other aspects of students’ applications between 2001 and 2015, including how admissions offices rated them. They focused their analysis on the most recent years, 2011 to 2015.
Though they had this data for a minority of the dozen top colleges, the researchers said they thought it was representative of the other colleges in the group (with the exception of M.I.T.). The other colleges admitted more students from high-income families, showed preferences for legacies and recruited athletes, and described similar admissions practices in conversations with the researchers, they said.
“Nobody has this kind of data; it’s completely unheard-of,” said Michael Bastedo, a professor at the University of Michigan’s School of Education, who has done prominent research on college admissions. “I think it’s really important to good faith efforts for reforming the system to start by being able to look honestly and candidly at the data.”
How the richest students benefit
Before this study, it was clear that colleges enrolled more rich students, but it was not known whether it was just because more applied. The new study showed that’s part of it: One-third of the difference in attendance rates was because middle-class students were somewhat less likely to apply or matriculate. But the bigger factor was that these colleges were more likely to accept the richest applicants.
Legacy admissions
The largest advantage for the 1 percent was the preference for legacies. The study showed — for the first time at this scale — that legacies were more qualified overall than the average applicant. But even when comparing applicants who were similar in every other way, legacies still had an advantage.

When high-income applicants applied to the college their parents attended, they were accepted at much higher rates than other applicants with similar qualifications — but at the other top-dozen colleges, they were no more likely to get in.
“This is not a sideshow, not just a symbolic issue,” Professor Bastedo said of the finding.
Athletes
One in eight admitted students from the top 1 percent was a recruited athlete. For the bottom 60 percent, that figure was one in 20. That’s largely because children from rich families are more likely to play sports, especially more exclusive sports played at certain colleges, like rowing and fencing. The study estimated that athletes were admitted at four times the rate of nonathletes with the same qualifications.
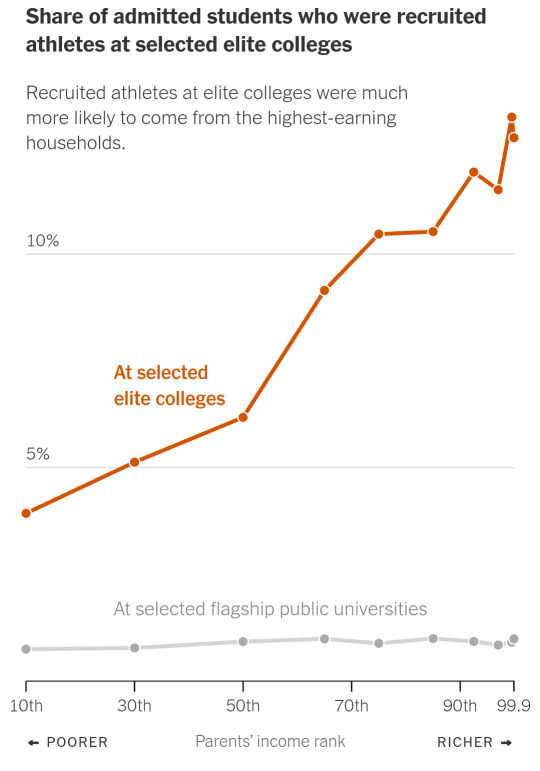
“There’s a common misperception that it’s about basketball and football and low-income kids making their way into selective colleges,” Professor Bastedo said. “But the enrollment leaders know athletes tend to be wealthier, so it’s a win-win.”
Nonacademic ratings
There was a third factor driving the preference for the richest applicants. The colleges in the study generally give applicants numerical scores for academic achievement and for more subjective nonacademic virtues, like extracurricular activities, volunteering and personality traits. Students from the top 1 percent with the same test scores did not have higher academic ratings. But they had significantly higher nonacademic ratings.

At one of the colleges that shared admissions data, students from the top 0.1 percent were 1.5 times as likely to have high nonacademic ratings as those from the middle class. The researchers said that, accounting for differences in the way each school assesses nonacademic credentials, they found similar patterns at the other colleges that shared data.
The biggest contributor was that admissions committees gave higher scores to students from private, nonreligious high schools. They were twice as likely to be admitted as similar students — those with the same SAT scores, race, gender and parental income — from public schools in high-income neighborhoods. A major factor was recommendations from guidance counselors and teachers at private high schools.
“Parents rattle off that a kid got in because he was first chair in the orchestra, ran track,” said John Morganelli Jr., a former director of admissions at Cornell and founder of Ivy League Admissions, where he advises high school students on applying to college. “They never say what really happens: Did the guidance counselor advocate on that kid’s behalf?”
Recommendation letters from private school counselors are notoriously flowery, he said, and the counselors call admissions officers about certain students.
“This is how the feeder schools get created,” he said. “Nobody’s calling on behalf of a middle- or lower-income student. Most of the public school counselors don’t even know these calls exist.”
The end of need-blind admissions?
Overall, the study suggests, if elite colleges had done away with the preferences for legacies, athletes and private school students, the children of the top 1 percent would have made up 10 percent of a class, down from 16 percent in the years of the study.
Legacy students, athletes and private school students do no better after college, in terms of earnings or reaching a top graduate school or firm, it found. In fact, they generally do somewhat worse.
The dean of admissions who spoke anonymously said change was easier said than done: “I would say there’s much more commitment to this than may be obvious. It’s just the solution is really complicated, and if we could have done it, we would have.”
For example, it’s not feasible to choose athletes from across the income spectrum if many college sports are played almost entirely by children from high-earning families. Legacies are perhaps the most complicated, the admissions dean said, because they tend to be highly qualified and their admission is important for maintaining strong ties with alumni.
Ending that preference, the person said, “is not an easy decision to make, given the alumni response, especially if you’re not in immediate concurrence with the rest of the Ivies.” (Though children of very large donors also get special consideration by admissions offices, they were not included in the analysis because there are relatively few of them.)
People involved in admissions say that achieving more economic diversity would be difficult without doing something else: ending need-blind admissions, the practice that prevents admissions officers from seeing families’ financial information so their ability to pay is not a factor. Some colleges are already doing what they call “need-affirmative admissions,” for the purpose of selecting more students from the low end of the income spectrum, though they often don’t publicly acknowledge it for fear of blowback.
There is a tool, Landscape from the College Board, to help determine if an applicant grew up in a neighborhood with significant privilege or adversity. But these colleges have no knowledge of parents’ income if students don’t apply for financial aid.
Ivy League colleges and their peers have recently made significant efforts to recruit more low-income students and subsidize tuition. Several now make attendance entirely free for families below a certain income — $100,000 at Stanford and Princeton, $85,000 at Harvard, and $60,000 at Brown.
At Princeton, one-fifth of students are now from low-income families, and one-fourth receive a full ride. It has recently reinstated a transfer program to recruit low-income and community college students. At Harvard, one-fourth of this fall’s freshman class is from families with incomes less than $85,000, who will pay nothing. The majority of freshmen will receive some amount of aid.
Dartmouth just raised $500 million to expand financial aid: “While we respect the work of Harvard’s Opportunity Insights, we believe our commitment to these investments and our admissions policies since 2015 tells an important story about the socioeconomic diversity among Dartmouth students,” said Jana Barnello, a spokeswoman.
Public flagships do admissions differently, in a way that ends up benefiting rich students less. The University of California schools forbid giving preference to legacies or donors, and some, like U.C.L.A., do not consider letters of recommendation. The application asks for family income, and colleges get detailed information about California high schools. Application readers are trained to consider students’ circumstances, like whether they worked to support their families in high school, as “evidence of maturity, determination and insight.”
The University of California system also partners with schools in the state, from pre-K through community college, to support students who face barriers. There’s a robust program for transfer students from California community colleges; at U.C.L.A., half are from low-income backgrounds.
M.I.T., which stands out among elite private schools as displaying almost no preference for rich students, has never given a preference to legacy applicants, said its dean of admissions, Stuart Schmill. It does recruit athletes, but they do not receive any preference or go through a separate admissions process (as much as it may frustrate coaches, he said).
“I think the most important thing here is talent is distributed equally but opportunity is not, and our admissions process is designed to account for the different opportunities students have based on their income,” he said. “It’s really incumbent upon our process to tease out the difference between talent and privilege.”
Source: Raj Chetty, David J. Deming and John N. Friedman, “Diversifying Society’s Leaders? The Determinants and Causal Effects of Admission to Highly Selective Private Colleges”
193 notes
·
View notes
Text
During the socialist state period in Hungary, for example, widespread soil acidification problems are traceable to heavy use of agrochemicals, like ammoniacal nitrate, but the problem could have been averted or at least reduced by refraining from producing the likes of sausages, fruits and vegetables for Western markets, especially West Germany and Austria, to fulfil loan repayment schedules imposed by Western financial institutions. In effect, the more an economy is integrated with international capital flows, the higher the ecological footprint. Accordingly, China, as a country embodying the main contradictions of the world capitalist economy, should be expected to have a worsening environmental record. As Peters et al. have shown, the wealthiest countries (largely liberal democracies) can overconsume fossil fuels and spew out the most greenhouse gases by appropriating natural wealth (e.g. fossil fuels) from the rest of the world, where there is chronic underconsumption relative to fossil fuel production.
Salvatore Engel-Di Mauro, Socialist States and the Environment: Lessons for Eco-Socialist Futures
68 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you have information on what John Hartnell was like? He seems well loved.
I wish with all my heart that I did. So far, we haven't found any letters written by him, and the letters written to him were for him and his brother, and neither were mentioned by name but instead as a pair. However, most of the people mentioned in Sarah's letter were the same age as John (born in 1820) and were close neighbors or church friends, so we can assume he must have been nice enough or charming enough to have a network of friends.
A couple things I think might inform us about what he might have been like as a person though:
One of the names in the Sarah letter, Goose, might refer to a neighbor John's age named Sarah Gosling. If this is the same person, then clearly someone in the Hartnell family had a pretty good sense of humor and puns.
He was never written up for any punishments while on the HMS Volage, which leads me to believe he was on his best behavior.
Some of his injuries/maladies were from repetitive motion, probably suggesting he was a very hard worker.
After age 13, he was more than likely the main breadwinner for his family after his father's death. He was immediately apprenticed as a shoemaker at that age. Again, possibly a hard worker with a lot of responsibilities foisted on him at a young age.
His apprenticeship form features the earliest sample of his handwriting I've been able to find. I've said it before, but he signed it very meticulously and carefully.
His youngest sister, Betsy, named a son after him. I think he'd probably have to at least be a decent person to earn that.
A descendant from the family that I've spoken to (on Betsy's line) said that family lore says that this side of the family "fell apart" after John and Thomas' deaths. This might be financial (although Sarah's last will shows they were living relatively comfortably by this point and all three remaining siblings were making good money) or it could be emotional, or both.
(Hilariously, the same descendant says that this side of the family was seen as a little bit uncouth and stubborn. I don't know if it was just Betsy, who was a character in her own right, or if that's a family trait.)
Some people point out the Crown debt as a potential issue, but the sheer amount of his debt doesn't line up with any fines I've seen from criminal courts. Instead, it looks like an amount taken out like a loan. Considering that his mother never remarried and he had to help care for four younger siblings on a shoemaker's pay, this isn't too far out of pocket to imagine.
The Volage record book records his appearance as "sallow", and some of the results of his autopsy and other notes from earlier exhumations in the 1850s suggest he was sickly from the get-go.
Not to talk about his grave goods forever and a day, but the sheer amount of love put into his burial does seem to suggest that he was a good enough person to earn that much a personal touch and the appearance of being comfortable.
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Biden-Harris Administration Advances Equity and Opportunity for Black Americans

Growing Economic Opportunity for Black Families and Communities
Through the President’s legislative victories, including the American Rescue Plan (ARP), the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL), the CHIPS and Science Act, and the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA)—as well as the President’s historic executive orders on racial equity—the Biden-Harris Administration is ensuring that federal investments through the President’s landmark Investing in America agenda are equitably flowing to communities to address longstanding economic inequities that impact people’s economic security, health, and safety. And this vision is already delivering results. The Biden-Harris Administration has:
Powered a historic economic recovery that created 2.6 million jobs for Black workers—and achieved both the lowest Black unemployment rate on record and the lowest gap between Black and White unemployment on record.
Helped Black working families build wealth. Black wealth is up by 60% relative to pre-pandemic—the largest increase on record.
Cut in half the number of Black children living in poverty in 2021 through ARP’s Child Tax Credit expansion. This expansion provided breathing room to the families of over 9 million Black children.
Began reversing decades of infrastructure disinvestment, including with $4 billion to reconnect communities that were previously cut off from economic opportunities by building needed transportation infrastructure in underserved communities, including Black communities.
Connected an estimated 5.5 million Black households to affordable high-speed internet through the Affordable Connectivity Program, closing the digital divide for millions of Black families.

Helping Black-Owned Businesses Grow and Thrive
Since the President entered office, a record 16 million new business applications have been filed, and the share of Black households owning a business has more than doubled. Building on this momentum, the Biden-Harris Administration has:
Achieved the fastest creation rate of Black-owned businesses in more than 30 years—and more than doubled the share of Black business owners from 2019 to 2022.
Improved the Small Business Administration’s (SBA) flagship loan guarantee programs to expand the availability of capital to underserved communities. Since 2020, the number and dollar value of SBA-backed loans to Black-owned businesses have more than doubled.
Launched a whole-of-government effort to expand access to federal contracts for small businesses, awarding a record $69.9 billion to small disadvantaged businesses in 2022.
Through Treasury’s State Small Business Credit Initiative, invested $10 billion to expand access to capital and invest in early-stage businesses in all 50 states—including $2.5 billion in funding and incentive allocations dedicated to support the provision of capital to underserved businesses with $1 billion of these funds to be awarded to the jurisdictions that are most successful in reaching underserved businesses.
Helped more than 37,000 farmers and ranchers who were in financial distress, including Black farmers and ranchers, stay on their farms and keep farming, thanks to resources provided through IRA. The IRA allocated $3.1 billion for the Department of Agriculture (USDA) to provide relief for distressed borrowers with at-risk agricultural operations with outstanding direct or guaranteed Farm Service Agency loans. USDA has provided over $2 billion and counting in timely assistance.
Supported small and disadvantaged businesses through CHIPS Act funding by requiring funding applicants to develop a workforce plan to create equitable pathways for economically disadvantaged individuals in their region, as well as a plan to support procurement from small, minority-owned, veteran-owned, and women-owned businesses.
Created the $27 billion Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund that will invest in clean energy projects in low-income and disadvantaged communities.

Increasing Access to Housing and Rooting Out Discrimination in the Housing Market for Black Communities
To increase access to housing and root out discrimination in the housing market, including for Black families and communities, the Biden-Harris Administration has:
Set up the first-ever national infrastructure to stop evictions, scaling up the ARP-funded Emergency Rental Assistance program in over 400 communities across the country, helping 8 million renters and their families stay in their homes. Over 40% of all renters helped are Black—and this support prevented millions of evictions, with the largest effects seen in majority-Black neighborhoods.
Published a proposed “Affirmatively Furthering Fair Housing” rule through the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), which will help overcome patterns of segregation and hold states, localities, and public housing agencies that receive federal funds accountable for ensuring that underserved communities have equitable access to affordable housing opportunities.
Created the Interagency Task Force on Property Appraisal and Valuation Equity, or PAVE, a first-of-its-kind interagency effort to root out bias in the home appraisal process, which is taking sweeping action to advance equity and remove racial and ethnic bias in home valuations, including cracking down on algorithmic bias and empowering consumers to take action against misvaluation.
Taken additional steps through HUD to support wealth-generation activities for prospective and current homeowners by expanding access to credit by incorporating a borrower’s positive rental payment history into the mortgage underwriting process. HUD estimates this policy change will enable an additional 5,000 borrowers per year to qualify for an FHA-insured loan.

Ensuring Equitable Educational Opportunity for Black Students
To expand educational opportunity for the Black community in early childhood and beyond, the Biden-Harris Administration has:
Approved more than $136 billion in student loan debt cancellation for 3.7 million Americans through various actions and launched a new student loan repayment plan—the Saving on a Valuable Education (SAVE) plan—to help many students and families cut in half their total lifetime payments per dollar borrowed.
Championed the largest increase to Pell Grants in the last decade—a combined increase of $900 to the maximum award over the past two years, affecting the over 60% of Black undergraduates who rely on Pell grants.
Fixed the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program, so all qualified borrowers get the debt relief to which they are entitled. More than 790,000 public servants have received more than $56 billion in loan forgiveness since October 2021. Prior to these fixes, only 7,000 people had ever received forgiveness through PSLF.
Delivered a historic investment of over $7 billion to support HBCUs.
Reestablished the White House Initiative on Advancing Educational Equity, Excellence, and Economic Opportunity for Historically Black Colleges and Universities and the White House Initiative on Advancing Educational Equity, Excellence, and Economic Opportunity for Black Americans.
Through ARP, secured $130 billion—the largest investment in public education in history—to help students get back to school, recover academically in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, and address student mental health.
Secured a 30% increase in child care assistance funding last year. Black families comprise 38% of families benefiting from federal child care assistance. Additionally, the President secured an additional $1 billion for Head Start, a program where more than 28% of children and pregnant women who benefit identify as Black.

Improving Health Outcomes for Black Families and Communities
To improve health outcomes for the Black community, the Biden-Harris Administration has:
Increased Black enrollment in health care coverage through the Affordable Care Act by 49%—or by around 400,000—from 2020 to 2022, helping more Black families gain health insurance than ever before.
Through IRA, locked in lower monthly premiums for health insurance, capped the cost of insulin at $35 per covered insulin product for Medicare beneficiaries, and helped further close the gap in access to medication by improving prescription drug coverage and lowering drug costs in Medicare.
Through ARP, expanded postpartum coverage from 60 days to 12 months in 43 states and Washington, D.C., covering 700,000 more women in the year after childbirth. Medicaid covers approximately 65% of births for Black mothers, and this investment is a critical step to address maternal health disparities.
Financed projects that will replace hundreds of thousands of lead pipes, helping protect against lead poisoning that disproportionately affects Black communities.
Provided 264 grants with $1 billion in Bipartisan Safer Communities Act funds to more than 40 states to increase the supply of school-based mental health professionals in communities with high rates of poverty.

Launched An Unprecedented Whole-Of-Government Equity Agenda to Ensure the Promise of America for All Communities, including Black Communities
President Biden believes that advancing equity, civil rights, racial justice, and equal opportunity is the responsibility of the whole of our government, which will require sustained leadership and partnership with all communities. To make the promise of America real for every American, including for the Black Community, the President has:
Signed two Executive Orders directing the Federal Government to advance an ambitious whole-of-government equity agenda that matches the scale of the challenges we face as a country and the opportunities we have to build a more perfect union.
Nominated the first Black woman to serve on the Supreme Court and more Black women to federal circuit courts than every President combined.
Countered hateful attempts to rewrite history including: the signing of the Emmett Till Antilynching Act; establishing Juneteenth as a national holiday; and designating the Emmett Till and Mamie Till-Mobley National Monument in Mississippi and Illinois. The Department of the Interior has invested more than $295 million in infrastructure funding and historic preservation grants to protect and restore places significant to Black history.
Created the Justice40 Initiative, which is delivering 40% of the overall benefits of certain Federal investments in clean energy, affordable and sustainable housing, clean water, and other programs to disadvantaged communities that are marginalized by underinvestment and overburdened by pollution as part of the most ambitious climate, conservation, and environmental justice agenda in history.

Protecting the Sacred Right to Vote for Black Families and Communities
Since their first days in office, President Biden and Vice President Harris have prioritized strengthening our democracy and protecting the sacred right to vote in free, fair, and secure elections. To do so, the President has:
Signed an Executive Order to leverage the resources of the Federal Government to provide nonpartisan information about the election process and increase access to voter registration. Agencies across the Federal Government are taking action to respond to the President’s call for an all-of-government effort to enhance the ability of all eligible Americans to participate in our democracy.
Repeatedly and forcefully called on Congress to pass essential legislation, including the John R. Lewis Voting Rights Advancement Act and the Freedom to Vote Act, including calling for an exception to the filibuster to pass voting rights legislation.
Increased funding for the Department of Justice’s Civil Rights Division, which has more than doubled the number of voting rights enforcement attorneys. The Justice Department also created the Election Threats Task Force to assess allegations and reports of threats against election workers, and investigate and prosecute these matters where appropriate.
Signed into law the bipartisan Electoral Reform Count Act, which establishes clear guidelines for our system of certifying and counting electoral votes for President and Vice President, to preserve the will of the people and to protect against the type of attempts to overturn our elections that led to the January 6 insurrection.

Addressing the Crisis of Gun Violence in Black Communities
Gun violence has become the leading cause of death for all youth and Black men in America, as well as the second leading cause of death for Black women. To address this national crisis, the President has:
Launched the first-ever White House Office of Gun Violence Prevention, and taken more executive action on gun violence than any President in history, including investments in violence reduction strategies that address the root causes of gun violence and address emerging threats like ghost guns. In 2022, the Administration’s investments in evidence-based, lifesaving programs combined with aggressive action to stop the flow of illegal guns and hold shooters accountable yielded a 12.4% reduction in homicides across the United States.
Signed into the law the Bipartisan Safer Communities Act, the most significant gun violence reduction legislation enacted in nearly 30 years, including investments in violence reduction strategies and historic policy changes to enhance background checks for individuals under age 21, narrow the dating partner loophole in the gun background check system, and provide law enforcement with tools to crack down on gun trafficking.
Secured the first-ever dedicated federal funding stream for community violence intervention programs, which have been shown to reduce violence by as much as 60%. These programs are effective because they leverage trusted messengers who work directly with individuals most likely to commit gun violence, intervene in conflicts, and connect people to social, health and wellness, and economic services to reduce the likelihood of violence as an answer to conflict.

Enhancing Public Trust and Strengthening Public Safety for Black Communities
Our criminal justice system must protect the public and ensure fair and impartial justice for all. These are mutually reinforcing goals. To enhance equal justice and public safety for all communities, including the Black community, the President has:
Signed a historic Executive Order to put federal policing on the path to becoming the gold standard of effectiveness and accountability by requiring federal law enforcement agencies to ban chokeholds; restrict no-knock warrants; mandate the use of body-worn cameras; implement stronger use-of-force policies; provide de-escalation training; submit use-of-force data; submit officer misconduct records into a new national accountability database; and restrict the sale or transfer of military equipment to local law enforcement agencies, among other things.
Taken steps to right the wrongs stemming from our Nation’s failed approach to marijuana by directing the Departments of Health and Human Services and Justice to expeditiously review how marijuana is scheduled under federal law and in October 2022 issued categorical pardons of prior federal and D.C. offenses of simple possession of marijuana and in December 2023 pardoned additional offenses of simple possession and use of marijuana under federal and D.C. law. While white, Black, and brown people use marijuana at similar rates, Black and brown people have been arrested, prosecuted, and convicted at disproportionately higher rates.
Announced over 100 concrete policy actions as part of a White House evidence-informed, multi-year Alternatives, Rehabilitation, and Reentry Strategic Plan to safely reduce unnecessary criminal justice system interactions so police officers can focus on fighting crime; supporting rehabilitation during incarceration; and facilitating successful reentry.
FACT SHEET
#Joe Biden#Thanks Biden#Black History Month#black americans#african american#kamala harris#politics#US Politics#Economy#student loan debt#marijuana#criminal justice#gun violence#voting rights#from the White House#long post#because a lot has happened
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
U.S. BANKS USED SLAVES AS COLLATERAL
Many of America’s key banks today were built on the back of slavery. In the South, they’d regard enslaved people as financial assets, accepting them as collateral on loans and mortgages - especially after the War of 1812, when slave prices shot up. The practice was particularly prevalent among ‘frontier banks’ in Kentucky, Tennessee, Mississippi and Louisiana.
In this video, Congressman Al Green grills JP Morgan Chase CEO Jamie Dimon on his bank’s involvement in slavery. The institution used more than 13,000 slaves as collateral and ended up owning 1,250 of them when borrowers defaulted - that’s according to a study based on the bank’s records.
JP Morgan apologized in 2005.
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
Radio Free Monday
Good morning everyone, and welcome to Radio Free Monday!
Ways to Give:
Anon linked to a fundraiser for mousedetective, who needs to pay off loans so she and her family can get off the street and into affordable housing; you can read more, reblog, and find giving information here.
Anon linked to a fundraiser for a friend, Hope, who is raising funds to cover housing debt from roommates who left abruptly, as well as medical bills; she worked through the pandemic in food service but has no emergency savings left after that. You can read more and support the fundraiser here.
Anon linked to a fundraiser for dashnite, who is raising funds to escape an abusive living situation and immigrate to be with their partner; you can read more, reblog, and find giving information here.
wolvereaux is raising funds to cover the unexpected replacement for their car's windshield; they drive delivery for a living and are losing several days of work until the replacement is done, making it even harder to cover the cost. You can read more, reblog, and find giving information here.
Follow Up:
melayneseahawk wanted to let folks know that after appearing in RFM, the Worlds Elsewhere Theatre Company's stream and fundraiser of Musica Universalis Book 2: Regenerational Trauma went extremely well! As of Sunday they had passed their fundraising goal and were working through the stretch goals; you can watch the recording of the stream here (or split into acts here) and they are still taking donations, which you can read more about and support here. They wanted to thank everyone who attended, donated, or shared the links so others could!
Recurring Needs:
Anon linked to a fundraiser for their friend dyken, a nonbinary lesbian from Latin America who along with their partner has been having trouble covering bills, food, and mental health treatment; their family is abusive and unwilling to help financially. They are accepting donations via paypal and commissions via ko-fi; you can read more, reblog, and find giving information here.
rilee16 is raising funds to get out of an abusive home situation where their roommate has been aggressive and stealing from them; with irregular work hours and a tax debt due, they also need funds to repair their phone, which is dying, and cover utility bills. You can read more, reblog, and find giving information here.
loversdoom is a college student from the Philippines, studying away from her family, and her parents are unexpectedly unable to support her education; she is dealing with a number of expenses and is now looking at costly medical procedures as well. You can read more and reblog here or give to the fundraiser here.
Anon linked to karla-hoshi or Hoshi on TikTok, who is raising funds for cancer treatment for her cat Naku; they caught the cancer early and hope that he can survive it, but can't continue treatment without funding, and they have recently had other emergency expenses to cover. You can read more, reblog, and support the fundraiser here.
And this has been Radio Free Monday! Thank you for your time. You can post items for my attention at the Radio Free Monday submissions form. If you're new to fundraising, you may want to check out my guide to fundraising here.
46 notes
·
View notes